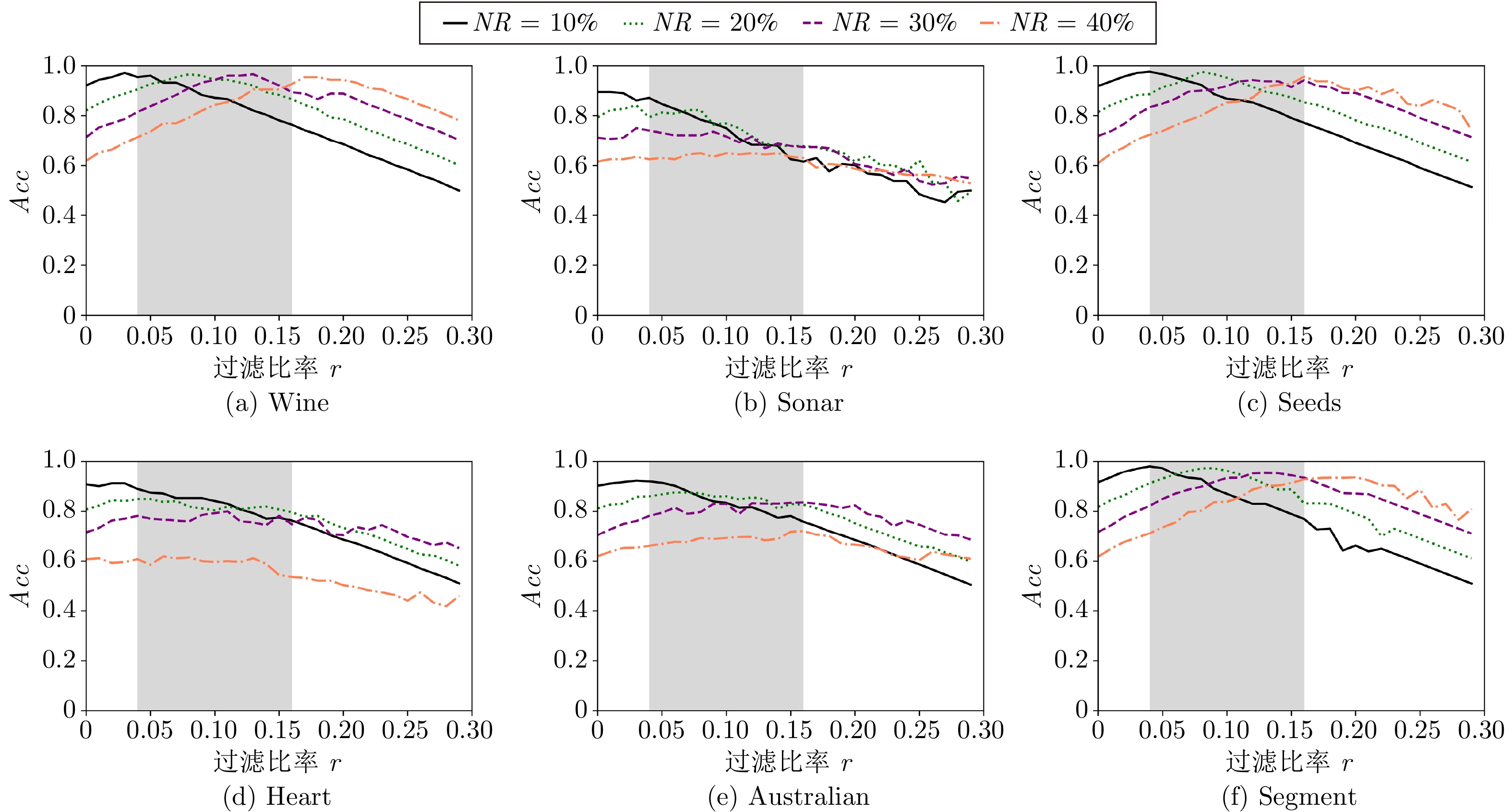
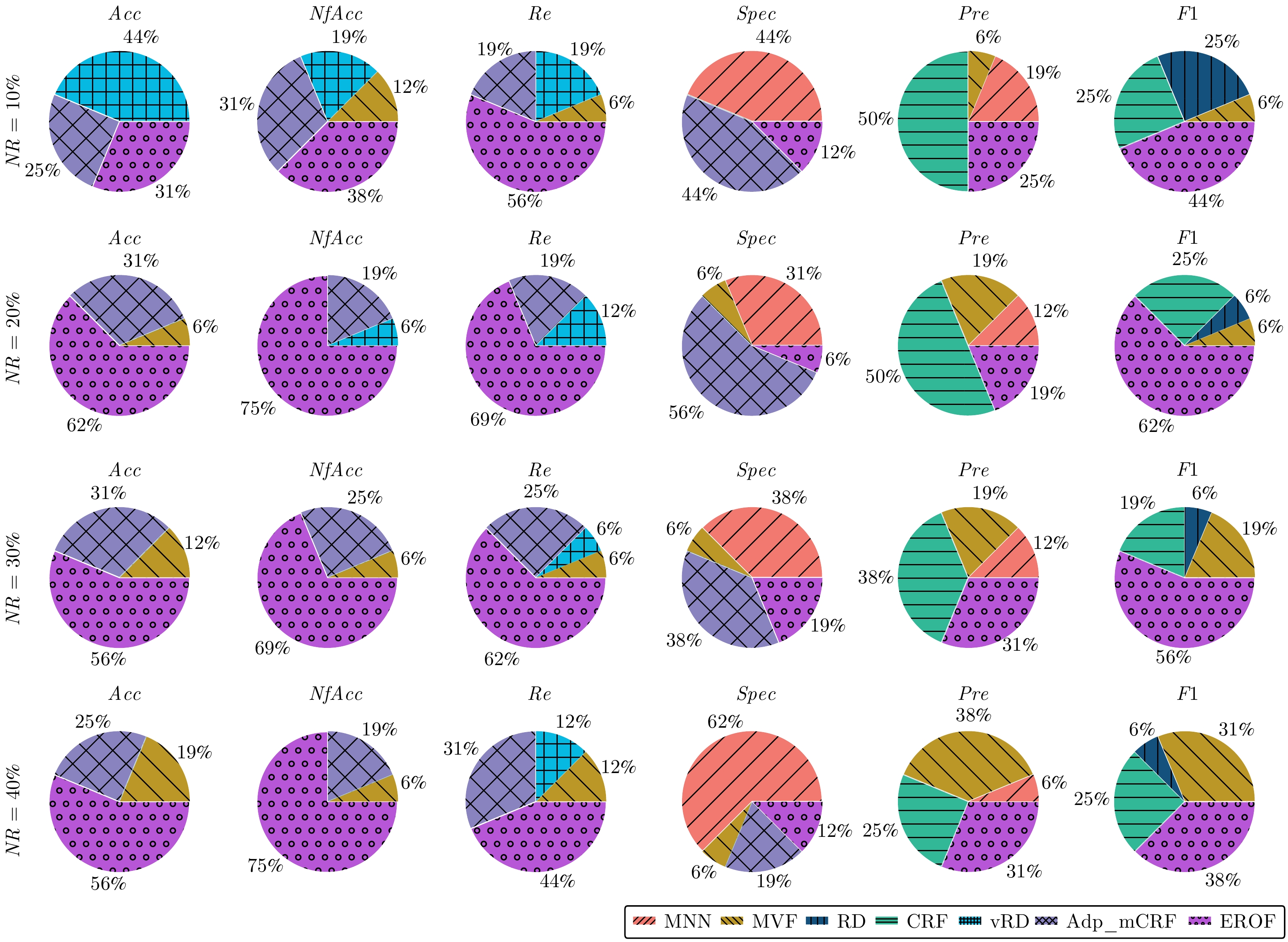
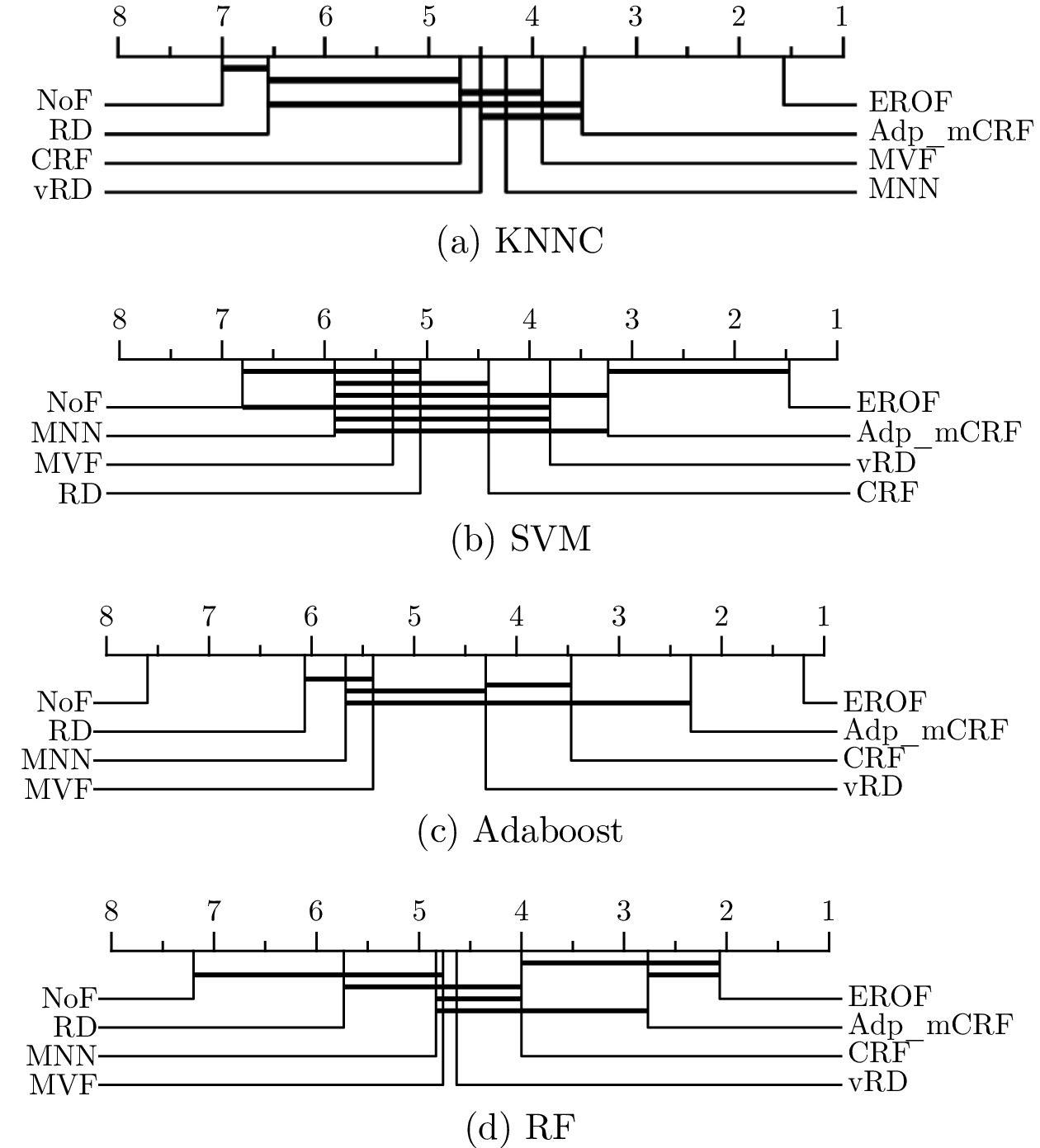
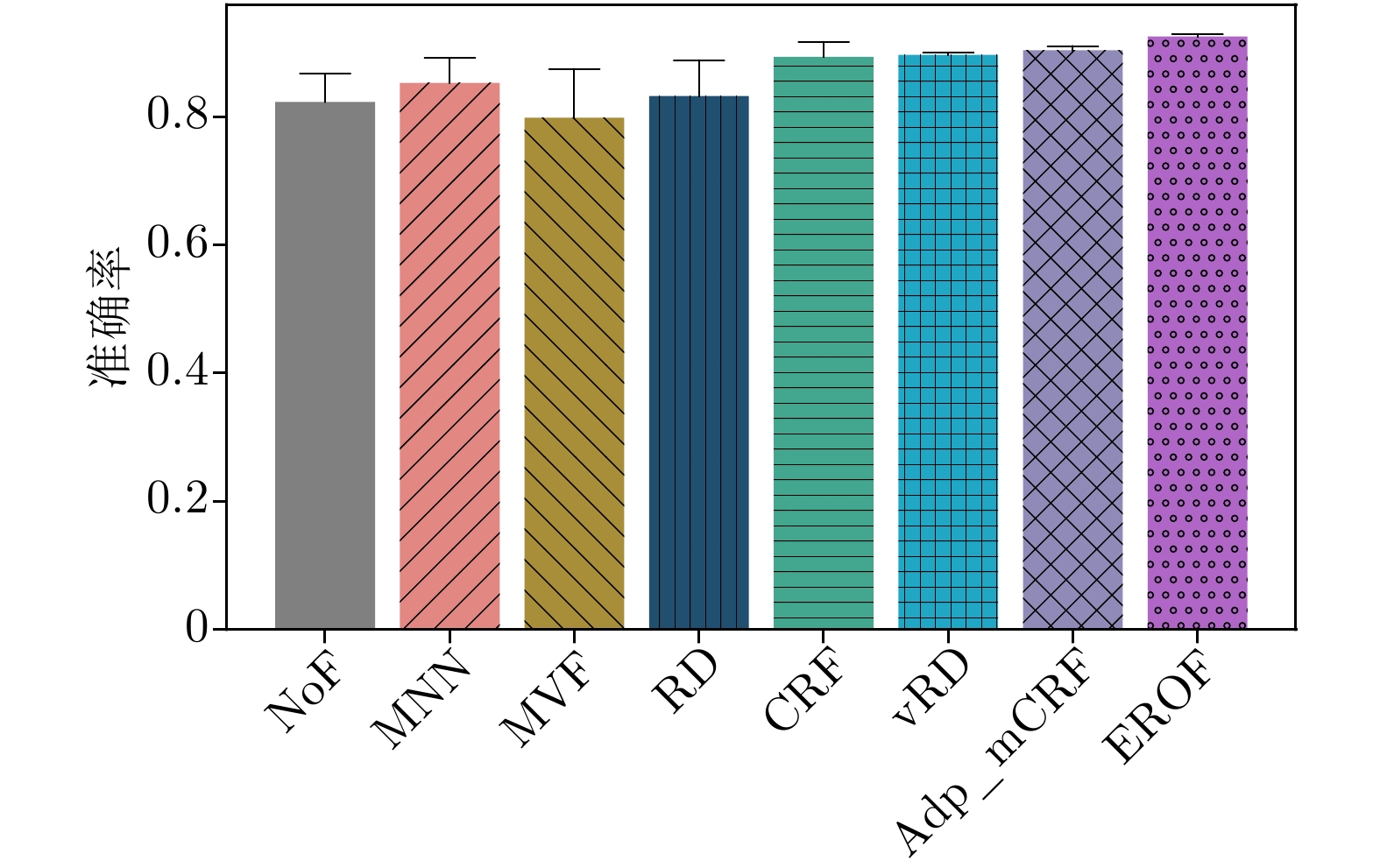
-
摘要: 分类任务中含有类别型标签噪声是传统数据挖掘中的常见问题, 目前还缺少针对性方法来专门检测类别型标签噪声. 离群点检测技术能用于噪声的识别与过滤, 但由于离群点与类别型标签噪声并不具有一致性, 使得离群点检测算法无法精确检测分类数据集中的标签噪声. 针对这些问题, 提出一种基于离群点检测技术、适用于过滤类别型标签噪声的方法 —— 基于相对离群因子(Relative outlier factor, ROF)的集成过滤方法(Label noise ensemble filtering method based on relative outlier factor, EROF). 首先, 通过相对离群因子对样本进行噪声概率估计; 然后, 再迭代联合多种离群点检测算法, 实现集成过滤. 实验结果表明, 该方法在大多数含有标签噪声的数据集上, 都能保持优秀的噪声识别能力, 并显著提升各种分类模型的泛化能力.Abstract: The presence of categorical label noise in classification tasks is a common issue in traditional data mining. Currently, there is a lack of targeted methods specifically designed to detect categorical label noise. While outlier detection techniques can be used for noise identification and filtering, the lack of consistency between outliers and categorical label noise renders outlier detection algorithms unable to accurately detect label noise in classification data sets. To address these issues, a method based on outlier detection techniques, called the label noise ensemble filtering method based on relative outlier factor (ROF) (EROF), is proposed for filtering categorical label noise. The EROF method estimates noise probability of samples by using relative outlier factor and then iteratively combinings multiple outlier detection algorithms for ensemble filtering. Experimental results show that this method maintains excellent noise identification capability in most data sets which contain label noise, and significantly improves the generalization ability of various classification models.
-
Key words:
- Classification /
- label noise /
- outlier detection /
- relative outlier factor (ROF) /
- noise filtering
-
表 1 数据集信息
Table 1 Information of data sets
序号 数据集名称 样本数 特征数 类别数 1 Wine 178 13 3 2 Sonar 208 60 2 3 Seeds 210 7 3 4 Heart 270 13 2 5 Votes 435 16 2 6 Musk 476 166 2 7 Wdbc 569 30 2 8 Australian 690 14 2 9 Credit Approval 690 15 2 10 Vehicle 846 18 4 11 Fourclass 862 2 2 12 German 1000 24 2 13 Svmguide3 1243 21 6 14 Isolet 1559 617 26 15 Segment 2310 18 7 16 Splice 3175 60 2 17 Satimage 4435 36 6 18 Banana 5300 2 2 19 Mushrooms 8124 22 2 20 Letter 20000 16 26 表 2 UCI上, 不同噪声比例下的分类准确率
Table 2 Classification accuracy with different noise ratios on UCI
NR 序号 NoF MNN MVF RD CRF vRD Adp_mCRF EROF NR 序号 NoF MNN MVF RD CRF vRD Adp_mCRF EROF 10% 1 0.926 0.981 0.963 0.921 0.943 0.963 0.963 0.981 20% 1 0.926 0.981 0.981 0.895 0.888 0.926 0.907 1.000 2 0.762 0.714 0.730 0.713 0.615 0.746 0.635 0.746 2 0.761 0.762 0.746 0.745 0.669 0.762 0.683 0.762 3 0.905 0.921 0.937 0.852 0.883 0.889 0.905 0.905 3 0.778 0.937 0.921 0.753 0.852 0.778 0.873 0.937 4 0.691 0.753 0.728 0.665 0.675 0.691 0.704 0.778 4 0.704 0.741 0.704 0.688 0.695 0.704 0.716 0.753 5 0.901 0.885 0.901 0.852 0.878 0.885 0.901 0.908 5 0.878 0.794 0.802 0.851 0.836 0.878 0.855 0.924 6 0.841 0.841 0.848 0.793 0.807 0.833 0.826 0.902 6 0.818 0.765 0.765 0.795 0.792 0.833 0.826 0.841 7 0.727 0.671 0.713 0.687 0.667 0.720 0.699 0.727 7 0.678 0.622 0.650 0.659 0.693 0.685 0.713 0.715 8 0.918 0.901 0.912 0.891 0.897 0.936 0.936 0.959 8 0.825 0.830 0.865 0.825 0.780 0.842 0.819 0.930 9 0.826 0.855 0.831 0.777 0.785 0.816 0.807 0.860 9 0.758 0.787 0.768 0.746 0.720 0.763 0.749 0.855 10 0.841 0.850 0.870 0.804 0.802 0.841 0.831 0.889 10 0.773 0.792 0.739 0.750 0.751 0.773 0.768 0.845 11 0.654 0.610 0.646 0.630 0.578 0.650 0.591 0.606 11 0.598 0.563 0.583 0.588 0.536 0.610 0.547 0.587 12 0.969 1.000 1.000 0.931 0.933 0.965 0.965 1.000 12 0.942 1.000 0.977 0.911 0.916 0.954 0.938 1.000 13 0.697 0.683 0.687 0.681 0.661 0.697 0.683 0.753 13 0.663 0.650 0.663 0.630 0.570 0.663 0.600 0.720 14 0.786 0.775 0.786 0.748 0.695 0.772 0.713 0.812 14 0.716 0.681 0.724 0.679 0.658 0.708 0.676 0.794 15 0.720 0.726 0.733 0.689 0.676 0.716 0.705 0.733 15 0.662 0.736 0.733 0.641 0.627 0.660 0.652 0.737 16 0.931 0.945 0.945 0.889 0.915 0.931 0.938 0.957 16 0.905 0.928 0.935 0.865 0.867 0.908 0.895 0.958 17 0.873 0.870 0.879 0.839 0.849 0.872 0.867 0.893 17 0.817 0.823 0.840 0.801 0.781 0.818 0.818 0.897 18 0.926 0.936 0.928 0.889 0.884 0.927 0.926 0.965 18 0.854 0.881 0.864 0.830 0.820 0.858 0.862 0.958 19 0.972 0.984 0.978 0.942 0.931 0.970 0.969 1.000 19 0.887 0.920 0.930 0.860 0.839 0.882 0.880 0.998 20 0.929 0.920 0.941 0.896 0.905 0.921 0.925 0.949 20 0.868 0.855 0.923 0.833 0.829 0.852 0.855 0.940 30% 1 0.833 0.944 0.907 0.743 0.686 0.759 0.704 0.963 40% 1 0.630 0.926 0.815 0.588 0.686 0.611 0.704 0.981 2 0.603 0.571 0.587 0.580 0.603 0.603 0.619 0.635 2 0.540 0.508 0.508 0.507 0.585 0.524 0.603 0.508 3 0.841 0.952 0.921 0.772 0.725 0.794 0.762 0.957 3 0.603 0.794 0.825 0.609 0.590 0.635 0.603 0.921 4 0.407 0.420 0.395 0.394 0.580 0.407 0.605 0.618 4 0.457 0.481 0.457 0.458 0.423 0.469 0.444 0.580 5 0.710 0.649 0.672 0.652 0.639 0.672 0.664 0.870 5 0.580 0.550 0.511 0.580 0.649 0.603 0.664 0.718 6 0.750 0.765 0.795 0.720 0.692 0.750 0.720 0.818 6 0.629 0.674 0.667 0.617 0.591 0.644 0.606 0.727 7 0.580 0.594 0.594 0.576 0.597 0.601 0.622 0.601 7 0.573 0.497 0.503 0.561 0.550 0.573 0.573 0.524 8 0.684 0.737 0.731 0.666 0.621 0.684 0.649 0.860 8 0.632 0.655 0.661 0.621 0.639 0.643 0.667 0.766 9 0.647 0.696 0.696 0.617 0.585 0.643 0.604 0.807 9 0.507 0.531 0.512 0.491 0.490 0.512 0.507 0.565 10 0.676 0.647 0.657 0.656 0.649 0.676 0.667 0.773 10 0.551 0.556 0.546 0.547 0.565 0.575 0.589 0.700 11 0.531 0.543 0.524 0.502 0.487 0.520 0.512 0.587 11 0.453 0.476 0.472 0.415 0.459 0.429 0.476 0.555 12 0.811 0.961 0.927 0.774 0.794 0.815 0.826 0.973 12 0.683 0.776 0.757 0.669 0.631 0.699 0.656 0.764 13 0.637 0.633 0.647 0.629 0.586 0.643 0.603 0.693 13 0.580 0.620 0.627 0.539 0.551 0.567 0.573 0.577 14 0.651 0.601 0.627 0.627 0.632 0.641 0.649 0.713 14 0.633 0.576 0.582 0.608 0.598 0.622 0.622 0.641 15 0.605 0.712 0.722 0.541 0.546 0.562 0.562 0.705 15 0.545 0.739 0.720 0.480 0.465 0.494 0.483 0.703 16 0.834 0.922 0.896 0.782 0.777 0.815 0.805 0.948 16 0.688 0.885 0.874 0.677 0.646 0.694 0.680 0.929 17 0.740 0.780 0.778 0.717 0.706 0.744 0.739 0.891 17 0.646 0.713 0.707 0.638 0.634 0.653 0.651 0.884 18 0.736 0.764 0.747 0.727 0.721 0.744 0.749 0.924 18 0.603 0.618 0.615 0.571 0.593 0.600 0.613 0.701 19 0.778 0.870 0.857 0.747 0.752 0.774 0.776 0.950 19 0.652 0.766 0.740 0.614 0.626 0.640 0.645 0.781 20 0.791 0.855 0.896 0.747 0.764 0.782 0.784 0.930 20 0.675 0.852 0.857 0.640 0.642 0.666 0.671 0.922 表 3 MNIST上的噪声识别性能
Table 3 Noise recognition performance on MNIST
评价指标 MNN MVF RD CRF vRD Adp_mCRF EROF Acc 0.664 0.732 0.791 0.780 0.801 0.844 0.872 NfAcc 0.372 0.436 0.489 0.545 0.563 0.651 0.713 Re 0.582 0.669 0.739 0.761 0.763 0.816 0.851 Spec 0.993 0.985 0.998 0.858 0.951 0.956 0.957 Pre 0.997 0.995 0.999 0.964 0.987 0.988 0.991 F1 0.735 0.797 0.850 0.837 0.851 0.885 0.916 -
[1] Bi Y T, Jeske D R. The efficiency of logistic regression compared to normal discriminant analysis under class-conditional classification noise. Academic Press, 2010, 101(7): 1622-1637 [2] Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa R A, Ko J, Swetter S M, Thrun S, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature, 2017, 542(7639): 115-118 doi: 10.1038/nature21056 [3] 廖海斌, 徐斌. 基于性别和年龄因子分析的鲁棒性人脸表情识别. 计算机研究与发展, 2021, 58(3): 528-538Liao Hai-Bin, Xu Bin. Robust face expression recognition based on genderand age factor analysis. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2021, 58(3):528-538 [4] Kermany D S, Goldbaum M, Cai W J, Valentim C C S, Liang H Y, Baxter S L, et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell, 2018, 172(5): 1122-1131 doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010 [5] Breve F A, Zhao L, Quiles M G. Particle competition and cooperation for semi-supervised learning with label noise. Neurocomputing, 2015, 160: 63-72 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.08.082 [6] Zhu X, Wu X. Class noise vs. attribute noise: a quantitative study. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2004, 22(3): 177-210 doi: 10.1007/s10462-004-0751-8 [7] Aversano L, Bernardi M L, Cimitile M, Pecori R, Veltri L. Effective anomaly detection using deep learning in IoT systems. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2021, 2021: 1-14 [8] Khoshgoftaar T M, Van H J. Identifying noisy features with the pairwise attribute noise detection algorithm. Intelligent Data Analysis, 2005, 9(6): 589-602 doi: 10.3233/IDA-2005-9606 [9] Frenay B, Verleysen M. Classification in the presence of label noise: a survey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(5): 845-869 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2292894 [10] Yao J C, Wang J J, Tsang I W, Zhang Y, Sun J, Zhang C Q, et al. Deep learning from noisy image labels with quality embedding. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28: 1909-1922 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2877939 [11] 姜高霞, 王文剑. 面向回归任务的数值型标签噪声过滤算法. 计算机研究与发展, 2022, 59(8): 1639-1652Jiang Gao-Xia, Wang Wen-Jian. A numerical label noise filtering algorithm for regression. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2022, 59(8): 1639-1652 [12] Sun J W, Zhao F Y, Wang C J, Chen S F. Identifying and correcting mislabeled training instances. In: Proceedings of the Future Generation Communication and Networking. Jeju Isl, South Korea: IEEE, 2007. 244−250 [13] Gamberger D, Lavrac N, Groselj C. Experiments with noise filtering in a medical domain. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Machine Learning. Bled, Slovenia: 1999. 143−151 [14] Angelova A, Abu-Mostafam Y, Perona P. Pruning training sets for learning of object categories. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2005. 494−501 [15] Brodley C E, Uiversity P, Friedl M A. Identifying mislabeled training data. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 1999, 11(6): 131-167 [16] Sanchez J S, Barandela R, Marques A I, Alejo R, Badenas J. Analysis of new techniques to obtain quality training sets. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2003, 24(7): 1015-1022 doi: 10.1016/S0167-8655(02)00225-8 [17] Sluban B, Gamberger D, Lavrac N. Advances in class noise detection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Lisbon, Portugal: IOS Press, 2010. 1105−1106 [18] Tomek I. An Experiment with the Edited Nearest-Neighbor Rule.IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics-systems, 2007, 6(6): 448-452 [19] Barandela R, Gasca E. Decontamination of training samples for supervised pattern recognition methods. In: Proceedings of the Joint International Workshops of the International Association of Pattern Recognition on Structural and Syntactic Pattern Recognition and Statistical Pattern Recognition. Alicante, Spain: Springer-Verlag, 2000. 621−630 [20] Liu H W, Zhang S C. Noisy data elimination using mutual k-nearest neighbor for classification mining. Journal of Systems and Software, 2012, 85(5): 1067-1074 doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2011.12.019 [21] 姜高霞, 樊瑞宣, 王文剑. 近邻感知的标签噪声过滤算法. 模式识别与人工智能, 2020, 33(6): 518-529Jiang Gao-Xia, Fan Rui-Xuan, Wang Wen-Jian. Label noise filtering viaperception of nearest neighbors. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 33(6): 518-529 [22] Xia S Y, Xiong Z Y, He Y, Li K, Dong L M, Zhang M. Relative density-based classification noise detection. Optik, 2014, 125(22): 6829-6834 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.08.091 [23] Xia S Y, Wang G Y, Chen Z Z, Duan Y L, Liu Q. Complete random forest based class noise filtering learning for improving the generalizability of classifiers. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2020, 31(11): 2063-2078 [24] Xia S Y, Chen B Y, Wang G Y, Zheng Y, Gao X B, Giem E, et al. mCRF and mRD: Two classification methods based on a novel multiclass label noise filtering learning framework. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 33(7): 2916-2930 [25] Huang L, Shao Y, Peng J. An adaptive voting mechanism based on relative density for filtering label noises. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Electronics Technology. Chengdu, China: ICET, 2022. 1327−1331 [26] Lu J, Zhou Z Y, Leung T, Li J J, Li F F. MentorNet: Learning data-driven curriculum for very deep neural networks on corrupted labels. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: JMLR, 2018. 2304−2313 [27] Han B, Yao Q M, Yu X R, Niu G, Xu M, Hu W H, et al. Co-teaching: Robust training of deep neural networks with extremely noisy labels. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: NIPS, 2018. 1−10 [28] Xiong H, Pandey G, Steinbach M, Kumar V. Enhancing data analysis with noise removal. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2006, 18(3): 304-319 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2006.46 [29] Zhang W N, Tan X Y. Combining outlier detection and reconstruction error minimization for label noise reduction. In: Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing. Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2019. 238−241 [30] Angiulli F, Pizzuti C. Fast outlier detection in high dimensional spaces. In: Proceedings of the Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 6th European Conference. Helsinki, Finland: Springer-Verlag, 2002. 15−27 [31] Breunig M, Kriegel H P, Ng R T, Sander J. LOF: Identifying density-based local outliers. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. Paris, France: ACM, 2000. 93−104 [32] Tang J, Chen Z, Fu A W C, Cheung D W. Enhancing effectiveness of outlier detections for low density patterns. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Taiwan, China: Springer Berlin, 2002. 535−548 [33] Kriegel H P, Schubert M, Zimek A. Angle-based outlier detection in high-dimensional data. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Las Vegas, USA: ACM, 2008. 444−452 [34] Schlkopf B, Platt J C, Shawe-Taylor J C, Smola A J, Williamson R C. Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution. Neural Computation, 2001, 13(7): 1443-1471 doi: 10.1162/089976601750264965 [35] Bandaragoda T R, Ting K M, Albrecht D, Liu F T, Zhu Y, Wells J R. Isolation-based anomaly detection using nearest-neighbor ensembles. Computational Intelligence, 2018, 34(4): 968-998 doi: 10.1111/coin.12156 [36] Ramaswamy S, Rastogi R, Shim K. Efficient algorithms for mining outliers from large data sets. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Management of Data. Dallas, USA: 2000. 427−438 [37] 金连文, 钟卓耀, 杨钊, 杨维信, 谢泽澄, 孙俊. 深度学习在手写汉字识别中的应用综述. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(8): 1125-1141 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150725Jin Lian-Wen, Zhong Zhuo-Yao, Yang Zhao, Yang Wei-Xin, Xie Ze-Cheng, Sun Jun. Applications of deep learning for handwritten Chinese character recognition:a review. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(8): 1125-1141 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150725 -




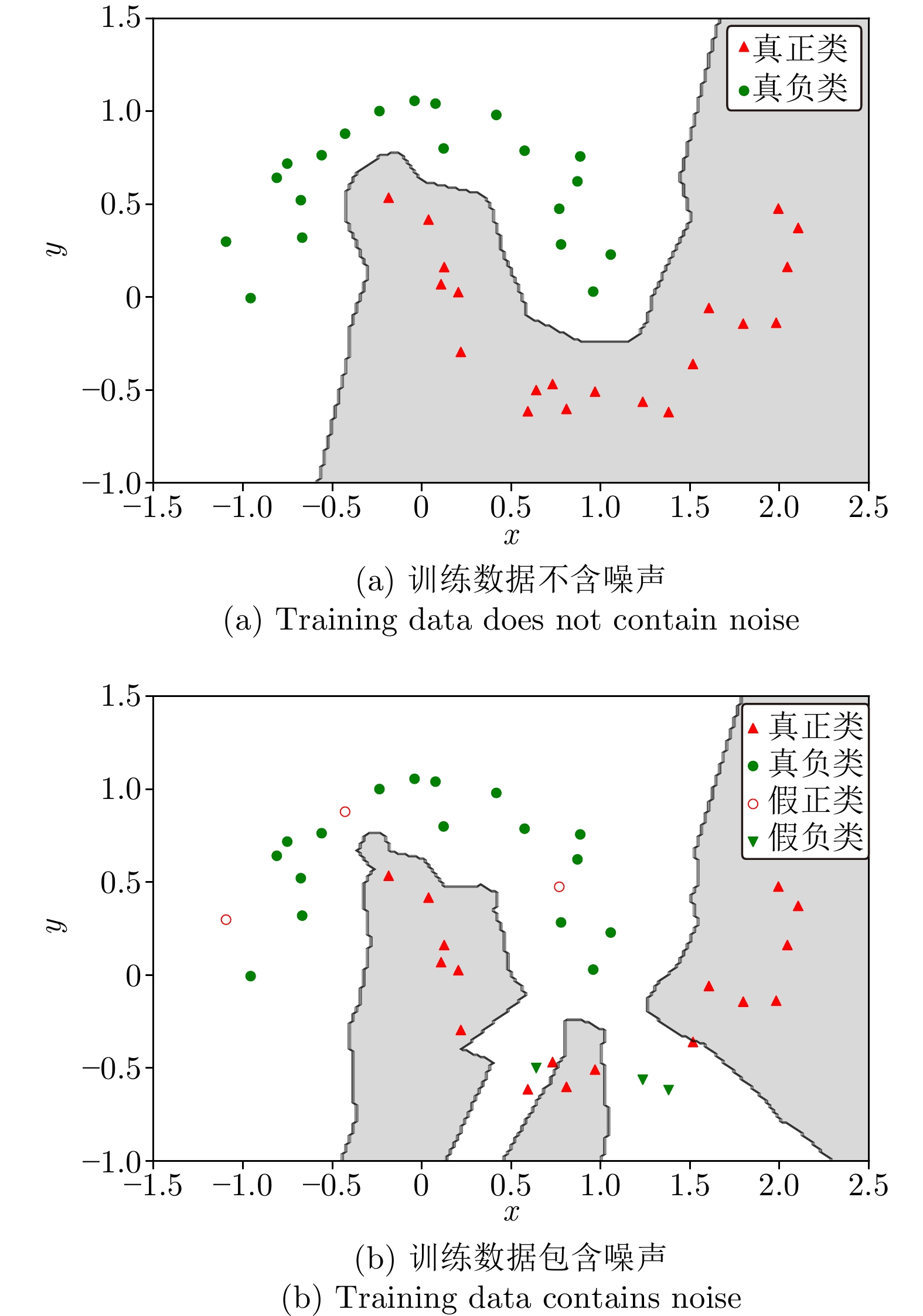
 下载:
下载: