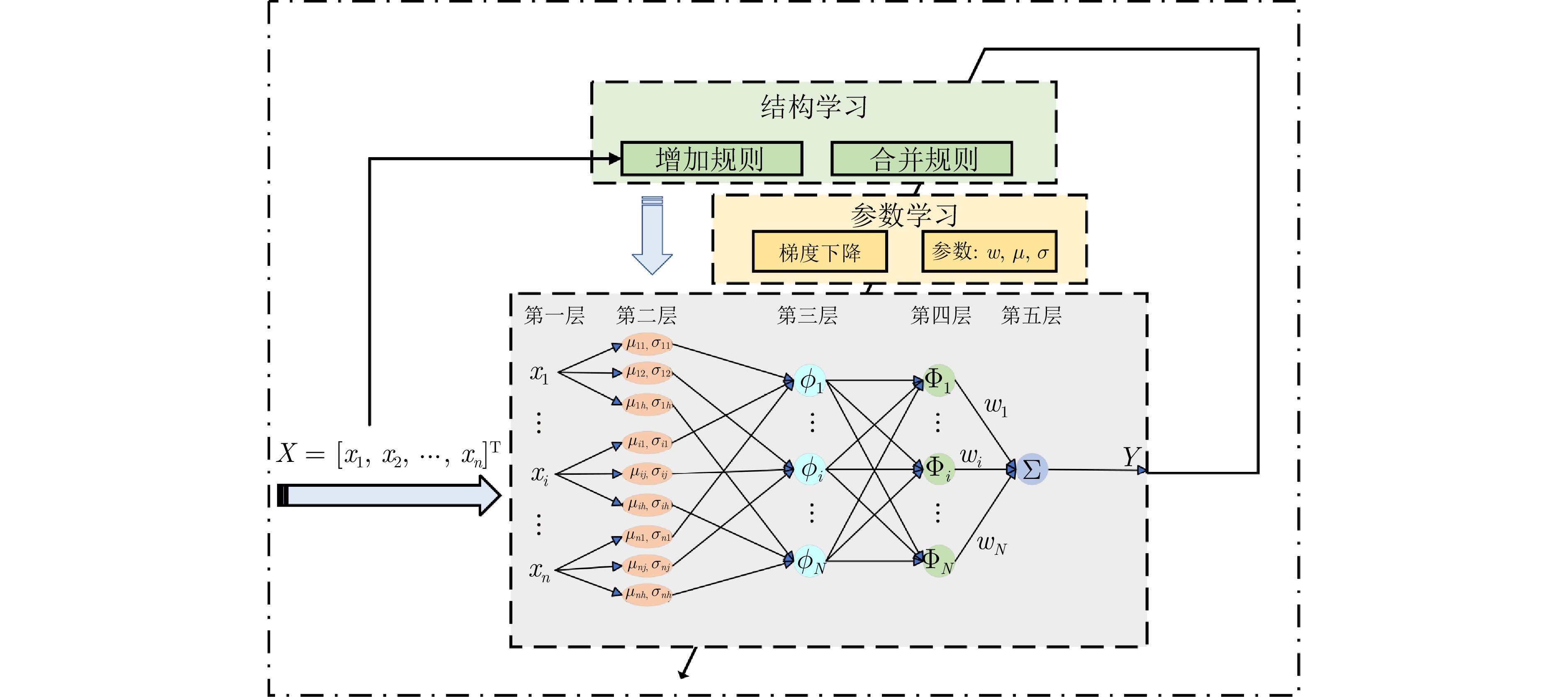
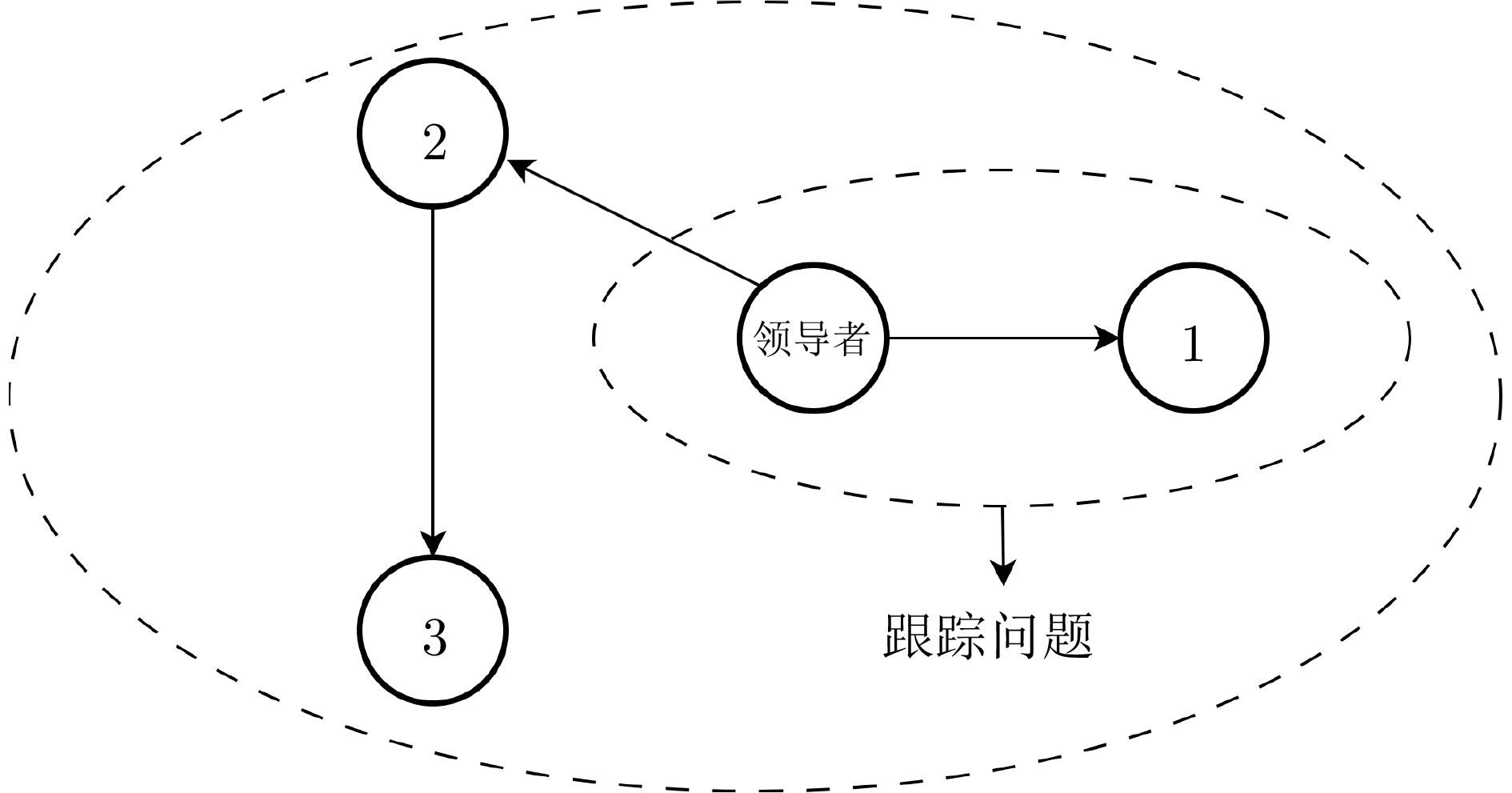
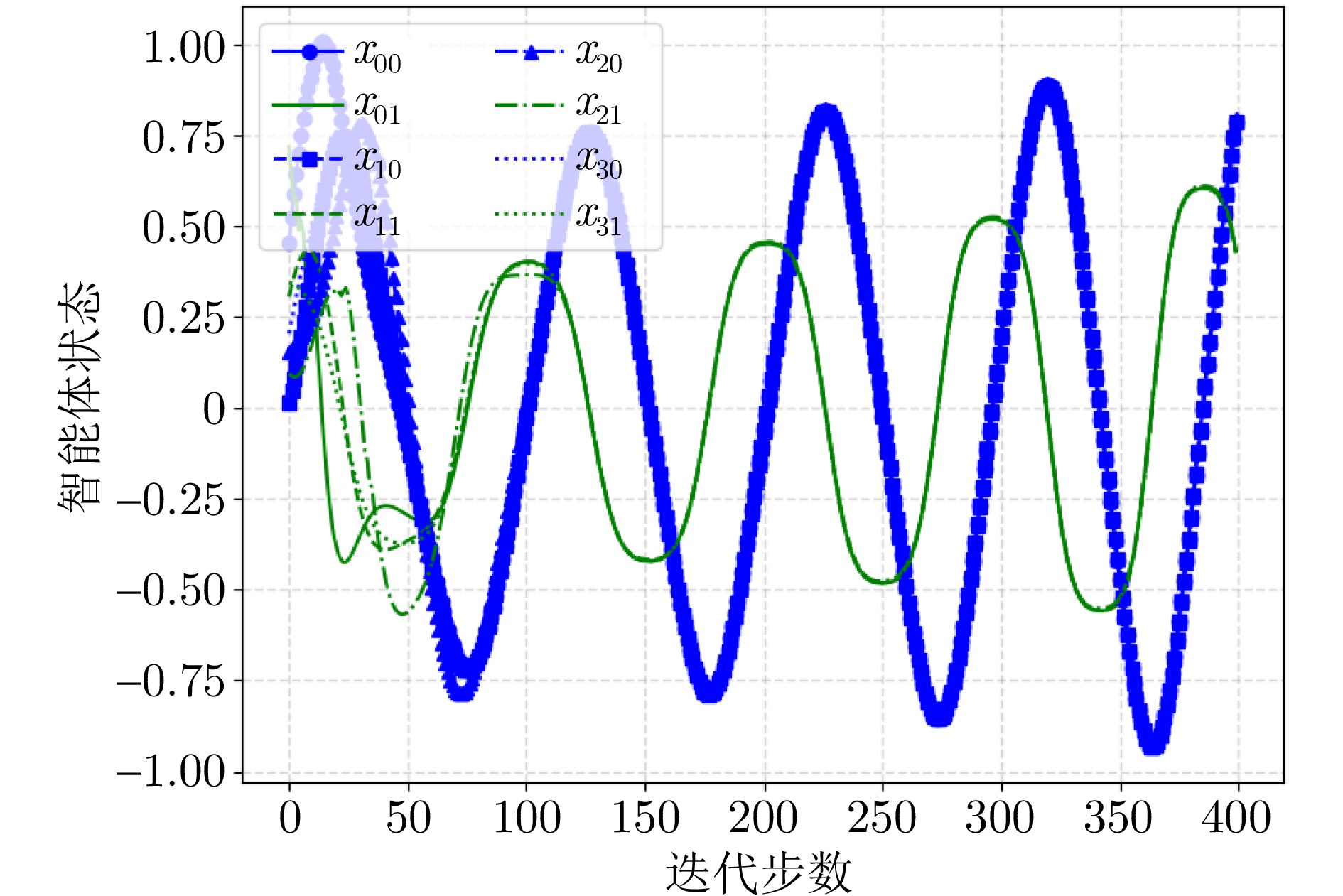
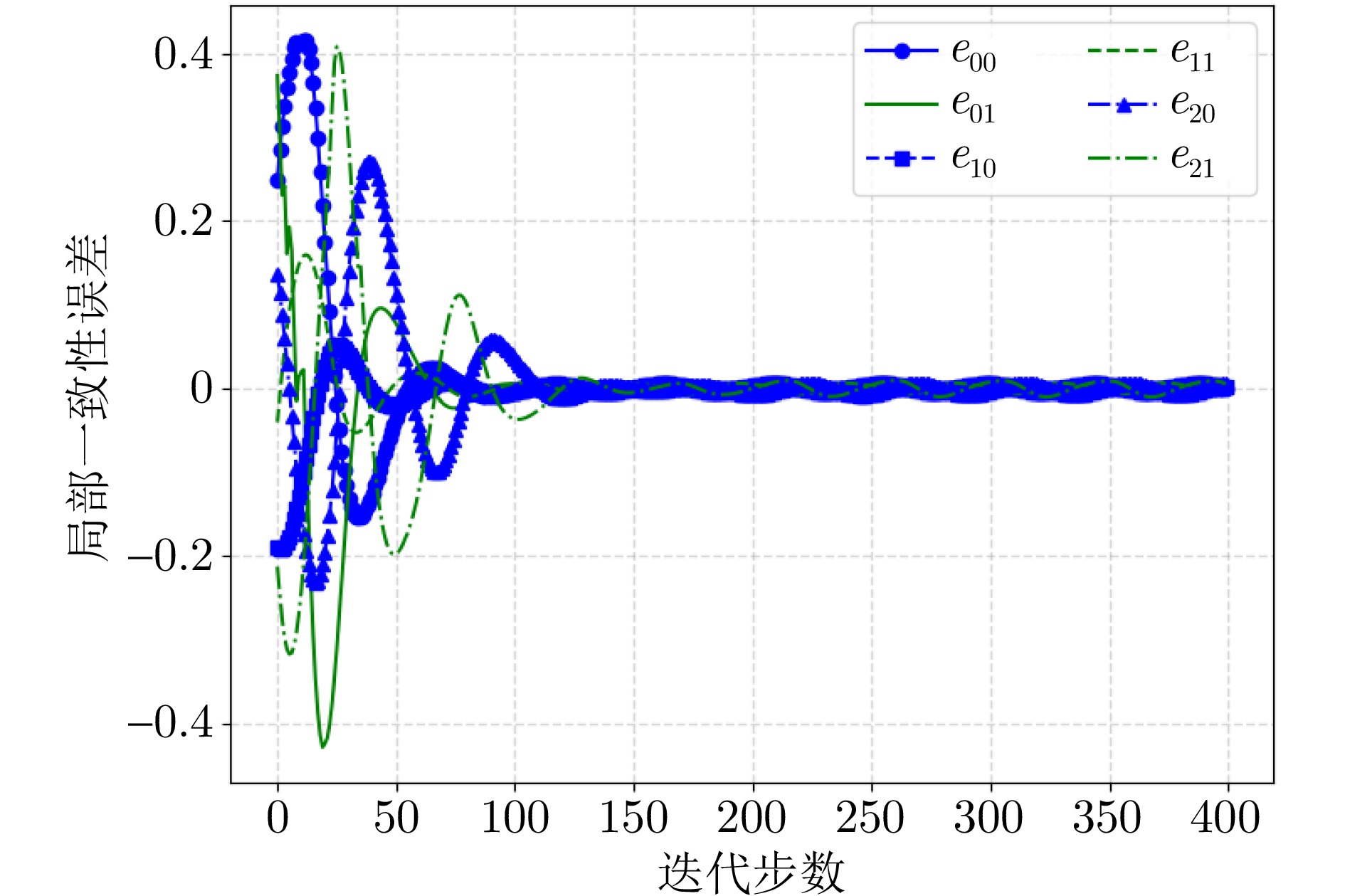
|
[1]
|
Zhao W, Li R, Zhang H. Leader-follower optimal coordination tracking control for multi-agent systems with unknown internal states. Neurocomputing, 2017, 249: 171−181 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.03.066
|
|
[2]
|
Cao Y, Yu W, Ren W, Chen G. An overview of recent progress in the study of distributed multi-agent coordination. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2012, 9(1): 427−438
|
|
[3]
|
Sun Y, Shi P, Lim C C. Adaptive consensus control for output-constrained nonlinear multi-agent systems with actuator faults. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2022, 359(9): 4216−4232 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2022.03.025
|
|
[4]
|
Zhang L, Che W W, Chen B, Lin C. Adaptive fuzzy output-feedback consensus tracking control of nonlinear multiagent systems in prescribed performance. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 53(3): 1932−1943
|
|
[5]
|
Zhang Y, Wang D, Peng Z, Li T. Distributed containment maneuvering of uncertain multiagent systems in MIMO strict-feedback form. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 51(2): 1354−1364
|
|
[6]
|
Yan Y C, Li T S, Yang H Q, Wang J H, Chen C L. Fuzzy finite-time consensus control for uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems with input delay. Information Sciences, 2023, 632: 51−68 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.02.082
|
|
[7]
|
Liu L, Shafiq M, Sonawane V, Murthy M, Reddy P, Reddy K. Spectrum trading and sharing in unmanned aerial vehicles based on distributed blockchain consortium system. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2022, 103: Article No. 108255 doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.108255
|
|
[8]
|
Sridevi K, Saifulla M. LBABC: Distributed controller load balancing using artificial bee colony optimization in an SDN. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2023, 16(2): 947−957 doi: 10.1007/s12083-023-01448-2
|
|
[9]
|
Zhang J, Zhang S, Deng X, Huang Z. Adaptive event-triggered dynamic distributed control of switched positive systems with switching faults. Nonlinear Analysis: Hybrid Systems, 2023, 48: Article No. 101328 doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2022.101328
|
|
[10]
|
Zhang R, Cai K. Localisation-based distributed control of timed discrete-event systems with communication delay. International Journal of Control, 2022, 95(2): 330−339 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2020.1793000
|
|
[11]
|
Tang F, Wang H, Zhang L, Xu N, Ahmad A. Adaptive optimized consensus control for a class of nonlinear multi-agent systems with asymmetric input saturation constraints and hybrid faults. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2023, 126: Article No. 107446 doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2023.107446
|
|
[12]
|
Wang W, Li Y, Tong S. Exact-optimal consensus of uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems based on fuzzy approximation. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, DOI: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3366999
|
|
[13]
|
Bai N, Duan Z, Wang Q. Distributed optimal consensus of multi-agent systems: A randomized parallel approach. Automatica, 2024, 159: Article No. 111339 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111339
|
|
[14]
|
Bai N, Wang Q, Duan Z, Chen G. Distributed optimal consensus control of constrained multi-agent systems: A non-separable optimization perspective. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, DOI: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3390849
|
|
[15]
|
Meng H, Pang D, Cao J, Guo Y, Niazi A. Optimal bipartite consensus control for heterogeneous unknown multi-agent systems via reinforcement learning. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2024, 476: Article No. 128785 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2024.128785
|
|
[16]
|
Jin N, Xu J, Zhang H. Distributed optimal consensus control of multi-agent systems involving state and control dependent multiplicative noise. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(12): 7787−7794 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3246422
|
|
[17]
|
朱永薪, 李永福, 朱浩, 于树友. 通信延时环境下基于观测器的智能网联车辆队列分层协同纵向控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(8): 1785−1798Zhu Yong-Xin, Li Yong-Fu, Zhu Hao, Yu Shu-You. Observer-based longitudinal control for connected and automated vehicles platoon subject to communication delay. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(8): 1785−1798
|
|
[18]
|
Fu X, Pan J, Wang H, Gao X. A formation maintenance and reconstruction method of UAV swarm based on distributed control. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 104: Article No. 105981 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105981
|
|
[19]
|
Tran Q V, Ahn H S. Distributed formation control of mobile agents via global orientation estimation. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2020, 7(4): 1654−1664 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2020.2993253
|
|
[20]
|
Wang B, Chen W, Wang J, Zhang B, Zhang Z, Qiu X. Cooperative tracking control of multiagent systems: A heterogeneous coupling network and intermittent communication framework. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 49(12): 4308−4320
|
|
[21]
|
Cui B, Zhao C, Ma T, Feng C. Leader-following consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems with switching topologies and unreliable communications. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016, 27: 909−915 doi: 10.1007/s00521-015-1905-0
|
|
[22]
|
Deng C, Yang G H. Distributed adaptive fault-tolerant control approach to cooperative output regulation for linear multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2019, 103: 62−68 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.01.013
|
|
[23]
|
Parsons S, Wooldridge M. Game theory and decision theory in multi-agent systems. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2002, 5: 243−254
|
|
[24]
|
Başar T, Olsder G J, Dynamic Noncooperative Game Theory. Pennsylvania: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1998. 71–83
|
|
[25]
|
He W, Chen X, Fu H. Dual ML-ADHDP method for heterogeneous discrete-time nonlinear multi-agent systems with unknown dynamics and time delay. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2022, 359(11): 5634−5657 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2022.04.040
|
|
[26]
|
Vamvoudakis K G, Lewis F L. Multi-player non-zero-sum games: Online adaptive learning solution of coupled Hamilton-Jacobi equations. Automatica, 2011, 47(8): 1556−1569 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.03.005
|
|
[27]
|
Werbos P. Approximate Dynamic Programming for Real-time Control and Neural Modeling. New York: Handbook of Intelligent Control, 1992. 12–23
|
|
[28]
|
Wei Q, Liu D. Data-driven neuro-optimal temperature control of water-gas shift reaction using stable iterative adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(11): 6399−6408 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2301770
|
|
[29]
|
Vamvoudakis K G, Lewis F L, Hudas G R. Multi-agent differential graphical games: Online adaptive learning solution for synchronization with optimality. Automatica, 2012, 48(8): 1598−1611 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.05.074
|
|
[30]
|
Zhang H, Feng T, Yang G H, Liang H. Distributed cooperative optimal control for multiagent systems on directed graphs: An inverse optimal approach. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 45(7): 1315−1326
|
|
[31]
|
Abouheaf M I, Lewis F L. Multi-agent differential graphical games: Nash online adaptive learning solutions. In: Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Firenze, Italy: IEEE, 2013. 5803–5809
|
|
[32]
|
Zhang H, Zhang J, Yang G H, Luo Y. Leader-based optimal coordination control for the consensus problem of multiagent differential games via fuzzy adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2014, 23(1): 152−163
|
|
[33]
|
Wei Q, Liu D, Lewis F L. Optimal distributed synchronization control for continuous-time heterogeneous multi-agent differential graphical games. Information Sciences, 2015, 317: 96−113 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.04.044
|
|
[34]
|
Abouheaf M I, Lewis F L, Vamvoudakis K G, Haesaert S, Babuska R. Multi-agent discrete-time graphical games and reinforcement learning solutions. Automatica, 2014, 50(12): 3038−3053 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.047
|
|
[35]
|
Abouheaf M, Lewis F, Haesaert S, Babuska R, Vamvoudakis K. Multi-agent discrete-time graphical games: Interactive Nash equilibrium and value iteration solution. In: Proceedings of 2013 American Control Conference. Washington DC, USA: IEEE, 2013. 4189–4195
|
|
[36]
|
Wang D, Liu D, Li H, Ma H. Neural-network-based robust optimal control design for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems via adaptive dynamic programming. Information Sciences, 2014, 282: 167−179 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.05.050
|
|
[37]
|
Zhang H, Jiang H, Luo Y, Xiao G. Data-driven optimal consensus control for discrete-time multi-agent systems with unknown dynamics using reinforcement learning method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 64(5): 4091−4100
|
|
[38]
|
Cai Y, Zhang H, Zhang K, Liu C. Fuzzy adaptive dynamic programming-based optimal leader-following consensus for heterogeneous nonlinear multi-agent systems. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(13): 8763−8781 doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04263-0
|
|
[39]
|
Wang W, Chen X, Chen L, Wu M. Model-free optimal consensus control for multi-agent systems using kernel-based ADP method. In: Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. Banff AB, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 2471–2476
|
|
[40]
|
Liu D, Wang D, Yang X. An iterative adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for optimal control of unknown discrete-time nonlinear systems with constrained inputs. Information Sciences, 2013, 220: 331−342 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2012.07.006
|
|
[41]
|
Wang X S, Cheng Y H, Yi J Q. A fuzzy actor-critic reinforcement learning network. Information Sciences, 2007, 177(18): 3764−3781 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2007.03.012
|
|
[42]
|
Khater A A, El-Nagar A M, El-Bardini M, El-Rabaie N. Online learning based on adaptive learning rate for a class of recurrent fuzzy neural network. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32: 8691−8710 doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04372-w
|
|
[43]
|
Khater A A, El-Nagar A M, El-Bardini M, El-Rabaie N. A novel structure of actor-critic learning based on an interval type-2 TSK fuzzy neural network. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 28(11): 3047−3061
|
|
[44]
|
Wang W, Chen X, Fu H, Wu M. Model-free distributed consensus control based on actor-critic framework for discrete-time nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 50(11): 4123−4134
|
|
[45]
|
Vrabie D, Lewis F. Neural network approach to continuous-time direct adaptive optimal control for partially unknown nonlinear systems. Neural Networks, 2009, 22(3): 237−246 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2009.03.008
|
|
[46]
|
伍世虔, 徐军. 动态模糊神经网络: 设计与应用. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2008. 27–28Wu Shi-Qian, Xv Jun. Dynamic Fuzzy Neural Network: Design and Application. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2008. 27–28
|
|
[47]
|
Hartmanis J, Stearns R E. On the computational complexity of algorithms. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 1965, 117: 285−306 doi: 10.1090/S0002-9947-1965-0170805-7
|
|
[48]
|
Han S, Wang L, Wang Y T. A potential field-based trajectory planning and tracking approach for automatic berthing and COLREGs-compliant collision avoidance. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266(3): Article No. 112877
|
|
[49]
|
Dong Z P, Zhang Z Q, Qi S J, Zhang H S, Li J K, Liu Y C. Autonomous cooperative formation control of underactuated USVs based on improved MPC in complex ocean environment. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 270: Article No. 113633 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.113633
|
|
[50]
|
Wang L, Chu X M, Liu C G. Different drive models of USV under the wind and waves disturbances MPC trajectory tracking simulation research. In: Proceedings of 2015 International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety. Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2015. 563–568
|




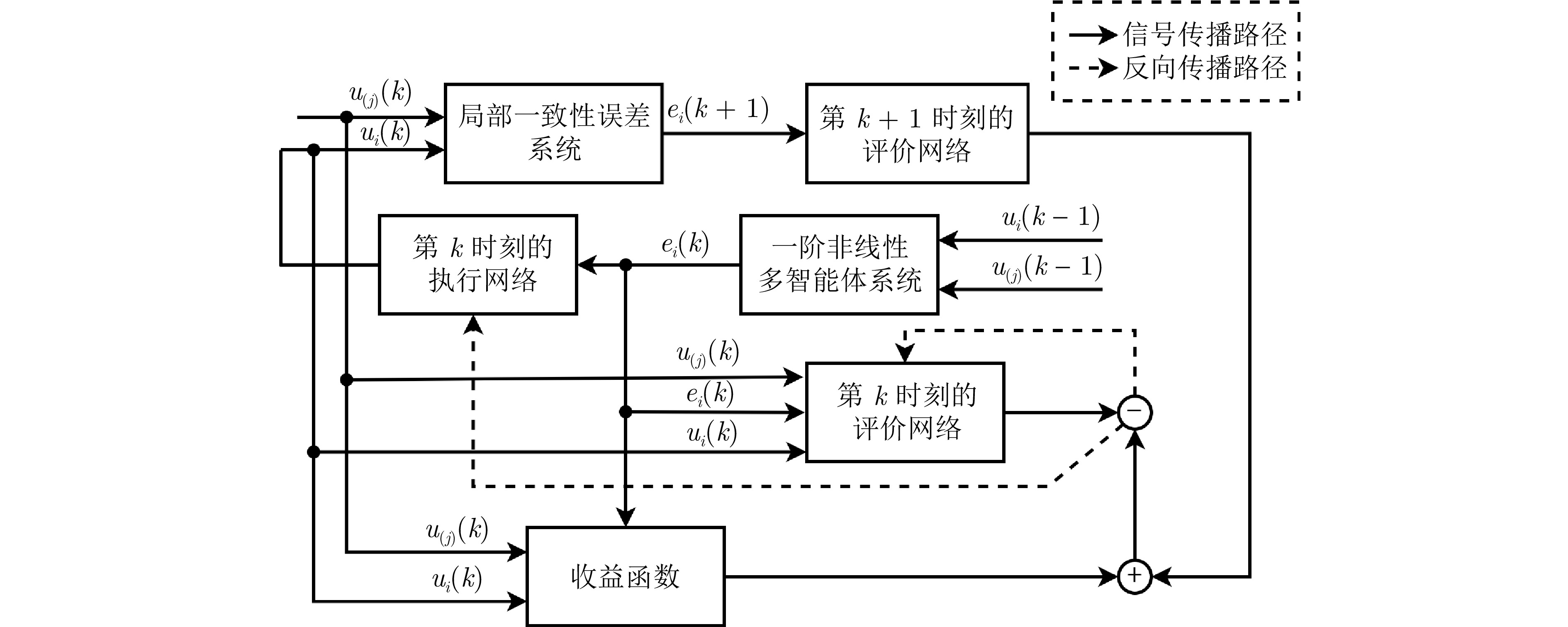
 下载:
下载: