Finite-horizon Consensus Control of Discrete-time Multi-agent Systems With Actuator Saturation
-
摘要: 针对执行器饱和的离散时间线性多智能体系统(Multi-agent systems, MASs)有限时域一致性控制问题, 将低增益反馈(Low gain feedback, LGF)方法与Q学习相结合, 提出采用后向时间迭代的模型无关控制方法. 首先, 将执行器饱和的有限时域一致性控制问题的求解转化为执行器饱和的单智能体有限时域最优控制问题的求解, 并证明可以通过求解修正的时变黎卡提方程 (Modified time-varying Riccati equation, MTVRE)实现有限时域最优控制. 随后, 引入时变参数化Q函数(Time-varying parameterized Q-function, TVPQF), 并提出基于Q学习的模型无关后向时间迭代算法, 可以更新低增益参数, 同时实现逼近求解MTVRE. 另外, 证明所提迭代求解算法得到的LGF控制矩阵收敛于MTVRE的最优解, 也可以实现全局有限时域一致性控制. 最后, 通过仿真实验结果验证了该方法的有效性.Abstract: A model-free control method using backward-in-time iteration by combining the low gain feedback (LGF) method with Q-learning is proposed for the finite-horizon consensus control problem for discrete-time linear multi-agent systems (MASs) with actuator saturation. First, the solution of the finite-horizon consensus control problem with actuator saturation is transformed into the solution of the finite-horizon optimal control problem of single agent with actuator saturation, and it is proved that the finite-horizon optimal control can be realized by solving the modified time-varying Riccati equation (MTVRE). Then, a time-varying parameterized Q-function (TVQPF) is introduced, and a model-free backward-in-time iteration algorithm based on Q-learning is proposed to update the low gain parameter and simultaneously approximate the solution of the MTVRE. In addition, it is demonstrated that the LGF control matrix obtained by the proposed iterative solution algorithm converges to the optimal solution of the MTVRE, and the global finite-horizon consensus control can also be realized. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by simulation results.
-
表 1 对比实验评价指标
Table 1 Evaluation indices of comparison experiments
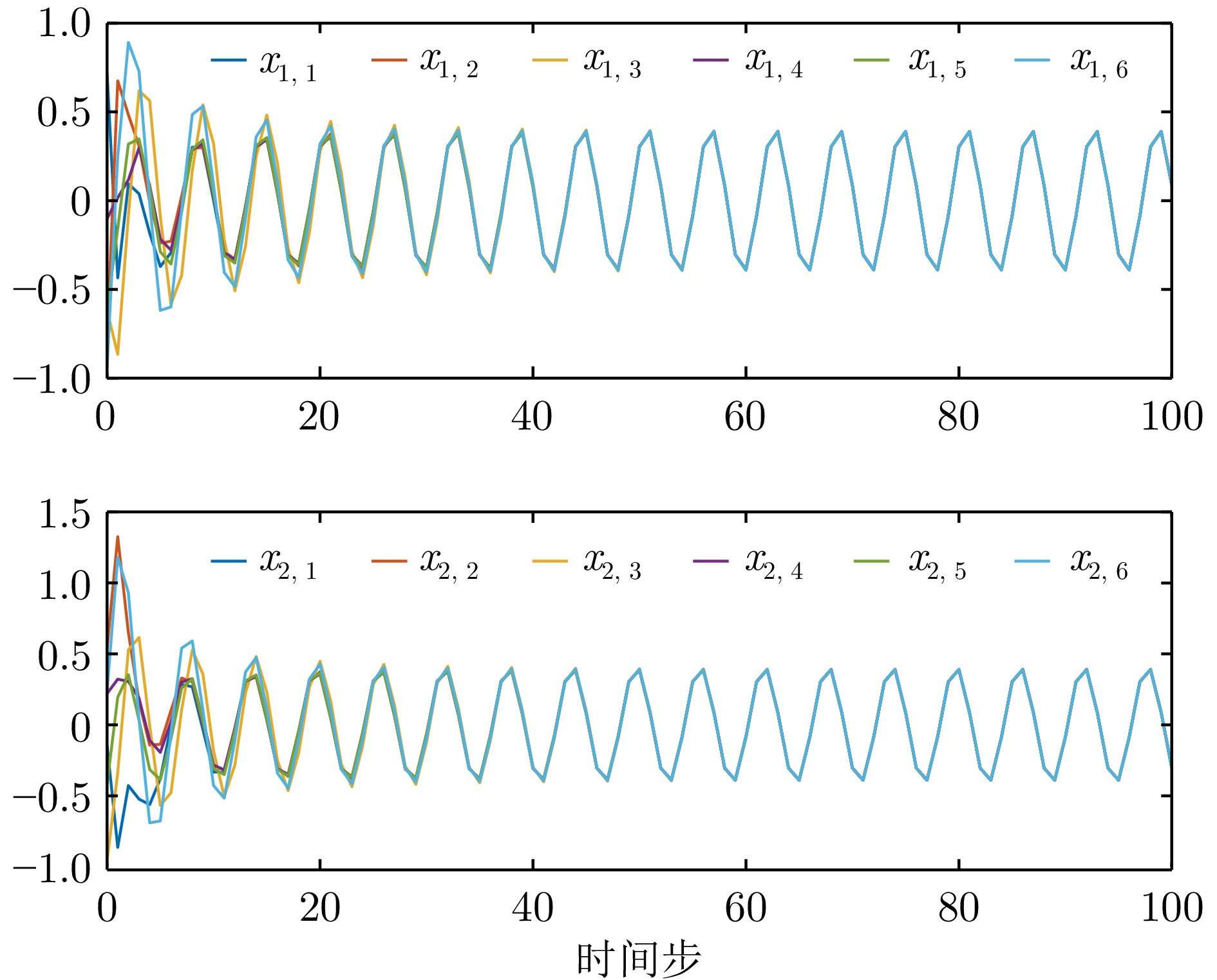
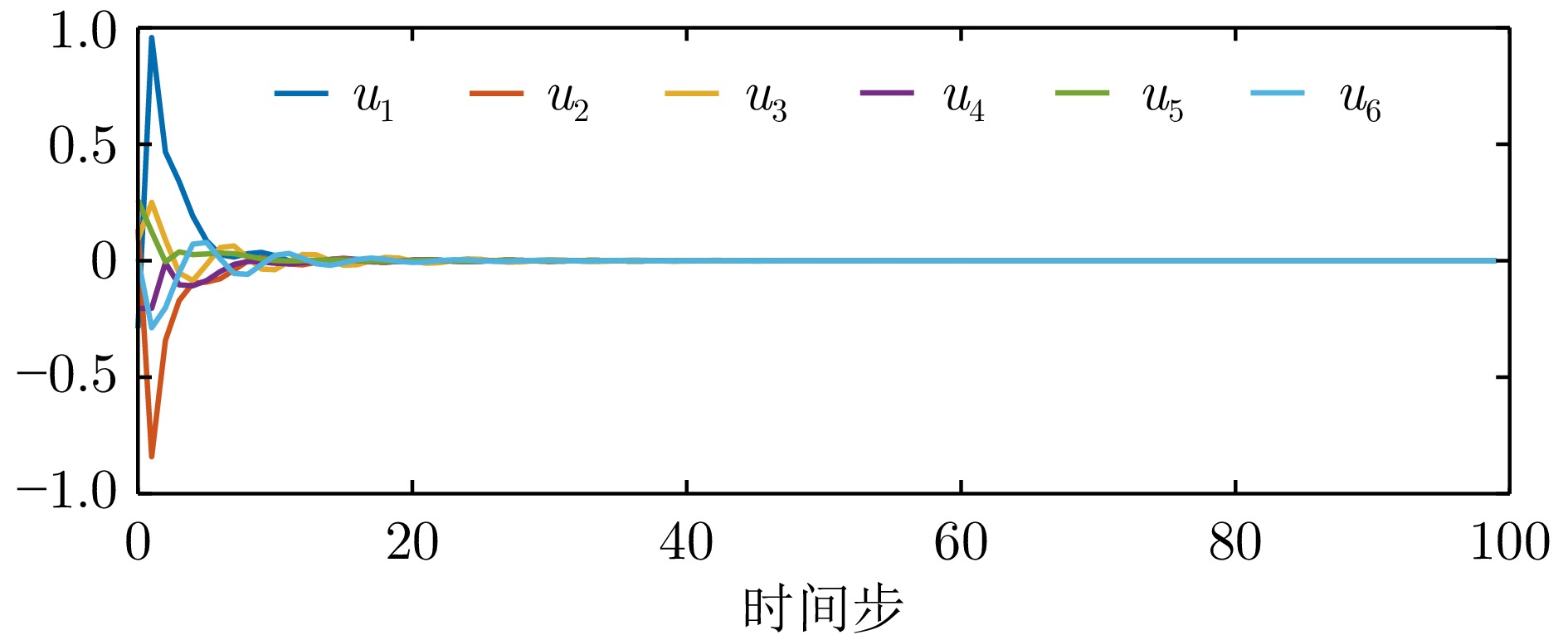
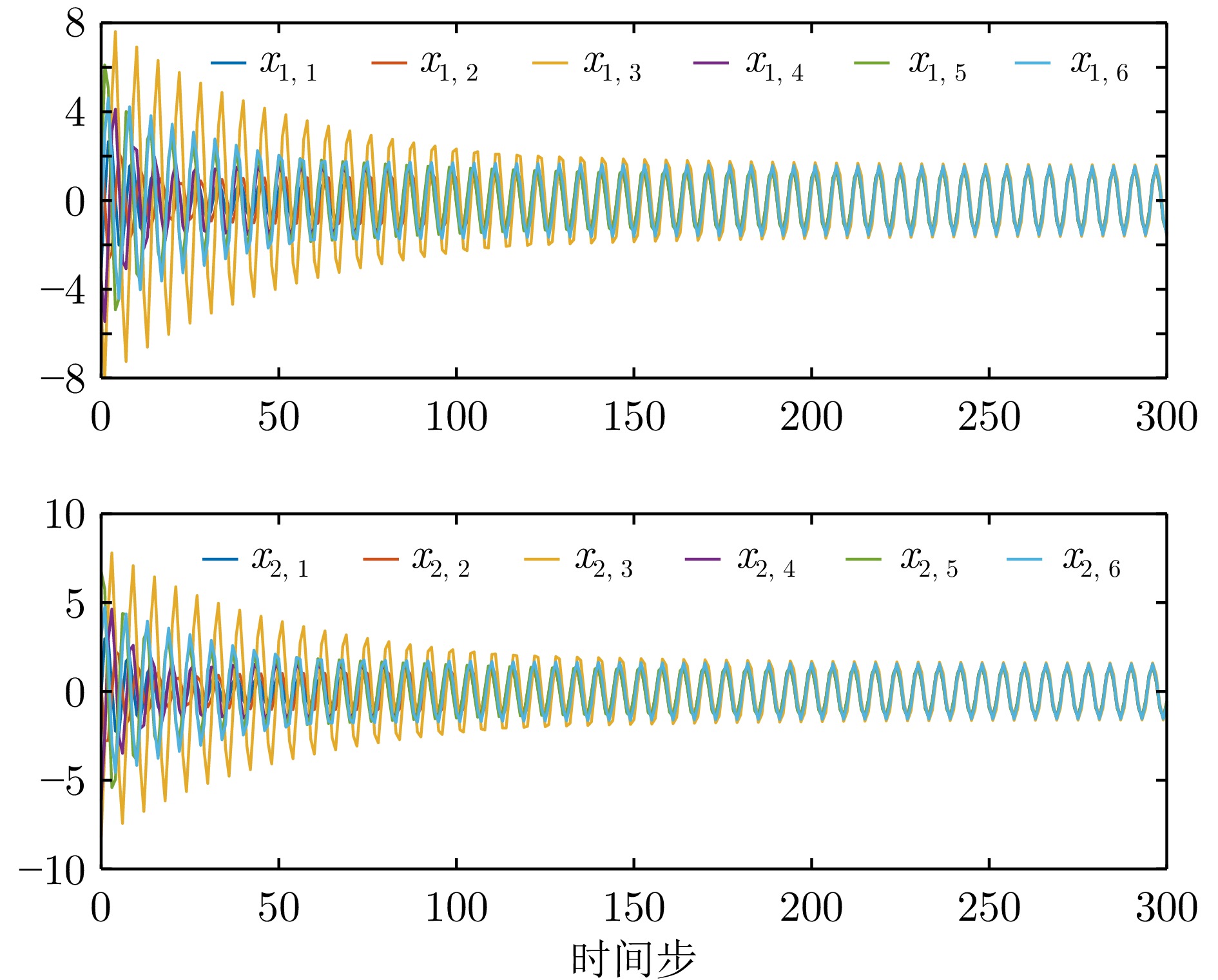
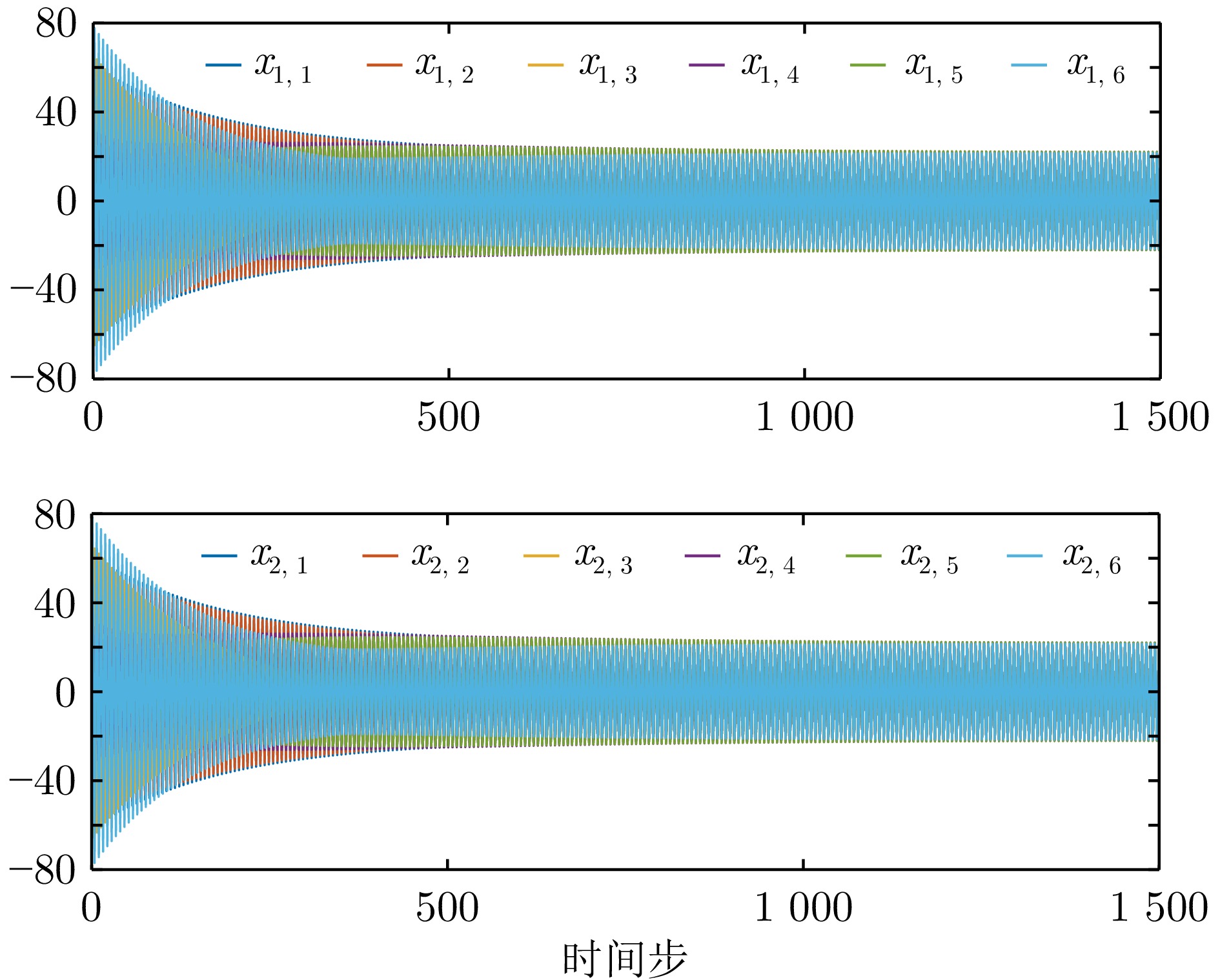
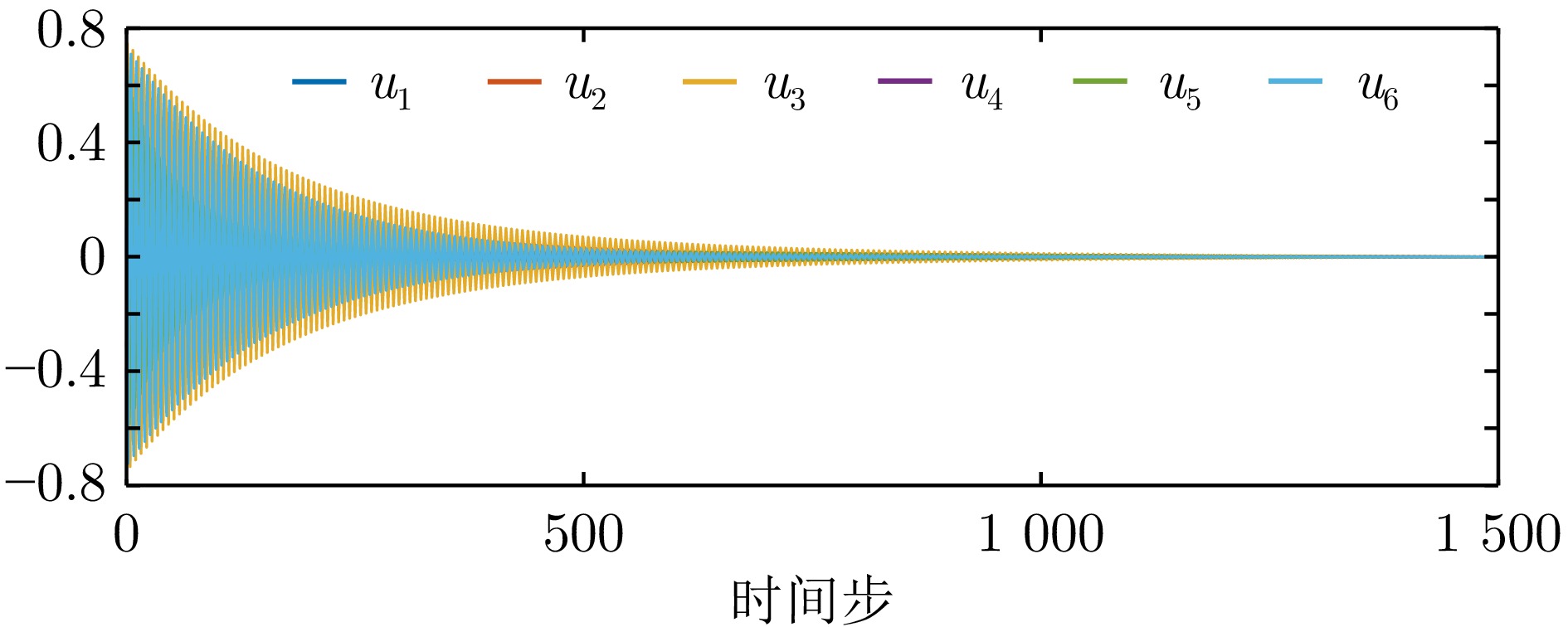
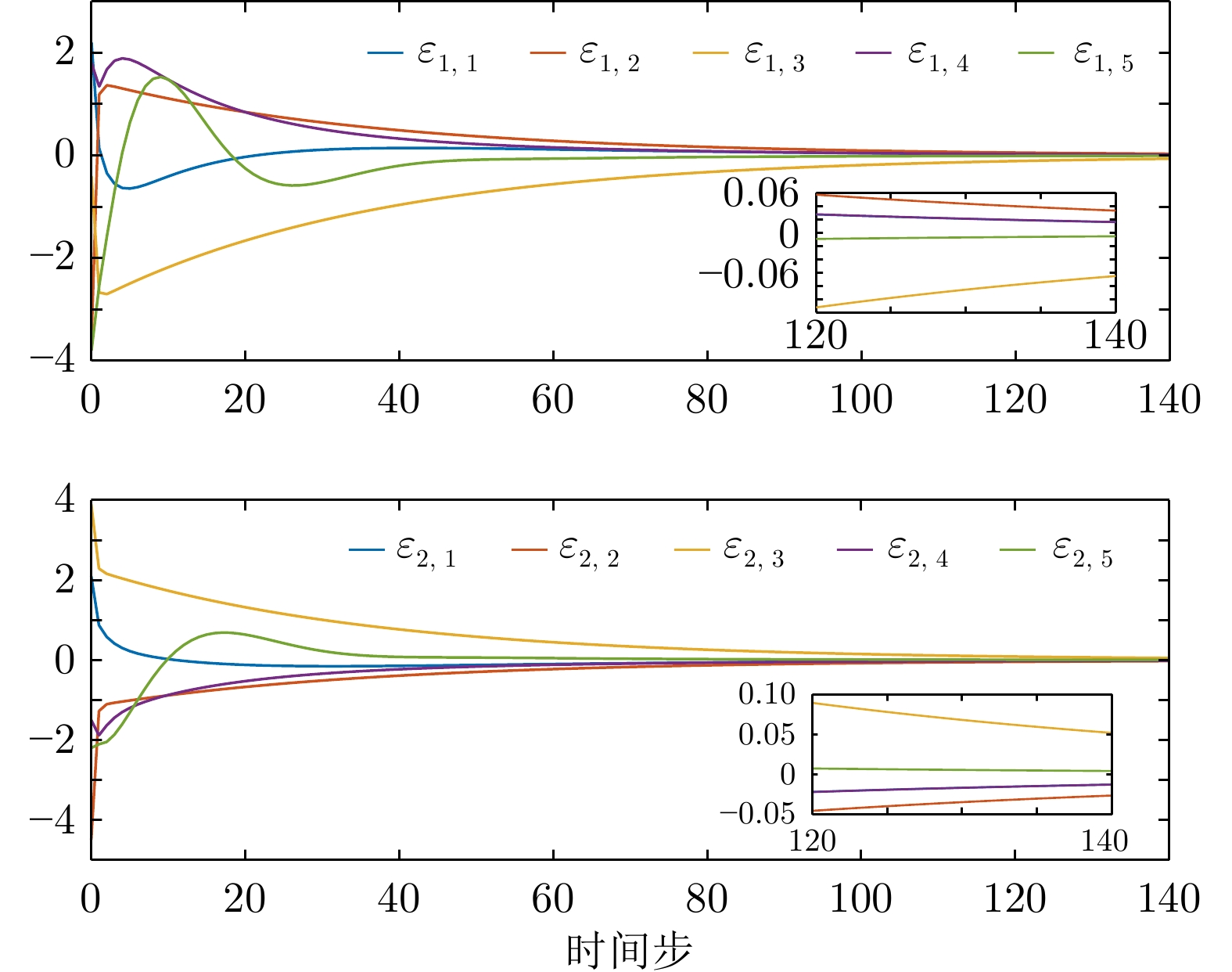
$100\le k \le 120$ ${\mathrm{IAE}}$ ${\mathrm{MSE}}$ 例1−有限时域方法 0.637 7 0.005 4 例1−无限时域方法 10.264 9 2.116 9 例2−有限时域方法 1.074 8 0.014 7 例2−无限时域方法 5.186 9 0.510 9 表 2 例1中一致性误差调节时间
Table 2 Consensus error setting time in example 1
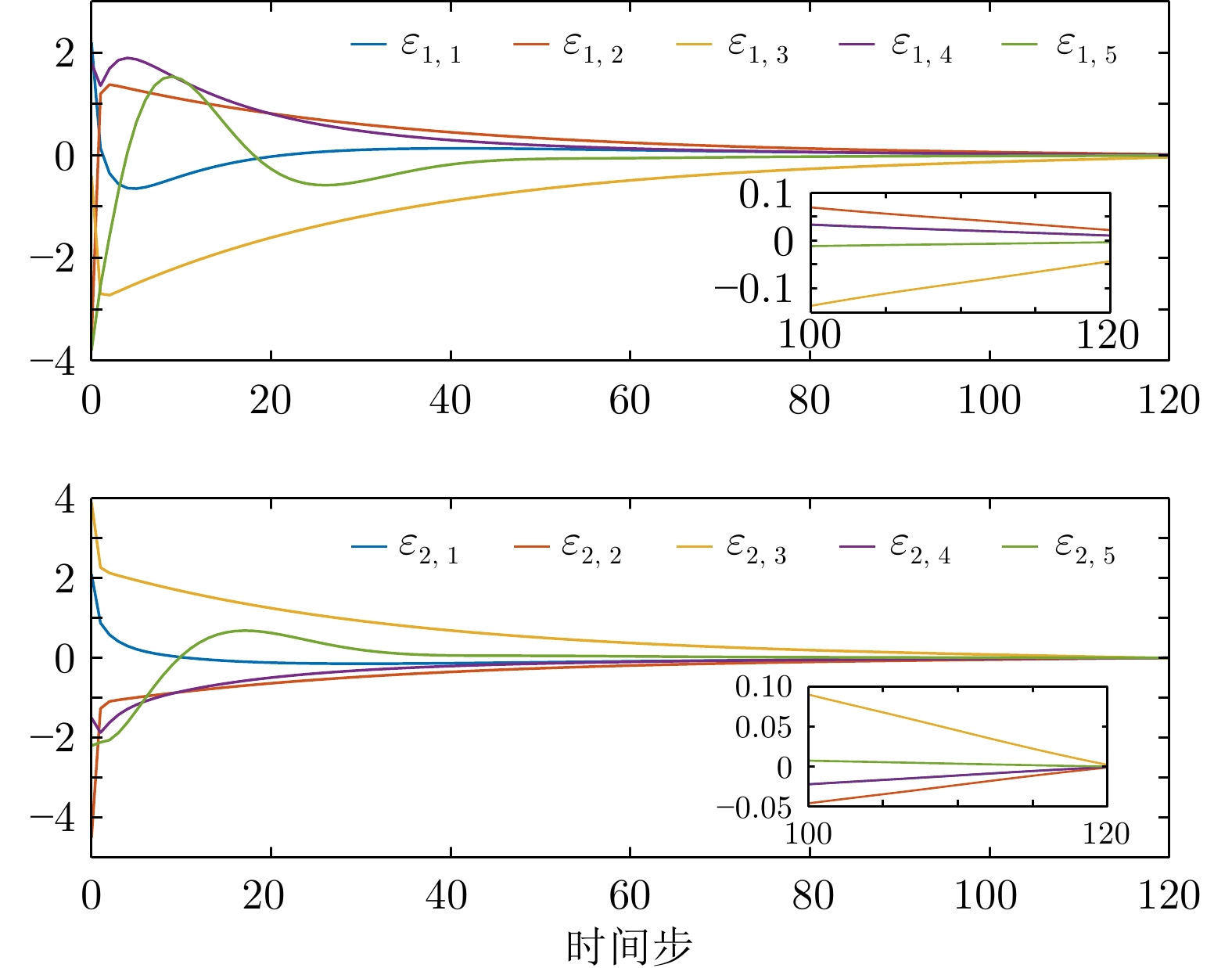
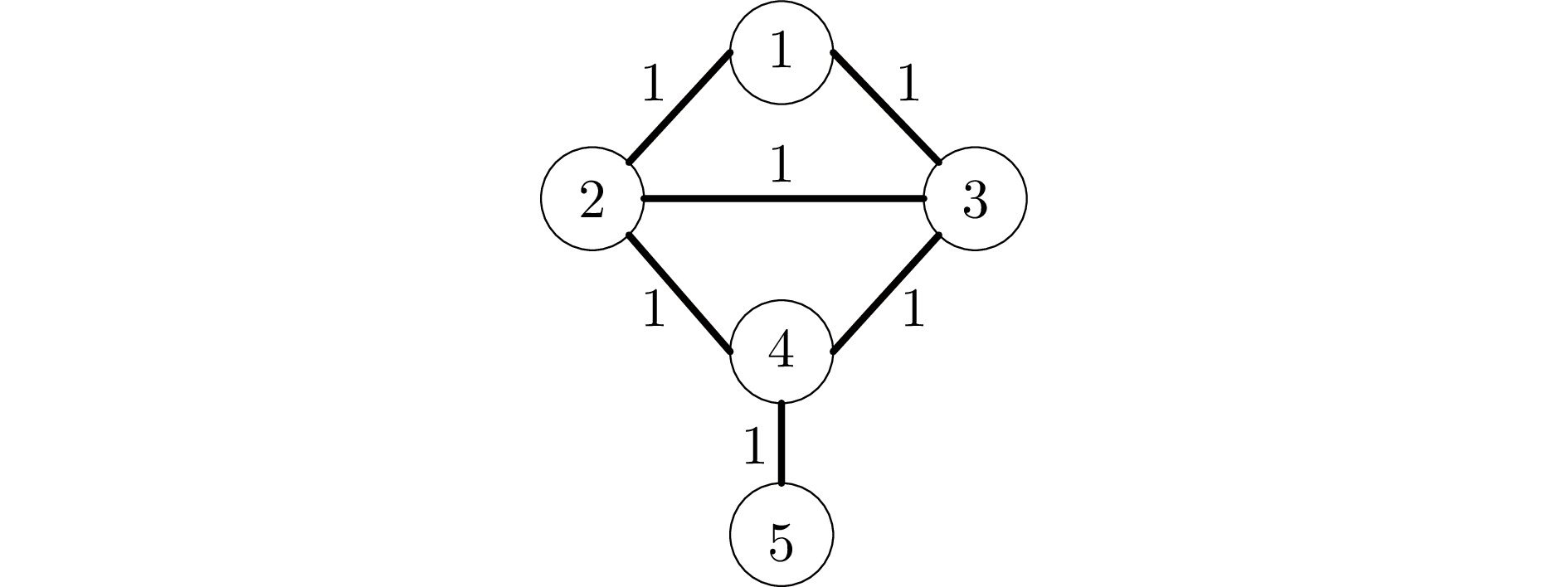
例1−调节时间 有限时域方法 无限时域方法 智能体1 109 137 智能体2 119 161 智能体3 104 127 智能体4 109 137 智能体5 90 110 表 3 例2中一致性误差调节时间
Table 3 Consensus error setting time in example 2
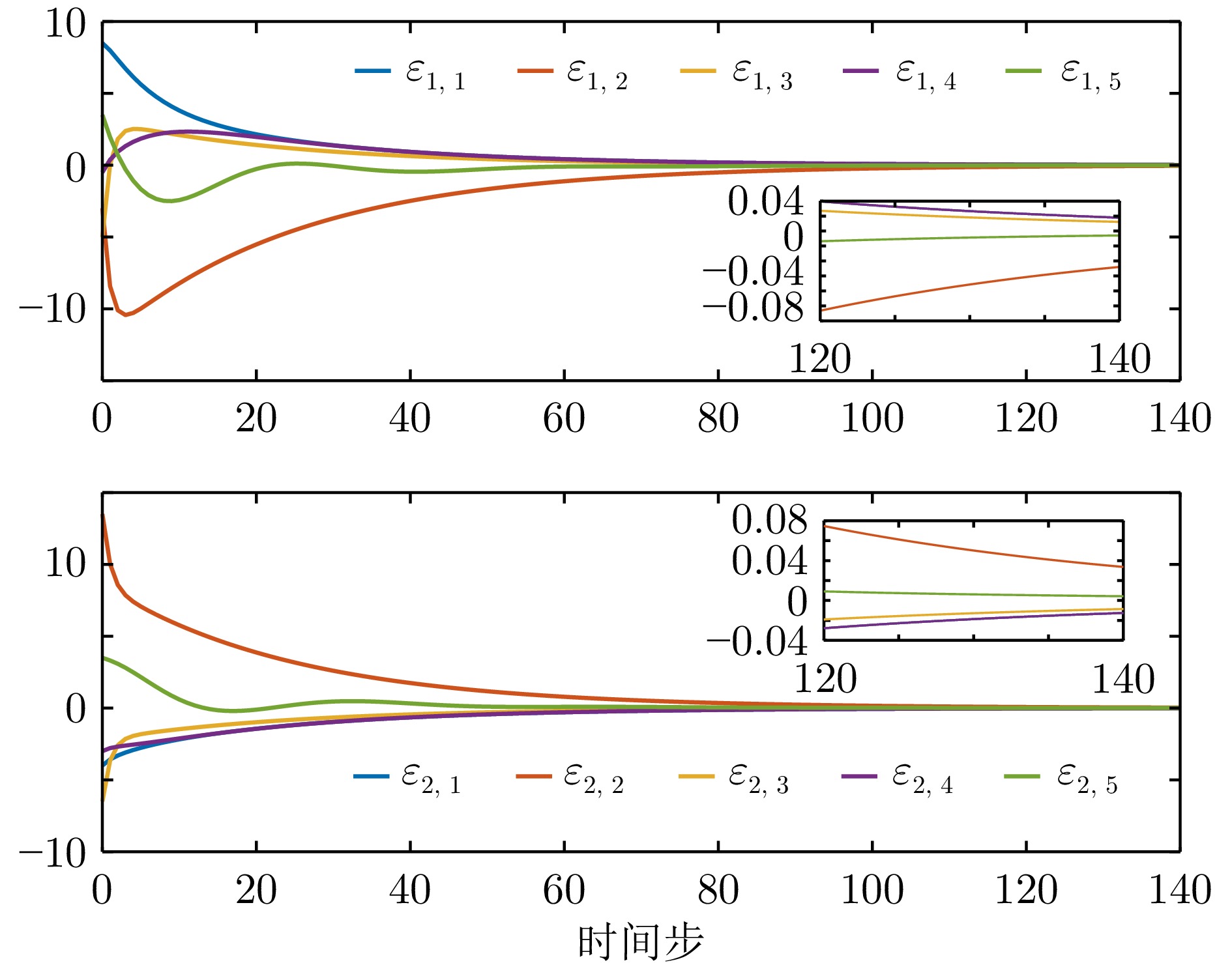
例2−调节时间 有限时域方法 无限时域方法 智能体1 108 131 智能体2 116 158 智能体3 120 183 智能体4 108 131 智能体5 84 93 -
[1] Huang Y, Fang W T, Chen Z Y, Li Y G, Yang C H. Flocking of multiagent systems with nonuniform and nonconvex input constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(7): 4329−4335 [2] Okine A A, Adam N, Naeem F, Kaddoum G. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for packet routing in tactical mobile sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2024, 21(2): 2155−2169 doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2024.3352014 [3] Mu C X, Liu Z Y, Yan J, Jia H J, Zhang X Y. Graph multi-agent reinforcement learning for inverter-based active voltage control. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2024, 15(2): 1399−1409 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2023.3298807 [4] Zhao Y W, Niu B, Zong G D, Zhao X D, Alharbi K H. Neural network-based adaptive optimal containment control for non-affine nonlinear multi-agent systems within an identifier-actor-critic framework. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2023, 360(12): 8118−8143 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2023.06.014 [5] Fan S J, Wang T, Qin C H, Qiu J B, Li M. Optimized backstepping attitude containment control for multiple spacecrafts. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2024, 32(9): 5248−5258 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2024.3418577 [6] An L W, Yang G H, Deng C, Wen C Y. Event-triggered reference governors for collisions-free leader-following coordination under unreliable communication topologies. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(4): 2116−2130 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3291654 [7] Wang W, Chen X. Model-free optimal containment control of multi-agent systems based on actor-critic framework. Neurocomputing, 2018, 314: 242−250 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.06.011 [8] Wang W, Chen X, Fu H, Wu M. Model-free distributed consensus control based on actor-critic framework for discrete-time nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(11): 4123−4134 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2883801 [9] Su H S, Miao S X. Consensus on directed matrix-weighted networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(4): 2529−2535 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3184630 [10] 杨洪勇, 郭雷, 张玉玲, 姚秀明. 离散时间分数阶多自主体系统的时延一致性. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(9): 2022−2028Yang Hong-Yong, Guo Lei, Zhang Yu-Ling, Yao Xiu-Ming. Delay consensus of fractional-order multi-agent systems with sampling delays. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9): 2022−2028 [11] 马煜文, 李贤伟, 李少远. 无控制器间通信的线性多智能体一致性的降阶协议. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(9): 1836−1844Ma Yu-Wen, Li Xian-Wei, Li Shao-Yuan. A reduced-order protocol for linear multi-agent consensus without inter-controller communication. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(9): 1836−1844 [12] He W P, Chen X, Zhang M L, Sun Y P, Sekiguchi A, She J H. Data-driven optimal consensus control for switching multiagent systems via joint communication graph. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(4): 5959−5968 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3342881 [13] Zhang H P, Yue D, Dou C X, Zhao W, Xie X P. Data-driven distributed optimal consensus control for unknown multiagent systems with input-delay. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(6): 2095−2105 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2819695 [14] Ji J W, Zhang Z C, Wang Y J, Zuo Z Q. Event-triggered consensus of discrete-time double-integrator multi-agent systems with asymmetric input saturation. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2024, 112(15): 13321−13334 doi: 10.1007/s11071-024-09761-y [15] Liu C, Liu L, Cao J D, Abdel-Aty M. Intermittent event-triggered optimal leader-following consensus for nonlinear multi-agent systems via actor-critic algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(8): 3992−4006 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3122458 [16] Wang J, Zhang Z T, Tian B L, Zong Q. Event-based robust optimal consensus control for nonlinear multiagent system with local adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(1): 1073−1086 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3180054 [17] Zattoni E. Structural invariant subspaces of singular Hamiltonian systems and nonrecursive solutions of finite-horizon optimal control problems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2008, 53(5): 1279−1284 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.921040 [18] Ferrari-Trecate G, Galbusera L, Marciandi M, Scattolini R. A model predictive control scheme for consensus in multi-agent systems with single-integrator dynamics and input constraints. In: Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2007. 1492−1497 [19] Aditya P, Werner H. A distributed linear-quadratic discrete-time game approach to multi-agent consensus. In: Proceedings of the 61st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2022. 6169−6174 [20] Han F, Wei G L, Ding D D, Song Y. Finite-horizon H∞-consensus control for multi-agent systems with random parameters: The local condition case. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2017, 354(14): 6078−6097 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.07.010 [21] Li J J, Wei G L, Ding D R. Finite-horizon H∞ consensus control for multi-agent systems under energy constraint. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(6): 3762−3780 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.01.016 [22] Chen W, Ding D R, Dong H L, Wei G L, Ge X H. Finite-horizon H∞ bipartite consensus control of cooperation-competition multiagent systems with round-robin protocols. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(7): 3699−3709 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977468 [23] Li X M, Yao D Y, Li P S, Meng W, Li H Y, Lu R Q. Secure finite-horizon consensus control of multiagent systems against cyber attacks. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(9): 9230−9239 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3052467 [24] Powell W B. Approximate Dynamic Programming: Solving the Curses of Dimensionality. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2007. [25] Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2018. [26] 庞文砚, 范家璐, 姜艺, Lewis Frank Leroy. 基于强化学习的部分线性离散时间系统的最优输出调节. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(9): 2242−2253Pang Wen-Yan, Fan Jia-Lu, Jiang Yi, Lewis Frank Leroy. Optimal output regulation of partially linear discrete-time systems using reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2242−2253 [27] Watkins C, Dayan P. Q-learning. Machine Learning, 1992, 8(3): 279−292 [28] Mu C X, Zhao Q, Gao Z K, Sun C Y. Q-learning solution for optimal consensus control of discrete-time multiagent systems using reinforcement learning. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(13): 6946−6967 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.06.007 [29] Liu J L, Dong Y H, Gu Z, Xie X P, Tian E G. Security consensus control for multi-agent systems under DoS attacks via reinforcement learning method. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2024, 361(1): 164−176 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2023.11.032 [30] Feng T, Zhang J L, Tong Y, Zhang H G. Q-learning algorithm in solving consensusability problem of discrete-time multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2021, 128: Article No. 109576 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109576 [31] Long M K, Su H S, Zeng Z G. Output-feedback global consensus of discrete-time multiagent systems subject to input saturation via Q-learning method. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(3): 1661−1670 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2987385 [32] Zhang H P, Park J H, Yue D, Xie X P. Finite-horizon optimal consensus control for unknown multiagent state-delay systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(2): 402−413 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2856510 [33] Liu C, Liu L. Finite-horizon robust event-triggered control for nonlinear multi-agent systems with state delay. Neural Processing Letters, 2023, 55(4): 5167−5191 doi: 10.1007/s11063-022-11085-0 [34] Guzey H M, Xu H, Sarangapani J. Neural network-based finite horizon optimal adaptive consensus control of mobile robot formations. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 2016, 37(5): 1014−1034 doi: 10.1002/oca.2222 [35] Yu D, Ge S S, Li D Y, Wang P. Finite-horizon robust formation-containment control of multi-agent networks with unknown dynamics. Neurocomputing, 2021, 458: 403−415 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.01.063 [36] Shi J, Yue D, Xie X P. Optimal leader-follower consensus for constrained-input multiagent systems with completely unknown dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(2): 1182−1191 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3011184 [37] Qin J H, Li M, Shi Y, Ma Q C, Zheng W X. Optimal synchronization control of multiagent systems with input saturation via off-policy reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(1): 85−96 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2832025 [38] Long M K, Su H S, Wang X L, Jiang G P, Wang X F. An iterative Q-learning based global consensus of discrete-time saturated multi-agent systems. Chaos, 2019, 29(10): Article No. 103127 doi: 10.1063/1.5120106 [39] Long M K, Su H S, Zeng Z G. Model-free algorithms for containment control of saturated discrete-time multiagent systems via Q-learning method. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(2): 1308−1316 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3019504 [40] Wang B J, Xu L, Yi X L, Jia Y, Yang T. Semiglobal suboptimal output regulation for heterogeneous multi-agent systems with input saturation via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(3): 3242−3250 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3191673 [41] Wang L J, Xu J H, Liu Y, Chen C L. Dynamic event-driven finite-horizon optimal consensus control for constrained multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(11): 16167−16180 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3292154 [42] Lin Z L. Low Gain Feedback. London: Springer, 1999. [43] Calafiore G C, Possieri C. Output feedback Q-learning for linear-quadratic discrete-time finite-horizon control problems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(7): 3274−3281 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3010304 [44] Wang W, Xie X P, Feng C Y. Model-free finite-horizon optimal tracking control of discrete-time linear systems. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2022, 433: Article No. 127400 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2022.127400 [45] Wu H, Su H S. Discrete-time positive edge-consensus for undirected and directed nodal networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2018, 65(2): 221−225 [46] Lewis F L, Vrabie D L, Syrmos V L. Optimal Control. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. [47] Jiang Y, Kiumarsi B, Fan J L, Chai T Y, Li J N, Lewis F L. Optimal output regulation of linear discrete-time systems with unknown dynamics using reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(7): 3147−3156 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2890046 [48] 姜艺, 范家璐, 贾瑶, 柴天佑. 数据驱动的浮选过程运行反馈解耦控制方法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(4): 759−770Jiang Yi, Fan Jia-Lu, Jia Yao, Chai Tian-You. Data-driven flotation process operational feedback decoupling control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(4): 759−770 -




 下载:
下载: