Precise Clock Synchronization in Industrial Internet of Things: Networked Control Perspective
-
摘要:
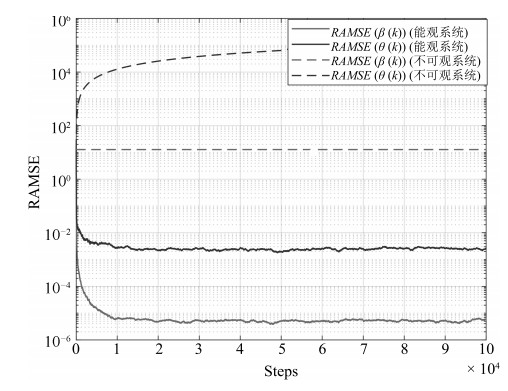
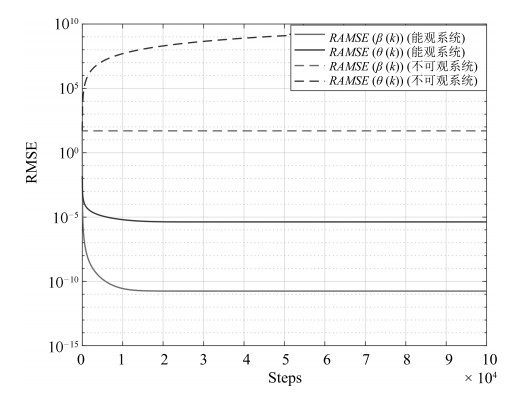
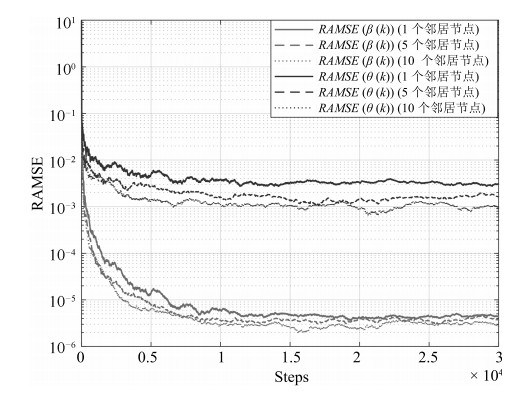
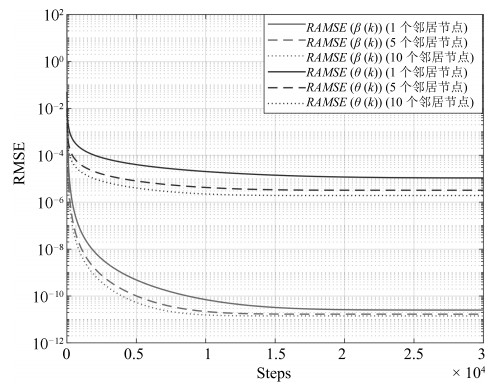
本文针对物联网中时变的时钟参数, 运用网络化控制理论观点, 通过对时钟状态建模的本质分析, 区别于"相对时钟建模", 提出了全分布规模化时钟状态追踪卡尔曼滤波(Kalman filtering). 考虑量测的丢失, 则扩展为追踪时钟参数的修正Kalman filtering算法. 我们提出了以BMU (Basic measurement unit)构建新的MMSE (Minimum mean square error)等价变换下的能观测性状态解耦量测模型, 新的量测模型能够实现MMSE量测规模化扩展, 且理论上分析了时钟同步的条件和计算了统计时钟同步误差的相应上界, 并且在时钟同步精度与潜在的通信网络质量间作出了量化均衡.
Abstract:In this paper, aiming at the time-varying clock parameters in the internet of things, the fully distributed scaled Kalman filtering for clock state tracking, which is different from the "relative clock modeling", has been proposed by using the point of view of the networked control theory through the essential analysis of the clock state modeling. Considering the loss of measurement, it can be extended to the modified Kalman filtering algorithm for tracking the clock parameters. We have proposed an observable state decoupling measurement model under a new MMSE (minimum mean square error) equivalent transformation based on BMU (basic measurement unit). The new measurement model is able to realize the scaled expansion of MMSE measurement, and theoretically analyze the conditions of clock synchronization and calculate the corresponding upper bound of statistical clock synchronization error, and quantify the balance between synchronization accuracy of clock and potential quality of the communication network.
-
表 1 不可靠量测丢包变量定义
Table 1 Definition of unreliable packet loss variables
名称 定义 $\pi_{i, k}^{\{i, j\}}$ 描述$S_i$和$S_j$间第$k$次信息交换. 交换成功, 则$\pi_{i, k}^{\{i, j\}}=1$; 否则$\pi_{i, k}^{\{i, j\}}=0$. 多链路下, $S_i$与任意邻居$S_{m_j}$间则为$\pi_{i, k}^{\{i, m_j\}}$ $\phi_{i, j}$ 描述$S_i$和$S_j$间的接收概率, $P(\pi_{i, k}^{\{i, j\}}=1)=\phi_{i, j}$, $P(\pi_{i, k}^{\{i, j\}}$ $=0)=1-\phi_{i, j}$. 多链路下, $S_i$与任意邻居$S_{m_j}$间则为$\phi_{i, m_j}$ $\boldsymbol{\chi}$ 表示一个同步周期, $S_i$与$|\mathcal{N}_i|$个邻居的$|\mathcal{N}_i|$次信息交换中, 丢包组合$\boldsymbol{\chi}=\{\chi_1, \chi_2, \cdots, \chi_g, \cdots, \chi_{2^{|\mathcal{N}_i|}}|g\in \{1$, $2$, $\cdots$, $2^{|\mathcal{N}_i|}\}\}$, $\chi_g$为第$g$种丢包情况, 共$2^{|\mathcal{N}_i|}$种 $\pi_{i, g, k}^{\{i, m_j\}}$ 描述第$k$个采样周期第$g$种丢包情况时($\chi_g$), $S_i$与$S_{m_j}$信息交换是否成功地取值. 若成功, $\pi_{i, g, k}^{\{i, m_j\}}=1$, 否则$\pi_{i, g, k}^{\{i, m_j\}}$ $=$ $0$ $\boldsymbol{L}_{i, g, k}$ 如$\pi_{i, g, k}^{\{i, m_j\}}$, 则$\boldsymbol{L}_{i, g, k}={\rm diag}\{\pi_{i, g, k}^{\{i, m_1\}}, \cdots, \pi_{i, g, k}^{\{i, m_j\}}$, $\cdots$, $\pi_{i, g, k}^{\{i, m_{|\mathcal{N}_i|}\}}\}$, 表示$S_i$与所有邻居在$\chi_g$情况时的丢包系数矩阵 $\eta_{i, g, k}$ 与所有邻居在$\chi_g$时的概率$\eta_{i, g, k}=\prod_{j=1}^{|\mathcal{N}_i|} \alpha_{i, m_j, k}$ $\alpha_{i, m_j, k}$ 表示$S_i$与$S_{m_j}$信息交换概率 $\alpha_{i, m_j, k}=\begin{cases} \phi_{i, m_j}, &\mbox{若}~ \pi_{i, k}^{\{i, m_j\}}=1\\ 1-\phi_{i, m_j}, &\mbox{若}~ \pi_{i, k}^{\{i, m_j\}}=0 \end{cases}$ $\boldsymbol{\gamma}_{i, g, k}$ 第$k$步绝对量测信息$\boldsymbol{\gamma}_{i, k}$在$\chi_g$情况时的具体表达式, $\boldsymbol{\gamma}_{i, g, k}$为构造的值, 实际量测中不可获得 $\boldsymbol{z}_{i, g}(k)$ 第$k$步相对量测信息$\boldsymbol{z}_{i}(k)$在$\chi_g$情况时的具体表达式, $\boldsymbol{z}_{i, g}(k)$为一个实际中能够量测的值 -
[1] 王恒, 陈鹏飞, 王平. 面向WIA-PA工业无线传感器网络的确定性调度算法. 电子学报, 2018, 46(1): 68-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.01.010Wang Heng, Chen Peng-Fei, Wang Ping. Deterministic scheduling algorithms for WIA-PA industrial wireless sensor networks. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(1): 68-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.01.010 [2] Luo B, Wu Y C. Distributed clock parameters tracking in wireless sensor network. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(12): 6464-6475 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.103013.130811 [3] Wu Y C, Chaudhari Q, Serpedin E. Clock synchronization of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2011, 28(1): 124-138 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.938757 [4] 王頲, 万羊所, 唐晓铭, 黄庆卿, 李永福. 不可靠WSN时钟同步网络化输出反馈MPC量化分析. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(7): 1798 -1808 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.07.029Wang Ting, Wan Yang-Suo, Tang Xiao-Ming, Huang Qing-Qing, Li Yong-Fu. Unreliable WSN clock synchronization networked output feedback model predictive control quantitative analysis. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(7): 1798-1808 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.07.029 [5] Schenato L, Fiorentin F. Average TimeSynch: A consensus-based protocol for clock synchronization in wireless sensor networks. Automatica, 2011, 47(9): 1878-1886 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.06.012 [6] He J P, Cheng P, Shi L, Chen J M, Sun Y X. Time synchronization in WSNs: A maximum-value-based consensus approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(3): 660-675 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2286893 [7] Garone E, Gasparri A, Lamonaca F. Clock synchronization protocol for wireless sensor networks with bounded communication delays. Automatica, 2015, 59: 60-72 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2015.06.014 [8] Bolognani S, Carli R, Lovisari E, Zampieri S. A randomized linear algorithm for clock synchronization in multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(7): 1711-1726 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2479136 [9] Sinopoli B, Schenato L, Franceschetti M, Poolla K, Jordan M I, Sastry S S. Kalman filtering with intermittent observations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1453-1464 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834121 [10] Huang M Y, Dey S. Stability of Kalman filtering with Markovian packet losses. Automatica, 2007, 43(4): 598-607 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.10.023 [11] Mo Y L, Sinopoli B. A characterization of the critical value for Kalman filtering with intermittent observations. In: Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2008. 2692-2697 [12] Sinopoli B, Schenato L, Franceschetti M, Poolla K, Jordan M I, Sastry S S. Kalman filtering with intermittent observations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1453-1464 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834121 [13] Plarre K, Bullo F. On Kalman filtering for detectable systems with intermittent observations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(2): 386-390 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.2008347 [14] You K Y, Fu M Y, Xie L H. Mean square stability for Kalman filtering with Markovian packet losses. Automatica, 2011, 47(12): 2647-2657 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.09.015 [15] Deshmukh S, Natarajan B, Pahwa A. State estimation over a lossy network in spatially distributed cyber-physical systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(15): 3911-3923 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2330810 [16] He X, Wang Z D, Wang X F, Zhou D H. Networked strong tracking filtering with multiple packet dropouts: Algorithms and applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(3): 1454-1463 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2261038 [17] Hu J, Wang Z D, Gao H J. Recursive filtering with random parameter matrices, multiple fading measurements and correlated noises. Automatica, 2013, 49(11): 3440-3448 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.08.021 [18] Hu J, Wang Z D, Gao H J, Stergioulas L K. Extended Kalman filtering with stochastic nonlinearities and multiple missing measurements. Automatica, 2012, 48(9): 2007- 2015 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.03.027 [19] Quevedo D E, Ahlen A, Johansson K H. State estimation over sensor networks with correlated wireless fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2013, 58(3): 581-593 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2012.2212515 [20] Wei G L, Wang Z D, Shu H S. Robust filtering with stochastic nonlinearities and multiple missing measurements. Automatica, 2009, 45(3): 836-841 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2008.10.028 [21] Sui T J, You K Y, Fu M Y. Stability conditions for multi-sensor state estimation over a lossy network. Automatica, 2015, 53: 1-9 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.12.022 [22] 王頲, 段斯静, 黄庆卿, 唐晓铭, 李永福. 工业物联网确定性调度中TDMA紧时隙时间精度边界可靠性分析. 仪器仪表学报, 2018, 39(6): 120-131 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB201806016.htmWang Ting, Duan Si-Jing, Huang Qing-Qing, Tang Xiao-Ming, Li Yong-Fu. Reliability analysis of time precision boundary for tight slots of TDMA in deterministic scheduling of industrial internet of things. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2018, 39(6): 120-131 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB201806016.htm [23] Li Y, Pan Y, Wang P. Research and implementation of a mobility management mechanism for wireless sensor networks based on IEEE 802.15.4. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems. Kunming, China: IEEE, 2011. 260-264 [24] Wang H, Ge G C, Chen J M, Wang P. A reliable routing protocol based on deterministic schedule for wireless industrial networks. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology. Chengdu, China: IEEE, 2010. pp. 368-372 [25] Watteyne T, Palattella M R, Grieco L A. Using IEEE 802.15.4e Time-Slotted Channel Hopping (TSCH) in the Internet of Things (IoT): Problem Statement. Internet Engineering Task Force, 2015. [Online], available: http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7554, June 18, 2021 [26] Wang T, Cai C Y, Guo D, Tang X M, Wang H. Clock synchronization in wireless sensor networks: A new model and analysis approach based on networked control perspective. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014, 2014(3): 1- 19 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/273876748_Clock_Synchronization_in_Wireless_Sensor_Networks_A_New_Model_and_Analysis_Approach_Based_on_Networked_Control_Perspective [27] Wang T, Guo D, Cai C Y, Tang X M, Wang H. Clock synchronization in wireless sensor networks: Analysis and design of error precision based on lossy networked control perspective. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 2015: Article ID 346521 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/275229110_Clock_Synchronization_in_Wireless_Sensor_Networks_Analysis_and_Design_of_Error_Precision_Based_on_Lossy_Networked_Control_Perspective [28] Cao X H, Cheng P, Chen J M, Ge S S, Cheng Y, Sun Y X. Cognitive radio based state estimation in cyber-physical systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2014, 32(3): 489-502 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2014.1403002 [29] Kay S M. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing, Volume I: Estimation Theory. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014. 307-309 [30] Elson J, Girod L, Estrin D. Fine-grained network time synchronization using reference broadcasts. ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review, 2002, 36(SI): 147-163 doi: 10.1145/844128.844143 [31] Maybeck P S. Stochastic Models, Estimation, and Control. New York: Academic Press, 1979. [32] Ackermann J E. On the synthesis of linear control systems with specified characteristics. Automatica, 1977, 13(1): 89- 94 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(77)90012-7 [33] Äström K J, Wittenmark B. Computer-Controlled Systems: Theory and Design. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice Hall, 1997. [34] Anderson B D O, Moore J B. Optimal Filtering. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1979. [35] Kucera V. The discrete riccati equation of optimal control. Kybernetica, 1972, 8(5): 430-447 http://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=332254 [36] 汪付强, 曾鹏, 于海斌. 一种低开销的双向时间同步算法. 仪器仪表学报, 2011, 32(6): 1357-1363 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB201106023.htmWang Fu-Qiang, Zeng Peng, Yu Hai-Bin. Low overhead two-way time synchronization algorithm. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2011, 32(6): 1357-1363 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB201106023.htm -





 下载:
下载: