|
[1]
|
Zhou J, Li P G, Zhou Y H, Wang B C, Zang J Y, Liu M. Toward new-generation intelligent manufacturing. Engineering, 2018, 4(1): 11-20 doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2018.01.002
|
|
[2]
|
柴天佑. 工业过程控制系统研究现状与发展方向. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2016, 46(8): 1003-1015 doi: 10.1360/N112016-00062Chai Tian-You. Industrial process control systems: Research status and development direction. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2016, 46(8): 1003-1015 doi: 10.1360/N112016-00062
|
|
[3]
|
周济. 智能制造——“中国制造2025”的主攻方向. 中国机械工程, 2015, 26(17): 2273-2284 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2015.17.001Zhou Ji. Intelligent manufacturing——main direction of "Made in China 2025". China Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 26(17): 2273-2284 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2015.17.001
|
|
[4]
|
李伯虎, 柴旭东, 侯宝存, 林廷宇, 张霖, 李潭, 等. 云制造系统3.0——一种“智能+”时代的新智能制造系统. 计算机集成制造系统, 2019, 25(12): 2997-3012Li Bo-Hu, Chai Xu-Dong, Hou Bao-Cun, Lin Ting-Yu, Zhang Lin, Li Tan, et al. Cloud manufacturing system 3.0——new intelligent manufacturing system in era of "Intelligence +". Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2019, 25(12): 2997-3012
|
|
[5]
|
Scharstein D, Szeliski R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2002, 47(1-3): 7-42
|
|
[6]
|
Martin J, Crowley J L. Experimental comparison of correlation techniques. In: Proceedings of the IAS-4, International Conference on Intelligent Autonomous Systems. 1995.
|
|
[7]
|
Zabih R, Woodfill J. Non-parametric local transforms for computing visual correspondence. In: Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Computer Vision. Stockholm, Sweden: Springer, 1994. 151−158
|
|
[8]
|
Tomasi C, Manduchi R. Bilateral filtering for gray and color images. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Vision (IEEE Cat. No.98CH36271). Bombay, India: IEEE, 1998. 839−846
|
|
[9]
|
De-Maeztu L, Villanueva A, Cabeza R. Near real-time stereo matching using geodesic diffusion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(2): 410-416 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.192
|
|
[10]
|
Hosni A, Rhemann C, Bleyer M, Rother C, Gelautz M. Fast cost-volume filtering for visual correspondence and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(2): 504-511 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.156
|
|
[11]
|
Zhang K, Lu J B, Lafruit G. Cross-based local stereo matching using orthogonal integral images. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2009, 19(7): 1073-1079 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2009.2020478
|
|
[12]
|
Zureiki A, Devy M, Chatila R. Stereo matching using reduced-graph cuts. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. San Antonio, USA: IEEE, 2007. I-237−I-240
|
|
[13]
|
Mozerov M G, van de Weijer J. One-view occlusion detection for stereo matching with a fully connected CRF model. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(6): 2936-2947 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2892668
|
|
[14]
|
Ahmadzadeh A, Madani H, Jafari K, Jazi F S, Daneshpajouh S, Gorgin S. Fast and adaptive BP-based multi-core implementation for stereo matching. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Formal Methods and Models for Codesign (MEMOCODE 2013). Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 135−138
|
|
[15]
|
Shen R, Cheng I, Li X B, Basu A. Stereo matching using random walks. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Tampa, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1−4
|
|
[16]
|
da Silva Vieira G, Soares F A A M N, Laureano G T, Parreira R T, Ferreira J C. A segmented consistency check approach to disparity map refinement. Canadian Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2018, 41(4): 218-223 doi: 10.1109/CJECE.2019.2890986
|
|
[17]
|
Sun L, Chen K, Song M L, Tao D C, Chen G, Chen C. Robust, efficient depth reconstruction with hierarchical confidence-based matching. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3331-3343 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2687101
|
|
[18]
|
Brandao M, Ferreira R, Hashimoto K, Takanishi T, Santos-Victor J. On stereo confidence measures for global methods: Evaluation, new model and integration into occupancy grids. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(1): 116-128 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2437381
|
|
[19]
|
Lee Y, Kyung C M. A memory-and accuracy-aware gaussian parameter-based stereo matching using confidence measure. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(6): 1845-1858 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2959613
|
|
[20]
|
Yan T M, Gan Y Z, Xia Z Y, Zhao Q F. Segment-based disparity refinement with occlusion handling for stereo matching. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(8): 3885-3897 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2903318
|
|
[21]
|
Yang L, Xu Y, Wang S R, Yuan C F, Zhang Z Q, Li B, et al. PDNet: Toward better one-stage object detection with prediction decoupling. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 5121-5133 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3193223
|
|
[22]
|
Wang X, Ma H M, Chen X Z, You S D. Edge preserving and multi-scale contextual neural network for salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(1): 121-134 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2756825
|
|
[23]
|
姚安庆, 徐建明. 基于双目视觉的电动汽车充电孔识别定位系统. 传感器与微系统, 2021, 40(7): 81-84 doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2021)07-0081-04Yao An-Qing, Xu Jian-Ming. Electric car charging hole identification and positioning system based on binocular vision. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2021, 40(7): 81-84 doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2021)07-0081-04
|
|
[24]
|
陈海永, 雷凤翔, 孙鹤旭, 杜晓琳. 带钢端部形状双目视觉检测系统的建模仿真. 自动化仪表, 2015, 36(1): 79-82 doi: 10.16086/j.cnki.issn1000-0380.201501022Chen Hai-Yong, Lei Feng-Xiang, Sun He-Xu, Du Xiao-Lin. Modeling and simulation of binocular visual detection system for the shape of ends of stripe steel. Process Automation Instrumentation, 2015, 36(1): 79-82 doi: 10.16086/j.cnki.issn1000-0380.201501022
|
|
[25]
|
马大智, 于斌超, 张彦泽, 刘巍, 乐毅, 杨继之, 等. 基于双目视觉的大型高反光构件测量系统. 应用光学, 2021, 42(4): 577-585 doi: 10.5768/JAO202142.0401002Ma Da-Zhi, Yu Bin-Chao, Zhang Yan-Ze, Liu Wei, Yue Yi, Yang Ji-Zhi, et al. Measurement system of large-scale high reflective component based on binocular vision. Journal of Applied Optics, 2021, 42(4): 577-585 doi: 10.5768/JAO202142.0401002
|
|
[26]
|
Cai C T, Wang B Y, Liu Y, Yan Y J. Unfeatured weld positioning technology based on neural network and machine vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC). Chongqing, China: IEEE, 2018. 477−481
|
|
[27]
|
Besl P J, McKay N D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(2): 239-256 doi: 10.1109/34.121791
|
|
[28]
|
Pomerleau F, Colas F, Siegwart R, Magnenat S. Comparing ICP variants on real-world data sets. Autonomous Robots, 2013, 34(3): 133-148 doi: 10.1007/s10514-013-9327-2
|
|
[29]
|
Menq C H, Yau H T, Lai G Y. Automated precision measurement of surface profile in CAD-directed inspection. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1992, 8(2): 268-278 doi: 10.1109/70.134279
|
|
[30]
|
Golyanik V, Ali S A, Stricker D. Gravitational approach for point set registration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 5802−5810
|
|
[31]
|
Chetverikov D, Svirko D, Stepanov D, Krsek P. The trimmed iterative closest point algorithm. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Quebec City, Canada: IEEE, 2002. 545−548
|
|
[32]
|
Jauer P, Kuhlemann I, Bruder R, Schweikard A, Ernst F. Efficient registration of high-resolution feature enhanced point clouds. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(5): 1102-1115 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2831670
|
|
[33]
|
Matabosch C, Fofi D, Salvi J, Batlle E. Registration of surfaces minimizing error propagation for a one-shot multi-slit hand-held scanner. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(6): 2055-2067 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2007.10.019
|
|
[34]
|
Wang W P, Pottmann H, Liu Y. Fitting B-spline curves to point clouds by curvature-based squared distance minimization. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2006, 25(2): 214-238 doi: 10.1145/1138450.1138453
|
|
[35]
|
Pottmann H, Huang Q X, Yang Y L, Hu S M. Geometry and convergence analysis of algorithms for registration of 3D shapes. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2006, 67(3): 277-296 doi: 10.1007/s11263-006-5167-2
|
|
[36]
|
Xie H, Li W L, Yin Z P, Ding H. Variance-minimization iterative matching method for free-form surfaces—Part I: Theory and method. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(3): 1181-1191 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2018.2875154
|
|
[37]
|
Li W L, Xie H, Zhang G, Yan S J, Yin Z P. 3-D shape matching of a blade surface in robotic grinding applications. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2016, 21(5): 2294-2306 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2016.2574813
|
|
[38]
|
Zhu D H, Feng X Z, Xu X H, Yang Z Y, Li W L, Yan S J, et al. Robotic grinding of complex components: A step towards efficient and intelligent machining-challenges, solutions, and applications. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2020, 65: Article No. 101908 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2019.101908
|
|
[39]
|
Shah G A, Polette A, Pernot J P, Giannini F, Monti M. Simulated annealing-based fitting of CAD models to point clouds of mechanical parts' assemblies. Engineering With Computers, 2021, 37(4): 2891−2909
|
|
[40]
|
Li L, Cao X Y, Sun J. Three-dimensional point cloud registration based on normal vector angle. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2019, 47(4): 585-593 doi: 10.1007/s12524-018-0918-4
|
|
[41]
|
Zhan X, Cai Y, He P. A three-dimensional point cloud registration based on entropy and particle swarm optimization. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, DOI: 10.1177/1687814018814330
|
|
[42]
|
Zeng A, Song S R, Nie\betaner M, Fisher M, Xiao J X, Funkhouser T. 3DMatch: Learning local geometric descriptors from RGB-D reconstructions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 199−208
|
|
[43]
|
Gojcic Z, Zhou C F, Wegner J D, Wieser A. The perfect match: 3D point cloud matching with smoothed densities. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5540−5549
|
|
[44]
|
Deng H W, Birdal T, Ilic S. PPFNet: Global context aware local features for robust 3D point matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 195−205
|
|
[45]
|
Deng H W, Birdal T, Ilic S. PPF-FoldNet: Unsupervised learning of rotation invariant 3D local descriptors. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 620−638
|
|
[46]
|
Charles R Q, Su H, Mo K C, Guibas L J. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 77−85
|
|
[47]
|
Choy C, Park J, Koltun V. Fully convolutional geometric features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 8957−8965
|
|
[48]
|
Choy C, Gwak J, Savarese S. 4D spatio-temporal ConvNets: Minkowski convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3070−3079
|
|
[49]
|
Bohg J, Morales A, Asfour T, Kragic D. Data-driven grasp synthesis-a survey. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2014, 30(2): 289-309 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2013.2289018
|
|
[50]
|
Hinterstoisser S, Holzer S, Cagniart C, Ilic S, Konolige K, Navab N, et al. Multimodal templates for real-time detection of texture-less objects in heavily cluttered scenes. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 858−865
|
|
[51]
|
Lepetit V, Moreno-Noguer F, Fua P. EPnP: An accurate O(n) solution to the PnP problem. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2009, 81(2): 155-166 doi: 10.1007/s11263-008-0152-6
|
|
[52]
|
Besl P J, McKay N D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes. In: Proceedings of SPIE 1611, Sensor Fusion IV: Control Paradigms and Data Structures. Boston, USA: SPIE, 1992. 586−606
|
|
[53]
|
Birdal T, Ilic S. Point pair features based object detection and pose estimation revisited. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision. Lyon, France: IEEE, 2015. 527−535
|
|
[54]
|
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788
|
|
[55]
|
Xiang Y, Schmidt T, Narayanan V, Fox D. PoseCNN: A convolutional neural network for 6D object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.00199, 2017.
|
|
[56]
|
Kehl W, Manhardt F, Tombari F, Ilic S, Navab N. SSD-6D: Making RGB-based 3D detection and 6D pose estimation great again. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1530−1538
|
|
[57]
|
Hu Y L, Hugonot J, Fua P, Salzmann M. Segmentation-driven 6D object pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3380−3389
|
|
[58]
|
Wang C, Xu D F, Zhu Y K, Martín-Martín R, Lu C W, Fei-Fei L, et al. DenseFusion: 6D object pose estimation by iterative dense fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3338−3347
|
|
[59]
|
He Y S, Sun W, Huang H B, Liu J R, Fan H Q, Sun J. PVN3D: A deep point-wise 3D keypoints voting network for 6DoF pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 11629−11638
|
|
[60]
|
He Y S, Huang H B, Fan H Q, Chen Q F, Sun J. FFB6D: A full flow bidirectional fusion network for 6D pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 3002−3012
|
|
[61]
|
Khatib O. Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. Autonomous Robot Vehicles. New York: Springer, 1986. 396−404
|
|
[62]
|
LAVALLE S M. Rapidly-exploring random trees: A new tool for path planning. Computer Science Dept, 1998, 98(11)
|
|
[63]
|
Karaman S, Frazzoli E. Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(7): 846-894 doi: 10.1177/0278364911406761
|
|
[64]
|
Lai T, Ramos F, Francis G. Balancing global exploration and local-connectivity exploitation with rapidly-exploring random disjointed-trees. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2019. 5537−5543
|
|
[65]
|
Naderi K, Rajamäki J, Hämäläinen P. RT-Rrt*: A real-time path planning algorithm based on RRT*. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Motion in Games. Paris, France: ACM, 2015. 113−118
|
|
[66]
|
Pardi T, Maddali V, Ortenzi V, Stolkin R, Marturi N. Path planning for mobile manipulator robots under non-holonomic and task constraints. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6749−6756
|
|
[67]
|
Prianto E, Kim M, Park J H, Bae J H, Kim J S. Path planning for multi-arm manipulators using deep reinforcement learning: Soft actor-critic with hindsight experience replay. Sensors, 2020, 20(20): Article No. 5911 doi: 10.3390/s20205911
|
|
[68]
|
Bonilla M, Pallottino L, Bicchi A. Noninteracting constrained motion planning and control for robot manipulators. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore: IEEE, 2017. 4038−4043
|
|
[69]
|
Vannoy J, Xiao J. Real-time adaptive motion planning (RAMP) of mobile manipulators in dynamic environments with unforeseen changes. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(5): 1199-1212 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.2003277
|
|
[70]
|
Wagner G, Choset H. M*: A complete multirobot path planning algorithm with performance bounds. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2011. 3260−3267
|
|
[71]
|
Sharon G, Stern R, Felner A, Sturtevant N R. Conflict-based search for optimal multi-agent pathfinding. Artificial Intelligence, 2015, 219: 40-66 doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2014.11.006
|
|
[72]
|
Park J, Kim J, Jang I, Kim H J. Efficient multi-agent trajectory planning with feasibility guarantee using relative Bernstein polynomial. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, France: IEEE, 2020. 434−440
|
|
[73]
|
Fiorini P, Shiller Z. Motion planning in dynamic environments using velocity obstacles. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 1998, 17(7): 760-772 doi: 10.1177/027836499801700706
|
|
[74]
|
Tordesillas J, How J P. MADER: Trajectory planner in multiagent and dynamic environments. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022, 38(1): 463-476 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3080235
|
|
[75]
|
Paull S, Ghassemi P, Chowdhury S. Learning scalable policies over graphs for multi-robot task allocation using capsule attention networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Philadelphia, USA: IEEE, 2022. 8815−8822
|
|
[76]
|
Hu H, Jia X L, He Q X, Fu S F, Liu K. Deep reinforcement learning based AGVs real-time scheduling with mixed rule for flexible shop floor in industry 4.0. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2020, 149: Article No. 106749
|
|
[77]
|
Sabattini L, Digani V, Secchi C, Fantuzzi C. Optimized simultaneous conflict-free task assignment and path planning for multi-AGV systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 1083−1088
|
|
[78]
|
Saraiva E S, Castro R S, Salton A T, Pimentel G A. A convex optimization based solution for the robotic manipulator control design problem subject to input saturation. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020, 53(2): 5467-5472 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.1551
|
|
[79]
|
Liu Z, Chen C, Zhang Y. Decentralized robust fuzzy adaptive control of humanoid robot manipulation with unknown actuator backlash. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(3): 605-616 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2321591
|
|
[80]
|
Han S I, Lee J M. Backstepping sliding mode control with FWNN for strict output feedback non-smooth nonlinear dynamic system. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2013, 11(2): 398-409 doi: 10.1007/s12555-012-9115-3
|
|
[81]
|
Quynh N X, Nan W Y, Yen V T. A novel robust adaptive control using RFWNNs and backstepping for industrial robot manipulators with dead-zone. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2020, 98(3): 679-692
|
|
[82]
|
Park S H, Han S I. Robust-tracking control for robot manipulator with deadzone and friction using backstepping and RFNN controller. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2011, 5(12): 1397-1417
|
|
[83]
|
Izadbakhsh A, Khorashadizadeh S. Robust impedance control of robot manipulators using differential equations as universal approximator. International Journal of Control, 2018, 91(10): 2170-2186 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2017.1336669
|
|
[84]
|
Yang Z Q, Peng J Z, Liu Y H. Adaptive neural network force tracking impedance control for uncertain robotic manipulator based on nonlinear velocity observer. Neurocomputing, 2019, 331: 263-280 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.068
|
|
[85]
|
Hogan N. Impedance control: An approach to manipulation. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 1984. 304−313
|
|
[86]
|
Li X, Liu Y H, Yu H Y. Iterative learning impedance control for rehabilitation robots driven by series elastic actuators. Automatica, 2018, 90: 1-7 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.12.031
|
|
[87]
|
徐建明, 王于玮, 董建伟, 禹鑫燚, 俞立. 基于阻抗控制的机器人砂带打磨的建模与仿真. 浙江工业大学学报, 2018, 46(2): 119-126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4303.2018.02.001Xu Jian-Ming, Wang Yu-Wei, Dong Jian-Wei, Yu Xin-Yi, Yu Li. Modeling and simulation of robotic belt grinding based on impedance control. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 2018, 46(2): 119-126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4303.2018.02.001
|
|
[88]
|
Zhang G J, Ni F L, Liu H, Jiang Z N, Yang G C, Li C Y. Learning impedance regulation skills for robot belt grinding from human demonstrations. Assembly Automation, 2021, 41(4): 431-440
|
|
[89]
|
Lakshminarayanan S, Kana S, Mohan D M, Manyar O M, Then D, Campolo D. An adaptive framework for robotic polishing based on impedance control. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 112(1): 401-417
|
|
[90]
|
Chen P F, Zhao H, Yan X, Ding H. Force control polishing device based on fuzzy adaptive impedance control. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications. Shenyang, China: Springer, 2019. 181−194
|
|
[91]
|
Li J F, Liu L, Wang Y B, Liang W Y. Adaptive hybrid impedance control of robot manipulators with robustness against environment's uncertainties. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2015. 1846−1851
|
|
[92]
|
Magrini E, Flacco F, De Luca A. Control of generalized contact motion and force in physical human-robot interaction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2015. 2298−2304
|
|
[93]
|
Mason M T. Compliance and force control for computer controlled manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1981, 11(6): 418-432 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1981.4308708
|
|
[94]
|
Raibert M H, Craig J J. Hybrid position/force control of manipulators. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1981, 103(2): 126-133 doi: 10.1115/1.3139652
|
|
[95]
|
Zhang H, Paul R. Hybrid control of robot manipulators. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. St. Louis, USA: IEEE, 1985. 602−607
|
|
[96]
|
Zhang H Y, Li L, Zhao J B, Zhao J C, Liu S J, Wu J J. Design and implementation of hybrid force/position control for robot automation grinding aviation blade based on fuzzy PID. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 107(3): 1741-1754
|
|
[97]
|
Johns E, Leutenegger S, Davison A J. Deep learning a grasp function for grasping under gripper pose uncertainty. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Daejeon, South Korea: IEEE, 2016. 4461−4468
|
|
[98]
|
Lenz I, Lee H, Saxena A. Deep learning for detecting robotic grasps. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2015, 34(4-5): 705-724 doi: 10.1177/0278364914549607
|
|
[99]
|
Shi H B, Chen J L, Pan W, Hwang K S, Cho Y Y. Collision avoidance for redundant robots in position-based visual servoing. IEEE Systems Journal, 2019, 13(3): 3479-3489 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2018.2865503
|
|
[100]
|
Park D H, Kwon J H, Ha I J. Novel position-based visual servoing approach to robust global stability under field-of-view constraint. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(12): 4735-4752 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2179270
|
|
[101]
|
Hutchinson S, Hager G D, Corke P I. A tutorial on visual servo control. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1996, 12(5): 651-670 doi: 10.1109/70.538972
|
|
[102]
|
Bechlioulis C P, Heshmati-Alamdari S, Karras G C, Kyriakopoulos K J. Robust image-based visual servoing with prescribed performance under field of view constraints. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2019, 35(4): 1063-1070 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2019.2914333
|
|
[103]
|
Oliva A A, Giordano P R, Chaumette F. A general visual-impedance framework for effectively combining vision and force sensing in feature space. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(3): 4441-4448 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3068911
|
|
[104]
|
Malis E, Chaumette F, Boudet S. 2 1/2 D visual servoing. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1999, 15(2): 238-250 doi: 10.1109/70.760345
|
|
[105]
|
Lippiello V, Cacace J, Santamaria-Navarro A, Andrade-Cetto J, Trujillo M Á, Esteves Y R R, et al. Hybrid visual servoing with hierarchical task composition for aerial manipulation. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2015, 1(1): 259-266
|
|
[106]
|
Mekonnen G, Kumar S, Pathak P M. Wireless hybrid visual servoing of omnidirectional wheeled mobile robots. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2016, 75: 450-462 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2015.08.008
|
|
[107]
|
Feng Z, Hu G Q, Sun Y J, Soon J. An overview of collaborative robotic manipulation in multi-robot systems. Annual Reviews in Control, 2020, 49: 113-127 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2020.02.002
|
|
[108]
|
Yan Z, Jouandeau N, Cherif A A. A survey and analysis of multi-robot coordination. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2013, 10(12): Article No. 399 doi: 10.5772/57313
|
|
[109]
|
Sun D, Mills J K. Adaptive synchronized control for coordination of multirobot assembly tasks. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 2002, 18(4): 498-510 doi: 10.1109/TRA.2002.802229
|
|
[110]
|
Yan L, Stouraitis T, Vijayakumar S. Decentralized ability-aware adaptive control for multi-robot collaborative manipulation. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(2): 2311-2318 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3060379
|
|
[111]
|
Nuño E, Ortega R. Achieving consensus of Euler-Lagrange agents with interconnecting delays and without velocity measurements via passivity-based control. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 26(1): 222-232 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2017.2661822
|
|
[112]
|
Hichri B, Fauroux J C, Adouane L, Doroftei I, Mezouar Y. Design of cooperative mobile robots for co-manipulation and transportation tasks. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 57: 412-421 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2019.01.002
|
|
[113]
|
Marvel J A, Bostelman R, Falco J. Multi-robot assembly strategies and metrics. ACM Computing Surveys, 2019, 51(1): Article No. 14
|
|
[114]
|
Vora H D, Sanyal S. A comprehensive review: Metrology in additive manufacturing and 3D printing technology. Progress in Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 5(4): 319-353 doi: 10.1007/s40964-020-00142-6
|
|
[115]
|
Frommknecht A, Kuehnle J, Effenberger I, Pidan S. Multi-sensor measurement system for robotic drilling. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2017, 47: 4-10 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2017.01.002
|
|
[116]
|
Ghorbani H, Khameneifar F. Accurate registration of point clouds of damaged aeroengine blades. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2021, 143(3): Article No. 031012
|
|
[117]
|
Zhong K, Li Z W, Zhou X H, Li Y F, Shi Y S, Wang C J. Enhanced phase measurement profilometry for industrial 3D inspection automation. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 76(9-12): 1563-1574 doi: 10.1007/s00170-014-6360-z
|
|
[118]
|
Scott W R, Roth G, Rivest J F. View planning for automated three-dimensional object reconstruction and inspection. ACM Computing Surveys, 2003, 35(1): 64-96 doi: 10.1145/641865.641868
|
|
[119]
|
Maver J, Bajcsy R. Occlusions as a guide for planning the next view. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1993, 15(5): 417-433 doi: 10.1109/34.211463
|
|
[120]
|
Pito R. A solution to the next best view problem for automated surface acquisition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1999, 21(10): 1016-1030 doi: 10.1109/34.799908
|
|
[121]
|
Chen S Y, Li Y F. Vision sensor planning for 3-D model acquisition. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2005, 35(5): 894-904 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2005.846907
|
|
[122]
|
Kriegel S, Rink C, Bodenmüller T, Suppa M. Efficient next-best-scan planning for autonomous 3D surface reconstruction of unknown objects. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2015, 10(4): 611-631 doi: 10.1007/s11554-013-0386-6
|
|
[123]
|
Connolly C. The determination of next best views. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. St. Louis, USA: IEEE, 1985. 432−435
|
|
[124]
|
Yamauchi B. A frontier-based approach for autonomous exploration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automation. Monterey, USA: IEEE, 1997. 146−151
|
|
[125]
|
Vasquez-Gomez J I, Sucar L E, Murrieta-Cid R, Herrera-Lozada J C. Tree-based search of the next best view/state for three-dimensional object reconstruction. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, DOI: 10.1177/1729881418754575
|
|
[126]
|
Vasquez-Gomez J I, Sucar L E, Murrieta-Cid R. View planning for 3D object reconstruction with a mobile manipulator robot. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Chicago, USA: IEEE, 2014. 4227−4233
|
|
[127]
|
Vasquez-Gomez J I, Sucar L E, Murrieta-Cid R. View/state planning for three-dimensional object reconstruction under uncertainty. Autonomous Robots, 2017, 41(1): 89-109 doi: 10.1007/s10514-015-9531-3
|
|
[128]
|
Monica R, Aleotti J. Contour-based next-best view planning from point cloud segmentation of unknown objects. Autonomous Robots, 2018, 42(2): 443-458 doi: 10.1007/s10514-017-9618-0
|
|
[129]
|
Sanderson A C. Assemblability based on maximum likelihood configuration of tolerances. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1999, 15(3): 568-572 doi: 10.1109/70.768188
|
|
[130]
|
Rupal B S, Anwer N, Secanell M, Qureshi A J. Geometric tolerance and manufacturing assemblability estimation of metal additive manufacturing (AM) processes. Materials & Design, 2020, 194: Article No. 108842
|
|
[131]
|
Ulaş C, Temeltaş H. 3D multi-layered normal distribution transform for fast and long range scan matching. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2013, 71(1): 85-108
|
|
[132]
|
Min Z, Wang J L, Meng M Q H. Joint rigid registration of multiple generalized point sets with hybrid mixture models. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(1): 334-347 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2019.2906391
|
|
[133]
|
Negri S P, Basile V, Valori M, Gambino B, Fassi I, Tosatti L M. A modular mobile robotic architecture for defects detection and repair in narrow tunnels of CFRP aeronautic components. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 55: 109-128 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2018.07.011
|
|
[134]
|
Tao Y, Zheng J Q, Lin Y C, Wang T M, Xiong H G, He G T, et al. Fuzzy PID control method of deburring industrial robots. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems: Applications in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 29(6): 2447-2455
|
|
[135]
|
Krishna S, Vasu S. Fuzzy PID based adaptive control on industrial robot system. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(5): 13055-13060 doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2018.02.292
|
|
[136]
|
Dass A, Srivastava S. Identification and control of dynamical systems using different architectures of recurrent fuzzy system. ISA Transactions, 2019, 85: 107-118 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2018.09.025
|
|
[137]
|
Liu Q, Li D Y, Ge S S, Ji R H, Ouyang Z, Tee K P. Adaptive bias RBF neural network control for a robotic manipulator. Neurocomputing, 2021, 447: 213-223 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.033
|
|
[138]
|
陶波, 赵兴炜, 丁汉. 大型复杂构件机器人移动加工技术研究. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2018, 48(12): 1302-1312 doi: 10.1360/N092018-00192Tao Bo, Zhao Xing-Wei, Ding Han. Study on robotic mobile machining techniques for large complex components. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2018, 48(12): 1302-1312 doi: 10.1360/N092018-00192
|
|
[139]
|
Zhao X W, Tao B, Han S B, Ding H. Accuracy analysis in mobile robot machining of large-scale workpiece. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2021, 71: Article No. 102153 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2021.102153
|
|
[140]
|
Zhao X W, Tao B, Ding H. Multimobile robot cluster system for robot machining of large-scale workpieces. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2022, 27(1): 561-571 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2021.3068259
|
|
[141]
|
Dietrich F, Buchholz D, Wobbe F, Sowinski F, Raatz A, Schumacher W, et al. On contact models for assembly tasks: Experimental investigation beyond the peg-in-hole problem on the example of force-torque maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Taipei, China: IEEE, 2010. 2313−2318
|
|
[142]
|
Liu Z, Song L B, Hou Z M, Chen K, Liu S L, Xu J. Screw insertion method in peg-in-hole assembly for axial friction reduction. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 148313-148325 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2946406
|
|
[143]
|
Lefebvre T, Xiao J, Bruyninckx H, de Gersem G. Active compliant motion: A survey. Advanced Robotics, 2005, 19(5): 479-499 doi: 10.1163/156855305323383767
|
|
[144]
|
Abdullah M W, Roth H, Weyrich M, Wahrburg J. An approach for peg-in-hole assembling using intuitive search algorithm based on human behavior and carried by sensors guided industrial robot. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2015, 48(3): 1476-1481 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.06.295
|
|
[145]
|
Inoue T, de Magistris G, Munawar A, Yokoya T, Tachibana R. Deep reinforcement learning for high precision assembly tasks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 819−825
|
|
[146]
|
Chen C, Lewis F L, Li B. Homotopic policy iteration-based learning design for unknown linear continuous-time systems. Automatica, 2022, 138: Article No. 110153 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.110153
|
|
[147]
|
Luo J L, Solowjow E, Wen C T, Ojea J A, Agogino A M, Tamar A, et al. Reinforcement learning on variable impedance controller for high-precision robotic assembly. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2019. 3080−3087
|
|
[148]
|
Scheer A W. Whitepaper-Industry 4.0: From vision to implementation. White Paper, 2015: 1–26
|
|
[149]
|
Ge J, Xie S R, Wang Y N, Liu J, Zhang H, Zhou B W, et al. A system for automated detection of ampoule injection impurities. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2017, 14(2): 1119-1128 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2015.2490061
|
|
[150]
|
张辉, 易俊飞, 王耀南, 吴刘宸, 陈瑞博. 医药质量检测关键技术及其应用综述. 仪器仪表学报, 2020, 41(3): 1-17 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2006049Zhang Hui, Yi Jun-Fei, Wang Yao-Nan, Wu Liu-Chen, Chen Rui-Bo. Review on key technologies and applications of pharmaceutical quality testing. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2020, 41(3): 1-17 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2006049
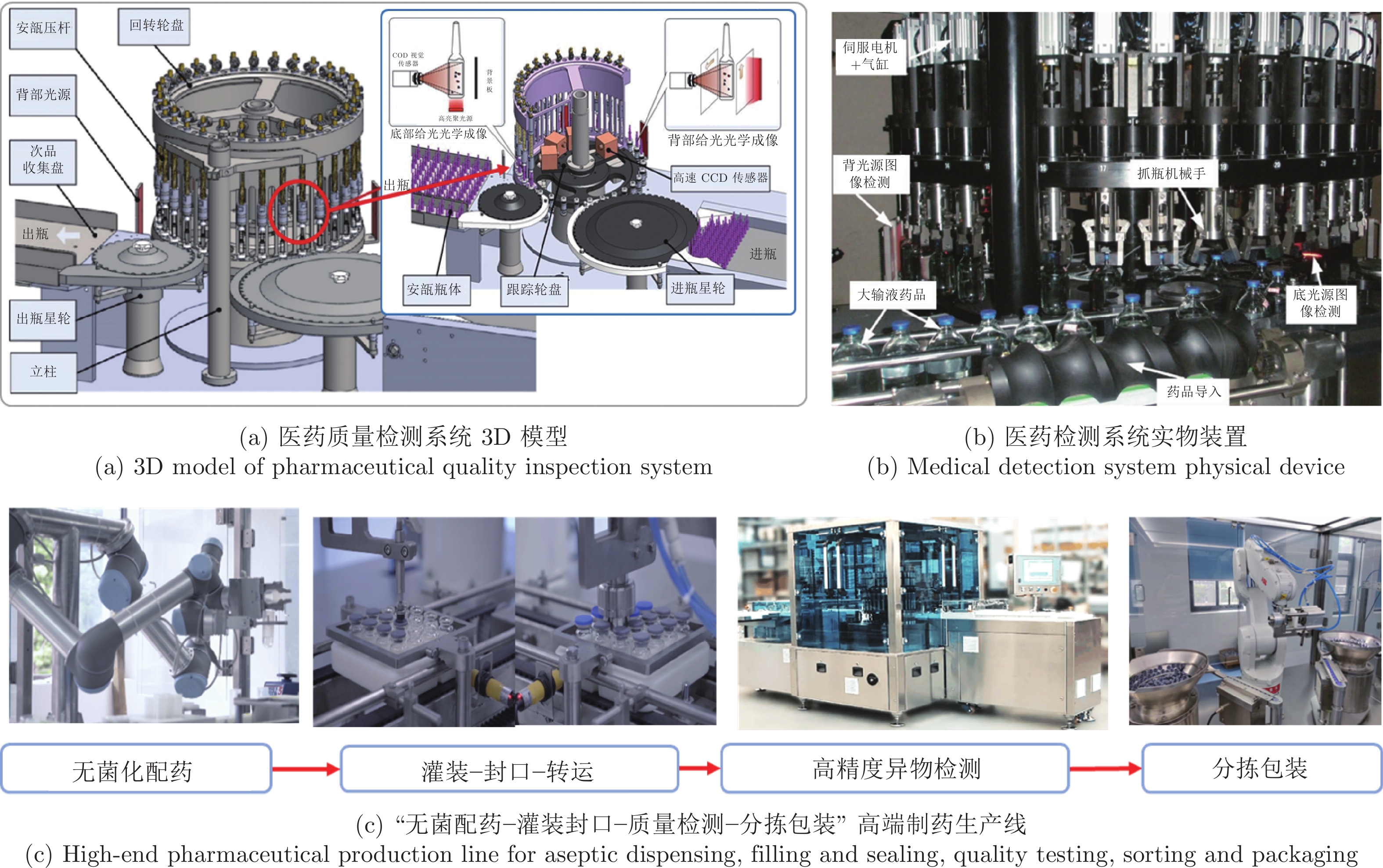
|




 下载:
下载: