Online Measurement of Molten Iron Temperature Field at Blast Furnace Taphole Based on Infrared and Visible Vision
-
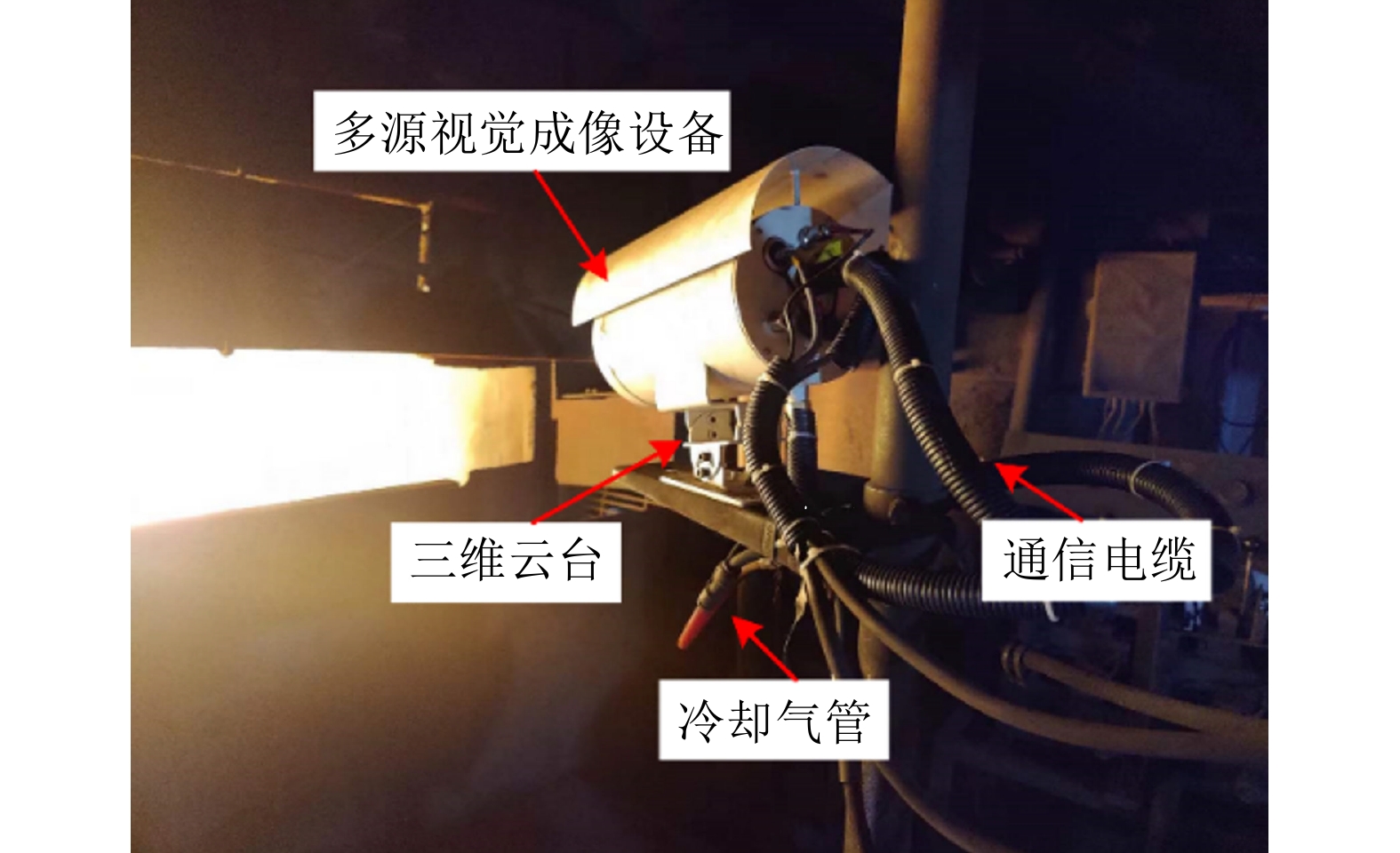
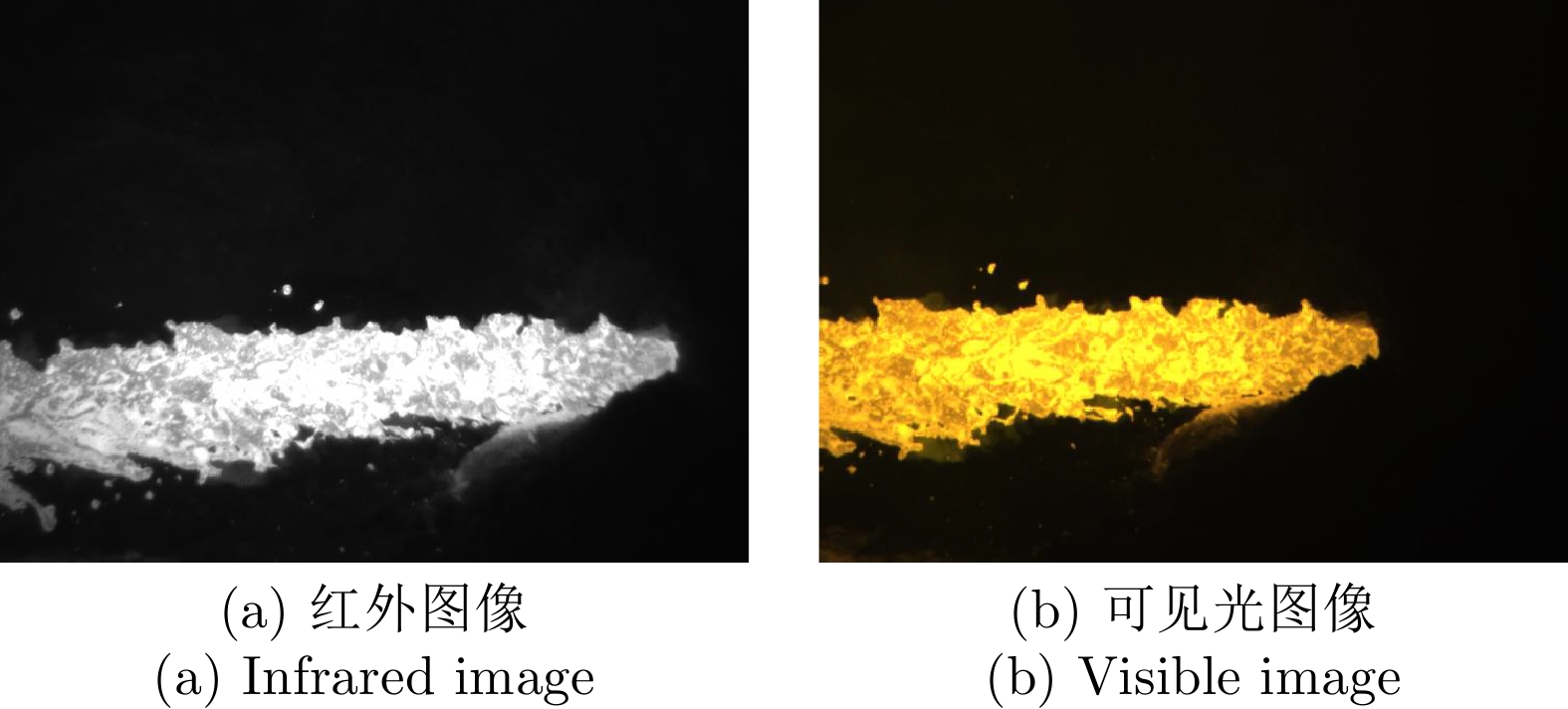
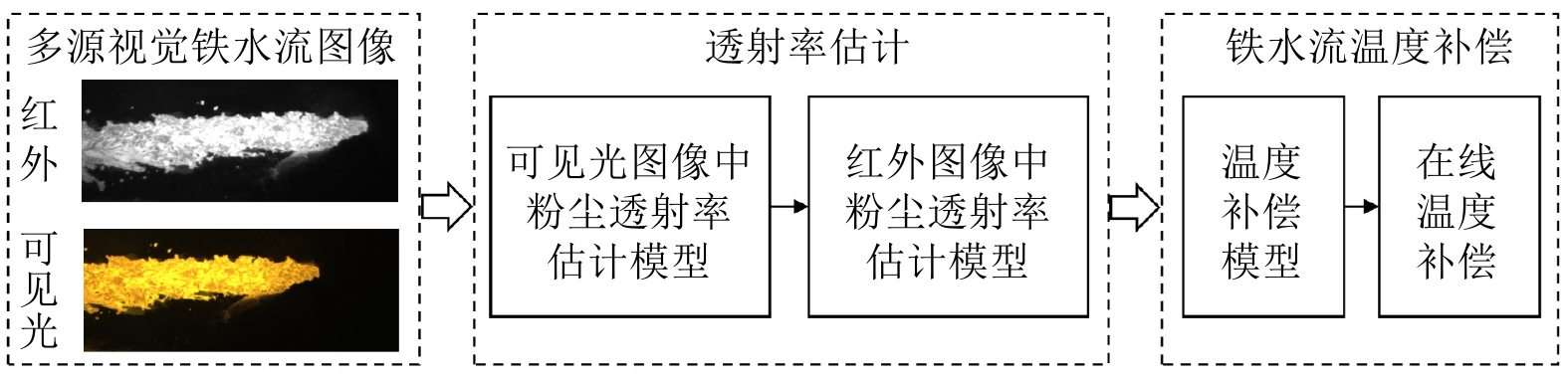
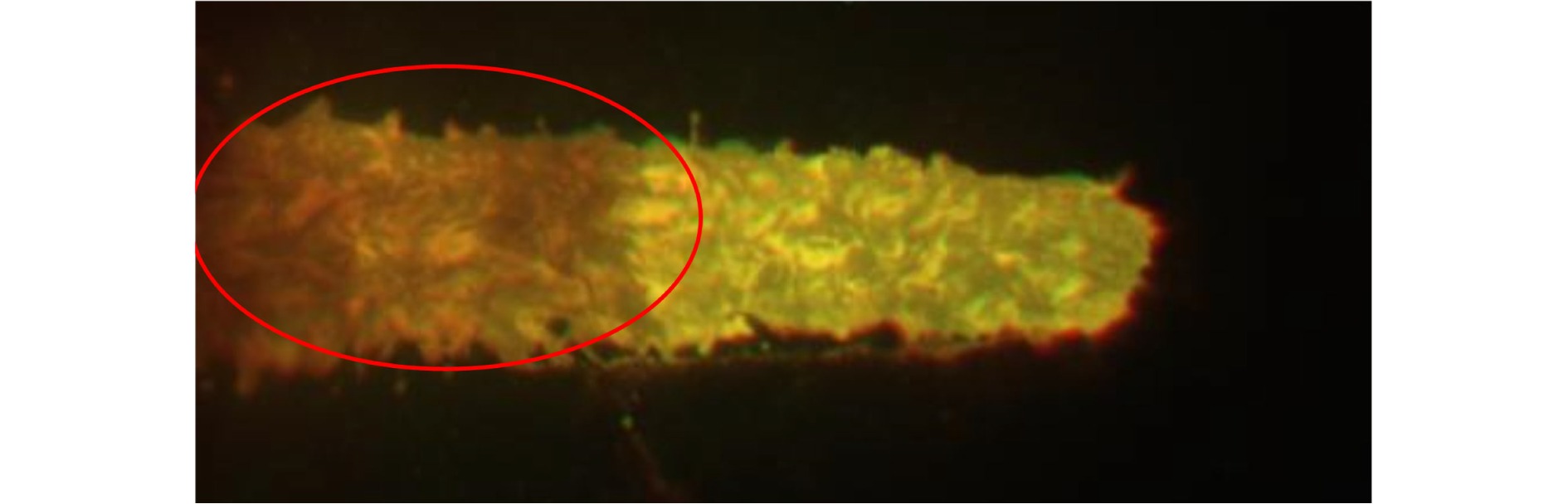
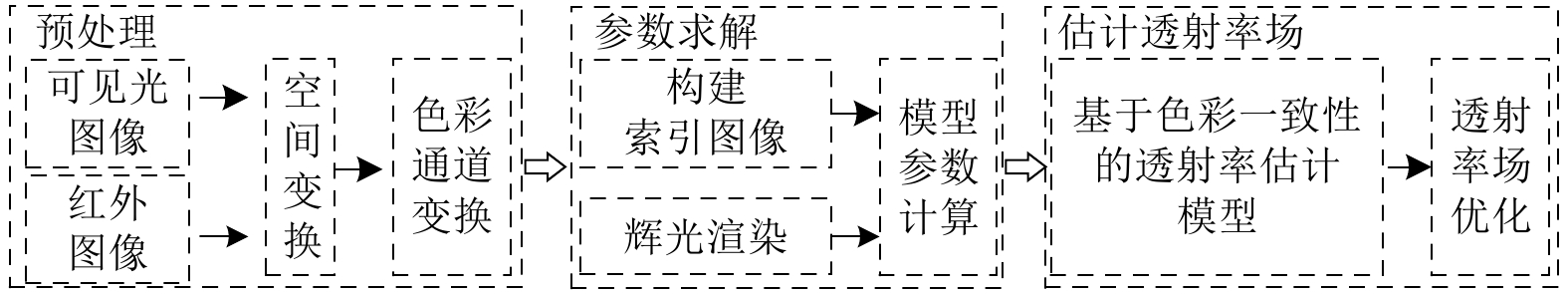
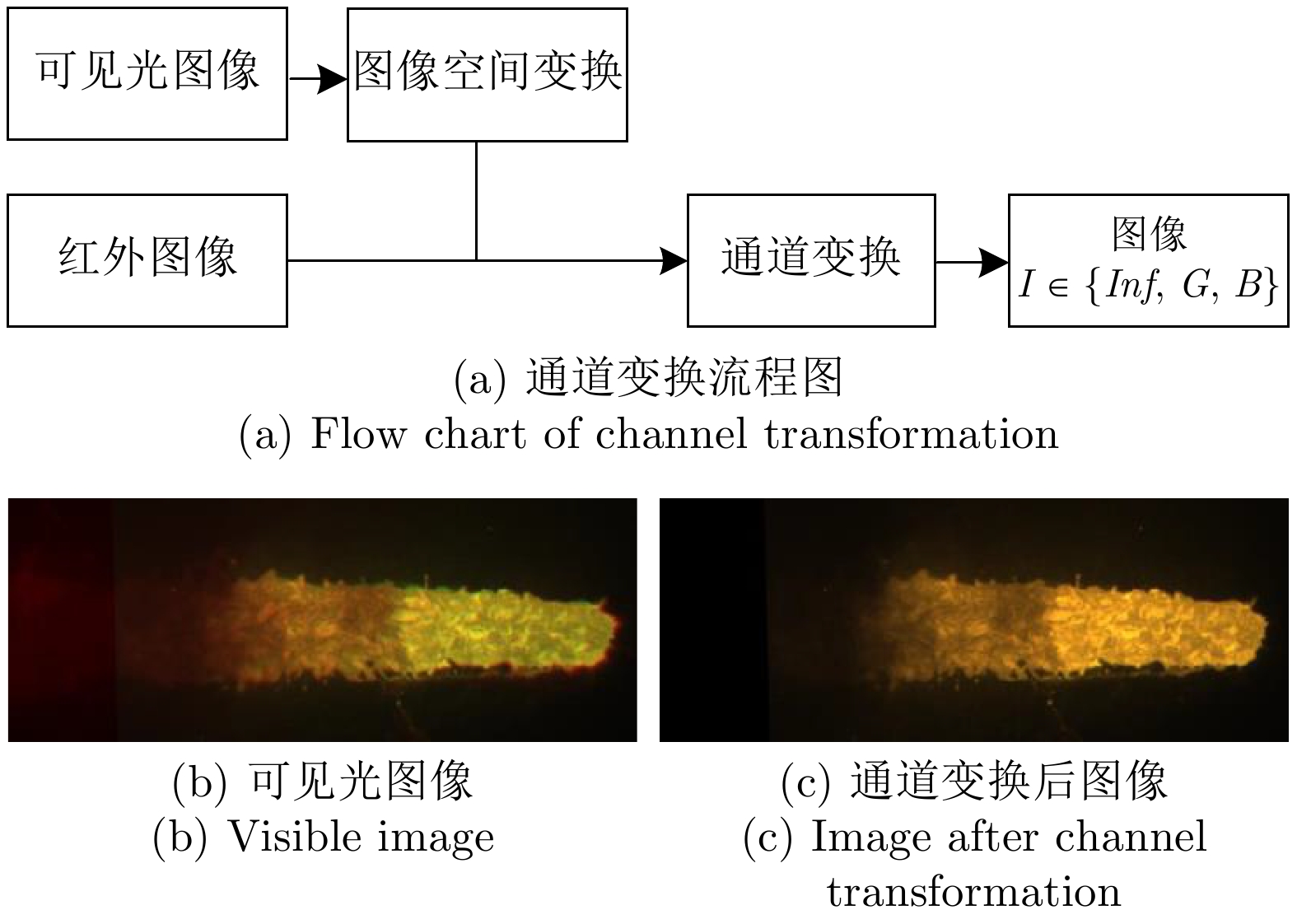
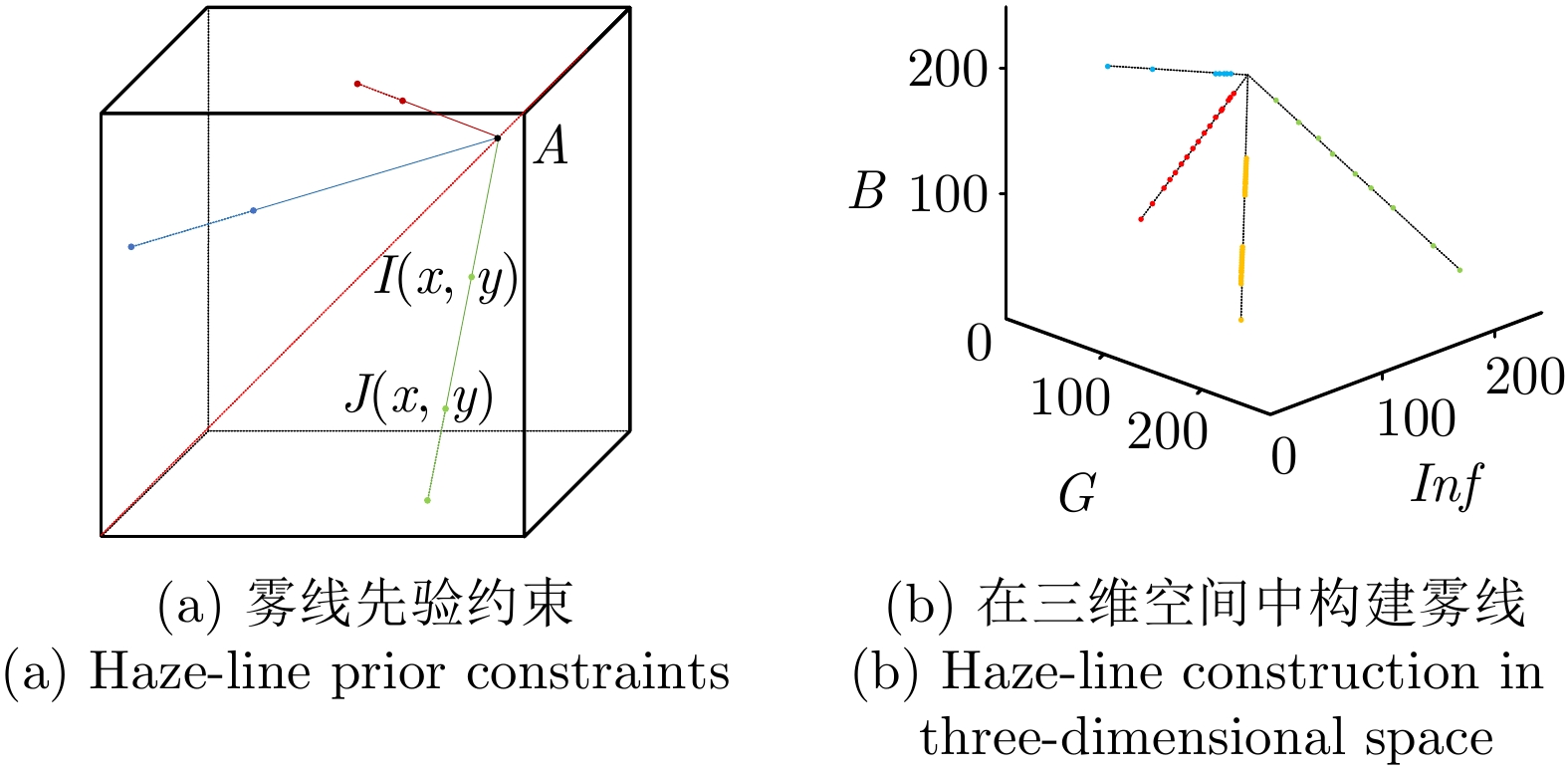
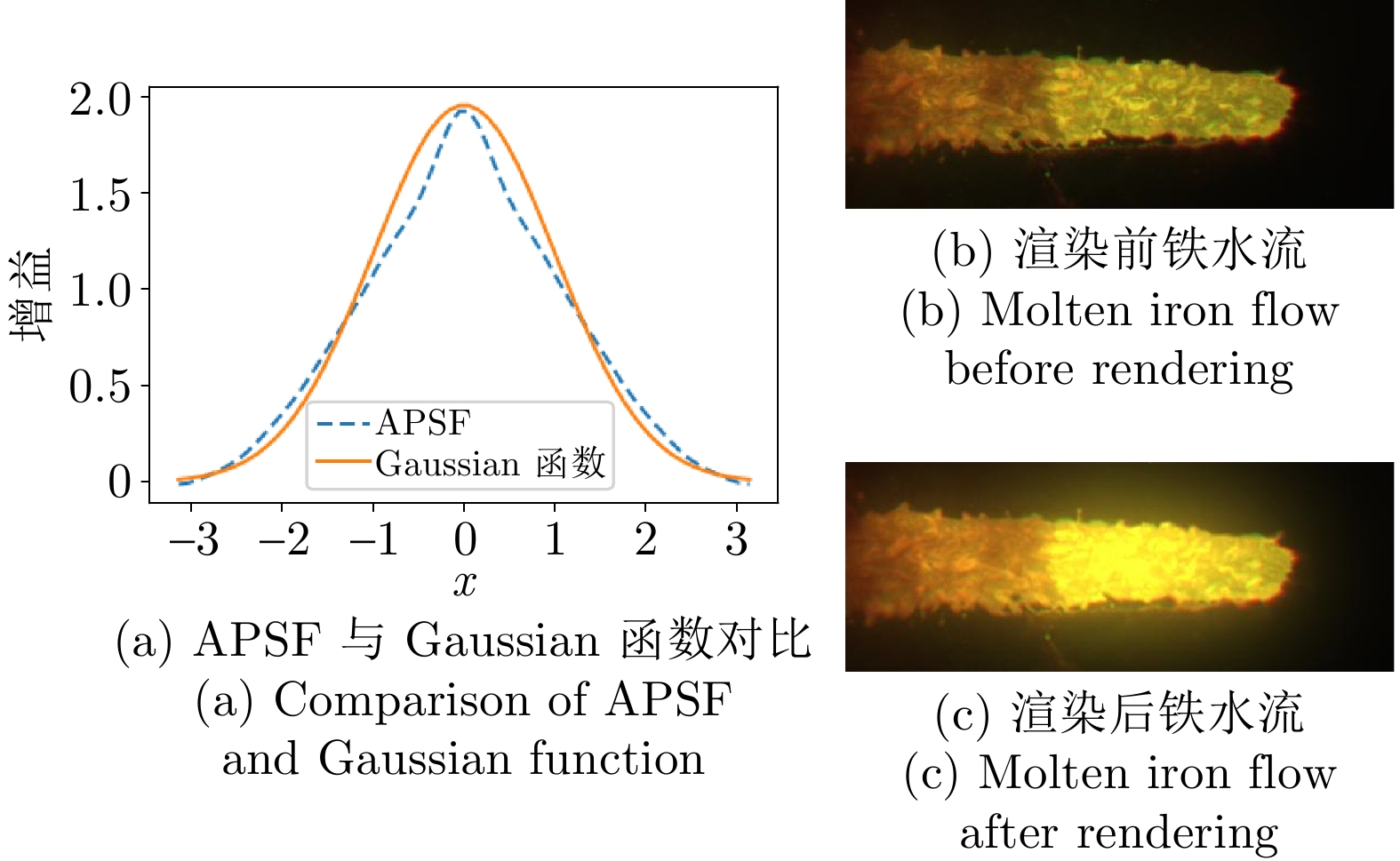
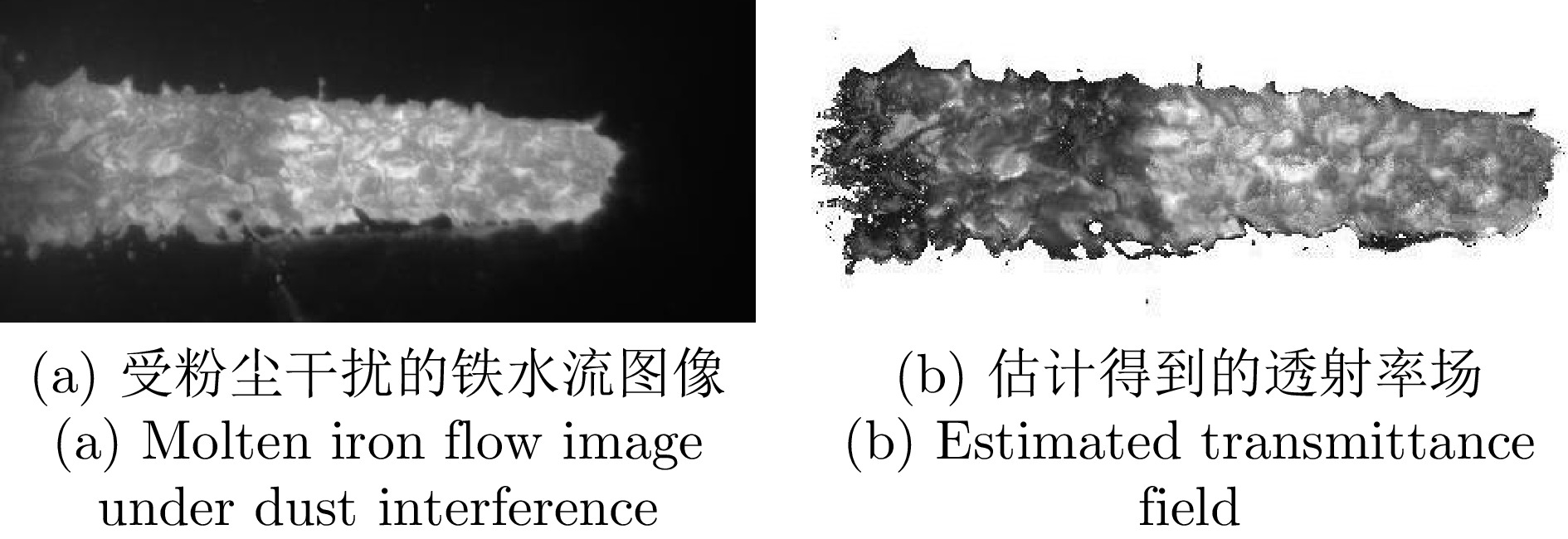
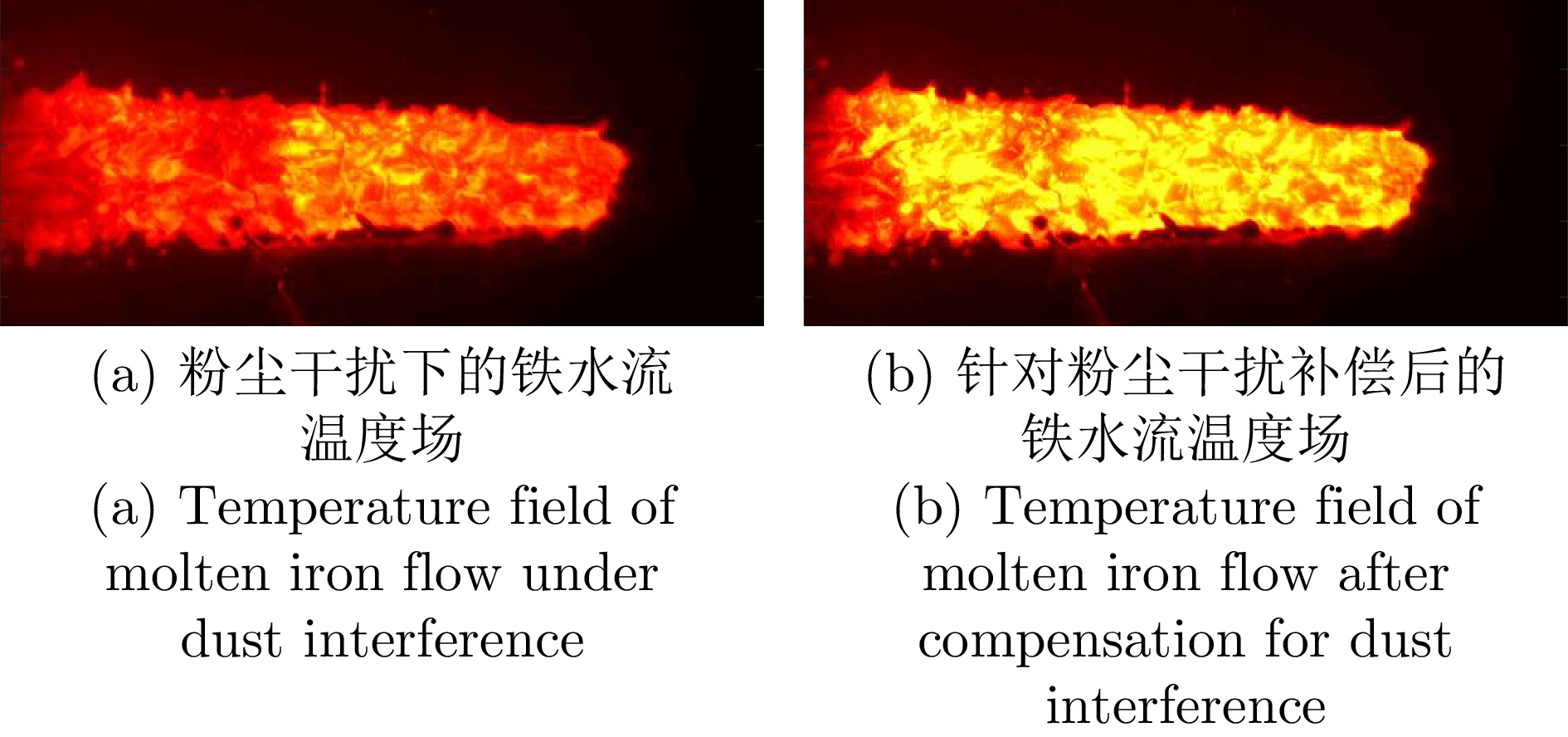
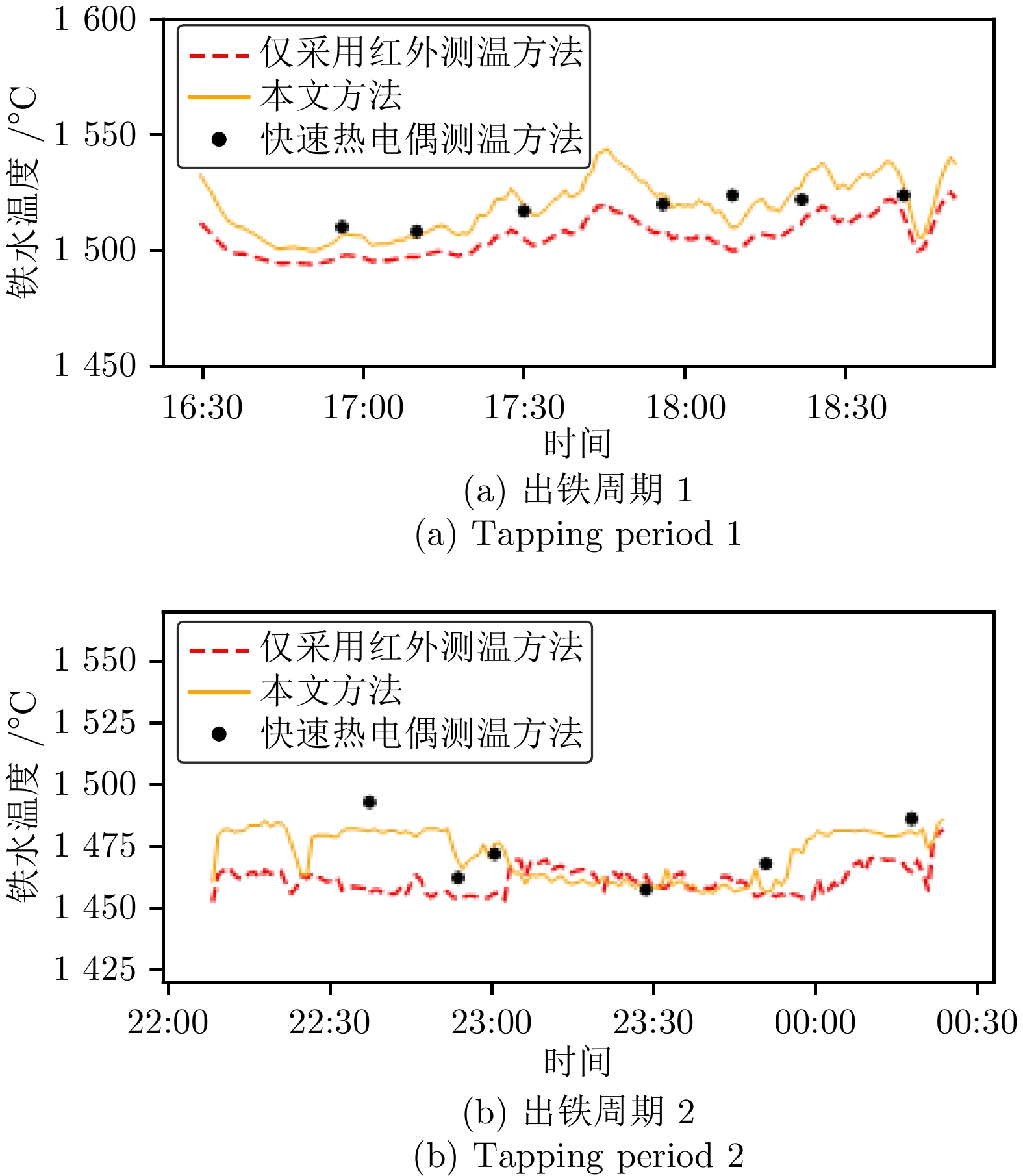
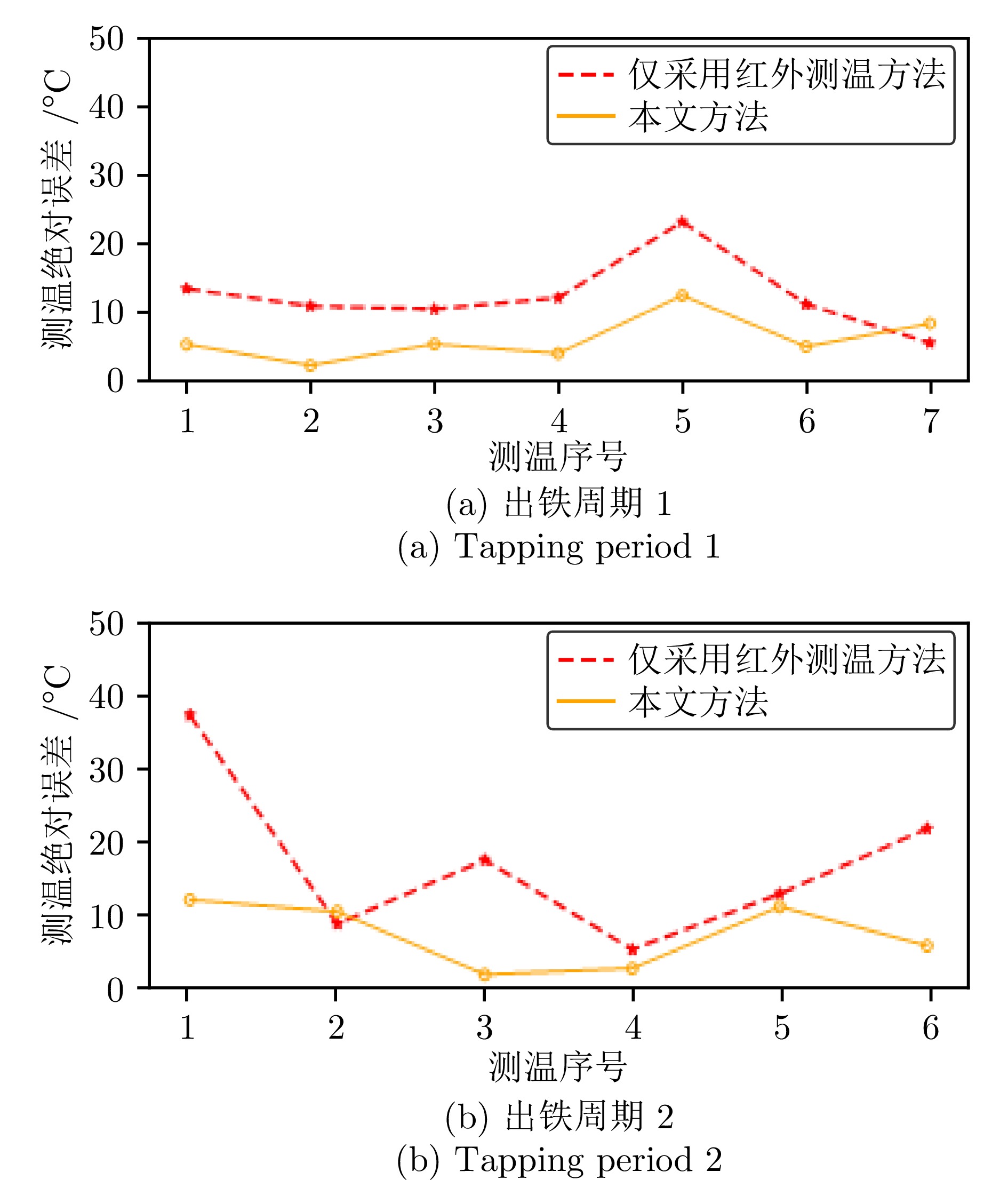
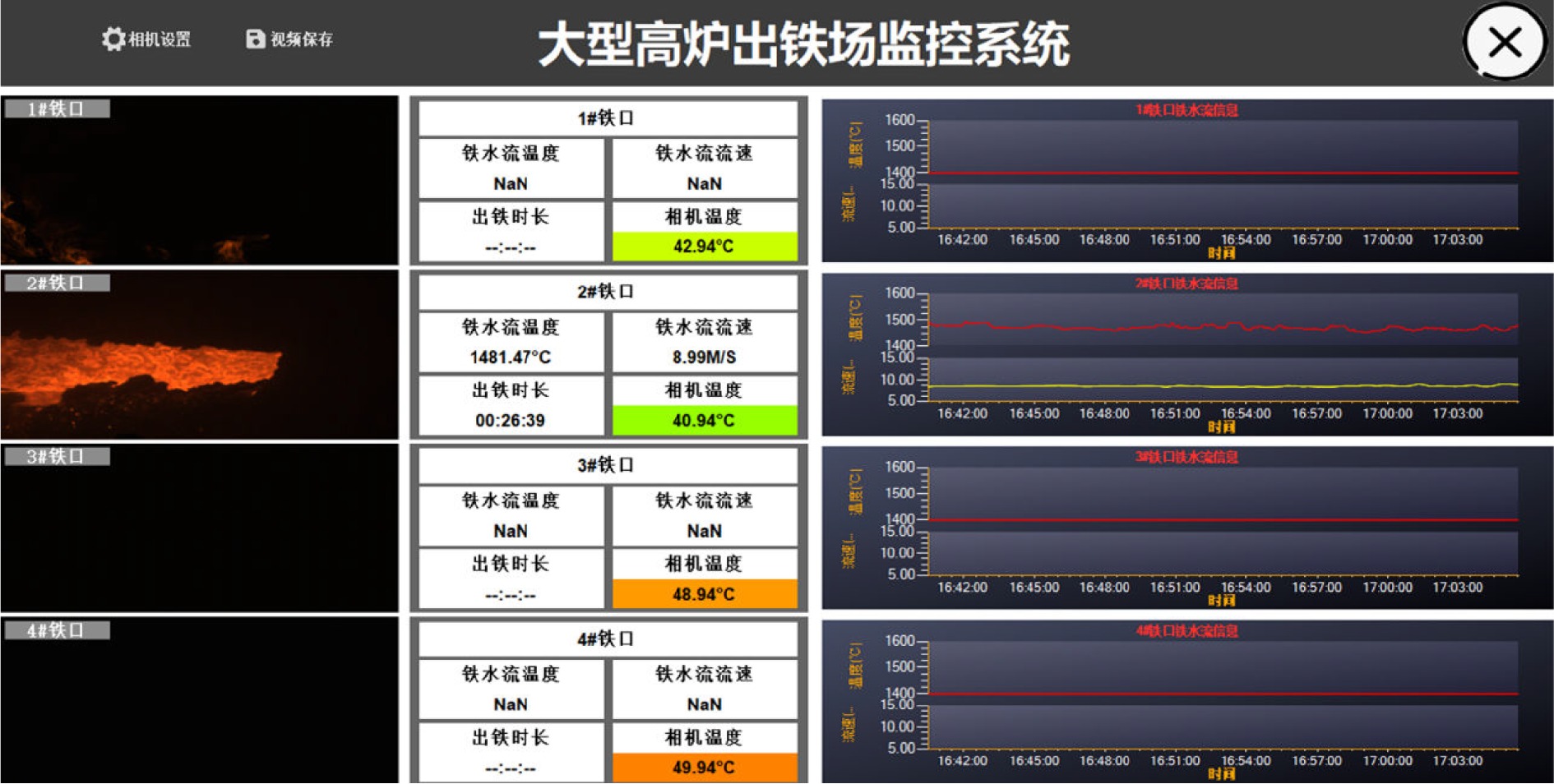
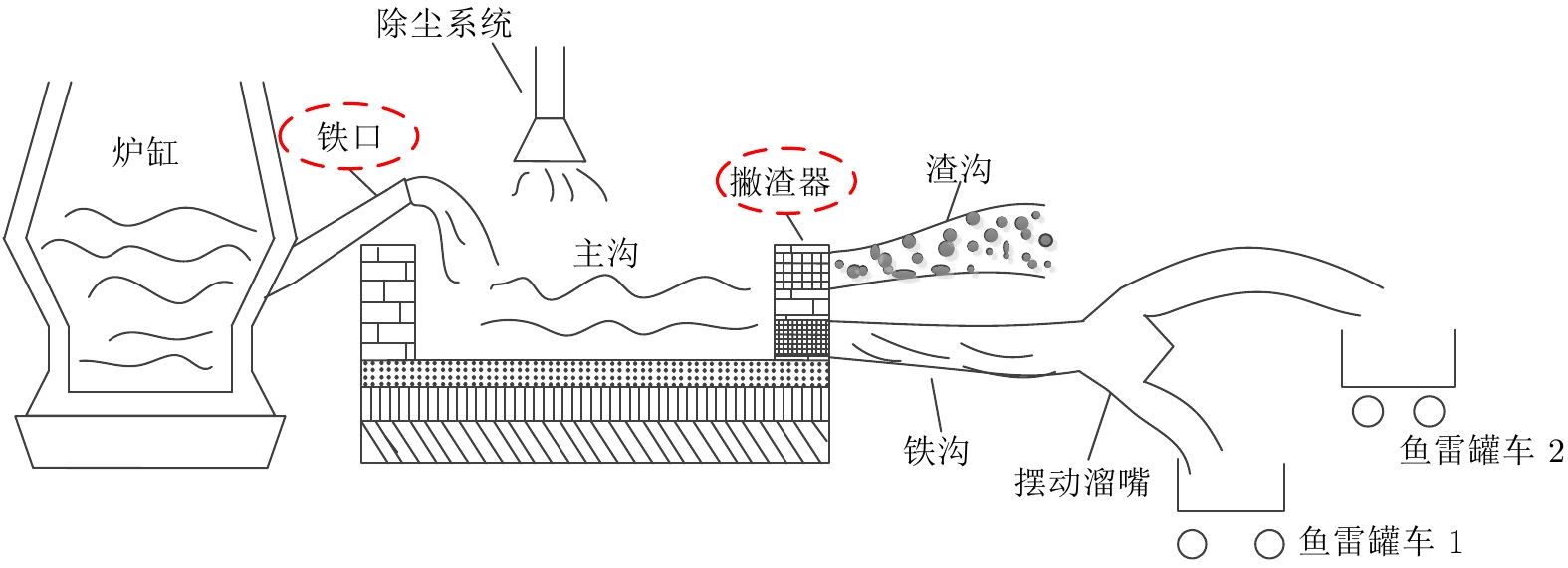
摘要: 高炉铁口铁水温度场 (Molten iron temperature field, MITF) 是表征铁水质量、判断炉温状况的重要信息. 然而高炉出铁场动态粉尘的干扰使得铁水温度场的在线准确获取充满挑战. 为此, 首次提出基于红外与可见光视觉的高炉铁口铁水温度场检测方法, 利用可见光图像为红外视觉测温提供先验粉尘干扰情况. 首先, 设计红外与可见光视觉协同的测温系统, 同步获取高炉铁口铁水流的红外图像和可见光图像, 铁水流红外图像表征铁水原始温度场信息, 可见光图像为量化粉尘透射率提供数据基础. 其次, 构建基于色彩一致性的可见光图像中粉尘透射率估计模型和基于雾线先验的红外图像中粉尘透射率估计模型, 得到红外波段下粉尘透射率. 最后, 结合红外辐射测温原理, 构建基于粉尘透射率的红外测温近似补偿模型, 实现铁水温度场的针对性补偿, 获取误差较小的铁水温度. 工业实验表明, 相比于仅利用红外视觉测量铁水温度场, 所提方法能够显著降低粉尘造成的测温误差, 为高炉调控提供连续可靠的铁水温度数据.Abstract: The molten iron temperature field (MITF) at blast furnace taphole is an important information for characterizing the molten iron quality and judging the furnace temperature condition. However, the interference of dynamic dust in the blast furnace casting field during the tapping process makes it challenging to obtain the MITF accurately online. To this end, this paper presents for the first time a measurement method for MITF at blast furnace taphole based on infrared and visible vision, which uses visible image to provide prior dust interference for infrared visual temperature measurement. Firstly, the infrared and visible vision coordination temperature measurement system is designed to obtain the infrared image and visible image of the molten iron flow at blast furnace taphole simultaneously. The infrared image of the molten iron flow represents the original MITF information, and the visible image provides the data basis for quantifying dust transmittance. Secondly, an estimation model of dust transmittance in visible images based on color consistency and an estimation model of dust transmittance in infrared images based on haze-line prior are proposed to obtain dust transmittance in infrared band. Finally, combined with the principle of infrared radiation temperature measurement, an approximate infrared temperature compensation model based on dust transmittance is constructed to realize the targeted compensation of MITF and obtain the accurate molten iron temperature with minimal error. Industrial experiments show that compared with only using infrared vision to measure the MITF, the proposed method can significantly reduce the temperature measurement error caused by dust and provide continuous and reliable molten iron temperature data for blast furnace control.
-
表 1 不同方法去除粉尘对铁水流干扰后的图像性能指标
Table 1 Performance indexes of molten iron flow images after removing dust interference using different methods
方法 FADE ENVR NIQE VIF STD DCID 0.6121 1.0568 5.7528 0.8151 42.6041 NHRG 0.4867 5.9504 5.7233 1.1632 59.4452 NLID 0.4343 2.6741 5.5326 1.1110 50.6340 SLID 0.4839 3.3695 5.0503 1.0318 52.0414 本文方法 0.3348 2.4984 5.9588 1.0712 25.9634 表 2 不同测温方法的性能指标对比 (℃)
Table 2 Comparison of performance indices of different temperature measurement methods (℃)
测温方法 $ {E}_{\text{max }} $ $ {E}_{\text{min }} $ $ {E}_{\text{avg}} $ $ {E}_{\text{std}} $ 红外测温 37.4963 4.9702 14.5571 8.4503 本文方法 12.5136 1.4967 6.5563 3.7164 -
[1] Xu C, Jiang Z H, Pan D, Yu H Y, Huang J C, Zhou K, et al. Multiscale neighborhood adaptive clustering image segmentation for molten iron flow slag-iron recognition. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(8): 4642−4654 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3388475 [2] Liu Y, Zhou P, Sun X, Chai T Y. Optimal tracking control of blast furnace molten iron quality based on Krotov's method and nonlinear subspace identification. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 71(8): 9610−9619 [3] 温亮, 周平. 基于多参数灵敏度分析与遗传优化的铁水质量无模型自适应控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(11): 2600−2613Wen Liang, Zhou Ping. Model free adaptive control of molten iron quality based on multi-parameter sensitivity analysis and GA optimization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2600−2613 [4] Zhou P, Zhang S, Chai T Y. Adaptive constraint penalty-based multiobjective operation optimization of an industrial dynamic system with complex multiconstraint. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(8): 4724−4737 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2023.3341982 [5] 潘冬, 蒋朝辉, 许川, 桂卫华. 高炉铁水温度检测方法的研究进展. 仪器仪表学报, 2023, 44(11): 280−296Pan Dong, Jiang Zhao-Hui, Xu Chuan, Gui Wei-Hua. Research progress of measurement methods of molten iron temperature in blast furnace. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2023, 44(11): 280−296 [6] 蒋朝辉, 许川, 蒋珂, 桂卫华. 基于最优工况迁移的高炉铁水硅含量预测方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 194−206Jiang Zhao-Hui, Xu Chuan, Jiang Ke, Gui Wei-Hua. Prediction method of hot metal silicon content in blast furnace based on optimal smelting condition migration. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 194−206 [7] Ma J C, Meng L H, Liu Z D, Z X. Rapid identification of liquid steel temperature in tundish based on blackbody cavity sensor. ISIJ International, 2024, 64(11): 1691−1698 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2023-499 [8] Shao H D, Li W, Cai B, Wan J F, Xiao Y M, Yan S. Dual-threshold attention-guided GAN and limited infrared thermal images for rotating machinery fault diagnosis under speed fluctuation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2009, 19(9): 9933−9942 [9] Vollmer M, Möllmann K P. Infrared Thermal Imaging: Fundamentals, Research and Applications. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2017. [10] Osornio-Rios R, Antonino-Daviu J, Romero-Troncoso R. Recent industrial applications of infrared thermography: A review. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(2): 615−625 doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2884738 [11] Usamentiaga R, Molleda J, Garcia D F. Temperature measurement of molten pig iron with slag characterization and detection using infrared computer vision. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2011, 61(5): 1149−1159 [12] Pan D, Jiang Z H, Xu C, Gui W H. Polymorphic temperature measurement method of molten iron after skimmer in ironmaking process. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1−11 [13] Pan D, Jiang Z H, Chen Z P, Gui W H, Xie Y F, Yang C H. Temperature measurement and compensation method of blast furnace molten iron based on infrared computer vision. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2018, 68(10): 3576−3588 [14] Pan D, Jiang Z H, Li Y T, Yu H Y, Gui W H. A novel compensation method for infrared temperature measurement using infrared vision and visible light vision under water mist interference. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 68(10): 3576−3588 [15] Zhang Y, Xie Z, Hu Z, Zhao S, Bai H. Online surface temperature measurement of billets in secondary cooling zone end-piece based on data fusion. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2014, 72: 1−9 [16] Tripathy H P, Bej D, Pattanaik P, Mishra D K, Kamilla S K, Tripathy R K. Measurement of zone temperature profile of a resistive heating furnace through RVM model. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(11): 4429−4435 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2826722 [17] Pan D, Jiang Z, Li Y, Yu H, Gui W H. Intelligent compensation method of infrared temperature measurement for multiple interference factors. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(19): 18550−18559 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3199264 [18] Pan D, Jiang Z H, Chen Z P, Jiang K, Gui W H. Compensation method for molten iron temperature measurement based on heterogeneous features of infrared thermal images. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(11): 7056−7066 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2972332 [19] He K, Sun J, Tang X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 33(12): 2341−2353 [20] Liu J, Liu R W, Sun J, Zeng T. Rank-one prior: Real-time scene recovery. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(7): 8845−8860 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3226276 [21] González-Sabbagh S, Robles-Kelly A. A survey on underwater computer vision. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(13): 1−39 [22] Hu H M, Guo Q, Zheng J, Wang H, Li B. Single image defogging based on illumination decomposition for visual maritime surveillance. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(6): 2882−2897 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2891901 [23] Emberton S, Chittka L, Cavallaro A. Underwater image and video dehazing with pure haze region segmentation. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2018, 168: 145−156 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2017.08.003 [24] Ding X, Wang Y, Zhang J, Fu X. Underwater image dehaze using scene depth estimation with adaptive color correction. In: Proceedings of the OCEANS 2017. Aberdeen, UK: IEEE, 2017. 1−5 [25] Cheng Y, Jia Z, Lai H, Yang J, Kasabov N K. Blue channel and fusion for sandstorm image enhancement. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 66931−66940 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2985869 [26] Berman D, Avidan S. Non-local image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1674−1682 [27] Jiang Z H, Chang Z R, Xu C, Pan D, Yu H Y, Gui W H. Detection method of molten iron flow velocity at blast furnace taphole combining visual perception and jet mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 1972, 73: 1−11 [28] Berman D, Treibitz T, Avidan S. Single image dehazing using haze-lines. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(3): 720−734 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2882478 [29] Narasimhan S G, Nayar S K. Shedding light on the weather. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Madison, USA: IEEE, 2003. I−I [30] 杨立, 杨桢. 红外热成像测温原理与技术. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. 15−28Yang Li, Yang Zhen. Principle and Technology of Infrared Thermal Imaging Temperature Measurement. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. 15−28 [31] Usamentiaga R, Venegas P, Guerediaga J, Vega L, Molleda J, Bulnes F G. Infrared thermography for temperature measurement and non-destructive testing. Sensors, 2014, 14(7): 12305−12348 doi: 10.3390/s140712305 [32] Zhang Z M, Tsai B K, Machin G. Radiometric Temperature Measurements: I. Fundamentals. Massachusetts: Academic press, 2009. [33] Pan D, Jiang Z, Gui W, Jiang K, Maldague X. Compensation method for the influence of dust in optical path on infrared temperature measurement. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 70: 1−11 [34] Ling P, Chen H, Tan X, Jin Y, Chen E. Single image dehazing using saturation line prior. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 3238−3253 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3279980 [35] Li Y, Tan R T, Brown M S. Nighttime haze removal with glow and multiple light colors. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 226−234 [36] Choi L K, You J, Bovik A C. Referenceless prediction of perceptual fog density and perceptual image defogging. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3888−3901 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2456502 [37] Hautiere N, Tarel J P, Aubert D. Blind contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges. Image Analysis and Stereology, 2008, 27(2): 87−95 [38] Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik A C. Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 209−212 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726 [39] Ding K, Ma K, Wang S Q, Simoncelli E P. Image quality assessment: Unifying structure and texture similarity. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 44(5): 2567−2581 -




 下载:
下载: