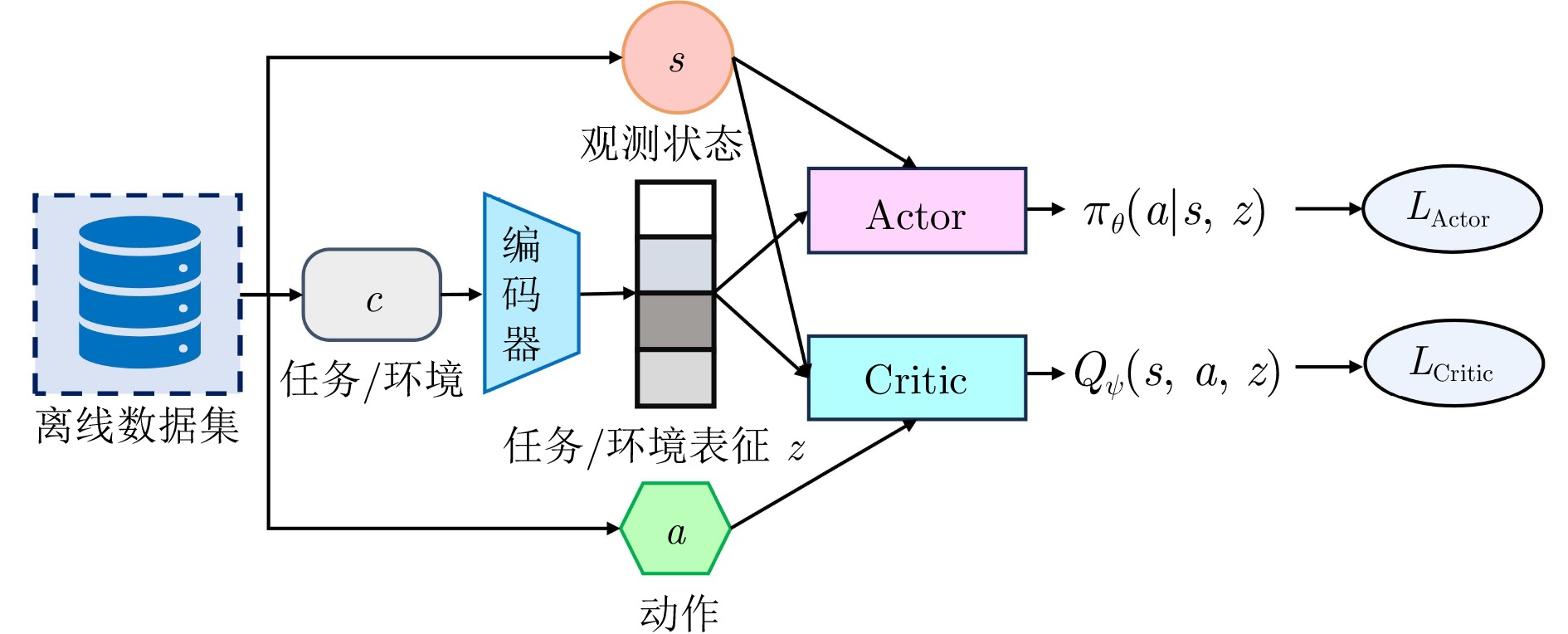
-
摘要: 强化学习(Reinforcement learning, RL)通过智能体与环境在线交互来学习最优策略, 近年来已成为解决复杂环境下感知决策问题的重要手段. 然而, 在线收集数据的方式可能会引发安全、时间或成本等问题, 极大限制了强化学习在实际中的应用. 与此同时, 原始数据的维度高且结构复杂, 解决复杂高维数据输入问题也是强化学习面临的一大挑战. 幸运的是, 基于表征学习的离线强化学习能够仅从历史经验数据中学习策略, 而无需与环境产生交互. 它利用表征学习技术将离线数据集中的特征表示为低维向量, 然后利用这些向量来训练离线强化学习模型. 这种数据驱动的方式为实现通用人工智能提供了新契机. 为此, 对近期基于表征学习的离线强化学习方法进行全面综述. 首先给出离线强化学习的形式化描述, 然后从方法、基准数据集、离线策略评估与超参数选择3个层面对现有技术进行归纳整理, 进一步介绍离线强化学习在工业、推荐系统、智能驾驶等领域中的研究动态. 最后, 对全文进行总结, 并探讨基于表征学习的离线强化学习未来所面临的关键挑战与发展趋势, 以期为后续的研究提供有益参考.Abstract: Reinforcement learning (RL), learning an optimal policy through online interaction between an agent and environment, has recently become an important tool to solve perceptual decision-making issues in complex environments. However, the online data collection may raise issues of security, time, or cost, greatly limiting the practical applications of reinforcement learning. Meanwhile, tackling intricate high-dimensional data input problems has also become a significant challenge for reinforcement learning due to the intricate and multifaceted nature of raw data. Fortunately, offline reinforcement learning based on representation learning can learn the policy only from historical experience data without interacting with the environment. It utilizes representation learning techniques to map the features of the offline dataset into low-dimensional vectors, which are subsequently employed to train the offline reinforcement learning model. This data-driven paradigm provides a new opportunity to realize the general artificial intelligence. To this end, this paper comprehensively reviews the recent research on offline reinforcement learning based on representation learning. Firstly, the problem setup of offline reinforcement learning is given. Then, the existing technologies are summarized from three aspects: Methodologies, benchmarks, offline policy evaluation and hyperparameter selection. Moreover, the study trends of offline reinforcement learning in industries, recommendation systems, intelligent driving, and other fields are introduced. Finally, the conclusion is drawn and the key challenges and development trends of offline reinforcement learning based on representation learning in the future are discussed, so as to provide a valuable reference for subsequent study.
-
表 1 基于表征学习的离线强化学习方法对比
Table 1 Comparison of offline reinforcement learning based on representation learning
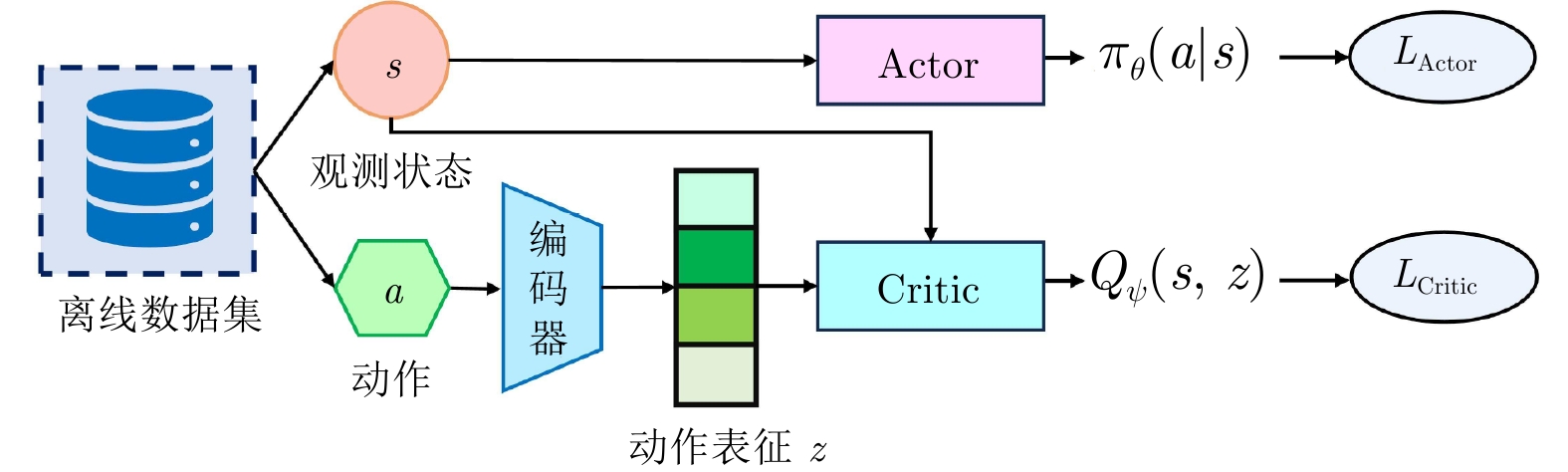
表征对象 参考文献 表征网络架构 环境建模方式 应用场景 特点 缺点 动作表征 [15−21] VAE 无模型 机器人控制、导航 状态条件下生成动作, 将目标
策略限制在行为策略范围内,
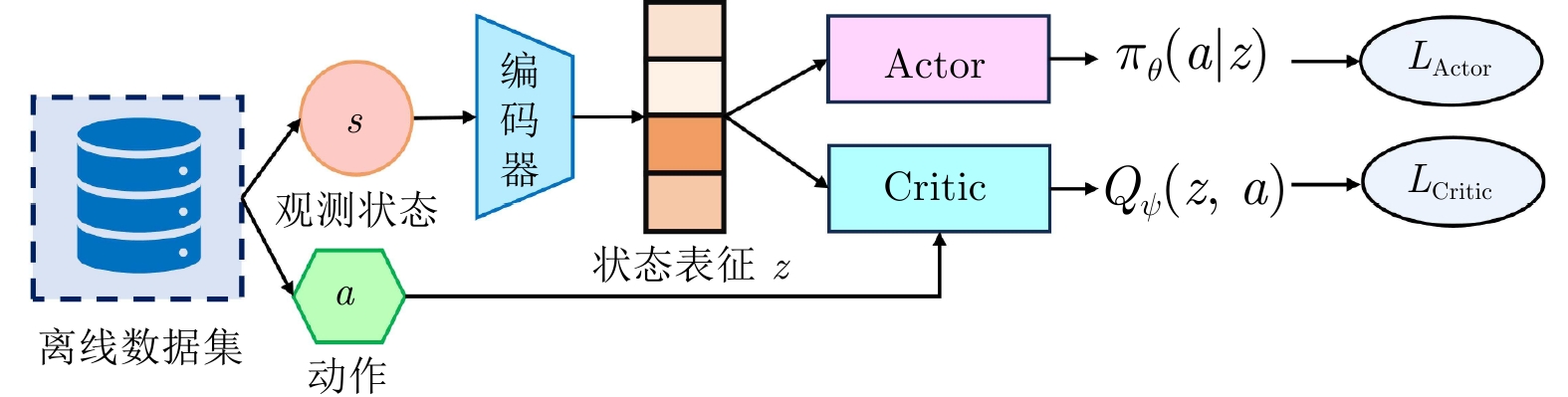
缓解分布偏移不适用于离散动作空间 [22−23] 流模型 [24−25] 扩散模型 状态表征 [26−27] VAE 无模型 基于视觉的机器人控制 压缩高维观测状态, 减少
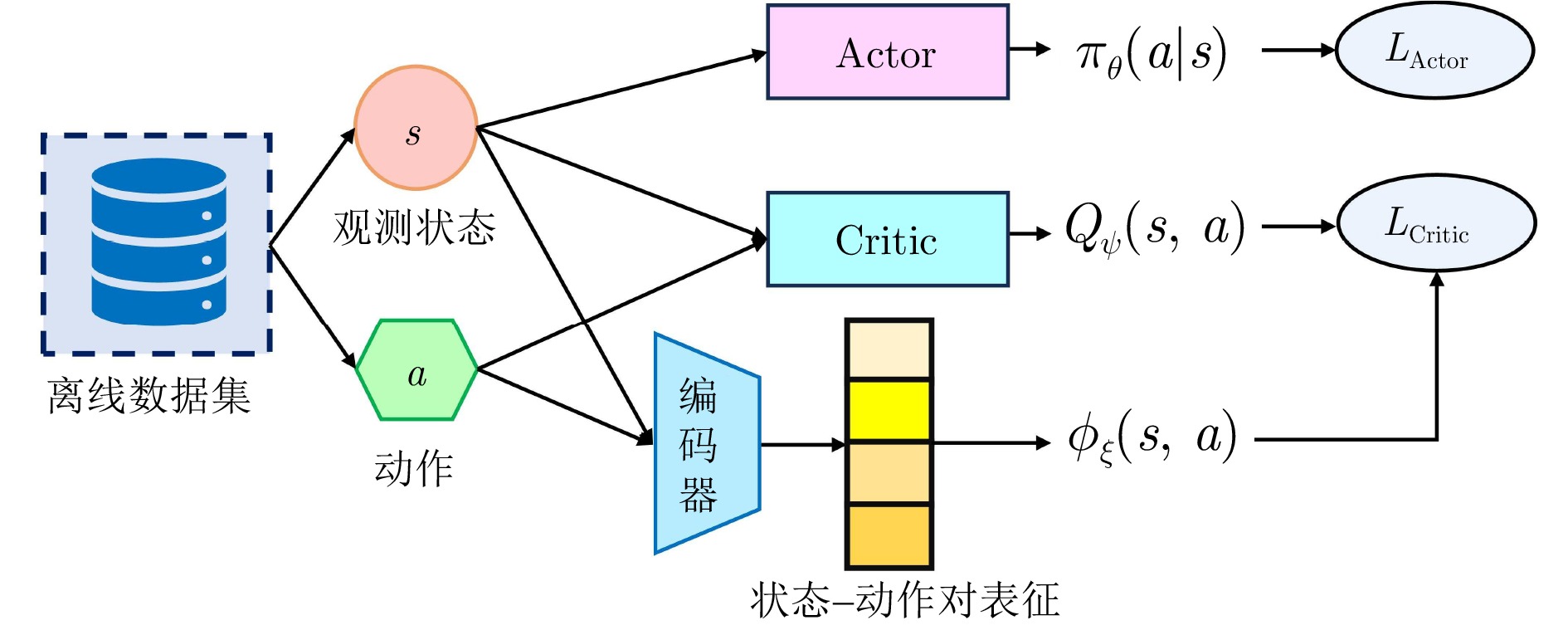
冗余信息, 提高泛化能力限定于图像(像素)输入 [28] VAE 基于模型 [29] GAN 基于模型 [30] 编码器架构 基于模型 [31−32] 编码器架构 无模型 状态−动作
对表征[33] 自编码器 基于模型 基于视觉的机器人控制、
游戏、自动驾驶学习状态−动作联合表征,
捕捉两者交互关系,
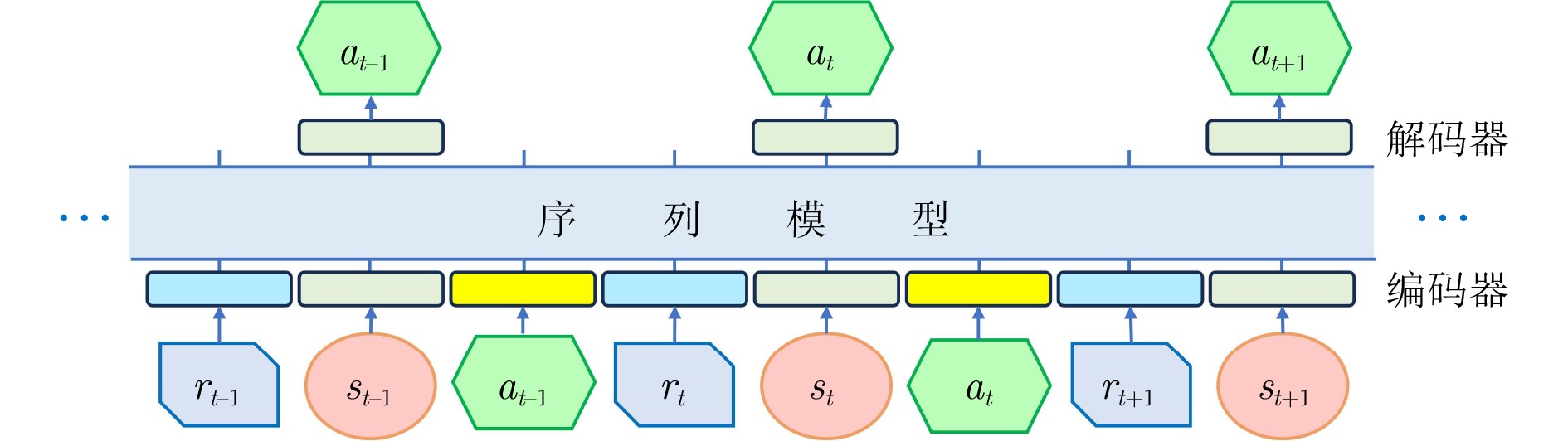
指导后续决策任务限定于图像(像素)输入 [34] VAE 基于模型 [35−36] 编码器架构 无模型 [37−38] 编码器架构 基于模型 轨迹表征 [39−44] Transformer 序列模型 机器人控制、导航、游戏 将强化学习视为条件序列建模
问题, 用于预测未来轨迹序列轨迹生成速度慢,
调优成本高[45−47] 扩散模型 任务表征 [48−49] 编码器架构 无模型 机器人控制、导航 借助元学习思想, 使智能体
快速适应新任务泛化能力依赖于任务或
环境之间的相似性环境表征 [50−51] 编码器架构 基于模型 表 2 离线强化学习基准数据集对比
Table 2 Comparison of benchmarking datasets for offline reinforcement learning
名称 领域 应用领域 数据集特性 RL Unplugged DeepMind控制套件 机器人连续控制 连续域, 探索难度由易到难 DeepMind运动套件 模拟啮齿动物的运动 连续域, 探索难度大 Atari 2600 视频游戏 离散域, 探索难度适中 真实世界强化学习套件 机器人连续控制 连续域, 探索难度由易到难 D4RL Maze2D 导航 非马尔科夫策略, 不定向与多任务数据 MiniGrid-FourRooms 导航, Maze2D的离散模拟 非马尔科夫策略, 不定向与多任务数据 AntMaze 导航 非马尔科夫策略, 稀疏奖励, 不定向与多任务数据 Gym-MuJoCo 机器人连续控制 次优数据, 狭窄数据分布 Adroit 机器人操作 非表示性策略, 狭窄数据分布, 稀疏奖励, 现实领域 Flow 交通流量控制管理 非表示性策略, 现实领域 FrankaKitchen 厨房机器人操作 不定向与多任务数据, 现实领域 CARLA 自动驾驶车道跟踪与导航 部分可观测性, 非表示性策略, 不定向与多任务数据, 现实领域 NeoRL Gym-MuJoCo 机器人连续控制 保守且数据量有限 工业基准 工业控制任务 高维连续状态和动作空间, 高随机性 FinRL 股票交易市场 高维连续状态和动作空间, 高随机性 CityLearn 不同类型建筑的储能控制 高维连续状态和动作空间, 高随机性 SalesPromotion 商品促销 由人工操作员与真实用户提供的数据 表 3 基于表征学习的离线强化学习应用综述
Table 3 Summarization of the applications for offline reinforcement learning based on representation learning
应用领域 文献 表征对象 表征网络架构 环境建模方式 所解决的实际问题 策略学习方法 工业 [68] 任务表征 编码器架构 无模型 工业连接器插入 从离线数据中元学习自适应策略 [104] 任务表征 编码器架构 无模型 工业连接器插入 利用域对抗神经网络的域不变性和变分信息瓶颈的
域特定信息流控制来实现策略泛化[67] 轨迹表征 Transformer 序列模型 工业芯片布局 采用因果自注意力掩码并通过自回归
输入标记来预测动作推荐系统 [57] 动作表征 VAE 基于模型 快速适应冷启动用户 利用逆强化学习从少量交互中恢复出
用户策略与奖励[60] 状态表征 编码器架构 基于模型 数据稀疏性 利用群体偏好注入的因果用户模型训练策略 [61] 状态表征 编码器架构 无模型 离线交互推荐 利用保守的Q函数来估计策略 智能驾驶 [58] 动作表征 VAE 无模型 交叉口生态驾驶控制 利用VAE生成动作 [69] 环境表征 VAE 基于模型 长视域任务 利用VAE生成动作 医疗 [63] 状态−动作对表征 编码器架构 基于模型 个性化诊断 使用在线模型预测控制方法选择策略 能源管理 [59] 动作表征 VAE 无模型 油电混动汽车能源利用效率 利用VAE生成动作 量化交易 [70] 环境表征 编码器架构 无模型 最优交易执行的过拟合问题 利用时序差分误差或策略梯度法来学习策略 -
[1] Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (Second edition). Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2018. [2] 孙悦雯, 柳文章, 孙长银. 基于因果建模的强化学习控制: 现状及展望. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 661−677Sun Yue-Wen, Liu Wen-Zhang, Sun Chang-Yin. Causality in reinforcement learning control: The state of the art and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 661−677 [3] Silver D, Huang A, Maddison C J, Guez A, Sifre L, van den Driessche G, et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 484−489 doi: 10.1038/nature16961 [4] Schrittwieser J, Antonoglou I, Hubert T, Simonyan K, Sifre L, Schmitt S, et al. Mastering atari, go, chess and shogi by planning with a learned model. Nature, 2020, 588(7839): 604−609 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03051-4 [5] Senior A W, Evans R, Jumper J, Kirkpatrick J, Sifre L, Green T, et al. Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning. Nature, 2020, 577(7792): 706−710 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1923-7 [6] Li Y J, Choi D, Chung J, Kushman N, Schrittwieser J, Leblond R, et al. Competition-level code generation with AlphaCode. Science, 2022, 378(6624): 1092−1097 doi: 10.1126/science.abq1158 [7] Degrave J, Felici F, Buchli J, Neunert M, Tracey B, Carpanese F, et al. Magnetic control of tokamak plasmas through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2022, 602(7897): 414−419 doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04301-9 [8] Fawzi A, Balog M, Huang A, Hubert T, Romera-Paredes B, Barekatain M, et al. Discovering faster matrix multiplication algorithms with reinforcement learning. Nature, 2022, 610(7930): 47−53 doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05172-4 [9] Fang X, Zhang Q C, Gao Y F, Zhao D B. Offline reinforcement learning for autonomous driving with real world driving data. In: Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). Macao, China: IEEE, 2022. 3417−3422 [10] 刘健, 顾扬, 程玉虎, 王雪松. 基于多智能体强化学习的乳腺癌致病基因预测. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(5): 1246−1258Liu Jian, Gu Yang, Cheng Yu-Hu, Wang Xue-Song. Prediction of breast cancer pathogenic genes based on multi-agent reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(5): 1246−1258 [11] Levine S, Kumar A, Tucker G, Fu J. Offline reinforcement learning: Tutorial, review, and perspectives on open problems. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2005.01643, 2020. [12] Prudencio R F, Maximo M R O A, Colombini E L. A survey on offline reinforcement learning: Taxonomy, review, and open problems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, DOI: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3250269 [13] 程玉虎, 黄龙阳, 侯棣元, 张佳志, 陈俊龙, 王雪松. 广义行为正则化离线Actor-Critic. 计算机学报, 2023, 46(4): 843−855 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.00843Cheng Yu-Hu, Huang Long-Yang, Hou Di-Yuan, Zhang Jia-Zhi, Chen Jun-Long, Wang Xue-Song. Generalized offline actor-critic with behavior regularization. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2023, 46(4): 843−855 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.00843 [14] 顾扬, 程玉虎, 王雪松. 基于优先采样模型的离线强化学习. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(1): 143−153Gu Yang, Cheng Yu-Hu, Wang Xue-Song. Offline reinforcement learning based on prioritized sampling model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(1): 143−153 [15] Fujimoto S, Meger D, Precup D. Off-policy deep reinforcement learning without exploration. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach, USA: PMLR, 2019. 2052−2062 [16] He Q, Hou X W, Liu Y. POPO: Pessimistic offline policy optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Singapore: IEEE, 2022. 4008−4012 [17] Wu J L, Wu H X, Qiu Z H, Wang J M, Long M S. Supported policy optimization for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 2268 [18] Lyu J F, Ma X T, Li X, Lu Z Q. Mildly conservative Q-learning for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 125 [19] Rezaeifar S, Dadashi R, Vieillard N, Hussenot L, Bachem O, Pietquin O, et al. Offline reinforcement learning as anti-exploration. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Virtual Event: AAAI Press, 2022. 8106−8114 [20] Zhou W X, Bajracharya S, Held D. PLAS: Latent action space for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 4th Conference on Robot Learning. Cambridge, USA: PMLR, 2020. 1719−1735 [21] Chen X, Ghadirzadeh A, Yu T H, Wang J H, Gao A, Li W Z, et al. LAPO: Latent-variable advantage-weighted policy optimization for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 2674 [22] Akimov D, Kurenkov V, Nikulin A, Tarasov D, Kolesnikov S. Let offline RL flow: Training conservative agents in the latent space of normalizing flows. In: Proceedings of Offline Reinforcement Learning Workshop at Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: OpenReview.net, 2022. [23] Yang Y Q, Hu H, Li W Z, Li S Y, Yang J, Zhao Q C, et al. Flow to control: Offline reinforcement learning with lossless primitive discovery. In: Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washington, USA: AAAI Press, 2023. 10843−10851 [24] Wang Z D, Hunt J J, Zhou M Y. Diffusion policies as an expressive policy class for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations. Kigali, Rwanda: OpenReview.net, 2023. [25] Chen H Y, Lu C, Ying C Y, Su H, Zhu J. Offline reinforcement learning via high-fidelity generative behavior modeling. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations. Kigali, Rwanda: OpenReview.net, 2023. [26] Zhang H C, Shao J Z, Jiang Y H, He S C, Zhang G W, Ji X Y. State deviation correction for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Virtual Event: AAAI Press, 2022. 9022−9030 [27] Weissenbacher M, Sinha S, Garg A, Kawahara Y. Koopman Q-learning: Offline reinforcement learning via symmetries of dynamics. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 23645−23667 [28] Rafailov R, Yu T H, Rajeswaran A, Finn C. Offline reinforcement learning from images with latent space models. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Annual Conference on Learning for Dynamics and Control. Zurich, Switzerland: PMLR, 2021. 1154−1168 [29] Cho D, Shim D, Kim H J. S2P: State-conditioned image synthesis for data augmentation in offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 838 [30] Gieselmann R, Pokorny F T. An expansive latent planner for long-horizon visual offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the RSS 2023 Workshop on Learning for Task and Motion Planning. Daegu, South Korea: OpenReview.net, 2023. [31] Zang H Y, Li X, Yu J, Liu C, Islam R, Combes R T D, et al. Behavior prior representation learning for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations. Kigali, Rwanda: OpenReview.net, 2023. [32] Mazoure B, Kostrikov I, Nachum O, Tompson J. Improving zero-shot generalization in offline reinforcement learning using generalized similarity functions. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 1819 [33] Kim B, Oh M H. Model-based offline reinforcement learning with count-based conservatism. In: Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning. Honolulu, USA: PMLR, 2023. 16728−16746 [34] Tennenholtz G, Mannor S. Uncertainty estimation using riemannian model dynamics for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 1381 [35] Ada S E, Oztop E, Ugur E. Diffusion policies for out-of-distribution generalization in offline reinforcement learning. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(4): 3116−3123 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3363530 [36] Kumar A, Agarwal R, Ma T Y, Courville A C, Tucker G, Levine S. DR3: Value-based deep reinforcement learning requires explicit regularization. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2022. [37] Lee B J, Lee J, Kim K E. Representation balancing offline model-based reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2021. [38] Chang J D, Wang K W, Kallus N, Sun W. Learning bellman complete representations for offline policy evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 2938−2971 [39] Chen L L, Lu K, Rajeswaran A, Lee K, Grover A, Laskin M, et al. Decision transformer: Reinforcement learning via sequence modeling. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Virtual Event: Curran Associates, Inc., 2021. 15084−15097 [40] Janner M, Li Q Y, Levine S. Offline reinforcement learning as one big sequence modeling problem. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Virtual Event: Curran Associates, Inc., 2021. 1273−1286 [41] Furuta H, Matsuo Y, Gu S S. Generalized decision transformer for offline hindsight information matching. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2022. [42] Liu Z X, Guo Z J, Yao Y H, Cen Z P, Yu W H, Zhang T N, et al. Constrained decision transformer for offline safe reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning. Honolulu, USA: JMLR.org, 2023. Article No. 893 [43] Wang Y Q, Xu M D, Shi L X, Chi Y J. A trajectory is worth three sentences: Multimodal transformer for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 39th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Pittsburgh, USA: JMLR.org, 2023. Article No. 208 [44] Zeng Z L, Zhang C, Wang S J, Sun C. Goal-conditioned predictive coding for offline reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2307.03406, 2023. [45] Janner M, Du Y L, Tenenbaum J B, Levine S. Planning with diffusion for flexible behavior synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 9902−9915 [46] Ajay A, Du Y L, Gupta A, Tenenbaum J B, Jaakkola T S, Agrawal P. Is conditional generative modeling all you need for decision making? In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations. Kigali, Rwanda: OpenReview.net, 2023. [47] Liang Z X, Mu Y, Ding M Y, Ni F, Tomizuka M, Luo P. AdaptDiffuser: Diffusion models as adaptive self-evolving planners. In: Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning. Honolulu, USA: JMLR.org, 2023. Article No. 854 [48] Yuan H Q, Lu Z Q. Robust task representations for offline meta-reinforcement learning via contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 25747−25759 [49] Zhao C Y, Zhou Z H, Liu B. On context distribution shift in task representation learning for online meta RL. In: Proceedings of the 19th Advanced Intelligent Computing Technology and Applications. Zhengzhou, China: Springer, 2023. 614−628 [50] Chen X H, Yu Y, Li Q Y, Luo F M, Qin Z W, Shang W J, et al. Offline model-based adaptable policy learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Virtual Event: Curran Associates, Inc., 2021. 8432−8443 [51] Sang T, Tang H Y, Ma Y, Hao J Y, Zheng Y, Meng Z P, et al. PAnDR: Fast adaptation to new environments from offline experiences via decoupling policy and environment representations. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vienna, Austria: IJCAI, 2022. 3416−3422 [52] Lou X Z, Yin Q Y, Zhang J G, Yu C, He Z F, Cheng N J, et al. Offline reinforcement learning with representations for actions. Information Sciences, 2022, 610: 746−758 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.08.019 [53] Kingma D P, Welling M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations. Banff, Canada: ICLR, 2014. [54] Mark M S, Ghadirzadeh A, Chen X, Finn C. Fine-tuning offline policies with optimistic action selection. In: Proceedings of NeurIPS Workshop on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2022. [55] 张博玮, 郑建飞, 胡昌华, 裴洪, 董青. 基于流模型的缺失数据生成方法在剩余寿命预测中的应用. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 185−196Zhang Bo-Wei, Zheng Jian-Fei, Hu Chang-Hua, Pei Hong, Dong Qing. Missing data generation method based on flow model and its application in remaining life prediction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 185−196 [56] Yang L, Zhang Z L, Song Y, Hong S D, Xu R S, Zhao Y, et al. Diffusion models: A comprehensive survey of methods and applications. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 56(4): Article No. 105 [57] Wang Y N, Ge Y, Li L, Chen R, Xu T. Offline meta-level model-based reinforcement learning approach for cold-start recommendation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2012.02476, 2020. [58] 张健, 姜夏, 史晓宇, 程健, 郑岳标. 基于离线强化学习的交叉口生态驾驶控制. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(4): 762−769 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2022.04.018Zhang Jian, Jiang Xia, Shi Xiao-Yu, Cheng Jian, Zheng Yue-Biao. Offline reinforcement learning for eco-driving control at signalized intersections. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(4): 762−769 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2022.04.018 [59] He H W, Niu Z G, Wang Y, Huang R C, Shou Y W. Energy management optimization for connected hybrid electric vehicle using offline reinforcement learning. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 72: Article No. 108517 doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.108517 [60] Nie W Z, Wen X, Liu J, Chen J W, Wu J C, Jin G Q, et al. Knowledge-enhanced causal reinforcement learning model for interactive recommendation. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 1129−1142 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3276505 [61] Zhang R Y, Yu T, Shen Y L, Jin H Z. Text-based interactive recommendation via offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Virtual Event: AAAI Press, 2022. 11694−11702 [62] Rigter M, Lacerda B, Hawes N. RAMBO-RL: Robust adversarial model-based offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. 16082−16097 [63] Agarwal A, Alomar A, Alumootil V, Shah D, Shen D, Xu Z, et al. PerSim: Data-efficient offline reinforcement learning with heterogeneous agents via personalized simulators. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Virtual Event: Curran Associates, Inc., 2021. 18564−18576 [64] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A N, et al. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 6000−6010 [65] Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X H, Unterthiner T, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2021. [66] 王雪松, 王荣荣, 程玉虎. 安全强化学习综述. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(9): 1813−1835Wang Xue-Song, Wang Rong-Rong, Cheng Yu-Hu. Safe reinforcement learning: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(9): 1813−1835 [67] Lai Y, Liu J X, Tang Z T, Wang B, Hao J Y, Luo P. ChiPFormer: Transferable chip placement via offline decision transformer. In: Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning. Honolulu, USA: PMLR, 2023. 18346−18364 [68] Zhao T Z, Luo J L, Sushkov O, Pevceviciute R, Heess N, Scholz J, et al. Offline meta-reinforcement learning for industrial insertion. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Philadelphia, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6386−6393 [69] Li Z N, Nie F, Sun Q, Da F, Zhao H. Boosting offline reinforcement learning for autonomous driving with hierarchical latent skills. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2309.13614, 2023. [70] Zhang C H, Duan Y T, Chen X Y, Chen J Y, Li J, Zhao L. Towards generalizable reinforcement learning for trade execution. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Macao, China: IJCAI, 2023. Article No. 553 [71] Gulcehre C, Wang Z Y, Novikov A, Le Paine T, Colmenarejo S G, Zołna K, et al. RL unplugged: A suite of benchmarks for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 608 [72] Fu J, Kumar A, Nachum O, Tucker G, Levine S. D4RL: Datasets for deep data-driven reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.07219, 2020. [73] Qin R J, Zhang X Y, Gao S Y, Chen X H, Li Z W, Zhang W N, et al. NeoRL: A near real-world benchmark for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 1795 [74] Song H F, Abdolmaleki A, Springenberg J T, Clark A, Soyer H, Rae J W, et al. V-MPO: On-policy maximum a posteriori policy optimization for discrete and continuous control. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Open Review.net, 2020. [75] Merel J, Hasenclever L, Galashov A, Ahuja A, Pham V, Wayne G, et al. Neural probabilistic motor primitives for humanoid control. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations. New Orleans, USA: OpenReview.net, 2019. [76] Merel J, Aldarondo D, Marshall J, Tassa Y, Wayne G, Olveczky B. Deep neuroethology of a virtual rodent. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: OpenReview.net, 2020. [77] Machado M C, Bellemare M G, Talvitie E, Veness J, Hausknecht M, Bowling M. Revisiting the arcade learning environment: Evaluation protocols and open problems for general agents. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2018, 61: 523−562 doi: 10.1613/jair.5699 [78] Dulac-Arnold G, Levine N, Mankowitz D J, Li J, Paduraru C, Gowal S, et al. An empirical investigation of the challenges of real-world reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2003.11881, 2020. [79] Abdolmaleki A, Springenberg J T, Tassa Y, Munos R, Heess N, Riedmiller M A. Maximum a posteriori policy optimisation. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: OpenReview.net, 2018. [80] Pomerleau D A. ALVINN: An autonomous land vehicle in a neural network. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, USA: MIT Press, 1988. 305−313 [81] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Rusu A A, Veness J, Bellemare M G, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529−533 doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [82] Barth-Maron G, Hoffman M W, Budden D, Dabney W, Horgan D, Dhruva T B, et al. Distributed distributional deterministic policy gradients. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: OpenReview.net, 2018. [83] Dabney W, Ostrovski G, Silver D, Munos R. Implicit quantile networks for distributional reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. 1104−1113 [84] Wu Y F, Tucker G, Nachum O. Behavior regularized offline reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1911.11361, 2019. [85] Siegel N, Springenberg J T, Berkenkamp F, Abdolmaleki A, Neunert M, Lampe T, et al. Keep doing what worked: Behavior modelling priors for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: OpenReview.net, 2020. [86] Agarwal A, Schuurmans D, Norouzi M. An optimistic perspective on offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Virtual Event: PMLR, 2020. 104−114 [87] Haarnoja T, Zhou A, Abbeel P, Levine S. Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. 1856−1865 [88] Kumar A, Fu J, Soh M, Tucker G, Levine S. Stabilizing off-policy Q-learning via bootstrapping error reduction. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates, Inc., 2019. 11761−11771 [89] Peng X B, Kumar A, Zhang G, Levine S. Advantage-weighted regression: Simple and scalable off-policy reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1910.00177, 2019. [90] Kumar A, Zhou A, Tucker G, Levine S. Conservative Q-learning for offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 100 [91] Nachum O, Dai B, Kostrikov I, Chow Y, Li L H, Schuurmans D. AlgaeDICE: Policy gradient from arbitrary experience. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1912.02074, 2019. [92] Wang Z Y, Novikov A, Żołna K, Springenberg J T, Reed S, Shahriari B, et al. Critic regularized regression. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 651 [93] Matsushima T, Furuta H, Matsuo Y, Nachum O, Gu S X. Deployment-efficient reinforcement learning via model-based offline optimization. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2021. [94] Yu T H, Thomas G, Yu L T, Ermon S, Zou J, Levine S, et al. MOPO: Model-based offline policy optimization. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 1185 [95] Le H M, Voloshin C, Yue Y S. Batch policy learning under constraints. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach, USA: PMLR, 2019. 3703−3712 [96] Koller D, Friedman N. Probabilistic Graphical Models: Principles and Techniques. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2009. [97] 王硕汝, 牛温佳, 童恩栋, 陈彤, 李赫, 田蕴哲, 等. 强化学习离线策略评估研究综述. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(9): 1926−1945 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.01926Wang Shuo-Ru, Niu Wen-Jia, Tong En-Dong, Chen Tong, Li He, Tian Yun-Zhe, et al. Research on off-policy evaluation in reinforcement learning: A survey. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2022, 45(9): 1926−1945 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.01926 [98] Fu J, Norouzi M, Nachum O, Tucker G, Wang Z Y, Novikov A, et al. Benchmarks for deep off-policy evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2021. [99] Schweighofer K, Dinu M, Radler A, Hofmarcher M, Patil V P, Bitto-nemling A, et al. A dataset perspective on offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Lifelong Learning Agents. McGill University, Canada: PMLR, 2022. 470−517 [100] Konyushkova K, Chen Y T, Paine T, Gülçehre C, Paduraru C, Mankowitz D J, et al. Active offline policy selection. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Virtual Event: Curran Associates, Inc., 2021. 24631−24644 [101] Kurenkov V, Kolesnikov S. Showing your offline reinforcement learning work: Online evaluation budget matters. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 11729−11752 [102] Lu C, Ball P J, Parker-Holder J, Osborne M A, Roberts S J. Revisiting design choices in offline model based reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2022. [103] Hu H, Yang Y Q, Zhao Q C, Zhang C J. On the role of discount factor in offline reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 9072−9098 [104] Nair A, Zhu B, Narayanan G, Solowjow E, Levine S. Learning on the job: Self-rewarding offline-to-online finetuning for industrial insertion of novel connectors from vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). London, United Kingdom: The IEEE, 2023. 7154−7161 [105] Kostrikov I, Nair A, Levine S. Offline reinforcement learning with implicit Q-learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2022. -




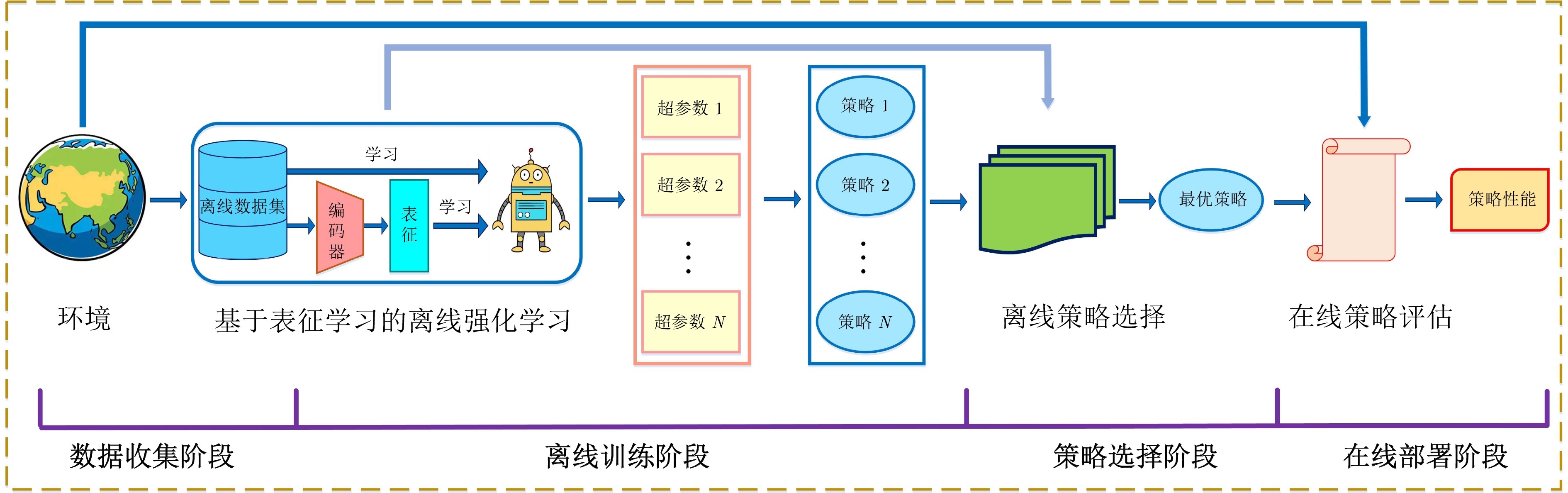
 下载:
下载: