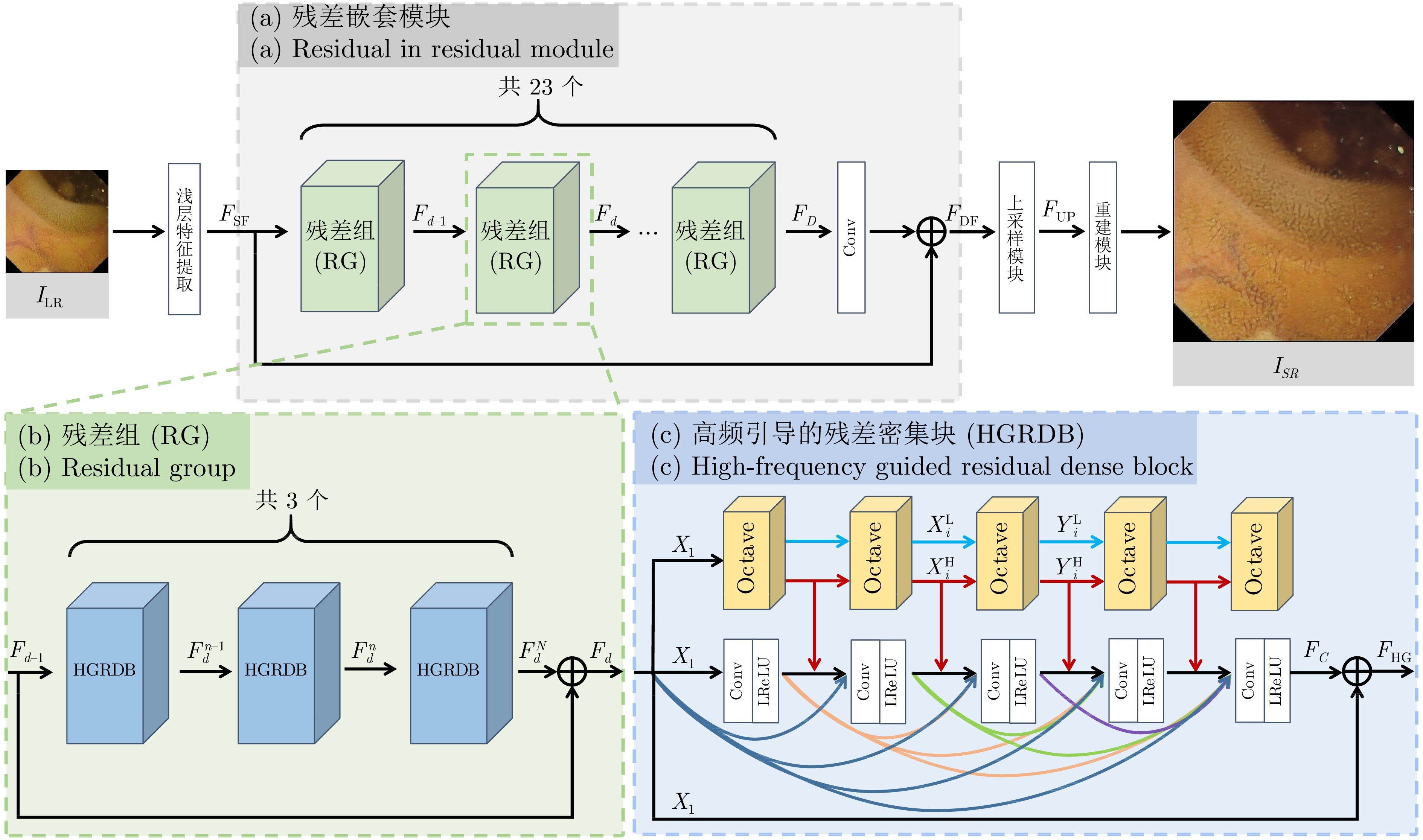
Super-resolution of Endoscopic Images Based on Real Degradation Estimation and High-frequency Guidance
-
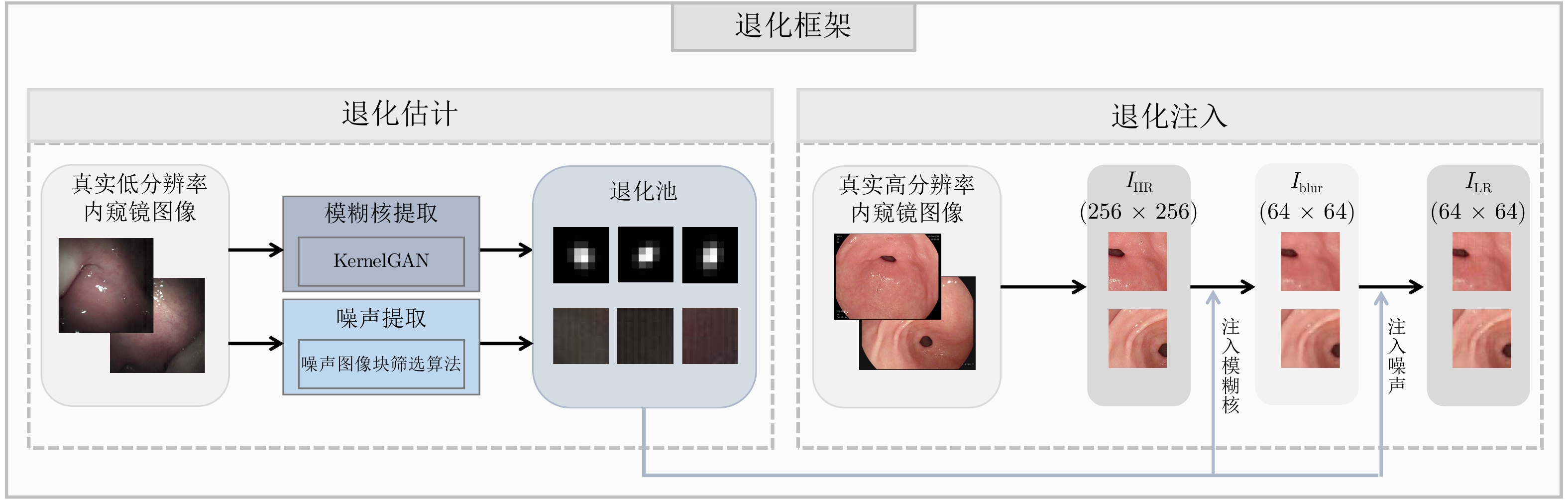
摘要: 内窥镜是诊断人体器官疾病的重要医疗设备, 然而受人体内腔环境影响, 内窥镜图像分辨率一般较低, 需对其进行超分辨处理. 目前多数基于深度学习的超分辨算法直接使用双三次插值下采样从高质量图像中获取低分辨率(Low-resolution, LR)图像以进行配对训练, 此种方式会导致纹理细节丢失, 不适用于医学图像. 为解决该问题, 针对医学内窥镜图像开发了一种新颖的退化框架, 首先从真实低质量内窥镜图像中提取丰富多样的真实模糊核与噪声模式, 之后提出一种退化注入算法, 利用提取的真实模糊核与噪声将高分辨率(High-resolution, HR)内窥镜图像退化为符合真实域的低分辨率图像. 同时, 提出一种高频引导的残差密集超分辨网络, 采用基于双频率信息交互的频率分离策略, 并设计多层级融合机制, 将提取的多级高频信息逐层嵌入残差密集模块的多层特征, 以充分恢复内窥镜图像的高频细节和低频内容. 在合成与真实数据集上的大量实验表明, 我们的方法优于对比方法, 具有更好的主客观质量评价.Abstract: Endoscopes are effective medical devices for diagnosing diseases of human organs. However, due to the influence of the internal cavity environment of the human body, the resolution of endoscope images is generally low. Most existing deep learning-based super-resolution algorithms directly use bicubic interpolation downsampling to obtain low-resolution (LR) images from high-quality images for paired training. However, these methods will lead to texture details loss and are not suitable for medical images. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a novel degradation framework for medical endoscopic images. First, diverse realistic blur kernels and noise patterns are extracted from real-world low-quality endoscopic images, and then a degradation injection algorithm is proposed. The extracted real blur kernels and noise degrade the high-resolution (HR) endoscopic image into a low-resolution image. In addition, this paper proposes a high-frequency guided residual dense super-resolution network, which adopts a frequency separation strategy based on dual-frequency information interaction. And a multi-level fusion mechanism is designed to embed the extracted multi-level high-frequency information into the multi-layer features of the residual dense module layer by layer. This helps recover the high-frequency details and low-frequency content of the endoscopic image. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets show that our method outperforms the contrastive methods with better subjective and objective quality evaluations.
-
表 1 各方法在定量测试集的客观结果
Table 1 The objective results of different methods in quantitative testsets
方法 定量测试集A 定量测试集B 定量测试集C 定量测试集D PSNR$\uparrow$ SSIM$\uparrow$ PSNR$\uparrow$ SSIM$\uparrow$ PSNR$\uparrow$ SSIM$\uparrow$ PSNR$\uparrow$ SSIM$\uparrow$ PDMSR[55] 29.21 0.723 28.60 0.773 27.78 0.761 24.40 0.776 RealSR[26] 28.08 0.652 28.09 0.621 25.41 0.581 25.16 0.561 RealESRGAN[53] 31.08 0.790 30.01 0.863 32.60 0.801 32.17 0.879 USRNet[54] 30.17 0.787 28.50 0.864 31.32 0.801 29.91 0.882 FSSR[31] 26.46 0.670 28.31 0.663 25.93 0.612 24.32 0.574 FAWDN[56] 31.62 0.792 32.96 0.894 32.33 0.802 33.58 0.905 BSRGAN[30] 30.73 0.777 29.86 0.848 31.30 0.792 29.89 0.864 HGRDN (Ours) 31.78 0.797 33.22 0.902 32.61 0.808 33.90 0.913 表 2 各方法在定量测试集的高频结果
Table 2 The high-frequency results of different methods in quantitative testsets
方法 定量测试集A 定量测试集B 高频PSNR$\uparrow$ 高频SSIM$\uparrow$ 高频PSNR$\uparrow$ 高频SSIM$\uparrow$ PDMSR[55] 26.95 0.573 26.07 0.573 RealSR[26] 27.52 0.523 27.13 0.513 RealESRGAN[53] 28.21 0.600 28.53 0.630 USRNet[54] 27.67 0.590 27.76 0.625 FSSR[31] 28.34 0.574 27.21 0.539 FAWDN[56] 29.51 0.601 29.80 0.649 BSRGAN[30] 27.13 0.543 27.65 0.580 HGRDN (Ours) 29.79 0.603 30.26 0.664 表 3 不同方法在定性测试集的客观结果
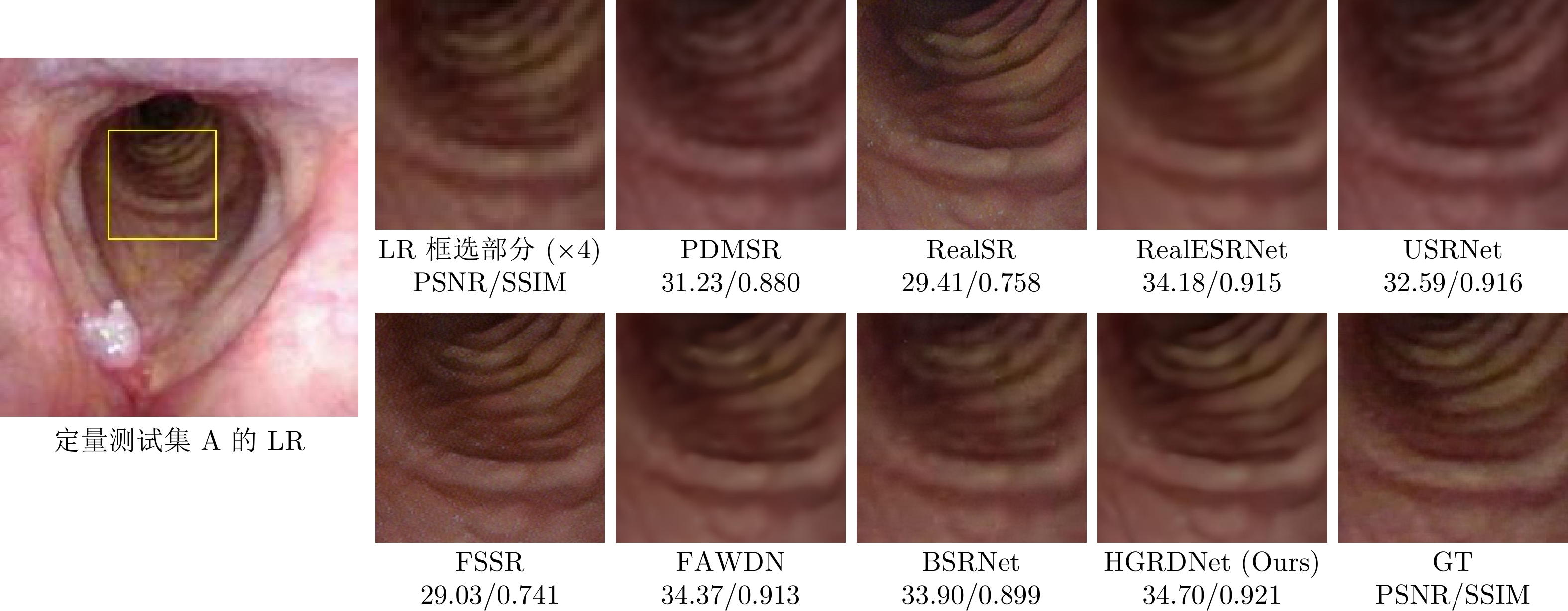
Table 3 The objective results of different methods in the qualitative testsets
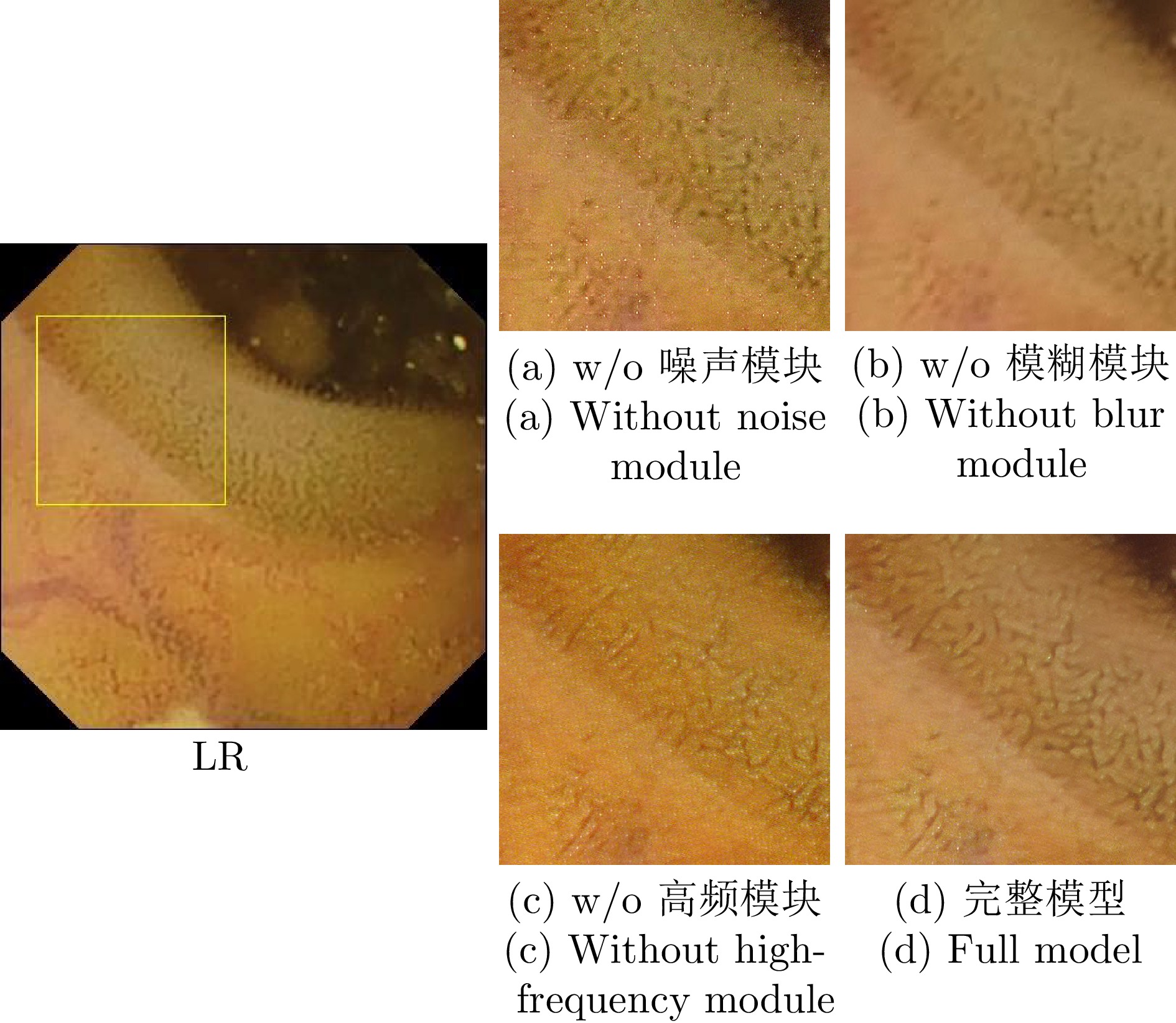
表 4 消融实验定量结果
Table 4 The quantitative results of the ablation experiments
方法 定量测试集A 定量测试集B PSNR$\uparrow$ SSIM$\uparrow$ PSNR$\uparrow$ SSIM$\uparrow$ 去除噪声模块 30.50 0.761 32.03 0.857 去除模糊模块 30.97 0.789 32.54 0.892 去除高频模块 30.61 0.792 32.29 0.898 完整模型 31.78 0.797 33.22 0.902 -
[1] Li B Z, Liao C R, Cai Z H, Zhou J, Zhao C, Jing L Q, et al. Femtosecond laser 3D printed micro objective lens for ultrathin fiber endoscope. Fundamental Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.fmre.2022.05.026 [2] Yang X R, Chen Y, Tao R, Zhang Y, Liu Z W, Shi Y G. Endoscopic image deblurring and super-resolution reconstruction based on deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2020. 168−172 [3] 王知音, 张二虎, 石争浩, 段敬红. 零参考样本下的逆光图像深度学习增强方法. 中国图象图形学报, 2022, 27(5): 1589-1603 doi: 10.11834/jig.210783Wang Zhi-Yin, Zhang Er-Hu, Shi Zheng-Hao, Duan Jing-Hong. Deep learning based backlight image enhancement method derived of zero-reference samples. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2022, 27(5): 1589-1603 doi: 10.11834/jig.210783 [4] 杨振, 邸拴虎, 赵于前, 廖苗, 曾业战. 基于级联Dense-UNet和图割的肝脏肿瘤自动分割. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(5): 1683-1693Yang Zhen, Di Shuan-Hu, Zhao Yu-Qian, Liao Miao, Zeng Ye-Zhan. Automatic liver tumor segmentation based on cascaded Dense-UNet and graph cuts. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(5): 1683-1693 [5] 张芳, 赵东旭, 肖志涛, 耿磊, 吴骏, 刘彦北. 单幅图像超分辨率重建技术研究进展. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(11): 2634-2654 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200777Zhang Fang, Zhao Dong-Xu, Xiao Zhi-Tao, Geng Lei, Wu Jun, Liu Yan-Bei. Research progress of single image super-resolution reconstruction technology. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2634-2654 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200777 [6] Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, Tang X O. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [7] Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, Caballero J, Cunningham A, Acosta A, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 105−114 [8] Lim B, Son S, Kim H, Nah S, Lee K M. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1132−1140 [9] Ahn N, Kang B, Sohn K A. Fast, accurate, and lightweight super-resolution with cascading residual network. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 256−272 [10] Qu J L, Jin K, Wang M, Huang G M. Real-time stripe noise removal method for endoscope image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology. Chengdu, China: IEEE, 2021. 865−870 [11] Chen Y H, Shi F, Christodoulou A G, Xie Y B, Zhou Z W, Li D B. Efficient and accurate MRI super-resolution using a generative adversarial network and 3D multi-level densely connected network. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Granada, Spain: Springer, 2018. 91−99 [12] Park J, Hwang D, Kim K Y, Kang S K, Kim Y K, Lee J S. Computed tomography super-resolution using deep convolutional neural network. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2018, 63(14): Article No. 145011 [13] Mahapatra D, Bozorgtabar B. Retinal vasculature segmentation using local saliency maps and generative adversarial networks for image super resolution. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.04783, 2017. [14] 蒋希, 袁奕萱, 王雅萍, 肖振祥, 朱美芦, 陈泽华, 等. 中国医学影像人工智能20年回顾和展望. 中国图象图形学报, 2022, 27(3): 655-671Jiang Xi, Yuan Yi-Xuan, Wang Ya-Ping, Xiao Zhen-Xiang, Zhu Mei-Lu, Chen Ze-Hua, et al. A 20-year retrospect and prospect of medical imaging artificial intelligence in China. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2022, 27(3): 655-671 [15] Gu X G, Zhou F X, Chen R F, Ren X Z, Zhou W J. Endoscopic single image super-resolution based on transformer and convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Life System Modeling and Simulation. Hangzhou, China: Springer, 2021. 24−32 [16] Song X W, Tang H, Yang C F, Zhou G Q, Wang Y G, Huang X J, et al. Deformable transformer for endoscopic video super-resolution. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 77: Article No. 103827 [17] Turan M. A generative adversarial network based super-resolution approach for capsule endoscopy images. Medicine Science, 2021, 10(3): 1002-1007 doi: 10.5455/medscience.2021.06.218 [18] Almalioglu Y, Ozyoruk K B, Gokce A, Incetan K, Gokceler G I, Simsek M A, et al. EndoL2H: Deep super-resolution for capsule endoscopy. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(12): 4297-4309 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3016744 [19] Dai T, Cai J R, Zhang Y B, Xia S T, Zhang L. Second-order attention network for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 11057−11066 [20] Pan J S, Liu S F, Sun D Q, Zhang J W, Liu Y, Ren J, et al. Learning dual convolutional neural networks for low-level vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3070−3079 [21] He X Y, Mo Z T, Wang P S, Liu Y, Yang M Y, Cheng J. ODE-inspired network design for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1732−1741 [22] Hu X C, Mu H Y, Zhang X Y, Wang Z L, Tan T N, Sun J. Meta-SR: A magnification-arbitrary network for super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1575−1584 [23] Li Z, Yang J L, Liu Z, Yang X M, Jeon G, Wu W. Feedback network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3862−3871 [24] Qiu Y J, Wang R X, Tao D P, Cheng J. Embedded block residual network: A recursive restoration model for single-image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 4179−4188 [25] Yin X, Tai Y, Huang Y G, Liu X M. FAN: Feature adaptation network for surveillance face recognition and normalization. In: Proceedings of the 15th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Kyoto, Japan: Springer, 2020. 301−319 [26] Ji X Z, Cao Y, Tai Y, Wang C J, Li J L, Huang F Y. Real-world super-resolution via kernel estimation and noise injection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1914−1923 [27] Wang W, Zhang H C, Yuan Z H, Wang C H. Unsupervised real-world super-resolution: A domain adaptation perspective. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 4298−4307 [28] Zhang K, Zuo W M, Zhang L. Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3262−3271 [29] Zhang K, Zuo W M, Zhang L. Deep plug-and-play super-resolution for arbitrary blur kernels. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1671−1681 [30] Zhang K, Liang J Y, Van Gool L, Timofte R. Designing a practical degradation model for deep blind image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 4771−4780 [31] Fritsche M, Gu S H, Timofte R. Frequency separation for real-world super-resolution. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3599−3608 [32] Lugmayr A, Danelljan M, Timofte R. Unsupervised learning for real-world super-resolution. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3408−3416 [33] Chen S J, Han Z, Dai E Y, Jia X, Liu Z L, Liu X, et al. Unsupervised image super-resolution with an indirect supervised path. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1924−1933 [34] Xie W B, Song D H, Xu C, Xu C J, Zhang H, Wang Y H. Learning frequency-aware dynamic network for efficient super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 4288−4297 [35] Yun J S, Yoo S B. Single image super-resolution with arbitrary magnification based on high-frequency attention network. Mathematics, 2022, 10(2): Article No. 275 doi: 10.3390/math10020275 [36] Xu R Y, Kang X J, Li C X, Chen H, Ming A L. DCT-FANet: DCT based frequency attention network for single image super-resolution. Displays, 2022, 74: Article No. 102220 doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2022.102220 [37] Guo T T, Mousavi H S, Monga V. Adaptive transform domain image super-resolution via orthogonally regularized deep networks. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(9): 4685-4700 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2913500 [38] Hung K W, Wang K, Jiang J M. Image up-sampling using deep cascaded neural networks in dual domains for images down-sampled in DCT domain. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2018, 56: 144-149 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.09.005 [39] Pang Y X, Li X, Jin X, Wu Y J, Liu J Z, Liu S, et al. FAN: Frequency aggregation network for real image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 468−483 [40] Liu Z B, Yuan L, Sun L. Frequency separation-based multi-scale cascading residual block network for image super resolution. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(5): 6827-6848 doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11724-z [41] Chen Y P, Fan H Q, Xu B, Yan Z C, Kalantidis Y, Rohrbach M, et al. Drop an octave: Reducing spatial redundancy in convolutional neural networks with octave convolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3434−3443 [42] Bell-Kligler S, Shocher A, Irani M. Blind super-resolution kernel estimation using an internal-GAN. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2019. Article No. 26 [43] Chen J W, Chen J W, Chao H Y, Yang M. Image blind denoising with generative adversarial network based noise modeling. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3155−3164 [44] Sudiro S A, Kardian A R, Madenda S, Hermanto L. Mean and variance statistic for image processing on FPGA. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(1): Article No. 2020115 [45] 陈晔曜, 蒋刚毅, 邵华, 姜浩, 郁梅. 高动态范围图像融合过程中的噪声抑制算法. 光电工程, 2018, 45(7): Article No. 180083Chen Ye-Yao, Jiang Gang-Yi, Shao Hua, Jiang Hao, Yu Mei. Noise suppression algorithm in the process of high dynamic range image fusion. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(7): Article No. 180083 [46] Luo Z X, Huang Y, Li S, Wang L, Tan T N. Unfolding the alternating optimization for blind super resolution. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 473 [47] Wang X T, Yu K, Wu S X, Gu J J, Liu Y H, Dong C, et al. ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 63−79 [48] Zhang Y L, Tian Y P, Kong Y, Zhong B N, Fu Y. Residual dense network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 2472−2481 [49] Zhang Y L, Li K P, Li K, Wang L C, Zhong B N, Fu Y. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 294−310 [50] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA: ICLR, 2015. [51] Pogorelov K, Randel K R, Griwodz C, Eskeland S L, de Lange T, Johansen D, et al. KVASIR: A multi-class image dataset for computer aided gastrointestinal disease detection. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACM on Multimedia Systems Conference. Taipei, China: Association for Computing Machinery, 2017. 164−169 [52] Smedsrud P H, Thambawita V, Hicks S A, Gjestang H, Nedrejord O O, Naess E, et al. Kvasir-Capsule, a video capsule endoscopy dataset. Scientific Data, 2021, 8(1): Article No. 142 doi: 10.1038/s41597-021-00920-z [53] Wang X T, Xie L B, Dong C, Shan Y. Real-ESRGAN: Training real-world blind super-resolution with pure synthetic data. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 1905−1914 [54] Zhang K, Van Gool L, Timofte R. Deep unfolding network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 3214−3223 [55] Luo Z X, Huang Y, Li S, Wang L, Tan T N. Learning the degradation distribution for blind image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6063−6072 [56] Chen L H, Yang X M, Jeon G, Anisetti M, Liu K. A trusted medical image super-resolution method based on feedback adaptive weighted dense network. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2020, 106: Article No. 101857 doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101857 [57] Gonzalez R C, Woods R E [著], 阮秋琦, 阮宇智[译]. 数字图像处理. 第3版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2011. 169−182Gonzalez R C, Woods R E [Author], Ruan Qiu-Qi, Ruan Yu-Zhi [Translator]. Digital Image Processing. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2011. 169−182 [58] Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik A C. Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 209-212 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726 [59] Blau Y, Mechrez R, Timofte R, Michaeli T, Zelnik-Manor L. The 2018 PIRM challenge on perceptual image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 334−355 -




 下载:
下载: