Study for the Application of Fractional Order PID Torque Control in Side-drive Coupled Tram
-
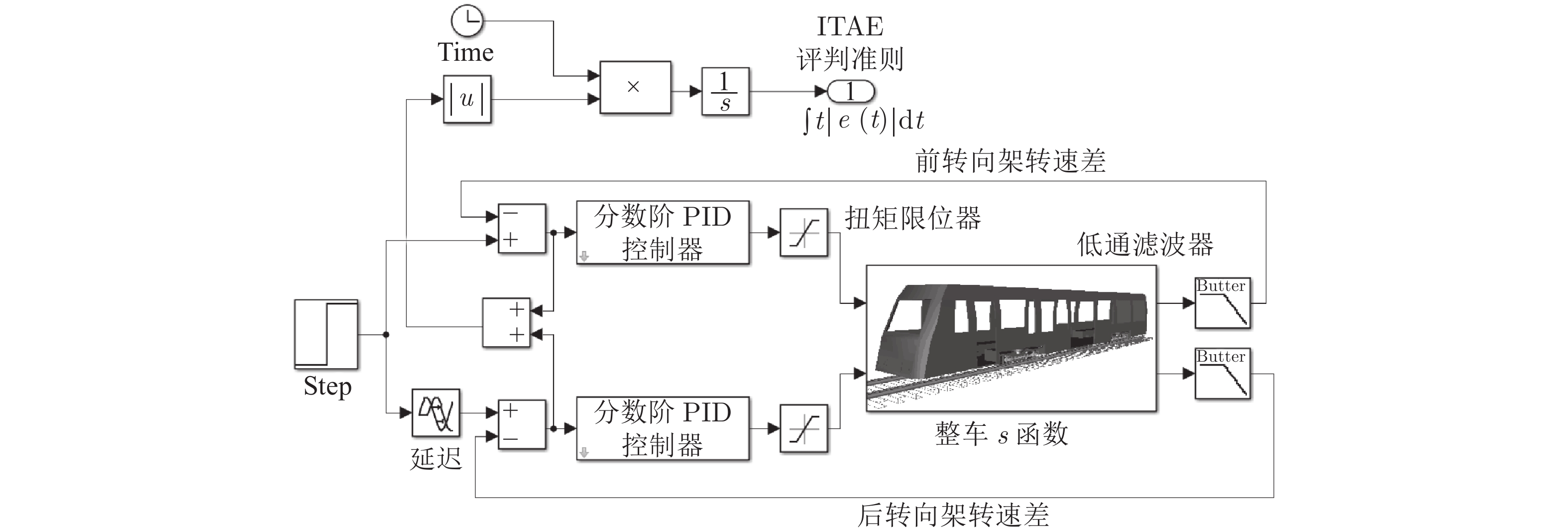
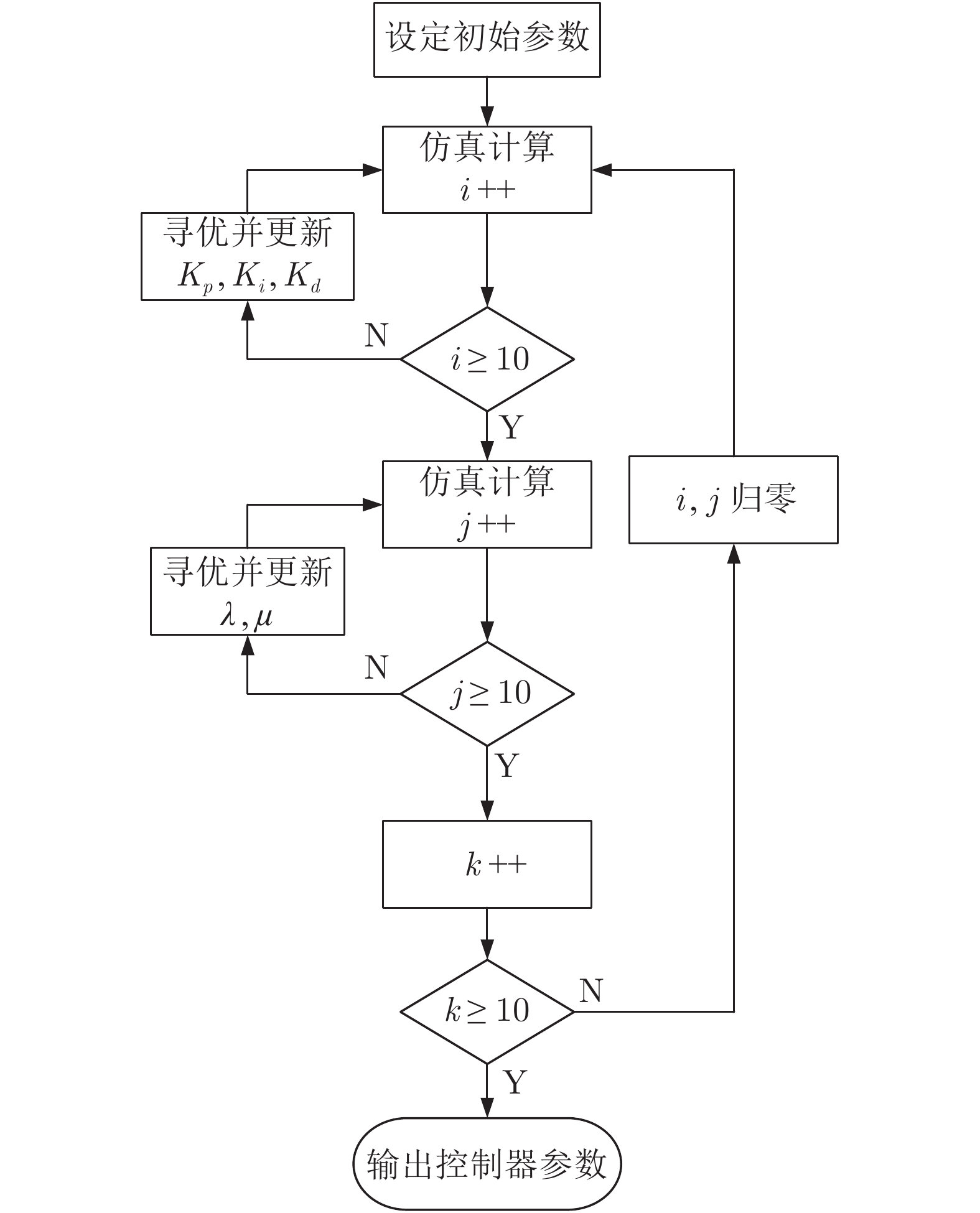
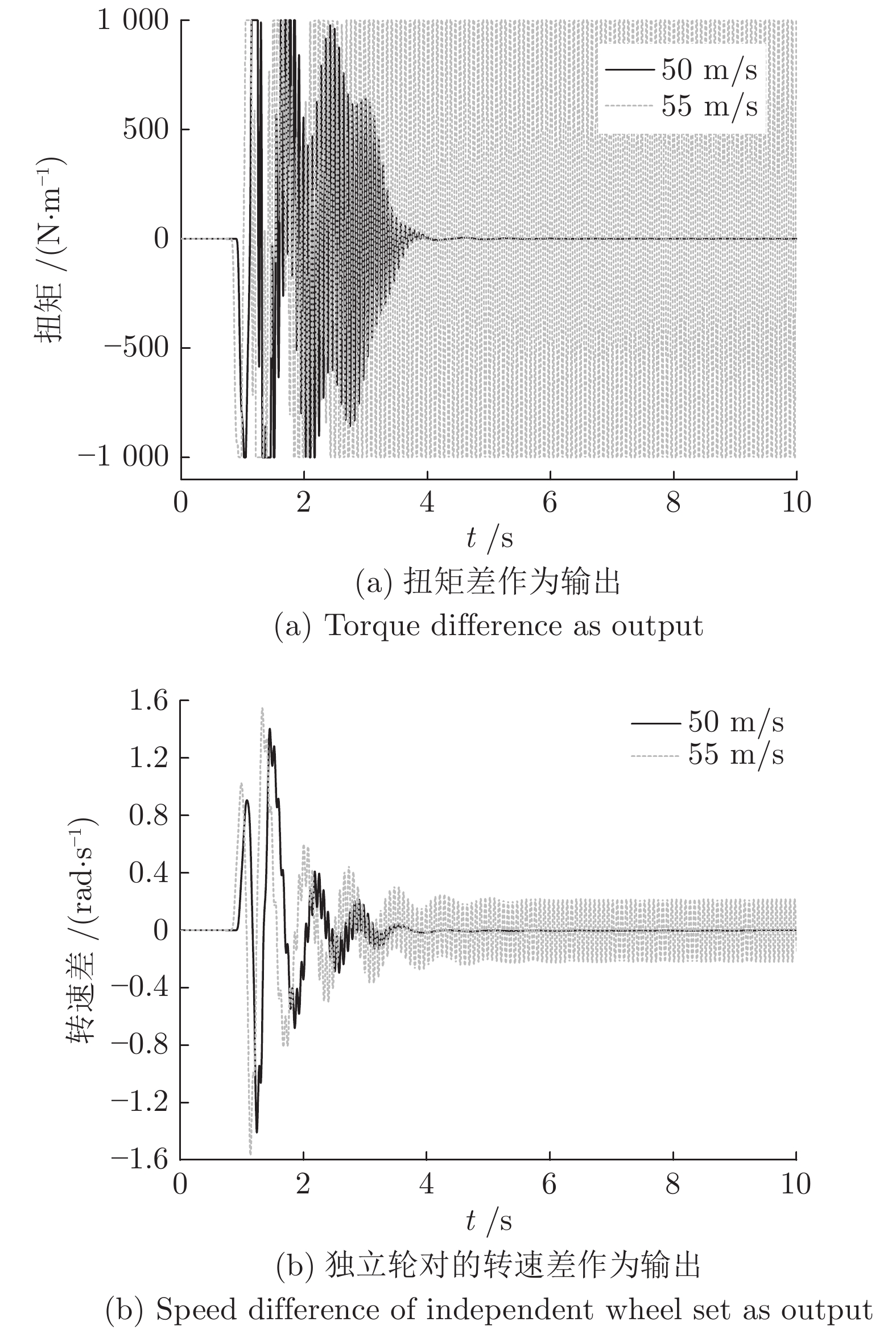
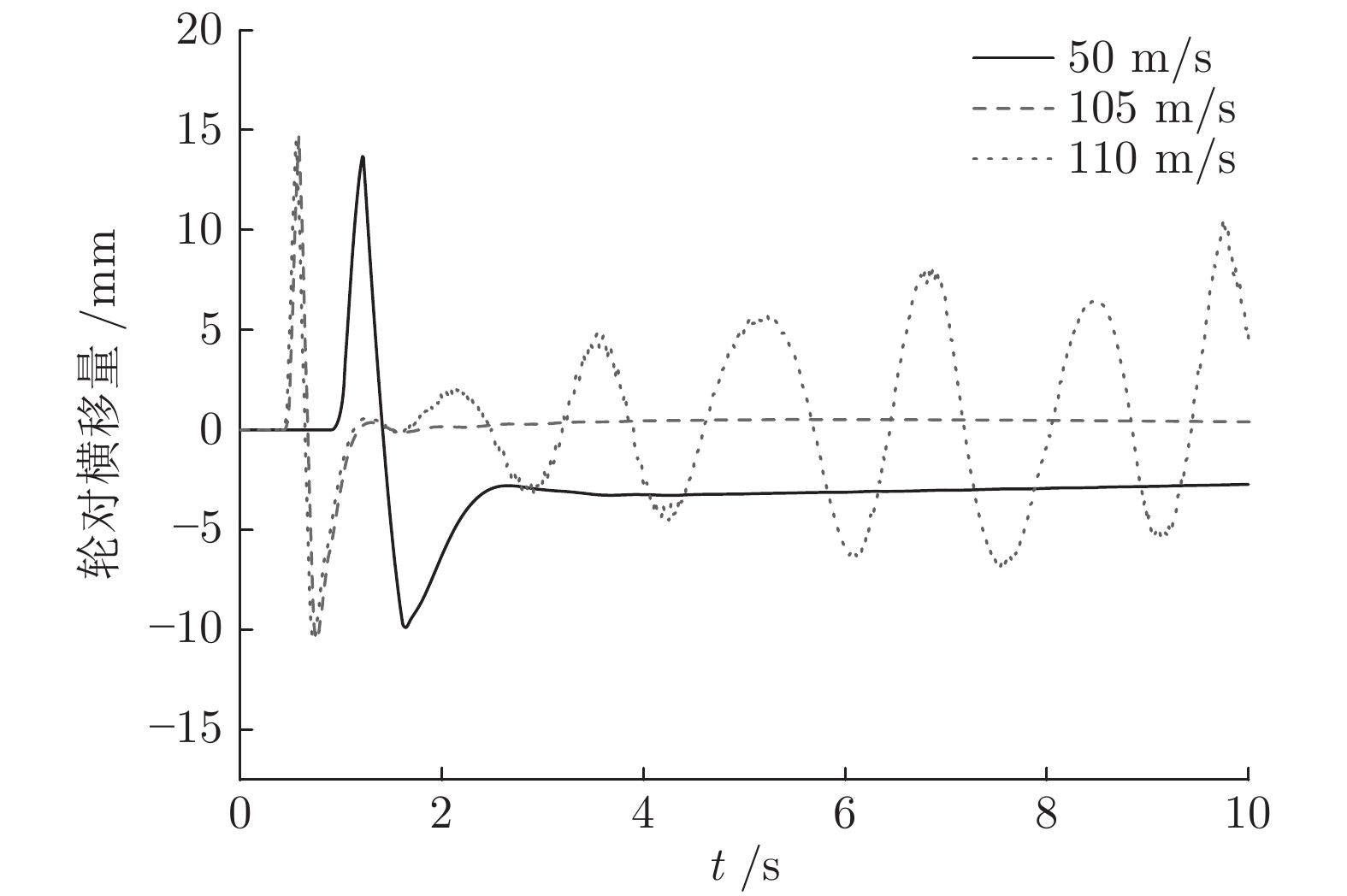
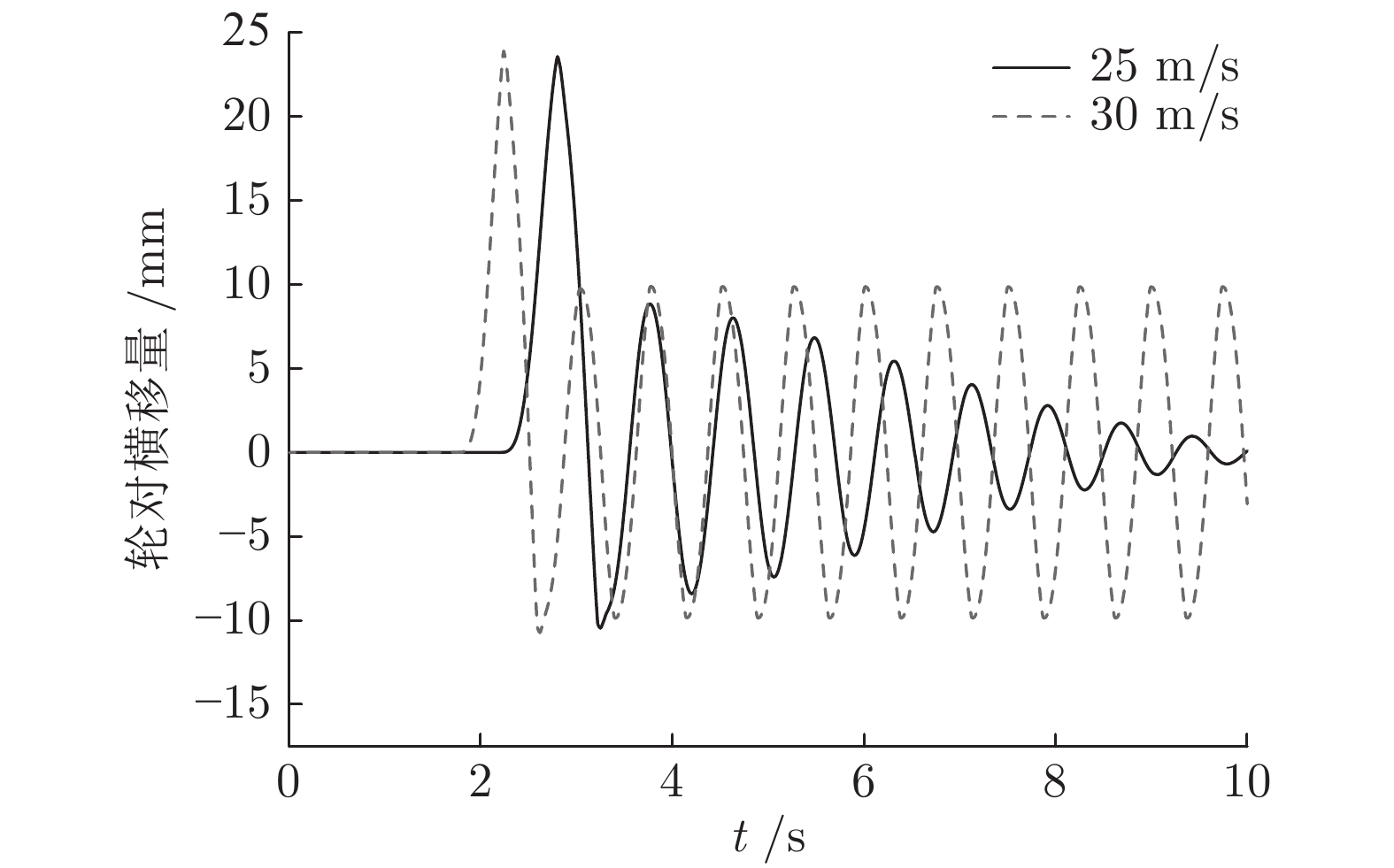
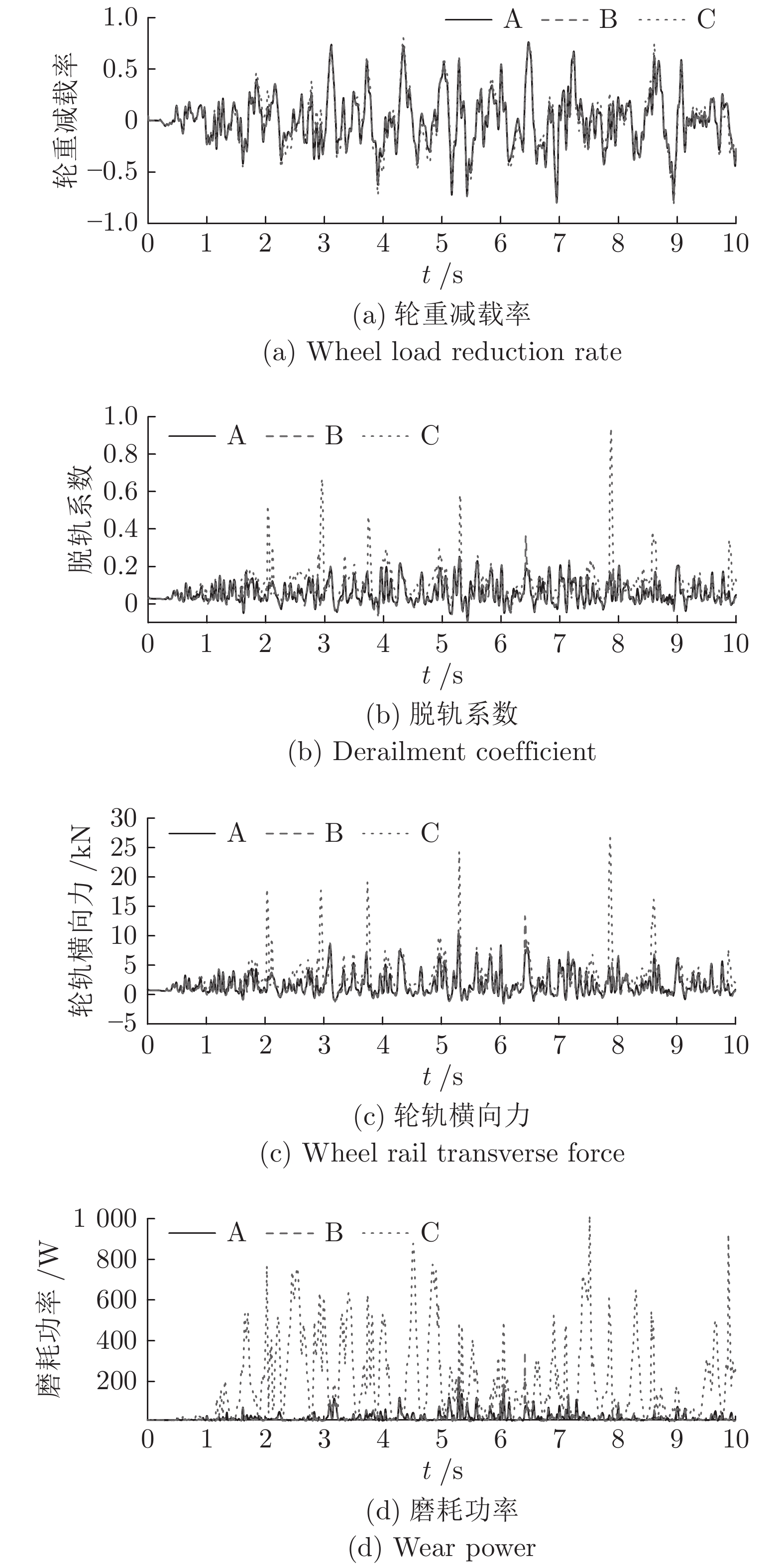
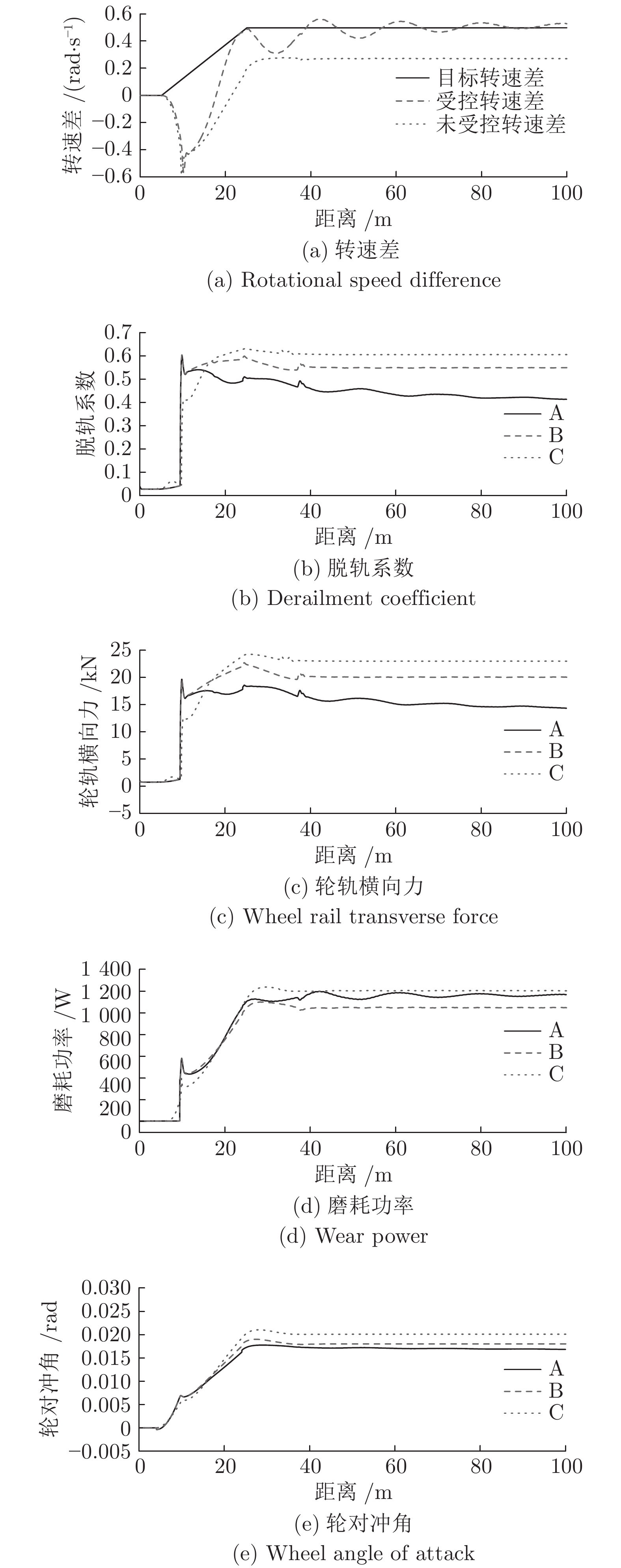
摘要: 边驱耦合独立轮对(Independently rotating wheelset, IRW)技术是 100 %低地板轻轨车(Low floor tram, LFT)的关键技术之一, 边驱电机的扭矩控制策略直接影响轻轨车的动力学性能. 本文基于5自由度独立轮对的轨行机理, 搭建了考虑边驱传动系统的单节轻轨车动力学模型. 应用了一种分数阶PID (Fractional order PID, FOPID)扭矩控制策略, 优化了车辆的曲线通过性能. 采用Riemann-Liouville (RL) 分数阶微积分理论及Oustaloup滤波器数值逼近法构成FOPID控制器, 通过寻优运算对FOPID参数进行整定, 在Simulink平台下建立了整车的集成控制系统.通过扭矩控制器与整车动力学模型s函数联合仿真的方式,开展了100 % 低地板轻轨车辆的直线与曲线运行特性研究, 并将计算结果与无控制的独立轮对模型、传统轮对模型进行了对比分析. 研究结果表明, 在直线运行下, FOPID控制下的轻轨车能够提高车辆的稳定性, 受控轮对的抗轨道不平顺激扰能力较强. 在大半径曲线下, 无控制的独立轮对曲线通过性较差, 而受分数阶PID控制的独立轮对能够表现出与传统轮对一样优异的曲线通过性能; 在小半径曲线下, 分数阶PID扭矩控制策略能够使轻轨车获得足够的导向力, 曲线通过性能明显优于其他模型.Abstract: Side-drive coupled independently rotating wheelset (IRW) is one of the key technologies for the 100 % low floor tram (LFT). The torque control strategy of side-drive electrical motor directly affects the dynamics behaviors of the LFT. Based on the track running mechanism of the IRW with 5 degrees of freedom, the dynamics model of a single LFT was constructed taking the side-drive transmission system into consideration. A fractional order PID (FOPID) torque control strategy was applied to optimize the vehicle′ s curve negotiation performance. The FOPID controller, which was achieved by Riemann-Liouville (RL) fractional integration and the Oustaloup filter approximation and whose parameters were set by the evolutionary operation, was built in the Simulink platform. The 100 % LFT′ s dynamics performance on tangent track and curve was studied by the co-simulation method between the torque controller and the s-function. The results were compared with the IRW model without controller and the traditional wheelset. The research indicates that, in the tangent track case, FOPID controller can improve the vehicle′ s stability and the controlled wheelset′ s robustness to track irregularity is stronger; in the large radius curve case, the curve negotiation performance of the IRW without controller is poor, while the IRW with FOPID controller can perform well like the traditional wheelset; in the small radius curve case, FOPID torque control strategy can provide enough leading force for the LFT on the small radius curve, which makes the curve negotiation performance of IRW with FOPID controller better than the other 2 models.1) 收稿日期 2019-02-12 录用日期 2019-10-28 Manuscript received February 12, 2019; accepted October 28, 2019 国家自然科学基金 (11790282, 11702179), 河北省自然科学基金 (A2018210064), 河北省高等学校青年拔尖人才计划项目 (BJ2017001) 资助 Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (11790282, 11702179), Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (A2018210064), and Program for the Top Young2) Innovative Talents of Higher Learning Institutions of Hebei Province (BJ2017001) 本文责任编委 阳春华 Recommended by Associate Editor YANG Chun-Hua 1. 石家庄铁道大学机械工程学院 石家庄 050043 2. 石家庄铁道大学电气工程学院 石家庄 050043 1. School of Mechanical Engineering, Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, Shijiazhuang 050043 2. School of Mechanical Engineering, Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, Shijiazhuang 050043
-
表 1 主要动力学参数
Table 1 Main dynamics parameters
项目 数值 单位 车辆定距 10 m 转向架轴距 1.8 m 名义滚动圆半径 0.3 m 等效踏面锥度 0.15 − 一系悬挂垂向刚度 1.6 MN/mm 一系悬挂水平刚度 5.0 MN/mm 二系悬挂垂向刚度 0.24 MN/mm 二系悬挂水平刚度 0.17 MN/mm 横向减振器阻尼 58.8 kN·s/m 车体质量 13 t 车体转动惯量(侧滚/点头/摇头) 30/150/150 t·m2 构架质量 1.4 t 构架转动惯量(侧滚/点头/摇头) 0.7/1.4/2.0 t·m2 锥齿轮传动比 2 − 表 2 控制器参数
Table 2 Parameters of controllers
参数 初始控制器 整定后控制器 整数阶控制器 Kp 100 371.52 371.52 Ki 100 60.61 60.61 Kd 100 130.18 130.18 λ 1 0.32 1 μ 1 0.86 1 ITAE 0.5678 0.1086 0.2183 -
[1] 李芾, 张丽平, 黄运华. 城市轻轨车辆发展及其应用前景. 西南交通大学学报, 2002, 37(2): 111−116 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2002.02.0011 Li Fu, Zhang Li-Ping, Huang Yun-Hua. The development and prospect of application of light rail vehicles. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2002, 37(2): 111−116 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2002.02.001 [2] 2 Novales M, Gerezo J A G, Ortega R. Light rail in alicante, spain improving the use of existing railway lines. Transportation Research Record, 2013, 2353: 69−81 doi: 10.3141/2353-07 [3] 3 Currie G, Delbosc A, Forbes P. World transit research trends in need, supply, and use. Transportation Research Record, 2012, 2276: 1−8 doi: 10.3141/2276-01 [4] 4 Kuba T, Lugner P. Dynamic behaviour of tramways with different kinds of bogies. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2012, 50: 277−289 doi: 10.1080/00423114.2012.666356 [5] 5 Péreza J, Busturia J M, Mei T X, Vinolas J. Combined active steering and traction for mechatronic bogie vehicles with independently rotating wheels. Annual Reviews in Control, 2004, 28(2): 207−217 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2004.02.004 [6] 6 Liang B, Iwnicki S D, Swift F J. Simulation of the behavior of a railway vehicle with independently driven wheels. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2002, 35(2): 755−759 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)34030-2 [7] 黄运华, 李芾. 基于独立旋转车轮的变轨距转向架研究. 中国铁道科学, 2004, 25(2): 139−141 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.02.0297 Huang Yun-Hua, Li Fu. Research on gauge-changeable bogie based on independently rotating wheel. China Railway Science, 2004, 25(2): 139−141 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.02.029 [8] 张济民, 寇杰, 周和超, 周俊华. 差速器耦合轮对车辆曲线通过性能. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(10): 94−998 Zhang Ji-Min, Kou Jie, Zhou He-Chao, Zhou Jun-Hua. Curving performance of the differential-coupled wheelset vehicle. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(10): 94−99 [9] 9 Wang W, Suda Y, Michitsuji Y. Running performance of steering truck with independently rotating wheel considering traction and braking. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2008, 46: 899−909 doi: 10.1080/00423110802037149 [10] 10 Andrea B, Gianluca M. Contact mechanics issues of a vehicle equipped with partially independently rotating wheelsets. Wear, 2016, 366−367: 233−240 doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2016.03.037 [11] 11 Sugiyama H, Matsumura R, Suda Y, Ezaki H. Dynamics of independently rotating wheel system in the analysis of multibody railroad vehicles. Journal of Computational and Nonlinear Dynamics, 2011, 6(1): 1−8 [12] 12 Cho Y, Kwak J. Development of a new analytical model for a railway vehicle equipped with independently rotating wheels. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2012, 13(7): 1047−1056 doi: 10.1007/s12239-012-0107-3 [13] 13 Wang, W J. Design of the wheel profile of an independently rotating wheel with inverse tread conicity by considering the trajectory of the center of gravity. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part F−Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2016, 230(3): 672−680 doi: 10.1177/0954409714555380 [14] 14 Jeong N T, Choi S U, Lee H Y, Baek K H, Han S Y , Kim W K, Suh M W. A study on the optimum design of high-speed low-floor bogie with independently rotating wheels. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2017, 31(5): 2105−2115 doi: 10.1007/s12206-017-0407-7 [15] 15 Kalker J J. Contact mechanical algorithms. Communications in Applied Numerical Methods, 1988, 4(1): 25−32 doi: 10.1002/cnm.1630040105 [16] 张丽平, 李芾. 独立旋转车轮轮轨蠕滑率研究. 中国铁道科学, 2002, 23(4): 18−23 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2002.04.00416 Zhang Li-Ping, Li Fu. Research on the creepages of independently rotating wheels. China Railway Science, 2002, 23(4): 18−23 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2002.04.004 [17] 17 Ahn H, Lee H, Go S, Cho Y, Lee J. Control of the lateral displacement restoring force of irws for sharp curved driving. Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology, 2016, 11: 1042−1048 doi: 10.5370/JEET.2016.11.4.1042 [18] 18 Lu Z G, Yang, Z, Huang Q, Wang X C. Robust active guidance control using the mu-synthesis method for a tramcar with independently rotating wheelsets. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part F−Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2019, 233: 33−48 doi: 10.1177/0954409718777374 [19] 19 Lu Z G, Sun X J, Yang J Q. Integrated active control of independently rotating wheels on rail vehicles via observers. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part F-Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2017, 231(3): 295−305 doi: 10.1177/0954409716629705 [20] 20 Oh Y J, Liu H C, Cho S, Won J H, Lee H, Lee J. Design, modeling, and analysis of a railway traction motor with independently rotating wheelsets. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2018, 54(11): 1−5 [21] 21 Ji Y J, Ren L H, Zhou J S. Boundary conditions of active steering control of independent rotating wheelset based on hub motor and wheel rotating speed difference feedback. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2018, 56(12): 1883−1898 doi: 10.1080/00423114.2018.1437273 [22] 季元进, 李锐, 任利惠. 基于轮毂电机和转速差反馈的独立车轮轮对主动导向控制的影响因素. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(8): 48−5622 Ji Yuan-Jin, Li Rui, Ren Li-Hui. Influence factors of active steering control of independent wheel set based on hub motor and speed difference feedback. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(8): 48−56 [23] 23 Oh Y J, Cho Y, Kim I G, Lee J, Lee H. Restoring torque control strategy of IPMSM for the independently rotating wheelsets in wireless trams. Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology, 2017, 12(4): 1683−1689 [24] 薛定宇, 赵春娜. 分数阶系统的分数阶PID控制器设计. 控制理论与应用, 2007, 24(5): 771−776 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8152.2007.05.01524 Xue Ding-Yu, Zhao Chun-Na. Fractional order PID controller design for fractional order system. Control Theory and Applications, 2007, 24(5): 771−776 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8152.2007.05.015 [25] 张冬丽, 唐英干, 关新平. 用改进的人工蜂群算法设计AVR系统最优分数阶PID控制器. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(5): 973−98025 Zhang Dong-Li, Tang Yin-Gan, Guan Xin-Ping. Optimum design of fractional order PID controller for an AVR system using an improved artiflcial bee colony algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(5): 973−980 [26] 高哲. 一类采用分数阶PIλ控制器的分数阶系统可镇定性判定准则. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(11): 1993−200226 Gao Zhe. Stabilization criterion for a class of interval fractional-order systems using fractional-order PIλ controllers. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(11): 1993−2002 [27] 27 Farahani G, Rahmani K. Speed control of a separately excited dc motor using new proposed fuzzy neural algorithm based on fopid controller. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 2019, 30(5): 728−740 doi: 10.1007/s40313-019-00485-8 [28] 魏立新, 王浩, 穆晓伟. 基于粒子群算法倒立摆分数阶PID参数优化. 控制工程, 2019, 26(2): 196−20128 Wei Li-Xin, Wang Hao, Mu Xiao-Wei. Control of revolving inverted pendulum based on PSO-FOPID controller. Control Engineerig of China, 2019, 26(2): 196−201 -





 下载:
下载: