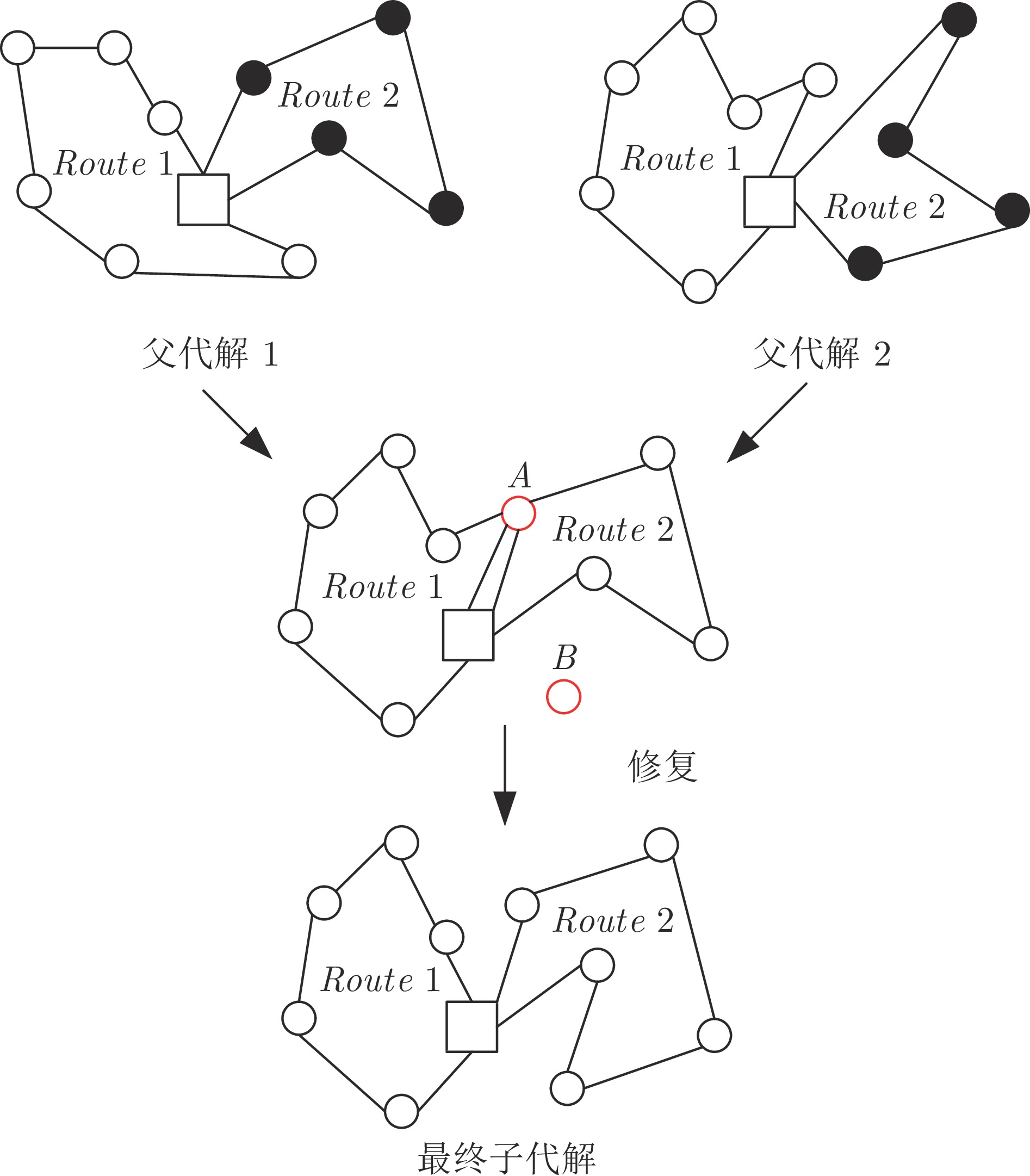
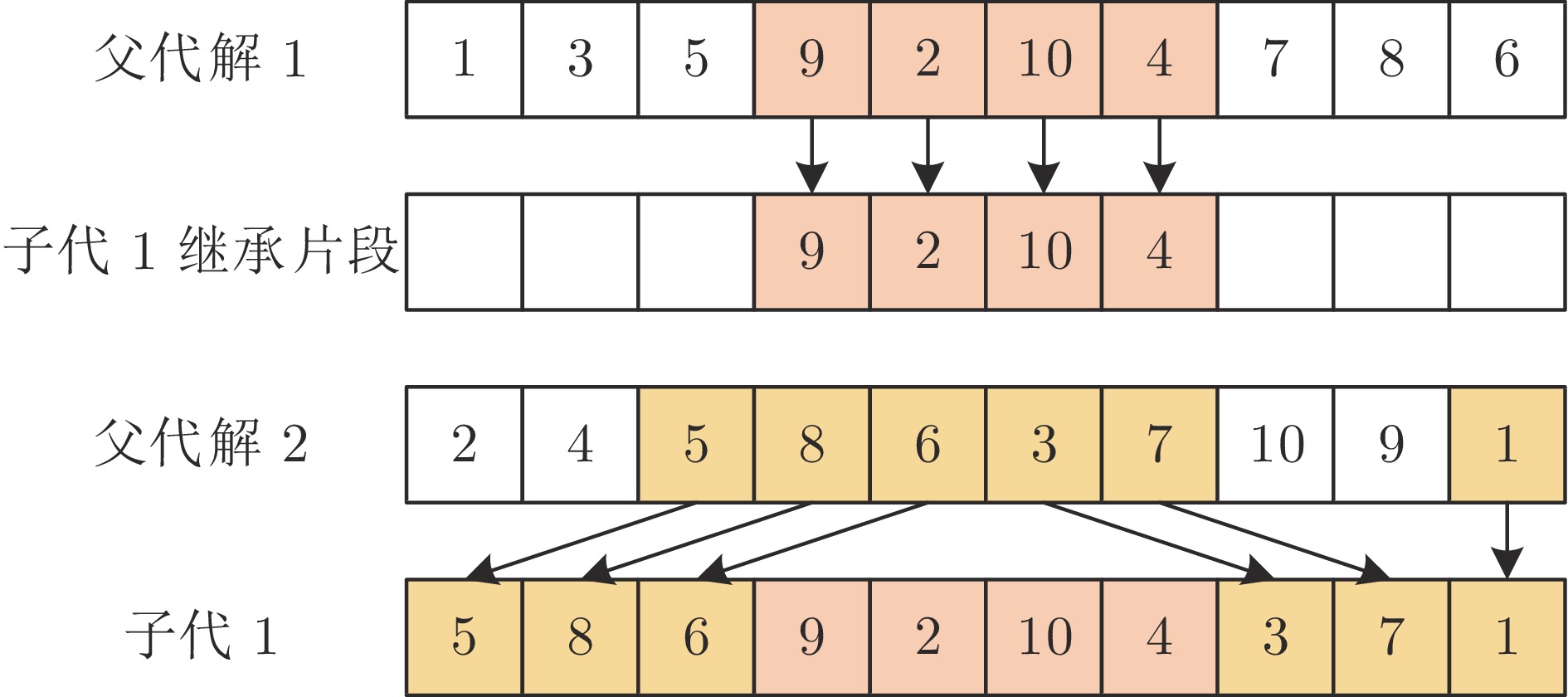
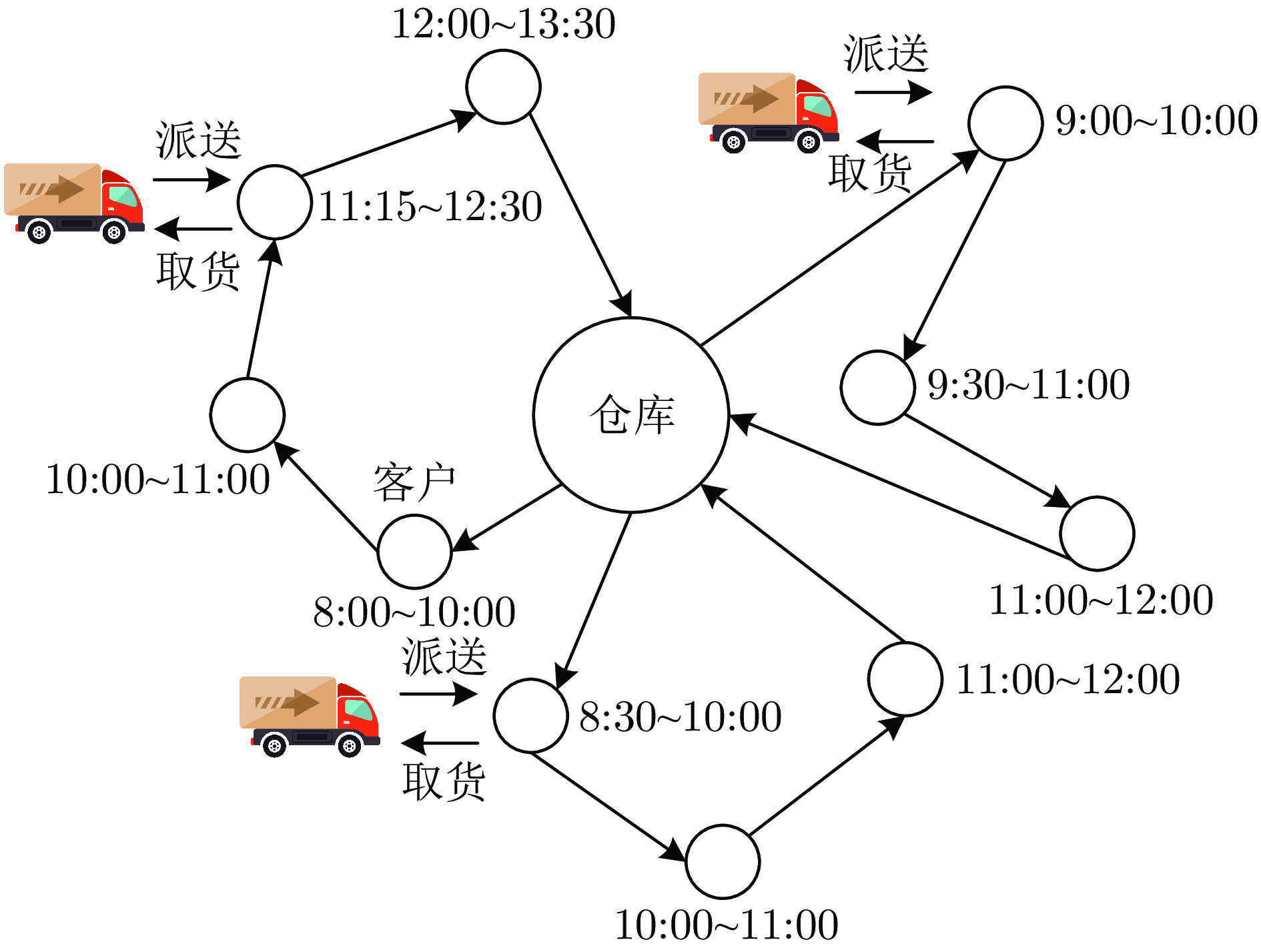
Multitask-based Assisted Evolutionary Algorithm for Vehicle Routing Problems inComplex Logistics Distribution Scenarios
-
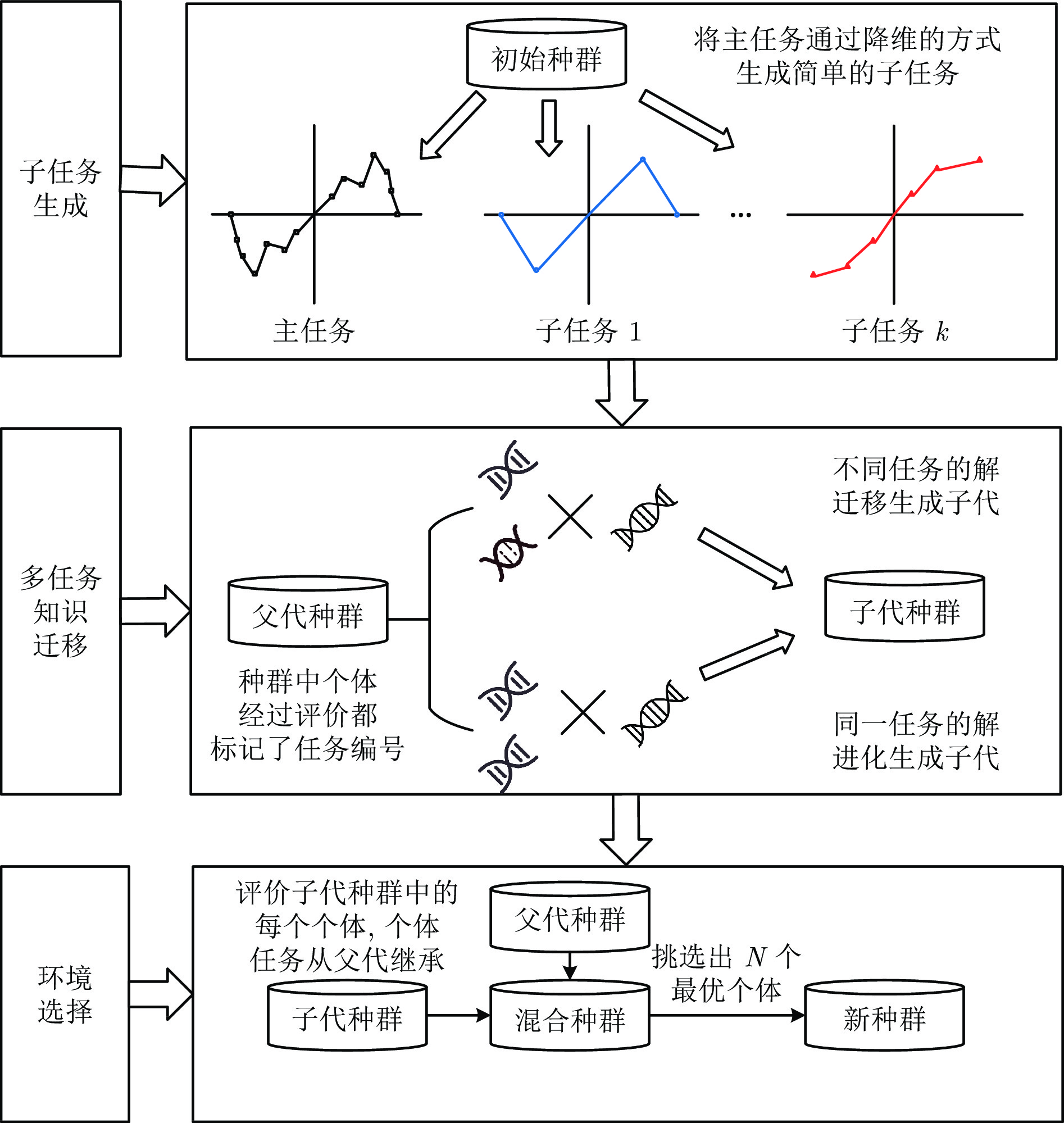
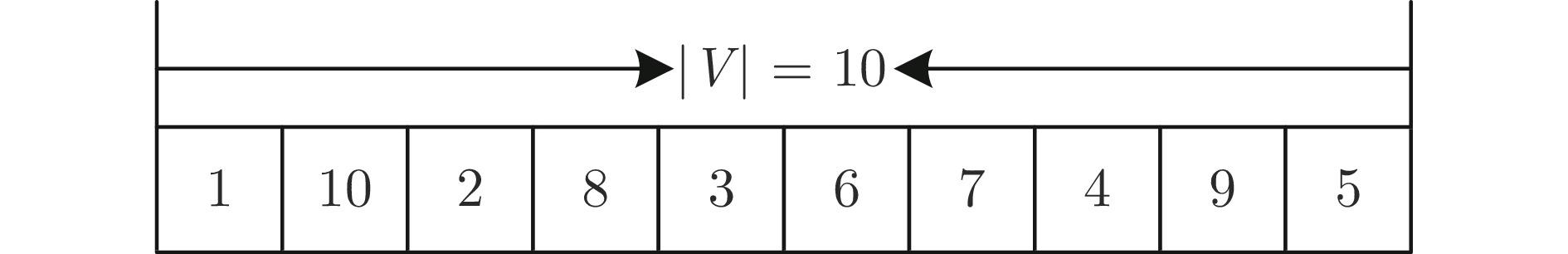
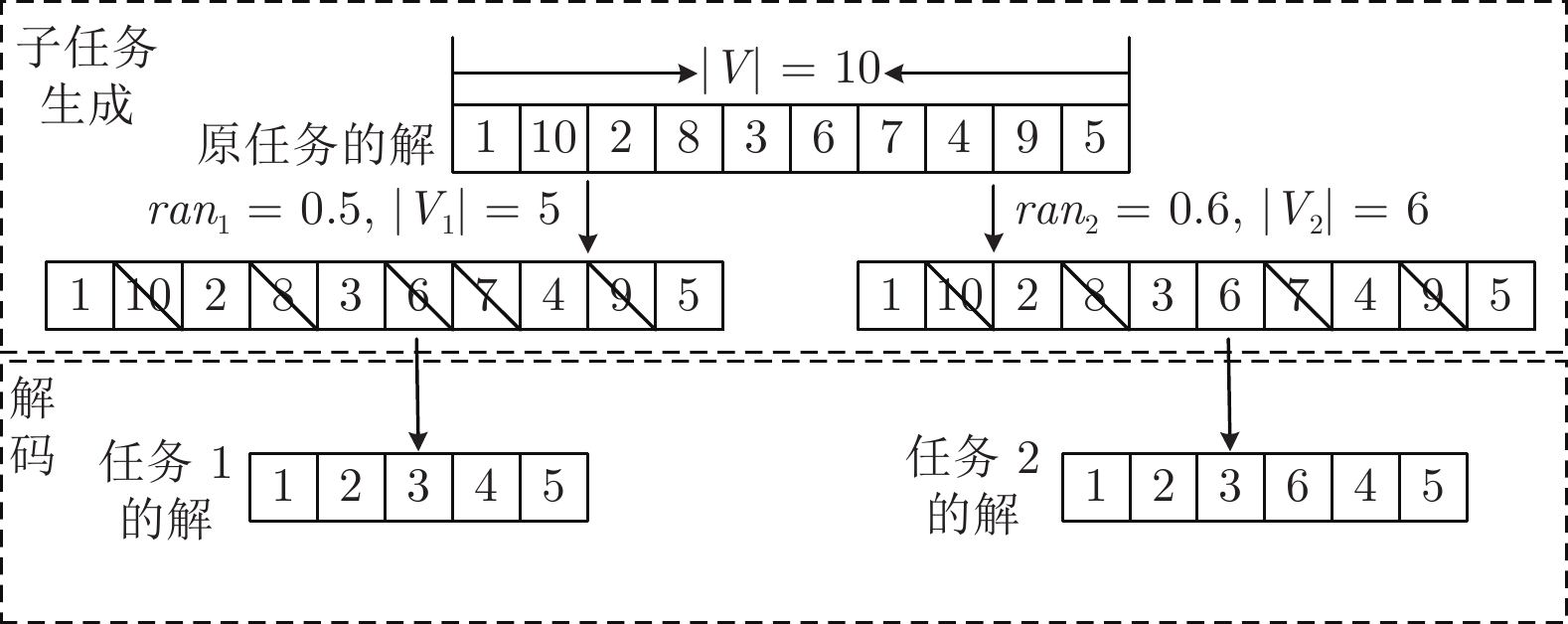
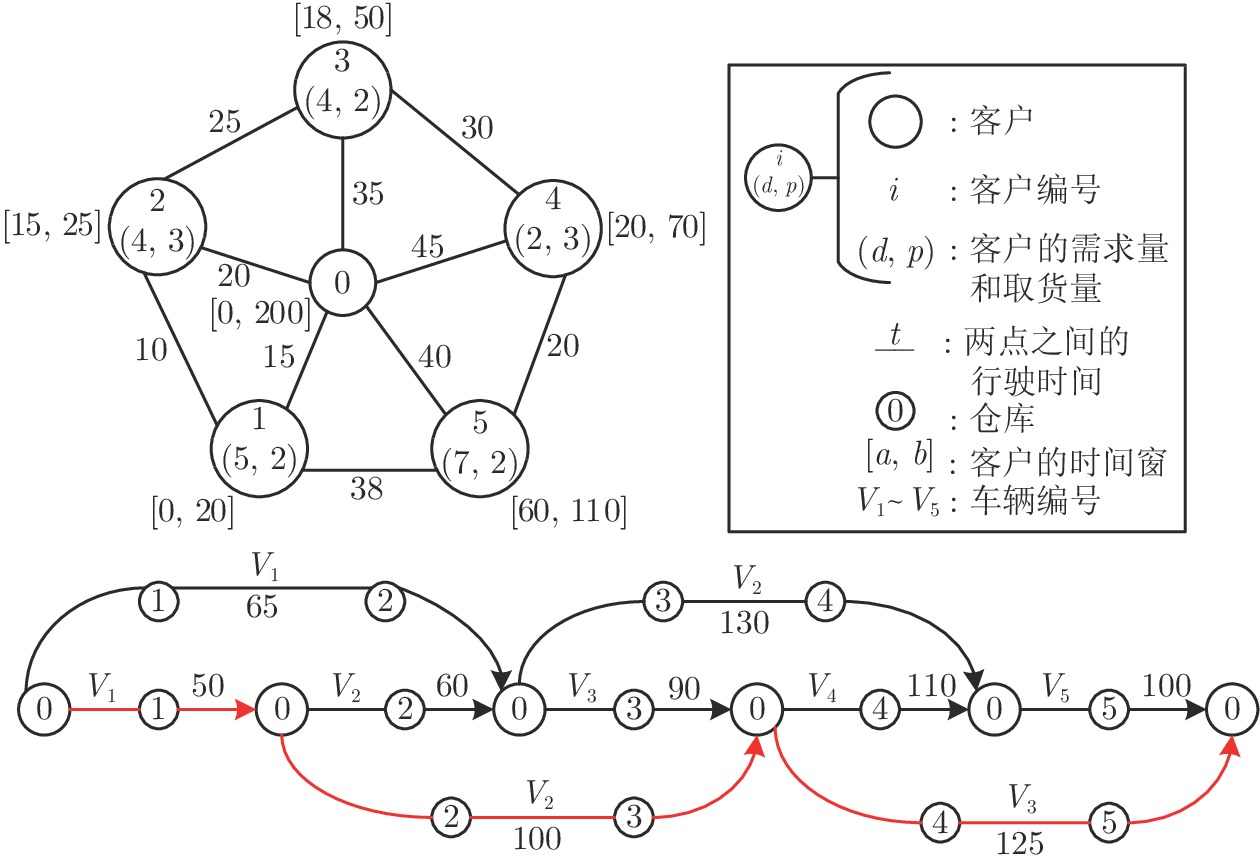
摘要: 在现代社会中, 复杂物流配送场景的车辆路径规划问题(Vehicle routing problem, VRP)一般带有时间窗约束且需要提供同时取送货的服务. 这种复杂物流配送场景的车辆路径规划问题是NP-难问题. 当其规模逐渐增大时, 一般的数学规划方法难以求解, 通常使用启发式方法在限定时间内求得较优解. 然而, 传统的启发式方法从原大规模问题直接开始搜索, 无法利用先前相关的优化知识, 导致收敛速度较慢. 因此, 提出面向复杂物流配送场景的车辆路径规划多任务辅助进化算法(Multitask-based assisted evolutionary algorithm, MBEA), 通过使用迁移优化方法加快算法收敛速度, 其主要思想是通过构造多个简单且相似的子任务用于辅助优化原大规模问题. 首先从原大规模问题中随机选择一部分客户订单用于构建多个不同的相似优化子任务, 然后使用进化多任务(Evolutional multitasking, EMT)方法用于生成原大规模问题和优化子任务的候选解. 由于优化子任务相对简单且与原大规模问题相似, 其搜索得到的路径特征可以通过任务之间的知识迁移辅助优化原大规模问题, 从而加快其求解速度. 最后, 提出的算法在京东物流公司快递取送货数据集上进行验证, 其路径规划效果优于当前最新提出的路径规划算法.Abstract: In complex logistics, addressing the vehicle routing problem (VRP) with simultaneous pickup and delivery and time windows, an NP-hard problem, becomes increasingly challenging as the scale expands. Traditional heuristic methods, often unable to leverage prior optimization knowledge, result in slow convergence. To address this, we introduce a multitask-based evolutionary algorithm (MBEA), which assists the optimization of the original large-scale problem by constructing multiple simple and similar subtasks and utilizing transfer learning to accelerate convergence speed. First, a subset of orders is randomly selected from the original problem to construct various subtasks, and then a multitask evolutionary approach is applied to generate candidate solutions for the original problem and subtasks. Given that the subtasks are simpler yet similar to the original problem, useful routing traits can be shared through knowledge transfer among the tasks, thereby speeding up its evolutionary search. To validate MBEA's efficacy, empirical studies were conducted on a large-scale express dataset from Jingdong, and the results demonstrate that MBEA outperforms recently proposed vehicle routing algorithms.
-
表 1 京东数据集的特性
Table 1 Properties of Jingdong dataset
问题 |V| C J $ {u_1} $ $ {u _2} $ F201 ~ F204 200 2.5 500 300 0.014 F401 ~ F404 400 2.5 500 300 0.014 F601 ~ F604 600 2.5 500 300 0.014 F801 ~ F804 800 2.5 500 300 0.014 F1001 ~ F1004 1 000 2.5 500 300 0.014 表 2 MBEA算法参数设置
Table 2 Parameter settings in MBEA
参数 含义 值 Evaluation 算法总评价次数 18 000 TE 每阶段的评价次数 3 600 N 种群大小 36 Nre 阶段数 5 Nbe 保留个体的数量 18 k 子任务个数 1 lower 子任务维度最低占比 0.7 表 3 MBEA和5种对比算法在京东数据集对比实验结果
Table 3 Comparative experimental results of MBEA and five compared algorithms on Jingdong dataset
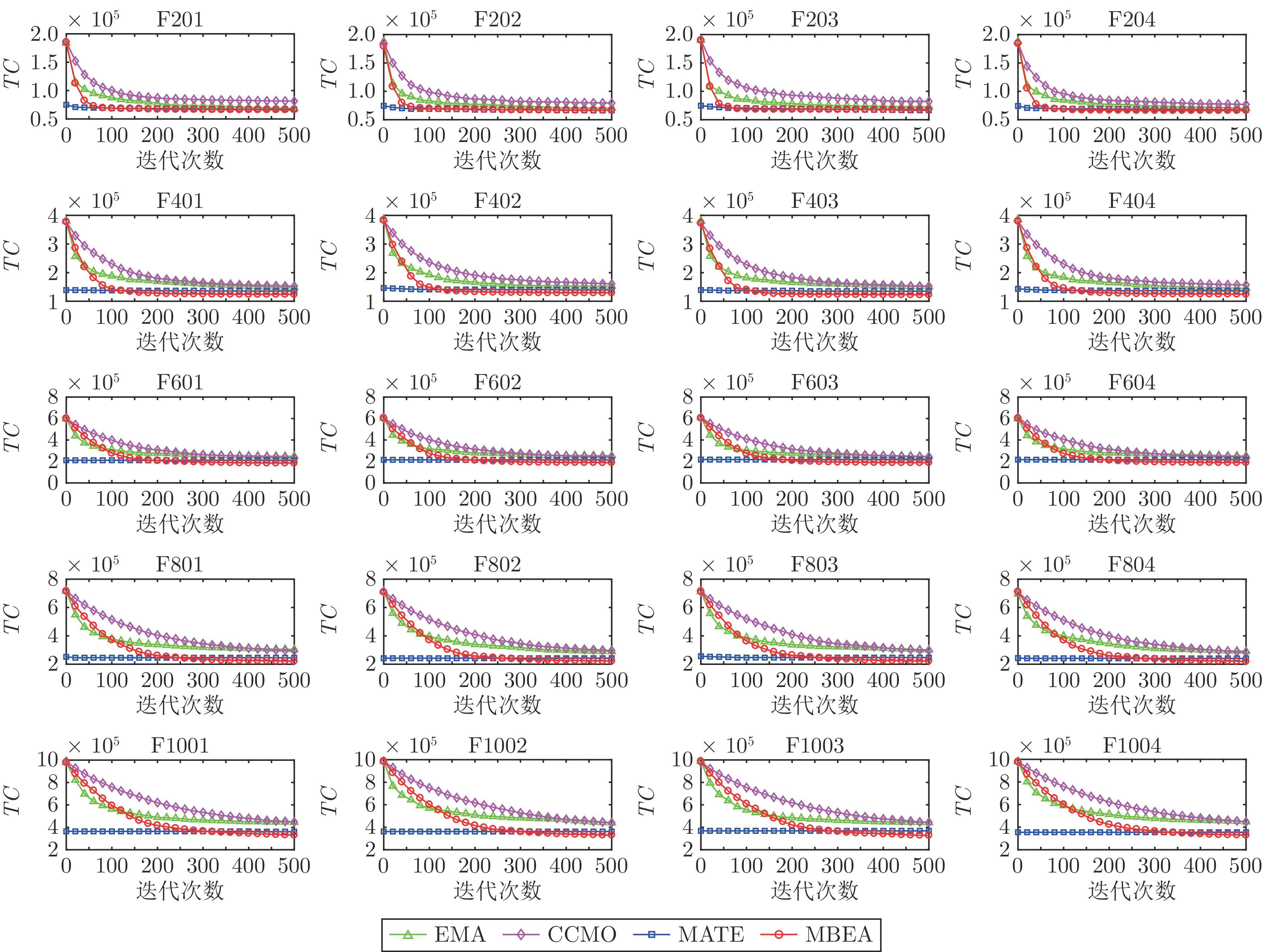
问题 MBEA EMA MATE CCMO GVNS VNSME NV TD TC 运行
时间 (s)NV TD TC 运行
时间 (s)NV TD TC 运行
时间 (s)NV TD TC 运行
时间 (s)NV TD TC 运行
时间 (s)NV TD TC 运行
时间 (s)F201 43 53 851 66 751 3 291 45 54 918 68 418 4 252 42 53 997 66 597 8 712 51 66 099 81 399 2 976 52 84 808 100 408 81 50 60 494 75 494 3 F202 44 53 155 66 355 3 270 47 56 288 70 388 4 340 43 53 649 66 609 14 194 52 63 782 79 382 2 839 53 67 756 83 656 252 49 59 728 74 428 2 F203 43 54 899 67 679 3 356 46 59 009 72 809 5 416 42 54 544 67 024 13 635 49 67 608 82 308 2 881 51 83 079 98 379 103 51 65 951 81 251 2 F204 43 53 311 66 211 2 983 46 56 456 70 256 3 986 43 54 398 67 238 9 929 48 62 329 76 729 2 970 52 74 571 90 171 300 51 60 415 75 715 2 F401 81 99 380 123 620 11 538 93 120 041 147 941 2 567 84 109 863 135 123 16 852 94 124 412 152 612 8 580 98 144 757 174 157 1 229 96 112 942 141 742 15 F402 84 103 091 128 351 13 338 101 122 636 152 936 2 535 87 113 871 139 971 10 742 100 130 655 160 655 7 923 101 160 822 191 122 268 98 117 970 147 370 12 F403 80 98 175 122 055 12 119 95 122 289 150 789 2 731 84 109 212 134 412 10 154 97 123 599 152 699 8 364 98 160 018 189 418 420 93 111 171 139 071 15 F404 83 99 809 124 649 12 656 95 116 269 144 769 2 694 86 110 555 136 295 13 709 100 127 209 157 209 8 154 101 136 483 166 783 651 94 110 775 138 975 17 F601 118 149 868 185 148 15 779 153 202 915 248 816 2 663 126 174 424 212 344 17 795 148 192 176 236 576 15 623 144 240 941 284 141 702 138 171 997 213 397 41 F602 121 153 129 189 429 19 571 164 204 772 253 972 2 656 129 177 851 216 551 18 839 146 199 278 243 078 15 505 141 227 723 270 023 1 624 143 175 068 217 968 49 F603 120 153 681 189 741 16 090 151 202 985 248 285 2 922 128 176 806 215 146 17 636 151 198 996 244 296 15 032 143 219 879 262 779 395 142 171 057 213 657 37 F604 122 153 477 190 137 18 569 157 204 541 251 641 2 886 128 176 943 215 403 18 789 154 196 028 242 228 15 201 145 204 293 247 793 757 141 172 956 215 256 33 F801 159 175 009 222 709 11 565 200 244 506 304 506 3 679 164 196 076 245 156 20 421 200 234 549 294 549 25 467 189 278 179 334 879 1 654 178 189 502 242 902 82 F802 157 173 598 220 577 13 077 210 226 736 289 736 3 657 164 194 325 243 465 20 835 199 236 794 296 494 25 879 184 271 798 326 998 1 153 179 192 243 245 943 107 F803 159 173 474 221 173 14 682 206 240 358 302 158 3 355 165 195 539 244 919 24 212 201 236 025 296 325 25 387 186 231 297 287 097 1 130 180 188 245 242 245 71 F804 156 171 956 218 756 12 743 213 227 247 291 147 3 324 161 191 853 240 033 21 884 198 226 353 285 753 25 707 181 231 743 286 043 1 490 174 186 214 238 414 81 F1001 212 265 385 329 044 9 698 275 363 035 445 535 3 874 222 293 298 359 838 25 957 279 364 136 447 836 34 957 239 391 293 462 993 1 236 232 278 192 347 792 154 F1002 211 264 034 327 213 8 655 279 356 200 439 900 3 858 225 291 180 358 740 27 482 284 354 899 440 099 34 582 240 352 092 424 092 2 847 234 278 465 348 665 126 F1003 212 265 409 329 008 8 910 275 358 768 441 268 3 917 227 295 806 363 786 26 217 283 359 276 444 176 33 748 243 408 770 481 670 554 231 274 553 343 853 126 F1004 212 262 117 325 656 10 331 285 362 496 447 996 3 914 223 289 035 355 815 26 180 289 360 481 447 181 33 515 234 348 460 418 660 890 233 276 896 346 796 123 最佳/
全部18/20 0/20 2/20 0/20 0/20 0/20 表 4 RBX和OX的消融实验结果
Table 4 Ablation experiment results of RBX and OX
问题 RBX OX RBX + OX F201 66 517 67 966 66 751 F202 66 365 67 744 66 355 F203 68 948 71 718 67 679 F204 66 970 69 372 66 211 F401 124 851 148 685 123 620 F402 128 798 146 954 128 351 F403 123 550 149 781 122 055 F404 125 247 155 403 124 649 F601 187 048 246 299 185 148 F602 192 623 253 252 189 429 F603 193 915 247 466 189 741 F604 193 410 245 400 190 137 F801 224 758 298 889 222 709 F802 228 345 296 430 220 577 F803 226 138 302 783 221 173 F804 220 988 294 788 218 756 F1001 342 544 442 939 329 044 F1002 339 143 440 007 327 213 F1003 341 946 446 173 329 008 F1004 336 077 445 518 325 656 最佳/全部 1/20 0/20 19/20 表 5 MBEA中参数lower的敏感性分析
Table 5 Sensitivity analysis of lower in MBEA
问题 TC (0.7) TC (0.5) TC (0.6) TC (0.8) TC (0.9) F201 66 751 66 664 66 926 66 895 66 971 F202 66 355 66 587 66 597 66 677 66 751 F203 67 679 68 206 67 919 68 027 67 783 F204 66 211 66 215 65 920 66 209 66 150 F401 123 620 123 826 123 103 122 861 122 672 F402 128 351 127 154 127 696 127 771 127 986 F403 122 055 122 428 122 703 122 343 122 270 F404 124 649 124 771 125 365 125 138 124 936 F601 185 148 185 831 186 163 185 579 186 371 F602 189 429 190 317 190 661 190 363 190 731 F603 189 741 189 160 189 740 189 986 189 683 F604 190 137 189 300 189 128 189 743 188 712 F801 222 709 221 057 221 905 221 221 220 910 F802 220 577 221 957 220 655 219 998 220 951 F803 221 173 222 172 222 227 221 495 221 377 F804 218 756 218 002 216 628 217 680 218 297 F1001 329 044 330 379 330 059 330 929 329 632 F1002 327 213 327 346 327 565 326 923 327 199 F1003 329 008 329 596 326 035 328 369 327 482 F1004 325 656 325 790 325 812 326 352 327 106 最佳/全部 9/20 3/20 3/20 2/20 3/20 表 6 MBEA中参数k的敏感性分析
Table 6 Sensitivity analysis of parameter k in MBEA
问题 TC (1) TC (0) TC (2) TC (3) F201 66 751 67 985 66 298 66 731 F202 66 355 67 920 67 002 67 111 F203 67 679 68 180 67 917 67 680 F204 66 211 66 621 66 524 65 730 F401 123 620 124 871 124 825 123 839 F402 128 351 127 377 128 292 127 603 F403 122 055 123 494 122 305 121 883 F404 124 649 126 338 124 959 125 486 F601 185 148 187 055 185 004 187 381 F602 189 429 192 343 192 178 189 516 F603 189 741 190 448 190 047 190 610 F604 190 137 191 208 189 940 189 096 F801 222 709 223 158 223 670 224 248 F802 220 577 222 758 223 576 225 523 F803 221 173 222 456 223 684 223 939 F804 218 756 218 393 217 485 220 373 F1001 329 044 330 374 331 387 332 643 F1002 327 213 329 829 329 525 326 603 F1003 329 008 331 877 330 099 329 200 F1004 325 656 330 725 326 082 331 858 最佳/全部 12/20 1/20 3/20 4/20 -
[1] Hu M, Liu W D, Peng K, Ma X Q, Cheng W Q, Liu J C, et al. Joint routing and scheduling for vehicle-assisted multidrone surveillance. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 1781-1790 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2878602 [2] 杨培颖, 唐加福, 于洋, 裴金翔. 面向最小碳排放量的接送机场服务的车辆路径与调度. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 424-432 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60042-7Yang Pei-Ying, Tang Jia-Fu, Yu Yang, Pei Jin-Xiang. Minimizing carbon emissions for vehicle routing and scheduling in picking up and delivering customers to airport service. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 424-432 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60042-7 [3] 韩月起, 张凯, 宾洋, 秦闯, 徐云霄, 李小川, 等. 基于凸近似的避障原理及无人驾驶车辆路径规划模型预测算法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 153-167Han Yue-Qi, Zhang Kai, Bin Yang, Qin Chuang, Xu Yun-Xiao, Li Xiao-Chuan, et al. Convex approximation based avoidance theory and path planning MPC for driver-less vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 153-167 [4] 徐杨, 陆丽萍, 褚端峰, 黄子超. 无人车辆轨迹规划与跟踪控制的统一建模方法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(4): 799-807Xu Yang, Lu Li-Ping, Chu Duan-Feng, Huang Zi-Chao. Unified modeling of trajectory planning and tracking for unmanned vehicle. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(4): 799-807 [5] 吴伟, 刘洋, 刘威, 吴国弘, 马万经. 自动驾驶环境下交叉口车辆路径规划与最优控制模型. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(9): 1971-1985Wu Wei, Liu Yang, Liu Wei, Wu Guo-Hong, Ma Wan-Jing. A novel autonomous vehicle trajectory planning and control model for connected-and-autonomous intersections. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(9): 1971-1985 [6] Abbatecola L, Fanti M P, Pedroncelli G, Ukovich W. A distributed cluster-based approach for pick-up services. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(2): 960-971 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2018.2879875 [7] 王素欣, 高利, 崔小光, 曹宏美. 多需求点车辆调度模型及其群体智能混合求解. 自动化学报, 2008, 34(1): 102-104Wang Su-Xin, Gao Li, Cui Xiao-Guang, Cao Hong-Mei. Study on multi-requirement points vehicle scheduling model and its swarm mix algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(1): 102-104 [8] 曾正洋, 许维胜, 徐志宇. 开放式两级车辆路径问题建模与多起始点变邻域下降法求解. 计算机科学, 2014, 41(10): 232-237Zeng Zheng-Yang, Xu Wei-Sheng, Xu Zhi-Yu. Modeling and multi-start variable neighborhood descent solution of two-echelon open vehicle routing problem. Computer Science, 2014, 41(10): 232-237 [9] Kheirkhah A, Navidi H, Bidgoli M M. An improved benders decomposition algorithm for an arc interdiction vehicle routing problem. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 2016, 63(2): 259-273 doi: 10.1109/TEM.2016.2542849 [10] 胡蓉, 李洋, 钱斌, 金怀平, 向凤红. 结合聚类分解的增强蚁群算法求解复杂绿色车辆路径问题. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(12): 3006-3023Hu Rong, Li Yang, Qian Bin, Jin Huai-Ping, Xiang Feng-Hong. An enhanced ant colony optimization combined with clustering decomposition for solving complex green vehicle routing problem. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(12): 3006-3023 [11] Xiao J H, Zhang T, Du J G, Zhang X Y. An evolutionary multiobjective route grouping-based heuristic algorithm for large-scale capacitated vehicle routing problems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(8): 4173-4186 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2950626 [12] Lin C H, Choy K L, Ho G T S, Chung S H, Lam H Y. Survey of green vehicle routing problem: Past and future trends. Expert Systems With Applications, 2014, 41(4): 1118-1138 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2013.07.107 [13] Kassem S, Chen M Y. Solving reverse logistics vehicle routing problems with time windows. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 68(1-4): 57-68 doi: 10.1007/s00170-012-4708-9 [14] Min H. The multiple vehicle routing problem with simultaneous delivery and pick-up points. Transportation Research Part A: General, 1989, 23(5): 377-386 doi: 10.1016/0191-2607(89)90085-X [15] Dethloff J. Vehicle routing and reverse logistics: The vehicle routing problem with simultaneous delivery and pick-up. OR-Spektrum, 2001, 23(1): 79-96 doi: 10.1007/PL00013346 [16] Berbeglia G, Cordeau J F, Laporte G. Dynamic pickup and delivery problems. European Journal of Operational Research, 2010, 202(1): 8-15 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2009.04.024 [17] Wang H F, Chen Y Y. A genetic algorithm for the simultaneous delivery and pickup problems with time window. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2012, 62(1): 84-95 doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2011.08.018 [18] Eksioglu B, Vural A V, Reisman A. The vehicle routing problem: A taxonomic review. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2009, 57(4): 1472-1483 doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2009.05.009 [19] 范厚明, 刘鹏程, 刘浩, 侯登凯. 多中心联合配送模式下集货需求随机的VRPSDP问题. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(7): 1646-1660Fan Hou-Ming, Liu Peng-Cheng, Liu Hao, Hou Deng-Kai. The multi-depot vehicle routing problem with simultaneous deterministic delivery and stochastic pickup based on joint distribution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1646-1660 [20] 陈萍, 黄厚宽, 董兴业. 求解卸装一体化的车辆路径问题的混合启发式算法. 计算机学报, 2008, 31(4): 565-73Chen Ping, Huang Hou-Kuan, Dong Xing-Ye. A hybrid heuristic algorithm for the vehicle routing problem with simultaneous delivery and pickup. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2008, 31(4): 565-573 [21] Gupta A, Heng C K, Ong Y S, Tan P S, Zhang A N. A generic framework for multi-criteria decision support in eco-friendly urban logistics systems. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 71: 288-300 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.09.033 [22] Wang J H, Weng T Y, Zhang Q F. A two-stage multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for multiobjective multidepot vehicle routing problem with time windows. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(7): 2467-2478 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2821180 [23] Wang C, Mu D, Zhao F, Sutherland J W. A parallel simulated annealing method for the vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pickup-delivery and time windows. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2015, 83: 111-122 [24] Mingyong L, Erbao C. An improved differential evolution algorithm for vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pickups and deliveries and time windows. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2010, 23(2): 188-195 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2009.09.001 [25] 黄务兰, 张涛. 基于改进全局人工鱼群算法的VRPSPDTW研究. 计算机工程与应用, 2016, 52(21): 21-29Huang Wu-Lan, Zhang Tao. Vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pick-up and delivery and time-windows based on improved global artificial fish swarm algorithm. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2016, 52(21): 21-29 [26] Shi Y, Zhou Y J, Boudouh T, Grunder O. A lexicographic-based two-stage algorithm for vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pickup-delivery and time window. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 95: Article No. 103901 [27] Hof J, Schneider M. An adaptive large neighborhood search with path relinking for a class of vehicle-routing problems with simultaneous pickup and delivery. Networks, 2019, 74(3): 207-250 doi: 10.1002/net.21879 [28] Iqbal M, Xue B, Al-Sahaf H, Zhang M J. Cross-domain reuse of extracted knowledge in genetic programming for image classification. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2017, 21(4): 569-587 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2017.2657556 [29] Di S, Zhang H G, Li C G, Mei X, Prokhorov D, Ling H B. Cross-domain traffic scene understanding: A dense correspondence-based transfer learning approach. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(3): 745-757 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2702012 [30] Chalmers E, Contreras E B, Robertson B, Luczak A, Gruber A. Learning to predict consequences as a method of knowledge transfer in reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(6): 2259-2270 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2690910 [31] Gupta A, Ong Y S, Feng L. Multifactorial evolution: Toward evolutionary multitasking. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 20(3): 343-357 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2015.2458037 [32] Gupta A, Ong Y S, Feng L, Tan K C. Multiobjective multifactorial optimization in evolutionary multitasking. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(7): 1652-1665 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2554622 [33] Bali K K, Ong Y S, Gupta A, Tan P S. Multifactorial evolutionary algorithm with online transfer parameter estimation: MFEA-Ⅱ. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 24(1): 69-83 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2906927 [34] Hao X X, Qu R, Liu J. A unified framework of graph-based evolutionary multitasking hyper-heuristic. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 25(1): 35-47 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2020.2991717 [35] Feng L, Zhou L, Gupta A, Zhong J H, Zhu Z X, Tan K C, et al. Solving generalized vehicle routing problem with occasional drivers via evolutionary multitasking. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(6): 3171-3184 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2955599 [36] Feng L, Huang Y X, Zhou L, Zhong J H, Gupta A, Tang K, et al. Explicit evolutionary multitasking for combinatorial optimization: A case study on capacitated vehicle routing problem. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(6): 3143-3156 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2962865 [37] Feng L, Zhou L, Zhong J H, Gupta A, Ong Y S, Tan K C, et al. Evolutionary multitasking via explicit autoencoding. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(9): 3457-3470 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2845361 [38] Feng L, Huang Y X, Tsang I W, Gupta A, Tang K, Tan K C, et al. Towards faster vehicle routing by transferring knowledge from customer representation. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(2): 952-965 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3018903 [39] Shang Q X, Huang Y X, Wang Y, Li M, Feng L. Solving vehicle routing problem by memetic search with evolutionary multitasking. Memetic Computing, 2022, 14(1): 31-44. doi: 10.1007/s12293-021-00352-7 [40] Braekers K, Ramaekers K, Van Nieuwenhuyse I. The vehicle routing problem: State of the art classification and review. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2016, 99: 300-313 [41] Huang M F, Hu X P. Large scale vehicle routing problem: An overview of algorithms and an intelligent procedure. International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control, 2012, 8(8): 5809-5819 [42] Shin K, Han S Y. A centroid-based heuristic algorithm for the capacitated vehicle routing problem. Computing and Informatics, 2011, 30(4): 721-732 [43] Angelelli E, Mansini R. The vehicle routing problem with time windows and simultaneous pick-up and delivery. Quantitative Approaches to Distribution Logistics and Supply Chain Management. Berlin: Springer, 2002. 249−267 [44] Dell'Amico M, Righini G, Salani M. A branch-and-price approach to the vehicle routing problem with simultaneous distribution and collection. Transportation Science, 2006, 40(2): 235-247 doi: 10.1287/trsc.1050.0118 [45] Rieck J, Zimmermann J. Exact solutions to the symmetric and asymmetric vehicle routing problem with simultaneous delivery and pick-up. Business Research, 2013, 6(1): 77-92 doi: 10.1007/BF03342743 [46] Subramanian A, Uchoa E, Pessoa A A, Ochi L S. Branch-cut-and-price for the vehicle routing problem with simul-taneous pickup and delivery. Optimization Letters, 2013, 7(7): 1569-1581 doi: 10.1007/s11590-012-0570-9 [47] Cao W J, Yang W S. A survey of vehicle routing problem. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2017, 100: Article No. 01006 [48] Elshaer R, Awad H. A taxonomic review of metaheuristic algorithms for solving the vehicle routing problem and its variants. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2020, 140: Article No. 106242 [49] Yu V F, Redi A A N P, Hidayat Y A, Wibowo O J. A simulated annealing heuristic for the hybrid vehicle routing problem. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 53: 119-132 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.12.027 [50] Schermer D, Moeini M, Wendt O. A hybrid VNS/Tabu search algorithm for solving the vehicle routing problem with drones and en route operations. Computers & Operations Research, 2019, 109: 134-158 [51] Ribeiro G M, Laporte G. An adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for the cumulative capacitated vehicle routing problem. Computers & Operations Research, 2012, 39(3): 728-735 [52] Avci M, Topaloglu S. A hybrid metaheuristic algorithm for heterogeneous vehicle routing problem with sim-ultaneous pickup and delivery. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 53: 160-171 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.01.038 [53] Zhou Y, Kong L J, Cai Y Q, Wu Z Y, Liu S P, Hong J M, et al. A decomposition-based local search for large-scale many-objective vehicle routing problems with simultaneous delivery and pickup and time windows. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(4): 5253-5264 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2959664 [54] Baker B M, Ayechew M A. A genetic algorithm for the vehicle routing problem. Computers & Operations Research, 2003, 30(5): 787-800 [55] Mohammed M A, Abd Ghani M K, Hamed R I, Mostafa S A, Ahmad M S, Ibrahim D A. Solving vehicle routing problem by using improved genetic algorithm for optimal solution. Journal of Computational Science, 2017, 21: 255-262 doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2017.04.003 [56] Sabar N R, Bhaskar A, Chung E, Turky A, Song A. An adaptive memetic approach for heterogeneous vehicle routing problems with two-dimensional loading constraints. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 58: Article No. 100730 [57] Ouaddi K, Mhada F, Benadada Y. Memetic algorithm for multi-tours dynamic vehicle routing problem with overtime (MDVRPOT). International Journal of Industrial Engineering Computations, 2020, 11(4): 643-662 [58] Zhang X Y, Duan H B. An improved constrained differential evolution algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle global route planning. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 26: 270-284 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2014.09.046 [59] Venkatesan S R, Logendran D, Chandramohan D. Optimization of capacitated vehicle routing problem using PSO. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2011, 3(10): 7469-7477 [60] Yu B, Yang Z Z, Yao B Z. An improved ant colony optimization for vehicle routing problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 2009, 196(1): 171-176 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2008.02.028 [61] Lee C Y, Lee Z J, Lin S W, Ying K C. An enhanced ant colony optimization (EACO) applied to capacitated vehicle routing problem. Applied Intelligence, 2010, 32(1): 88-95 doi: 10.1007/s10489-008-0136-9 [62] Liu S C, Tang K, Yao X. Memetic search for vehicle routing with simultaneous pickup-delivery and time windows. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 66: Article No. 100927 [63] Ma Y F, Li Z M, Yan F, Feng C Y. A hybrid priority-based genetic algorithm for simultaneous pickup and delivery problems in reverse logistics with time windows and multiple decision-makers. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(15): 6697-6714 doi: 10.1007/s00500-019-03754-5 [64] Wang J H, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Zhang J, Chen C L P, Zheng Z B. Multiobjective vehicle routing problems with simultaneous delivery and pickup and time windows: Formulation, instances, and algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(3): 582-594 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2409837 [65] Lagos C, Guerrero G, Cabrera E, Moltedo A, Johnson F, Paredes F. An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for the VRP with simultaneous pickup and delivery and time windows. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 2018, 16(6): 1732-1740 doi: 10.1109/TLA.2018.8444393 [66] Potvin J Y, Bengio S. The vehicle routing problem with time windows Part Ⅱ: Genetic search. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 1996, 8(2): 165-172 doi: 10.1287/ijoc.8.2.165 [67] Oliver I M, Smith D J, Holland J R C. A study of permutation crossover operators on the traveling salesman problem. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Genetic Algorithms on Genetic Algorithms and Their Application. Cambridge, USA: L. Erlbaum Associates Inc., 1987. [68] Tian Y, Zhang T, Xiao J H, Zhang X Y, Jin Y C. A coevolutionary framework for constrained multiobjective opti-mization problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 25(1): 102-116 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2020.3004012 [69] Fleszar K, Osman I H, Hindi K S. A variable neighbourhood search algorithm for the open vehicle routing problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 2009, 195(3): 803-809 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2007.06.064 [70] Cai J C, Zhu Q L, Lin Q Z. Variable neighborhood search for a new practical dynamic pickup and delivery problem. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2022, 75: Article No. 101182 -




 下载:
下载: