-
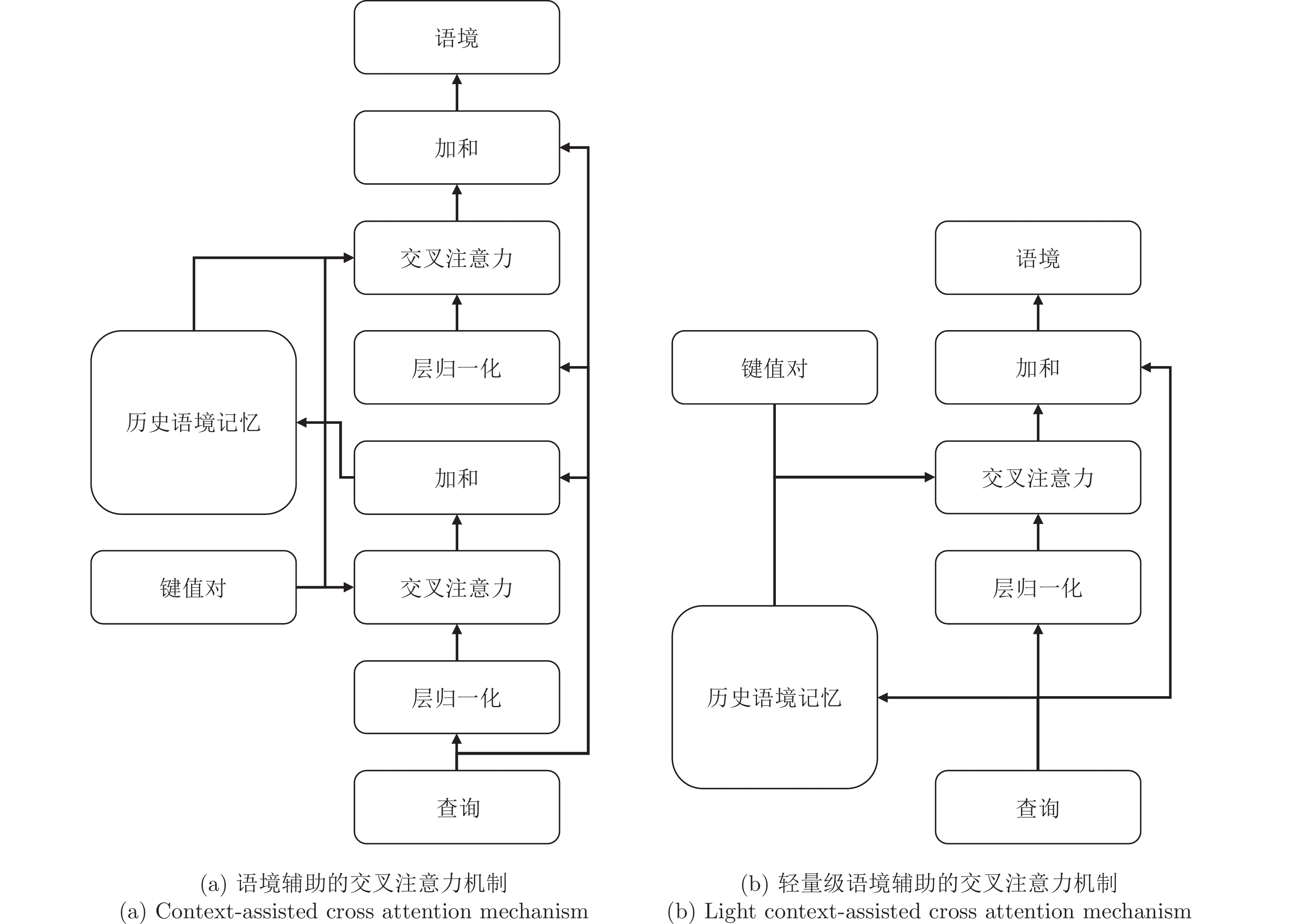
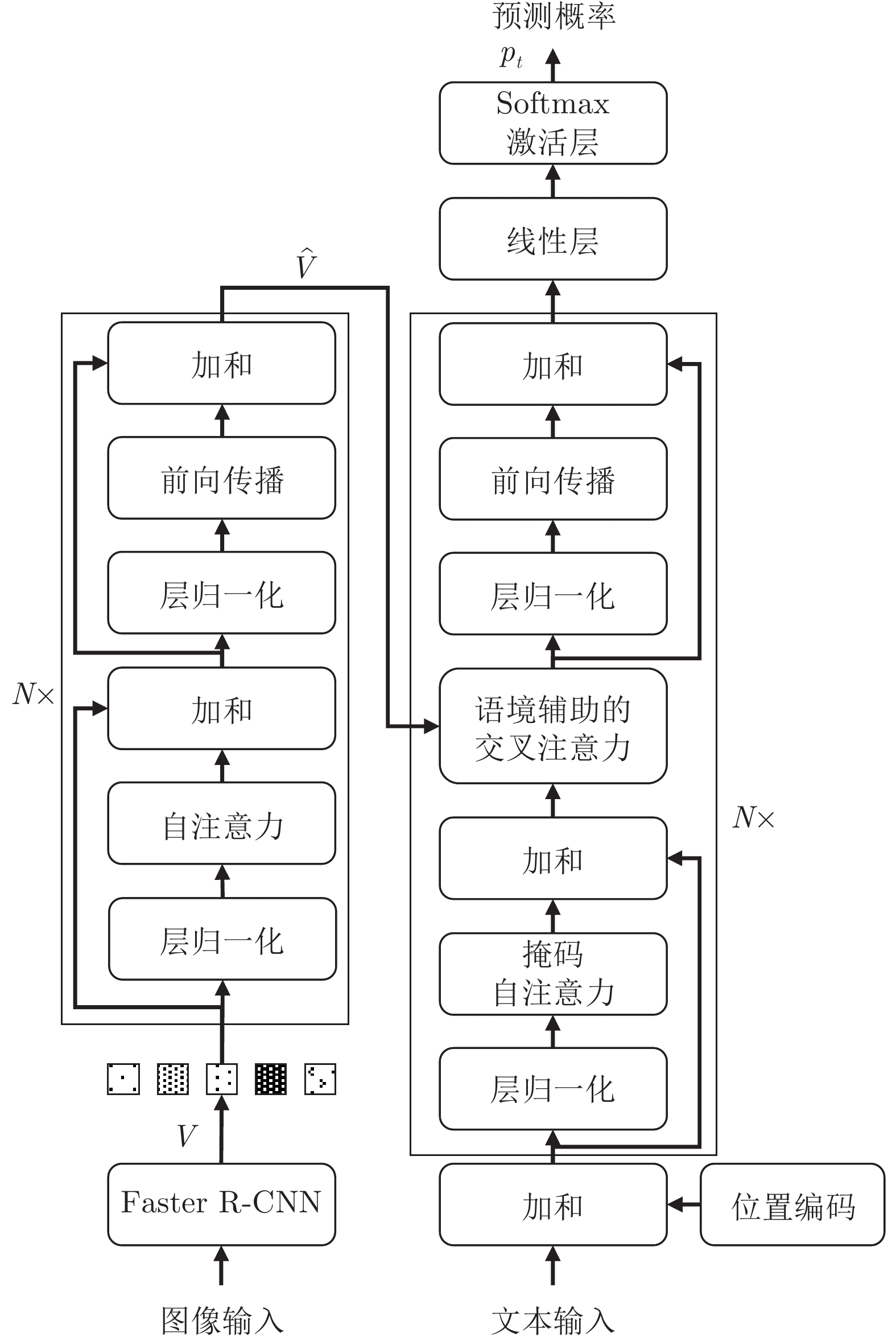
摘要: 在图像标题生成领域, 交叉注意力机制在建模语义查询与图像区域的关系方面, 已经取得了重要的进展. 然而, 其视觉连贯性仍有待探索. 为填补这项空白, 提出一种新颖的语境辅助的交叉注意力(Context-assisted cross attention, CACA)机制, 利用历史语境记忆(Historical context memory, HCM), 来充分考虑先前关注过的视觉线索对当前注意力语境生成的潜在影响. 同时, 提出一种名为“自适应权重约束(Adaptive weight constraint, AWC)” 的正则化方法, 来限制每个CACA模块分配给历史语境的权重总和. 本文将CACA模块与AWC方法同时应用于转换器(Transformer)模型, 构建一种语境辅助的转换器(Context-assisted transformer, CAT)模型, 用于解决图像标题生成问题. 基于MS COCO (Microsoft common objects in context)数据集的实验结果证明, 与当前先进的方法相比, 该方法均实现了稳定的提升.Abstract: The cross attention mechanism has made significant progress in modeling the relationship between semantic queries and image regions in image captioning. However, its visual coherence remains to be explored. To fill this gap, we propose a novel context-assisted cross attention (CACA) mechanism. With the help of historical context memory (HCM), CACA fully considers the potential impact of previously attended visual cues on the generation of current attention context. Moreover, we present a regularization method, called adaptive weight constraint (AWC), to restrict the total weight assigned to the historical contexts of each CACA module. We apply CACA and AWC to the Transformer model and construct a context-assisted transformer (CAT) for image captioning. Experimental results on the MS COCO (microsoft common objects in context) dataset demonstrate that our method achieves consistent improvement over the current state-of-the-art methods.
-
Key words:
- Image captioning /
- attention mechanism /
- transformer /
- visual coherence
-
表 1 基于Transformer的图像标题生成模型结合(轻量级)语境辅助的交叉注意力机制在MS COCO数据集上的性能表现 (%)
Table 1 Performance of Transformer-based image captioning models combined with (Light)CACA on MS COCO dataset (%)
模型名称 BLEU-1 BLEU-4 METEOR ROUGE-L CIDEr-D SPICE Transformer 80.0 38.0 28.5 57.9 126.5 22.4 Transformer + CACA (CAT) 80.8 38.9 28.9 58.6 129.6 22.6 Transformer + LightCACA (LightCAT) 80.6 38.4 28.6 58.2 127.8 22.5 $\mathcal{M}^{2}$Transformer[25] 80.8 39.1 29.2 58.6 131.2 22.6 $\mathcal{M}^{2}$Transformer + CACA 81.2 39.4 29.5 59.0 132.4 22.8 $\mathcal{M}^{2}$Transformer + LightCACA 81.2 39.3 29.4 58.8 131.9 22.8 DLCT[27] 81.4 39.8 29.5 59.1 133.8 23.0 DLCT + CACA 81.6 40.2 29.6 59.2 134.3 23.2 DLCT + LightCACA 81.4 40.0 29.5 59.2 134.1 23.0 $\mathcal{S}^{2}$Transformer[28] 81.1 39.6 29.6 59.1 133.5 23.2 $\mathcal{S}^{2}$Transformer + CACA 81.5 40.0 29.7 59.3 134.2 23.3 $\mathcal{S}^{2}$Transformer + LightCACA 81.3 39.7 29.6 59.3 133.8 23.3 DIFNet[29] 81.7 40.0 29.7 59.4 136.2 23.2 DIFNet + CACA 82.0 40.5 29.9 59.7 136.8 23.4 DIFNet + LightCACA 81.9 40.1 29.7 59.5 136.4 23.2 表 2 基于LSTM的图像标题生成模型结合语境辅助的交叉注意力机制在MS COCO数据集上的性能表现 (%)
Table 2 Performance of LSTM-based image captioning models combined with CACA on MS COCO dataset (%)
表 3 语境辅助的交叉注意力机制对Transformer推理效率的影响(ms)
Table 3 The effect of context-assisted cross attention mechanism on Transformer's reasoning efficiency (ms)
模型名称 单轮贪心解码时间 单轮集束搜索解码时间 Transformer 4.7 63.9 CAT 6.1 86.6 LightCAT 4.9 68.1 表 4 本文模型与先进方法在MS COCO数据集上的性能对比(%)
Table 4 Performance comparison between our models and the state-of-the-art (%)
模型名称 BLEU-1 BLEU-4 METEOR ROUGE-L CIDEr-D SPICE Att2in[31] — 33.3 26.3 55.3 111.4 — Att2all[31] — 34.2 26.7 55.7 114.0 — BUTD[16] 79.8 36.3 27.7 56.9 120.1 21.4 AoANet[18] 80.2 38.9 29.2 58.8 129.8 22.4 $\mathcal{M}^{2}$Transformer[25] 80.8 39.1 29.2 58.6 131.2 22.6 X-LAN[19] 80.8 39.5 29.5 59.2 132.0 23.4 X-Transformer[19] 80.9 39.7 29.5 59.1 132.8 23.4 DLCT[27] 81.4 39.8 29.5 59.1 133.8 23.0 RSTNet (ResNext101)[26] 81.1 39.3 29.4 58.8 133.3 23.0 BUTD + CATT[20] — 38.6 28.5 58.6 128.3 21.9 Transformer + CATT[20] — 39.4 29.3 58.9 131.7 22.8 $\mathcal{S}^{2}$Transformer[28] 81.1 39.6 29.6 59.1 133.5 23.2 DIFNet[29] 81.7 40.0 29.7 59.4 136.2 23.2 ${\rm{CIIC}}_{\mathcal{O}}$ [39] 81.4 40.2 29.3 59.2 132.6 23.2 ${\rm{CIIC}}_{\mathcal{G}}$ [39] 81.7 40.2 29.5 59.4 133.1 23.2 Transformer + CACA (CAT) 80.8 38.9 28.9 58.6 129.6 22.6 $\mathcal{M}^{2}$Transformer + CACA 81.2 39.4 29.5 59.0 132.4 22.8 DLCT + CACA 81.6 40.2 29.6 59.2 134.3 23.2 $\mathcal{S}^{2}$Transformer + CACA 81.5 40.0 29.7 59.3 134.2 23.3 DIFNet + CACA 82.0 40.5 29.9 59.7 136.8 23.4 表 5 传统交叉注意力机制结合不同语境辅助策略在MS COCO数据集上的表现(%)
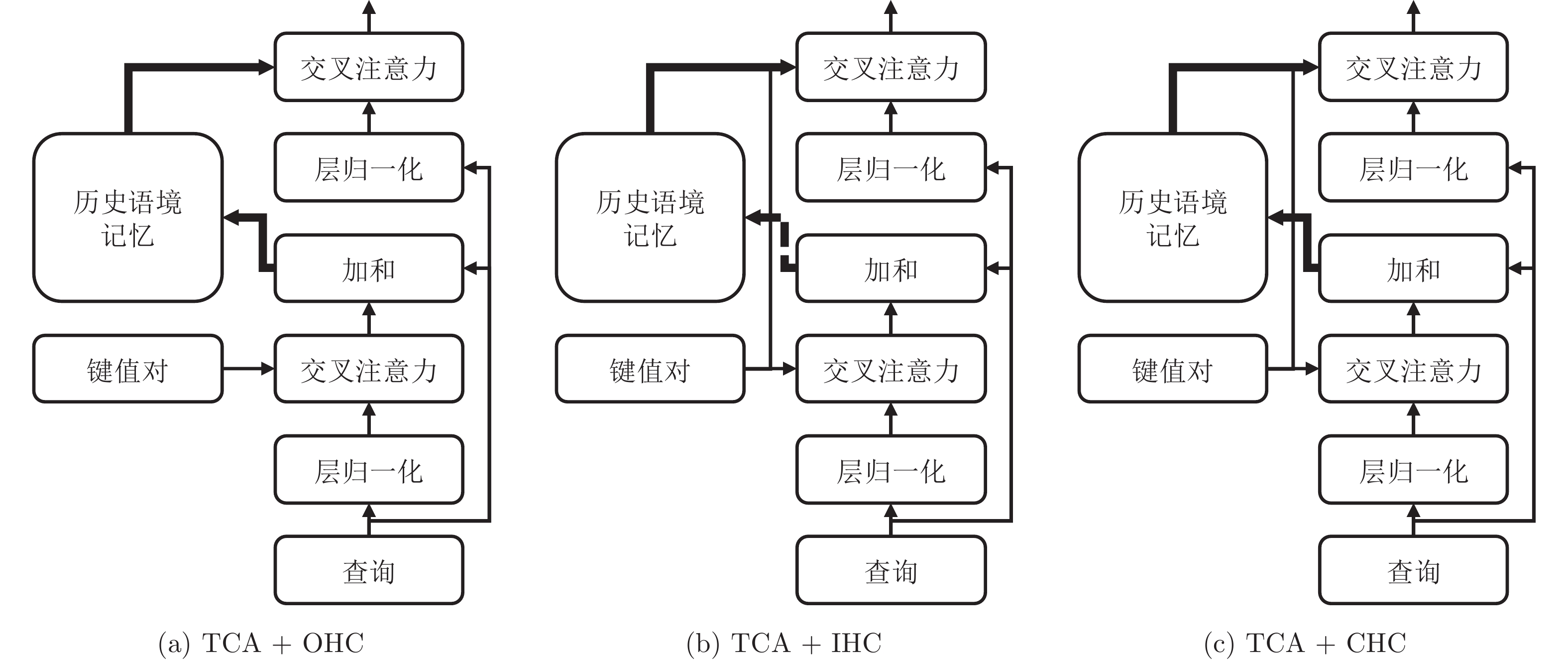
Table 5 Performance of the traditional cross attention mechanism combined with different context-assisted strategies on MS COCO dataset (%)
模型名称 BLEU-1 BLEU-4 METEOR ROUGE-L CIDEr-D SPICE TCA (base) 80.0 38.0 28.5 57.9 126.5 22.4 TCA + OHC 80.4 37.8 28.2 57.4 126.8 21.8 TCA + IHC 80.8 38.2 28.5 58.1 128.2 22.2 TCA + CHC (CACA) 81.2 38.6 28.6 58.2 128.9 22.6 表 6 不同解码器层数的CAT模型在共享与不共享交叉注意力模块参数时的性能表现(%)
Table 6 Performance of CAT models with different decoder layers when sharing or not sharing parameters of the cross attention module (%)
解码器层数 交叉注意力模块设置 BLEU-1 BLEU-4 METEOR ROUGE-L CIDEr-D SPICE $N=2$ TCA 78.8 37.4 28.0 57.4 125.4 21.8 $N=2$ CACA (Shared) 80.4 38.0 28.2 57.8 128.0 22.3 $N=2$ CACA (Not shared) 80.8 38.4 28.5 58.2 128.8 22.5 $N=3$ TCA 80.0 38.0 28.5 57.9 126.5 22.4 $N=3$ CACA (Shared) 81.2 38.6 28.6 58.2 128.9 22.6 $N=3$ CACA (Not shared) 81.0 38.8 28.8 58.3 129.3 22.7 $N=4$ TCA 79.6 37.8 28.5 57.8 126.2 22.2 $N=4$ CACA (Shared) 79.8 37.5 28.4 57.6 125.8 21.9 $N=4$ CACA (Not shared) 79.0 36.8 28.1 57.1 124.3 21.5 表 7 采用自适应权重约束的CAT模型在MS COCO数据集上的表现(%)
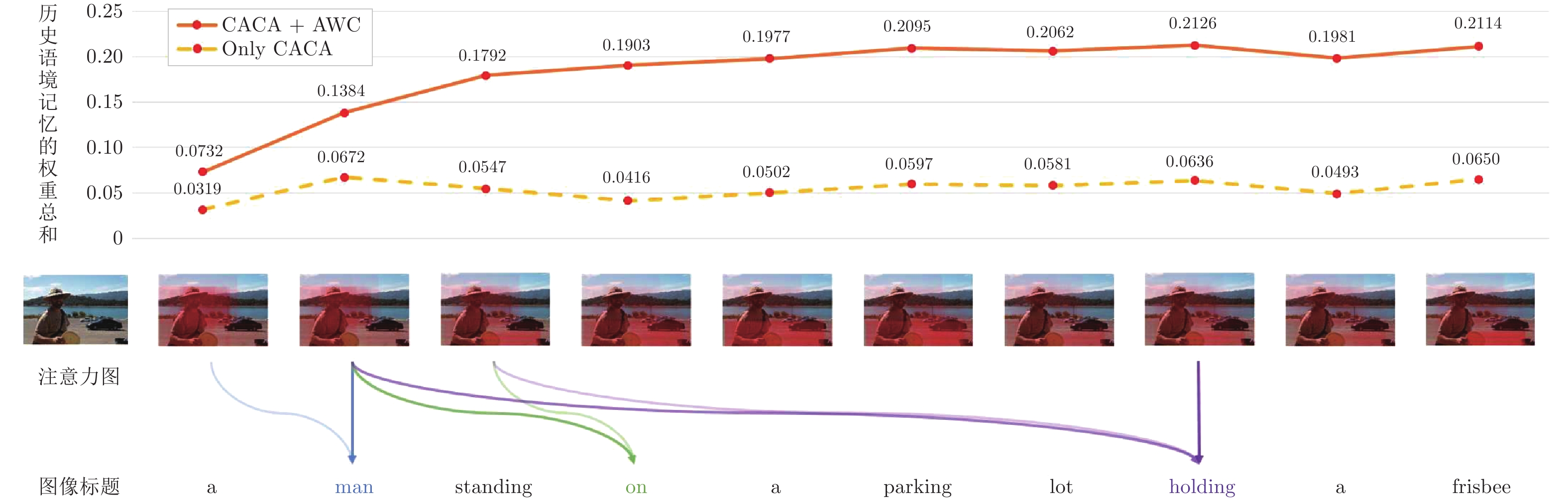
Table 7 Performance of the CAT model with adaptive weight constraint on MS COCO dataset (%)
权重约束方式 BLEU-4 METEOR ROUGE-L CIDEr-D 无权重约束 38.6 28.6 58.2 128.9 固定权重约束$\beta=0.1$ 38.4 28.4 58.1 127.8 固定权重约束$\beta=0.3$ 38.7 28.6 58.3 128.7 固定权重约束$\beta=0.5$ 38.9 28.7 58.4 129.3 固定权重约束$\beta=0.7$ 38.5 28.4 58.1 128.4 固定权重约束$\beta=0.9$ 38.1 28.2 57.6 127.2 自适应权重约束 38.9 28.9 58.6 129.6 表 8 Transformer与CAT模型的人工评价(%)
Table 8 Human evaluation of Transformer and CAT (%)
模型名称 更强的相关性 更强的一致性 Transformer 8.8 7.4 CAT 10.2 12.4 -
[1] Ji J, Luo Y, Sun X, Chen F, Luo G, Wu Y, et al. Improving image captioning by leveraging intra- and inter-layer global representation in Transformer network. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Virtual Conference: 2021. 1655−1663 [2] Fang Z, Wang J, Hu X, Liang L, Gan Z, Wang L, et al. Injecting semantic concepts into end-to-end image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, Louisiana, USA: IEEE, 2022. 18009−18019 [3] Tan J H, Tan Y H, Chan C S, Chuah J H. Acort: a compact object relation transformer for parameter efficient image captioning. Neurocomputing, 2022, 482: 60-72 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.01.081 [4] Fei Z. Attention-aligned Transformer for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada: 2022. 607−615 [5] Stefanini M, Cornia M, Baraldi L, Cascianelli S, Fiameni G, Cucchiara R. From show to tell: a survey on deep learning-based image captioning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 45(1): 539-559 [6] Vinyals O, Toshev A, Bengio S, Erhan D. Show and tell: lessons learned from the 2015 mscoco image captioning challenge. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2016, 39(4): 652-663 [7] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A N, et al. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: 2017. 5998−6008 [8] Cover T M, Thomas J A. Elements of Information Theory. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. [9] Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S J, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, et al. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: 2014. 740−755 [10] Qin Y, Du J, Zhang Y, Lu H. Look back and predict forward in image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 8367−8375 [11] Aneja J, Deshpande A, Schwing A G. Convolutional image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018. 5561−5570 [12] 汤鹏杰, 王瀚漓, 许恺晟. LSTM逐层多目标优化及多层概率融合的图像描述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(7): 1237-1249Tang Peng-Jie, Wang Han-Li, Xu Kai-Sheng. Multi-objective layer-wise optimization and multi-level probability fusion for image description generation using lstm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(7): 1237-1249 [13] Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A C, Salakhutdinov R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: 2015. 2048−2057 [14] You Q, Jin H, Wang Z, Fang C, Luo J. Image captioning with semantic attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA: 2016. 4651−4659 [15] Lu J, Xiong C, Parikh D, Socher R. Knowing when to look: Adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3242−3250 [16] Anderson P, He X, Buehler C, Teney D, Johnson M, Gould S, et al. Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6077−6086 [17] Chen S, Zhao Q. Boosted attention: Leveraging human attention for image captioning. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: 2018. 68−84 [18] Huang L, Wang W, Chen J, Wei X. Attention on attention for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 4633−4642 [19] Pan Y, Yao T, Li Y, Mei T. X-linear attention networks for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 10968−10977 [20] Yang X, Zhang H, Qi G, Cai J. Causal attention for vision-language tasks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Virtual Conference: 2021. 9847−9857 [21] 王鑫, 宋永红, 张元林. 基于显著性特征提取的图像描述算法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 735-746Wang Xin, Song Yong-Hong, Zhang Yuan-Lin. Salient feature extraction mechanism for image captioning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 735-746 [22] Herdade S, Kappeler A, Boakye K, Soares J. Image captioning: transforming objects into words. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: 2019. 11135−11145 [23] Li G, Zhu L, Liu P, Yang Y. Entangled transformer for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 8927−8936 [24] Yu J, Li J, Yu Z, Huang Q. Multimodal transformer with multi-view visual representation for image captioning. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2019, 30(12): 4467-4480 [25] Cornia M, Stefanini M, Baraldi L, Cucchiara R. Meshed-memory transformer for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 10575−10584 [26] Zhang X, Sun X, Luo Y, Ji J, Zhou Y, Wu Y, et al. Rstnet: Captioning with adaptive attention on visual and non-visual words. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Virtual Conference: 2021. 15465−15474 [27] Luo Y, Ji J, Sun X, Cao L, Wu Y, Huang F, et al. Dual-level collaborative transformer for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Virtual Conference: 2021. 2286−2293 [28] Zeng P, Zhang H, Song J, Gao L. S2 transformer for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence. Vienna, Austria: 2022. [29] Wu M, Zhang X, Sun X, Zhou Y, Chen C, Gu J, et al. Difnet: Boosting visual information flow for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, Louisiana, USA: 2022. 18020−18029 [30] Lian Z, Li H, Wang R, Hu X. Enhanced soft attention mechanism with an inception-like module for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Tools With Artificial Intelligence. Virtual Conference: 2020. 748−752 [31] Rennie S J, Marcheret E, Mroueh Y, Ross J, Goel V. Self-critical sequence training for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: 2017. 1179−1195 [32] Vedantam R, Zitnick C L, Parikh D. Cider: Consensus-based image description evaluation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: 2015. 4566−4575 [33] Karpathy A, Li F F. Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: 2015. 3128−3137 [34] Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T, Zhu W J. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Philadelphia, USA: 2002. 311−318 [35] Denkowski M J, Lavie A. Meteor universal: Language specific translation evaluation for any target language. In: Proceedings of the 9th Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: 2014. 376−380 [36] Lin C Y. Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Proceedings of Workshop on Text Summarization Branches Out, Post-Conference Workshop of ACL 2004. Barcelona, Spain: 2004. 74−81 [37] Anderson P, Fernando B, Johnson M, Gould S. Spice: Semantic propositional image caption evaluation. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: 2016. 382−398 [38] Krishna R, Zhu Y, Groth O, Johnson J, Hata K, Kravitz J, et al. Visual genome: connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017, 123(1): 32-73 doi: 10.1007/s11263-016-0981-7 [39] Liu B, Wang D, Yang X, Zhou Y, Yao R, Shao Z, et al. Show, deconfound and tell: Image captioning with causal inference. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, Louisiana, USA: 2022. 18041−18050 -




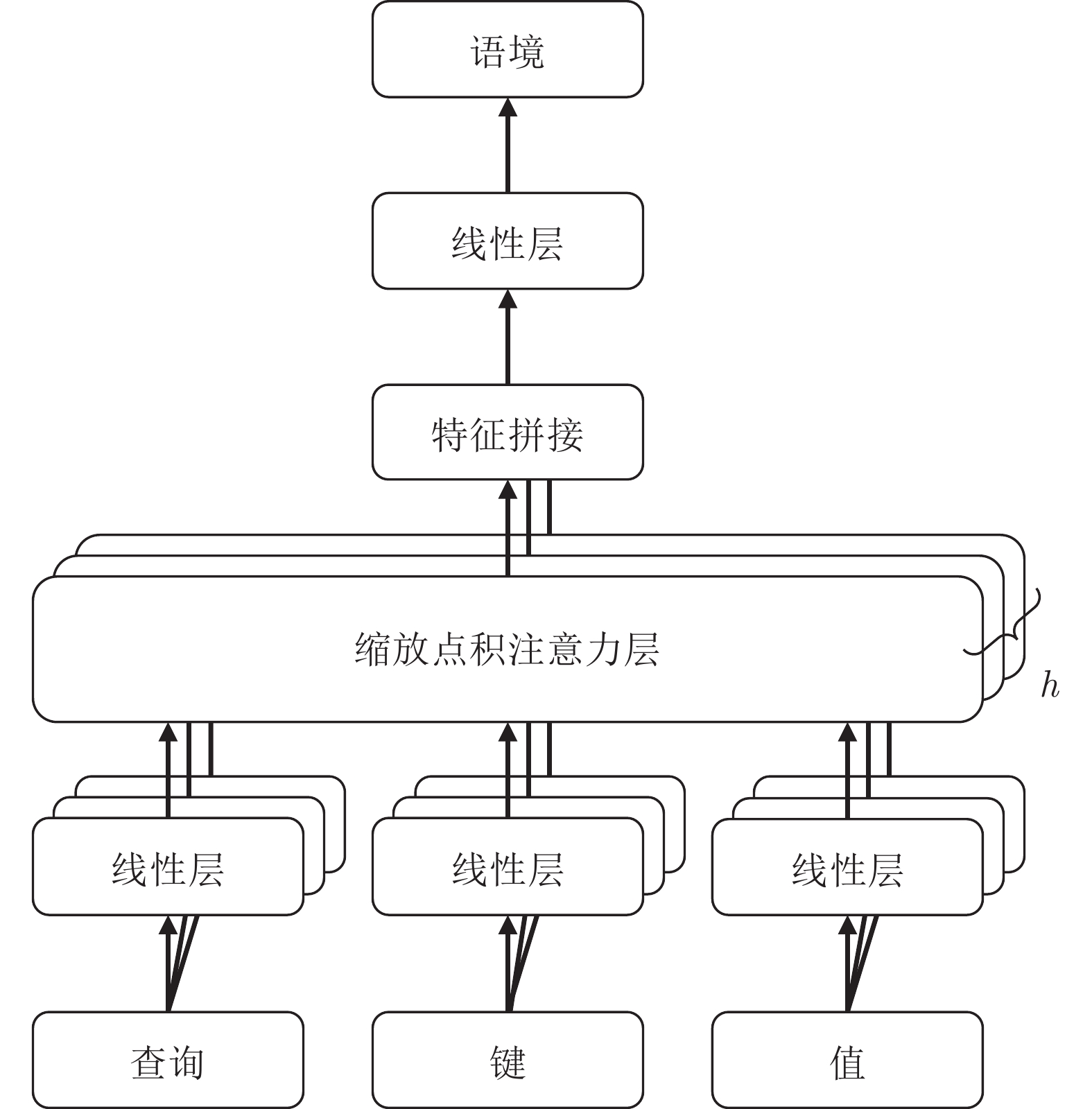
 下载:
下载: