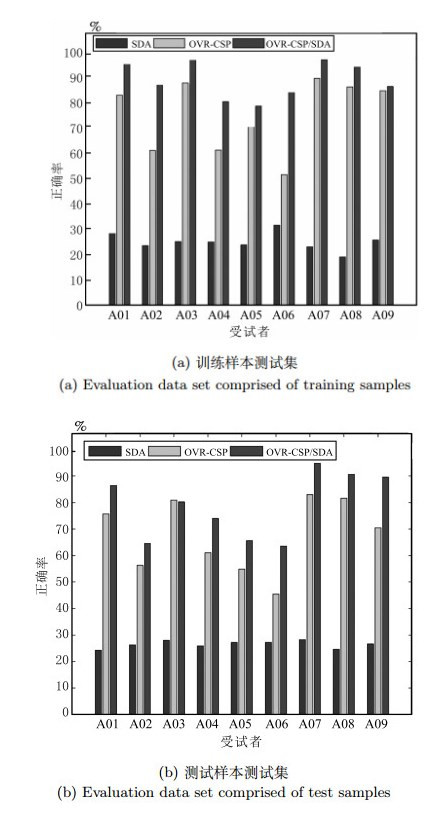
-
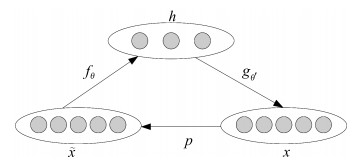
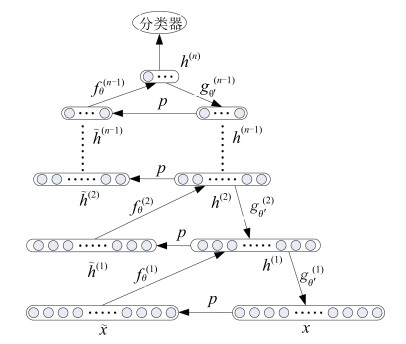
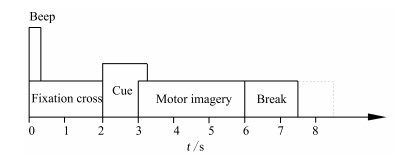
摘要: 共同空间模式(Common spatial pattern,CSP)是运动想象脑机接口(Brain-computer interface,BCI)中常用的特征提取方法,但对多类任务的分类正确率却明显低于两类任务.通过引入堆叠降噪自动编码器(Stacked denoising autoencoders,SDA),提出了一种多类运动想象脑电信号(Electroencephalogram,EEG)的两级特征提取方法.首先利用一对多CSP(One versus rest CSP,OVR-CSP)将脑电信号变换到使信号方差区别最大的低维空间,然后通过SDA网络提取其中可以更好表达类别属性的高层抽象特征,最后使用Softmax分类器进行分类.在对BCI竞赛IV中Data-sets 2a的4类运动想象任务进行的分类实验中,平均Kappa系数达到0.69,表明了所提出的特征提取方法的有效性和鲁棒性.Abstract: Common spatial pattern (CSP) is a popular method of feature extraction for motor imagery based brain-computer interface (BCI). However, the classification accuracy of multi-class tasks is obviously lower than that of two-class tasks with CSP. By employing the stacked denoising autoencoders (SDA), a two-level feature extraction method for multi-class motor imagery electroencephalogram (EEG) is proposed. Firstly, one versus rest CSP (OVR-CSP) is adopted to convert EEG into low dimensional space in which the discrimination of signal variances is maximized. Then, SDA network is used to extract the higher level abstract features which can characterize the category attributes more effectively. Finally, the motor imagery tasks are classified with Softmax classifier. In the classification experiment with four-class motor imagery tasks from Data-sets 2a of the BCI competition IV, this method achieves the average Kappa value of 0.69. The results show that the proposed method is effective and robust.1) 本文责任编委 程龙
-
表 1 均Kappa系数随隐含层层数的变化
Table 1 Mean Kappa coefficient variation with the number of hidden layers
层数 2 4 6 8 Kappa 0.61 0.68 0.62 0.59 表 2 平均Kappa系数随隐含层单元数组合的变化
Table 2 Mean Kappa coefficient variation with the combination of the number of units in the hidden layer
组合 24-24-24-24 24-20-16-8 24-28-32-40 Kappa 0.680 0.691 0.689 表 3 本文方法与BCI竞赛前三名以及其他文献方法的Kappa系数比较
Table 3 Comparison of Kappa coefficient obtained from proposed method, first three teams of the competition and other reference method
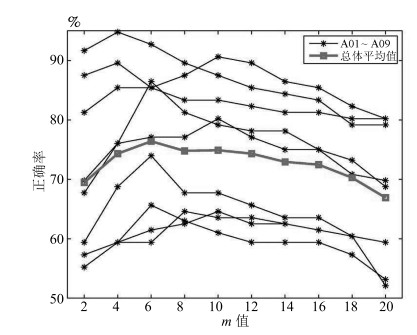
受试者 A01 A02 A03 A04 A05 A06 A07 A08 A09 总体均值 第1名 0.68 0.42 0.75 0.48 0.4 0.27 0.77 0.75 0.61 0.57±0.183 第2名 0.69 0.34 0.71 0.44 0.16 0.21 0.66 0.73 0.69 0.52±0.230 第3名 0.38 0.18 0.48 0.33 0.07 0.14 0.29 0.49 0.44 0.31±0.153 文献[22] 0.73 0.46 0.76 0.48 0.21 0.33 0.76 0.75 0.81 0.59±0.221 本文 0.82
±0.1040.49
±0.0840.68
±0.1090.65
±0.1260.54
±0.1180.51
±0.1340.86
±0.1050.81
±0.0890.81
±0.0960.69
±0.146 -
[1] 王行愚, 金晶, 张宇, 王蓓.脑控:基于脑-机接口的人机融合控制.自动化学报, 2013, 39(3):208-221 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60023-3Wang Xing-Yu, Jin Jing, Zhang Yu, Wang Bei. Brain control:human-computer integration control based on brain-computer interface. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(3):208-221 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60023-3 [2] Nicolas-Alanso L F, Corralejo R, Gomez-Pilar J, álvarez D, Hornero R. Adaptive stacked generalization for multiclass motor imagery-based brain computer interfaces. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2015, 23(4):702-712 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2015.2398573 [3] Aghaei A S, Mahanta M S, Plataniotis K N. Separable common spatio-spectral patterns for motor imagery BCI systems. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 63(1):15-29 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2487738 [4] 李明爱, 刘净瑜, 郝冬梅.基于改进CSP算法的运动想象脑电信号识别方法.中国生物医学工程学报, 2009, 28(2):161-165 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSWY200902001.htmLi Ming-Ai, Liu Jing-Yu, Hao Dong-Mei. EEG recognition of motor imagery based on improved CSP algorithm. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2009, 28(2):161-165 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSWY200902001.htm [5] Zhang H H, Chin Z Y, Ang K K, Guan C T, Wang C C. Optimum spatio-spectral filtering network for brain-computer interface. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(1):52-63 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2084099 [6] Wu W, Gao X R, Gao S K. One-versus-the-rest (OVR) algorithm:an extension of common spatial patterns (CSP) algorithm to multi-class case. In:Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and the 27th Biology Annual Conference. Shanghai, China:IEEE, 2006. 2387-2390 [7] 刘广权, 黄淦, 朱向阳.共空域模式方法在多类别分类中的应用.中国生物医学工程学报, 2009, 28(6):935-938 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSWY200906025.htmLiu Guang-Quan, Huang Gan, Zhu Xiang-Yang. Application of CSP method in multi-class classification. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2009, 28(6):935-938 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSWY200906025.htm [8] Zhang Y, Zhou G X, Jin J, Wang X Y, Cichocki A. Optimizing spatial patterns with sparse filter bands for motor-imagery based brain-computer interface. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2015, 255:85-91 doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.08.004 [9] Ang K K, Chin Z Y, Wang C C, Guan C T, Zhang H H. Filter bank common spatial pattern algorithm on BCI competition IV datasets 2a and 2b. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2012, 6:39 [10] Vincent P, Larochelle H, Lajoie I, Bengio Y, Manzagol P A. Stacked denoising autoencoders:learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11:3371-3408 http://www.docin.com/p-904440224.html [11] Li J H, Struzik Z, Zhang L Q, Cichocki A. Feature learning from incomplete EEG with denoising autoencoder. Neurocomputing, 2015, 165:23-31 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.08.092 [12] 耿杰, 范剑超, 初佳兰, 王洪玉.基于深度协同稀疏编码网络的海洋浮筏SAR图像目标识别.自动化学报, 2016, 42(4):593-604 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18846.shtmlGeng Jie, Fan Jian-Chao, Chu Jia-Lan, Wang Hong-Yu. Research on marine floating raft aquaculture SAR image target recognition based on deep collaborative sparse coding network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4):593-604 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18846.shtml [13] 徐守晶, 韩立新, 曾晓勤.基于改进型SDA的自然图像分类与检索.模式识别与人工智能, 2014, 27(8):750-757 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MSSB201408010.htmXu Shou-Jing, Han Li-Xin, Zeng Xiao-Qin. Natural images classification and retrieval based on improved SDA. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2014, 27(8):750-757 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MSSB201408010.htm [14] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 1986, 323(6088):533-536 doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [15] Vincent P, Larochelle H, Bengio Y, Manzagol P A. Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In:Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. Helsinki, Finland:ACM, 2008. 1096-1103 [16] Erhan D, Bengio Y, Courville A, Manzagol P A, Vincent P, Bengio Y. Why does unsupervised pre-training help deep learning? The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11:625-660 http://www.stat.cmu.edu/~ryantibs/journalclub/deep.pdf [17] Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7):1527-1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [18] Tangermann M, Müller K R, Aertsen A, Birbaumer N, Braun C, Brunner C, Leeb R, Mehring C, Miller K J, Müller-Putz G R, Nolte G, Pfurtscheller G, Preissl H, Schalk G, Schlġl A, Vidaurre C, Waldert S, Blankertz B. Review of the BCI competition IV. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2012, 6:55 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229077218_Review_of_the_BCI_competition_IV [19] Ramoser H, Muller-Gerking J, Pfurtscheller G. Optimal spatial filtering of single trial EEG during imagined hand movement. IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, 2000, 8(4):441-446 doi: 10.1109/86.895946 [20] Wang H X, Xu D. Comprehensive common spatial patterns with temporal structure information of EEG data:minimizing nontask related EEG component. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 59(9):2496-2505 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2205383 [21] Berlin Brain-Computer Interface. BCI competition IV-final results[Online], available:http://www.bbci.de, January 1, 2016 [22] 刘冲, 颜世玉, 赵海滨, 王宏.多类运动想象任务脑电信号的KNN分类研究.仪器仪表学报, 2013, 33(8):1714-1720 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB201208006.htmLiu Chong, Yan Shi-Yu, Zhao Hai-Bin, Wang Hong. Study on multi-class motor imagery EEG classification based on KNN. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2013, 33(8):1714-1720 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQXB201208006.htm -




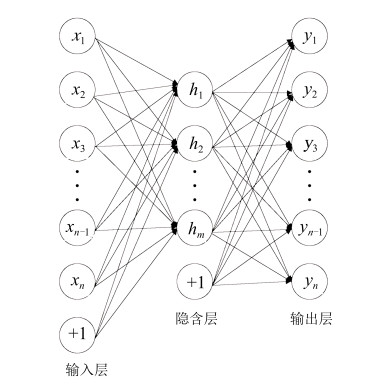
 下载:
下载: