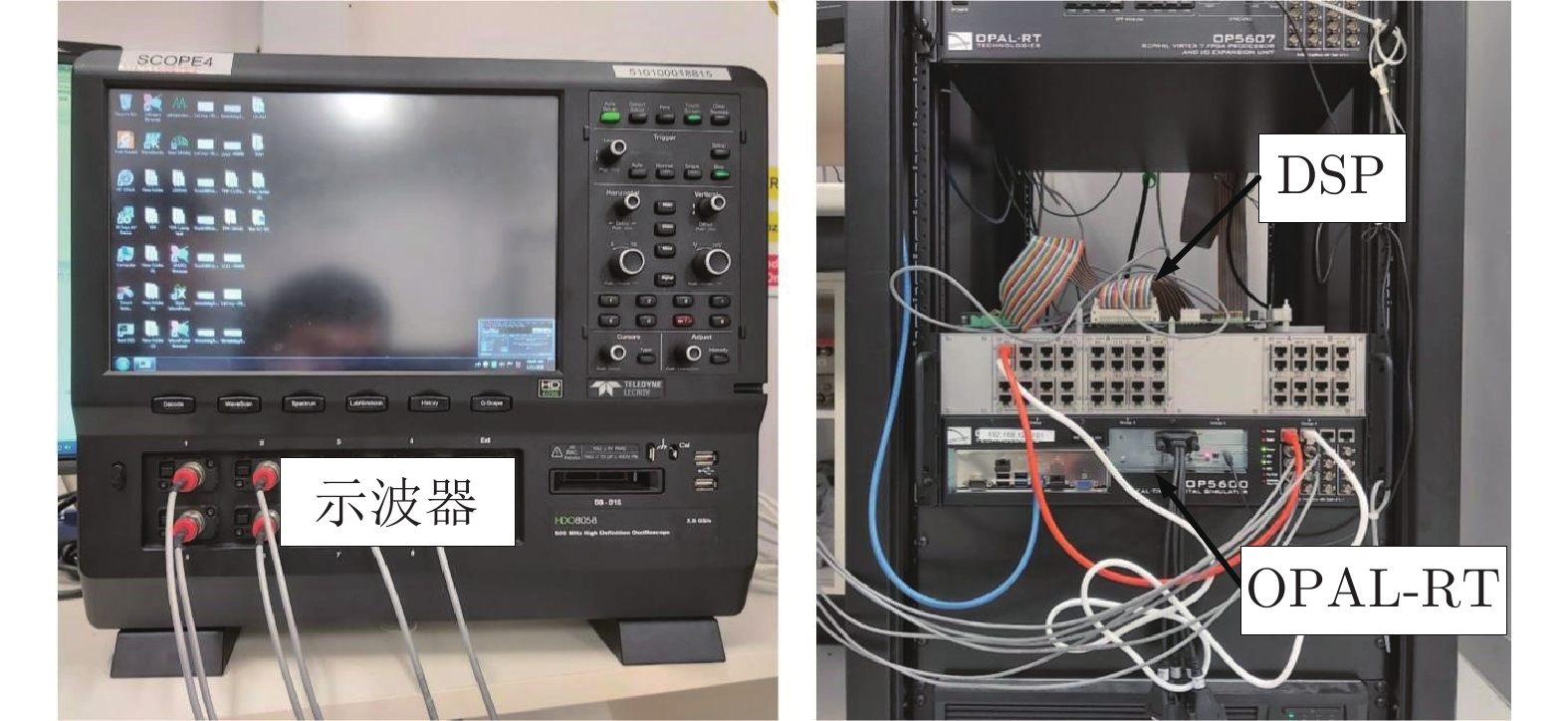
-
摘要: 尽管信息物理系统的稳定性已经得到了广泛的研究, 但大部分的学者皆关注于通信网络延时或攻击下的信息物理系统的稳定性问题, 无网络通信的信息物理系统的信物融合稳定性分析策略亟待提出. 其中, 内嵌数字控制系统的并网逆变器系统是一种最简单、最典型的信息能源系统. 同时, 从效率的角度出发, 逆变器的开关/采样频率总是选择尽可能低的频率, 其势必产生系统固有延迟时间(控制理论中称为时间延迟). 这种延迟时间往往容易引起系统的低频/次同步振荡, 弱电网将加剧此现象. 为此, 提出一种信息能源系统的信−物融合稳定性分析技术. 首先, 基于柏德近似方法, 建立了具有等效延迟时间的信息物理系统阻抗模型. 该等效延迟时间由三部分组成, 即信息/物理层的采样延迟时间、信息层的计算延迟时间和物理层的脉宽调制延迟时间, 其有效地反映了信息−物理相互融合作用的影响. 进而设计了稳定禁止区域判据, 利用空间映射使开关/采样频率求解过程转化为Hurwitz矩阵辨识问题. 在这些空间映射的基础上, 最小开关/采样频率通过自适应步长搜索算法获得. 最后, 仿真和实验结果验证了该方法的有效性.Abstract: Although the cyber-physical system stability has been widely studied, most scholars pay more attention on system stability with communication time delay or attack. It is urgent for numerous scholars to provide one guide regarding cyber-physical system without communication network. Therein, the system regarding grid-connected inverters with the digital control system is regarded as one simplest and typical cyber-physical energy system. Meanwhile, the switching/sampling frequency of the inverter is always selected as low as possible from an efficiency viewpoint, resulting in unavoidable delay time (time delay in control theory). This delay time is always apt to cause the system low frequency/sub-synchronous oscillation, which is more prone to severity under weak grid. To this end, this paper provides one stability-oriented analysis approach of cyber-physical fusion in cyber-energy systems, which is suitable for grid-connected inverters under weak grid. Firstly, the system impedance model with equivalent delay time is constructed, which is based on the Pade approximate approach. This equivalent delay time consists of three parts, i.e., sampling delay time in cyber/physical level, calculation delay time in cyber level and pulse-width modulation delay time in physical level, which reflects the cyber-physical interaction impact. Furthermore, the stability forbidden criterion is applied to make the switching/sampling frequency solving process become a Hurwitz matrix identification problem through space mappings. Based on these space mappings, the adaptive step collection algorithm is adopted to obtain the minimum switching/sampling frequency. Finally, the simulation and experiment results illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.1) 收稿日期 2021-06-01 录用日期 2021-10-18 Manuscript received June 1, 2021; accepted October 18, 2021 国家自然科学基金 (U20A20190, 62073065), 国家重点研发计划 (2018YFA0702200) 资助 Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A20190, 62073065) and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0702200) 本文责任编委 诸兵 Recommended by Associate Editor ZHU Bing 1. 东北大学信息科学与工程学院 沈阳 110819 2. 东北大学流程工业综合自动化国家重点实验室 沈阳 110819 1. College of Information Science and Engineering, Northeast-2) ern University, Shenyang 110819 2. State Key Laboratory of Synthetical Automation for Process Industries, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819
-
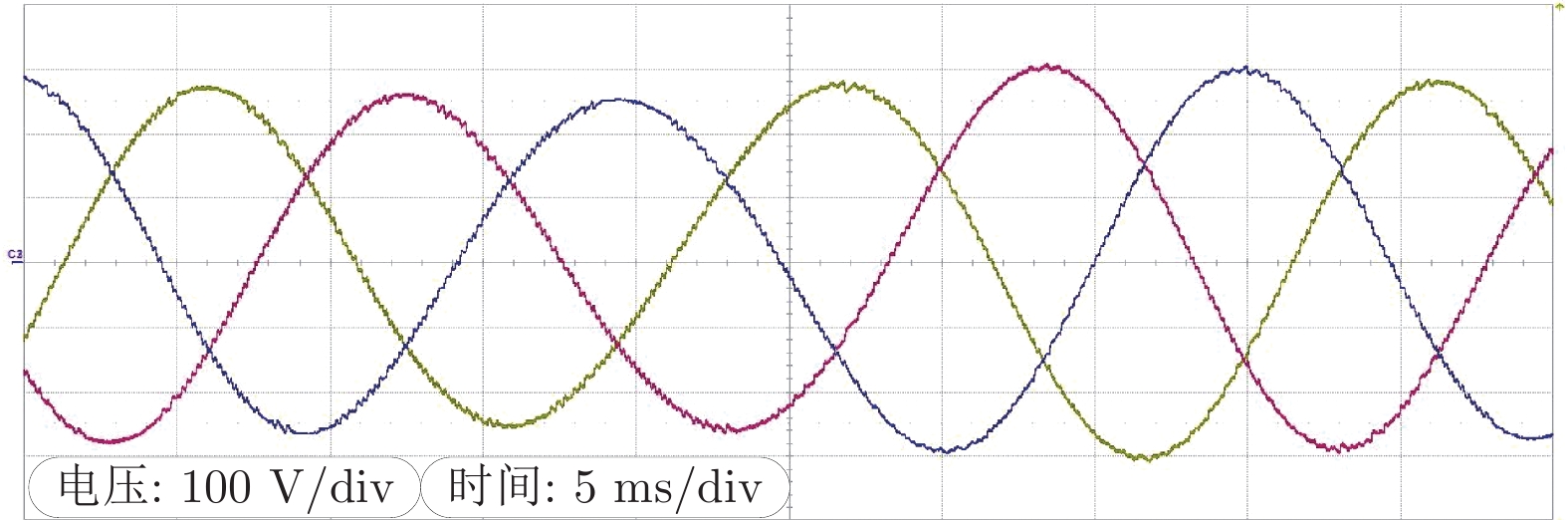
表 1 仿真系统参数表
Table 1 Simulation system parameters
参数 数值 电压控制器 $G_v^{inv} = 1 + 8/{ {s} }$ 电流控制器 $G_c^{inv} = 4 + 150/{ {s} }$ 母线电压 700 V 额定电压 220 V 额定频率 50 Hz 截止频率 5 Hz 滤波器电容 600 μF 滤波器电感 6 mH -
[1] 杨涛, 柴天佑. 分布式协同优化的研究现状与展望. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2020, 50(11): 1414-1425 doi: 10.1360/SST-2020-0040Yangtao, Chai Tianyou. Research status and prospects of distributed collaborative optimization. SCIENTIA SINICA Technologica, 2020, 50(11): 1414-1425 doi: 10.1360/SST-2020-0040 [2] 孙长银, 吴国政, 王志衡, 等. 自动化学科面临的挑战. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(02): 464-474Sun Changyin, Wu Guozheng, Wang Zhiheng, et al. On Challenges in Automation Science and Technology. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2021, 47(02): 464-474 [3] 原豪男, 郭戈. 交通信息物理系统中的车辆协同运行优化调度. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(01): 143-152Yuan Haonan, Guo Ge. Vehicle Cooperative Optimization Scheduling in Transportation Cyber Physical Systems. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2019, 39(14): 4015-4025 [4] H. Georg, S. C. Müller, C. Rehtanz, et al. Analyzing Cyber-Physical Energy Systems: The INSPIRE Cosimulation of Power and ICT Systems Using HLA. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2014, 10(4): 2364-2373 doi: 10.1109/TII.2014.2332097 [5] 杨飞生, 汪璟, 潘泉, 康沛沛. 网络攻击下信息物理融合电力系统的弹性事件触发控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(01): 110-119.Yang Feisheng, Wang Jing, Pan Quan, Kang Peipei. Resilient Event-triggered Control of Grid Cyber-physical Systems Against Cyber Attack. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2019, 45(01): 110-119. [6] B. Satchidanandan, P. R. Kumar. Dynamic Watermarking: Active Defense of Networked Cyber–Physical Systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(2): 219-240 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2575064 [7] Cao Jie, Liu Jinliang, Tian Engang, et al. Hybrid-triggered-based security controller design for networked control system under multiple cyber attacks. Information Sciences, 2021, 548(10): 69-84. [8] D. Lv, A. Eslami and S. Cui. Load-Dependent Cascading Failures in Finite-Size Erdes-Rényi Random Networks. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2017, 4(2): 129-139 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2017.2685582 [9] D. J. Miller, Z. Xiang and G. Kesidi. Adversarial Learning Targeting Deep Neural Network Classification: A Comprehensive Review of Defenses Against Attacks. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2020, 108(3): 402-433 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.2970615 [10] Xu L, Guo Q, Wang Z, Sun H. Modeling of time-delayed distributed cyber-physical power systems for small-signal stability analysis. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, DOI: 10.1109/TSG. 2021.3052303 [11] 张一媚, 董朝宇, 董晓红, 等. 含电动汽车集群调频的信息能源系统谱特征和稳定性评估. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(02): 12-20Zhang Yimei, Dong Chaoyu, Dong Xiaohong, et al. Spectral Feature and Stability Assessment for Cyber-Energy System with Frequency Regulation of Electric Vehicle Cluster. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(02): 12-20 [12] R. Wang, Q. Sun, P. Zhang, et al. Reduced-Order Transfer Function Model of the Droop-Controlled Inverter via Jordan Continued-Fraction Expansion. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2020, 35(3): 1585-1595 doi: 10.1109/TEC.2020.2980033 [13] X. He, R. Wang, J. Wu, et al. Nature of power electronics and integration of power conversion with communication for talkative power. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2479-2490. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16262-0 [14] C. Dong, Q. Xiao, M. Wang, et al. Distorted Stability Space and Instability Triggering Mechanism of EV Aggregation Delays in the Secondary Frequency Regulation of Electrical Grid-Electric Vehicle System. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11(6): 5084-5098 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2020.3008333 [15] M. Rasheduzzaman, J. A. Mueller, J. W. Kimball. Reduced-Order Small-Signal Model of Microgrid Systems. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2015, 6(4): 1292-1305 doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2015.2433177 [16] L. Luo, S. V. Dhople. Spatiotemporal Model Reduction of Inverter-Based Islanded Microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2014, 29(4): 823-832 doi: 10.1109/TEC.2014.2348716 [17] F. Dorfler, F. Bullo. Kron Reduction of Graphs With Applications to Electrical Networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2013, 60(1): 150-163 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215780 [18] 王睿, 孙秋野, 张化光. 微电网的电流均衡/电压恢复自适应动态规划策略研究. 自动化学报, 在线 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210015Wang Rui, Sun Qiu-Ye, Zhang Hua-Guang. Research on current sharing/voltage recovery based adaptive dynamic programming control strategy of microgrids. Acta Automatica Sinica, online doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210015 [19] J. Zhou, Peng Shi, Deqiang Gan, et al, Large-Scale Power System Robust Stability Analysis Based on Value Set Approach. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32(5): 4012-4023 doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2017.2657642 [20] W. Wu et al. A Virtual Phase-Lead Impedance Stability Control Strategy for the Maritime VSC–HVDC System. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(12): 5475-5486 doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2804670 [21] F. Liu, J. Liu, H. Zhang, et al. Stability Issues of Z+Z Type Cascade System in Hybrid Energy Storage System (HESS). IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(11): 5846-5859 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2013.2295259 [22] Y. Ren, R. Duan, L. Chen, et al. Stability Assessment of Grid-Connected Converter System Based on Impedance Model and Gershgorin Theorem. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2020, 35(3): 1559-1566 doi: 10.1109/TEC.2020.2978490 [23] W. Rui, S. Qiuye, M. Dazhong, et al. Line Inductance Stability Operation Domain Assessment for Weak Grids With Multiple Constant Power Loads. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2021, 36(2): 1045-1055. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2020.3021070 [24] 卢自宝, 钟尚鹏, 郭戈. 基于分布式策略的直流微电网下垂控制设计. 自动化学报, 在线 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190628Lu Zi-Bao, Zhong Shang-Peng, Guo Ge. Design of droop controller for DC microgrid based on distributed strategy. Acta Automatica Sinica, online doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190628 [25] D. Pan, X. Ruan, C. Bao, et al. Capacitor-Current-Feedback Active Damping With Reduced Computation Delay for Improving Robustness of LCL-Type Grid-Connected Inverter. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(7): 3414-3427 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2013.2279206 [26] A. A. A. Radwan and Y. A. I. Mohamed. Analysis and Active-Impedance-Based Stabilization of Voltage-Source-Rectifier Loads in Grid-Connected and Isolated Microgrid Applications. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2013, 4(3): 563-576 doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2012.2227981 [27] R. Wang, Q. Sun, D. Ma, et al. The small-signal stability analysis of the droop-controlled converter in electromagnetic timescale. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, 10(3): 1459–1469. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2019.2894633 [28] A. Riccobono and E. Santi. Comprehensive review of stability criteria for DC power distribution systems. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2014, 50(5): 3525–3535. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2014.2309800 [29] Z. Liu, J. Liu, W. Bao, et al. Infinity-Norm of Impedance Based Stability Criterion for Three Phase AC Distributed Power Systems With Constant Power Loads. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2015, 30(6): 3030-3043. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2014.2331419 [30] R. Wang, Q. Sun, W. Hu, et al. Stability-Oriented Droop Coefficients Region Identification for Inverters Within Weak Grid: An Impedance-Based Approach. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(4): 2258-2268. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3034243 -





 下载:
下载: