-
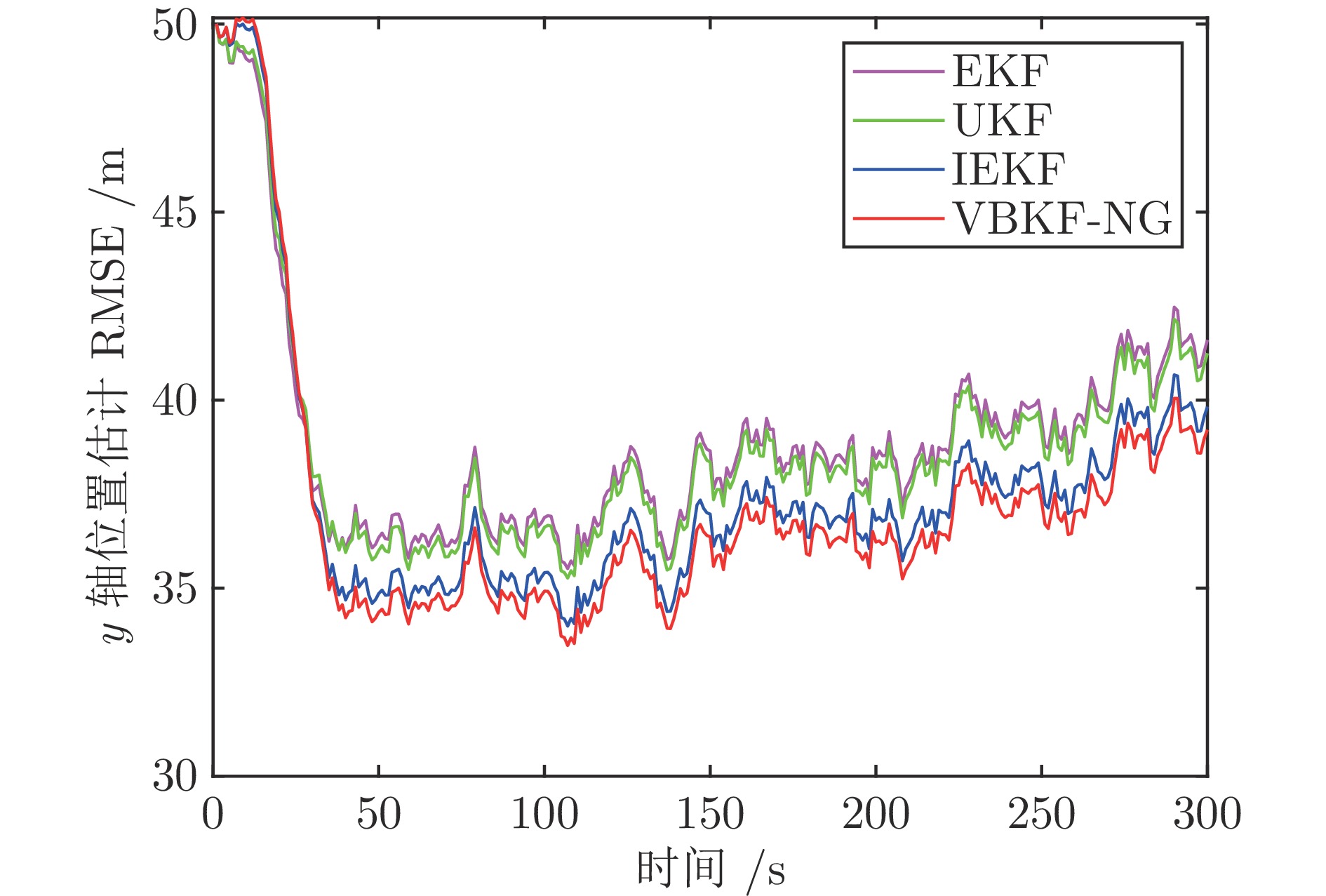
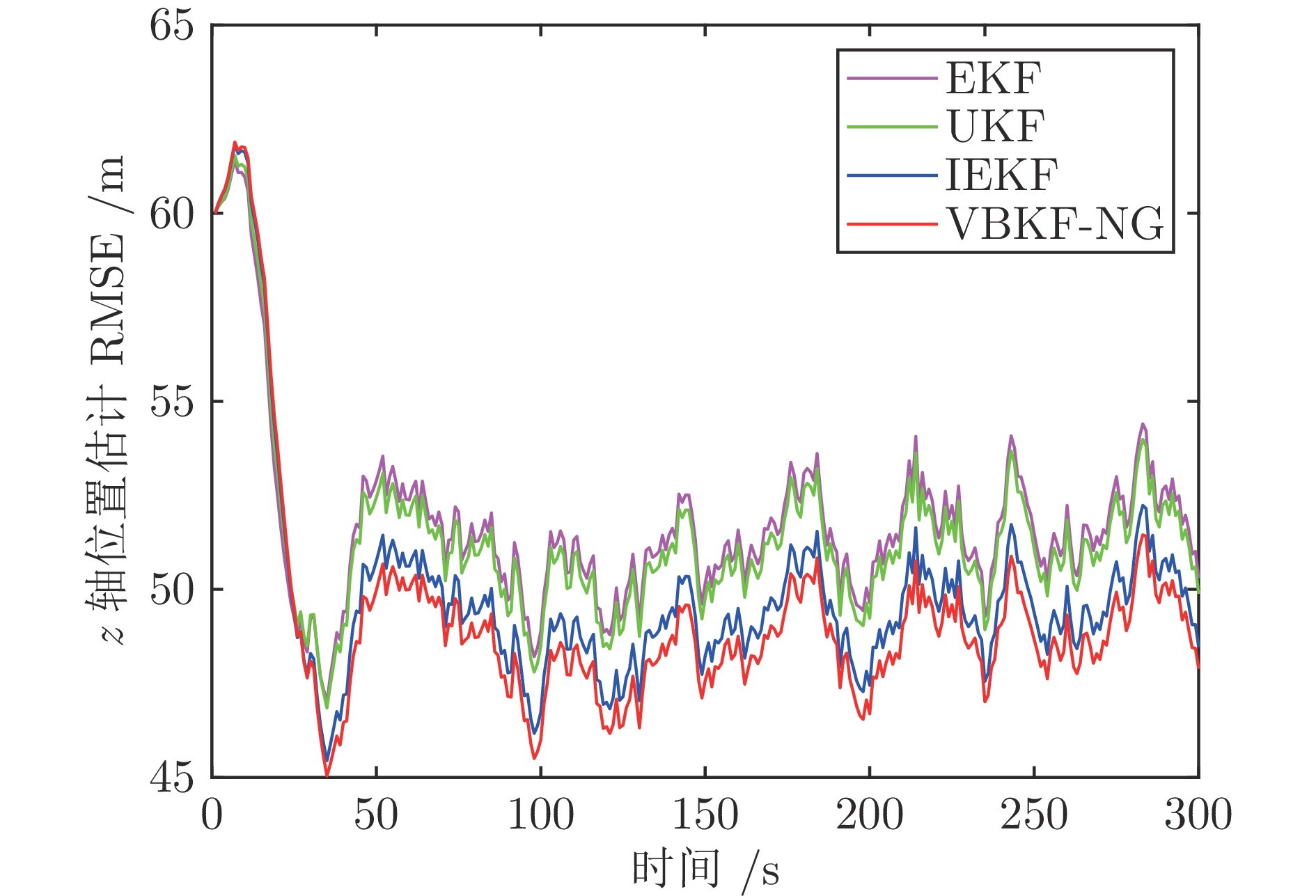
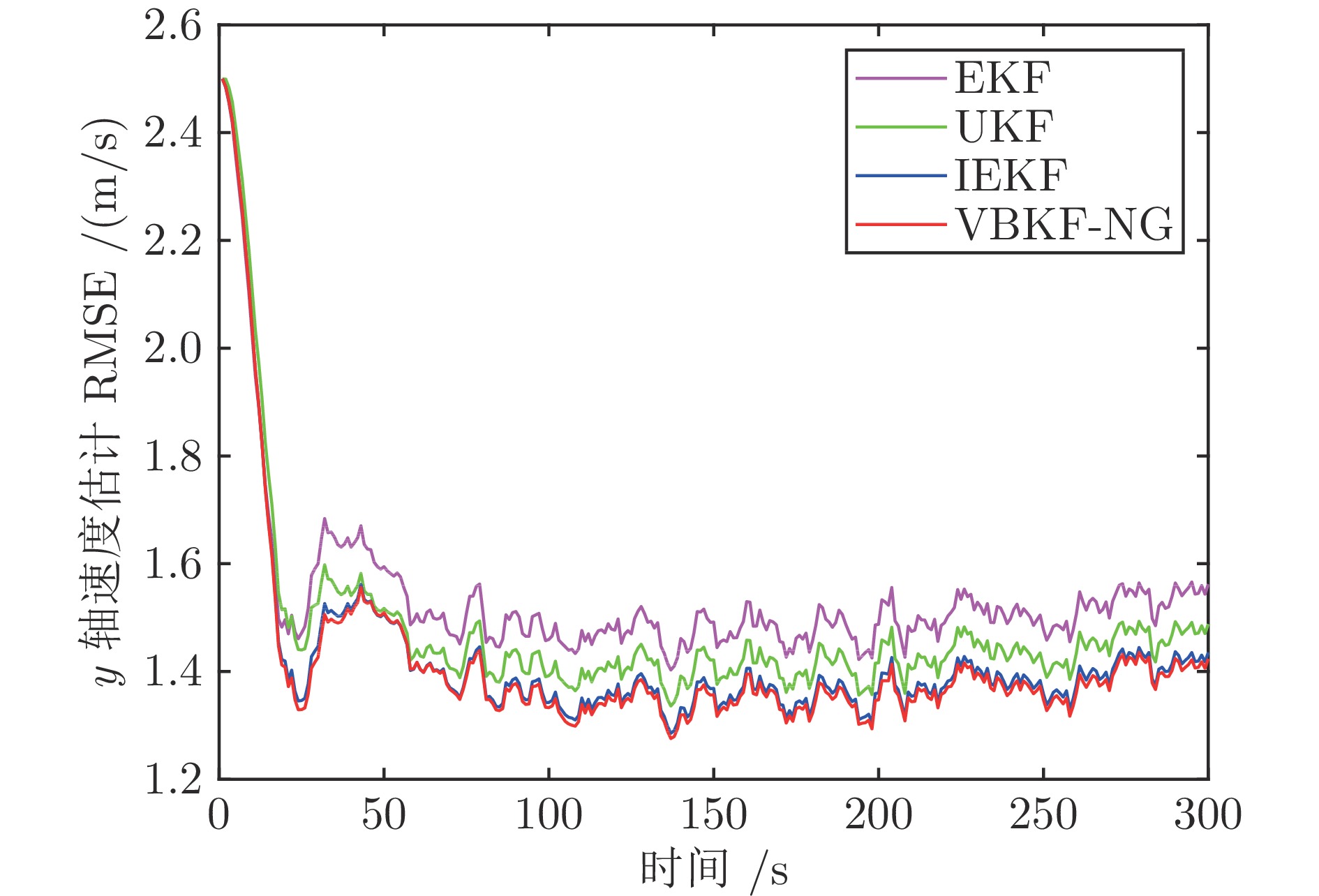
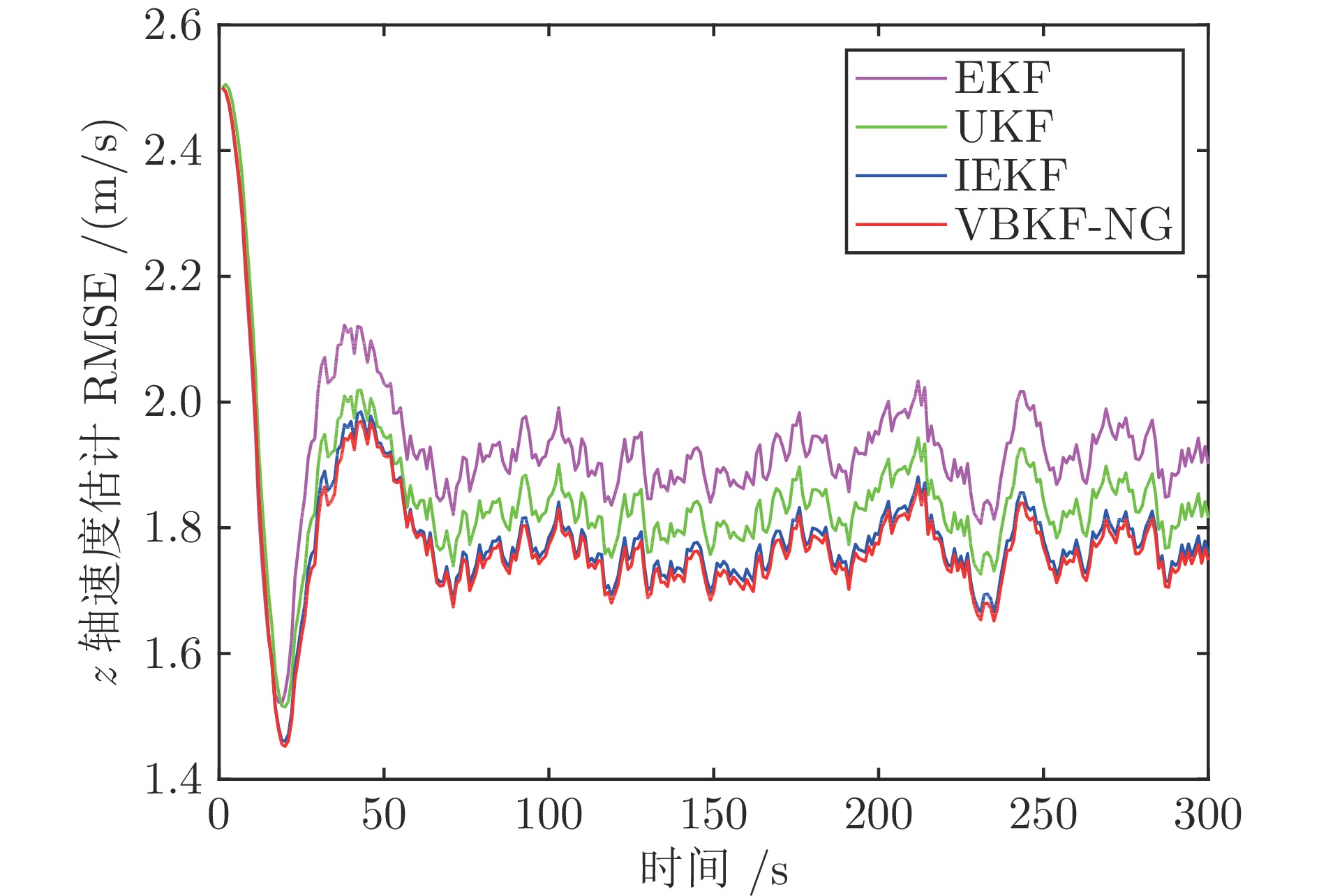
摘要: 在统计流形空间中, 从信息几何角度考虑非线性状态后验分布近似的实质是后验分布与相应参数化变分分布之间的Kullback-Leibler (KL)散度最小化问题, 同时也可以转化为变分置信下界的最大化问题. 为了提升非线性系统状态估计的精度, 在高斯系统假设条件下结合变分贝叶斯(Variational Bayes, VB)推断和Fisher信息矩阵推导出置信下界的自然梯度, 并通过分析其信息几何意义, 阐述在统计流形空间中置信下界沿其方向不断迭代增大, 实现变分分布与后验分布的“紧密”近似; 在此基础上, 以状态估计及其误差协方差作为变分超参数, 结合最优估计理论给出一种基于自然梯度的非线性变分贝叶斯滤波算法; 最后, 通过天基光学传感器量测条件下近地轨道卫星跟踪定轨和纯角度被动传感器量测条件下运动目标跟踪仿真实验验证, 与对比算法相比, 所提算法具有更高的精度.
-
关键词:
- 非线性滤波 /
- 信息几何 /
- 变分贝叶斯推断 /
- 自然梯度 /
- Fisher信息矩阵
Abstract: In statistical manifold space, the essence of nonlinear state posterior distribution approximation from the perspective of information geometry is minimizing Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between posterior distribution and the corresponding approximated distribution; Meanwhile, it is equivalent to maximizing evidence low bound. Aiming at the problem of improving the estimation accuracy of nonlinear system state, the natural gradient of evidence lower bound is derived under Gaussian system assumption by combining with Fisher information matrix and variational Bayesian (VB) inference, which produces a faster movement direction to the posterior distribution, and realizing a close approximation between variational distribution and the posterior. On this basis, a variational Bayesian Kalman filtering algorithm using natural gradient is proposed for updating the variational hyperparameters of state estimation and the associated error covariance. Simulations in low earth orbit target tracking system with space-based optical sensors and bearing-only target tracking system are presented verifying that the proposed algorithm has higher accuracy than the comparison algorithms. -
表 1 文中变量和符号含义
Table 1 The meaning of variables and symbols
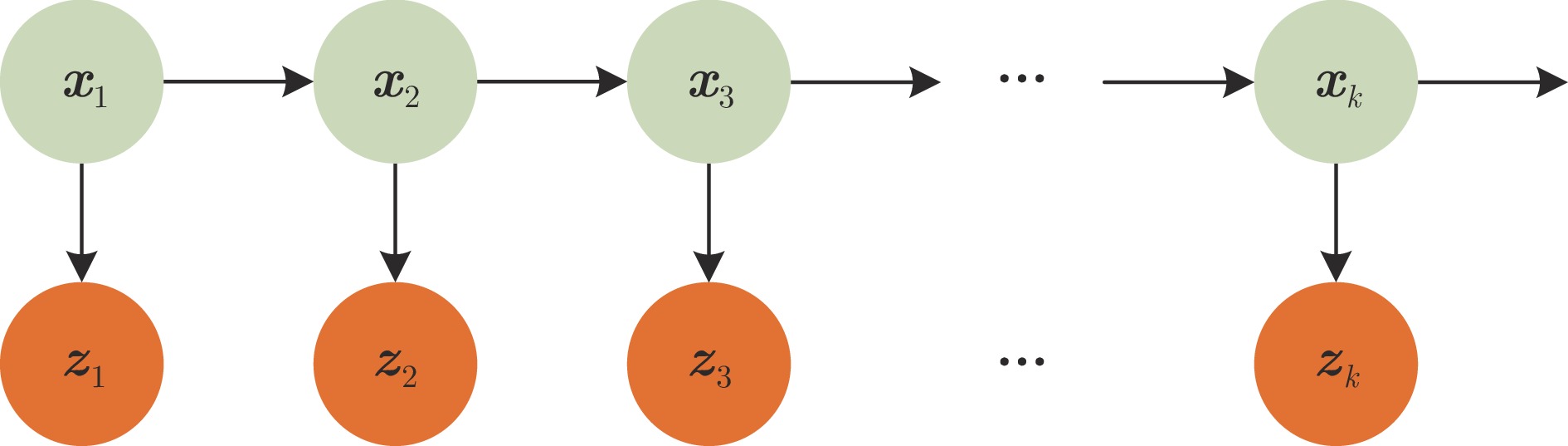
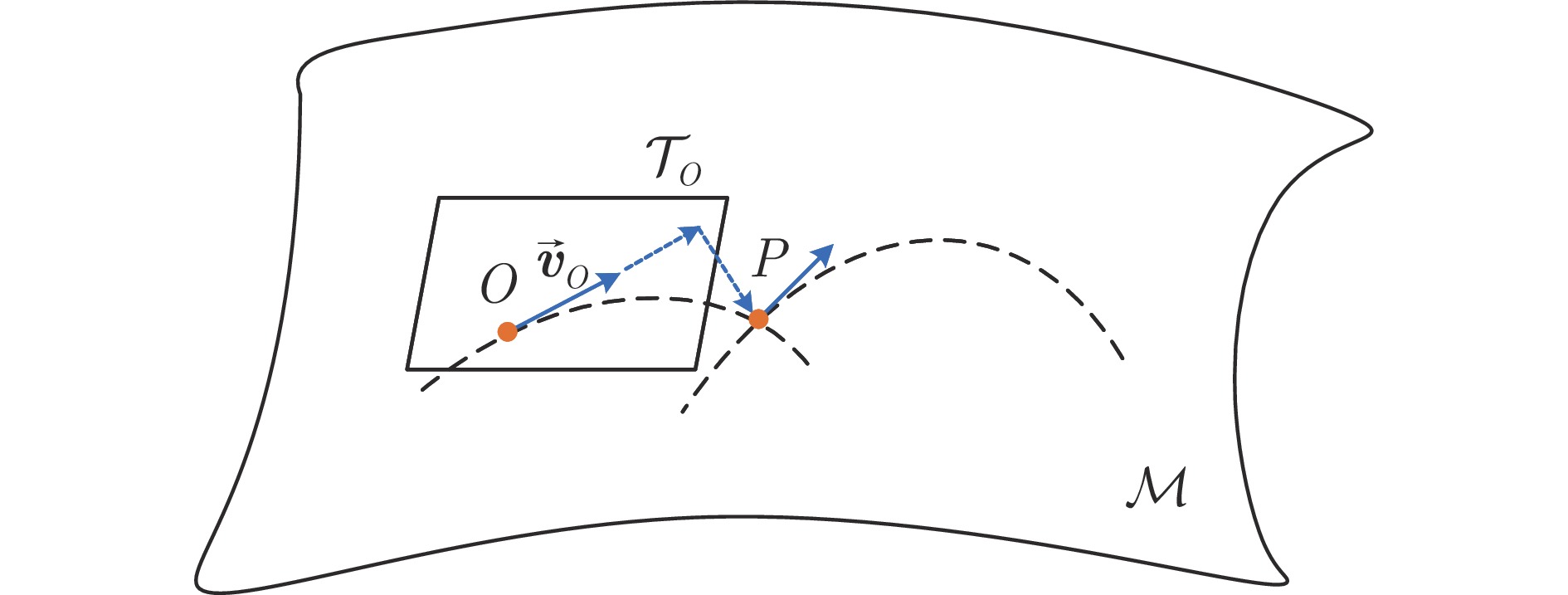
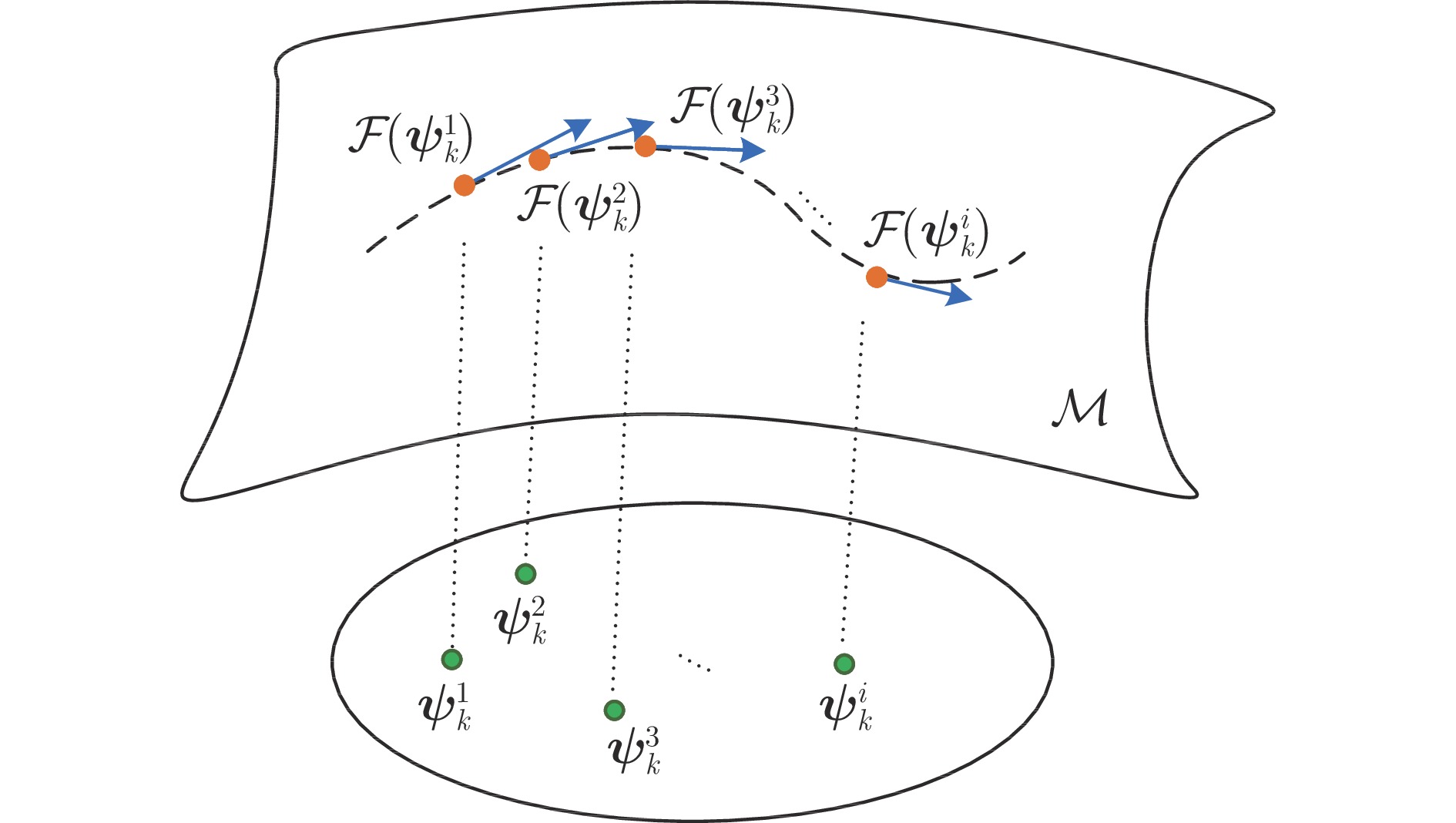
变量 符号含义 $ {\boldsymbol x}_k $ $ k $时刻目标状态真实值 $ {\boldsymbol x}_{k|k} $ $ k $时刻目标状态估计值 $ {\boldsymbol P}_{k|k} $ $ k $时刻目标状态估计误差协方差 $ {\boldsymbol z}_k $ 传感器在$ k $时刻的量测值 $ {\boldsymbol\omega}_k $ $ k $时刻的系统噪声 $ {\boldsymbol\upsilon}_k $ $ k $时刻的量测噪声 $ {\boldsymbol Q}_k $ $ k $时刻系统噪声方差 $ {\boldsymbol R}_k $ $ k $时刻量测噪声方差 $ d_x $ 目标状态向量的维数 $ d_z $ 量测向量的维数 $ {\boldsymbol F}_{k|k-1} $ $ k-1 $时刻到$ k $时刻的状态转移矩阵 $ {\boldsymbol H}_{k} $ $ k $时刻量测矩阵 $ {\boldsymbol\psi}_{k} $ 变分分布参数 $ p\left({\boldsymbol x}_k|{\boldsymbol z}_{k}\right) $ $ k $时刻目标状态后验分布 $ q\left({\boldsymbol x}_k|{\boldsymbol\psi}_{k}\right) $ 以$ {\boldsymbol\psi}_{k} $为参数的变分分布 $ \mathcal{L}\left({\boldsymbol\psi}_{k}\right) $ 以$ {\boldsymbol\psi}_{k} $为变分分布参数的置信下界 ${\cal{D}}\left(q\left({\boldsymbol x}_k|{\boldsymbol\psi}_{k}\right)|| p\left({\boldsymbol x}_k|{\boldsymbol z}_{k}\right)\right)$ 变分分布$ q\left({\boldsymbol x}_k|{\boldsymbol\psi}_{k}\right) $与状态后验分布$ p\left({\boldsymbol x}_k|{\boldsymbol z}_{k}\right) $的KL散度 $ {\boldsymbol J}_{{\boldsymbol\psi}_k} $ 以$ {{\boldsymbol\psi}_k} $为参数的 Fisher 信息矩阵 $ \mathcal{M} $ 流形空间 $ \mathcal{S} $ 流形空间中的概率分布集合 $ \mathcal{F} $ 流形空间中的平滑映射函数 ${{\boldsymbol v} }_{OP}$ 流形空间中的$ O $点处指向$ P $点的切向量 $|{{\boldsymbol v} }_{OP}|$ 切向量${{\boldsymbol v} }_{OP}$的模 表 2 目标的轨道根数
Table 2 The orbital elements of target
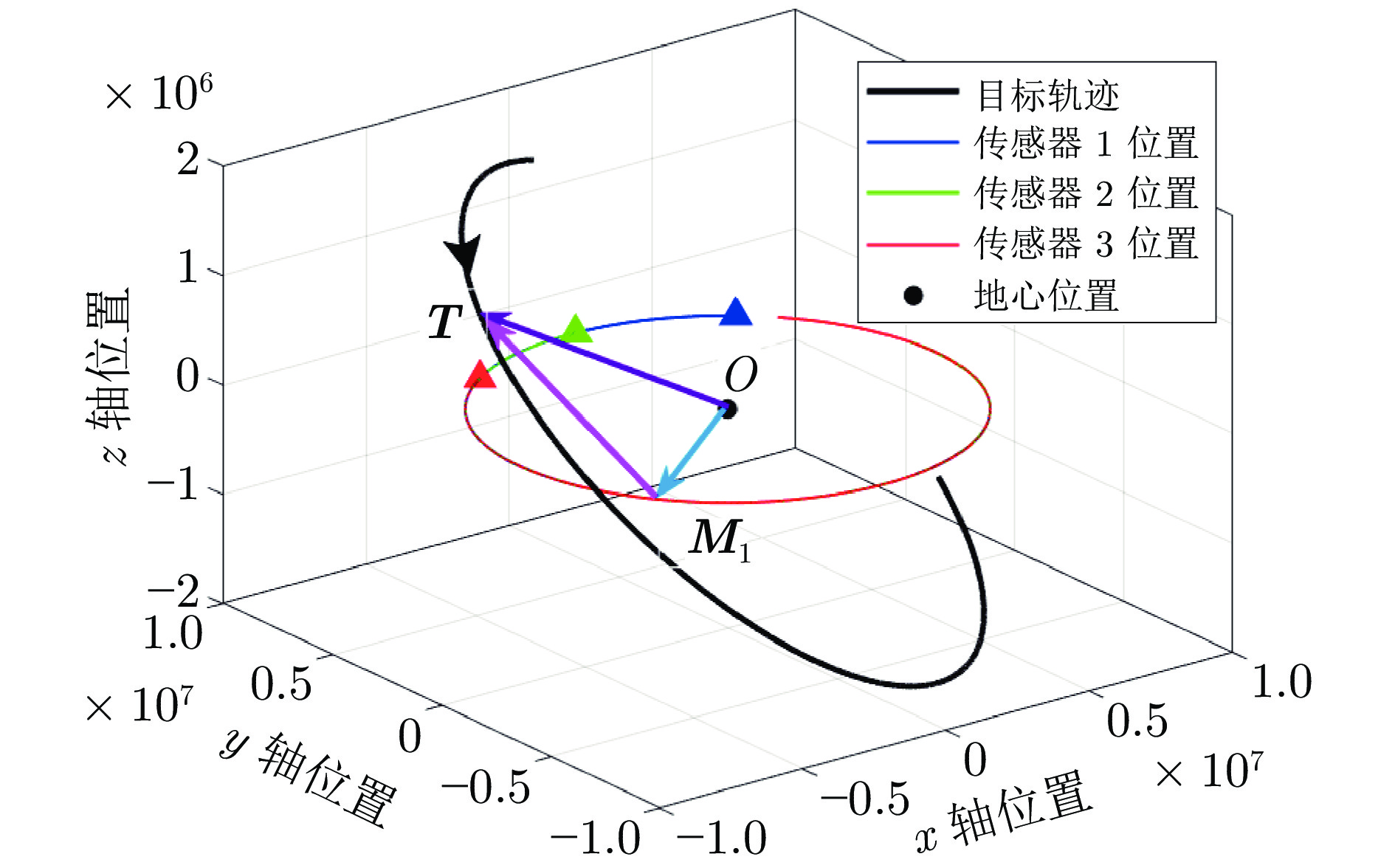
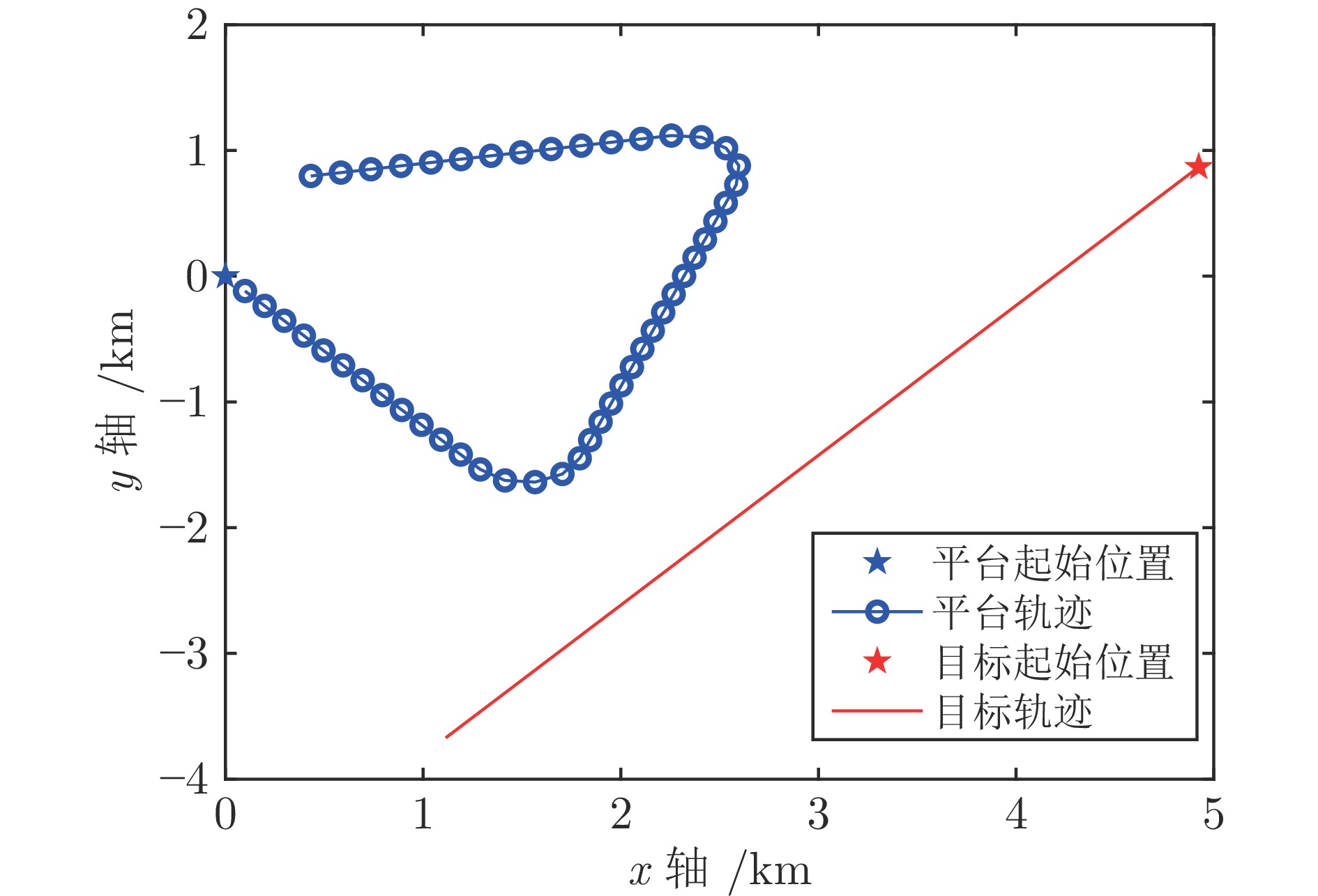
半长轴 (km) 离心率 倾角 (deg) 近地点角 (deg) 升交点赤经 (deg) 7500 0.1 15 30 12 表 3 算法平均估计误差均值的对比
Table 3 Comparison of the mean estimation errors of the algorithm
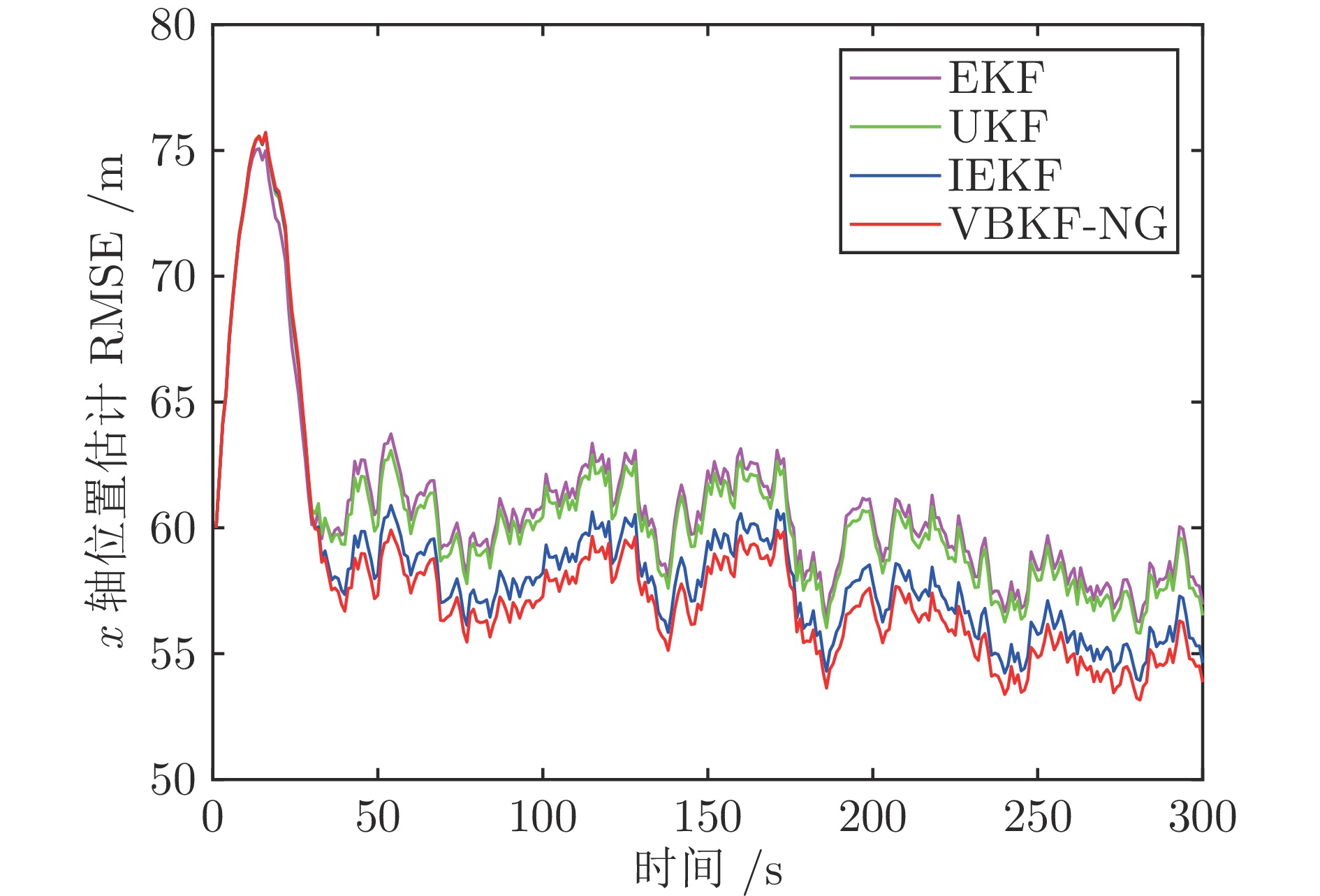
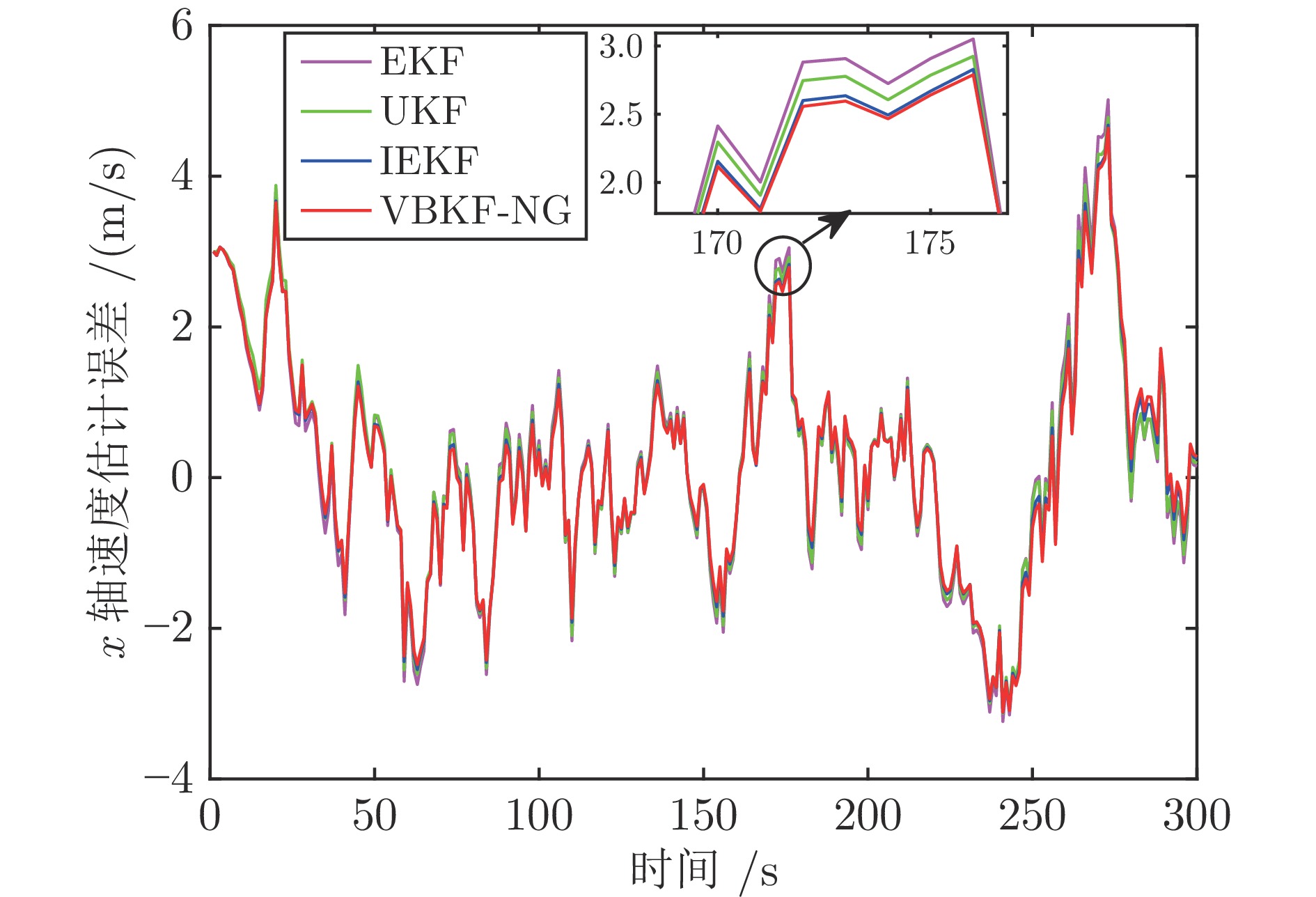
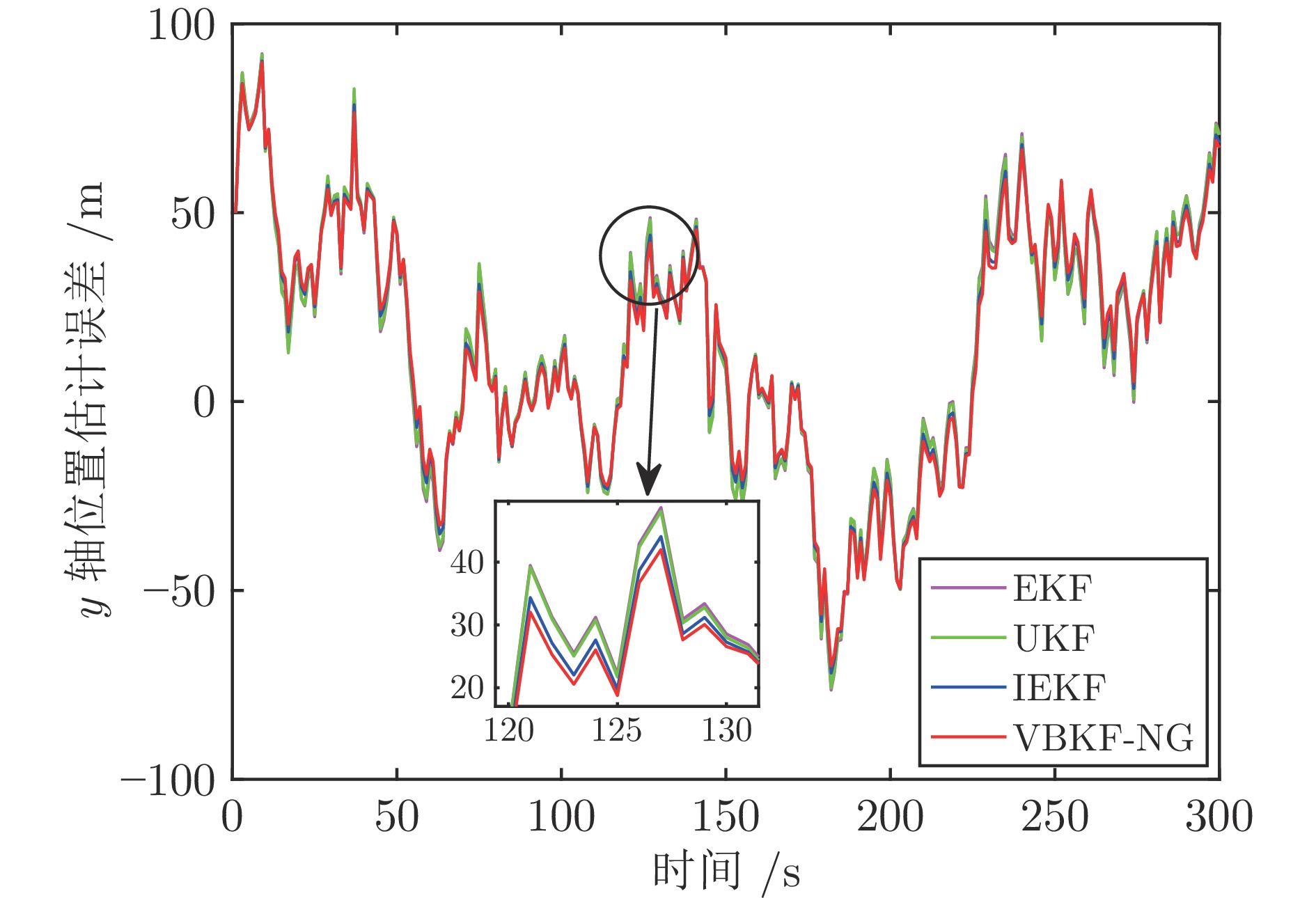
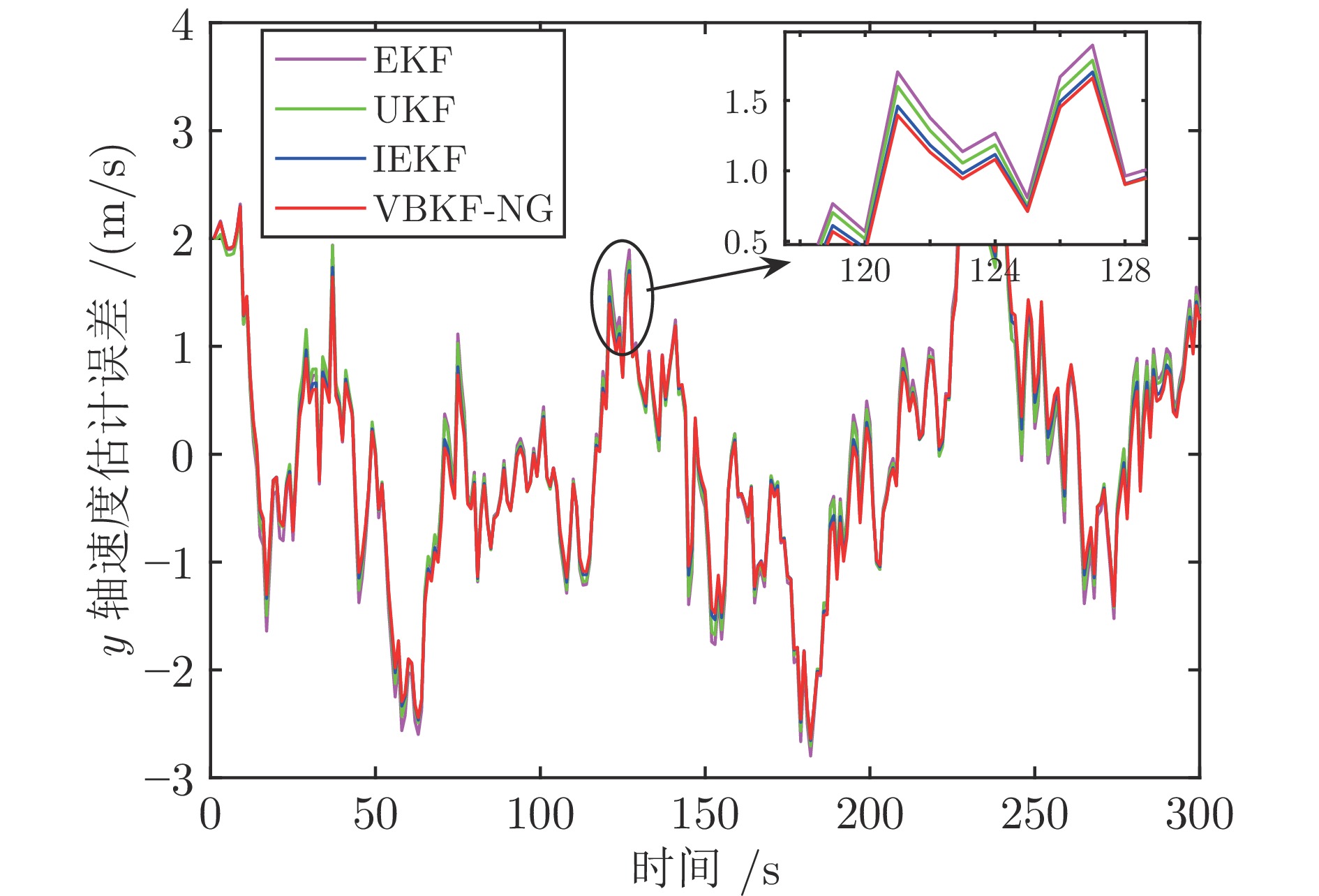
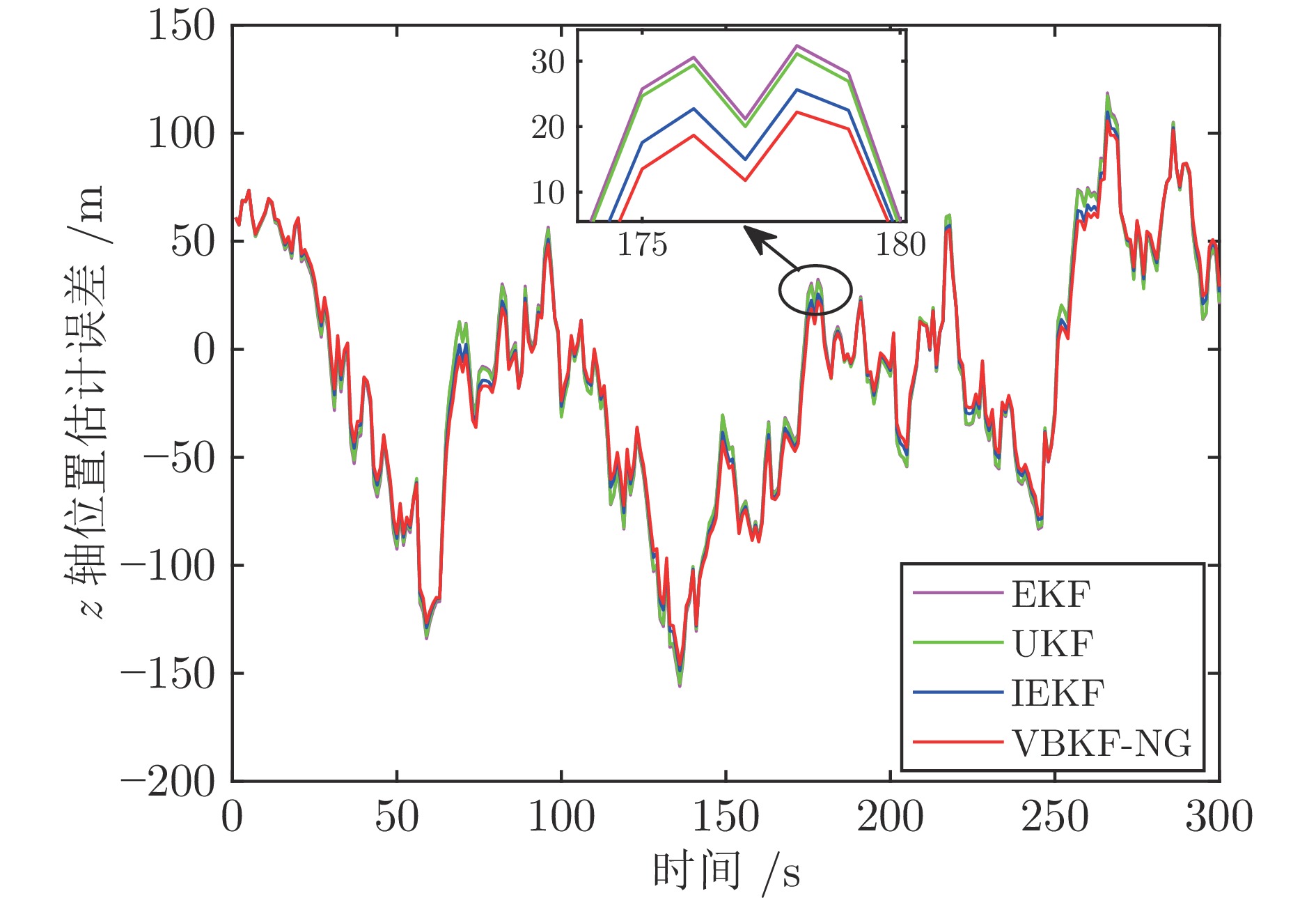
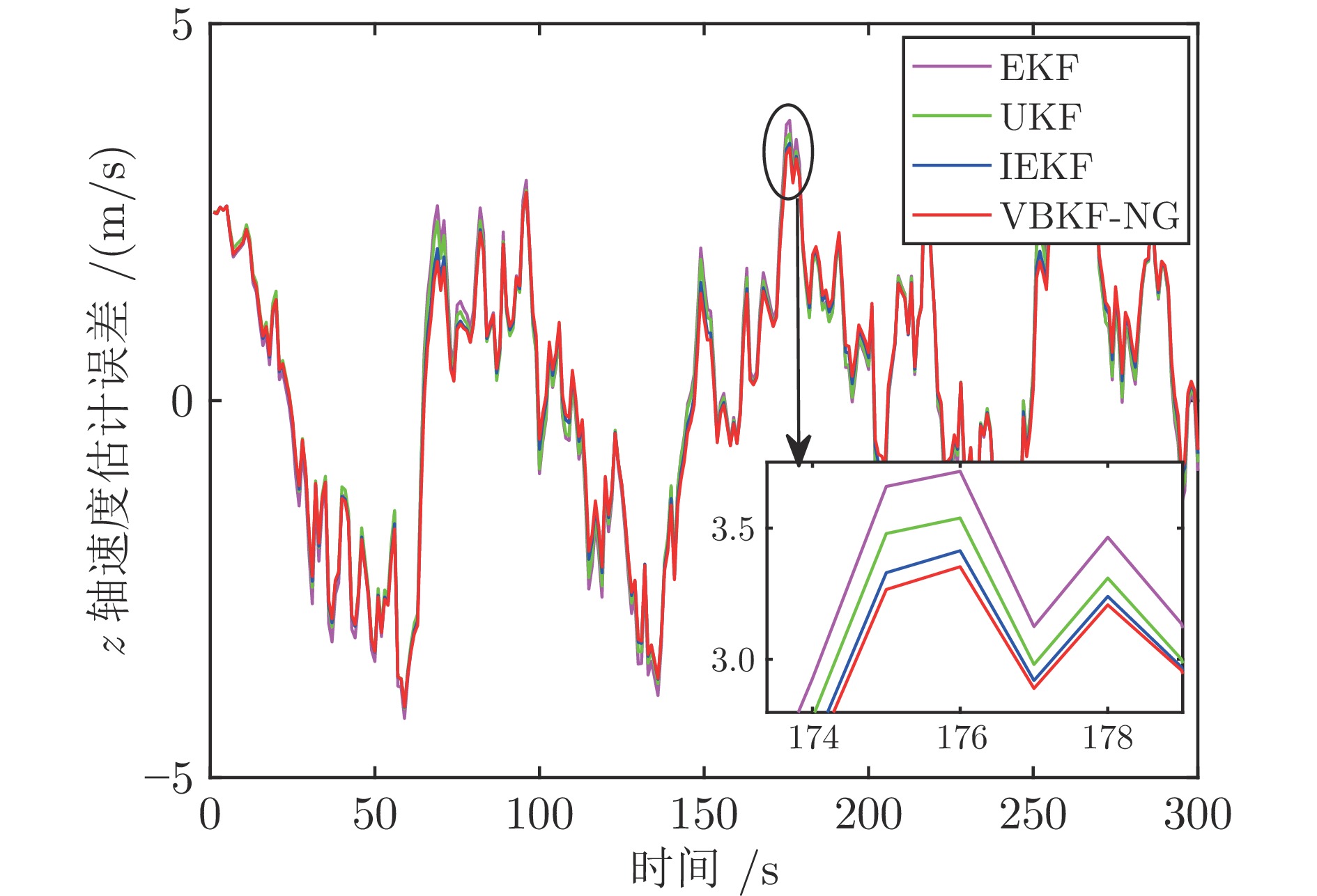
算法 EKF UKF IEKF VBKF-NG x 轴位置 6.8731 6.8493 6.8290 6.6025 x 轴速度 − 0.0382 0.0418 − 0.0368 − 0.0241 y 轴位置 2.8793 2.8770 2.8688 2.7563 y 轴速度 − 0.0257 − 0.0243 − 0.0222 − 0.0103 z 轴位置 4.7665 4.6759 4.5546 4.3286 z 轴速度 0.1272 0.1097 0.1076 0.1062 表 4 算法平均运行时间$( \times 10^{-4}\;{\rm{s}}) $的对比
Table 4 The comparison of the average run time $( \times 10^{-4}\;{\rm{s}}) $ of algorithms
算法 EKF UKF IEKF VBKF-NG 时间 0.2580 0.9542 1.0989 1.1205 表 5 算法平均RMSE的对比
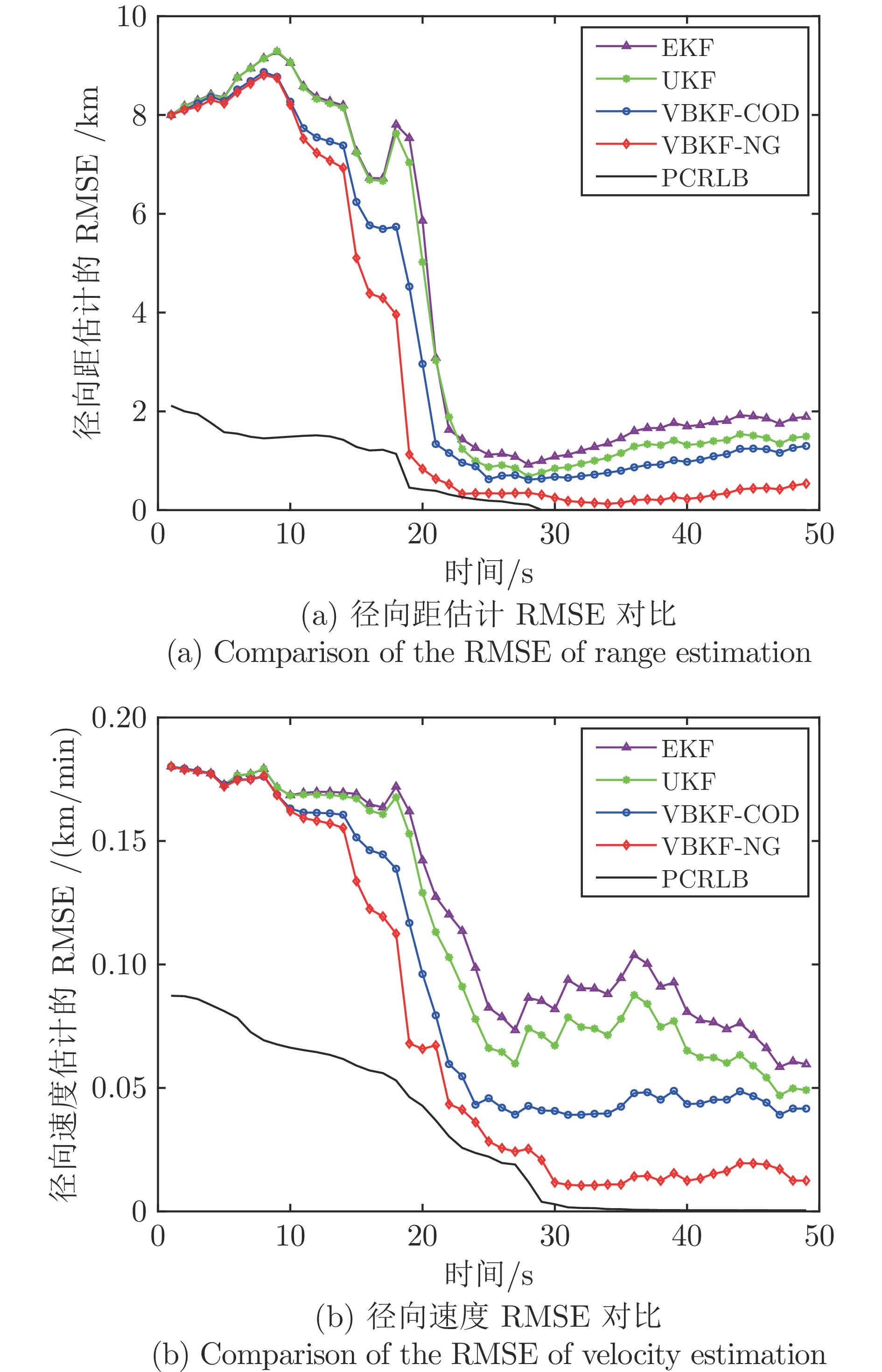
Table 5 Comparison of average RMSE between algorithms
算法 径向距(km) 径向速度(km/min) EKF 1.5052 0.0813 UKF 1.1833 0.0670 VBKF-COD 0.9181 0.0432 VBKF-NG 0.2990 0.0161 -
[1] 潘泉, 胡玉梅, 兰华, 孙帅, 王增福, 杨峰. 信息融合理论研究进展: 基于变分贝叶斯的联合优化. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1207−1233Pan Quan, Hu Yu-Mei, Lan Hua, Sun Shuai, Wang Zeng-Fu, Yang Feng. Information fusion progress: Joint optimization based on variational Bayesian theory. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1207−1233 [2] Ito K, Xiong K Q. Gaussian filters for nonlinear filtering problems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(5): 910−927 doi: 10.1109/9.855552 [3] Hu Y M, Wang X Z, Pan Q, Hu Z T, Moran B. Variational Bayesian Kalman filter using natural gradient. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(5): 1−10 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.08.033 [4] Gu D B. A game theory approach to target tracking in sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2011, 41(1): 2−13 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2010.2040733 [5] 潘泉, 胡玉梅, 马季容. 基于变分贝叶斯联合优化的情报监视与侦察. 指挥信息系统与技术, 2020, 11(2): 1−8Pan Quan, Hu Yu-Mei, Ma Ji-Rong. Intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance based on variational Bayesian joint optimization. Command Information System and Technology, 2020, 11(2): 1−8 [6] Hu X Y, Yang L Q, Xiong W. A novel wireless sensor network frame for urban transportation. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2015, 2(6): 586−595 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2015.2475639 [7] Spantini A, Baptista R, Marzouk Y. Coupling techniques for nonlinear ensemble filtering. SIAM Review, 2022, 64(4): 921−953 doi: 10.1137/20M1312204 [8] Silva B, Fisher R M, Kumar A, Hancke G P. Experimental link quality characterization of wireless sensor networks for underground monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2015, 11(5): 1099−1110 doi: 10.1109/TII.2015.2471263 [9] Vu T, Rahmani A. Distributed consensus-based Kalman filter estimation and control of formation flying spacecraft: Simulation and validation. In: Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference. Kissimmee, USA: AIAA, 2015. 7−12 [10] Wang B H, Chen W S, Zhang B, Shi P, Zhang H Y. A nonlinear observer-based approach to robust cooperative tracking for heterogeneous spacecraft attitude control and formation applications. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(1): 400−407 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3143082 [11] Tronarp F, García-Fernández Á F, Särkkä S. Iterative filtering and smoothing in nonlinear and non-Gaussian systems using conditional moments. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(3): 408−412 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2794767 [12] Humpherys J, West J. Kalman filtering with Newton's method. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2010, 30(6): 101−106 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2010.938485 [13] Alessandri A, Gaggero M. Moving-horizon estimation for discrete-time linear and nonlinear systems using the gradient and newton methods. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2906−2911 [14] Akyildiz Ö D, Chouzenoux É, Elvira V, Míguez J. A probabilistic incremental proximal gradient method. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(8): 1257−1261 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2926926 [15] Gultekin S, Paisley J. Nonlinear Kalman filtering with divergence minimization. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(23): 6319−6331 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2752729 [16] Hoffman M D, Blei D M, Wang C, Paisley J. Stochastic variational inference. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2013, 14(1): 1303−1347 [17] Salimans T, Kingma D P, Welling M. Markov chain Monte Carlo and variational inference: Bridging the gap. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: JMLR.org, 2015. 1218−1226 [18] Acerbi L. Variational Bayesian Monte Carlo. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2018. 8223−8233 [19] Acerbi L. Variational Bayesian Monte Carlo with noisy likelihoods. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 688 [20] Wang P Y, Blunsom P. Collapsed variational Bayesian inference for hidden Markov models. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Scottsdale, USA: AISTATS, 2013. 599−607 [21] Amari S I. Natural gradient works efficiently in learning. Neural Computation, 1998, 10(2): 251−276 doi: 10.1162/089976698300017746 [22] 李宇波. 基于信息几何理论的滤波方法研究 [博士学位论文], 国防科技大学, 中国, 2017.Li Yu-Bo. Study of Filtering Methods via Information Geometry [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, China, 2017. [23] Zhang G D, Sun S Y, Duvenaud D, Grosse R B. Noisy natural gradient as variational inference. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: ICML, 2018. 5847−5856 [24] Ollivier Y. Online natural gradient as a Kalman filter. Electronic Journal of Statistics, 2018, 12(2): 2930−2961 [25] Cheng Y Q, Wang X Z, Morelande M, Moran B. Information geometry of target tracking sensor networks. Information Fusion, 2013, 14(3): 311−326 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2012.02.005 [26] Schmitt L, Fichter W. Globally valid posterior Cramér-Rao bound for three-dimensional bearings-only filtering. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(4): 2036−2044 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2881352 [27] 胡玉梅, 潘泉, 胡振涛, 郭振. 基于自然梯度的噪声自适应变分贝叶斯滤波算法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(10): 2094−2108Hu Yu-Mei, Pan Quan, Hu Zhen-Tao, Guo Zhen. A novel noise adaptive variational Bayesian filter using natural gradient. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(10): 2094−2108 [28] Duan T, Avati A, Ding D Y, Thai K K, Basu S, Ng A, et al. NGBoost: Natural gradient boosting for probabilistic prediction. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. JMLR.org. Vienna, Austria: 2020. Article No. 252 [29] Tseng P. An analysis of the EM algorithm and entropy-like proximal point methods. Mathematics of Operations Research, 2004, 29(1): 27−44 doi: 10.1287/moor.1030.0073 [30] Khan M E, Baqué P, Fleuret F, Fua P. Kullback-Leibler proximal variational inference. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 3402−3410 [31] Smidl V, Quinn A. Variational Bayesian filtering. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(10): 5020−5030 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.928969 [32] Beal M J, Ghahramani Z. The Variational Kalman Smoother, Technical Report GCNU TR, 2001, 3, Computational Neuroscience Unit, University College London, UK, 2001. [33] Hu Y M, Wang X Z, Lan H, Wang Z F, Moran B, Pan Q. An iterative nonlinear filter using variational Bayesian optimization. Sensors, 2018, 18(12): Article No. 4222 [34] Ble D M, Kucukelbir A, McAuliffe J D. Variational inference: A review for statisticians. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2017, 112(518): 859−877 doi: 10.1080/01621459.2017.1285773 [35] Sain R, Mittal V, Gupta V. A comprehensive review on recent advances in variational Bayesian inference. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computer Engineering and Applications. Ghaziabad, India: IEEE, 2015. 488−492 [36] Beal M J. Variational Algorithms for Approximate Bayesian Inference [Ph.D. dissertation], Cambridge University, UK, 2003. [37] Amari S I. Information Geometry and Its Applications. Tokyo: Springer, 2016. [38] Amari S, Douglas S C. Why natural gradient? In: Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 1998. 1213−1216 [39] Rezende D J, Mohamed S, Wierstra D. Stochastic backpropagation and approximate inference in deep generative models. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: JMLR.org, 2014. II-1278−II-1286 [40] Lan H, Liang Y, Zhang W, Yang F, Pan Q. Iterated minimum upper bound filter for tracking orbit maneuvering targets. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Fusion. Istanbul, Turkey: IEEE, 2013. 1051−1057 -




 下载:
下载: