Adaptive Reliable Control of Multi-agent Systems Based on Dynamic Event-triggered Communication Protocol
-
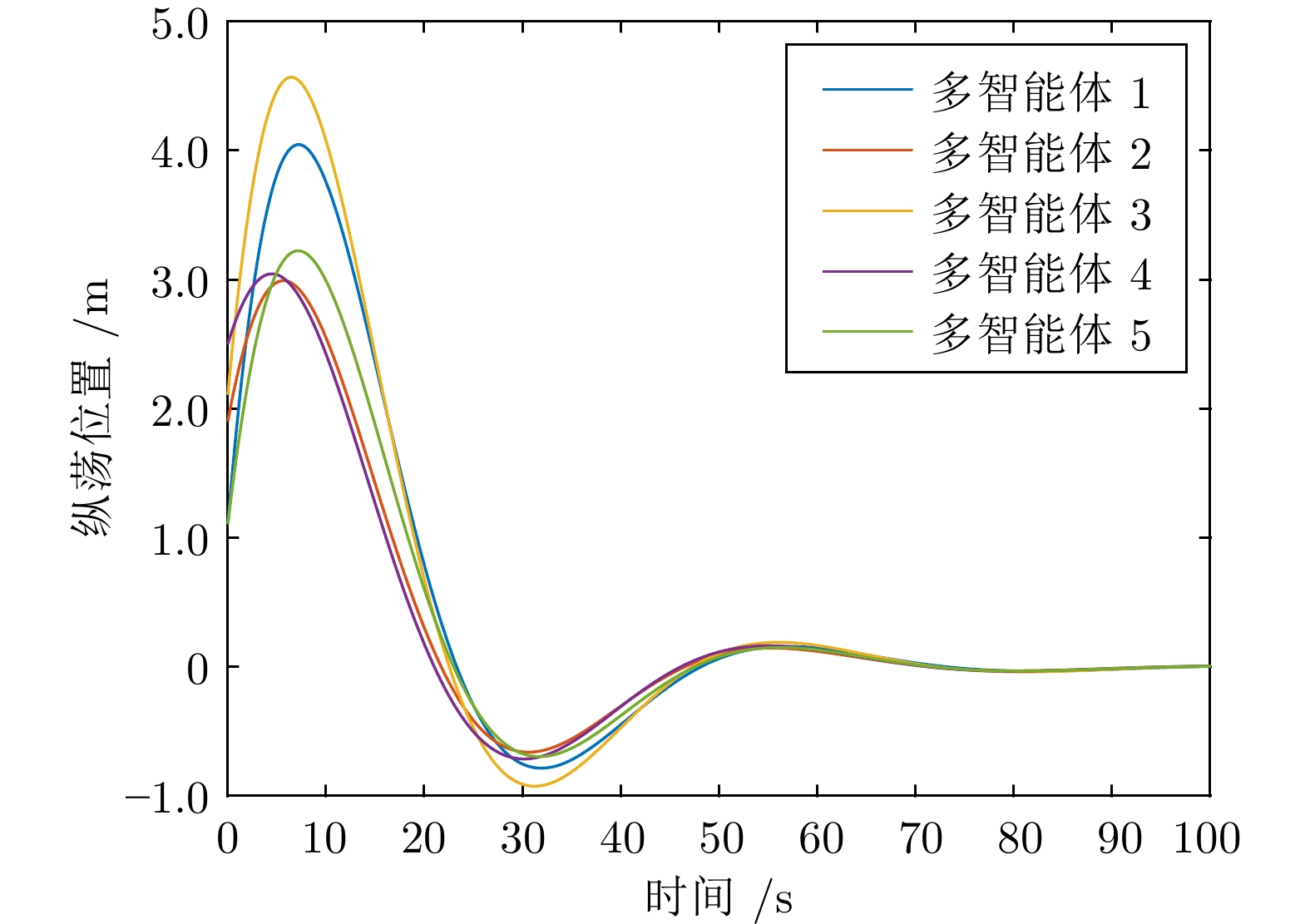
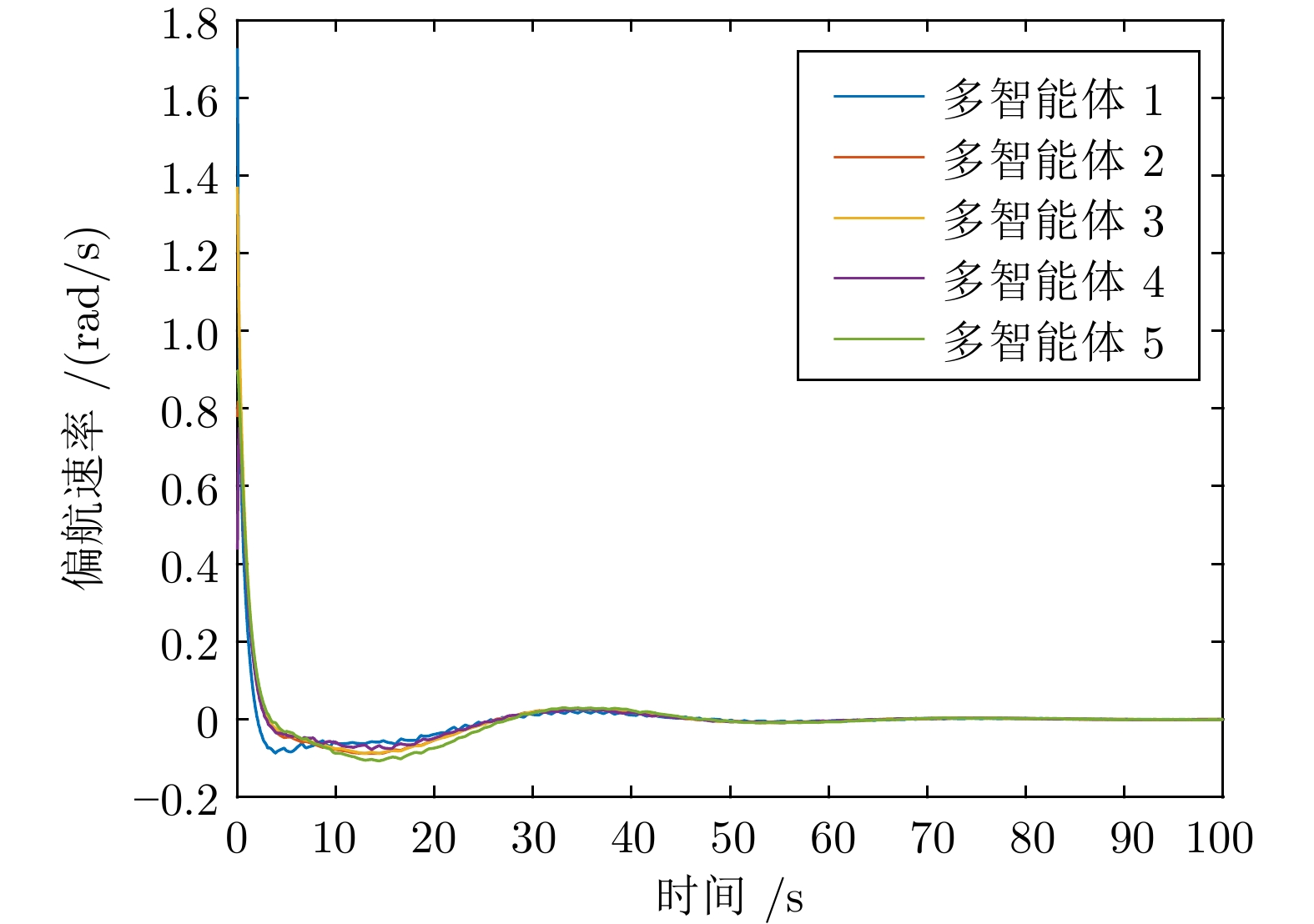
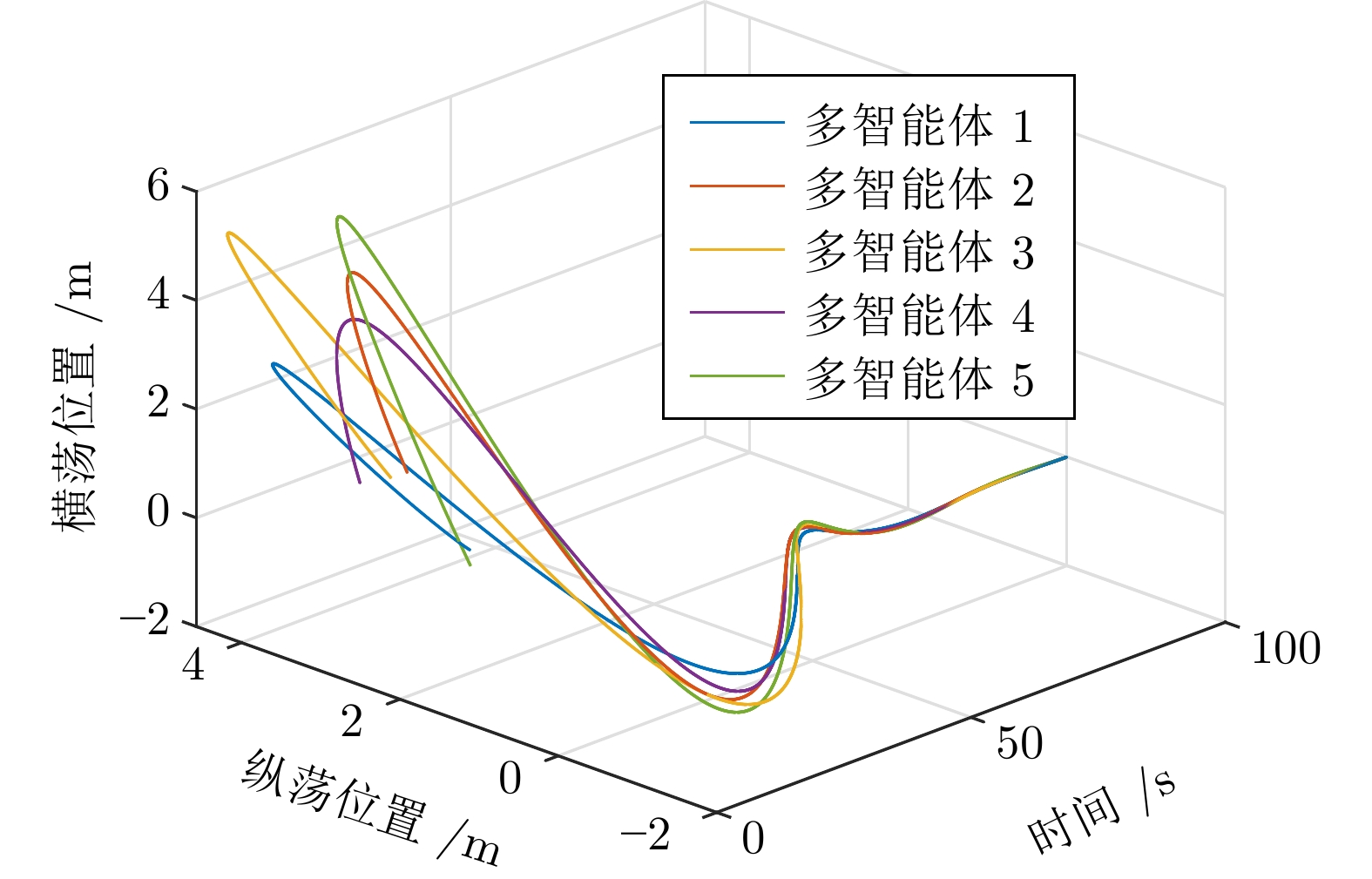
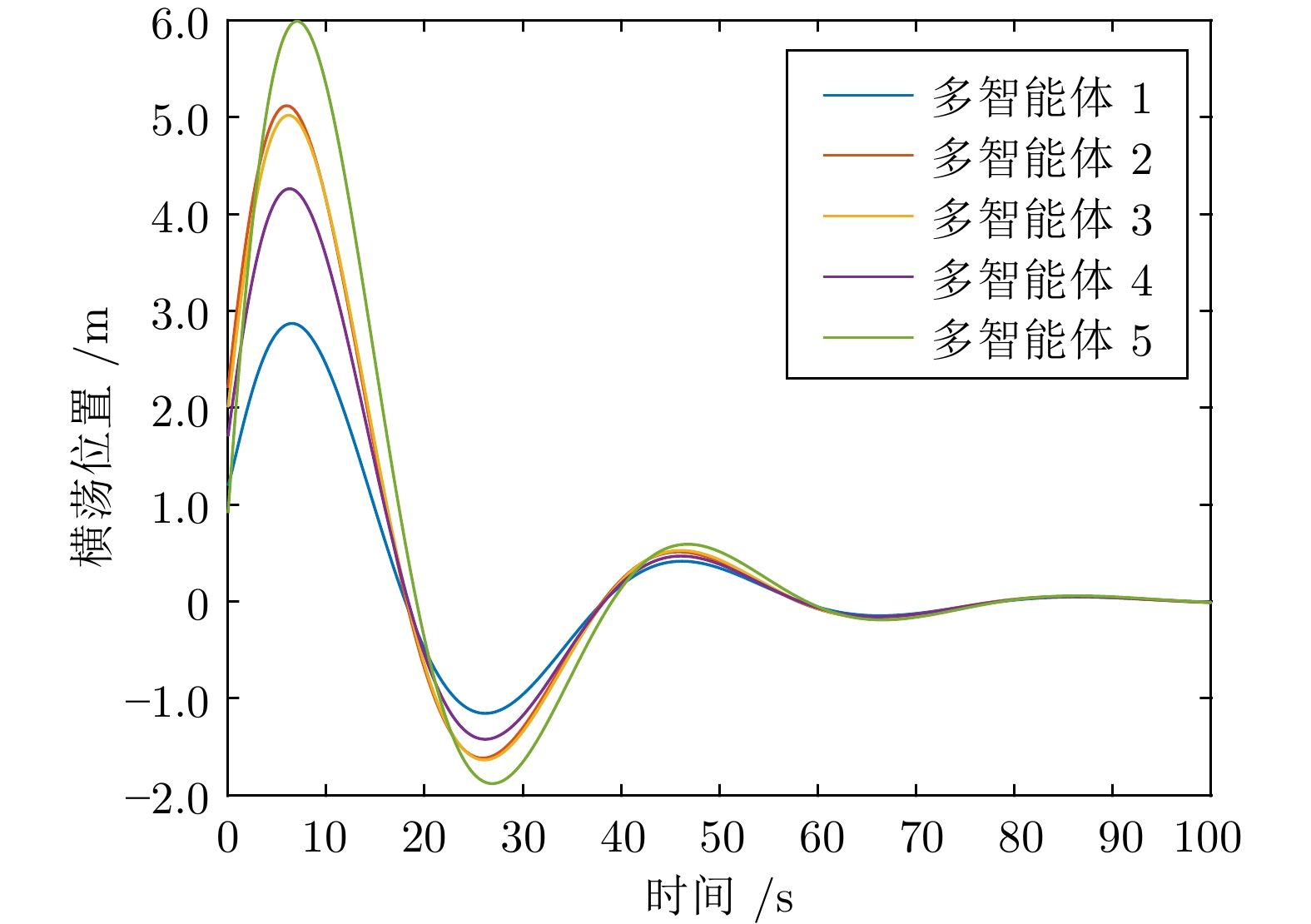
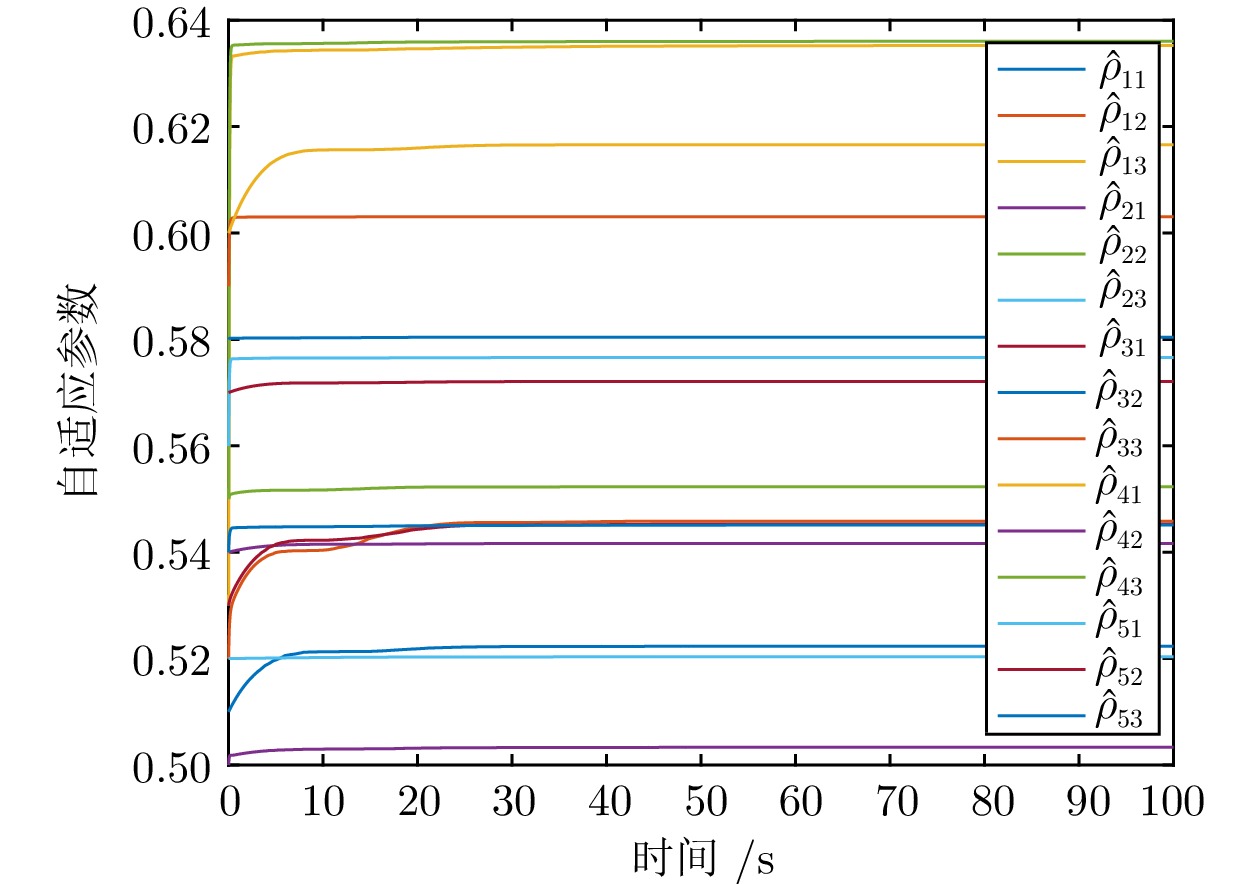
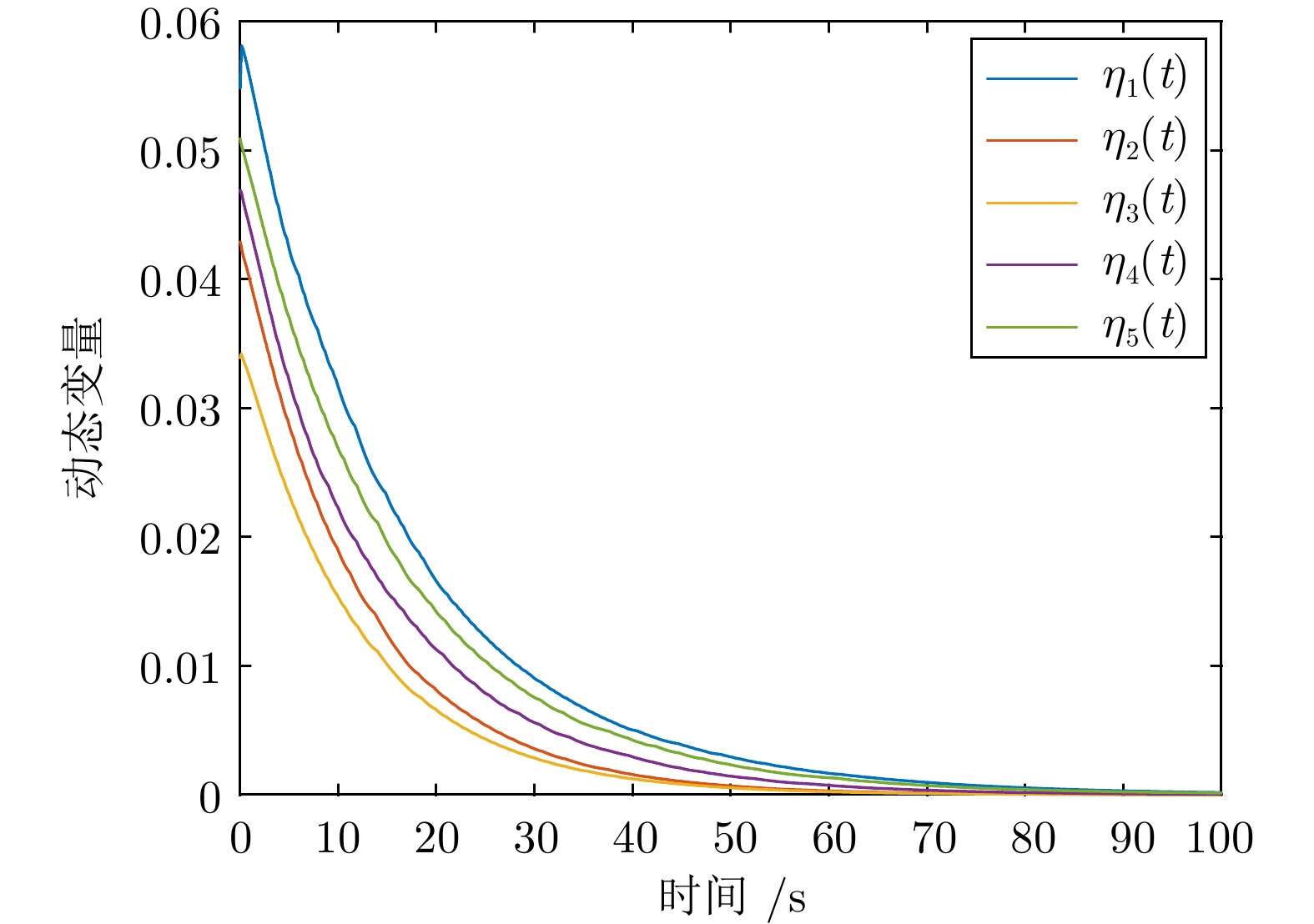
摘要: 针对多智能体系统中邻居节点间通信资源受限的情况, 研究基于动态事件触发通信协议的多智能体系统自适应可靠一致性控制问题. 首先, 设计一种基于自适应参数估计技术的容错控制策略, 来应对未知执行器故障. 其次, 提出一种新型动态事件触发函数, 通过增加具有自适应调节能力的动态变量来延长事件触发间隔. 在此基础上, 证明在智能体之间非连续通信的情况下, 所提方法仅依靠智能体与邻居在触发时刻的交互信息就可以确保一致性误差的收敛. 此外, 从理论上说明智能体间的事件触发通信不存在芝诺现象. 最后, 针对无人船编队系统开展仿真, 结果能够说明所提自适应事件触发可靠控制方法的有效性.Abstract: In view of the limited communication resources between neighboring nodes in multi-agent systems, this paper studies the adaptive reliable consensus control problem of multi-agent systems based on dynamic event-triggered communication protocol. Firstly, a fault-tolerant control policy based on adaptive parameter estimation technology is designed to address unknown actuator faults. Secondly, a novel dynamic event-triggered function is proposed, which prolongs the event-triggered interval by introducing a dynamic variable with adaptive adjustment capability. On this basis, it has been proved that the proposed method can ensure the convergence of consensus error solely based on the interaction information between the intelligent agent and its neighbors at the triggering time, in the case of discontinuous communication between agents. In addition, this paper theoretically demonstrates that there is no Zeno phenomenon in event-triggered communication between agents. Finally, a simulation of unmanned ship formation system is carried out, and the result can illustrate the effectiveness of the adaptive event-triggered reliable control method proposed in this paper.
-
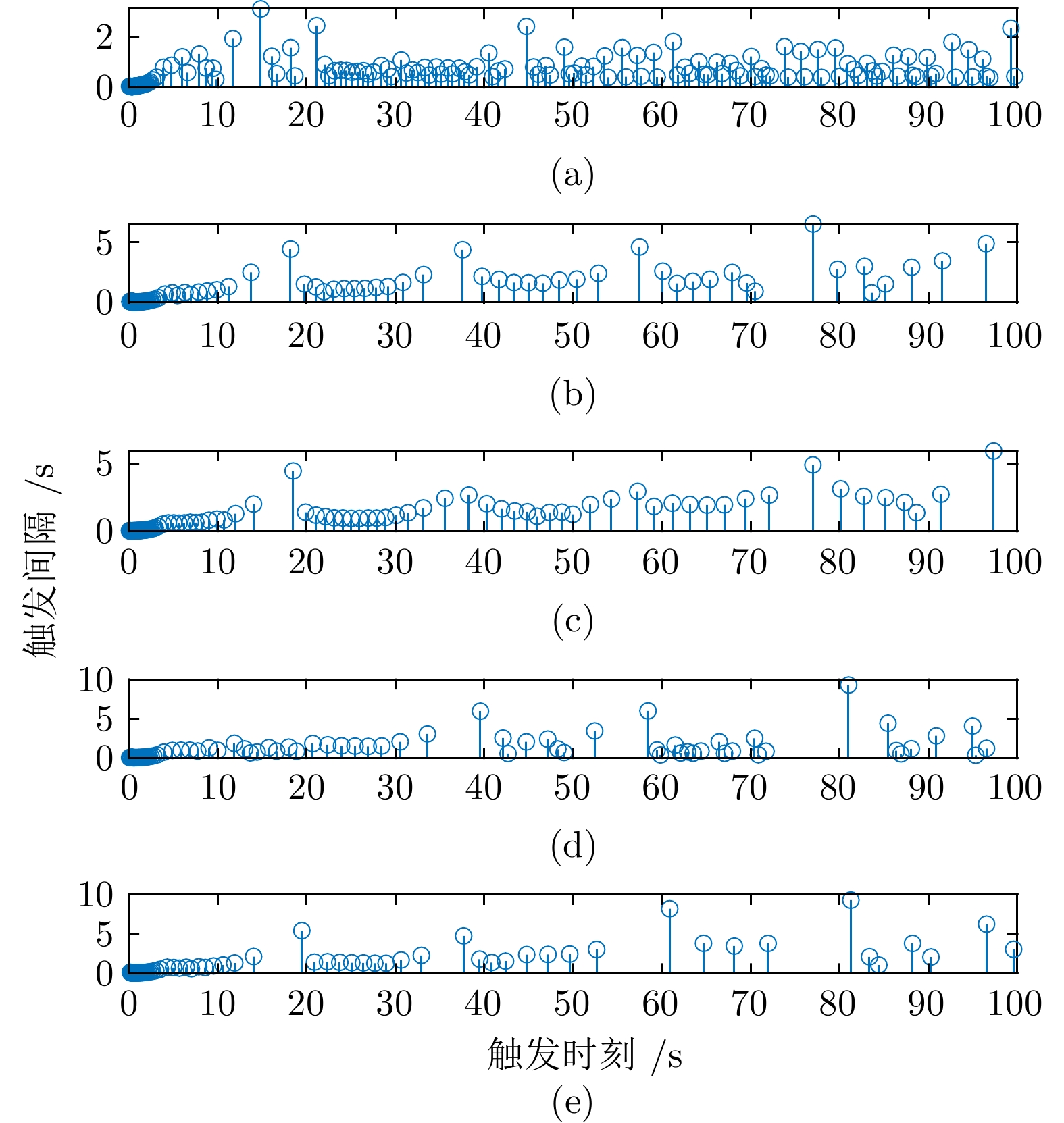
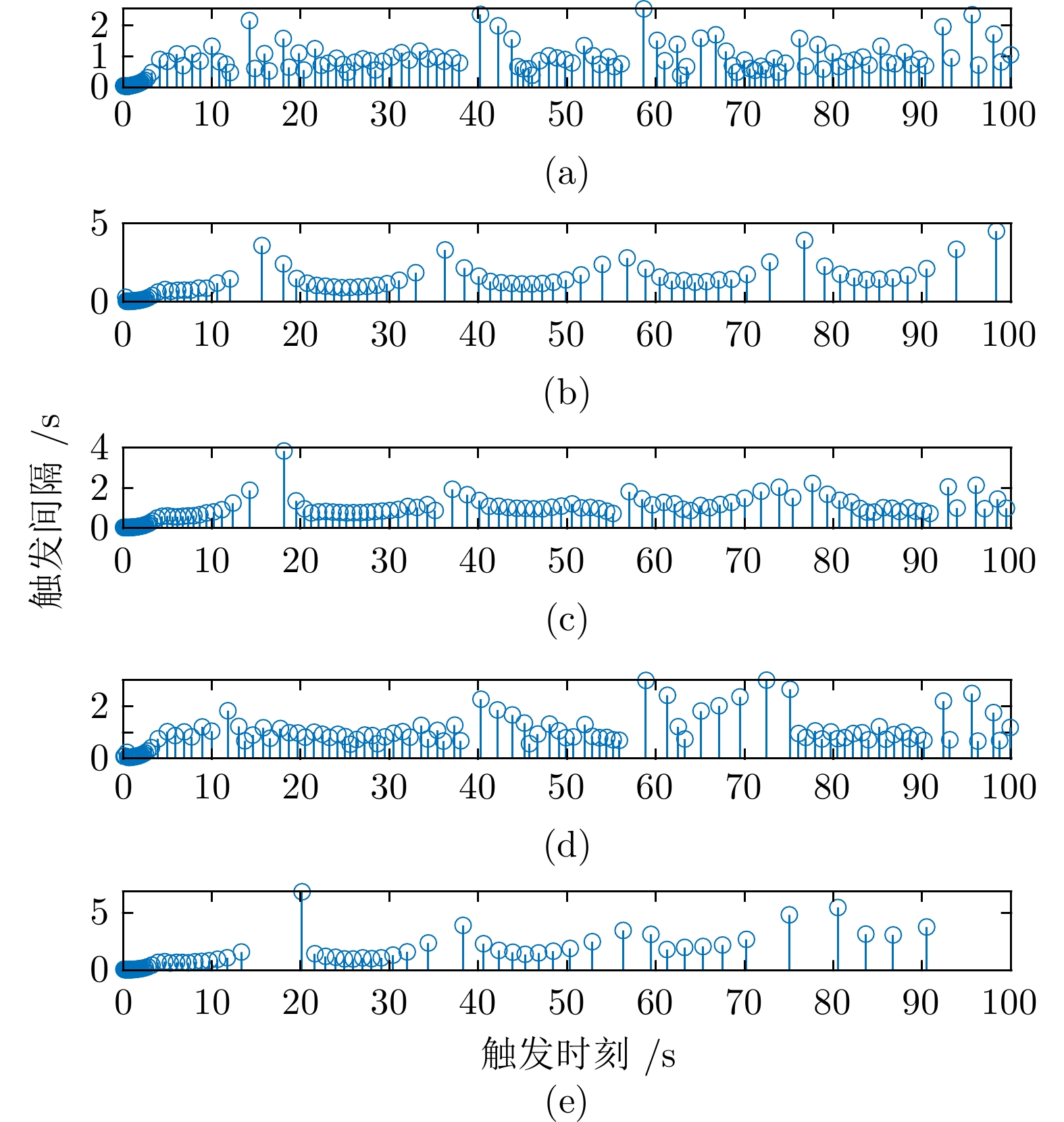
图 9 基于触发通信协议(8)的触发时刻和触发间隔, (a)、(b)、(c)、(d) 和(e)分别表示智能体1、智能体2、智能体3、智能体4和智能体5的触发时刻和触发间隔
Fig. 9 Triggering moment and triggering interval for each agent by communication protocol (8), where (a), (b), (c), (d) and (e) indicate the triggering moment and triggering interval of the agent 1, agent 2, agent 3, agent 4 and agent 5 respectively
图 10 基于文献[25]的触发时刻和触发间隔, (a)、(b)、(c)、(d) 和(e)分别表示智能体1、智能体2、智能体3、智能体4和智能体5的触发时刻和触发间隔
Fig. 10 Triggering moment and triggering interval for each agent in reference [25], where (a), (b), (c), (d) and (e) indicate the triggering moment and triggering interval of the agent 1, agent 2, agent 3, agent 4 and agent 5 respectively
-
[1] Yang X K, Wang W, Huang P. Distributed optimal consensus with obstacle avoidance algorithm of mixed-order UAVs-USVs-UUVs systems. ISA Transactions, 2020, 107: 270−286 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.07.028 [2] Shou Y X, Xu B, Zhang A D, Mei T. Virtual guidance-based coordinated tracking control of multi-autonomous underwater vehicles using composite neural learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(12): 5565−5574 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3057068 [3] Nair A S, Hossen T, Campion M, Selvaraj D F, Goveas N, Kaabouch N, et al. Multi-agent systems for resource allocation and scheduling in a smart grid. Technology and Economics of Smart Grids and Sustainable Energy, 2018, 3: Article No. 15 doi: 10.1007/s40866-018-0038-9 [4] Shou Y X, Xu B, Lu H B, Zhang A D, Mei T. Finite-time formation control and obstacle avoidance of multi-agent system with application. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2022, 32(5): 2883−2901 doi: 10.1002/rnc.5641 [5] Seyboth G S, Ren W, Allgower F. Cooperative control of linear multi-agent systems via distributed output regulation and transient synchronization. Automatica, 2016, 68: 132−139 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.01.068 [6] Li Y J, Tan C. A survey of the consensus for multi-agent systems. Systems Science & Control Engineering, 2019, 7(1): 468−482 [7] Xie C H, Yang G H. Cooperative guaranteed cost fault-tolerant control for multi-agent systems with time-varying actuator faults. Neurocomputing, 2016, 214: 382−390 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.06.022 [8] Liu Y, Yang G H. Integrated design of fault estimation and fault-tolerant control for linear multi-agent systems using relative outputs. Neurocomputing, 2019, 329: 468−475 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.005 [9] Khalili M, Zhang X D, Polycarpou M M, Parisini T, Cao Y C. Distributed adaptive fault-tolerant control of uncertain multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2018, 87: 142−151 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.09.002 [10] Deng C, Yang G H. Distributed adaptive fault-tolerant control approach to cooperative output regulation for linear multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2019, 103: 62−68 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.01.013 [11] Wang X, Yang G H. Adaptive reliable coordination control for linear agent networks with intermittent communication constraints. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2018, 5(3): 1120−1131 [12] Yang P, Ma B, Dong Y, Liu J W. Fault-tolerant consensus of leader-following multi-agent systems based on distributed fault estimation observer. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2018, 16(5): 2354−2362 doi: 10.1007/s12555-017-0223-y [13] Lü S Y, Jin X Z, Wu X M, Ding L J, Chi J. Robust adaptive event-triggered fault-tolerant control for time-varying systems against perturbations and faulty actuators. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2022, 426: Article No. 127133 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2022.127133 [14] Li H Y, Wu Y, Chen M. Adaptive fault-tolerant tracking control for discrete-time multiagent systems via reinforcement learning algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(3): 1163−1174 [15] Zhao G L, Wang Z, Fu X W. Fully distributed dynamic event-triggered semiglobal consensus of multi-agent uncertain systems with input saturation via low-gain feedback. International Jour nal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2021, 19(4): 1451−1460 doi: 10.1007/s12555-019-1080-7 [16] Guo X G, Zhang D Y, Wang J L, Ahn C K. Adaptive memory event-triggered observer-based control for nonlinear multi-agent systems under DoS attacks. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2021, 8(10): 1644−1656 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2021.1004132 [17] Bernuau E, Moulay E, Coirault P, Isfoula F. Practical consensus of homogeneous sampled-data multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(11): 4691−4697 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2904442 [18] Josse F, Bernuau E, Moulay E, Coirault P. Robustness of sampled-data homogeneous systems. Automatica, 2021, 123: Article No. 109345 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.109345 [19] Xu Y, Wu Z G. Data-based collaborative learning for multi-agent systems under distributed denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2024, 16 (1): 75−85 [20] Zheng S Q, Shi P, Agarwal R K, Lim C P. Periodic event-triggered output regulation for linear multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2020, 122: Article No. 109223 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.109223 [21] Zhang H, Feng G, Yan H C, Chen Q J. Observer-based output feedback event-triggered control for consensus of multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(9): 4885−4894 [22] Liu T, Cao M, De Persis C, Hendrickx J M. Distributed event-triggered control for asymptotic synchronization of dynamical networks. Automatica, 2017, 86: 199−204 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.08.026 [23] Ruan X L, Feng J W, Xu C, Wang J Y. Observer-based dynamic event-triggered strategies for leader-following consensus of multi-agent systems with disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(4): 3148−3158 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.3017493 [24] Zhu W, Jiang Z P, Feng G. Event-based consensus of multi-agent systems with general linear models. Automatica, 2014, 50(2): 552−558 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.11.023 [25] Deng C, Yang G H. Leaderless and leader-following consensus of linear multi-agent systems with distributed event-triggered estimators. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(1): 309−333 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.10.001 [26] Deng C, Wen C Y, Wang W, Li X Y, Yue D. Distributed adaptive tracking control for high-order nonlinear multiagent systems over event-triggered communication. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(2): 1176−1183 [27] Guo X G, Liu P M, Wang J L, Ahn C K. Event-triggered adaptive fault-tolerant pinning control for cluster consensus of heterogeneous nonlinear multi-agent systems under aperiodic DoS attacks. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(2): 1941−1956 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3077766 [28] Ge X H, Han Q L, Zhang X M, Ding D R. Dynamic event-triggered control and estimation: A survey. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 2021, 18(6): 857−886 doi: 10.1007/s11633-021-1306-z [29] Liu D, Yang G H. Dynamic event-triggered control for linear time-invariant systems with $L_2\text{-gain} $ performance. Internation al Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2019, 29(2): 507−518 doi: 10.1002/rnc.4403 [30] Girard A. Dynamic triggering mechanisms for event-triggered control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(7): 1992−1997 [31] Hao R L, Wang H B, Zheng W. Dynamic event-triggered adaptive command filtered control for nonlinear multi-agent systems with input saturation and disturbances. ISA Transactions, 2022, 130: 104−120 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2022.03.011 [32] Qian Y Y, Liu L, Feng G. Distributed dynamic event-triggered control for cooperative output regulation of linear multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(7): 3023−3032 [33] Ruan X L, Xu C, Feng J W, Wang J Y, Zhao Y. Adaptive dynamic event-triggered control for multi-agent systems with matched uncertainties under directed topologies. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2022, 586: Article No. 126450 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2021.126450 [34] Ye D, Chen M M, Yang H J. Distributed adaptive event-triggered fault-tolerant consensus of multiagent systems with general linear dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(3): 757−767 [35] Xu Y, Wu Z G. Distributed adaptive event-triggered fault-tolerant synchronization for multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(2): 1537−1547 [36] Hou Q H, Dong J X. Robust adaptive event-triggered fault-tolerant consensus control of multiagent systems with a positive minimum interevent time. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53 (7): 4003−4014 [37] Sader M, Chen Z Q, Liu Z X, Deng C. Distributed robust fault-tolerant consensus control for a class of nonlinear multi-agent systems with intermittent communications. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2021, 403: Article No. 126166 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2021.126166 [38] Huang J Y, Jia W, Wan T X, Xiao S Y, Wang L Q, Dong J X. Adaptive event-triggered fault-tolerant consensus of linear heterogeneous multiagent systems via hierarchical approach. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2023, 447: Article No. 127909 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2023.127909 [39] Li H Y, Wu Y, Chen M, Lu R Q. Adaptive multigradient recursive reinforcement learning event-triggered tracking control for multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(1): 144−156 [40] Zhu Z B, Wang F Y, Yin Y H, Liu Z X, Chen Z Q. Distributed fault-tolerant containment control for a class of non-linear multi-agent systems via event-triggered mechanism. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2022, 430: Article No. 127250 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2022.127250 [41] Yang Y, Yue D, Xu C. Dynamic event-triggered leader-following consensus control of a class of linear multi-agent systems. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2018, 355(15): 7706−7734 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.08.007 [42] Zhang Z, Zhang S X, Li H P, Yan W S. Cooperative robust optimal control of uncertain multi-agent systems. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2020, 357(14): 9467−9483 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.07.021 -




 下载:
下载: