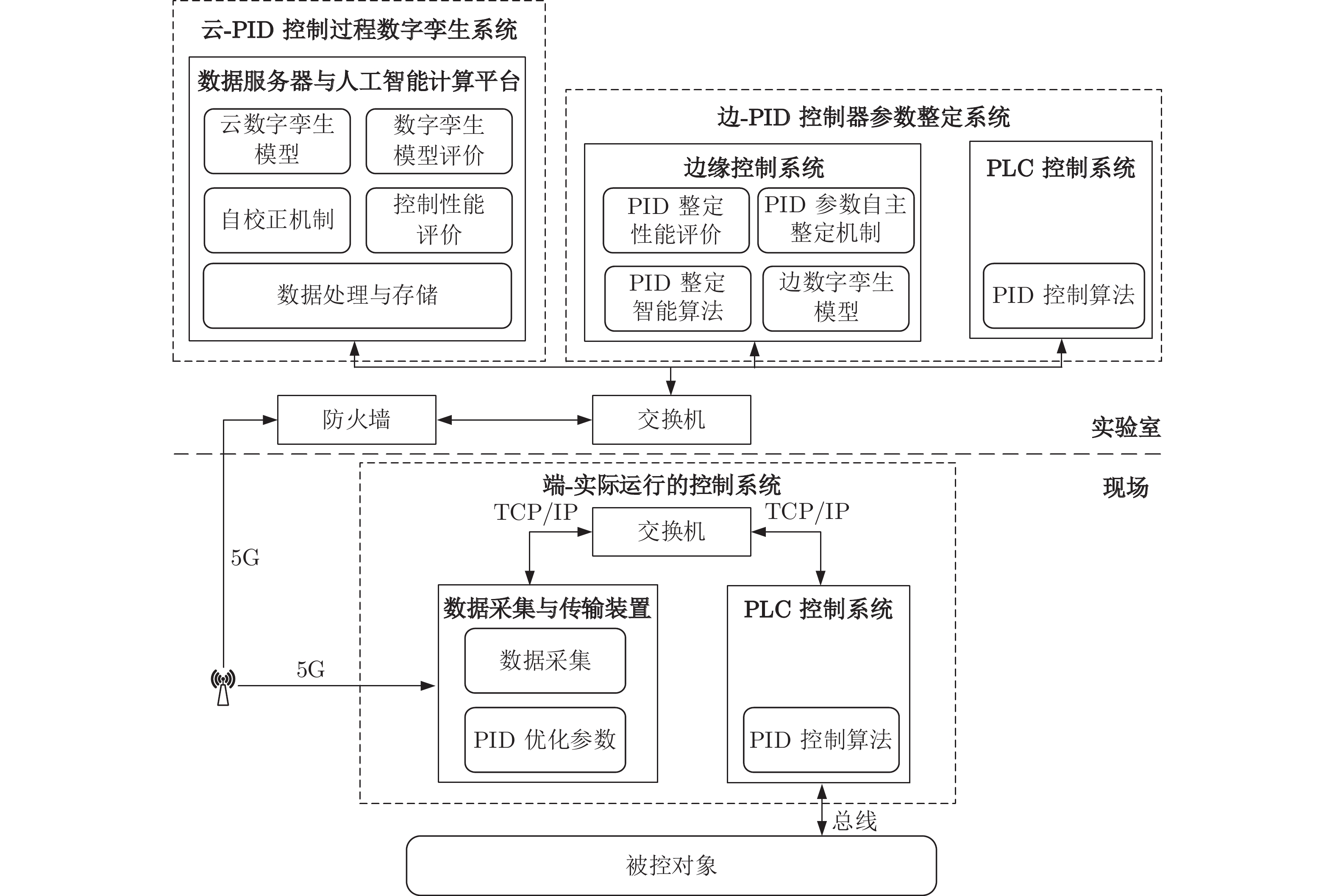
-
摘要: 本文在分析智能制造对PID整定的新需求及PID整定面临的挑战难题的基础上, 将自动化的建模、控制与优化和人工智能的深度学习与强化学习深度融合与协同, 提出了自适应与自主的PID整定的智能优化方法, 包括端边云协同的PID控制过程数字孪生模型和强化学习与数字孪生模型相结合的PID整定算法. 将工业互联网的端边云协同技术与PLC控制系统相结合, 研制了PID整定智能系统, 并在重大耗能设备 — 电熔镁炉成功应用. 该系统安全、可靠与优化运行, 取得显著的节能减排效果. 最后, 提出了控制系统智能化研究方向需要进一步深入研究的内容.Abstract: Based on the analysis of the new requirements of intelligent manufacturing for PID tuning and the challenges and difficulties faced by PID tuning, this paper proposes an adaptive and autonomous PID tuning intelligent optimization method by deeply integrates and coordinates the modeling, control and optimization in automation and deep learning and reinforcement learning in artificial intelligence. The proposed method contains the digital twin model of the PID control process based on end-edge-cloud collaboration and the PID tuning algorithm combining reinforcement learning and digital twin model. Furthermore, the PID tuning intelligent system is developed by combining the end-edge-cloud collaboration technology of Industrial Internet with the PLC control system, and has been successfully applied to the energy intensive equipment — Fused magnesium furnace. This system operates safely, reliably and optimally, achieving remarkable effects in energy conservation and emission reduction. Finally, the further research content in the intelligent research direction of control system is proposed.
-
表 1 数字孪生模型精度评价表
Table 1 The evaluation table of the accuracy of the digital twin model
云数字孪生模型 边数字孪生模型 MAE RMSE MAE RMSE y1(k) 429.144 535.359 466.751 651.642 y2(k) 369.998 474.175 375.679 487.996 y3(k) 341.209 450.719 363.354 451.023 表 2 常规PID方法和本文方法的控制性能评价表(N =
1000 )Table 2 The evaluation table of the control performance of the conventional PID method and the proposed method
MSE×10−6 IAE×10−6 ${e_1}(k)$ ${e_2}(k)$ ${e_3}(k)$ ${e_1}(k)$ ${e_2}(k)$ ${e_3}(k)$ 常规PID方法 1.2579 1.5044 1.4332 2.7705 3.7629 3.3114 本文方法 0.6732 0.7107 0.8462 1.2579 1.5044 1.4332 -
[1] Guo L. Feedback and uncertainty: Some basic problems and results. Annual Reviews in Control, 2020, 49: 27−36 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2020.04.001 [2] Samad T. A survey on industry impact and challenges thereof [technical activities]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2017, 37(1): 17−18 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2016.2621438 [3] Borase R, Maghade D K, Sondkar S Y, Pawar S N. A review of PID control, tuning methods and applications. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2021, 9(2): 818−827 doi: 10.1007/s40435-020-00665-4 [4] Åström K J, Hägglund T. PID Controllers: Theory, Design, and Tuning (Second edition). Research Triangle Park: ISA, 1995. [5] Somefun O A, Akingbade K, Dahunsi F. The dilemma of PID tuning. Annual Reviews in Control, 2021, 52: 65−74 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2021.05.002 [6] Ziegler J G, Nichols N B. Optimum settings for automatic controllers. Transactions of the ASME, 1942, 64(8): 759−765 [7] Åström K J, Hägglund T. Automatic tuning of simple regulators with specifications on phase and amplitude margins. Automatica, 1984, 20(5): 645−651 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(84)90014-1 [8] Ho W K, Lim K W, Xu W. Optimal gain and phase margin tuning for PID controllers. Automatica, 1998, 34(8): 1009−1014 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(98)00032-6 [9] Ho W K, Lim K W, Hang C C, Ni L Y. Getting more phase margin and performance out of PID controllers. Automatica, 1999, 35(9): 1579−1585 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00055-2 [10] Silva G J, Datta A, Bhattacharyya S P. On the stability and controller robustness of some popular PID tuning rules. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(9): 1638−1641 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2003.817008 [11] Åström K J, Hägglund T. Revisiting the Ziegler-Nichols step response method for PID control. Journal of Process Control, 2004, 14(6): 635−650 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2004.01.002 [12] Bazanella A S, Pereira L F A, Parraga A. A new method for PID tuning including plants without ultimate frequency. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(2): 637−644 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2016.2557723 [13] Grimholt C, Skogestad S. Optimal PI and PID control of first-order plus delay processes and evaluation of the original and improved SIMC rules. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 70: 36−46 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2018.06.011 [14] Hägglund T. The one-third rule for PI controller tuning. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2019, 127: 25−30 [15] 刘宁, 柴天佑. PID 控制器参数的优化整定方法. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c220795Liu Ning, Chai Tian-You. An optimal tuning method of PID controller parameters. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c220795 [16] Tan K K, Zhao S, Xu J X. Online automatic tuning of a proportional integral derivative controller based on an iterative learning control approach. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2007, 1(1): 90−96 [17] Lequin O, Gevers M, Mossberg M, Bosmans E, Triest L. Iterative feedback tuning of PID parameters: Comparison with classical tuning rules. Control Engineering Practice, 2003, 11(9): 1023−1033 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(02)00303-9 [18] Ho W K, Hong Y, Hansson A, Hjalmarsson H, Deng J W. Relay auto-tuning of PID controllers using iterative feedback tuning. Automatica, 2003, 39(1): 149−157 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(02)00201-7 [19] Son D, Choi H. Iterative feedback tuning of the proportional-integral-differential control of flow over a circular cylinder. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 27(4): 1385−1396 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2018.2828381 [20] Lawrence N P, Forbes M G, Loewen P D, Mcclement D G, Backström J U, Gopaluni R B. Deep reinforcement learning with shallow controllers: An experimental application to PID tuning. Control Engineering Practice, 2022, 121: Article No. 105046 [21] Dogru O, Velswamy K, Ibrahim F, Wu Y Q, Sundaramoorthy A S, Huang B, et al. Reinforcement learning approach to autonomous PID tuning. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2022, 161: Article No. 107760 [22] McClement D G, Lawrence N P, Backstrom J U, Loewen P D, Forbes M G, Gopaluni R B. Meta reinforcement learning for adaptive control: An offline approach. arXiv: 2203.09661, 2022. [23] Åström K J, Hägglund T. Advanced PID Control. Research Triangle Park: ISA, 2006. [24] Åström K J, Hägglund T. Design methods: PID control. Control System Fundamentals (Second edition). Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017. [25] Garpinger O, Hägglund T, Åström K J. Performance and robustness trade-offs in PID control. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24(5): 568−577 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.02.020 [26] Ortega R, Kelly R. PID self-tuners: Some theoretical and practical aspects. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1984, IE-31(4): 332−338 doi: 10.1109/TIE.1984.350087 [27] Kim J H, Choi K K. Design of direct pole placement PID self-tuners. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1987, IE-34(3): 351−356 doi: 10.1109/TIE.1987.350984 [28] Wang Q G, Zhang Z P, Åström K J, Chek L S. Guaranteed dominant pole placement with PID controllers. Journal of Process Control, 2009, 19(2): 349−352 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2008.04.012 [29] Ho W K, Lee T H, Han H P, Hong Y. Self-tuning IMC-PID control with interval gain and phase margins assignment. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2001, 9(3): 535−541 doi: 10.1109/87.918905 [30] Verma B, Padhy P K. Indirect IMC-PID controller design. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 13(2): 297−305 [31] Åström K J, Panagopoulos H, Hägglund T. Design of PI controllers based on non-convex optimization. Automatica, 1998, 34(5): 585−601 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(98)00011-9 [32] Sekara T B, Matausek M R. Optimization of PID controller based on maximization of the proportional gain under constraints on robustness and sensitivity to measurement noise. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(1): 184−189 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.2008359 [33] Mercader P, Åström K J, Baños A, Hägglund T. Robust PID design based on QFT and convex-concave optimization. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(2): 441−452 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2016.2562581 [34] PoulinÉ, Pomerleau A, Desbiens A, Hodouin D. Development and evaluation of an auto-tuning and adaptive PID controller. Automatica, 1996, 32(1): 71−82 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(95)00105-0 [35] Yang Y, Cui K X, Shi D W, Mustafa G, Wang J D. PID control with PID event triggers: Theoretic analysis and experimental results. Control Engineering Practice, 2022, 128: Article No. 105322 [36] Kuc T Y, Han W G. An adaptive PID learning control of robot manipulators. Automatica, 2000, 36(5): 717−725 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00198-3 [37] Yamamoto T, Takao K, Yamada T. Design of a data-driven PID controller. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2009, 17(1): 29−39 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2008.921808 [38] Yu H, Guan Z, Chen T W, Yamamoto T. Design of data-driven PID controllers with adaptive updating rules. Automatica, 2020, 121: Article No. 109185 [39] Zhong S, Huang Y, Guo L. A parameter formula connecting PID and ADRC. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(9): Article No. 192203 [40] Wang L Y, Jia Y, Chai T Y, Xie W F. Dual-rate adaptive control for mixed separation thickening process using compensation signal based approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(4): 3621−3632 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2752144 [41] Wang L H, Chai T Y. Signal compensation based adaptive cascade control for regrinding processes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(10): 8732−8742 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2947804 [42] Jia Y, Chai T Y, Wang H, Su C Y. A signal compensation based cascaded PI control for an industrial heat exchange system. Control Engineering Practice, 2020, 98: Article No. 104372 [43] Wei C, Chai T Y, Xin X, Chen X K, Wang L Y, Chen Y H. A signal compensation-based robust swing-up and balance control method for the pendubot. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(3): 3007−3016 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3065621 [44] Wang W Z, Chai T Y, Wang H, Qu Z W. Signal-compensation-based adaptive PID control for fused magnesia smelting processes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3212392 [45] Kern A. Pros and cons of autotuning — The big story [Online], available: https://www.controleng.com/articles/pros-and-cons-of-autotuning-the-big-story/, August 2, 2018 [46] Control Engineering. Pros and cons of autotuning control: Part 2 [Online], available: https://www.controleng.com/articles/pros-and-cons-of-autotuning-control-part-2/, August 2, 2018 [47] Retch B. Reflections on the learning-to-control renaissance. In: Proceedings of the 21st IFAC World Congress. Berlin, Germany: IFAC, 2020. [48] Koelsch J R. Tuning tools maintain harmony in PID loops [Online], available: https://www.automationworld.com/products/software/article/13311005/, February 21, 2014 [49] Cyber-physical systems [Online], available: https://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2008/nsf08611/nsf08611.pdf, July 21, 2009 [50] Stone P, Brooks R, Brynjolfsson E, Calo R, Etzioni O, Hager G, et al. Artificial intelligence and life in 2030: The one hundred year study on artificial intelligence [Online], available: http://ai100.stanford.edu/2016-report, September 6, 2016 [51] Mao W L, Zhao Z W, Chang Z, Min G Y, Gao W F. Energy-efficient industrial internet of things: Overview and open issues. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(11): 7225−7237 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3067026 [52] Chai T Y, Zhang J W, Yang T. Demand forecasting of the fused magnesia smelting process with system identification and deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(12): 8387−8396 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3065930 [53] 柴天佑, 丁进良. 流程工业智能优化制造. 中国工程科学, 2018, 20(4): 51−58Chai Tian-You, Ding Jin-Liang. Smart and optimal manufacturing for process industry. Strategic Study of CAE, 2018, 20(4): 51−58 [54] 柴天佑, 刘强, 丁进良, 卢绍文, 宋延杰, 张艺洁. 工业互联网驱动的流程工业智能优化制造新模式研究展望. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2022, 52(1): 14−25 doi: 10.1360/SST-2021-0405Chai Tian-You, Liu Qiang, Ding Jin-Liang, Lu Shao-Wen, Song Yan-Jie, Zhang Yi-Jie. Perspectives on industrial-internet-driven intelligent optimized manufacturing mode for process industries. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2022, 52(1): 14−25 doi: 10.1360/SST-2021-0405 [55] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735−1780 doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [56] Silver D, Lever G, Heess N, Degris T, Wierstra D, Riedmiller M. Deterministic policy gradient algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: PMLR, 2014. 387−395 [57] Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N, Erez T, Tassa Y. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations. San Juan, USA: ICLR, 2016. [58] Isermann R. Digital Control Systems. Berlin: Springer, 1981. [59] Kruse R, Borgelt C, Klawonn F, Moewes C, Steinbrecher M, Held P. Multi-layer perceptrons. Computational Intelligence. London: Springer, 2013. -





 下载:
下载: