Research on Robust Probabilistic System Identification Method With Asymmetric and Skewed Noise
-
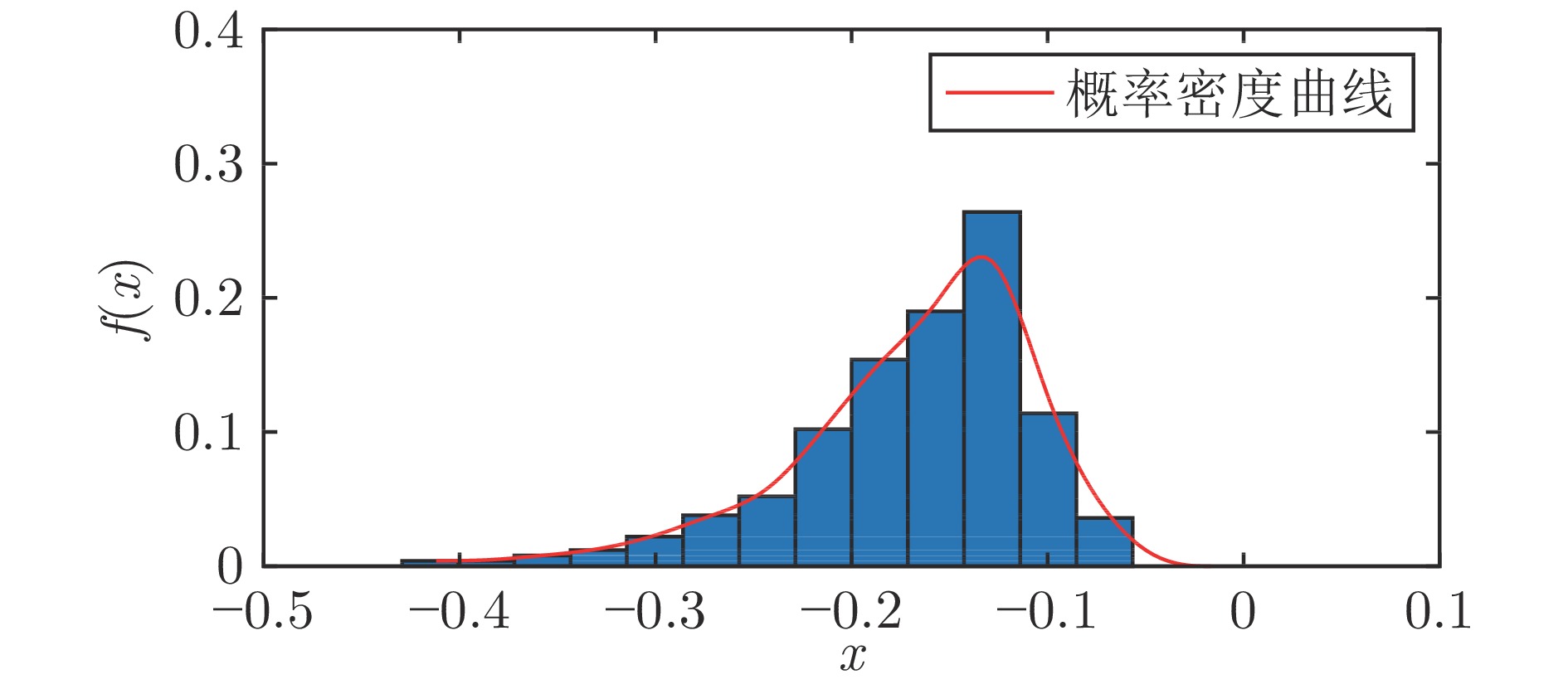
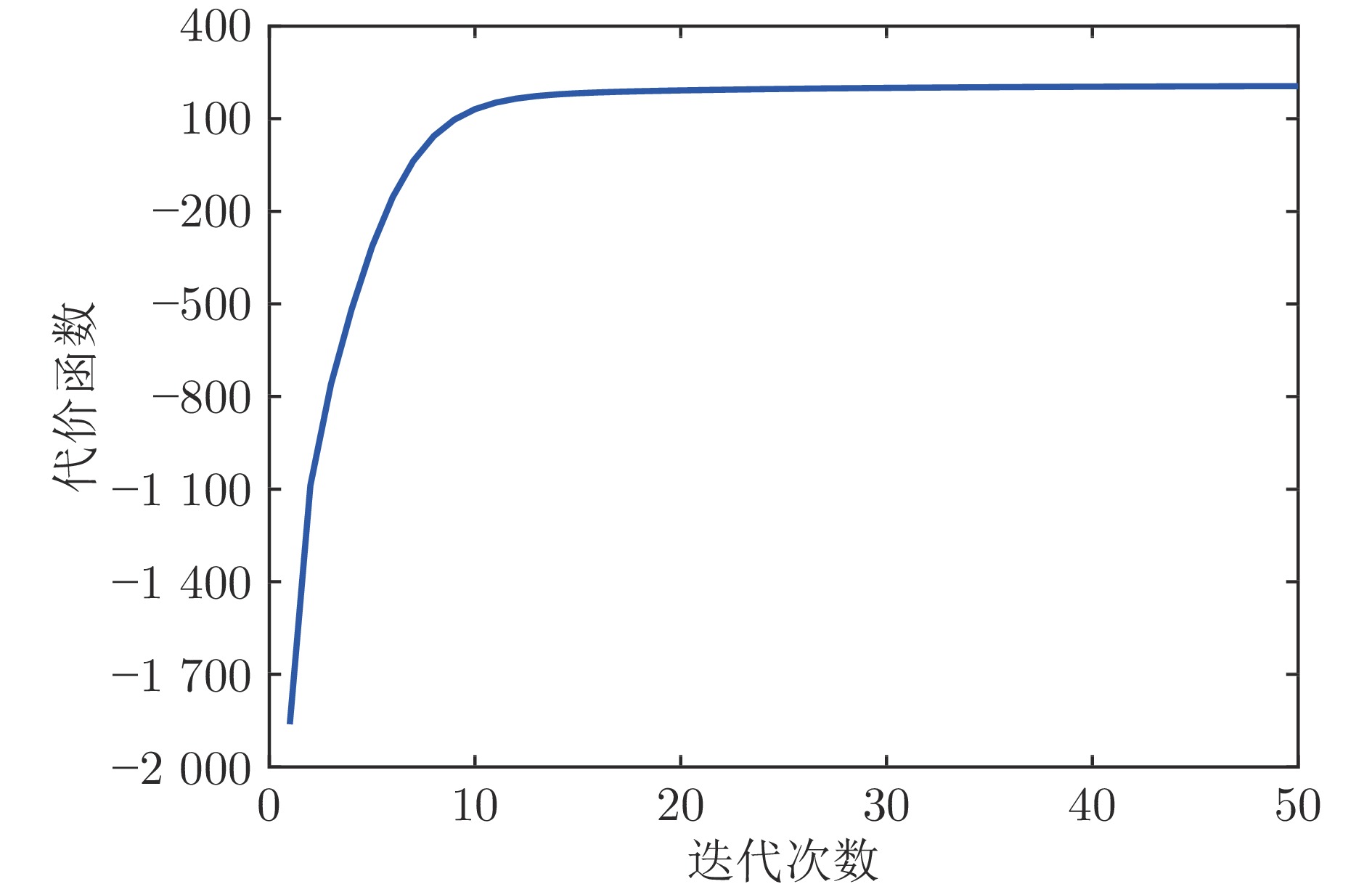
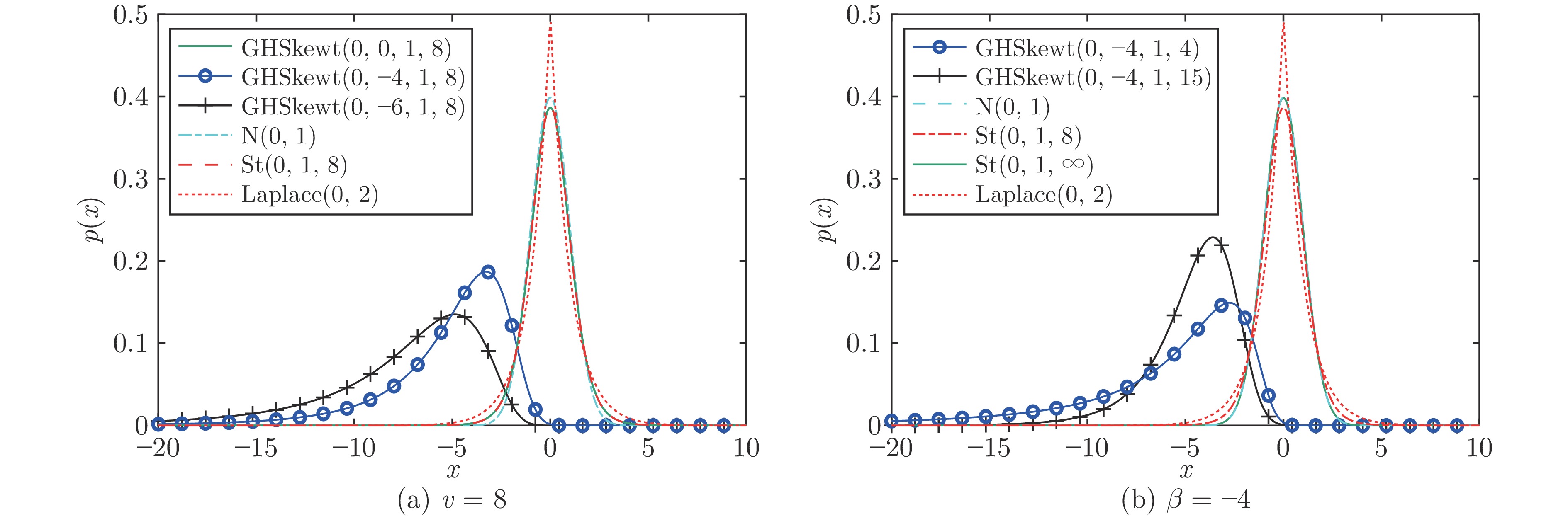
摘要: 在现有的系统辨识算法中, 常用的高斯、学生氏t (Student's t, St)、拉普拉斯等噪声分布均呈现出对称的统计特性, 难以描述非对称性、有偏的输出噪声, 使得在非对称偏斜噪声条件下算法的性能下降. 基于此, 研究一类广义双曲倾斜学生氏t (Generalized hyperbolic skew student's t, GHSkewt)分布, 并在非对称偏斜噪声条件下, 提出一种线性系统鲁棒辨识算法. 首先, 对GHSkewt分布的重尾特性和偏斜特性进行详细阐述, 数学上证明了标准学生氏t分布可看作是GHSkewt分布的一个特例; 其次, 引入隐含变量将GHSkewt分布进行数学分解, 以方便算法的推导和实现; 最后, 在期望最大化(Expectation-maximization, EM)算法下, 重构具有隐含变量系统的代价函数, 通过迭代优化的方式, 不断从被污染数据集中学习过程的动态特性和噪声分布, 实现噪声参数和模型参数的联合估计.
-
关键词:
- 鲁棒系统辨识 /
- 非对称偏斜噪声 /
- 广义双曲倾斜学生氏t分布 /
- 期望最大化算法
Abstract: In the existing system identification algorithms, the commonly used Gaussian, student's t (St) and Laplace distributions all show symmetric statistical characteristics which makes them difficult to describe the asymmetric and skewed noise, therefore the performance of the corresponding algorithms may largely degrade with the skewed noise. To this end, this paper introduces the generalized hyperbolic skew student's t (GHSkewt) distribution and proposes a robust identification algorithm for linear systems with the asymmetric and skewed noise. Firstly, the thick-tailed and skewed characteristics of the GHSkewt distribution are introduced detailedly and it is also proved that the standard student's t-distribution can be regarded as a special case of the GHSkewt distribution; Secondly, the latent variables are introduced to mathematically decompose the GHSkewt distribution in order to facilitate the derivation and implementation of the algorithm; Finally, the system cost function with the latent variables is reconstructed under the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm. The dynamic characteristics and noise distribution of the system are continuously learned from the contaminated data with iterative optimization, then the estimation of noise parameters and model parameters are realized. -
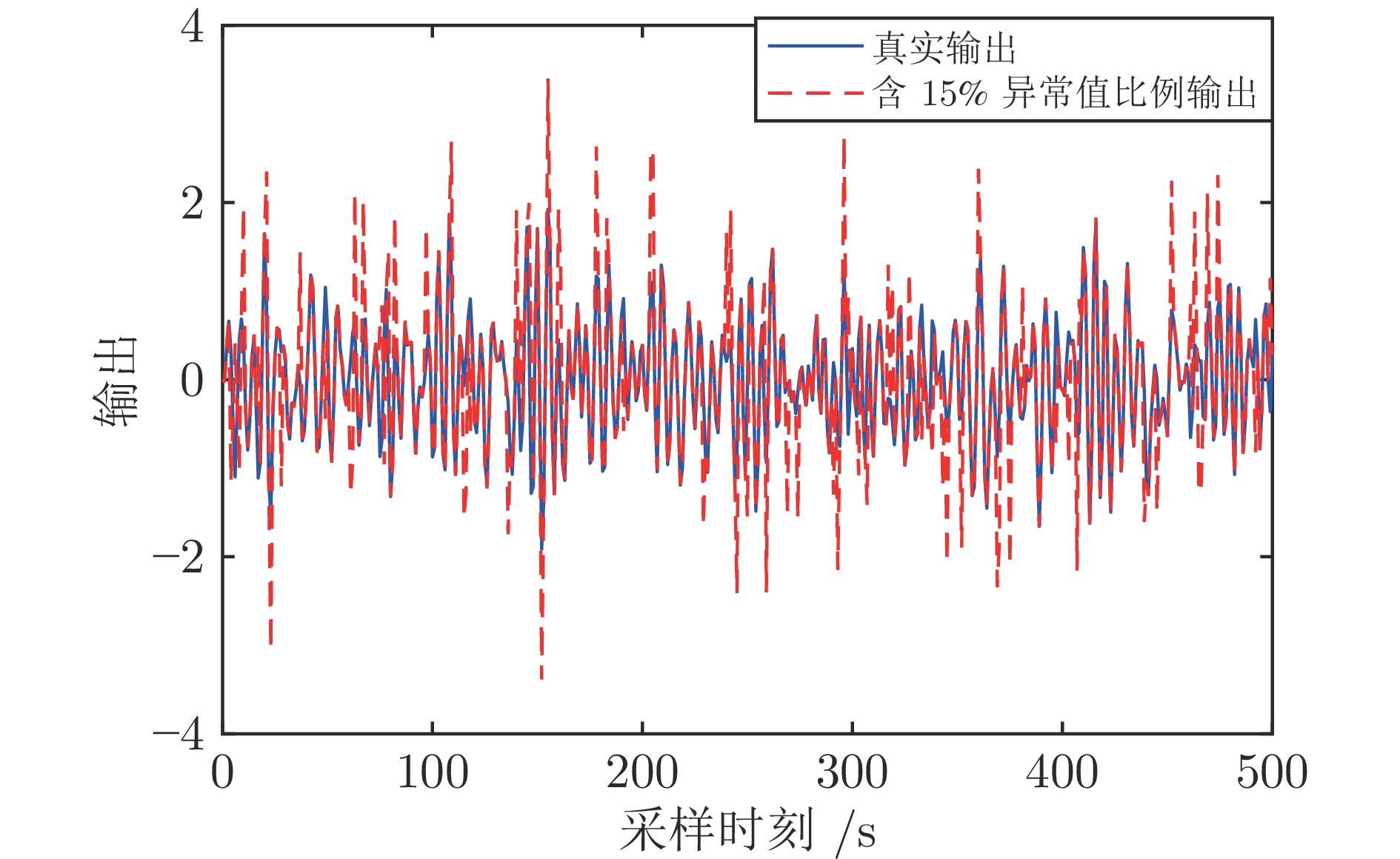
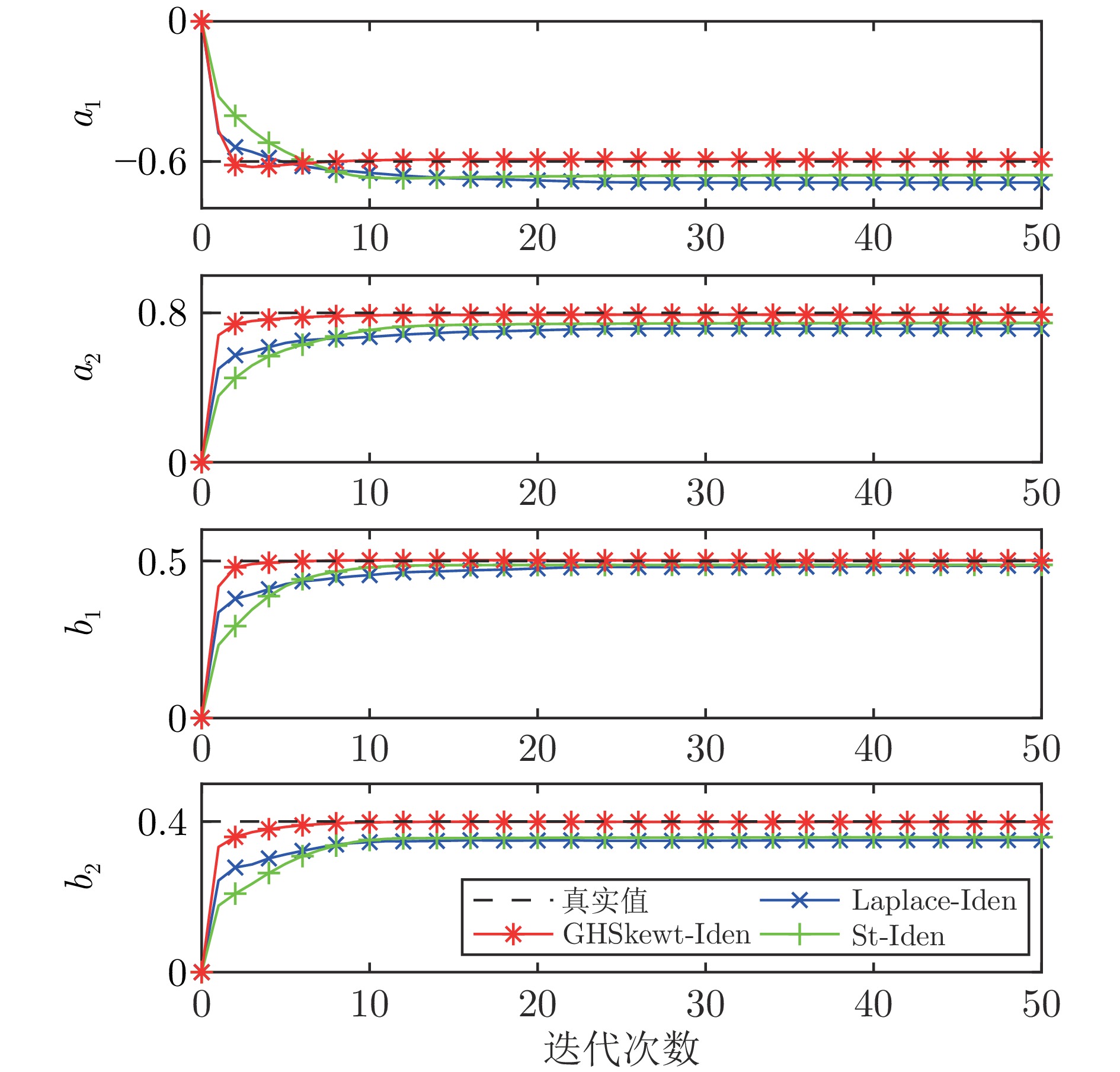
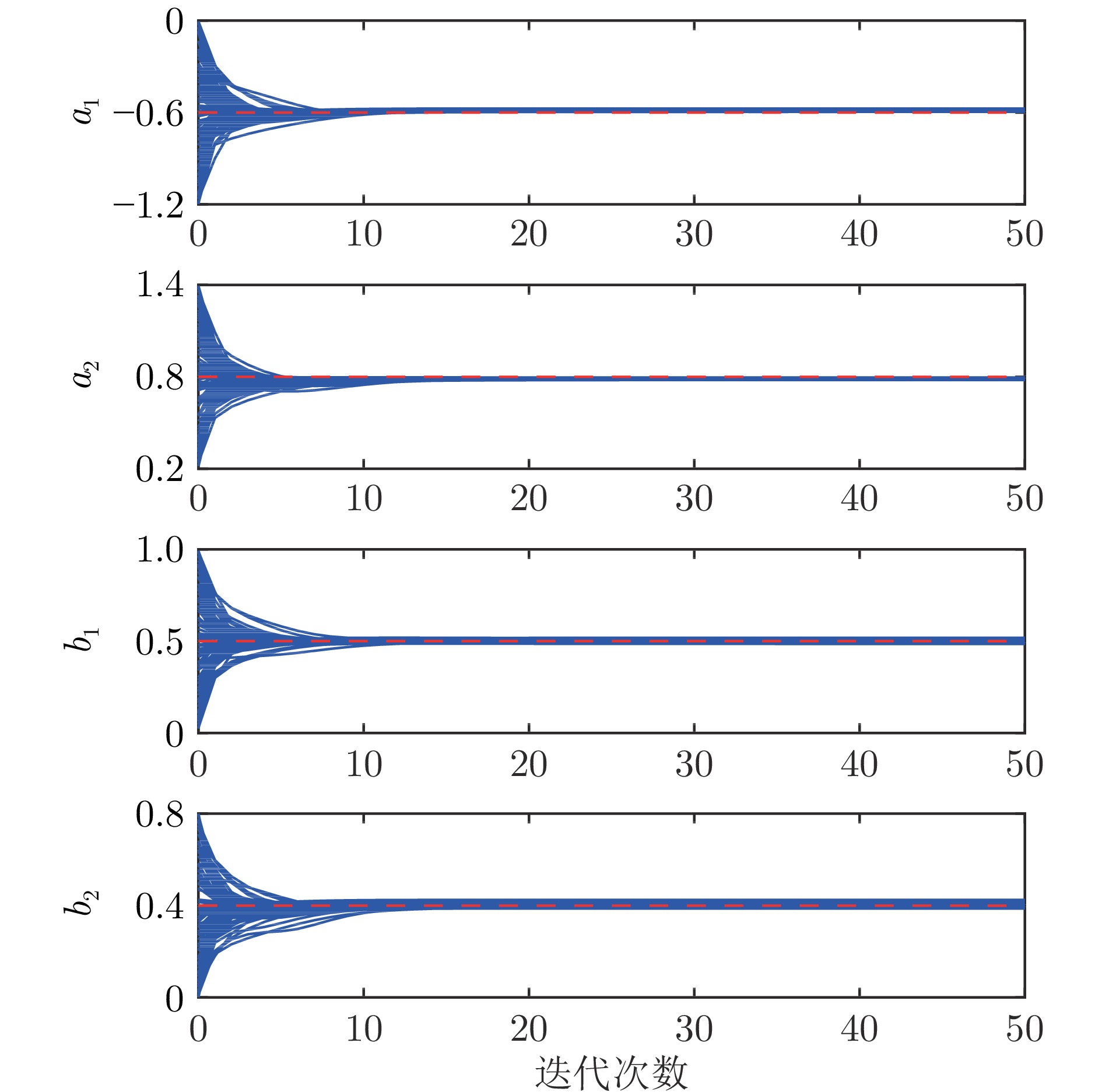
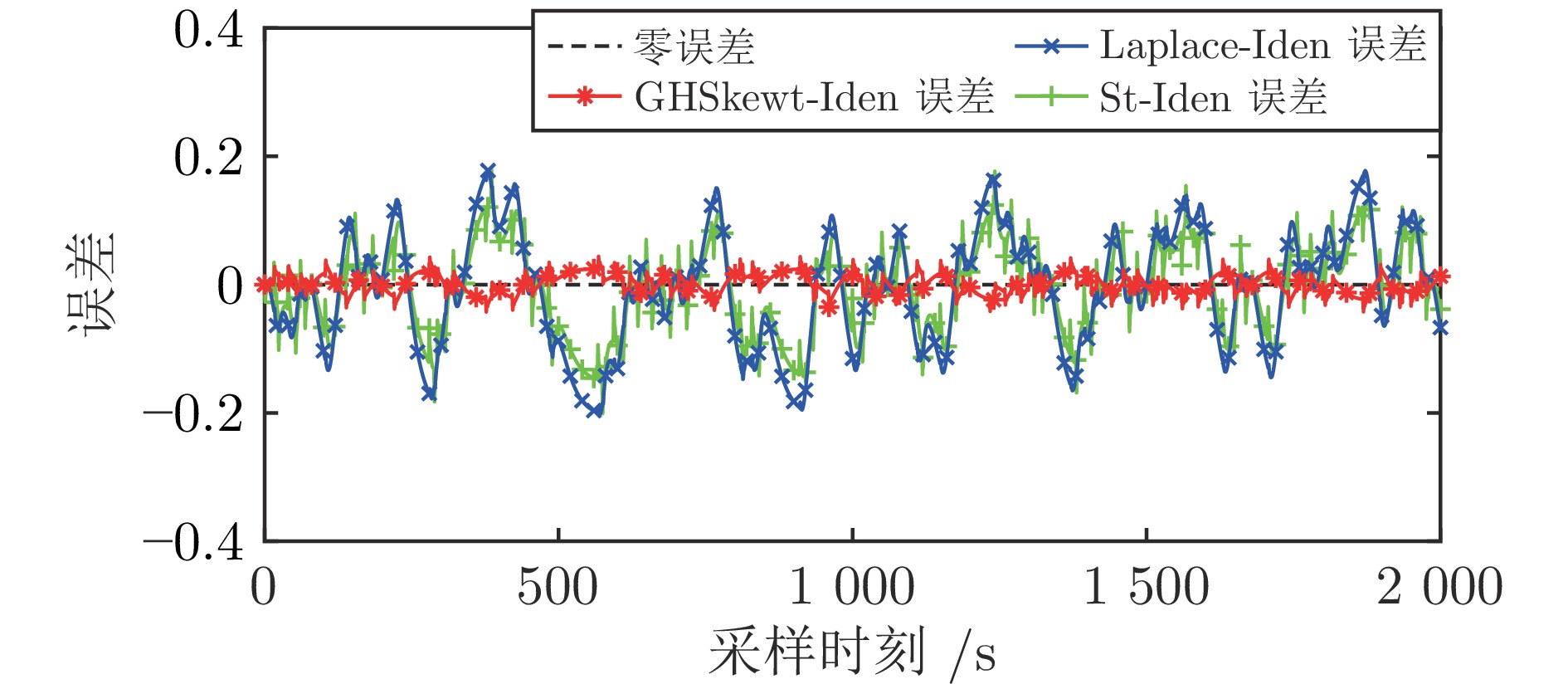
表 1 异常值比例为15%时, 蒙特卡洛仿真实验参数估计结果的均值和标准差
Table 1 The mean and standard deviation of the Monte Carlo parameter estimation results with 15% of outlier points
算法 参数$ {a_1} $ 参数$ {a_2} $ 参数$ {b_1} $ 参数$ {b_2} $ 均值 标准差 均值 标准差 均值 标准差 均值 标准差 Laplace-Iden − 0.5751 $ {3.6 \times 10^{ - 4}} $ 0.7739 $ {1.9 \times 10^{-4}} $ 0.5083 $ {2.8 \times 10^{-4}} $ 0.4085 $ {2.7 \times 10^{-4}} $ St-Iden − 0.5878 $ {3.2 \times 10^{-8}} $ 0.7899 $ {1.1 \times 10^{-8}} $ 0.5043 $ {6.5 \times 10^{-8}} $ 0.4028 $ {2.0 \times 10^{-8}} $ GHSkewt-Iden − 0.5876 $ {6.5 \times 10^{-7}} $ 0.7899 $ {2.5 \times 10^{-7}} $ 0.5042 $ {1.1 \times 10^{-7}} $ 0.4030 $ {4.0 \times 10^{-7}} $ 真实值 − 0.6000 — 0.8000 — 0.5000 — 0.4000 — 表 2 不同异常值比例下蒙特卡洛仿真实验的平均RPEE、RMSE和$ {\rm{R}}^2 $
Table 2 The averaged RPEE、RMSE and$ {\rm{R}}^2 $for the Monte Carlo with different ratios of outlier points
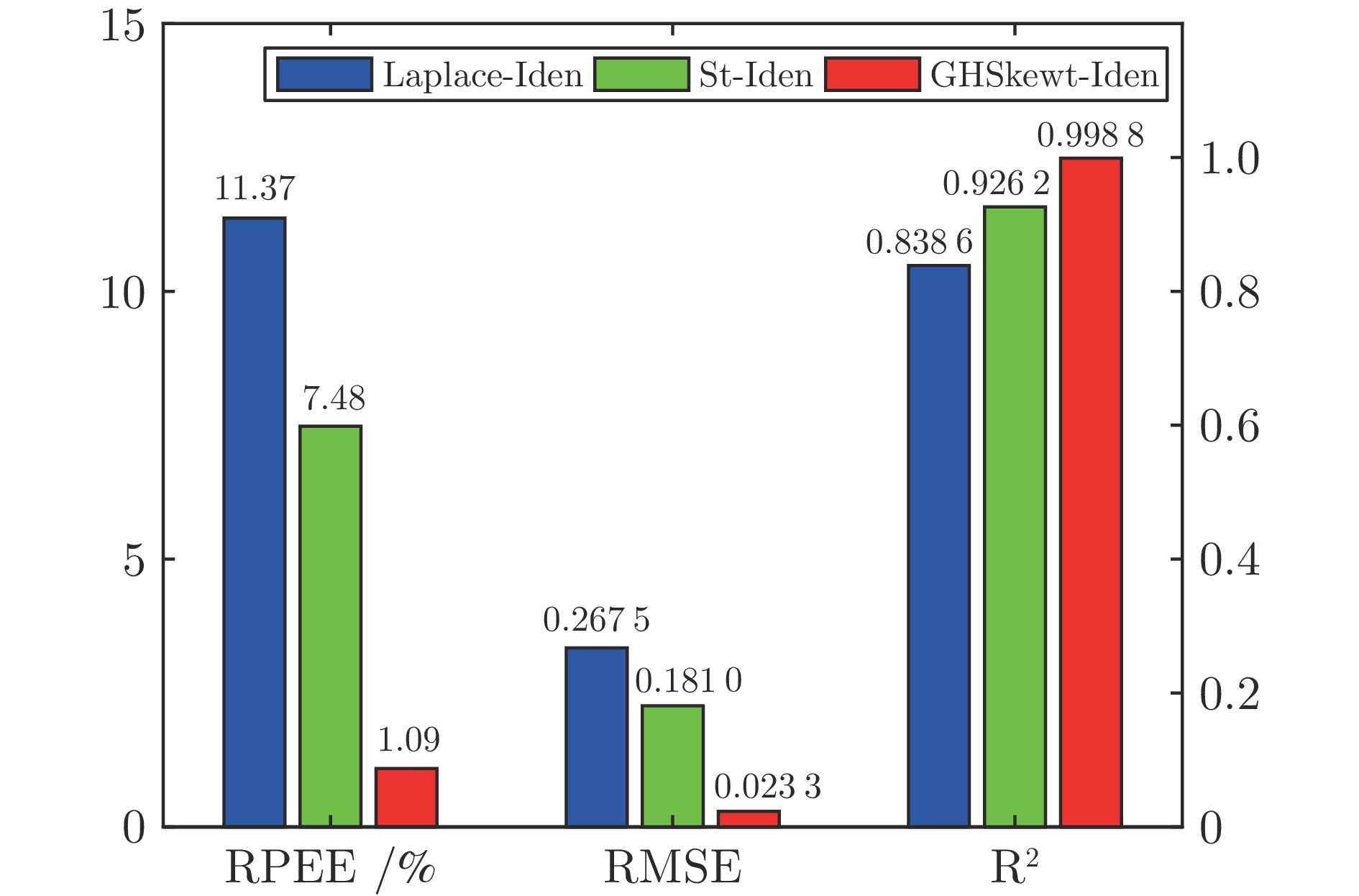
异常值比例 Laplace-Iden St-Iden GHSkewt-Iden RPEE (%) RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ RPEE (%) RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ RPEE (%) RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ 5% 0.71 0.0144 0.9995 0.61 0.0104 0.9998 0.39 0.0072 0.9999 10% 2.44 0.0475 0.9949 1.20 0.0186 0.9992 1.13 0.0192 0.9992 15% 3.20 0.0564 0.9928 1.40 0.0267 0.9984 1.42 0.0271 0.9983 20% 5.33 0.0880 0.9826 2.70 0.0499 0.9944 2.74 0.0503 0.9943 表 3 不同偏斜噪声下蒙特卡洛仿真的平均RPEE、RMSE和$ {\rm{R}}^2 $
Table 3 The averaged RPEE、RMSE and$ {\rm{R}}^2 $for the Monte Carlo with different levels of skewed noise
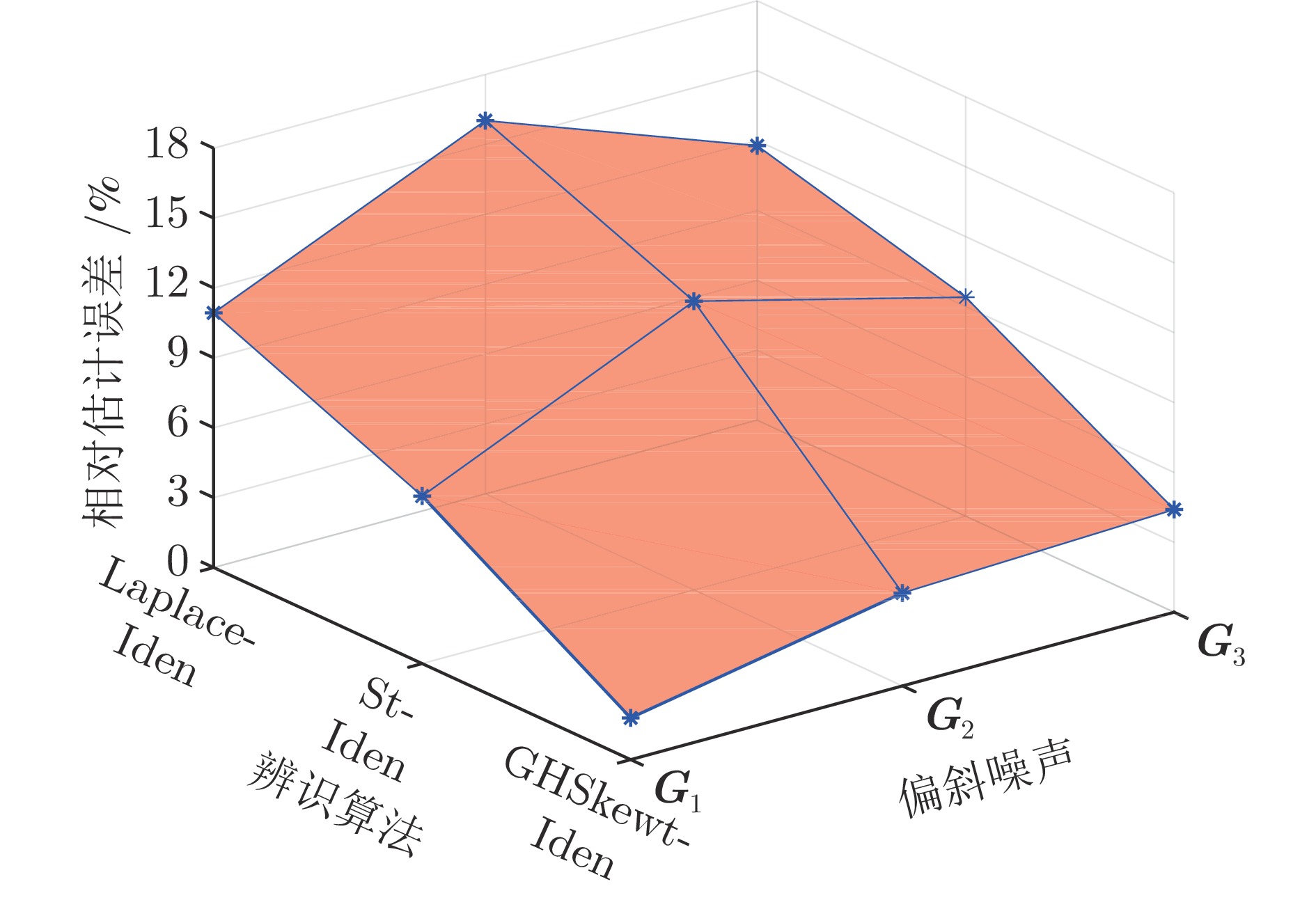
偏斜噪声 Laplace-Iden St-Iden GHSkewt-Iden RPEE (%) RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ RPEE (%) RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ RPEE (%) RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ $ {\boldsymbol{G}}_1 $ 10.93 0.2615 0.8416 7.19 0.1889 0.9175 1.79 0.0315 0.9978 $ {\boldsymbol{G}}_2 $ 16.02 0.3381 0.7356 12.39 0.2825 0.8155 3.99 0.0699 0.9884 $ {\boldsymbol{G}}_3 $ 11.78 0.2607 0.8426 9.40 0.2184 0.8886 4.41 0.0779 0.9855 表 4 参数初始值不同时蒙特卡洛仿真的均值和标准差
Table 4 The mean and standard deviation of the Monte Carlo with different parameter initial values
模型参数 真实值 均值 标准差 $ {{a_1}} $ − 0.6000 − 0.5860 0.0045 $ {{a_2}} $ 0.8000 0.7872 0.0033 $ {{b_1}} $ 0.5000 0.5028 0.0068 $ {{b_2}} $ 0.4000 0.4037 0.0080 表 5 自我验证的RMSE和$ {\rm{R}}^2 $
Table 5 The RMSE and$ {\rm{R}}^2 $for self-verification
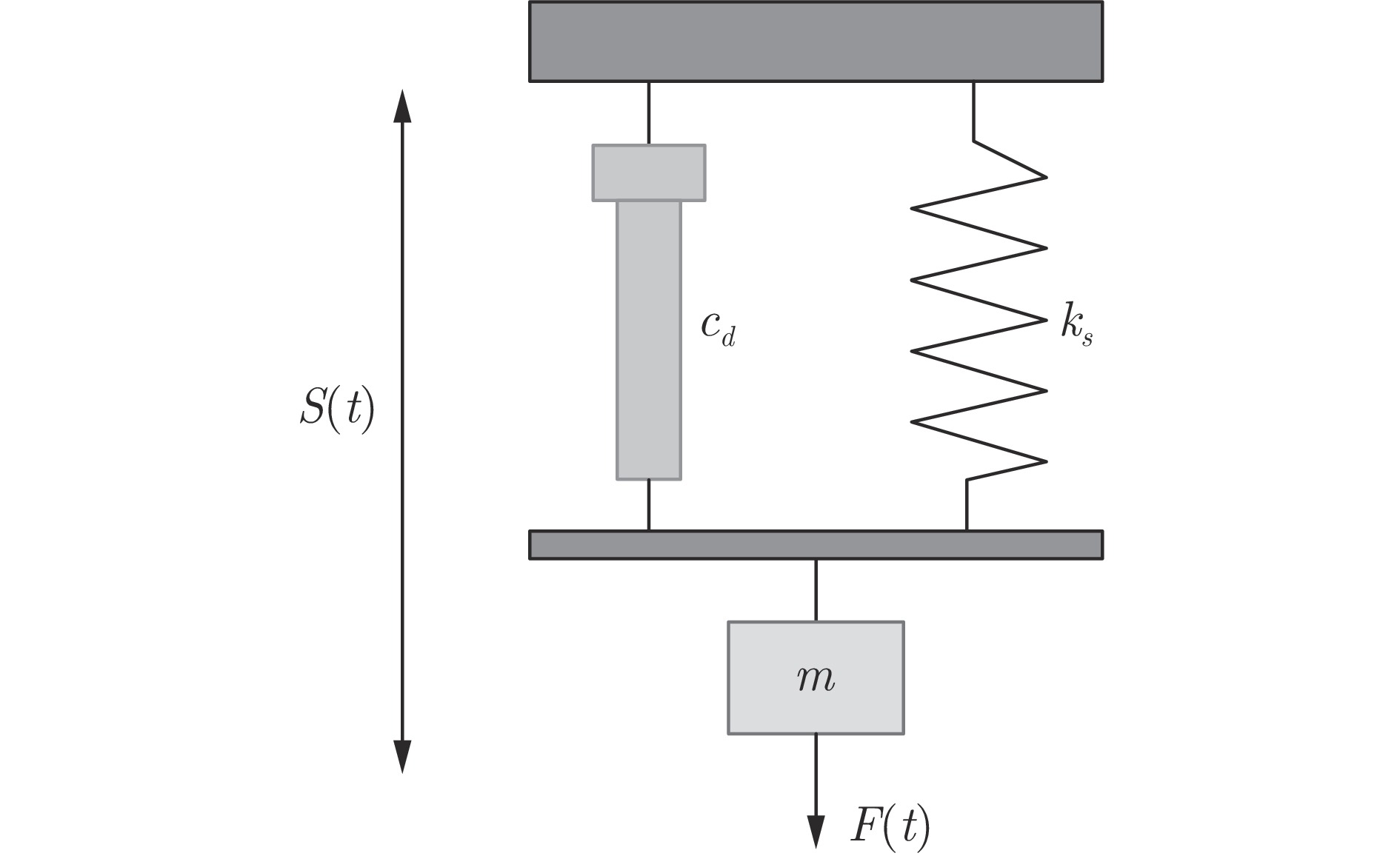
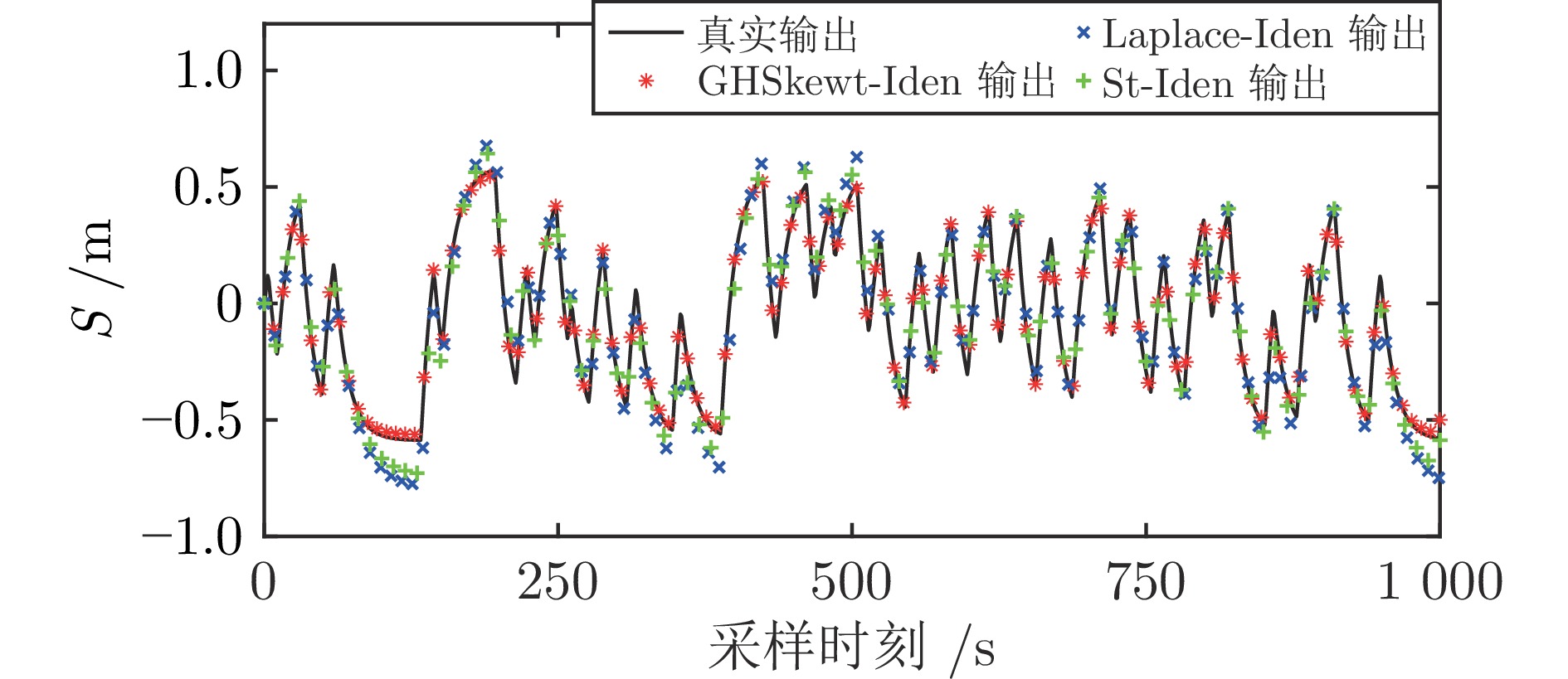
质量块位置 Laplace-Iden St-Iden GHSkewt-Iden RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ $ {{S}} \ ({\rm{m}})$ 0.0795 0.9373 0.0607 0.9635 0.0137 0.9981 表 6 交叉验证的RMSE和$ {\rm{R}}^2 $
Table 6 The RMSE and$ {\rm{R}}^2 $for cross-verification
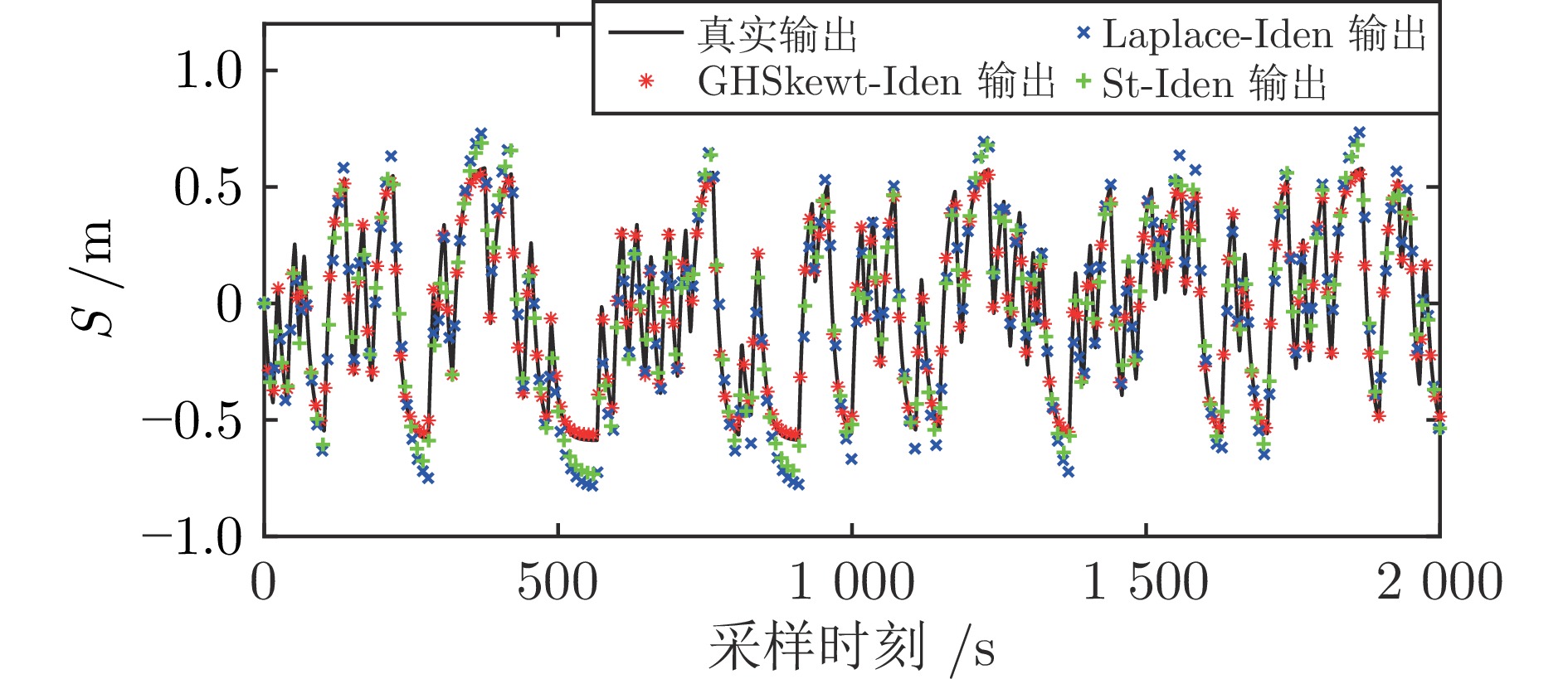
质量块位置 Laplace-Iden St-Iden GHSkewt-Iden RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ RMSE $ {\rm{R}}^2 $ $ {{S}} \ ({\rm{m}})$ 0.0894 0.9345 0.0674 0.9627 0.0148 0.9982 -
[1] Kodamana H, Huang B, Ranjan R, Zhao Y J, Tan R, Sammaknejad N. Approaches to robust process identification: A review and tutorial of probabilistic methods. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 66: 68−83 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2018.02.011 [2] 王国庆, 杨春雨, 马磊, 代伟. 基于高斯–广义双曲混合分布的非线性卡尔曼滤波. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 448−460Wang Guo-Qing, Yang Chun-Yu, Ma Lei, Dai Wei. Nonlinear Kalman filter based on Gaussian-generalized-hyperbolic mixing distribution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(2): 448−460 [3] Adeniran A A, El Ferik S. Modeling and identification of nonlinear systems: A review of the multimodel approach. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 47(7): 1149−1159 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2560147 [4] Chen X, Zhao S Y, Liu F. Robust identification of linear ARX models with recursive EM algorithm based on student's t-distribution. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2021, 358(1): 1103−1121 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.06.003 [5] Zhang J H, Zhang F, Chen M, Ding R Q, Xu B, Zong H Z. Parameter identification of hydraulic manipulators considering physical feasibility and control stability. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(1): 718−728 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3250753 [6] Yang X Q, Yin S, Kaynak O. Robust identification of LPV time-delay system with randomly missing measurements. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 48(12): 2198−2208 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2689920 [7] Hou J, Su H, Yu C Q, Chen F W, Li P H. Bias-correction errors-in-variables Hammerstein model identification. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(7): 7268−7279 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3199931 [8] Mohammad J M. Online system identification using fractional-order Hammerstein model with noise cancellation. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2023, 111: 7911−7940 doi: 10.1007/s11071-023-08249-5 [9] 刘鑫. 时滞取值概率未知下的线性时滞系统辨识方法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(10): 2136−2144Liu Xin. Identification of linear time-delay systems with unknown delay distributions in its value range. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(10): 2136−2144 [10] Liu X, Zhang T T, Liu X F. Robust identification method for LPV ARX systems and its application to a mechanical unit. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 164418−164428 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2952891 [11] Liu X P, Yang X Q. Variational identification of linearly parameterized nonlinear state-space systems. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2023, 31(4): 1844−1854 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2023.3249042 [12] Liu X, Yang X Q, Yin S. Nonlinear system identification with robust multiple model approach. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2020, 28(6): 2728−2735 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2947868 [13] Yang X Q, Lin X, Li Z. Multimodel approach to robust identification of multiple-input single-output nonlinear time-delay systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(4): 2413−2422 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2933030 [14] Baldacchino T, Worden K, Rowson J. Robust nonlinear system identification: Bayesian mixture of experts using the t-distribution. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 85: 977− 992 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.08.045 [15] Ferdowsi H, Jagannathan S, Zawodniok M. An online outlier identification and removal scheme for improving fault detection performance. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(5): 908−919 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2283456 [16] Pearson R K. Outliers in process modeling and identification. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2002, 10(1): 55−63 doi: 10.1109/87.974338 [17] Chen X, Zhao S, Liu F, Tao C B. Laplace distribution based online identification of linear systems with robust recursive expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(8): 9028−9036 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3225026 [18] Fang Y, Jeong M K. Robust probabilistic multivariate calibration model. Technometrics, 2008, 50(3): 305−316 doi: 10.1198/004017008000000073 [19] Jin X, Huang B. Robust identification of piecewise/switching autoregressive exogenous process. AIChE Journal, 2010, 56(7): 1829−1844 doi: 10.1002/aic.12112 [20] Yang X Q, Lu Y J, Yan Z B. Robust global identification of linear parameter varying systems with generalised expectation-maximisation algorithm. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2015, 9(7): 1103−1110 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2014.0694 [21] Yang X Q, Liu X, Yin S. Robust identification of nonlinear systems with missing observations: The case of state-space model structure. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(5): 2763−2774 doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2871194 [22] Liu X, Lou S C, Dai W. Further results on “System identification of nonlinear state-space models”. Automatica, 2023, (2): Article No. 110760 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110760 [23] Yang X Q, Liu X P, Xu C. Robust mixture probabilistic partial least squares model for soft sensing with multivariate Laplace distribution. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measureent, 2021, 70: 1−9 [24] Waheed A, Cai L. Alternative design for optical incremental encoder measurement systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology. Taipei, China: IEEE, 2016. 634−639 [25] Nurminen H, Ardeshiri T, Piche R, Gustafsson F. Skew-t filter and smoother with improved covariance matrix approximation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(21): 5618−5633 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2865434 [26] Aas K, Haff I H. The generalized hyperbolic skew student's t-distribution. Journal of Financial Econometrics, 2006, 4(2): 275−309 doi: 10.1093/jjfinec/nbj006 [27] Jouchi N, Yasuhiro O. Stochastic volatility model with leverage and asymmetrically heavy-tailed error using GHSkew student's t-distribution. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 2012, 56(11): 3690−3704 doi: 10.1016/j.csda.2010.07.012 [28] Bai M M, Huang Y L, Chen B D, Zhang Y G. A novel robust Kalman filtering framework based on normal-skew mixture distribution. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(11): 6789−6805 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3098299 [29] Hasegawa T, Yamaguchi R, Kakuta M, Ando M, Songee J, Tokuda I, et al. Application of state-space model with skew-t measurement noise to blood test value prediction. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 100: 365−378 doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2021.08.007 [30] Liu X, Wang C, Dai W. Probability-based identification of Hammerstein systems with asymmetric noise characteristics. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 1−11 [31] Jia J T, Guo K X, Li W S, Xiang Y, Guo L. Composite filtering for UWB-based localization of quadrotor UAV with skewed measurements and uncertain dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1−13 [32] Yu M, Yang X Q, Liu X P. LPV system identification with multiple-model approach based on shifted asymmetric Laplace distribution. International Journal of Systems Science, 2021, 52(7): 1452−1465 doi: 10.1080/00207721.2020.1859158 [33] Liu X P, Yang X Q. Identification of nonlinear state-space systems with skewed measurement noises. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(11): 4654−4662 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3193444 [34] Saha S. Noise robust online inference for linear dynamic systems. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(11): 1898−1902 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2437456 [35] Yang X Q, Lu Y J, Yan Z B. Robust global identification of linear parameter varying systems with generalised expectation-maximisation algorithm. Journal of Financial Econometrics, 2015, 9(7): 1103−1110 -




 下载:
下载: