Data-driven Model-free Adaptive Integral Sliding Mode Predictive Control for High-speed Electric Multiple Unit
-
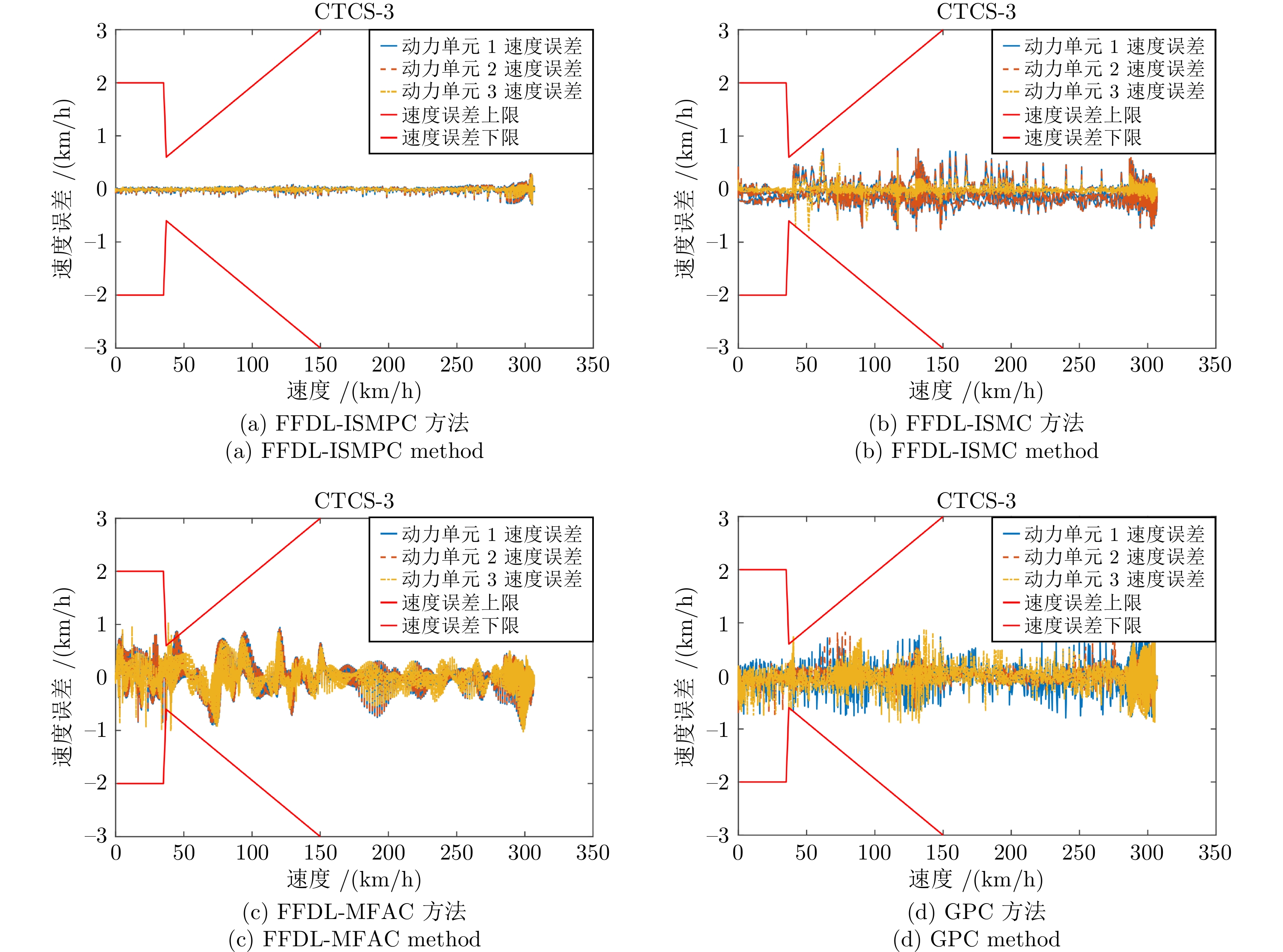
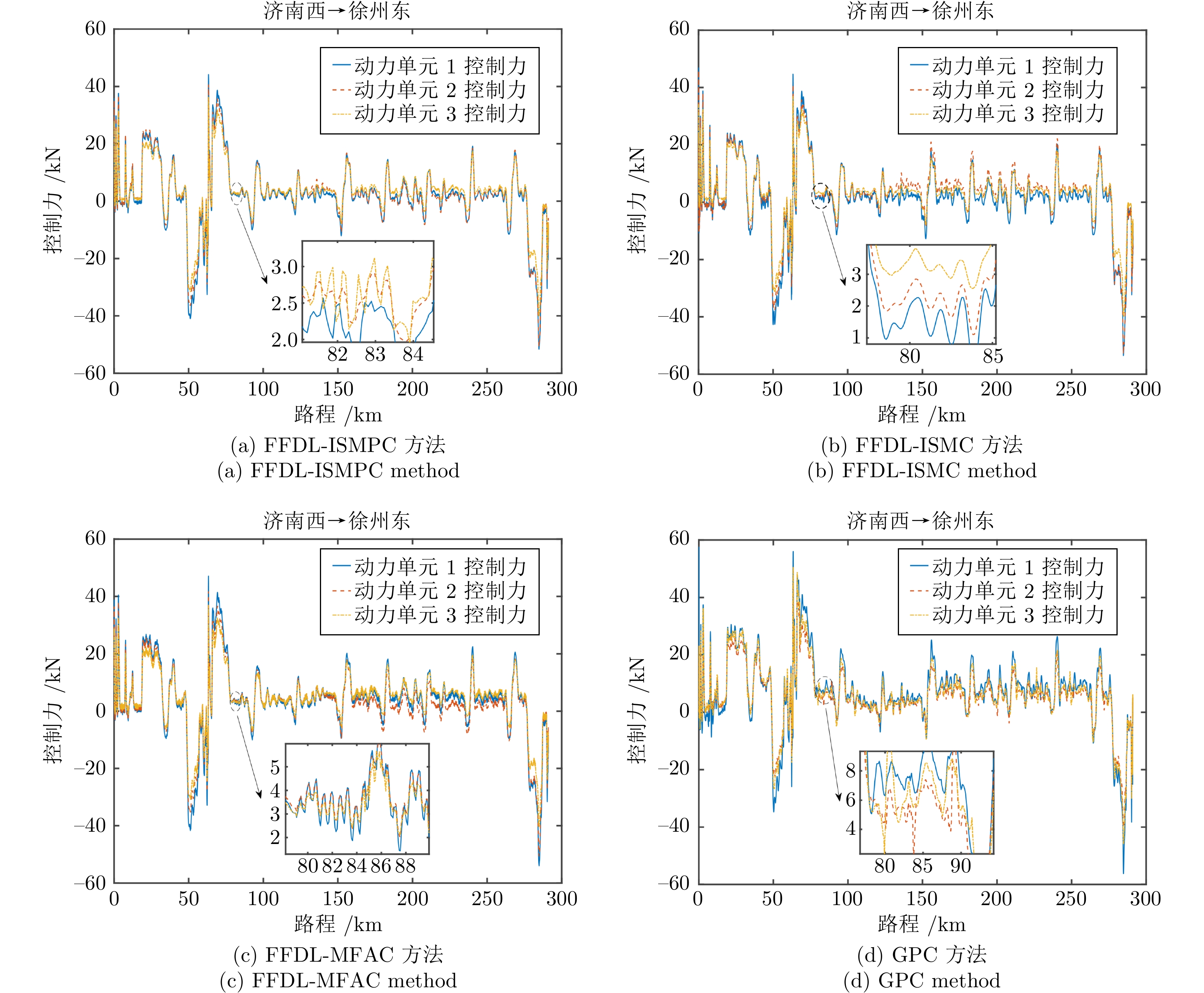
摘要: 同许多复杂系统一样, 动车组(Electric multiple unit, EMU) 运行过程也具有多变量、强耦合以及非线性等特性, 这严重影响着列控系统的性能. 针对包含外部扰动的动车组自动驾驶系统, 提出一种新型的多输入多输出(Multi-input-multi-output, MIMO) 数据驱动积分滑模预测控制(Integral sliding mode predictive control, ISMPC)算法. 首先, 该算法基于与动车组运行过程等效的全格式动态线性化(Full format dynamic linearization, FFDL)数据模型, 设计一种离散积分滑模控制(Integral sliding mode control, ISMC) 律. 为了使系统能够获得更高的输出跟踪误差精度, 利用模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC) 代替ISMC的切换控制, 进一步推导出ISMPC算法. 同时, 通过对FFDL 数据模型的未知扰动、参数误差等不确定项进行延时估计, 提升了算法的控制性能和对系统的等价描述程度. 在提供两种算法的稳定性证明分析之后, 以实验室配备的 CRH380A 型动车组仿真实验台对提出的ISMC和ISMPC算法进行仿真测试, 并与其他方法进行对比, 仿真结果表明ISMPC算法控制性能较好, 动车组各动力单元速度跟踪误差均在 ±0.132 km/h 以内, 满足列车的跟踪精度需求; 控制力和加速度分别在[−52 kN, 42 kN] 和 ±0.9249 m/s2 以内且变化平稳.Abstract: Like many complex systems, the electric multiple unit (EMU) operation process also has the characteristics of multivariable, strong coupling and nonlinearity, which seriously affect the performance of the train control system. A new multi-input-multi-output (MIMO) data-driven integral sliding mode predictive control (ISMPC) algorithm is proposed for the EMU autopilot system with external disturbances. Based on the full format dynamic linearization (FFDL) data model equivalent to the EMU operation process, a discrete integral sliding mode control (ISMC) law is designed. To achieve higher output tracking error accuracy, the switching control with ISMC is replaced by model predictive control (MPC), leading to the further derivation of the ISMPC algorithm. Through the delay estimation of the unknown disturbance, parameter error and other uncertainties of the FFDL data model, the control performance of the algorithm and the equivalent description of the system are improved. After providing the stability proof analysis of the two algorithms, the ISMC and ISMPC algorithms proposed in this paper are simulated and tested on the CRH380A EMU simulation test bench equipped in the laboratory, and compared with other methods. The simulation results show that the ISMPC algorithm has better control performance, and the speed tracking error of each power unit of the EMU is within ±0.132 km/h, which meets the tracking accuracy requirements of the train; The control force and acceleration are within [−52 kN, 42 kN] and ±0.9249 m/s2 respectively and change smoothly.
-
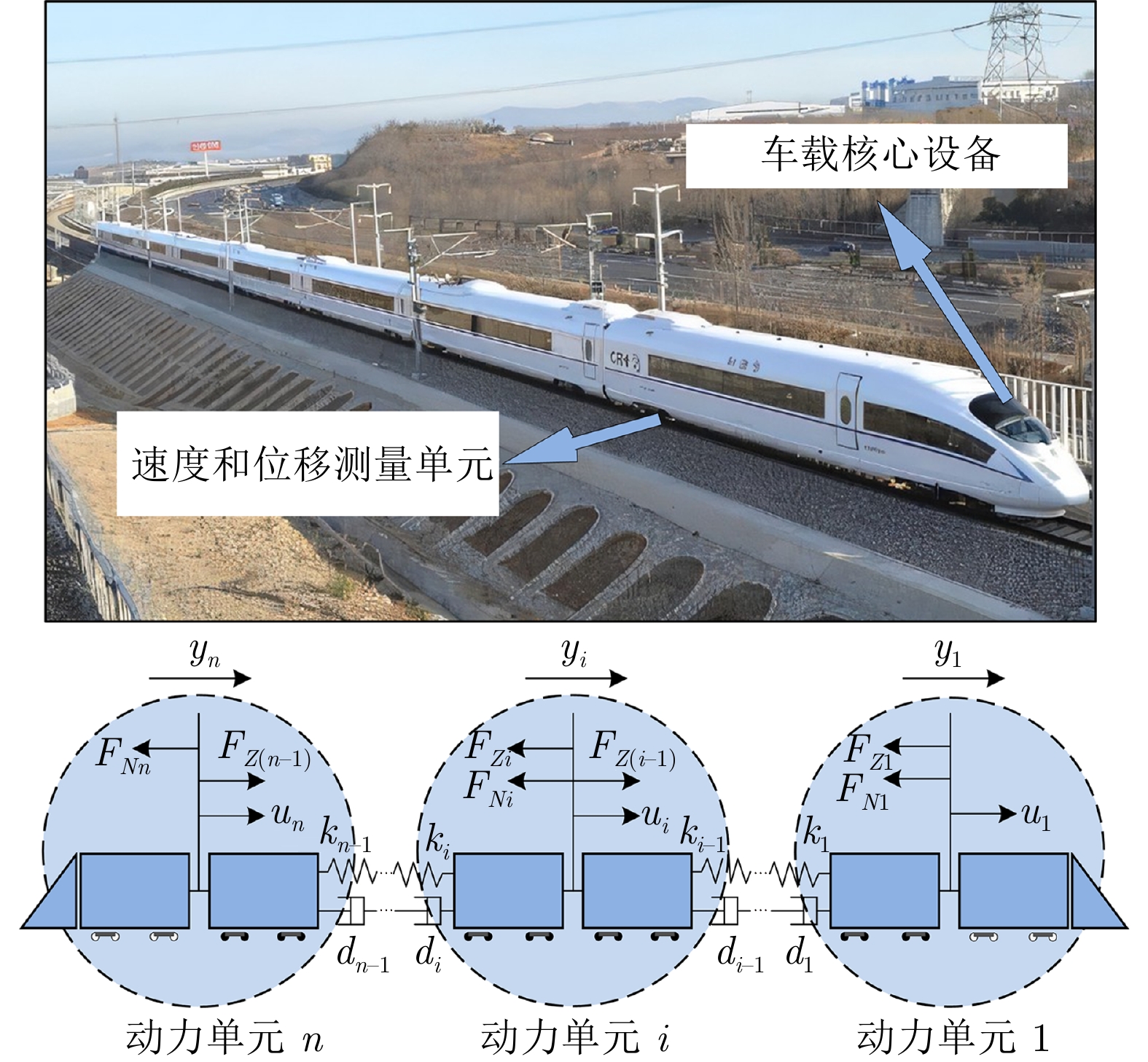
表 1 CRH380A 型动车组模型参数
Table 1 The CRH380A EMU model parameters
参数名称 参数值 单位 动力单元质量$M_1$ $ 1.836 \times 10^5$ kg 动力单元质量$M_2$ $ 1.123 \times 10^5 $ kg 动力单元质量$M_3$ $ 1.836 \times 10^5 $ kg 列车阻力系数$a_r$ 5.200 N/kg 列车阻力系数$b_r$ $ 3.600 \times 10^{-2} $ N·s2/(kg·m) 列车阻力系数$c_r$ $ 1.200 \times 10^{-3} $ N·s2/(kg·m2) 车钩弹性系数$k$ $ 2.000 \times 10^7 $ N/m 车钩阻尼系数$d$ $ 5.000 \times 10^6 $ N·s/m 表 2 各个控制方法的若干性能指标对比
Table 2 Comparison of several performance indexes of each control method
控制方法 MSE IAE MA FFDL-ISMPC 0.052 324 0.9249 FFDL-ISMC 0.161 940 0.9432 FFDL-MFAC 0.287 1814 0.9749 GPC 0.346 2421 1.0124 -
[1] Zhang K P, Jiang B, Chen F Y. Multiple-model based diagnosis of multiple faults with high speed train applications using second level adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(7): 6257-6266 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2994867 [2] Yang H, Fu Y T, Wang D H. Multi-ANFIS model based synchronous tracking control of high-speed electric multiple unit. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(3): 1472-1484 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2725819 [3] 杨辉, 张芳, 张坤鹏, 李中奇, 付雅婷. 基于分布式模型的动车组预测控制方法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(9): 1912-1921Yang Hui, Zhang Fang, Zhang Kun-Peng, Li Zhong-Qi, Fu Ya-Ting. Predictive control using a distributed model for electric multiple unit. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9): 1912-1921 [4] Yuan H, Huang D Q, Li X F. Adaptive speed tracking control for high speed trains under stochastic operation environments. Automatica, 2023, 147: Article No. 110674 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110674 [5] 李中奇, 周靓, 杨辉. 高速动车组数据驱动无模型自适应控制方法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 1-11Li Zhong-Qi, Zhou Liang, Yang Hui. Data-driven model-free adaptive control method for high-speed electric multiple unit.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(2): 1-11 [6] 贾超. 考虑安全约束的列车自动驾驶多质点非线性预测控制[博士学位论文], 北京交通大学, 中国, 2020.Jia Chao. Nonlinear Predictive Control for Automatic Train Operation With Consideration of Safety Constraints and Multi-point Model [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing Jiaotong University, China, 2020. [7] Mao Z H, Tao G, Jiang B, Yan X G. Adaptive control design and evaluation for multibody high-speed train dynamic models. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2021, 29(3): 1061-1074 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2020.2991119 [8] 李中奇, 金柏, 杨辉, 谭畅, 付雅婷. 高速动车组强耦合模型的分布式滑模控制策略. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(3): 495-508Li Zhong-Qi, Jin Bai, Yang Hui, Tan Chang, Fu Ya-Ting. Predictive control using a distributed model for electric multiple unit. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 495-508 [9] 李中奇, 丁俊英, 杨辉, 刘江. 基于控制器匹配的高速列车广义预测控制方法. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(9): 82-89Li Zhong-Qi, Ding Jun-Ying, Yang Hui, Liu Jiang. Generalized predictive control tuning for high-speed train based on controller matching method. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(9): 82-89 [10] 李中奇, 杨辉, 刘明杰, 刘杰民. 高速动车组制动过程的建模及跟踪控制. 中国铁道科学, 2016, 37(5): 80-86Li Zhong-Qi, Yang Hui, Liu Ming-Jie, Liu Jie-Min. Modeling and tracking control for braking process of high-speed electric multiple unit. China Railway Science, 2016, 37(5): 80-86 [11] 杨辉, 刘盼, 李中奇. 基于 Elman 模型的高速列车速度跟踪控制. 控制理论与应用, 2017, 34(1): 125-130Yang Hui, Liu Pan, Li Zhong-Qi. Speed tracking control for high-speed train with an Elman model. Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 34(1): 125-130 [12] Yang H, Zhang K P, Liu H E. Online regulation of high speed train trajectory control based on T-S fuzzy bilinear model. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(6): 1496-1508 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2497320 [13] 杨辉, 张坤鹏, 王昕, 衷路生. 高速列车多模型广义预测控制方法. 铁道学报, 2011, 33(8): 80-87Yang Hui, Zhang Kun-Peng, Wang Xin, Zhong Lu-Sheng. Generalized multiple model predictive control method of high-speed train. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(8): 80-87 [14] 侯忠生. 非线性系统参数辩识、自适应控制及无模型学习自适应控制[博士学位论文], 东北大学, 中国, 1994.Hou Zhong-Sheng. Nonlinear System Parameter Identification, Adaptive Control and Model Free Adaptive Learning Control [Ph.D. dissertation], Northeastern University, China, 1994. [15] Wang H J, Hou Z S. Model-free adaptive fault-tolerant control for subway trains with speed and traction/braking force constraints. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 14(12): 1557-1566 [16] Ma Y S, Che W W, Deng C. Dynamic event-triggered model-free adaptive control for nonlinear CPSs under aperiodic DoS attacks. Information Sciences : An International Journal, 2022, 589: 790-801 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.01.009 [17] Liu S D, Hou Z S, Zhang X, Ji H H. Model-free adaptive control method for a class of unknown MIMO systems with measurement noise and application to quadrotor aircraft. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 14(15): 2084-2096 [18] Xiong S S, Hou Z S. Model-free adaptive control for unknown MIMO nonaffine nonlinear discrete-time systems with experimental validation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(4): 1727-1739 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3043711 [19] Hui Y, Chi R H, Huang B, Hou Z S, Jin S T. Observer-based sampled-data model-free adaptive control for continuous-time nonlinear nonaffine systems with input rate constraints. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(12): 7813-7822 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.2982491 [20] Wang W H, Hou Z S. New adaptive quasi-sliding mode control for nonlinear discrete-time systems.Journal of Systems Engineering & Electronics, 2008, 19(1): 154-160 [21] 侯忠生, 王卫红, 金尚泰.一类非线性离散系统自适应准滑模控制. 控制理论与应用, 2009, 26(5): 505-509Hou Zhong-Sheng, Wang Wei-Hong, Jin Shang-Tai. Adaptive quasi-sliding-mode control for a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems. Control Theory & Applications, 2009, 26(5): 505-509 [22] 江浩斌, 冯张棋, 洪阳珂, 韦奇志, 皮健. 应用于车辆纵向控制的无模型自适应滑模预测控制方法. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(3): 319-329Jiang Hao-Bin, Feng Zhang-Qi, Hong Yang-Ke, Wei Qi-Zhi, Pi Jian. Model-free adaptive sliding mode predictive control algorithm for vehicle longitudinal control. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(3): 319-329 [23] Wang X F, Li X, Wang J H, Fang X K, Zhu X F. Data-driven model-free adaptive sliding mode control for the multi degree-of-freedom robotic exoskeleton. Information Sciences : An International Journal, 2016, 327(C): 246-257 [24] Xu Q S. Digital integral terminal sliding mode predictive control of piezoelectric-driven motion system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(6): 3976-3984 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2504343 [25] Incremona G P, Ferrara A, Magni L. MPC for robot manipulators with integral sliding modes generation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(3): 1299-1307 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2674701 [26] Xu Y T, Wu A G. Integral sliding mode predictive control with disturbance attenuation for discrete-time systems. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 16(17): 1751-1766 [27] Wang Y S, Hou M D. Model-free adaptive integral terminal sliding mode predictive control for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems. ISA Transactions, 2019, 93(C): 209-217 [28] Zhou L, Li Z Q, Yang H, Fu Y T, Yan Y. Data-driven model-free adaptive sliding mode control based on FFDL for electric multiple units. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(21): Article No. 10983 doi: 10.3390/app122110983 [29] Hou Z S, Xiong S S. On model-free adaptive control and its stability analysis. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(11): 4555-4569 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2894586 [30] Bu X H, Yu W, Yu Q X, Hou Z S, Yang J Q. Event-triggered model-free adaptive iterative learning control for a class of nonlinear systems over fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(9): 9597-9608 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3058997 [31] 段莉. 数据驱动迭代学习控制及在列车自动驾驶控制系统中的应用[硕士学位论文], 北京交通大学, 中国, 2020.Duan Li. Data-based Iterative Learning Control With Applications in Automatic Train Operation [Master thesis], Beijing Jiaotong University, China, 2020. [32] Lin P, Tian Y, Gui G, Yang C H. Cooperative control for multiple train systems: Self-adjusting zones, collision avoidance and constraints. Automatica, 2022, 144: Article No. 110470 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110470 [33] Liu Y F, Zhou Y, Su S, Xun J, Tang T. An analytical optimal control approach for virtually coupled high-speed trains with local and string stability.Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 125: Article No. 102886 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2020.102886 -




 下载:
下载: