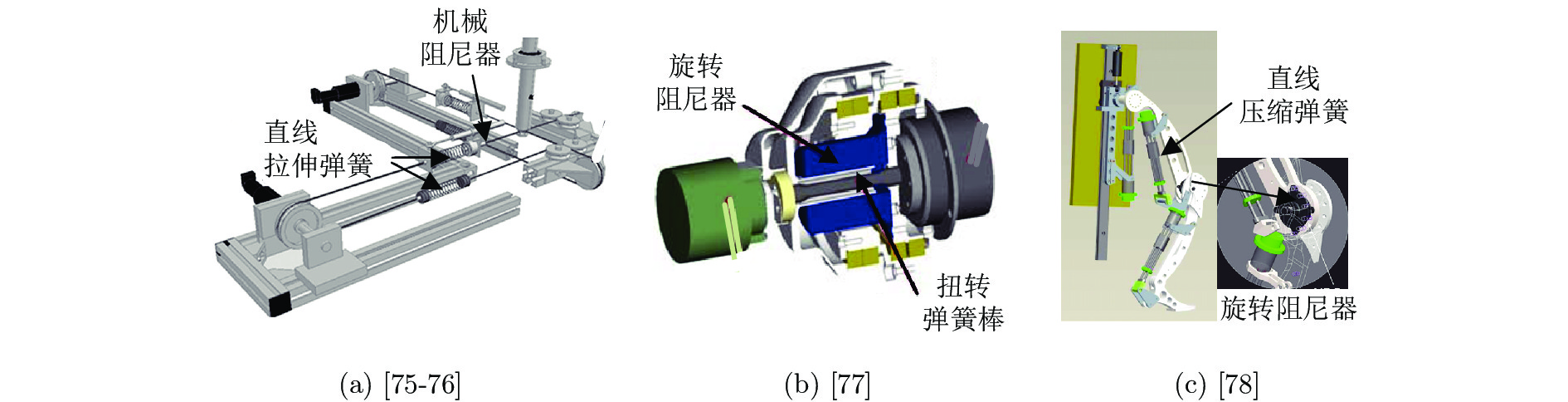
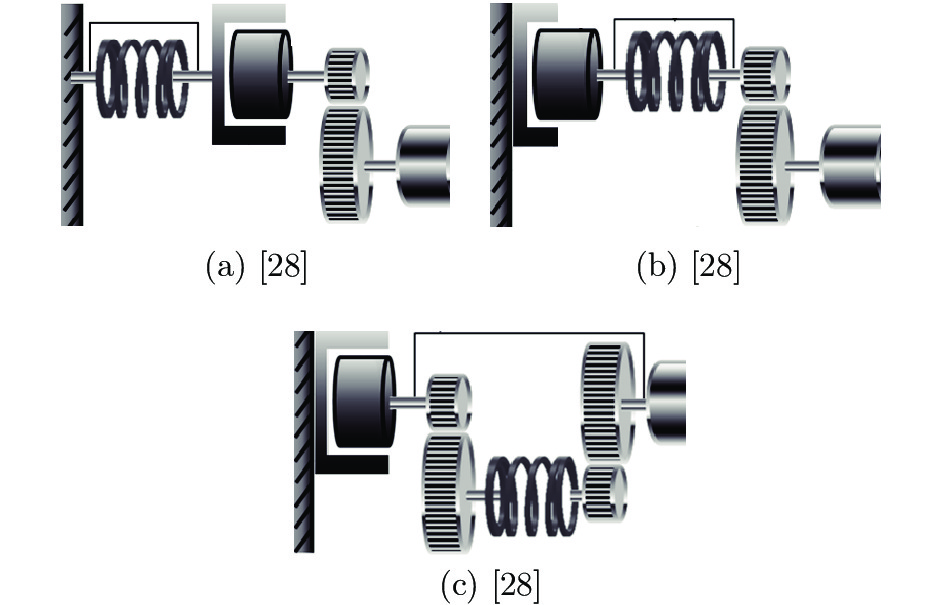
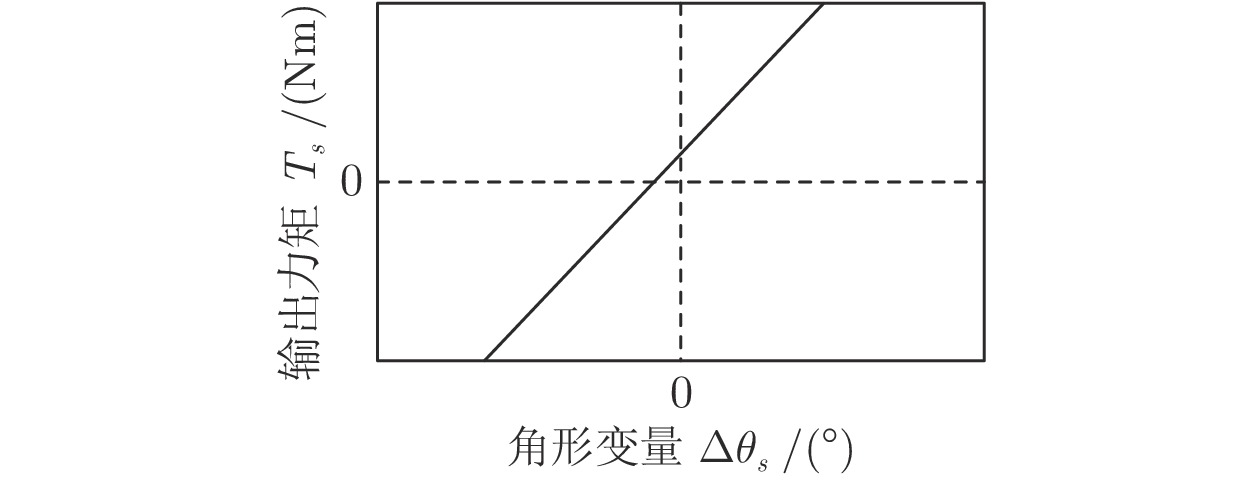
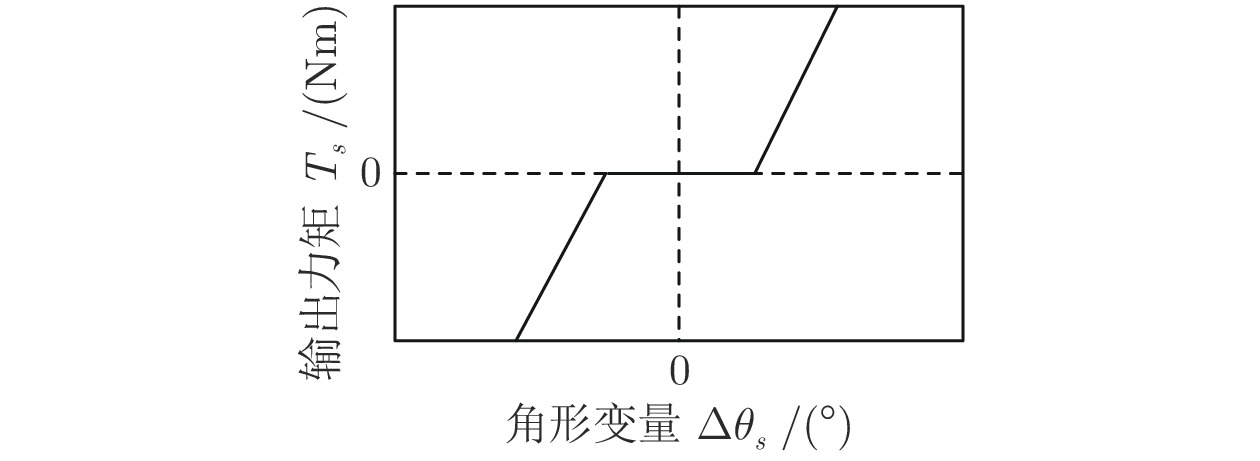
-
摘要:
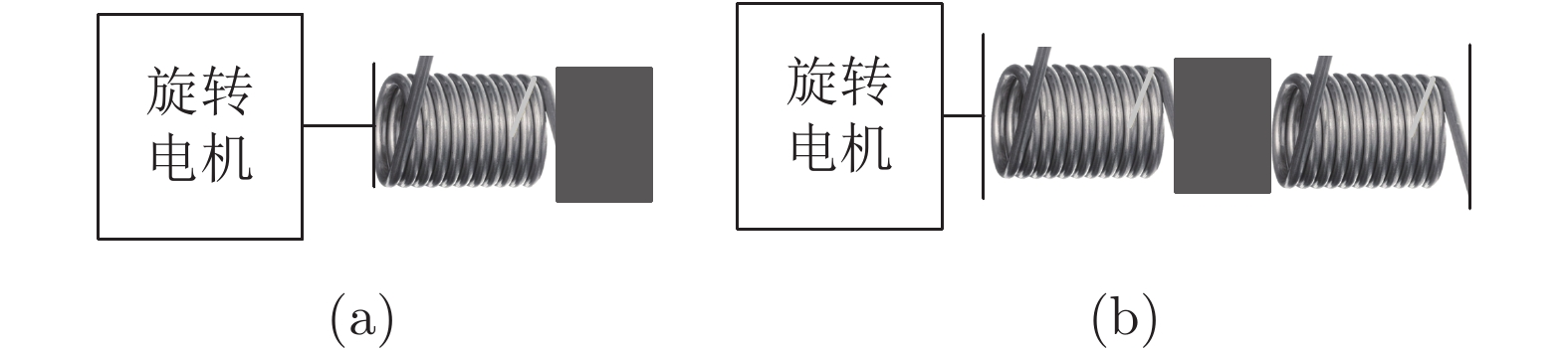
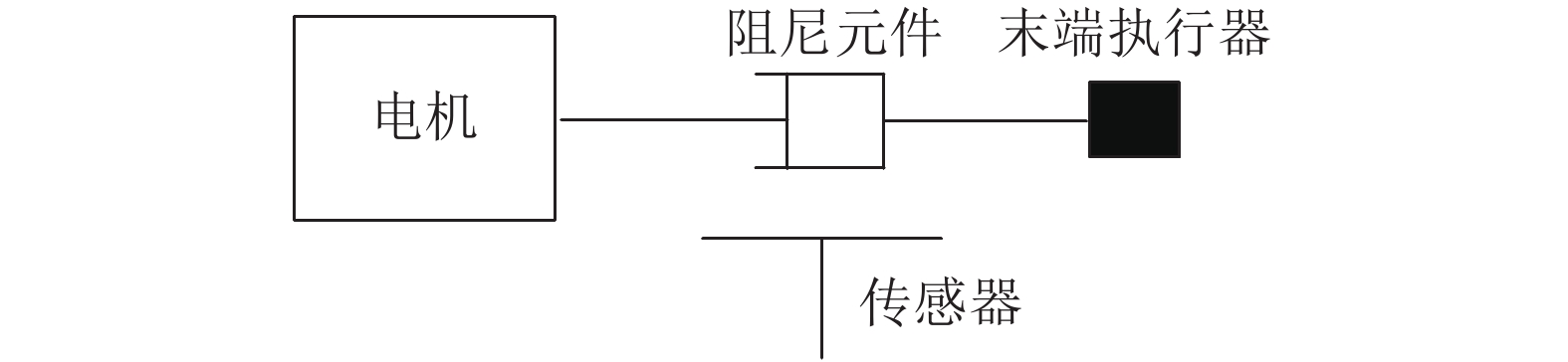
相比于传统的刚性驱动器, 串联弹性驱动器(Series elastic actuator, SEA)具有被动柔顺性、阻抗低、抗冲击、力感知等诸多优点, 因而已被广泛应用于各种机器人系统中. 首先根据弹性和阻尼特性将串联弹性驱动器分为弹性型、阻尼型和弹性−阻尼型串联弹性驱动器, 介绍不同类型串联弹性驱动器的优缺点, 并详细概述弹性和阻尼特性的机械实现方式; 然后对各类串联弹性驱动器作为力传感器的建模方法进行介绍; 接着叙述串联弹性驱动器在机器人系统中的主要应用, 如力传感器、安全保护、降低能耗; 最后展望串联弹性驱动器未来的发展方向.
Abstract:Compared with traditional rigid actuators, series elastic actuator (SEA) has many advantages such as passive compliance, low impedance, impact resistance, and force sensing, and so they have been widely used in various robot systems. Firstly, according to the elasticity and damping characteristics, SEAs are divided into elastic SEAs, damped SEAs and elastic-damped SEAs. The advantages and disadvantages of each SEA are introduced, and the mechanical implementation methods of elasticity and damping characteristics are summarized in detail. Then, the modeling methods of SEAs as force sensors are presented. Next, the main applications of SEAs in the robot systems are described, such as force sensors, safety protection and energy consumption reduction. Finally, the future development directions of SEAs are recommended.
-
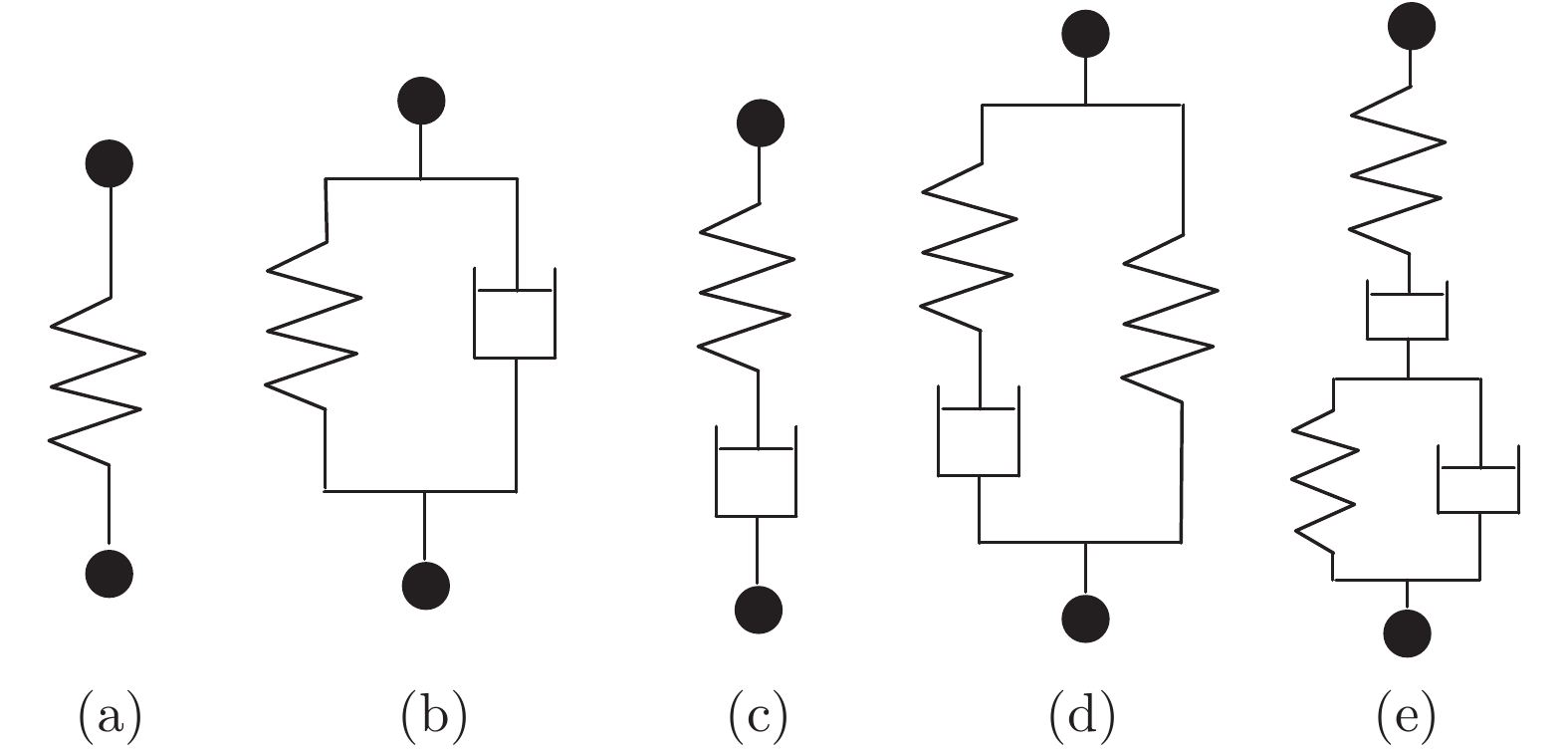
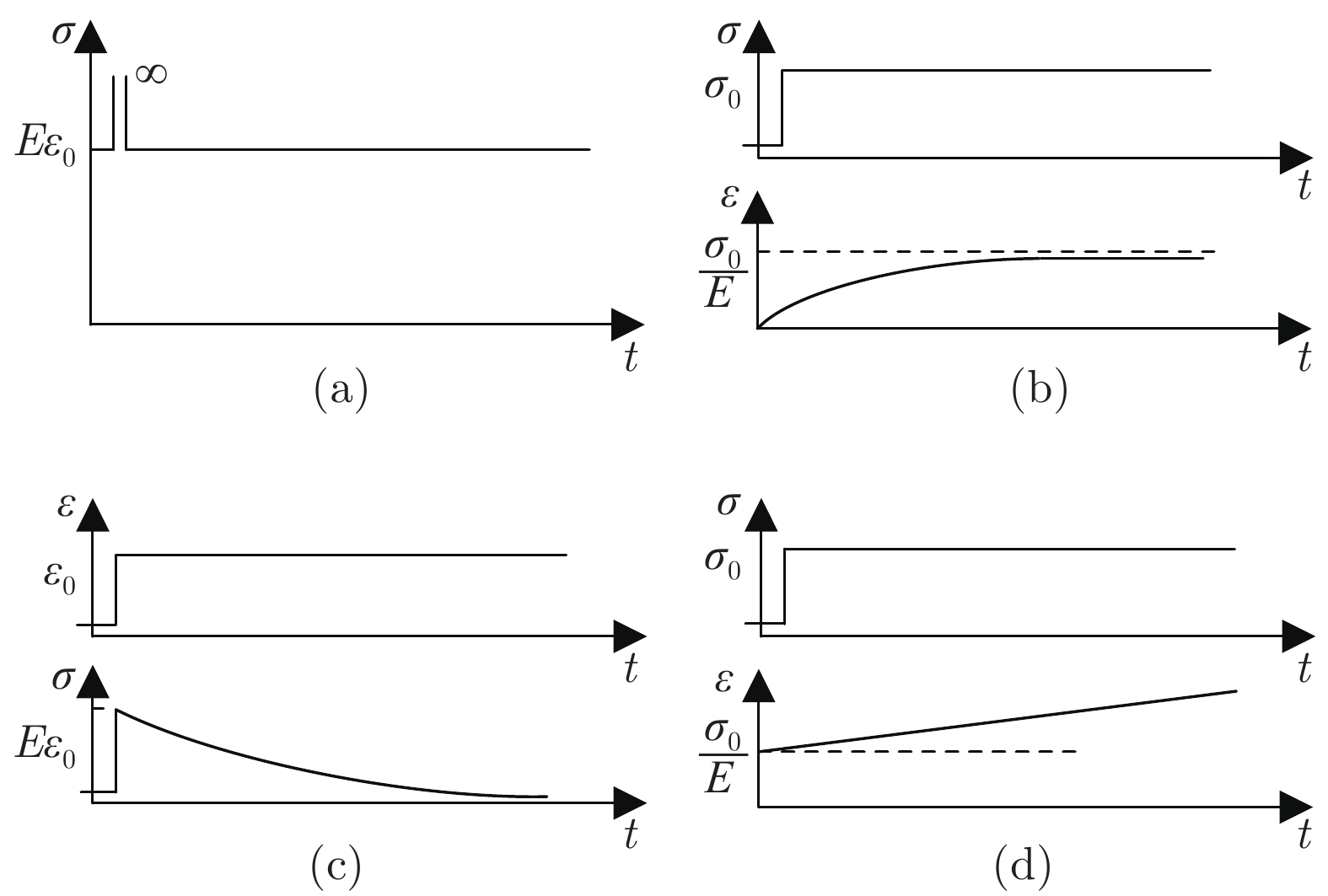
表 1 各类串联弹性驱动器机械实现方式及比较
Table 1 Mechanical realization and comparison of various series elastic actuators
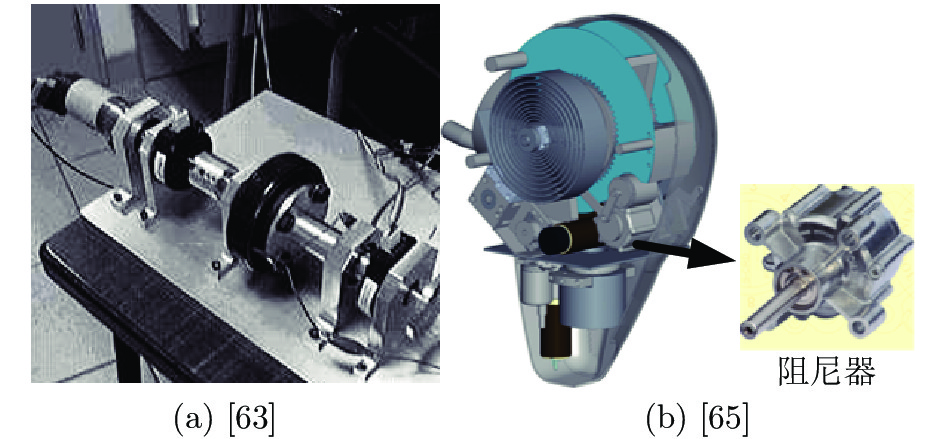
类型 物理特性 机械实现方式 系统力带宽 能量特性 安全性 弹性型串联弹性驱动器 弹性 直线压缩弹簧 一般 效率高 高 直线拉伸弹簧 螺旋扭转弹簧 结构弹簧 阻尼型串联弹性驱动器 阻尼 磁流变液阻尼器 较高 效率低 低 弹性-阻尼型串联弹性驱动器 弹性和阻尼 粘弹性元件 高 效率一般 一般 弹性与阻尼元件并联组合装置 弹性元件放置位置 表 2 各类串联弹性驱动器建模方法
Table 2 Modeling methods of various series elastic actuators
类型 建模方法 模型参数 复杂度 弹性型 胡克定律 1 简单 阻尼型 线性粘性阻尼 1 简单 弹性-阻尼型 粘弹性元件 Maxwell 模型、指数模型等 多 复杂 弹性和阻尼元件并联组合装置 线性粘性阻尼与胡克定律 弹性元件放置位置 动力学 -
[1] Li J, Li S Q, Tian G H, Shang H C. Muscle tension training method for series elastic actuator (SEA) based on gain-scheduled method. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 121: Article No. 103253 [2] Pratt G A, Williamson M M. Series elastic actuators. In: Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Pittsburgh, USA: IEEE, 1995. 399−406 [3] Chew C M, Hong G S, Zhou W. Series damper actuator: A novel force/torque control actuator. In: Proceedings of the 4th IEEE/RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots. Santa Monica, USA: IEEE, 2004. 533−546 [4] Hurst J W, Rizzi A A, Hobbelen D. Series elastic actuation: Potential and pitfalls. In: Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Climbing and Walking Robots. 2004. [5] Vallery H, Veneman J, Van Asseldonk E, Ekkelenkamp R, Buss M, Van Der Kooij H. Compliant actuation of rehabilitation robots. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2008, 15(3): 60−69 [6] Refour E R, Sebastian B, Chauhan R J, Ben-Tzvi P. A general purpose robotic hand exoskeleton with series elastic actuation. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2019, 11(6): Article No. 060902 [7] Vantilt J, Tanghe K, Afschrift M, Bruijnes A K B D, Junius K, Geeroms J, et al. Model-based control for exoskeletons with series elastic actuators evaluated on sit-to-stand movements. Journal of Neuro Engineering and Rehabilitation. 2019, 16: Article No. 65 [8] Trigili E, Crea S, Moise M, Baldoni A, Cempini M, Ercolini G, et al. Design and experimental characterization of a shoulder-elbow exoskeleton with compliant joints for post-stroke rehabilitation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, 24(4): 1485−1496 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2019.2907465 [9] Lee H D, Moon J I, Kang T H. Design of a series elastic tendon actuator based on gait analysis for a walking assistance exosuit. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2019, 17(11): 2940−2947 doi: 10.1007/s12555-018-0492-0 [10] Zhang T, Huang H. Design and control of a series elastic actuator with clutch for hip exoskeleton for precise assistive magnitude and timing control and improved mechanical safety. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, 24(5): 2215−2226 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2019.2932312 [11] Guenther F, Quy Vu H, Lida F. Improving legged robot hopping by using coupling-based series elastic actuation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, 24(2): 413−423 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2019.2893235 [12] Verstraten T, Furnémont R, Beckerle P, Vanderborght B, Lefeber D. A hopping robot driven by a series elastic dual-motor actuator. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(3): 2310−2316 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2902071 [13] Lee C, Oh S. Development, analysis, and control of series elastic actuator-driven robot leg. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2019, 13: Article No. 17 [14] Werner A, Henze B, Keppler M, Loeffl F, Leyendecker S, Ott C. Structure preserving multi-contact balance control for series-elastic and visco-elastic humanoid robots. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2018. 1233−1240 [15] Bellicoso C D, Jenelten F, Fankhauser P, Gehring C, Hwangbo J, Hutter M. Dynamic locomotion and whole-body control for quadrupedal robots. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 3359−3365 [16] Zhu Q G, Mao Y C, Xiong R, Wu J. Adaptive torque and position control for a legged robot based on a series elastic actuator. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2016, 13(1): Article No. 26 [17] Werner A, Turlej W, Ott C. Generation of locomotion trajectories for series elastic and viscoelastic bipedal robots. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 5853−5860 [18] Pfeifer S, Pagel A, Riener R, Vallery H. Actuator with angle-dependent elasticity for biomimetic transfemoral prostheses. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2015, 20(3): 1384−1394 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2014.2337514 [19] Convens B, Dong D B, Furnemont R, Verstraten T, Cherelle P, Lefeber D, et al. Modeling, design and test-bench validation of a semi-active propulsive ankle prosthesis with a clutched series elastic actuator. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(2): 1823−1830 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2897993 [20] Sun X J, Sugai F, Okada K, Inaba M. Variable transmission series elastic actuator for robotic prosthesis. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, Australia: IEEE, 2018. 2796−2803 [21] Sun X J, Sugai F, Okada K, Inaba M. Design, control and preliminary test of robotic ankle prosthesis. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2018. 2787−2793 [22] Zhu J Y, Wang Q N, Wang L. On the design of a powered transtibial prosthesis with stiffness adaptable ankle and toe joints. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(9): 4797−4807 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2293691 [23] Baccelliere L, Kashiri N, Muratore L, Laurenzi A, Kamedula M, Margan A, et al. Development of a human size and strength compliant bi-manual platform for realistic heavy manipulation tasks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 5594−5601 [24] Hu Y, Mombaur K. Optimal control based push recovery strategy for the iCub humanoid robot with series elastic actuators. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 5846-5852 [25] Nava G, Pucci D, Nori F. Momentum control of humanoid robots with series elastic actuators. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 2185−2191 [26] Lee C, Lee J, Malzahn J, Tsagarakis N, Oh S. A two-staged residual for resilient external torque estimation with series elastic actuators. In: Proceedings of the IEEE-RAS 17th International Conference on Humanoid Robotics (Humanoids). Birmingham, England: IEEE, 2017. 817−823 [27] Tsagarakis N G, Laffranchi M, Vanderborght B, Caldwell D G. A compact soft actuator unit for small scale human friendly robots. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Kobe, Japan: IEEE, 2009. 4356−4362 [28] Lee C, Kwak S, Kwak J, Oh S. Generalization of series elastic actuator configurations and dynamic behavior comparison. Actuators, 2017, 6(3): Article No. 26 [29] Vanderborght B, Albu-Schaeffer A, Bicchi A, Burdet E, Caldwell D G, Carloni R, et al. Variable impedance actuators: A review. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2013, 61(12): 1601−1614 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2013.06.009 [30] 魏敦文, 葛文杰, 高涛. 仿生灵感下的弹性驱动器的研究综述. 机器人, 2017, 39(4): 541−550Wei Dun-Wen, Ge Wen-Jie, Gao Tao. Review of elastic actuator research from bionic inspiration. Robot, 2017, 39(4): 541−550 [31] Hsieh H C, Chen D F, Chien L, Lan C C. Design of a parallel actuated exoskeleton for adaptive and safe robotic shoulder rehabilitation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(5): 2034−2045 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2717874 [32] Lee J W, Kim G. Design and control of a lifting assist device for preventing lower back injuries in industrial athletes. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2019, 20(10): 1825−1838 doi: 10.1007/s12541-019-00183-0 [33] 孙雷, 孙伟超, 王萌, 刘景泰. 基于RISE反馈的串联弹性驱动器最优控制方法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(12): 2170−2178Sun Lei, Sun Wei-Chao, Wang Meng, Liu Jing-Tai. Optimal control for series elastic actuator using RISE feedback. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 2170−2178 [34] Rouse E J, Mooney L M, Herr H M. Clutchable series-elastic actuator: Implications for prosthetic knee design. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2014, 33(13): 1611−1625 doi: 10.1177/0278364914545673 [35] Agarwal P, Yun Y, Fox J, Madden K, Deshpande A D. Design, control, and testing of a thumb exoskeleton with series elastic actuation. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2017, 36(3): 355−375 doi: 10.1177/0278364917694428 [36] Marconi D, Baldoni A, McKinney Z, Cempini M, Crea S, Vitiello N. A novel hand exoskeleton with series elastic actuation for modulated torque transfer. Mechatronics, 2019, 61: 69−82 doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2019.06.001 [37] Gim K G, Hong D W. Design of a series elastic resistance mechanism for exercise and rehabilitation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE-RAS 16th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids). Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2016. 1239−1244 [38] Yu N B, Zou W L, Tan W, Yang Z. Augmented virtual stiffness rendering of a cable-driven SEA for human-robot interaction. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(4): 714−723 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510637 [39] Yu N B, Zou W L, Sun Y B. Passivity guaranteed stiffness control with multiple frequency band specifications for a cable-driven series elastic actuator. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 117: 709−722 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.08.007 [40] Rao P, Deshpande A D. Analyzing and improving cartesian stiffness control stability of series elastic tendon-driven robotic hands. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, Australia: IEEE, 2018. 5415−5420 [41] Rao P, Thomas G C, Sentis L, Deshpande A D. Analyzing achievable stiffness control bounds of robotic hands with coupled finger joints. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore: IEEE, 2017. 3447−3452 [42] 尹伟, 孙雷, 王萌, 刘景泰. 针对串联弹性驱动器抖动抑制的轨迹规划和跟踪控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(8): 1436−1445Yin Wei, Sun Lei, Wang Meng, Liu Jing-Tai. Motion planning and tracking control of series elastic actuator for vibration suppression. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(8): 1436−1445 [43] Yin W, Sun L, Wang M, Liu J T. Position control of a series elastic actuator based on global sliding mode controller design. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(3): 850−858 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911498 [44] Chen T Y, Casas R, Lum P S. An elbow exoskeleton for upper limb rehabilitation with series elastic actuator and cable-driven differential. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2019, 35(6): 1464−1474 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2019.2930915 [45] Jung Y, Bae J. An asymmetric cable-driven mechanism for force control of exoskeleton systems. Mechatronics, 2016, 40: 41−50 doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2016.10.013 [46] DeBoon B, Nokleby S, La Delfa N, Rossa C. Differentially-clutched series elastic actuator for robot-aided musculoskeletal rehabilitation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2019. 1507−1513 [47] Ates S, Sluiter V I, Lammertse P, Stienen A H A. ServoSEA concept: Cheap, miniature series-elastic actuators for orthotic, prosthetic and robotic hands. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics. Sao Paulo, Brazil: IEEE, 2014. 752−757 [48] Agarwal P, Deshpande A D. Series elastic actuators for small-scale robotic applications. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2017, 9(3): Article No. 031016 [49] Carpino G, Accoto D, Sergi F, Tagliamonte N L, Guglielmelli E. A novel compact torsional spring for series elastic actuators for assistive wearable robots. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2012, 134(12): Article No. 121002 [50] Irmscher C, Woschke E, May E, Daniel C. Design, optimisation and testing of a compact, inexpensive elastic element for series elastic actuators. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2018, 52: 84−89 [51] Ruiken D, Cummings J P, Savaria U R, Sup F C, Grupen R A. uBot-7: A dynamically balancing mobile manipulator with series elastic actuators. In: Proceedings of the IEEE-RAS 17th International Conference on Humanoid Robotics. Birmingham, England: IEEE, 2017. 676−682 [52] Lagoda C, Schouten A C, Stienen A H A, Hekman E E G, Van Der Kooij H. Design of an electric series elastic actuated joint for robotic gait rehabilitation training. In: Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics. Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 2010. 21−26 [53] Wang Y P, Chen Y L, Chen K B, Wu Y X, Huang Y J. A flat torsional spring with corrugated flexible units for series elastic actuators. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM). Hefei, China: IEEE, 2017. 138−143 [54] Dos Santos W M, Caurin G A P, Siqueira A A G. Torque control characterization of a rotary series elastic actuator for knee rehabilitation. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Advanced Robotics. Montevideo, Uruguay: IEEE, 2013. 1−6 [55] Yildirim M C, Sendur P, Bilgin O, Gulek B, Yapici G G, Ugurlu B. An integrated design approach for a series elastic actuator: Stiffness formulation, fatigue analysis, thermal management. In: Proceedings of the IEEE-RAS 17th International Conference on Humanoid Robotics. Birmingham, England: IEEE, 2017. 384−389 [56] Georgiev N, Burdick J. Design and analysis of planar rotary springs. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 4777−4784 [57] Zhang T, Tran M, Huang H. Design and experimental verification of hip exoskeleton with balance capacities for walking assistance. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2018, 23(1): 274−285 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2018.2790358 [58] Koopaee M J, Bal S, Pretty C, Chen X Q. Design and development of a wheel-less snake robot with active stiffness control for adaptive pedal wave locomotion. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2019, 16(4): 593−607 doi: 10.1007/s42235-019-0048-x [59] Paine N, Mehling J S, Holley J, Radford N A, Johnson G, Fok C L, et al. Actuator control for the NASA-JSC valkyrie humanoid robot: A decoupled dynamics approach for torque control of series elastic robots. Journal of Field Robotics, 2015, 32(3): 378−396 doi: 10.1002/rob.21556 [60] Yasuda K, Ikeura R, Hayakawa S, Sawai H. Stability of impedance control of a series elastic actuator with a torque controlled actuator for improving the system performance. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Zhuhai, China: IEEE, 2015. 2163−2168 [61] Lee Y F, Chu C Y, Xu J Y, Lan C C. A humanoid robotic wrist with two-dimensional series elastic actuation for accurate force/torque interaction. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2016, 21(3): 1315−1325 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2016.2530746 [62] Bianchi M, Cempini M, Conti R, Meli E, Ridolfi A, Vitiello N, et al. Design of a series elastic transmission for hand exoskeletons. Mechatronics, 2018, 51: 8−18 doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2018.02.010 [63] Zhou W, Chew C M, Hong G S. Inverse dynamics control for series damper actuator based on MR fluid damper. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics. Monterey, California, USA: IEEE, 2005. 473−478 [64] Zhou W, Chew C M, Hong G S. Design of series damper actuator. Robotica, 2009, 27(3): 379−387 doi: 10.1017/S0263574708004797 [65] Westerveld A J, Aalderink B J, Hagedoorn W, Buijze M, Schouten A C, Van Der Kooij H. A damper driven robotic end-point manipulator for functional rehabilitation exercises after stroke. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2014, 61(10): 2646−2654 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2014.2325532 [66] Kim D H, Oh J H. Hysteresis modeling for torque control of an elastomer series elastic actuator. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, 24(3): 1316−1324 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2019.2906698 [67] Rollinson D. Control and Design of Snake Robots [Ph. D. dissertation], Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 2014 [68] Jarrett C, McDaid A. Modeling and feasibility of an elastomer-based series elastic actuator as a haptic interaction sensor for exoskeleton robotics. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, 24(3): 1325−1333 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2019.2906918 [69] Austin J, Schepelmann A, Geyer H. Control and evaluation of series elastic actuators with nonlinear rubber springs. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Hamburg, Germany: IEEE, 2015. 6563−6568 [70] Shepherd M K, Rouse E J. Design and validation of a torque-controllable knee exoskeleton for sit-to-stand assistance. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(4): 1695−1704 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2704521 [71] Van Dijk W, Meijneke C, Van Der Kooij H. Evaluation of the achilles ankle exoskeleton. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2017, 25(2): 151−160 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2527780 [72] Kang I, Hsu H, Young A. The effect of hip assistance levels on human energetic cost using robotic hip exoskeletons. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(2): 430−437 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2890896 [73] Caputo J M, Collins S H. A universal ankle-foot prosthesis emulator for human locomotion experiments. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 2014, Article No. 65(3): Article No. 035002 [74] Senturk Y M, Patoglu V. MRI-VisAct: A Bowden-cable-driven MRI-compatible series viscoelastic actuator. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2018, 40(8): 2440−2453 doi: 10.1177/0142331217730429 [75] Oblak J, Matjačić Z. Design of a series visco-elastic actuator for multi-purpose rehabilitation haptic device. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 2011, 8: Article No. 3 [76] Mancisidor A, Zubizarreta A, Cabanes I, Bengoa P, Marcos M, Jung J H. Enhanced force control using force estimation and nonlinearity compensation for the universal haptic pantograph. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Hamburg, Germany: IEEE, 2015. 5599−5604 [77] Iwata H, Sugano S. Design of human symbiotic robot TWENDY-ONE. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Kobe, Japan: IEEE, 2009. 580−586 [78] Garcia E, Arevalo J C, Muñoz G, Gonzalez-De-Santos P. Combining series elastic actuation and magneto-rheological damping for the control of agile locomotion. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2011, 59(10): 827−839 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2011.06.006 [79] Paine N, Oh S, Sentis L. Design and control considerations for high-performance series elastic actuators. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2014, 19(3): 1080−1091 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2013.2270435 [80] Lee H, Kwak S, Oh S. Force control of series elastic actuators-driven parallel robot. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, Australia: IEEE, 2018. 5401−5406 [81] Isik K, He S D, Ho J, Sentis L. Re-engineering a high performance electrical series elastic actuator for low-cost industrial applications. Actuators, 2017, 6(1): Article No. 5 doi: 10.3390/act6010005 [82] Lens T, Von Stryk O. Design and dynamics model of a lightweight series elastic tendon-driven robot arm. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Karlsruhe, Germany: IEEE, 2013. 4512−4518 [83] Lee C, Oh S. Configuration and performance analysis of a compact planetary geared elastic actuator. In: Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. Florence, Italy: IEEE, 2016. 6391−6396 [84] Lauria M, Legault M A, Lavoie M A, Michaud F. Differential elastic actuator for robotic interaction tasks. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Pasadena, CA, USA: IEEE, 2008. 3606−3611 [85] Kim S, Bae J. Force-mode control of rotary series elastic actuators in a lower extremity exoskeleton using model-inverse time delay control. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(3): 1392−1400 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2687979 [86] Oh S, Kong K. High-precision robust force control of a series elastic actuator. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(1): 71−80 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2016.2614503 [87] Kim S, Bae J. Force-mode control of rotary series elastic actuators in a lower extremity exoskeleton using model-inverse time delay control (MiTDC). In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Daejeon, South Korea: IEEE, 2016. 3836−3841 [88] Oh S, Lee C, Kong K. Force control and force observer design of series elastic actuator based on its dynamic characteristics. In: Proceedings of the 41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. Yokohama, Japan: IEEE, 2015. 4639−4644 [89] Calanca A, Fiorini P. A rationale for acceleration feedback in force control of series elastic actuators. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(1): 48−61 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2765667 [90] Zhao Y, Paine N, Jorgensen S J, Sentis L. Impedance control and performance measure of series elastic actuators. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(3): 2817−2827 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2745407 [91] Zhang J J, Collins S H. The passive series stiffness that optimizes torque tracking for a lower-limb exoskeleton in human walking. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2017, 11: Article No. 68 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2017.00068 [92] Calanca A, Muradore R, Fiorini P. Impedance control of series elastic actuators: Passivity and acceleration-based control. Mechatronics, 2017, 47: 37−48 doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2017.08.010 [93] Lee Y H, Lee Y H, Lee H, Phan L T, Kang H, Kim Y B, et al. Development of torque controllable leg for running robot, AiDIN-IV. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 4125−4130 [94] 毛翊超. 采用串联弹性驱动器的仿生腿足式机器人跳跃与自适应平衡控制研究[博士学位论文], 浙江大学, 中国, 2018Mao Yi-Chao. Hopping and Adaptive Balance Control of Bionic Legged Robot Based on Series Elastic Actuators [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, China, 2018 [95] 李占卫, 李治军. 磁流变阻尼器动力学模型的研究现状. 机械制造与自动化, 2012, 41(1): 142−145 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5276.2012.01.048Li Zhan-Wei, Li Zhi-Jun. Status of researching on dynamical models of MR damper. Machine Building & Automation, 2012, 41(1): 142−145 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5276.2012.01.048 [96] Parietti F, Baud-Bovy G, Gatti E, Riener R, Guzzella L, Vallery H. Series viscoelastic actuators can match human force perception. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2011, 16(5): 853−860 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2011.2162076 [97] Karlsson F, Persson A. Modelling Non-linear Dynamics of Rubber Bushings-Parameter Identification and Validation [Master dissertation], Lund University, Sweden, 2003 [98] Abe K, Suga T, Fujimoto Y. Control of a biped robot driven by elastomer-based series elastic actuator. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control. Sarajevo, Bosnia-Herzegovina: IEEE, 2012. 1−6 [99] Kikuchi M, Aiken I D. An analytical hysteresis model for elastomeric seismic isolation bearings. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 1997, 26(2): 215−231 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9845(199702)26:2<215::AID-EQE640>3.0.CO;2-9 [100] Choi W, Won J, Lee J, Park J. Low stiffness design and hysteresis compensation torque control of SEA for active exercise rehabilitation robots. Autonomous Robots, 2017, 41: 1221−1242 doi: 10.1007/s10514-016-9591-z [101] Schepelmann A, Geberth K A, Geyer H. Compact nonlinear springs with user defined torque-deflection profiles for series elastic actuators. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2014. 3411−3416 [102] Paskarbeit J, Annunziata S, Basa D, Schneider A. A self-contained, elastic joint drive for robotics applications based on a sensorized elastomer coupling-design and identification. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2013, 199: 56−66 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2013.04.028 [103] Laffranchi M, Chen L S, Kashiri N, Lee J, Tsagarakis N G, Caldwell D G. Development and control of a series elastic actuator equipped with a semi active friction damper for human friendly robots. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2014, 62(12): 1827−1836 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2014.06.007 [104] Park Y, Oh S, Zoe H. Dynamic analysis of reaction force sensing series elastic actuator as unlumped two mass system. In: Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. Florence, Italy: IEEE, 2016. 5784−5789 [105] Kong K, Bae J, Tomizuka M. A compact rotary series elastic actuator for human assistive systems. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2012, 17(2): 288−297 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2010.2100046 [106] Sariyildiz E, Yu H Y, Nozaki T, Murakami T. Robust force control of series elastic actuators using sliding mode control and disturbance observer. In: Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. Florence, Italy: IEEE, 2016. 619−624 [107] Sariyildiz E, Chen G, Yu H Y. An acceleration-based robust motion controller design for a novel series elastic actuator. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(3): 1900−1910 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2512228 [108] Losey D P, Erwin A, McDonald C G, Sergi F, O' Malley M K. A time-domain approach to control of series elastic actuators: Adaptive torque and passivity-based impedance control. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2016, 21(4): 2085−2096 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2016.2557727 [109] Negrello F, Garabini M, Catalano M G, Malzahn J, Caldwell D G, Bicchi A, et al. A modular compliant actuator for emerging high performance and fall-resilient humanoids. In: Proceedings of the IEEE-RAS 15th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2015. 414−420 [110] Bicchi A, Tonietti G. Fast and “soft-arm” tactics. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2004, 11(2): 22−33 [111] Nieto E A B, Rezazadeh S, Gregg R D. Minimizing energy consumption and peak power of series elastic actuators: A convex optimization framework for elastic element design. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, 24(3): 1334−1345 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2019.2906887 [112] Roozing W, Malzahn J, Kashiri N, Caldwell D G, Tsagarkis N G. On the stiffness selection for torque-controlled series-elastic actuators. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(4): 2255−2262 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2726141 -




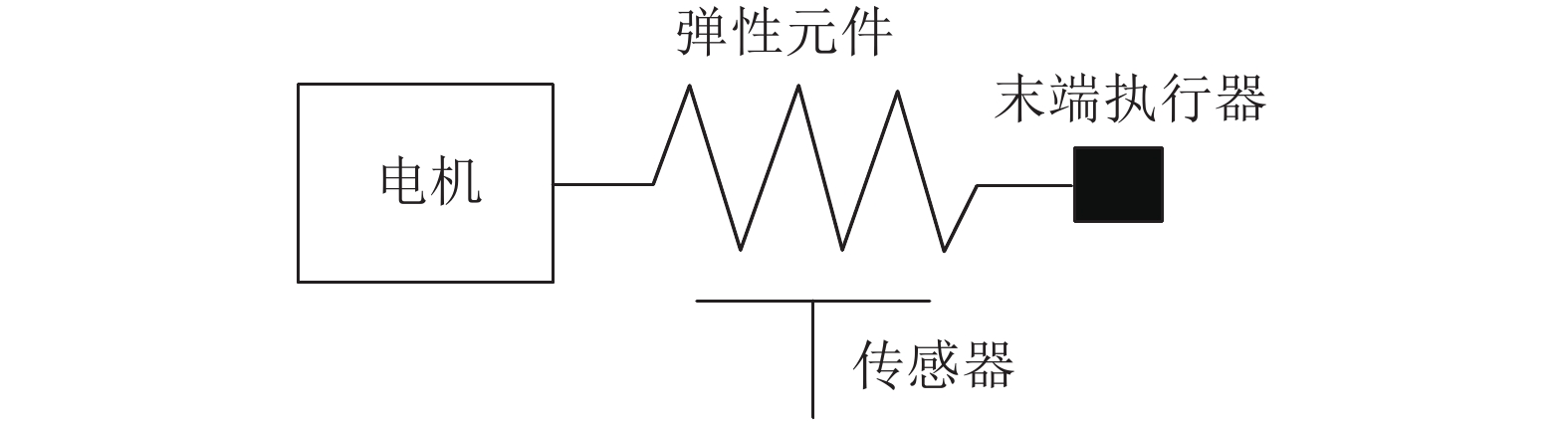
 下载:
下载: