-
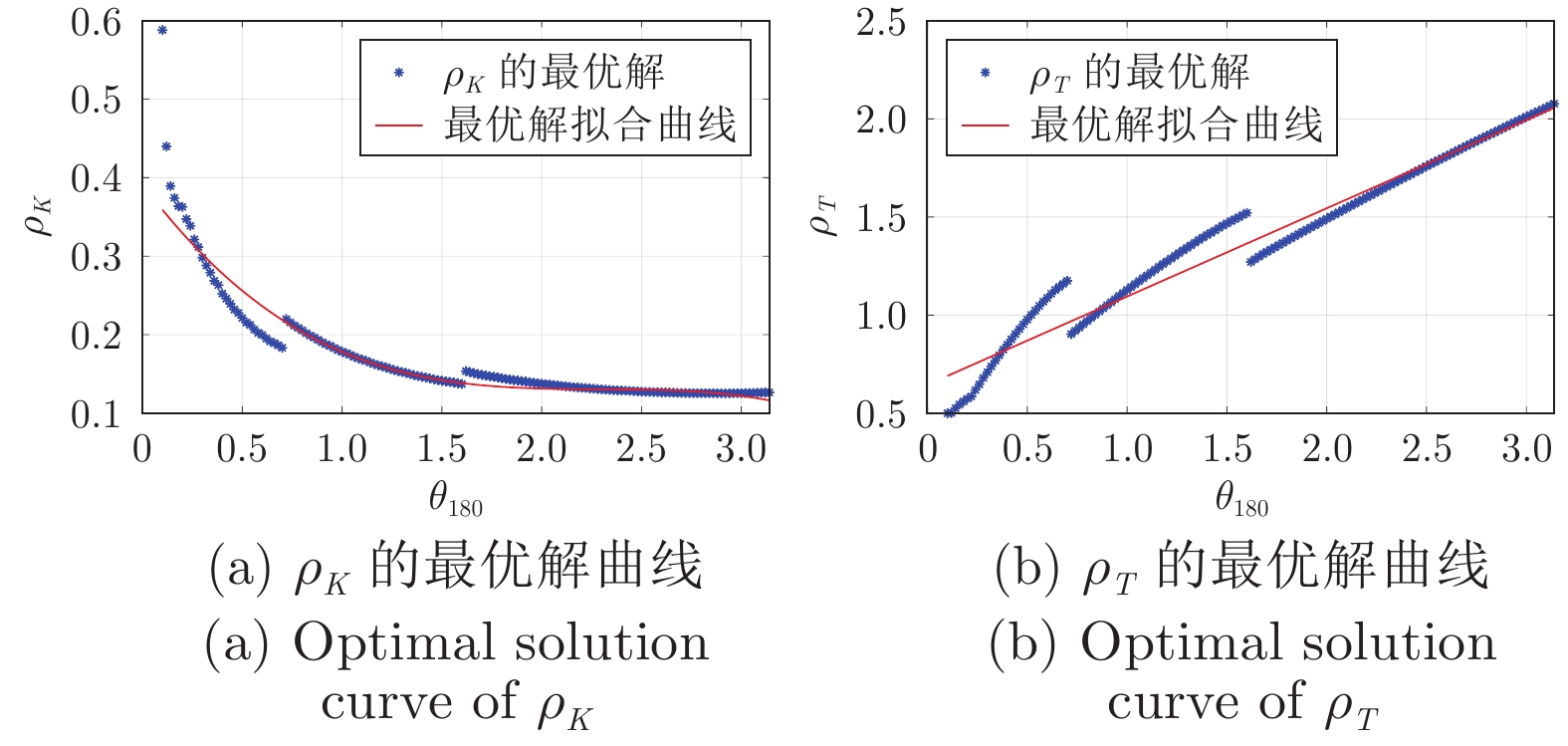
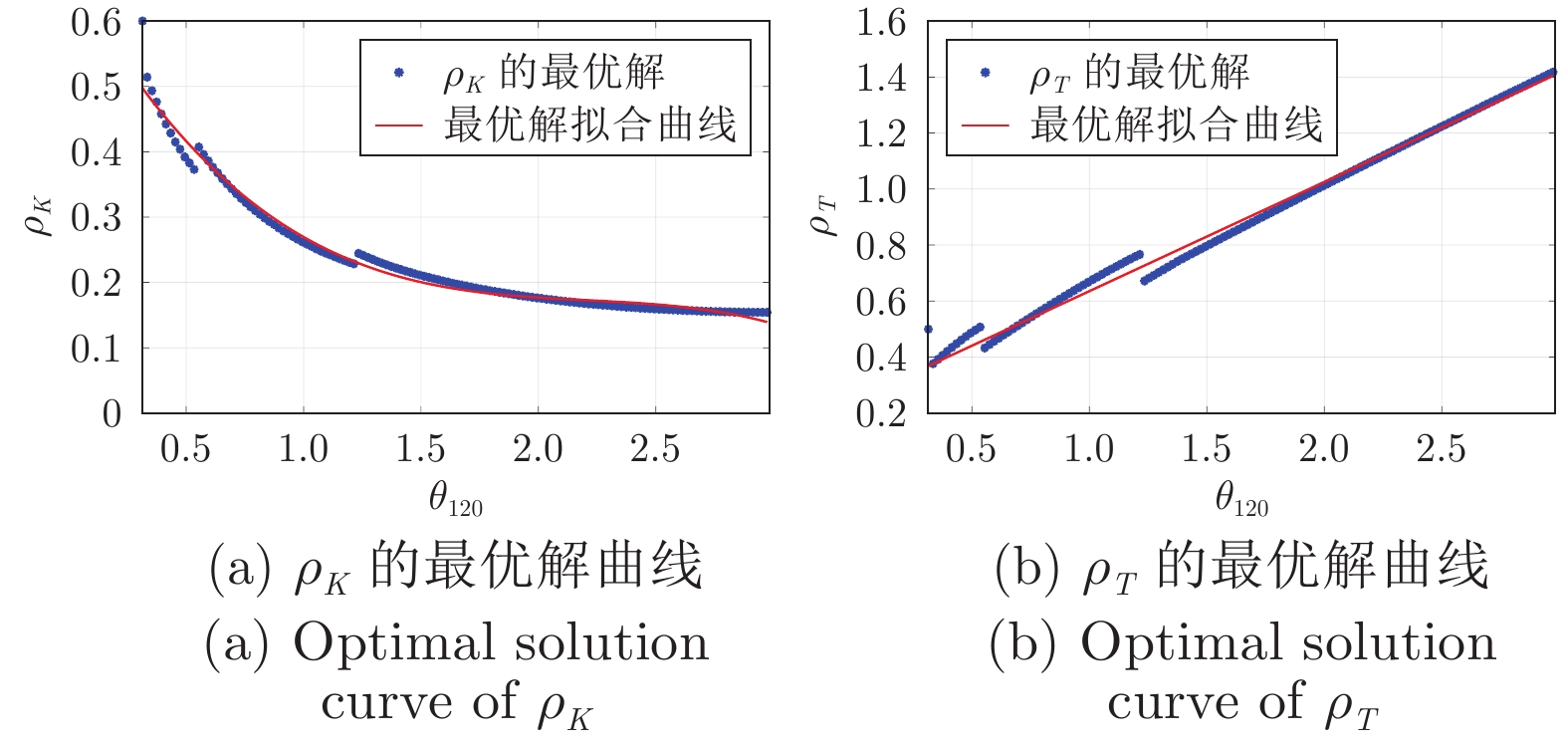
摘要: 针对存在临界点的A类被控对象及不存在临界点的B类被控对象, 分别采用其$-180^\circ$和$-120^\circ$相位点的频率和增益提出了PID (Proportional-integral-derivative) 控制器参数的优化整定方法. 基于Tchebyshev多项式和分数阶积分器求取被控对象$-180^\circ$或$-120^\circ$相位点的频率和增益, 建立其积分滞后模型. 采用负载扰动下跟踪误差平方和(Sum of squares of tracking errors, SSE)最小作为优化指标, 使闭环系统具有强的鲁棒性的最大灵敏度和最大补灵敏度为约束方程, 针对两类被控对象, 分别建立了基于$-180^\circ$和$-120^\circ$相位点频率和增益的PID控制器比例、积分与微分三个参数的优化整定规则. 通过与其他常用PID控制方法的仿真与物理对比实验, 表明所提方法的优越性.
-
关键词:
- PID控制 /
- Tchebyshev多项式 /
- 积分滞后模型 /
- 跟踪误差平方和 /
- 优化整定规则
Abstract: In this paper, a tuning method of PID (proportional-integral-derivative) controller parameters is proposed for class A controlled object with critical point and class B controlled object without critical point using the frequency and gain of the point at which its phase is $-180^\circ$ and $-120^\circ$ respectively. The frequency and gain of the controlled object at which its phase is $-180^\circ$ or $-120^\circ$ are obtained based on Tchebyshev polynomial and fractional order integrator, and the gain-integrator-delay model is established for the controlled object. Taking the minimum sum of squares of tracking error (SSE) under load disturbance as the optimization objective, and the maximum sensitivity and maximum complementary sensitivity as the constraint equations that give the closed-loop system strong robustness, a tuning rule of the proportion, integral and differential parameters of PID controller is established for two classes of plants based on the frequency and gain at which the phase is $-180^\circ$ and $-120^\circ$ respectively. Through simulation and physical comparison experiments with other common PID control methods, the superiority of the proposed method is demonstrated. -
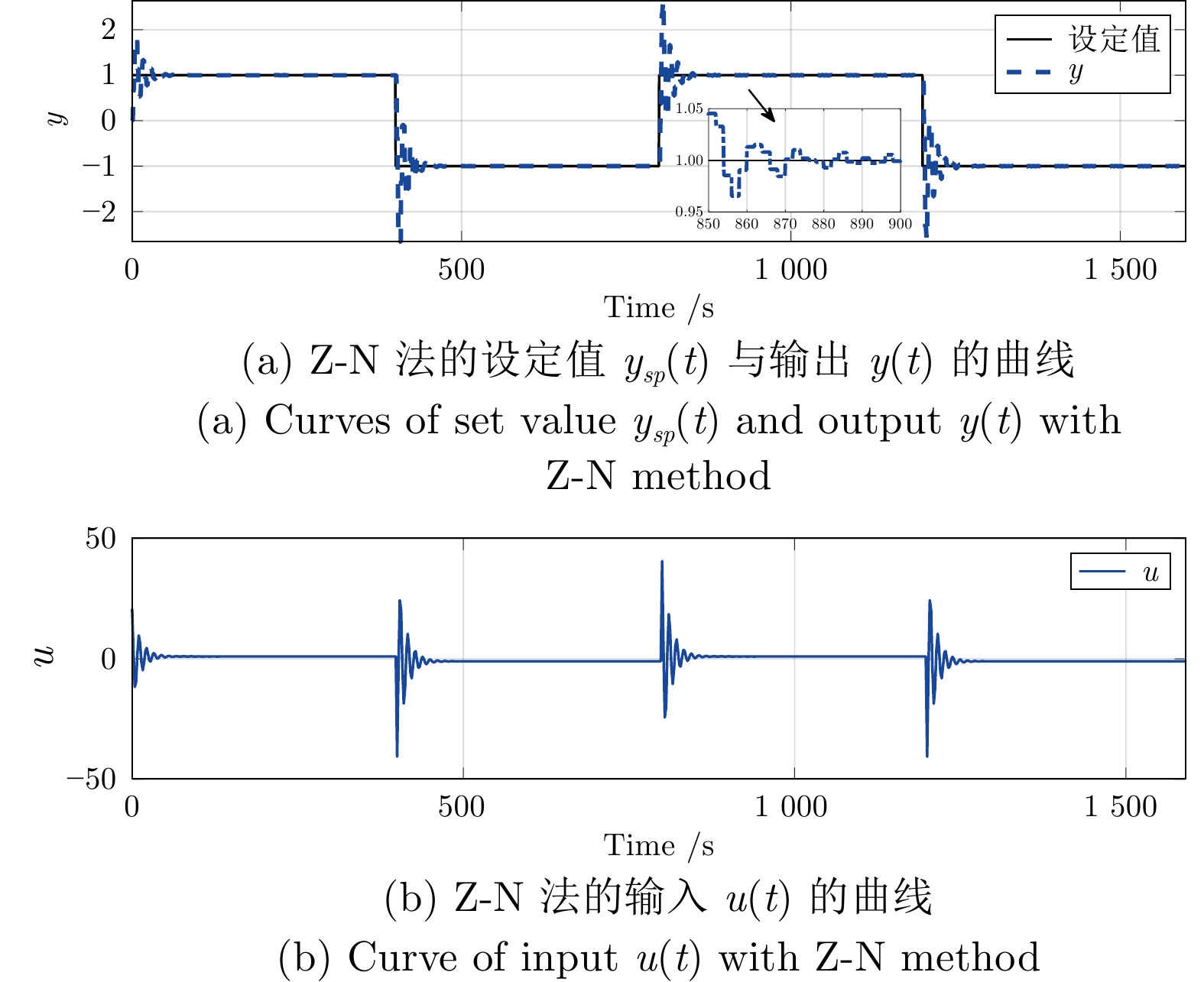
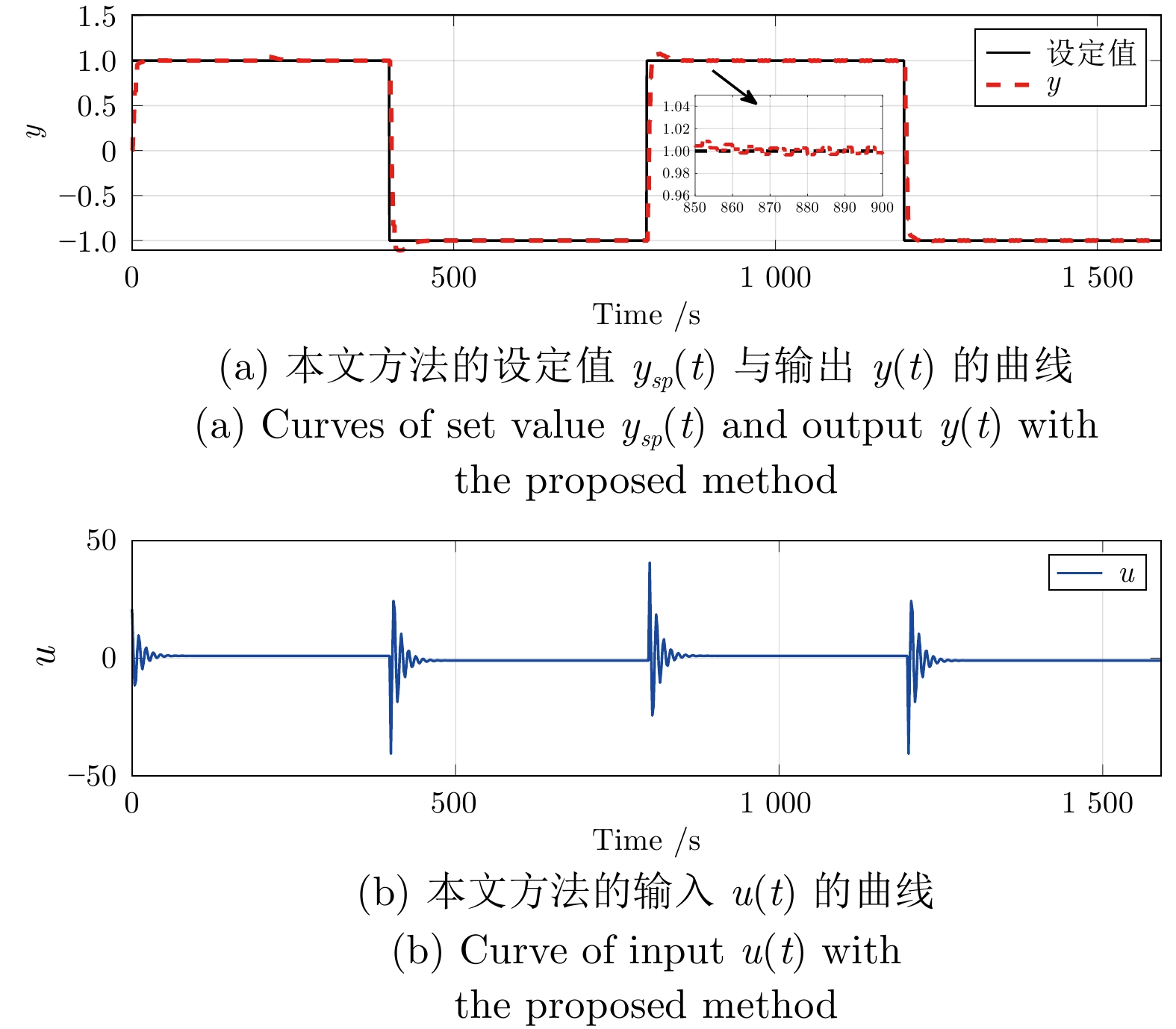
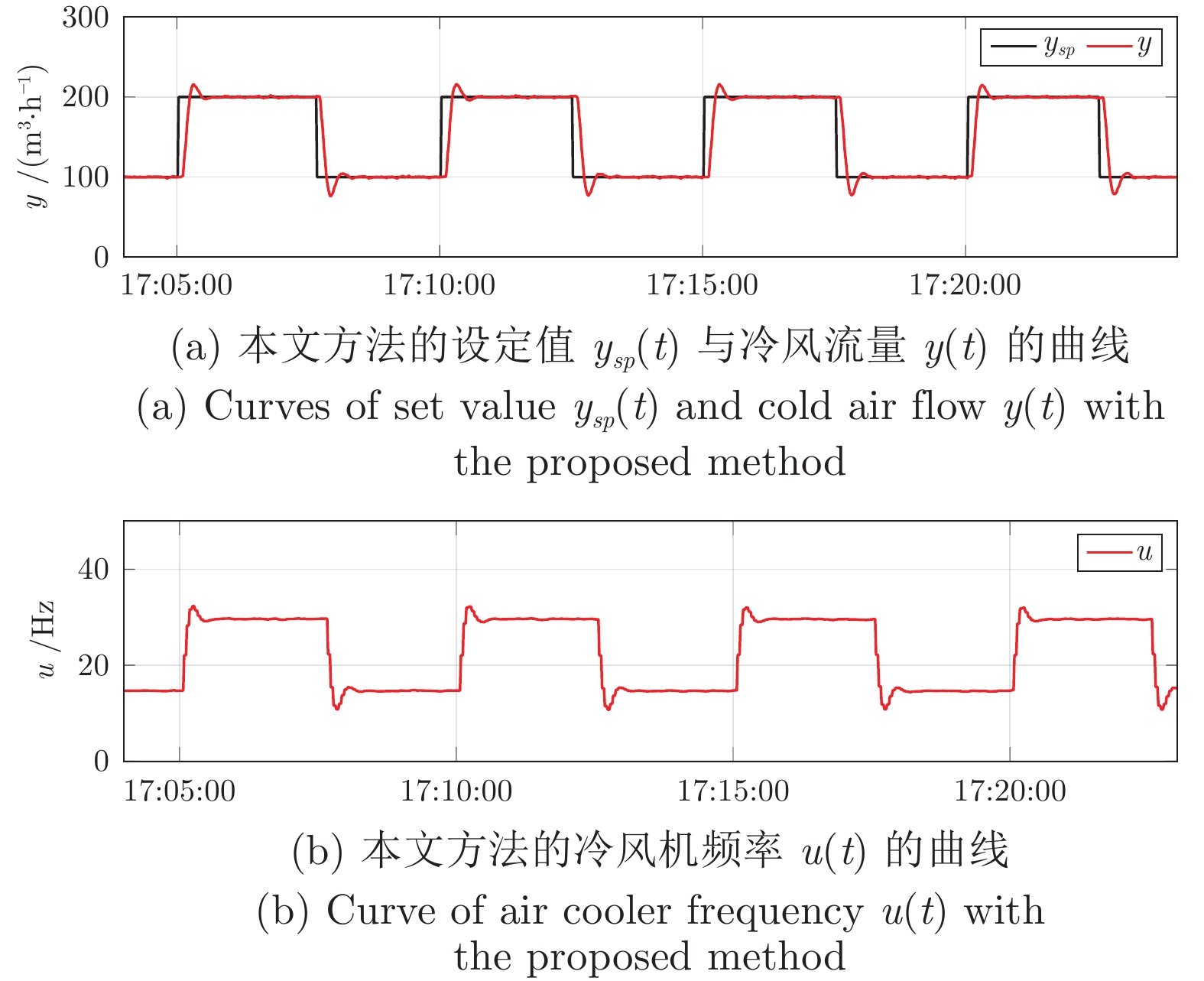
表 1 本文方法与Z-N法下误差$ e(t)$的性能评价
Table 1 Performance evaluation of error $ e(t)$ with the proposed method and Z-N method
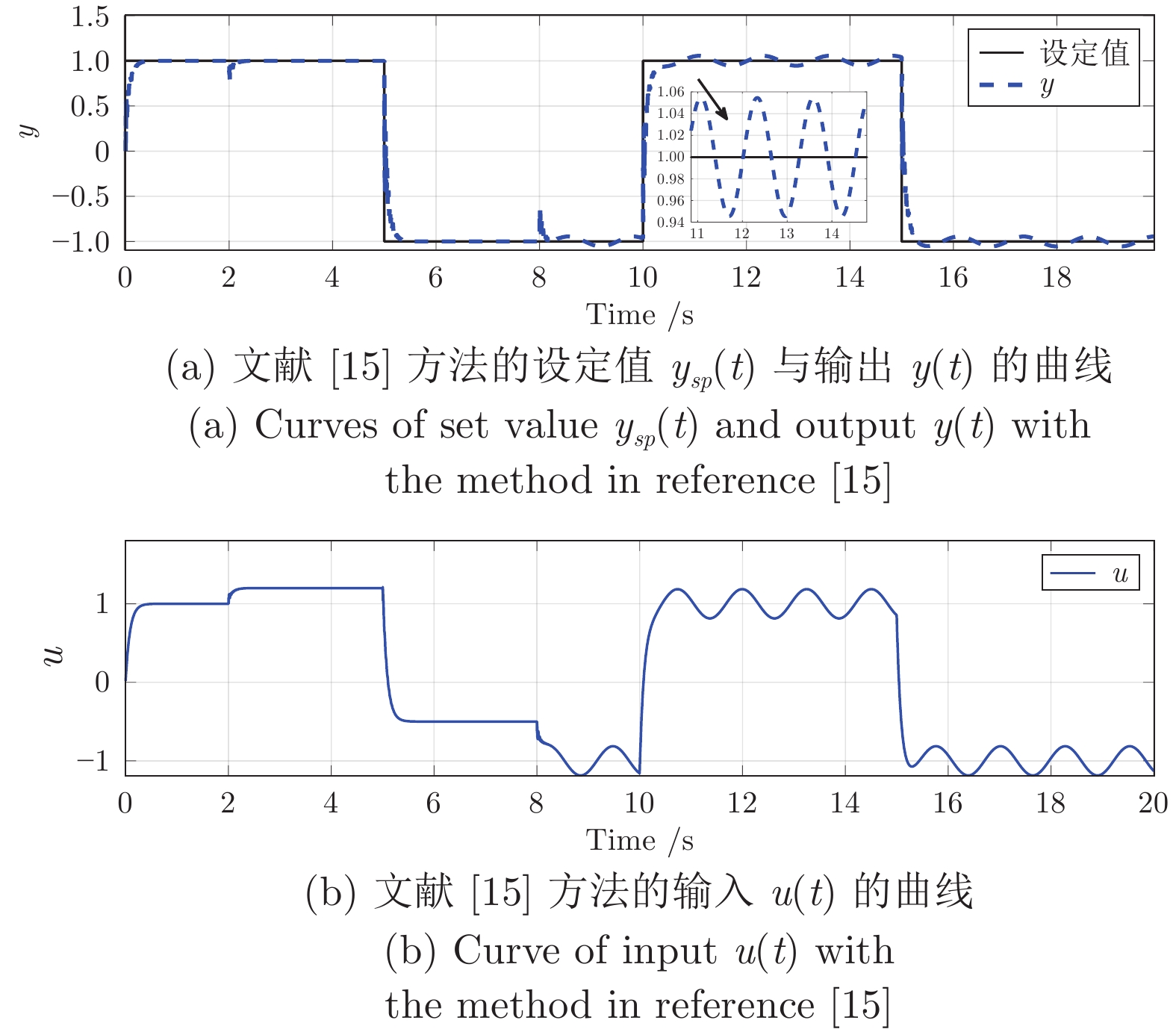
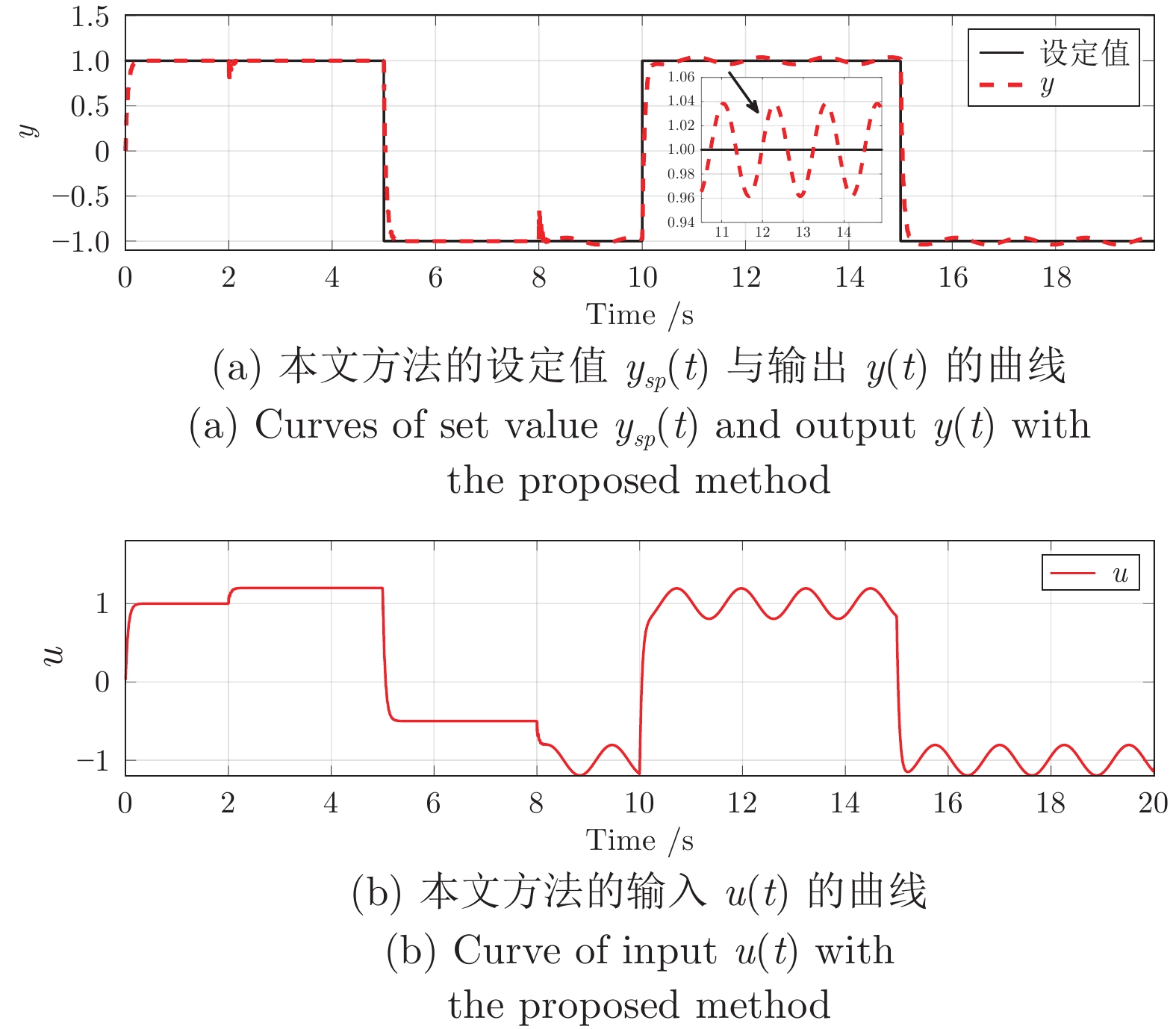
整定方法 性能指标 SAE MSE 本文 3835.3081 0.0274 Z-N法 8004.8341 0.0479 表 2 本文方法与文献[15]方法下误差$e(t)$的性能评价
Table 2 Performance evaluation of error $e(t)$ with the proposed method and the method in reference [15]
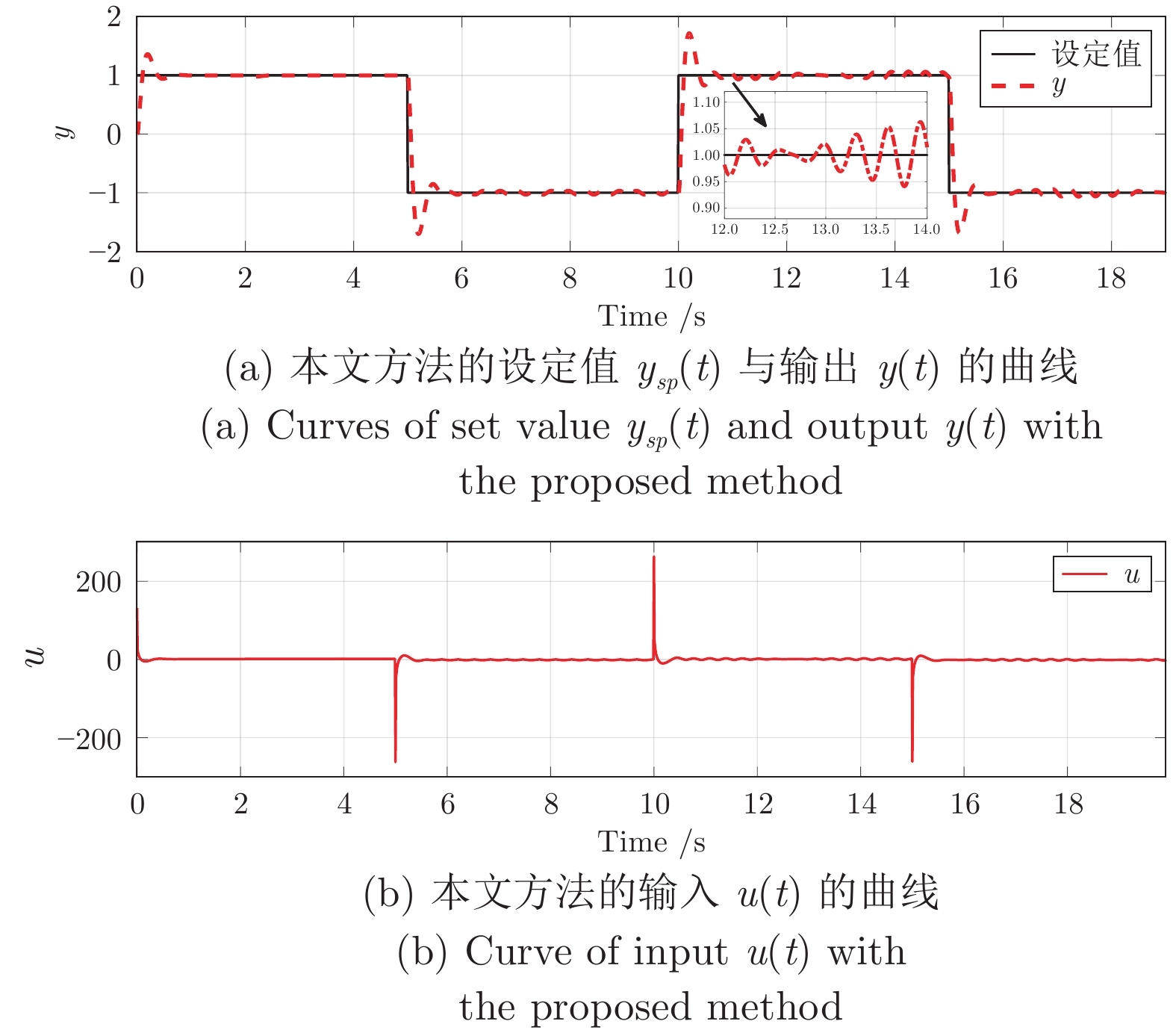
整定方法 性能指标 SAE MSE 本文 635.7247 0.0164 文献[15] 993.0357 0.0277 表 3 本文方法与文献[14]方法下误差$ e(t)$的性能评价
Table 3 Performance evaluation of error $ e(t)$ with the proposed method and the method in reference [14]
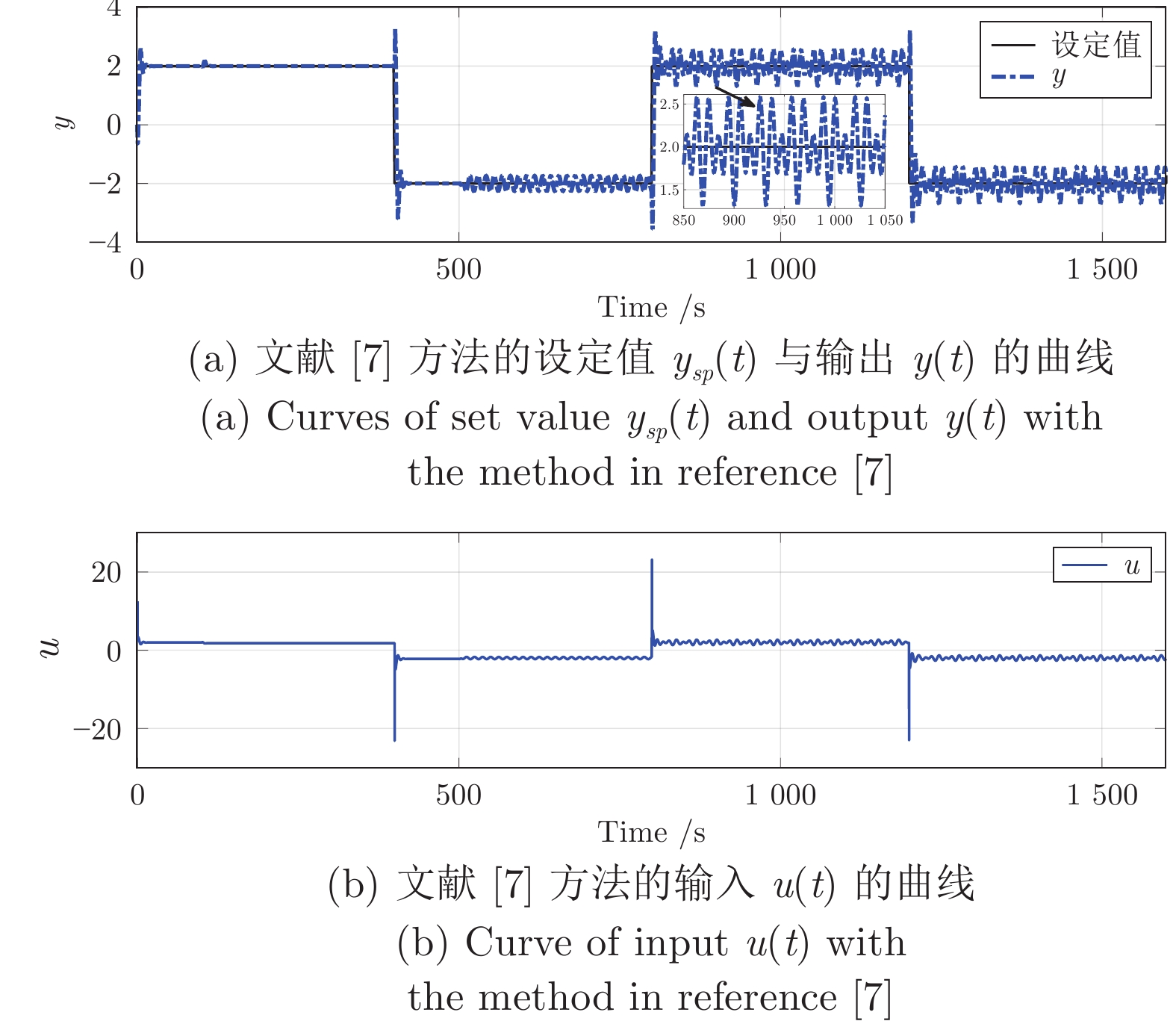
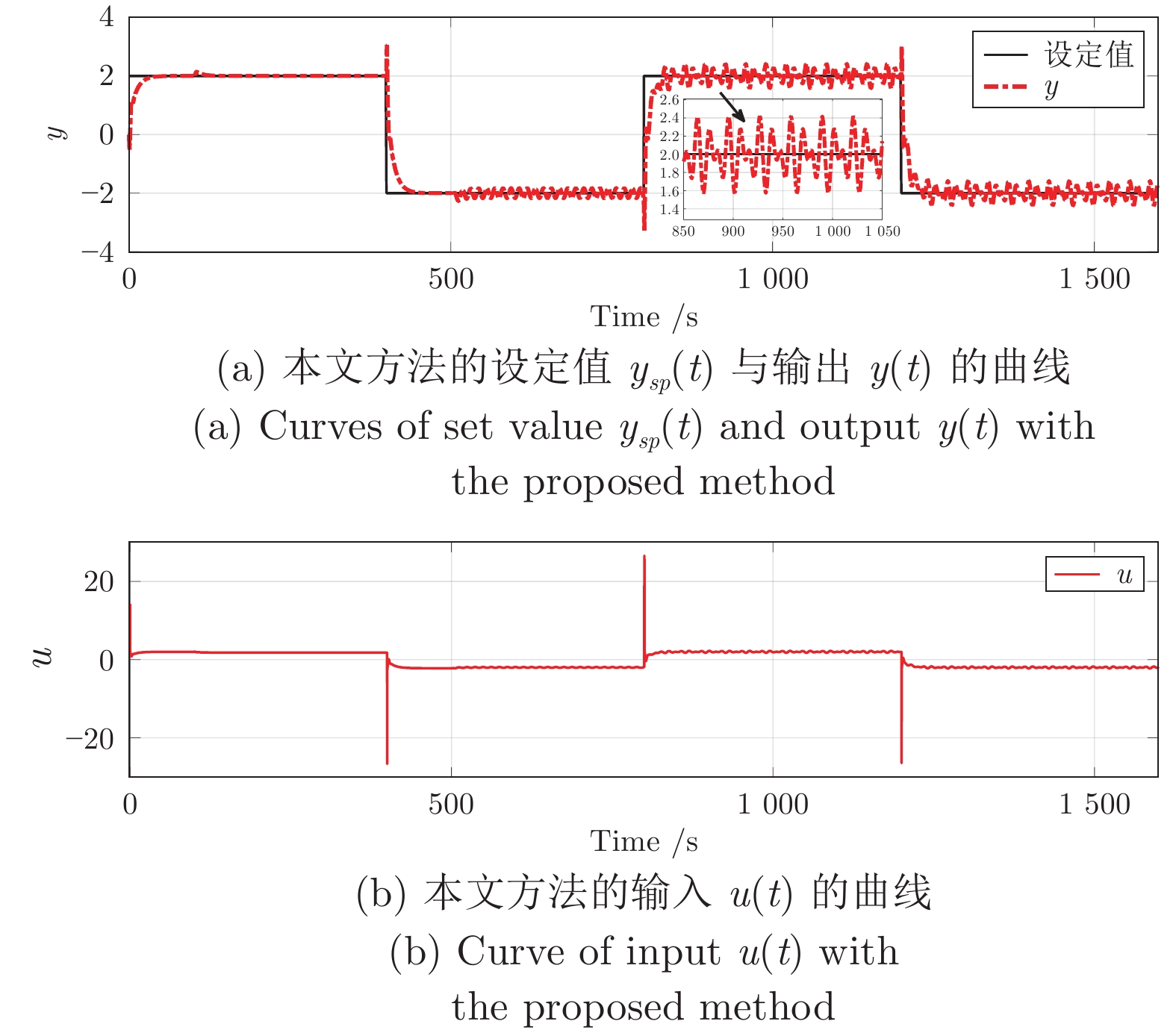
整定方法 性能指标 SAE MSE 本文 142.6175 0.0473 文献[14] 176.5287 0.0536 表 4 本文方法与文献[7]方法下误差$ e(t)$的性能评价
Table 4 Performance evaluation of error $ e(t)$ with the proposed method and the method in reference [7]
整定方法 性能指标 SAE MSE 本文 28889.3906 0.1806 文献[7] 34598.9258 0.1914 表 5 三种整定方法下PID控制器参数
Table 5 PID controller parameters with three tuning methods
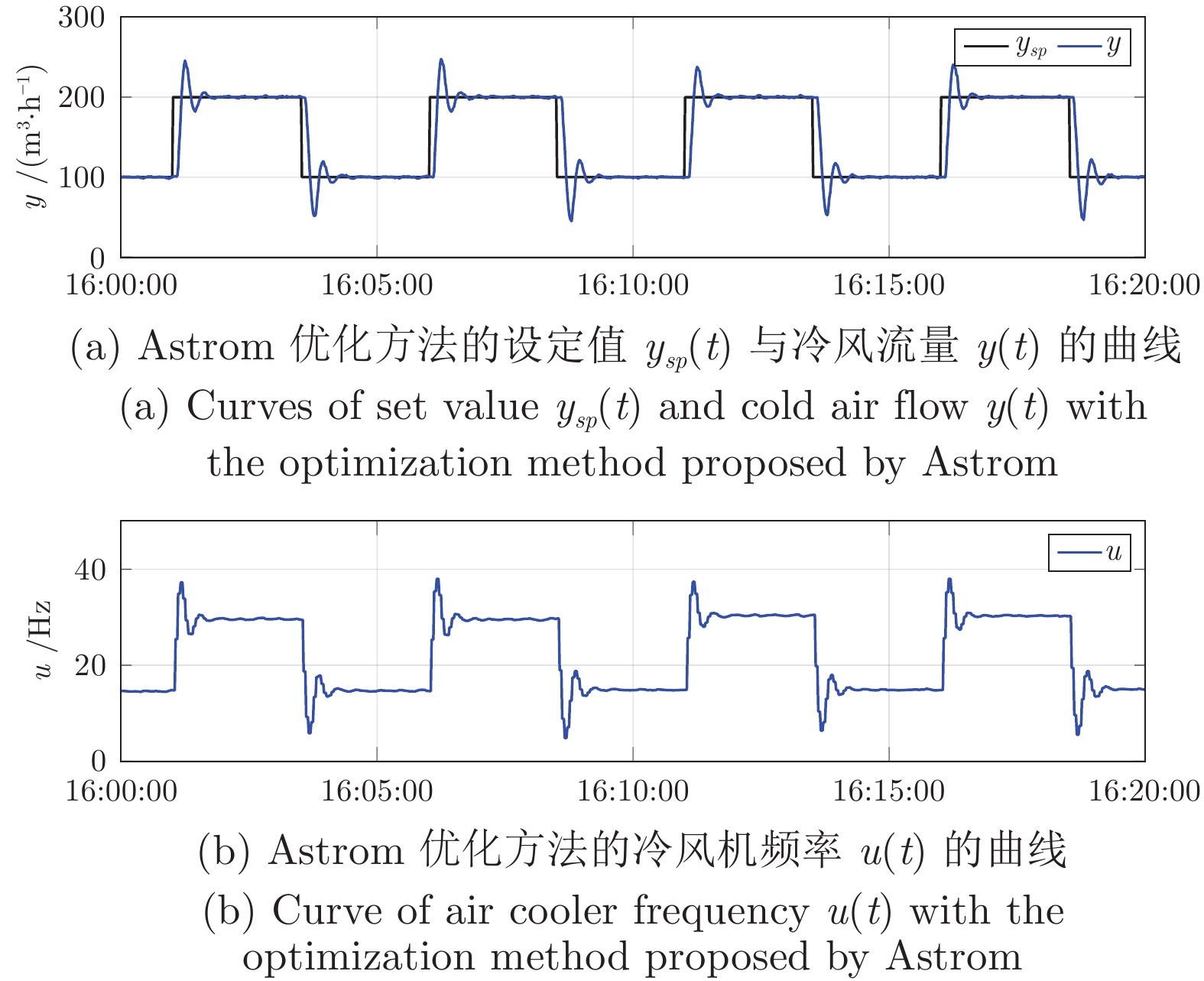
整定方法 PID参数 $K_P$ $T_I$ $T_D$ Z-N法 0.3158 3.3412 0.8353 Astrom方法 0.1377 2.6910 1.1111 本文 0.0974 7.1364 1.7841 表 6 三种方法下误差$ e(t)$的性能评价
Table 6 Performance evaluation of error $ e(t)$ with the three methods
整定方法 性能指标 SAE MSE Z-N法 37624.0129 1736.8307 Astrom方法 10905.8089 570.0473 本文 8904.2220 514.4361 -
[1] Guo L. Feedback and uncertainty: Some basic problems and results. Annual Reviews in Control, 2020, 49: 27-36 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2020.04.001 [2] Samad T. A survey on industry impact and challenges thereof[Technical Activities]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2017, 37(1): 17-18 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2016.2621438 [3] Borase R P, Maghade D K, Sondkar S Y, Pawar S N. A review of PID control, tuning methods and applications. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2021, 9(2): 818-827 doi: 10.1007/s40435-020-00665-4 [4] Somefun O A, Akingbade K, Dahunsi F. The dilemma of PID tuning. Annual Reviews in Control, 2022, 52: 65-74 [5] Ziegler J G, Nichols N B. Optimum settings for automatic controllers. Transactions of the ASME, 1942, 64: 759-768 [6] Åström K J, Hang C C, Persson P, Ho W K. Towards intelligent PID control. Automatica, 1992, 28(1): 1-9 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(92)90002-W [7] Nie Z Y, Li Z Y, Wang Q G, Gao Z Q, Luo J L. A unifying Ziegler-nichols tuning method based on active disturbance rejection. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2022, 32(18): 9525-9541 doi: 10.1002/rnc.5848 [8] Åström K J, Hägglund T. Automatic tuning of simple regulators with specifications on phase and amplitude margins. Automatica, 1984, 20(5): 645-651 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(84)90014-1 [9] Åström K J, Hägglund T. PID Controllers: Theory, Design, and Tuning (Second edition). Research Triangle Park: ISA, 1995. [10] Poulin E, Pomerleau A. PI settings for integrating processes based on ultimate cycle information. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 1999, 7(4): 509-511 doi: 10.1109/87.772167 [11] Ossareh H R, Wisotzki S, Seeds J B, Jankovic M. An internal model control-based approach for characterization and controller tuning of turbocharged gasoline engines. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2021, 29(2): 866-875 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2955917 [12] Huang H P, Jeng J C, Luo K Y. Auto-tune system using single-run relay feedback test and model-based controller design. Journal of Process Control, 2005, 15(6): 713-727 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2004.11.004 [13] Mataušek M R, Šekara T B. PID controller frequency-domain tuning for stable, integrating and unstable processes, including dead-time. Journal of Process Control, 2011, 21(1): 17-27 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2010.09.007 [14] Åström K J, Hägglund T. Advanced PID Control. Pittsburgh: ISA, 2006. [15] Bazanella A S, Pereira L F A, Parraga A. A new method for PID tuning including plants without ultimate frequency. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(2): 637-644 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2016.2557723 [16] Lorenzini C, Bazanella A S, Pereira L F A, da Silva G R G. The generalized forced oscillation method for tuning PID controllers. ISA Transactions, 2019, 87: 68-87 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2018.11.014 [17] Takahashi Y, Chan C S, Auslander D M. Parametereinstellung bei linearen DDC-algorithmen. at - Automatisierungstechnik, 1971, 19(JG): 237-284 doi: 10.1524/auto.1971.19.jg.237 [18] Bobál V, Böhm J, Fessl J, Macháček J. Digital Self-tuning Controllers: Algorithms, Implementation and Applications. London: Springer, 2005. [19] Bazanella A S, Parraga A. Tuning PID controllers from sampled-data relay feedback experiments. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(4): 125-130 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.06.106 [20] Rad A B, Lo W L, Tsang K M. Self-tuning PID controller using Newton-raphson search method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1997, 44(5): 717-725 doi: 10.1109/41.633479 [21] Díaz-Rodríguez I D, Han S J, Bhattacharyya S P. Analytical Design of PID Controllers. Switzerland: Springer, 2019. [22] Chen Y Q, Vinagre B M, Podlubny I. Continued fraction expansion approaches to discretizing fractional order derivatives—an expository review. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2004, 38(1-4): 155-170 doi: 10.1007/s11071-004-3752-x [23] Zhang Q, Song B Y, Zhao H D, Zhang J S. Discretization of fractional order differentiator and integrator with different fractional orders. Intelligent Control and Automation, 2017, 8(2): 75-85 doi: 10.4236/ica.2017.82006 [24] 崔凤午, 梁怀学. 棣莫弗公式在推导倍角公式中的应用. 松辽学刊(自然科学版), 1997(4): 64-65Cui Feng-Wu, Liang Huai-Xue. The application of Demoivre Formula in the derivation of double Angle formula. Songliao Journal (Natural Science Edition), 1997(4): 64-65 [25] Huba M, Vrančič D. Introduction to the discrete time $ PID^m_n$ control for the IPDT plant. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(6): 119-124 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.07.140 [26] Vítečcková M, Viteček A. 2DOF analog and digital controller tunning for integrating plants with time delay. Acta Mechanica Slovaca, 2009, 13(4): 48-53 doi: 10.2478/v10147-010-0036-y [27] Veinović S, Stojić D, Joksimović D. Optimized four-parameter PID controller for AVR systems with respect to robustness. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2022, 135: Article No. 107529 [28] Wallén A, Årström K J, Hägglun T. Loop-shaping design of PID controllers with constant Ti/Td ratio. Asian Journal of Control, 2002, 4(4): 403-409 [29] 胡寿松. 自动控制原理. 第5版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007.Hu Shou-Song. Automatic Control Theory (Fifth edition). Beijing: Science Press, 2007. [30] Solodov M V. On the sequential quadratically constrained quadratic programming methods. Mathematics of Operations Research, 2004, 29(1): 64-79 doi: 10.1287/moor.1030.0069 [31] Qi M, Zhang G P. An investigation of model selection criteria for neural network time series forecasting. European Journal of Operational Research, 2001, 132(3): 666-680 doi: 10.1016/S0377-2217(00)00171-5 [32] Haberstich C, Nouy A, Perrin G. Boosted optimal weighted least-squares. Mathematics of Computation, 2022, 91(335): 1281−1315 [33] Åström K J, Wittenmark B. Computer-controlled Systems: Theory and Design (Second edition). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1990. [34] Hägglund T. A control-loop performance monitor. Control Engineering Practice, 1995, 3(11): 1543-1551 doi: 10.1016/0967-0661(95)00164-P [35] Ghanassi M, Champagne B, Kabal P. On the steady-state mean squared error of the fixed-point LMS algorithm. Signal Processing, 2007, 87(12): 3226-3233 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2007.05.029 [36] Euzébio T A M, Barros P R. Optimal integral gain for smooth PI control. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2013, 46(11): 529-533 doi: 10.3182/20130703-3-FR-4038.00125 -




 下载:
下载: