Optimal Wireless Control Over State-dependent Fading Channels for Heterogeneous Industrial Internet of Things Systems
-
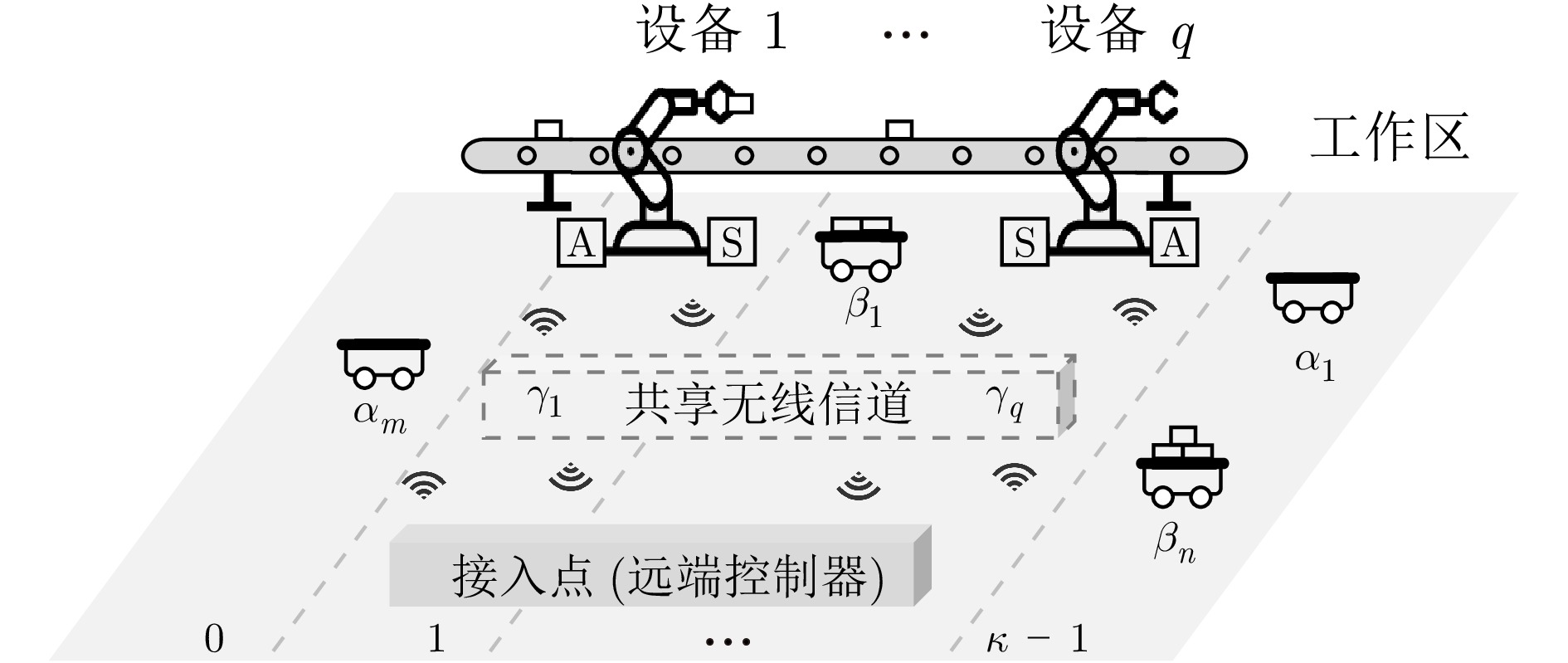
摘要: 随着工业4.0的发展, 移动智能体系统 (Mobile agent system, MAS) 与多回路无线控制系统 (Wireless control system, WCS) 被部署到工厂中, 构成异构工业物联网(Industrial internet of things, IIoT)系统, 协作执行智能制造任务. 在协作过程中, MAS与WCS紧密耦合, 导致状态相关衰落, 两者性能相互制约. 为解决这一问题, 研究异构工业物联网系统的最优控制问题, 满足WCS控制性能约束与MAS安全生产约束的同时, 最小化系统平均通信成本. 首先, 利用有限域系统描述MAS在不同阴影衰落程度工作区间的转移, 刻画MAS与WCS耦合下的状态相关衰落信道模型. 基于此, 利用矩阵半张量积理论, 通过构建受限跟随者状态转移图(Follower state transition graph, FSTG), 建立最优控制问题可行性图判据, 给出关于受限集合镇定的充分必要条件. 其次, 基于加权跟随者状态转移图的最小平均环理论, 建立领航−跟随MAS最优控制序列的构造算法, 并证明其最优性. 最后, 通过仿真验证算法的有效性.Abstract: With the development of Industry 4.0, the mobile agent system (MAS) and wireless control system (WCS) are deployed in factories to collaboratively perform smart manufacturing tasks, forming a heterogeneous industrial internet of things (IIoT) system. In this process, the WCS is coupled with the MAS, leading to state-dependent fading and restricting each other in performance. To address this issue, this paper focuses on the optimal control of the heterogeneous IIoT system to ensure the control performance constraints of WCS and the safety production constraints of MAS, while minimizing the average communication cost of the system. Firstly, the transition of MAS between cells with different levels of shadow effects is modeled by the finite-field system, and the state-dependent fading channel is characterized under MAS and WCS coupling. Based on this, using the theory of semi-tensor product of matrices, a graphical criterion is presented for the feasibility of the optimal control problem by constructing the constrained follower state transition graph (FSTG), and criteria in terms of constrained set stabilization are established. Secondly, by minimum-mean cycles for weighted follower state transition graph, an algorithm is proposed to construct optimal control sequences for the leader-follower MAS, and the optimality is proved. Finally, an illustrative simulation example is provided to demonstrate effectiveness of the algorithm.
-
表 1 符号说明
Table 1 Notations
符号 含义 $ {\bf{N}} $ 自然数集合 $ \mathcal{D}_n $ 逻辑域$ \{0,\;1,\;\cdots,\;n-1\} $ $ \mathcal{D}_n^m $ 笛卡尔乘积$ \underbrace{\mathcal{D}_n\times\cdots\times\mathcal{D}_n}_m $ $ I_n $ $ n $维单位阵 $ \delta_n^i $ 单位阵$ I_n $的第$ i $列 $ [A]_{:,\;j} $ 矩阵$ A $的第$ j $列 $ [A]_{i,\;j} $ 矩阵$ A $的$ (i,\;j) $元 $ \delta_m[i_1\;i_2\;\cdots\;i_n] $ 逻辑矩阵$ A $, $ [A]_{:,\;j}=\delta_m^{i_j} $ $ {\mathcal{L}}^{m\times n} $ $ m\times n $逻辑矩阵集合 $ {{\bf{R}}}^{m\times n} $ $ m\times n $实矩阵集合 $ Col(A) $ 矩阵$ A\in{{\bf{R}}}^{m\times n} $所有列构成的集合 $ \ltimes $ 矩阵的半张量积 $ \otimes $ 克罗内克积 $ \mathcal{A}\setminus\mathcal{B} $ 集合$ \{x\in\mathcal{A}: x\notin\mathcal{B}\} $ $ |A| $ 集合$ A $的基数 表 2 状态相关衰落信道参数
Table 2 State-dependent fading channel parameters
$ (i,\;b,\;a) $ $ (1,\;1,\;0) $ $ (1,\;1,\;1) $ $ (1,\;2,\;2) $ $ (1,\;2,\;3) $ $ (2,\;1,\;0) $ $ (2,\;1,\;1) $ $ (2,\;2,\;2) $ $ (2,\;2,\;3) $ $ \mathcal{Z}_1 $ 0.60 0.20 0.60 0.10 0.63 0.20 0.63 0.50 0.44 0.20 0.44 0.10 0.46 0.00 0.46 0.70 $ \mathcal{Z}_2 $ 0.17 0.30 0.17 0.10 0.18 0.20 0.18 0.40 0.33 0.20 0.33 0.10 0.35 0.50 0.35 0.20 $ \mathcal{Z}_3 $ 0.58 0.10 0.58 0.10 0.62 0.30 0.62 0.50 0.42 0.10 0.42 0.10 0.45 0.10 0.45 0.70 $ \mathcal{Z}_4 $ 0.50 0.00 0.50 0.20 0.53 0.10 0.53 0.70 0.60 0.20 0.60 0.10 0.64 0.10 0.64 0.60 注: 粗体数字表示$\bar{\gamma}_i(a,\;z)$, 其他数字表示$\bar{\eta}_i(b,\;z)$; $\mathcal{Z}_i$, $i=1,\;\cdots,\;4$表示MAS状态集合. -
[1] 关新平, 陈彩莲, 杨博, 华长春, 吕玲, 朱善迎. 工业网络系统的感知−传输−控制一体化: 挑战和进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(1): 25−36Guan Xin-Ping, Chen Cai-Lian, Yang Bo, Hua Chang-Chun, Lv Ling, Zhu Shan-Ying. Towards the integration of sensing, transmission and control for industrial network systems: Challenges and recent developments. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 25−36 [2] Sisinni E, Saifullah A, Han S, Jennehag U, Gidlund M. Industrial internet of things: Challenges, opportunities, and directions. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(11): 4724−4734 doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2852491 [3] 于海斌, 曾鹏, 梁炜, 王忠锋, 刘阳, 许驰. 无线化工业控制系统: 架构、关键技术及应用. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 540−549Yu Hai-Bin, Zeng Peng, Liang Wei, Wang Zhong-Feng, Liu Yang, Xu Chi. Wireless industrial control system: Architecture, key technologies and applications. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 540−549 [4] 裘莹, 张敬宣, 柯杰, 方梦园, 徐伟强. 工业无线网络实时传输调度算法研究综述. 自动化学报, 2024, 50 (11): 2102−2127 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220939Qiu Ying, Zhang Jing-Xuan, Ke Jie, Fang Meng-Yuan, Xu Wei-Qiang. A survey of real-time transmission scheduling algorithms for industrial wireless network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50 (11): 2102−2127 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220939 [5] Baumann D, Mager F, Wetzker U, Thiele L, Zimmerling M, Trimpe S. Wireless control for smart manufacturing: Recent approaches and open challenges. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(4): 441−467 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.3032633 [6] Park P, Ergen S C, Fischione C, Lu C Y, Johansson K H. Wireless network design for control systems: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2018, 20(2): 978−1013 [7] Chen K C, Lin S C, Hsiao J H, Liu C H, Molisch A F, Fettweis G P. Wireless networked multirobot systems in smart factories. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(4): 468−494 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.3033753 [8] Agrawal P, Ahlén A, Olofsson T, Gidlund M. Long term channel characterization for energy efficient transmission in industrial environments. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2014, 62(8): 3004−3014 doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2014.2332876 [9] Ahlen A, Akerberg J, Eriksson M, Isaksson A J, Iwaki T, Johansson K H, et al. Toward wireless control in industrial process automation: A case study at a paper mill. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2019, 39(5): 36−57 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2019.2925226 [10] 杨小军, 邢科义. 无线多跳传感器网络下基于粒子滤波的信道容错的目标跟踪方法. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(4): 440−448 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.00440Yang Xiao-Jun, Xing Ke-Yi. Channel fault tolerant target tracking in multi-hop wireless sensor networks based on particle filtering. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(4): 440−448 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.00440 [11] Liu W C, Quevedo D E, Johansson K H, Vucetic B, Li Y H. Stability conditions for remote state estimation of multiple systems over multiple Markov fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(7): 4273−4280 [12] Hu B, Lemmon M D. Using channel state feedback to achieve resilience to deep fades in wireless networked control systems. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Conference on High Confidence Networked Systems. Philadelphia, USA: ACM, 2013. 41−48 [13] Yaron O, Sidi M. Performance and stability of communication networks via robust exponential bounds. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 1993, 1(3): 372−385 doi: 10.1109/90.234858 [14] Hu B, Lemmon M D. Distributed switching control to achieve almost sure safety for leader-follower vehicular networked systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(12): 3195−3209 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2418451 [15] Hu B. Event-based adaptive power control in vehicular networked systems with state-dependent bursty fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2020, 67 (3): 506−510 [16] Hu B, Wang Y B, Orlik P V, Koike-Akino T, Guo J L. Co-design of safe and efficient networked control systems in factory automation with state-dependent wireless fading channels. Automatica, 2019, 105: 334−346 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.04.009 [17] Hu B, Tamba T A. Optimal transmission power and controller design for networked control systems under state-dependent Markovian channels. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(10): 5669−5676 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3181758 [18] Wang S L, Li P Z, Zhu S Y, Chen C L. Opportunistic wireless control over state-dependent fading channels. In: Proceedings of the 61st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2022. 3896−3901 [19] Chen F, Cheng Z Q, Xiang L Y, Liu Z X, Yuan Z Z. Reaching a consensus via pinning control. Automatica, 2009, 45: 1215−1220 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2008.12.027 [20] 关永强, 纪志坚, 张霖, 王龙. 多智能体系统能控性研究进展. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(4): 421−431 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.40419Guan Yong-Qiang, Ji Zhi-Jian, Zhang Lin, Wang Long. Recent developments on controllability of multi-agent systems. Control Theory and Applications, 2015, 32(4): 421−431 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.40419 [21] 程代展, 齐洪胜. 矩阵的半张量积——理论与应用, 第二版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011.Cheng Dai-Zhan, Qi Hong-Sheng. Semi-tensor Product of Matrices: Theory and Application, 2nd Edition. Beijing: Science Press, 2011. [22] Cheng D Z, Qi H S, Zhao Y. An Introduction to Semi-tensor Product of Matrices and Its Applications. Singapore: World Scientific, 2012. [23] Hespanha J P. Linear Systems Theory, 2nd edition. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 2018. [24] Pasqualetti F, Borra D, Bullo F. Consensus networks over finite fields. Automatica, 2014, 50: 349−358 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.11.011 [25] Sundaram S, Hadjicostis C N. Structural controllability and observability of linear systems over finite fields with applications to multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2013, 58(1): 60−73 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2012.2204155 [26] Lidl R, Niederreiter H. Finite Fields. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1996. [27] Gatsis K, Pajic M, Ribeiro A, Pappas G J. Opportunistic control over shared wireless channels. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(12): 3140−3155 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2416922 [28] Gatsis K, Ribeiro A, Pappas G. Random access design for wireless control systems. Automatica, 2018, 91: 1−9 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.01.021 [29] Li Y L, Li H T, Ding X Y. Set stability of switched delayed logical networks with application to finite-field consensus. Automatica, 2020, 113: Article No. 108768 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108768 [30] Cormen T H, Leiserson C E, Rivest R L, Stein C. Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2009. [31] Zhao Y, Qi H S, Cheng D Z. Input-state incidence matrix of Boolean control networks and its applications. Systems and Control Letters, 2010, 59: 767−774 [32] Wu L Y, Sun J T. Optimal preview pinning control of Boolean networks. ISA Transactions, 2024, 146: 291−296 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2023.12.029 [33] Wu Y H, Guo Y Q, Toyoda M. Policy iteration approach to the infinite horizon average optimal control of probabilistic Boolean networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(7): 2910−2924 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3008960 [34] Kharade S, Sutavani S, Yerudkar A, Wagh S, Liu Y, Vecchio C D, et al. Optimal control of Boolean control networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(2): 1316−1323 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3301818 [35] Gao S H, Sun C K, Xiang C, Qin K R, Lee T H. Infinite-horizon optimal control of switched Boolean control networks with average cost: An efficient graph-theoretical approach. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(4): 2314−2328 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3003552 [36] Gao S H, Xiang C, Lee T H. Set invariance and optimal set stabilization of Boolean control networks: A graphical approach. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2021, 8(1): 400−412 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2020.3027788 [37] Chaturvedi M, McConnell R M. A note on finding minimum mean cycle. Information Processing Letters, 2017, 127: 21−22 doi: 10.1016/j.ipl.2017.06.007 [38] Karp R M. A characterization of the minimum cycle mean in a digraph. Discrete Mathematics, 1978, 23(3): 309−311 doi: 10.1016/0012-365X(78)90011-0 -




 下载:
下载: