Finite-time Synchronization Between Uncertain Complex Networks Based on Unidirectional Coupling Method
-
摘要:
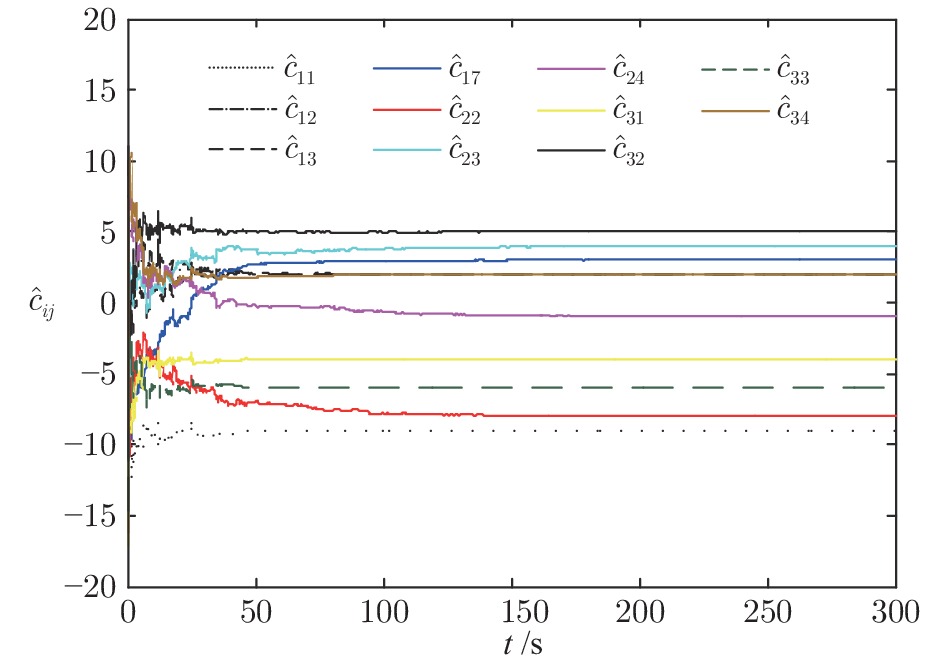
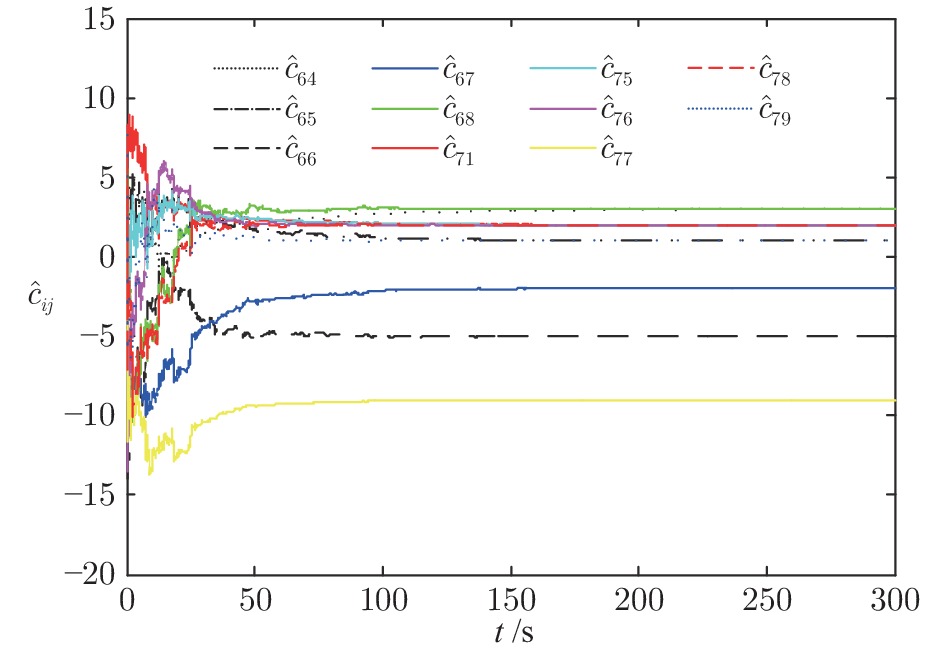
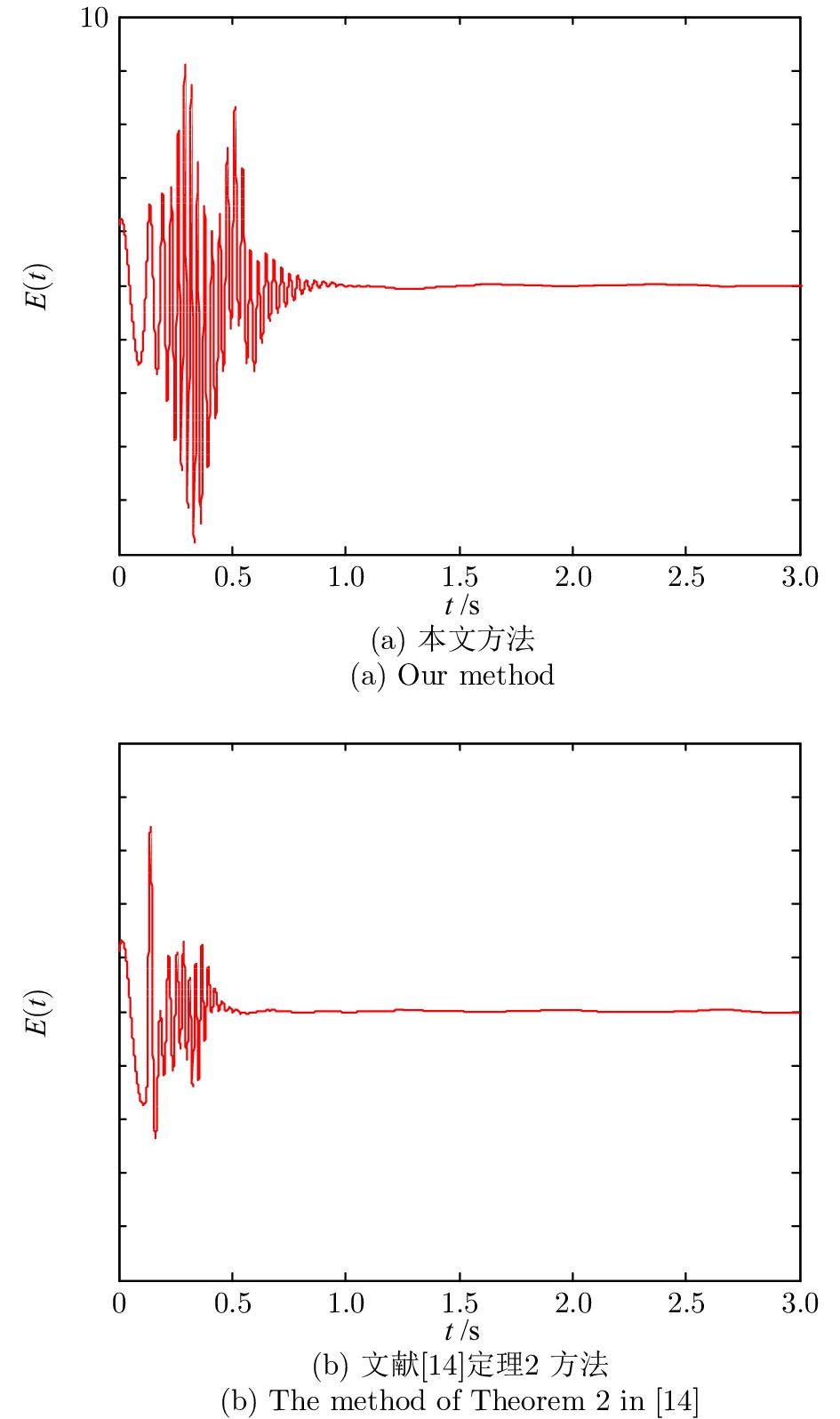
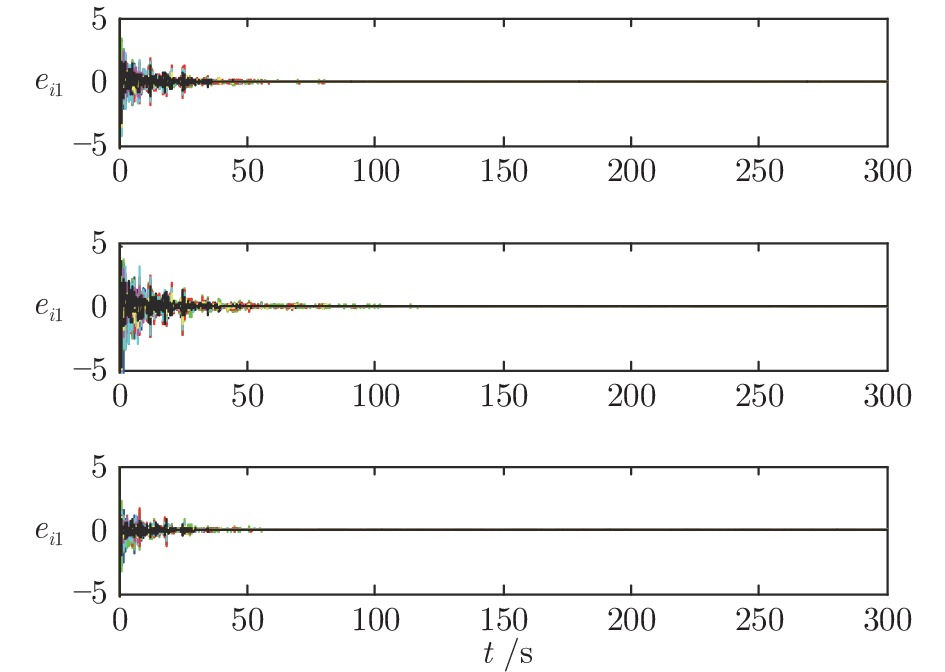
针对具有不确定性的复杂网络有限时间同步问题, 提出一种新颖的单向耦合控制方法. 构建含有未知参量及未知拓扑结构的驱动−响应复杂网络模型, 考虑两个网络具有不同的节点数, 同时受到时变耦合时滞的影响, 并且网络内部分别具有不同的节点系统. 基于有限时间稳定性理论和线性矩阵不等式变换, 通过在响应网络中引入单向耦合项, 实现两个网络间的有限时间同步, 同时准确辨识未知参量及未知拓扑结构. 仿真实验验证所提同步方法的有效性, 对比实验结果表明所提方法在减少耦合数量的同时具有更快的同步速率及更小的波动范围.
Abstract:To solve the problem of finite-time synchronization of uncertain complex networks, a novel unidirectional coupling control method is proposed. First, a drive-response complex network model with unknown parameters and unknown topological structure is constructed. The two networks have different sizes, and each of which contains two types of nonidentical nodes and time-varying coupling delay. Based on the finite-time stability theory and the linear matrix inequality, the finite-time synchronization between two networks is realized by adding a unidirectional coupling term in the response network, the unknown parameters and the unknown topological structure can be identified, simultaneously. The simulation experiments verify the validity of the proposed scheme. Moreover, the comparison experiments show that the proposed method achieves faster synchronization rate and smaller fluctuation range as well as reduced coupling quantity.
-
同步时间 Sync time (s) 波动范围 Fluctuation range 本文方法 0.657 [−4.5, 5.5] 文献[14] 定理1 1.698 [−6.5, 7.4] -
[1] 席裕庚. 大系统控制论与复杂网络 — 探索与思考. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(11): 1758−1768 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01758Xi Yu-Geng. Large-scale systems control and complex networks-exploration and thinking. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1758−1768 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01758 [2] Tran S N, Garcez A S A. Deep logic networks: Inserting and extracting knowledge from deep belief networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learn Systems, 2018, 29(2): 246−258 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2603784 [3] Watts D J, Strogatz S H. Collective dynamics of “small-world” networks. Nature, 1998, 393(6684): 440−442 doi: 10.1038/30918 [4] Barabási A L, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science, 1999, 286(5439): 509−512 doi: 10.1126/science.286.5439.509 [5] 陈关荣. 复杂动态网络环境下控制理论遇到的问题与挑战. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 312−321 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60032-4Chen Guan-Rong. Problems and challenges in control theory under complex dynamical network environments. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 312−321 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60032-4 [6] Lakshmanan S, Prakash M, Lim C P, Rakkiyappan R, Balasubramaniam P, Nahavandi S. Synchronization of an inertial neural network with time-varying delays and its application to secure communication. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learn Systems, 2018, 29(1): 195−207 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2619345 [7] Suarez O J, Vega C J, Sanchez E N, Chen G R, Elviraceja J S, Rodriguez D I. Neural sliding-mode pinning control for output synchronization for uncertain general complex networks. Automatica, 2020, 112: 108694 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108694 [8] 吕金虎. 复杂网络的同步: 理论、方法、应用与展望. 力学进展, 2008, 38(6): 713−722 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2008.06.007Lv Jin-Hu. Synchronization of complex networks: theories, approaches, applications and prospects. Advances in Mechanics, 2008, 38(6): 713−722 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2008.06.007 [9] 韦相, 赵军产, 胡春华. 两个异构复杂网络的广义同步与参数识别. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(4): 595−603Wei Xiang, Zhao Jun-Chan, Hu Chun-Hua. Generalized synchronization and system parameters identification between two different complex networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(4): 595−603 [10] Yang X, Lam J, Ho D W C, Feng Z. Fixed-time synchronization of complex networks with impulsive effects via nonchattering control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(11): 5511−5521 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2691303 [11] 韩敏, 张雅美, 张檬. 具有双重时滞的时变耦合复杂网络的牵制外同步研究. 物理学报, 2015, 64(7): 70506Han Min, Zhang Ya-Mei, Zhang Meng. Outer synchronization analysis of two time-varying networks with double delays based on pinning control. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(7): 70506 [12] Zhang Z M, He Y, Wu M. Exponential synchronization of neural networks with time-varying delays via dynamic intermittent output feedback control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(3): 612−622 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2753944 [13] Xu Y H, Zhou W N, Fang J A, Lu H Q. Structure identification and adaptive synchronization of uncertain general complex dynamical networks. Physics Letters A, 2009, 374(2): 272−278 doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2009.10.079 [14] Mei J, Jiang M, Wang J. Finite-time structure identification and synchronization of drive-response systems with uncertain parameter. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2013, 18(4): 999−1015 doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2012.08.039 [15] Han M, Zhang M, Zhang Y M. Projective synchronization between two delayed networks of different sizes with nonidentical nodes and unknown parameters. Neurocomputing, 2016, 171(1): 605−614 [16] 杜洪越, 孙琬双, 胡革, 齐丽华. 两个分数阶复杂动态网络的函数投影同步. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(2): 226−234Du Hong-Yue, Sun Wan-Shuang, Hu Ge, Qi Li-Hua. Function projective synchronization of two fractional-order complex dynamical networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(2): 226−234 [17] Andrieu V, Jayawardhana B, Tarbouriech S. Some results on exponential synchronization of nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(4): 1213−1219 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2789244 [18] Perruquetti W, Floquet T, Moulay E. Finite-time observers: application to secure communication. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2008, 53(1): 356−360 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2007.914264 [19] He P, Ma S H, Fan T. Finite-time mixed outer synchronization of complex networks with coupling time-varying delay. Chaos, 2012, 22(4): 043151(1−11 [20] Velmurugan G, Rakkiyappan R, Cao J. Finite-time synchronization of fractional-order memristor-based neural networks with time delays. Neural Networks, 2016, 73: 36−46 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2015.09.012 [21] Yang X, Lu J. Finite-time synchronization of coupled networks with Markovian topology and impulsive effects. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(8): 2256−2261 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2484328 [22] Gao J, Zhu P, Alsaedi A, Alsaadi F E, Hayat T. A new switching control for finite-time synchronization of memristor-based recurrent neural networks. Neural Networks, 2017, 86: 1−9 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2016.10.008 [23] Liu H, Lu J A, Lü J, Hill D J. Structure identification of uncertain general complex dynamical networks with time delay. Automatica, 2009, 45(8): 1799−1807 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.03.022 [24] Che Y Q, Li R X, Han C X, Cui S G, Wang J, Wei X L, Deng B. Topology identification of uncertain nonlinearly coupled complex networks with delays based on anticipatory synchronization. Chaos, 2013, 23(1): 013127−7 doi: 10.1063/1.4793541 [25] Mei J, Jiang M, Xu W, Wang B. Finite-time synchronization control of complex dynamical networks with time delay. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2013, 18(9): 2462−2478 doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2012.11.009 [26] Abdurahman A, Jiang H, Hu C, Teng Z. Parameter identification based on finite-time synchronization for Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with time-varying delays. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2015, 20(3): 348−366 [27] Jing T Y, Chen F Q, Li Q H. Finite-time mixed outer synchronization of complex networks with time-varying delay and unknown parameters. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2015, 39(23): 23−24 [28] 罗毅平, 周笔锋. 时滞扩散性复杂网络同步保性能控制. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(1): 147−156Luo Yi-Ping, Zhou Bi-Feng. Guaranteed cost synchronization control of diffusible complex network systems with time delay. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(1): 147−156 [29] Lorenz E N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. Journal of the atmospheric sciences, 1963, 20(2): 130−141 doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1963)020<0130:DNF>2.0.CO;2 [30] Chen G, Ueta T. Yet another chaotic attractor. International Journal of Bifurcation and chaos, 1999, 9(7): 1465−1466 doi: 10.1142/S0218127499001024 -






 下载:
下载: