-
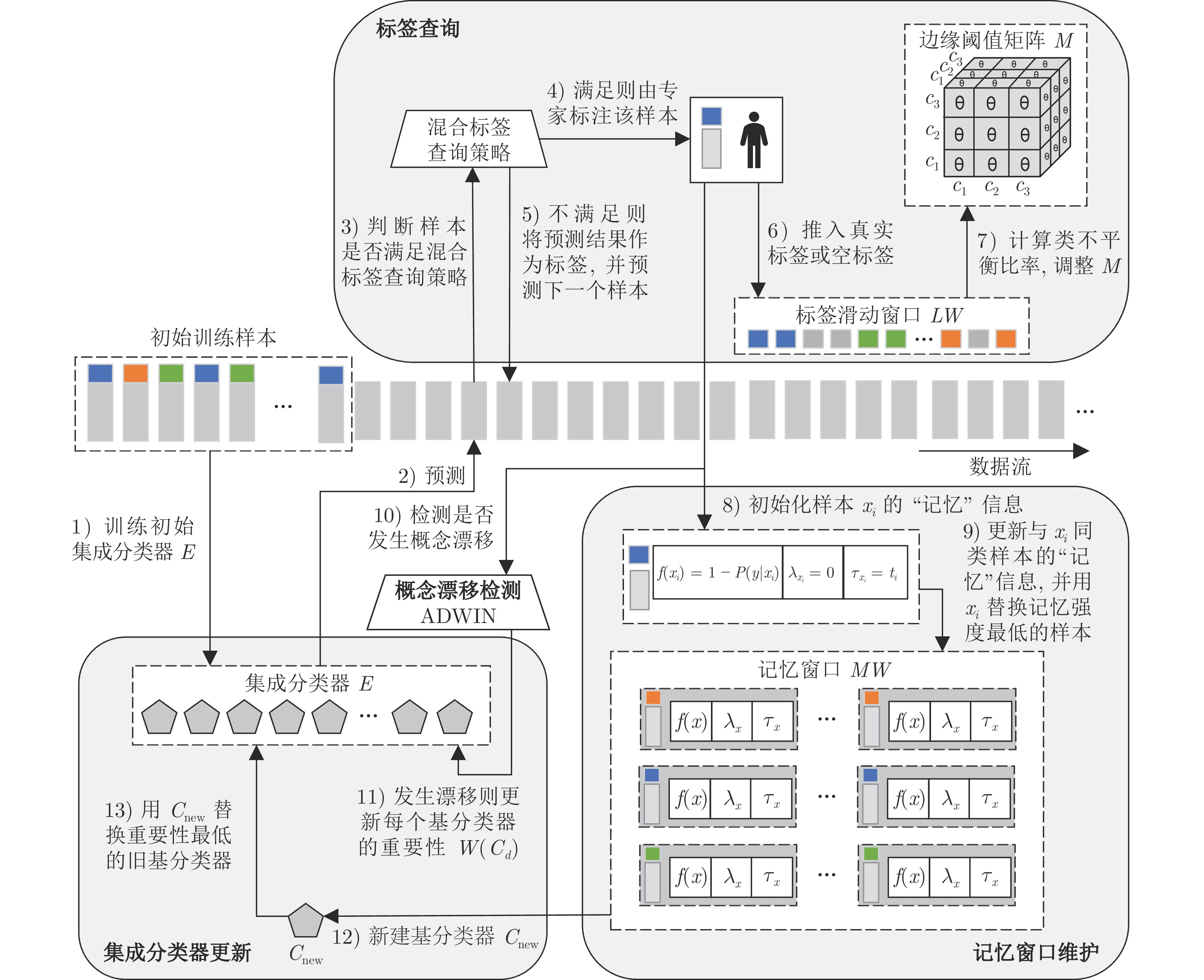
摘要: 数据流分类研究在开放、动态环境中如何提供更可靠的数据驱动预测模型, 关键在于从实时到达且不断变化的数据流中检测并适应概念漂移. 目前, 为检测概念漂移和更新分类模型, 数据流分类方法通常假设所有样本的标签都是已知的, 这一假设在真实场景下是不现实的. 此外, 真实数据流可能表现出较高且不断变化的类不平衡比率, 会进一步增加数据流分类任务的复杂性. 为此, 提出一种非平衡概念漂移数据流主动学习方法(Active learning method for imbalanced concept drift data stream, ALM-ICDDS). 定义基于多预测概率的样本预测确定性度量, 提出边缘阈值矩阵的自适应调整方法, 使得标签查询策略适用于类别数较多的非平衡数据流; 提出基于记忆强度的样本替换策略, 将难区分、少数类样本和代表当前数据分布的样本保存在记忆窗口中, 提升新基分类器的分类性能; 定义基于分类精度的基分类器重要性评价及更新方法, 实现漂移后的集成分类器更新. 在7个合成数据流和3个真实数据流上的对比实验表明, 提出的非平衡概念漂移数据流主动学习方法的分类性能优于6种概念漂移数据流学习方法.Abstract: Data stream classification researchs how to provide more reliable data-driven prediction models in open and dynamic environment. The key is how to detect and adapt to concept drift from continuously changing data stream that arrive in real-time. Currently, in order to detect concept drift and update classification models, data stream classification methods usually assume that the labels of all samples are known, which is unrealistic in real scenarios. Additionally, real data stream may exhibit a high and constantly changing class imbalance ratios, further increasing the complexity of the data stream classification task. In this paper, we propose an active learning method for imbalanced concept drift data stream (ALM-ICDDS). Firstly, we define a sample prediction certainty measure based on multiple prediction probabilities and propose an adaptive adjustment method for the margin threshold matrix, which makes the label query strategy suitable for imbalanced data stream with a number of categories. Then, we propose a sample replacement strategy based on memory strength, which saves the samples that are difficult-to-distinguish, minority class and represent the current data distribution in the memory window, and improves the classification performance of new base classifier. Finally, we define the importance evaluation and update method of base classifier based on classification accuracy, which realizes the ensemble classifier update after drift. Comparative experiments on seven synthetic data streams and three real data streams show that the active learning method for imbalance concept drift data stream is better than six concept drift data stream learning methods in classification performance.
-
Key words:
- Data stream classification /
- active learning /
- concept drift /
- multi-class imbalance
-
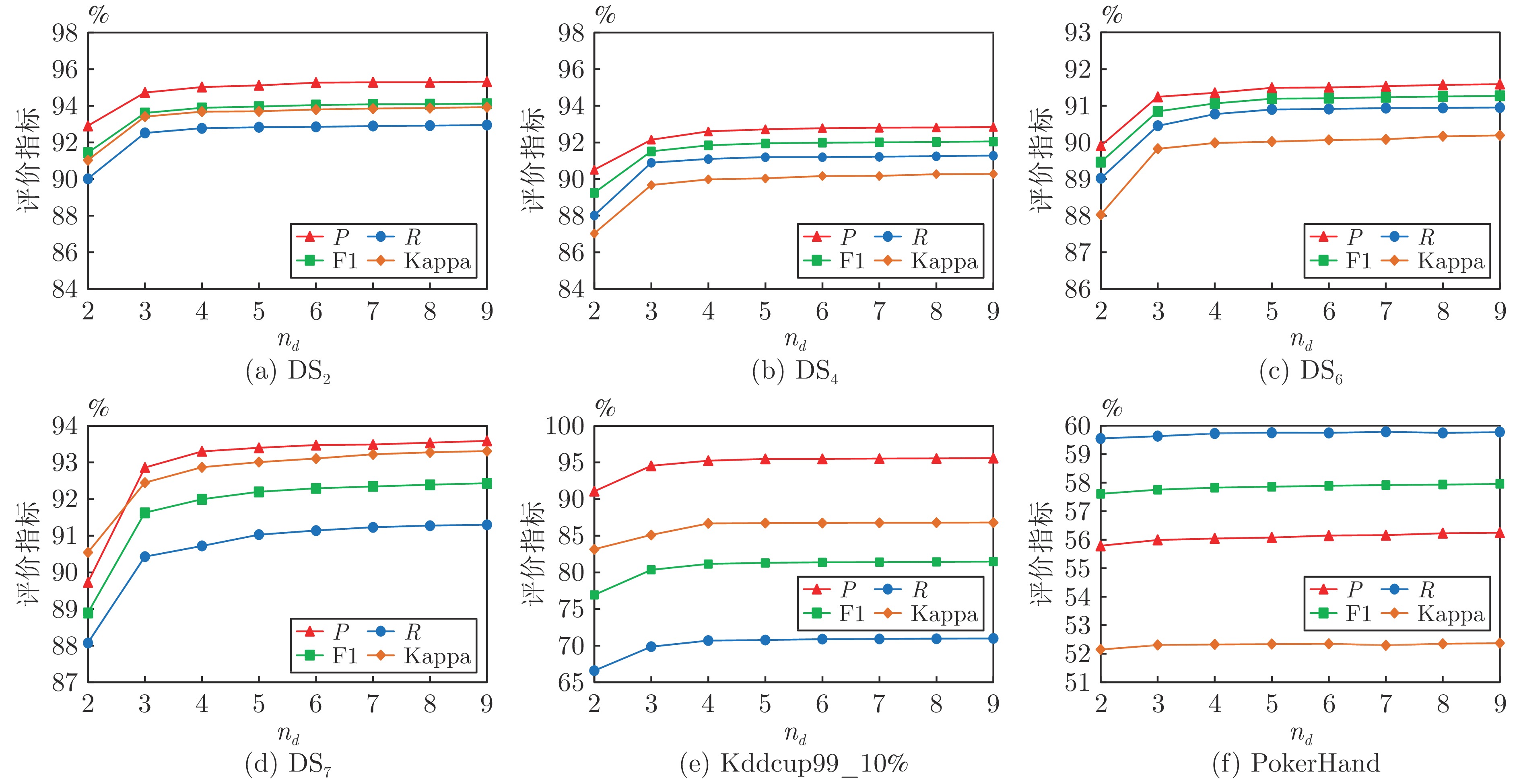
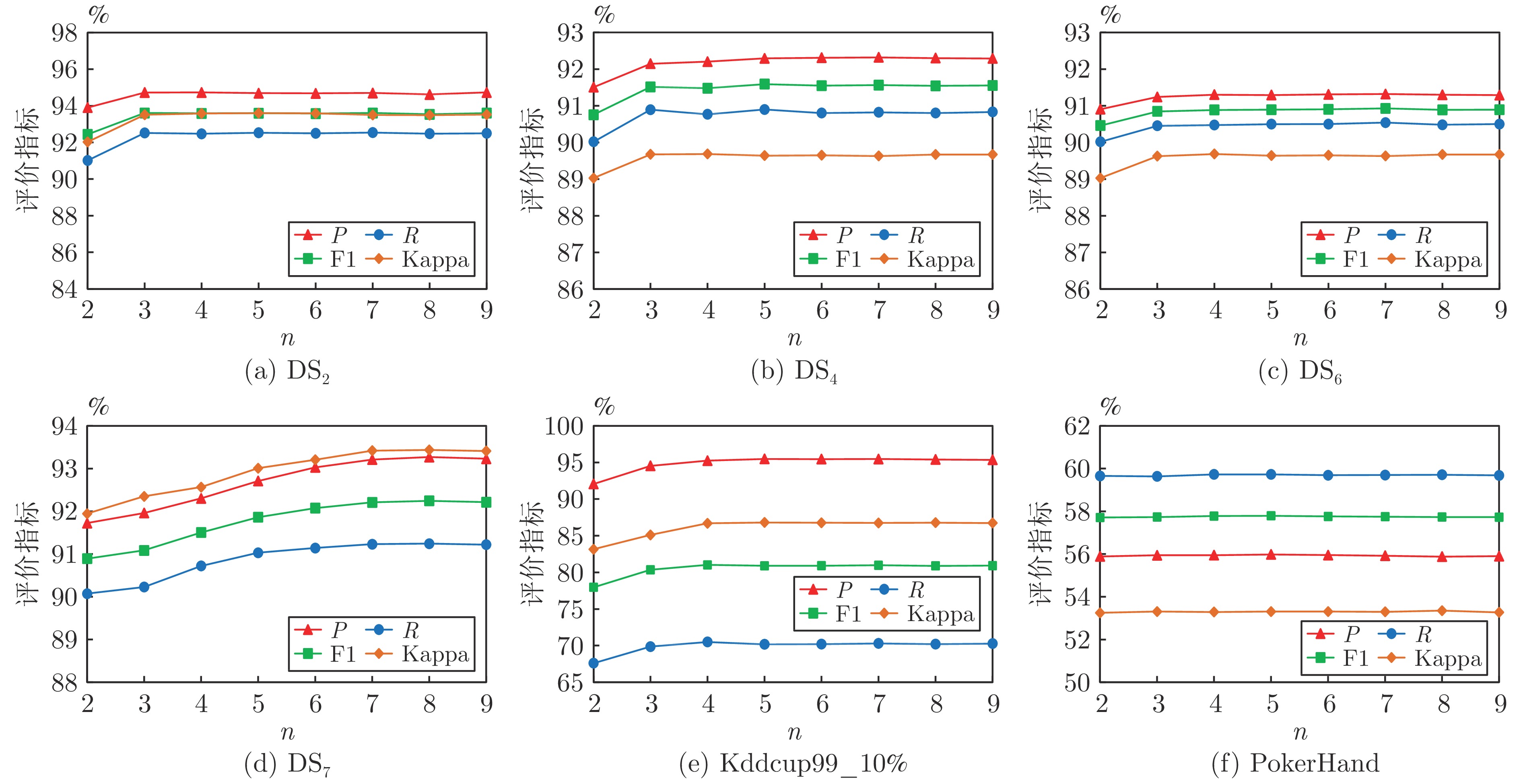
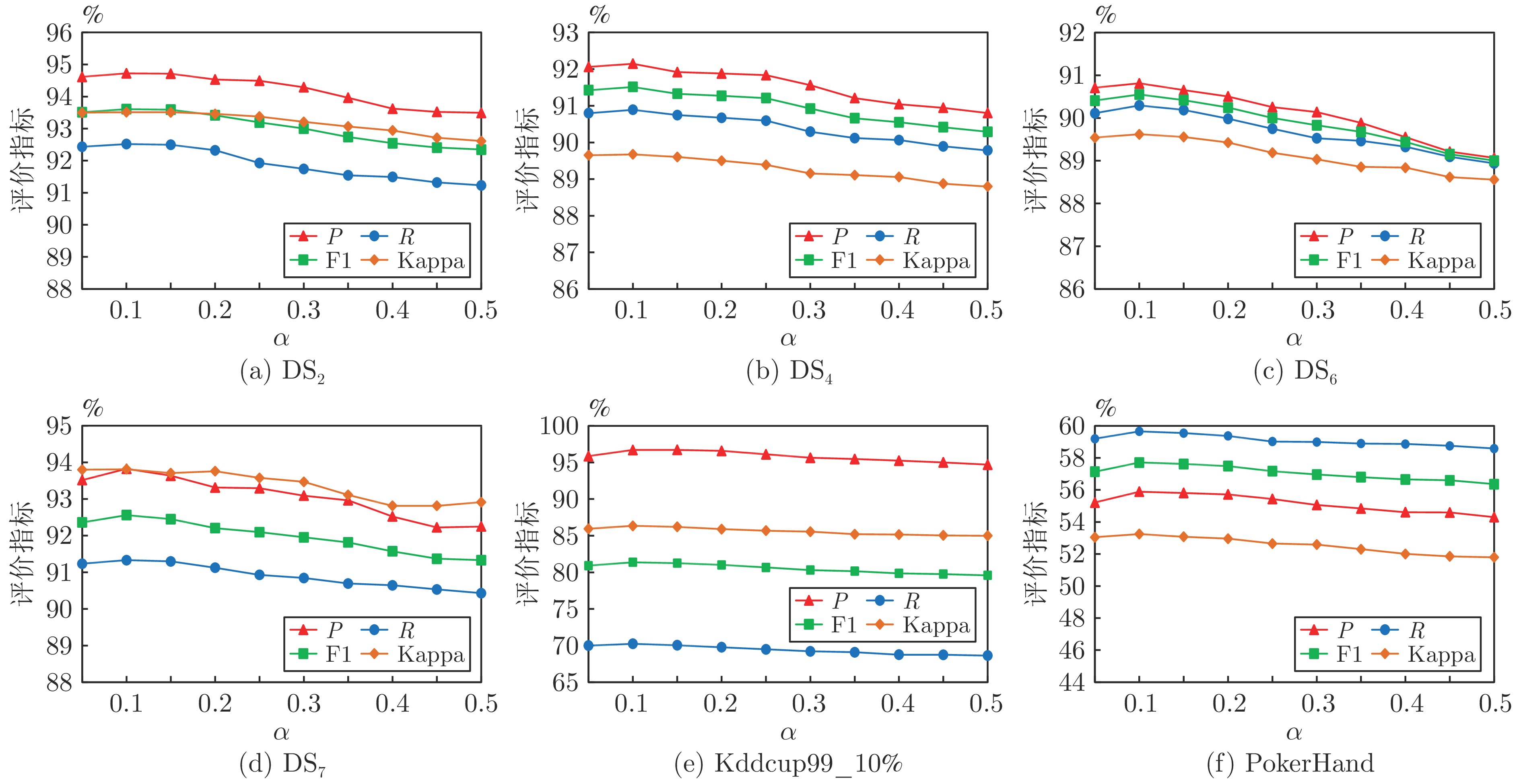
表 1 数据流特征
Table 1 Data stream feature
编号 数据流 样本数 特征数 类别数 类分布 异常点(%) 漂移次数 1 DS1 400000 25 15 类平衡 0 0 2 DS2 400000 25 15 类平衡 5 3 3 DS3 400000 25 15 (1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/2/2/3/3/5) 0 0 4 DS4 400000 25 15 (1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/2/2/3/3/5) 5 3 5 DS5 400000 25 15 (1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/2/2/3/3/5), 0 0 (2/2/3/3/5/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1) 6 DS6 400000 25 15 (1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/2/2/3/3/5), 5 3 (2/2/3/3/5/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1) 7 DS7 400000 25 50 类平衡 5 3 8 Kddcup99_10% 494000 42 23 — — — 9 Shuttle 570000 10 7 — — — 10 PokerHand 830000 10 10 — — — 表 2 概念漂移数据流特征
Table 2 Concept drift data stream feature
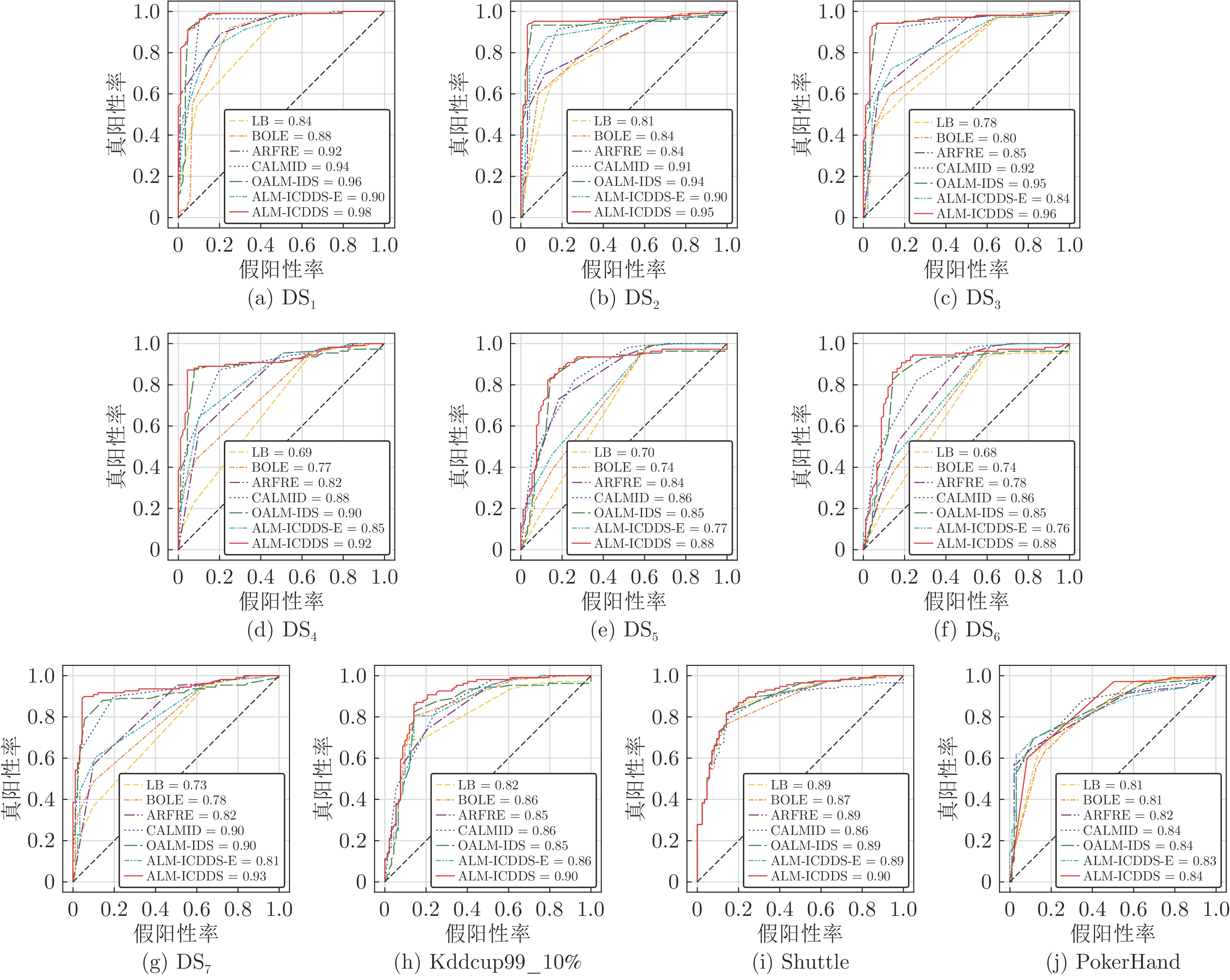
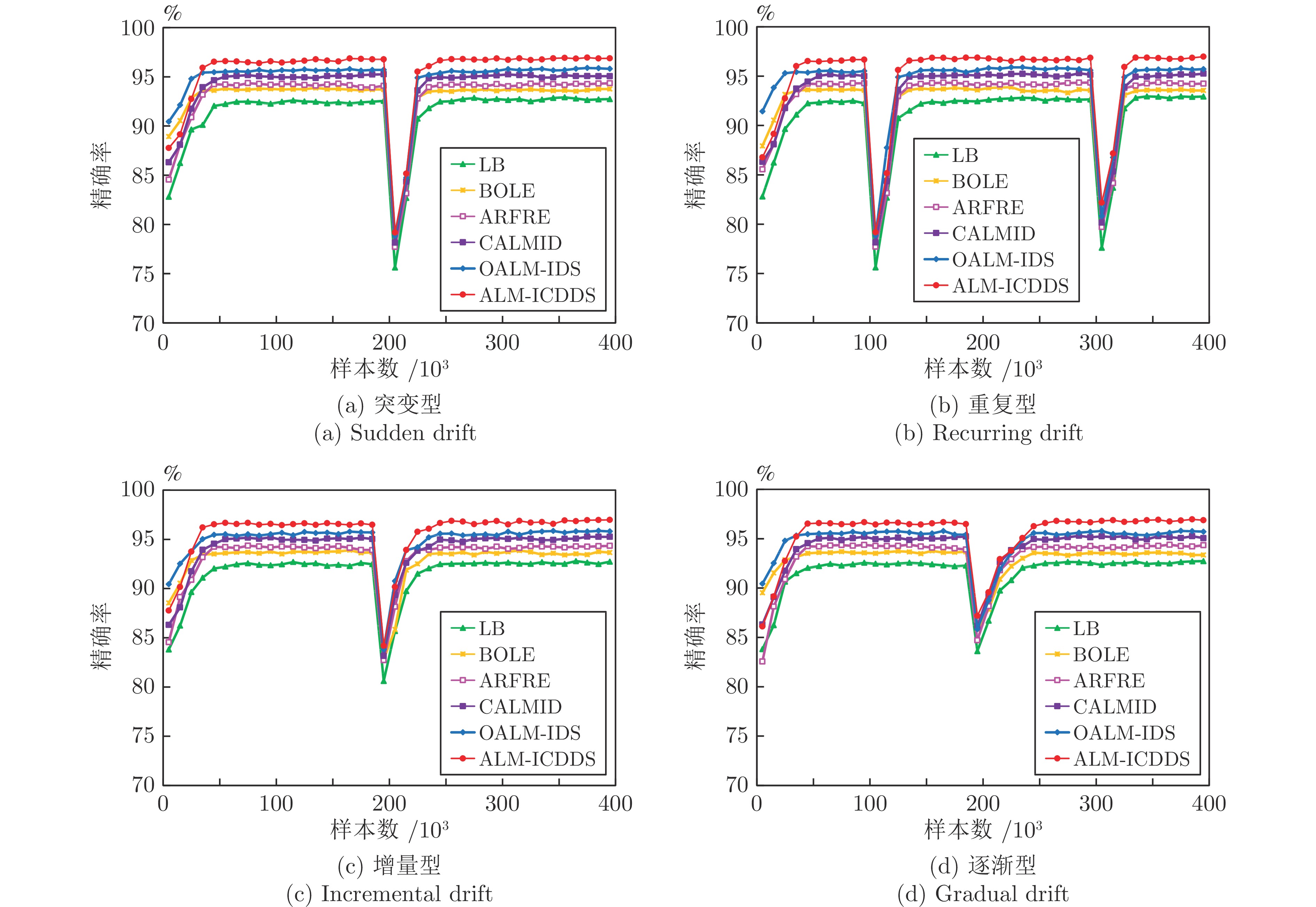
编号 数据流 概念漂移类型 样本数 特征数 类别数 漂移宽度 1 DS8 突变型 400000 25 15 1 2 DS9 重复型 400000 25 15 1 3 DS10 增量型 400000 25 15 10000 4 DS11 逐渐型 400000 25 15 10000 表 3 7种算法的P值(%)
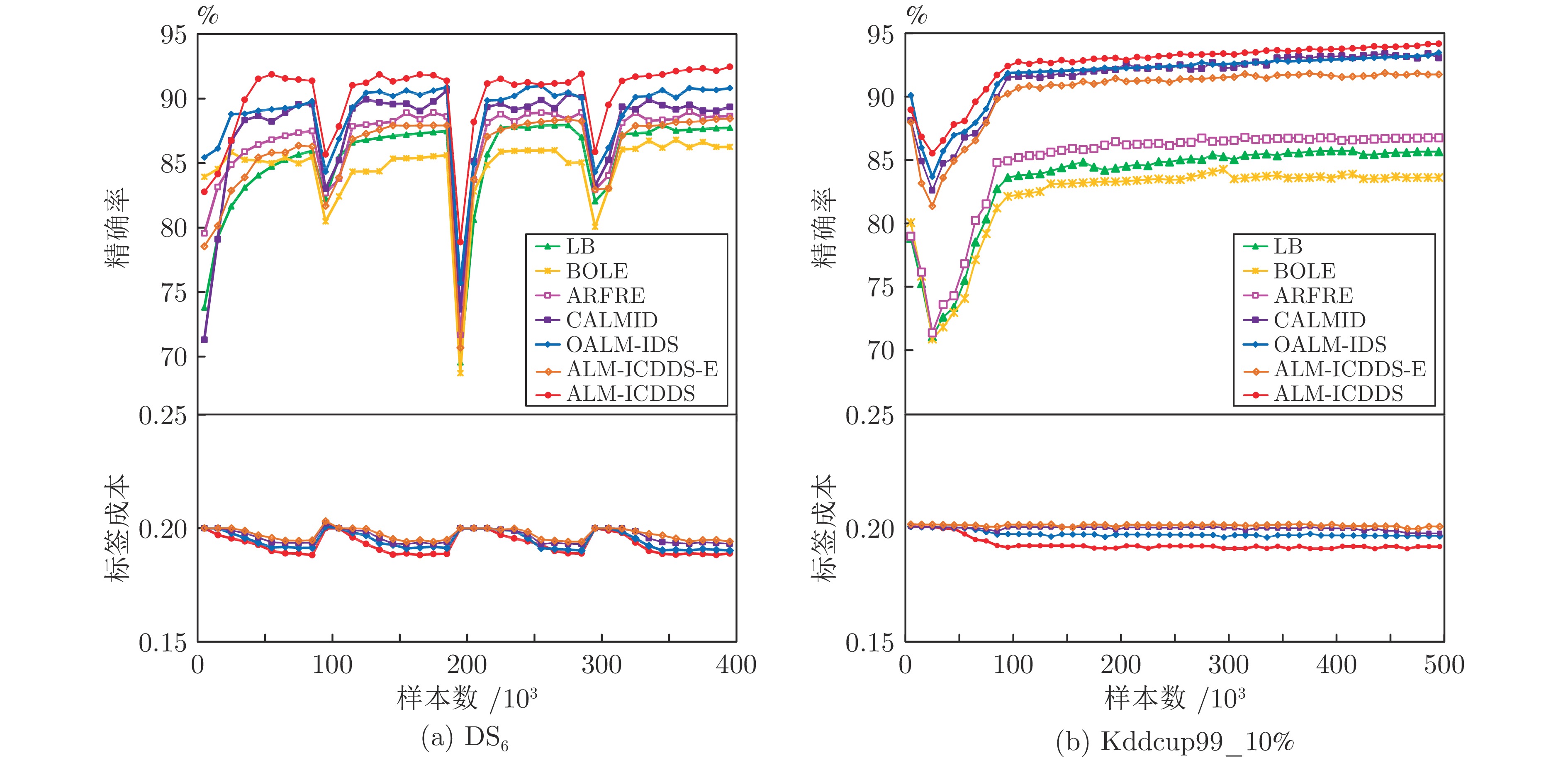
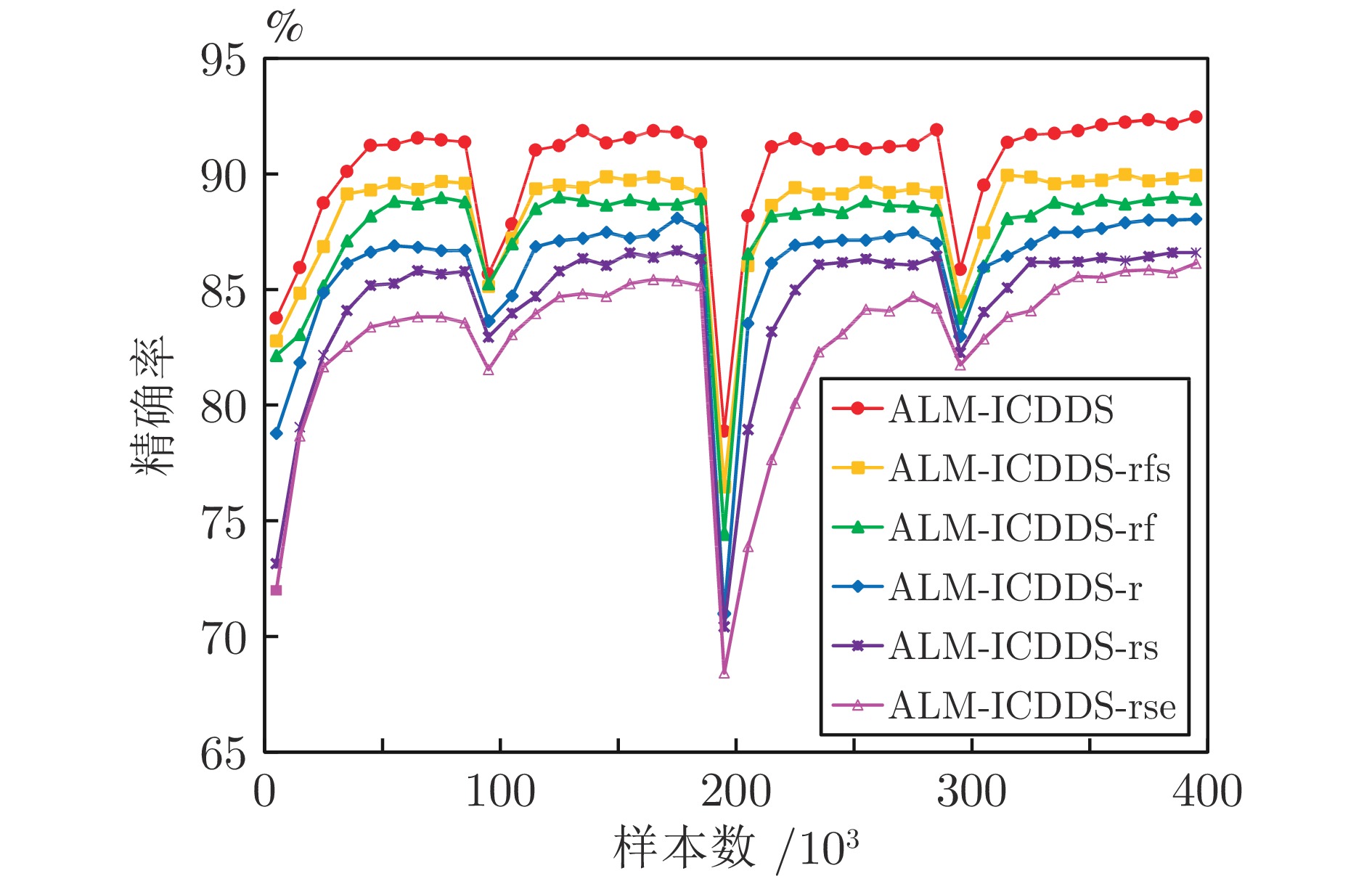
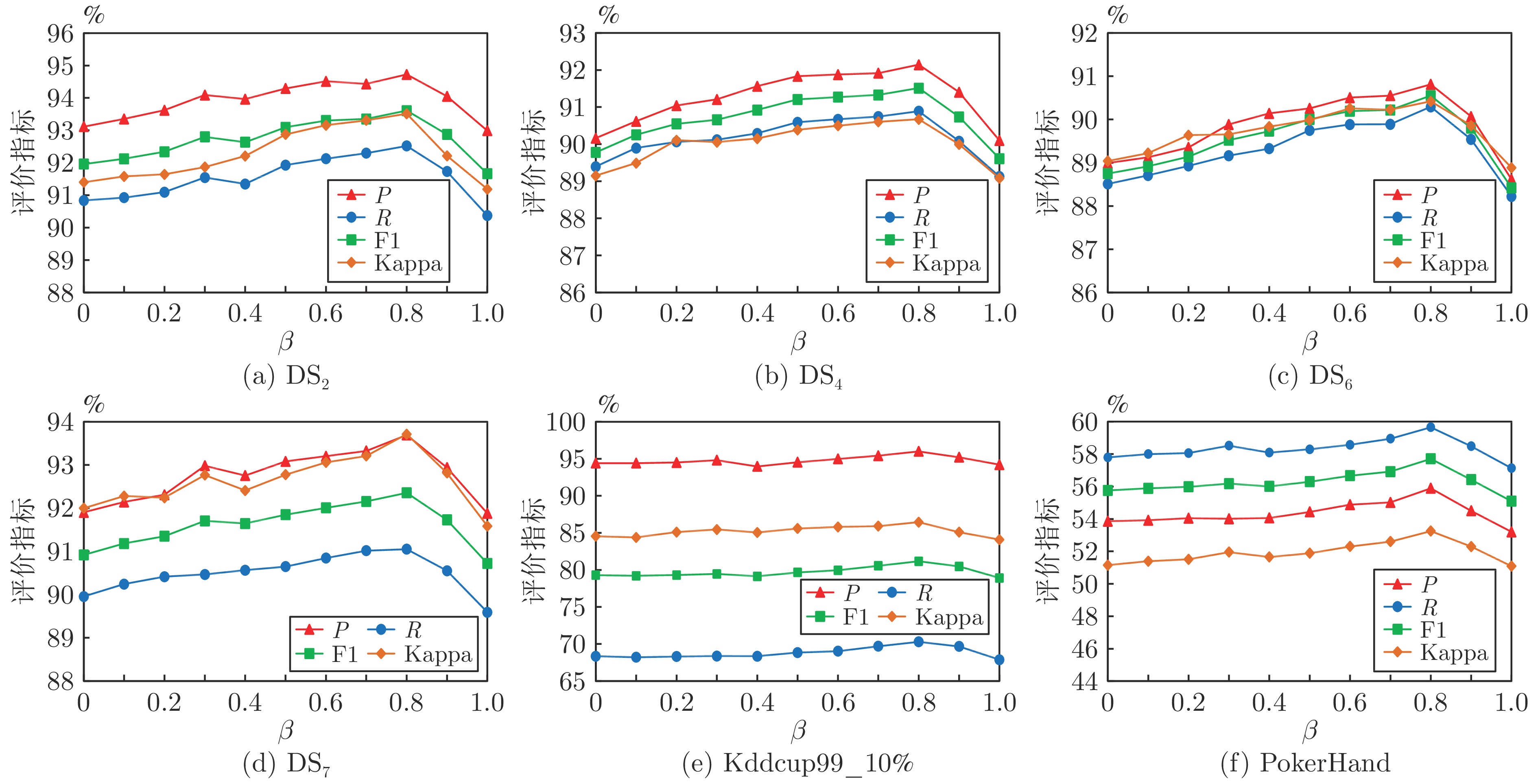
Table 3 P value of seven algorithms (%)
数据流 LB BOLE ARFRE CALMID OALM-IDS ALM-ICDDS-E ALM-ICDDS DS1 96.89±0.31 96.36±0.11 98.07±0.43 98.01±0.41 98.03±0.25 97.18±0.48 99.07±0.34 DS2 90.61±0.21 88.63±0.54 92.77±0.42 93.31±0.14 93.27±0.49 91.97±0.26 94.64±0.15 DS3 94.41±0.11 96.07±0.23 96.74±0.45 96.64±0.34 96.75±0.56 96.46±0.61 97.84±0.24 DS4 86.91±0.45 85.23±0.52 88.30±0.29 89.90±0.28 90.27±0.42 89.70±0.72 92.06±0.28 DS5 93.60±0.48 94.04±0.52 96.30±0.18 94.65±0.49 95.47±0.32 94.24±0.35 96.17±0.19 DS6 86.59±0.19 84.69±0.48 88.02±0.47 88.44±0.19 88.65±0.25 87.41±0.40 90.86±0.37 DS7 88.25±0.86 87.21±0.79 90.16±0.92 90.49±0.47 90.51±0.53 89.32±0.38 93.67±0.40 Kddcup99_10% 83.85±0.59 81.10±0.15 85.56±0.54 92.12±0.45 92.13±0.31 91.24±0.51 95.80±0.17 Shuttle 64.63±0.42 63.85±0.27 79.07±0.31 85.35±0.14 85.70±0.32 83.48±0.25 85.99±0.13 PokerHand 51.63±0.39 50.36±0.35 52.51±0.56 53.93±0.28 54.57±0.50 52.90±0.18 55.89±0.51 表 6 7种算法的${\rm{Kappa }}$值(%)
Table 6 ${\rm{Kappa }}$ value of seven algorithms (%)
数据流 LB BOLE ARFRE CALMID OALM-IDS ALM-ICDDS-E ALM-ICDDS DS1 95.09±0.43 95.47±0.26 97.11±0.33 97.84±0.18 97.52±0.50 96.31±0.53 98.72±0.18 DS2 89.66±0.50 88.28±0.45 91.80±0.17 92.55±0.25 92.65±0.28 91.27±0.29 93.56±0.46 DS3 93.08±0.13 95.68±0.22 95.62±0.53 96.50±0.46 96.46±0.60 96.05±0.36 97.69±0.21 DS4 86.97±0.46 85.86±0.13 88.18±0.25 89.94±0.24 89.99±0.36 88.61±0.46 90.19±0.57 DS5 92.32±0.37 94.18±0.45 95.86±0.28 94.40±0.50 95.52±0.14 94.29±0.20 95.81±0.35 DS6 86.59±0.32 85.25±0.29 87.81±0.54 88.90±0.51 89.00±0.13 87.68±0.47 89.80±0.25 DS7 88.28±0.46 87.51±0.97 89.93±0.71 90.01±0.92 90.19±0.40 89.51±0.59 93.67±0.54 Kddcup99_10% 80.94±0.22 75.68±0.25 79.36±0.35 83.32±0.24 85.83±0.50 84.87±0.16 86.81±0.33 Shuttle 58.73±0.39 61.54±0.22 73.78±0.20 79.39±0.43 80.11±0.53 80.97±0.24 83.56±0.54 PokerHand 50.34±0.58 49.86±0.40 50.36±0.16 51.24±0.21 51.39±0.16 50.55±0.41 52.25±0.35 表 4 7种算法的R值(%)
Table 4 R value of seven algorithms (%)
数据流 LB BOLE ARFRE CALMID OALM-IDS ALM-ICDDS-E ALM-ICDDS DS1 94.78±0.13 96.04±0.24 96.81±0.59 97.87±0.24 97.92±0.25 96.15±0.31 98.63±0.17 DS2 88.65±0.25 87.86±0.53 90.35±0.30 91.54±0.54 91.84±0.58 90.78±0.70 92.30±0.24 DS3 92.55±0.45 95.92±0.32 94.80±0.43 96.12±0.14 97.92±0.54 95.99±0.52 98.55±0.29 DS4 87.03±0.49 87.08±0.39 88.23±0.31 90.50±0.30 91.07±0.52 90.13±0.43 91.15±0.11 DS5 91.54±0.11 92.33±0.51 96.04±0.20 93.82±0.55 94.94±0.27 92.91±0.42 96.53±0.42 DS6 86.56±0.50 85.48±0.24 87.83±0.49 89.43±0.18 88.85±0.36 88.39±0.34 90.63±0.21 DS7 87.19±0.42 86.12±0.11 87.29±0.36 88.41±0.50 88.77±0.43 87.87±0.20 91.61±0.78 Kddcup99_10% 60.89±0.50 63.05±0.50 58.26±0.38 61.88±0.38 63.71±0.54 63.42±0.67 69.34±0.57 Shuttle 61.40±0.21 50.84±0.31 54.36±0.35 59.52±0.41 63.12±0.59 61.79±0.16 64.59±0.29 PokerHand 43.57±0.30 44.78±0.46 55.21±0.60 56.84±0.11 52.77±0.54 55.36±0.25 59.57±0.43 表 5 7种算法的${\rm{F}}1$值 (%)
Table 5 ${\rm{F}}1$ value of seven algorithms (%)
数据流 LB BOLE ARFRE CALMID OALM-IDS ALM-ICDDS-E ALM-ICDDS DS1 95.82±0.18 96.20±0.16 97.44±0.50 97.94±0.30 97.97±0.25 96.66±0.37 98.85±0.23 DS2 89.62±0.23 88.24±0.53 91.54±0.35 92.42±0.22 92.55±0.53 91.37±0.43 93.46±0.18 DS3 93.47±0.18 95.99±0.27 95.76±0.44 96.38±0.20 97.33±0.55 96.22±0.57 98.19±0.26 DS4 86.97±0.47 86.15±0.45 88.26±0.30 90.20±0.29 90.67±0.46 89.91±0.59 91.60±0.16 DS5 92.55±0.17 93.18±0.30 96.17±0.19 94.23±0.52 95.20±0.29 93.57±0.38 96.35±0.26 DS6 86.57±0.27 85.08±0.32 87.92±0.48 88.93±0.18 88.75±0.30 87.90±0.35 90.74±0.27 DS7 87.72±0.56 86.66±0.19 88.70±0.52 89.44±0.48 89.61±0.47 88.59±0.29 92.63±0.40 Kddcup99_10% 70.55±0.54 70.94±0.23 69.32±0.45 74.03±0.22 75.33±0.39 74.82±0.54 80.45±0.49 Shuttle 62.97±0.28 56.61±0.29 64.43±0.33 70.13±0.21 72.70±0.41 71.01±0.20 73.77±0.18 PokerHand 47.26±0.34 47.41±0.40 53.83±0.57 55.35±0.16 56.12±0.52 54.10±0.23 57.67±0.72 -
[1] Liao G, Zhang P, Yin H, Luo T, Lin J. A novel semi-supervised classification approach for evolving data streams. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 215: 119273 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119273 [2] 朱飞, 张煦尧, 刘成林. 类别增量学习研究进展和性能评价. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 1−26Zhu Fei, Zhang Xu-Yao, Liu Cheng-Lin. Class incremental learning: A review and performance evaluation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 1−26 [3] Zhou Z H. Open-environment machine learning. National Science Review, 2022, 9(8): 211−221 [4] Wang P, Jin N, Woo W L, Woodward J R, Davies D. Noise tolerant drift detection method for data stream mining. Information Sciences, 2022, 609: 1318−1333 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.07.065 [5] Yu H, Liu W, Lu J, Wen Y, Luo X, Zhang G. Detecting group concept drift from multiple data streams. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 134: 109113 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109113 [6] Suárez-Cetrulo A L, Quintana D, Cervantes A. A survey on machine learning for recurring concept drifting data streams. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 213: 118934 [7] Yang L, Shami A. A lightweight concept drift detection and adaptation framework for IoT data streams. IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 2021, 4(2): 96−101 doi: 10.1109/IOTM.0001.2100012 [8] Bayram F, Ahmed B S, Kassler A. From concept drift to model degradation: An overview on performance-aware drift detectors. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 245: 108632 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108632 [9] Karimian M, Beigy H. Concept drift handling: A domain adaptation perspective. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 224: 119946 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119946 [10] Lu J, Liu A, Dong F, Gu F, Gama J, Zhang G. Learning under concept drift: A review. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2018, 31(12): 2346-2363 [11] Shahraki A, Abbasi M, Taherkordi A, Jurcut A D. Active learning for network traffic classification: A technical study. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 8(1): 422−439 [12] Pham T, Kottke D, Sick B, Krempl G. Stream-based active learning for sliding windows under the influence of verification latency. Machine Learning, 2022, 111(6): 2011−2036 doi: 10.1007/s10994-021-06099-z [13] Khowaja S A, Khuwaja P. Q-learning and LSTM based deep active learning strategy for malware defense in industrial IoT applications. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(10): 14637−14663 doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-10371-0 [14] Wang S, Luo H, Huang S, Li Q, Liu L, Su G, et al. Counterfactual-based minority oversampling for imbalanced classification. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 122: 106024 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106024 [15] Malialis K, Panayiotou C G, Polycarpou M M. Nonstationary data stream classification with online active learning and siamese neural networks. Neurocomputing, 2022, 512: 235−252 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.09.065 [16] Du H, Zhang Y, Gang K, Zhang L, Chen Y. Online ensemble learning algorithm for imbalanced data stream. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 107(1): 107378 [17] Wang W, Sun D. The improved AdaBoost algorithms for imbalanced data classification. Information Sciences, 2021, 563: 358−374 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.03.042 [18] Gao J, Fan W, Han J, Yu P. A general framework for mining concept-drifting data streams with skewed distributions. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Mining. Minnesota, USA: 2007. 3−14 [19] Lu Y, Cheung Y, Tang Y Y. Dynamic weighted majority for incremental learning of imbalanced data streams with concept drift. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Melbourne, Australia: AAAI, 2017. 2393−2399 [20] Jiao B, Guo Y, Gong D, Chen Q. Dynamic ensemble selection for imbalanced data streams with concept drift. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(1): 1278-1291 [21] Guo H S, Zhang S, Wang W J. Selective ensemble-based online adaptive deep neural networks for streaming data with concept drift. Neural Networks, 2021, 142: 437−456 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2021.06.027 [22] Wang S, Minku L L, Yao X. Resampling-based ensemble methods for online class imbalance learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2014, 27(5): 1356−1368 [23] Cano A, Krawczyk B. ROSE: Robust online self-adjusting ensemble for continual learning on imbalanced drifting data streams. Machine Learning, 2022, 111(7): 2561−2599 doi: 10.1007/s10994-022-06168-x [24] Bifet A, Gavalda R. Learning from time-changing data with adaptive windowing. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Mining. Minnesota, USA: 2007. 443−448 [25] Barros R S M, Carvalho Santos S G T, Júnior P M G. A boosting-like online learning ensemble. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Vancouver, Canada: 2016. 1871−1878 [26] Gama J, Medas P, Castillo G, Rodrigues P. Learning with drift detection. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Artificial Intelligence. Maranhao, Brazil: Springer, 2004. 286−295 [27] 张永清, 卢荣钊, 乔少杰, 韩楠, Gutierrez L A, 周激流. 一种基于样本空间的类别不平衡数据采样方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(10): 2549−2563Zhang Yong-Qing, Lu Rong-Zhao, Qiao Shao-Jie, Han Nan, Gutierrez L A, Zhou Ji-Liu. A sampling method of imbalanced data based on sample space. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2549−2563 [28] Bifet A, Holmes G, Pfahringer B. Leveraging bagging for evolving data stream. In: Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Barcelona, Spain: Springer, 2010. 135−150 [29] Ferreira L E B, Gomes H M, Bifet A, Oliveira L. Adaptive random forests with resampling for imbalanced data streams. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2019. 1−6 [30] Gu Q, Tian J, Li X, Song J. A novel random forest integrated model for imbalanced data classification problem. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 250: 109050 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109050 [31] Martins V E, Cano A, Junior S B. Meta-learning for dynamic tuning of active learning on stream classification. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 138: 109359 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109359 [32] Yin C Y, Chen S S, Yin Z C. Clustering-based active learning classification towards data stream. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2023, 14(2): 1−18 [33] Xu W H, Zhao F F, Lu Z C. Active learning over evolving data streams using paired ensemble framework. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence. Chiang Mai, Thailand: 2016. 180−185 [34] Liu S X, Xue S, Wu J, Zhou C, Yang J, Li Z, et al. Online active learning for drifting data streams. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(1): 186−200 [35] Liu W K, Zhang H, Ding Z Y, Liu Q B, Zhu C. A comprehensive active learning method for multiclass imbalanced data streams with concept drift. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 215: 106778 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.106778 [36] 李艳红, 任霖, 王素格, 李德玉. 非平衡数据流在线主动学习方法. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c211246Li Yan-Hong, Ren Lin, Wang Su-Ge, Li De-Yu. Online active learning method for imbalanced data stream. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c211246 [37] Zhao P, Cai L W, Zhou Z H. Handling concept drift via model reuse. Machine learning, 2020, 109: 533−568 doi: 10.1007/s10994-019-05835-w [38] Karimi M R, Gürel N M, Karlas B, Rausch J, Zhang C, Krause A. Online active model selection for pre-trained classifiers. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. San Diego, California, USA: 2021. 307−315 [39] Zyblewski P, Wozniak M, Sabourin R. Preprocessed dynamic classifier ensemble selection for highly imbalanced drifted data streams. Information Fusion, 2021, 66: 138−154 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2020.09.004 [40] Moraes M, Gradvohl A. MOAFS: A Massive Online Analysis library for feature selection in data streams. The Journal of Open Source Software, 2020, 5: 1970 doi: 10.21105/joss.01970 -




 下载:
下载: