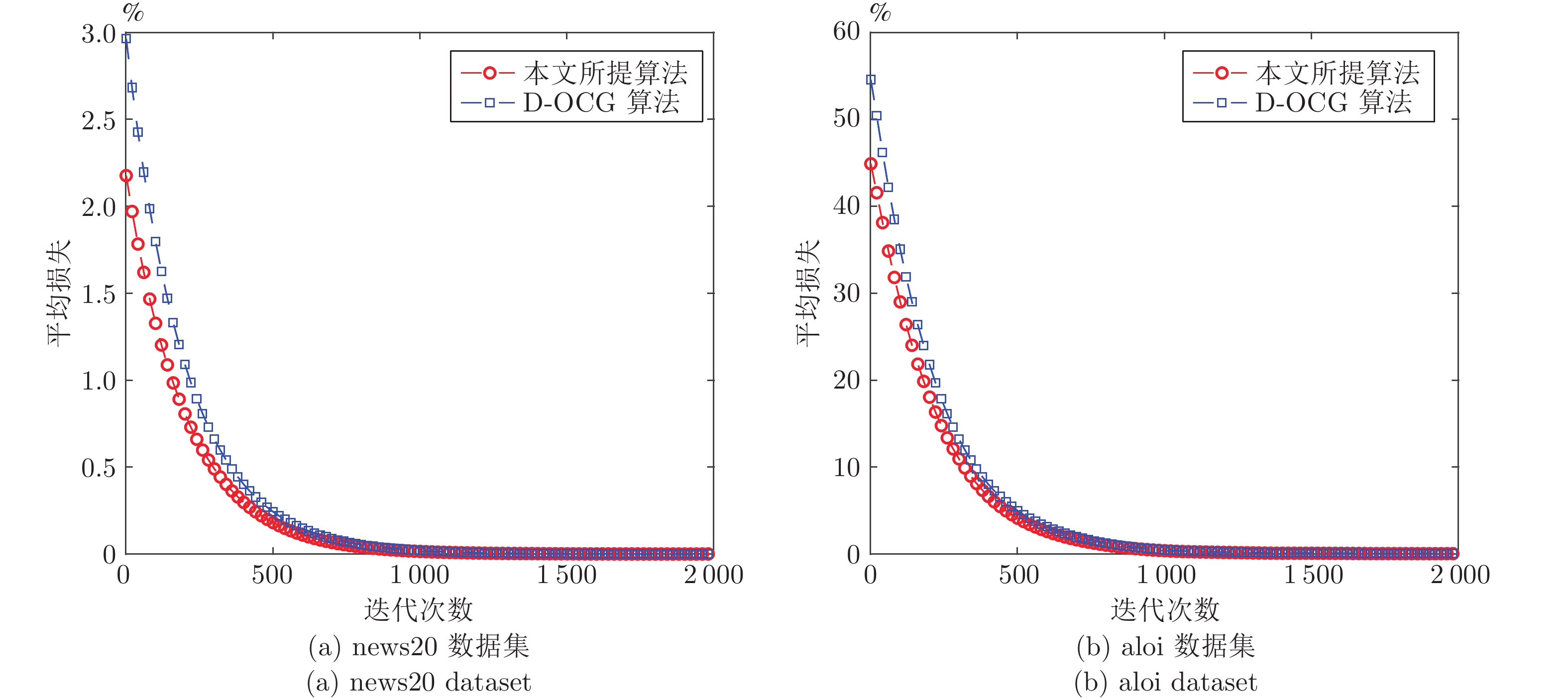
|
[1]
|
Zhu J L, Xu C Q, Guan J F, Wu D P. Differentially private distributed online algorithms over time-varying directed networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2018, 4(1): 4−17
|
|
[2]
|
Rabbat M, Nowak R. Distributed optimization in sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor NetworksProc. Berkeley, USA: IEEE, 2004. 20−27
|
|
[3]
|
Zhang M C, Hao B W, Ge Q B, Zhu J L, Zheng R J, Wu Q T. Distributed adaptive subgradient algorithms for online learning over time-varying networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(7): 4518−4529
|
|
[4]
|
Abu-Elkheir M, Hayajneh M, Abu A N. Data management for the internet of things: design primitives and solution. Sensors, 2013, 13(11): 15582-15612 doi: 10.3390/s131115582
|
|
[5]
|
孙路明, 张少敏, 姬涛, 李翠平, 陈红. 人工智能赋能的数据管理技术研究. 软件学报, 2020, 31(3): 600-619SUN Lu-Ming, ZHANG Shao-Min, JI Tao, LI Cui-Ping, CHEN Hong. Survey of data management techniques powered by artificial intelligence. Journal of Software, 2020, 31(3): 600-619
|
|
[6]
|
黄刚, 李军华. 基于 AC-DSDE 进化算法多 UAVs协同目标分配. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(1): 173-184Huang Gang, Li Jun-Hua. Multi-UAV cooperative target allocation based on AC-DSDE evolutionary algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(1): 173-184
|
|
[7]
|
Beck A, Nedić A, Ozdaglar A, Teboulle M. An ${\rm{ O}}(1/k)$ gradient method for network resource allocation problems. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2014, 1(1): 64-73 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2014.2309751
|
|
[8]
|
刘妹琴, 韩学艳, 张森林, 郑荣濠, 兰剑. 基于水下传感器网络的目标跟踪技术研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(2): 235-251Liu Mei-Qin, Han Xue-Yan, Zhang Sen-Lin, Zheng Rong-Hao, Lan Jian. Research status and prospect of target tracking technologies via underwater sensor networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(2): 235-251
|
|
[9]
|
蒋弘毅, 王永娟, 康锦煜. 目标检测模型及其优化方法综述. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(6): 1232-1255Jiang Hong-Yi, Wang Yong-Juan, Kang Jin-Yu. A survey of object detection models and its optimization methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(6): 1232-1255
|
|
[10]
|
Wen G H, Yu X H, Liu Z W, Yu W W. Adaptive consensus-based robust strategy for economic dispatch of smart grids subject to communication uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(6): 2484-2496 doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2772088
|
|
[11]
|
李小玲, 王怀民, 郭长国, 丁博, 李小勇. 分布式约束优化问题研究及其进展. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(8): 1656-1671 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2015.01656LI Xiao-Ling, WANG Huai-Min, GUO Chang-Guo, DING Bo, LI Xiao-Yong. Research and development of distributed constraint optimization problems. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(8): 1656-1671 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2015.01656
|
|
[12]
|
Nedić A, Olshevsky A. Distributed optimization over time-varying directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(3): 601-615 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2364096
|
|
[13]
|
Qu G N, Li N. Harnessing smoothness to accelerate distributed optimization. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2018, 5(3): 1245-1260 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2017.2698261
|
|
[14]
|
Shalev-Shwartz S. Online learning and online convex optimization. Foundations and Trends R in Machine Learning, 2011, 4(2): 107-194 doi: 10.1561/2200000018
|
|
[15]
|
Hazan E, Kalai A, Kale S, Agarwal A. Logarithmic regret algorithms for online convex optimization. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Learning Theory. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2006. 499−513
|
|
[16]
|
Mateos-Núñez D, Cortés J. Distributed online convex optimization over jointly connected digraphs. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2014, 1(1): 23-37 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2014.2363554
|
|
[17]
|
Xu C Q, Zhu J L, Wu D O. Decentralized online learning methods based on weight-balancing over time-varying digraphs. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2021, 5(3): 394-406 doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2018.2880771
|
|
[18]
|
Akbari M, Gharesifard B, Linder T. Distributed online convex optimization on time-varying directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2017, 4(3): 417-428 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2015.2505149
|
|
[19]
|
Raginsky M, Kiarashi N, Willett R. Decentralized online convex programming with local information. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2011. 5363−5369
|
|
[20]
|
Hosseini S, Chapman A, Mesbahi M. Online distributed convex optimization on dynamic networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(11): 3545-3550 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2525928
|
|
[21]
|
Yan F, Sundaram S, Vishwanathan S V N, Qi Y. Distributed autonomous online learning: regrets and intrinsic privacy-preserving properties. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2013, 25(11): 2483-2493 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2012.191
|
|
[22]
|
Liu S, Xie L H, Quevedo D E. Event-Triggered quantized communication-based distributed convex optimization. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2018, 5(1): 167-178 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2016.2585305
|
|
[23]
|
Liang Q K, Modiano E. Network utility maximization in adversarial environments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2018. 594−602
|
|
[24]
|
Frank M, Wolfe P. An algorithm for quadratic programming. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 1956, 3(1-2): 95-110 doi: 10.1002/nav.3800030109
|
|
[25]
|
Jaggi M. Revisiting Frank-Wolfe: Projection-free sparse convex optimization. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference Machine Learning. Atlanta, USA: JMLR, 2013. 427−435
|
|
[26]
|
Clarkson K L. Coresets, sparse greedy approximation, and the Frank-Wolfe algorithm. ACM Transactions on Algorithms, 2010, 6(4): 1-34
|
|
[27]
|
Zhu J L, Wu Q T, Zhang M C, Zheng R J, Li K Q. Projection-free decentalized online learning for submodular maximization over time-varying networks. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2021, 22: 1-42
|
|
[28]
|
Hazan E, Kale S. Projection-free online learning. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference Machine Learning. Edinburgh, UK: JMLR, 2012. 521−528
|
|
[29]
|
Garber D, Hazan E. A linearly convergent variant of the conditional gradient algorithm under strong convexity, with applications to online and stochastic optimization. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2016, 26(3): 1493-1528 doi: 10.1137/140985366
|
|
[30]
|
Lafond J, Wai H T, Moulines E. On the online Frank-Wolfe algorithms for convex and non-convex optimizations. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1510.01171, 2016.
|
|
[31]
|
Hazan E, Luo H P. Variance-reduced and projection-free stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: JMLR, 2016. 1263−1271
|
|
[32]
|
Wai H T, Lafond J, Scaglione A, Moulines E. Decentralized Frank-Wolfe algorithm for convex and non-convex problems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(11): 5522-5537 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2685559
|
|
[33]
|
Zhang W P, Zhao P L, Zhu W W, Hoi S, Zhang T. Projection-free distributed online learning in networks. In: Proceedings of the 34th Intentional Conference of Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: PMLR, 2017. 4054−4062
|
|
[34]
|
Wan Y Y, Tu W W, Zhang L J. Projection-free distributed online convex optimization with ${{\rm{ O}}(\sqrt{T})}$ communication complexity. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Virtual Event: PMLR, 2020. 9818−9828
|
|
[35]
|
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L. Convex Optimization. Cambridge: Cambridge University, 2004.
|
|
[36]
|
Liu S, Qiu Z R, Xie L H. Convergence rate analysis of distributed optimization with projected subgradient algorithm. Automatica, 2017, 83: 162-169 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.06.011
|
|
[37]
|
Watts D J, Strogatz S H. Collective dynamics of 'small-world' networks. Nature, 1998, 393: 440-442 doi: 10.1038/30918
|




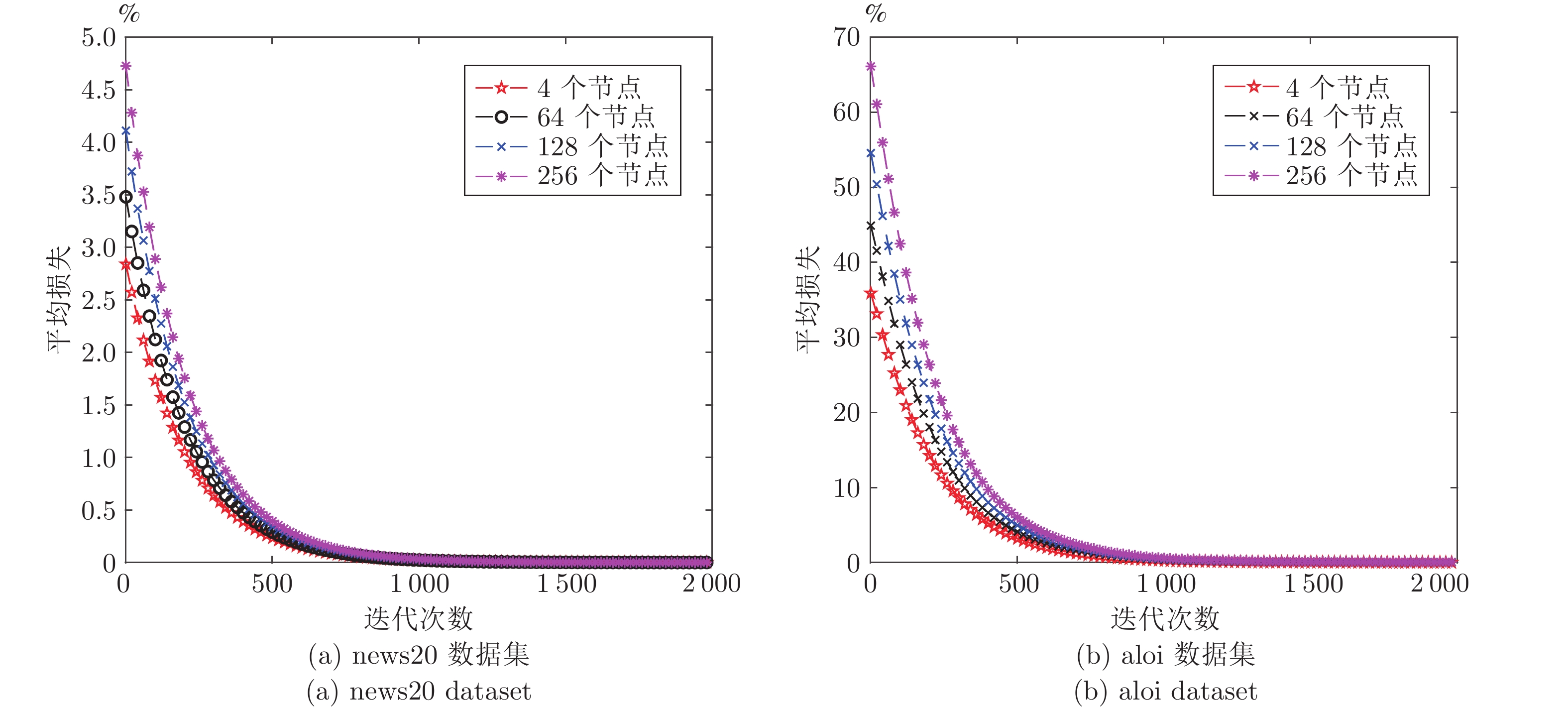
 下载:
下载: