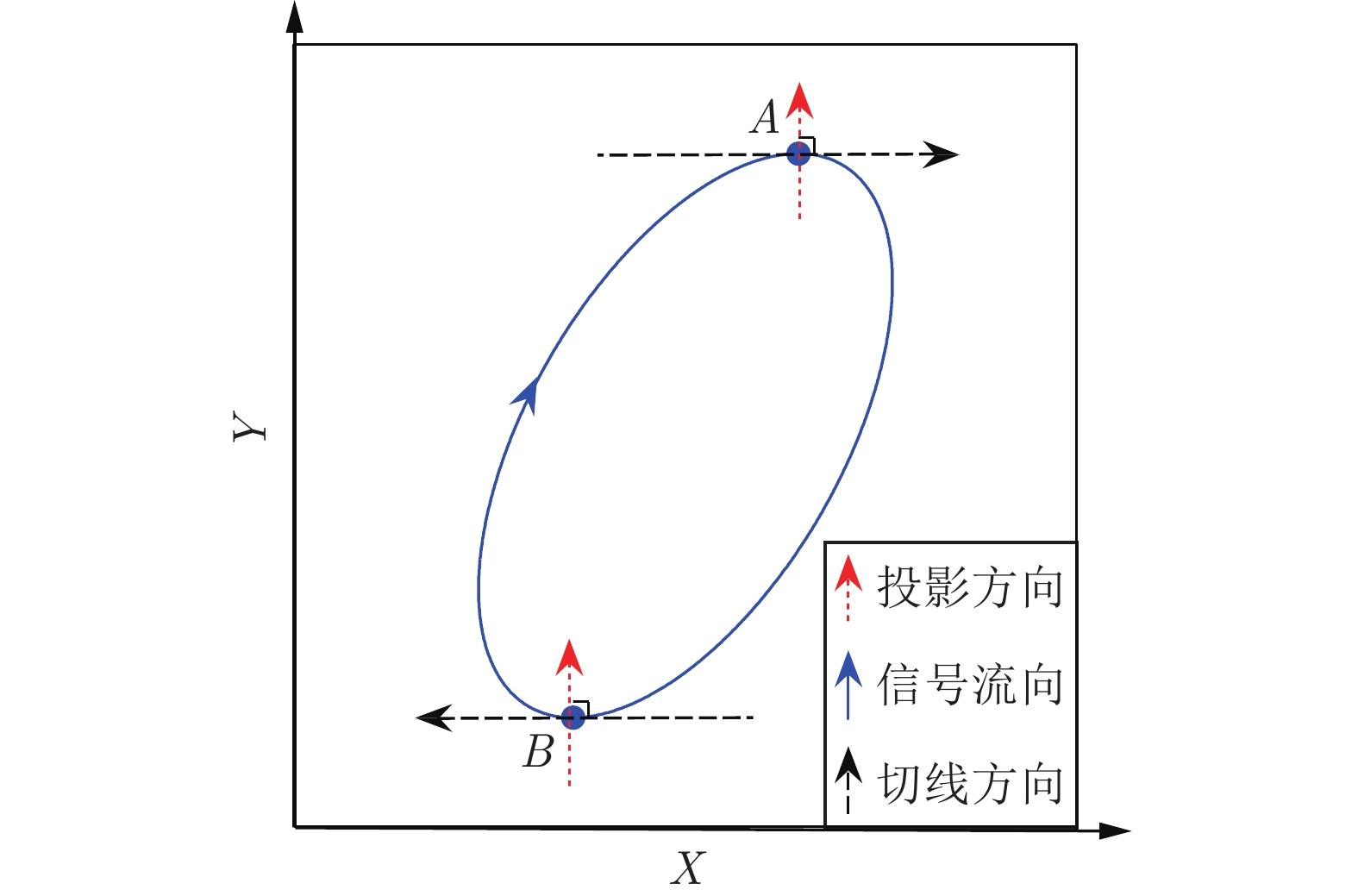
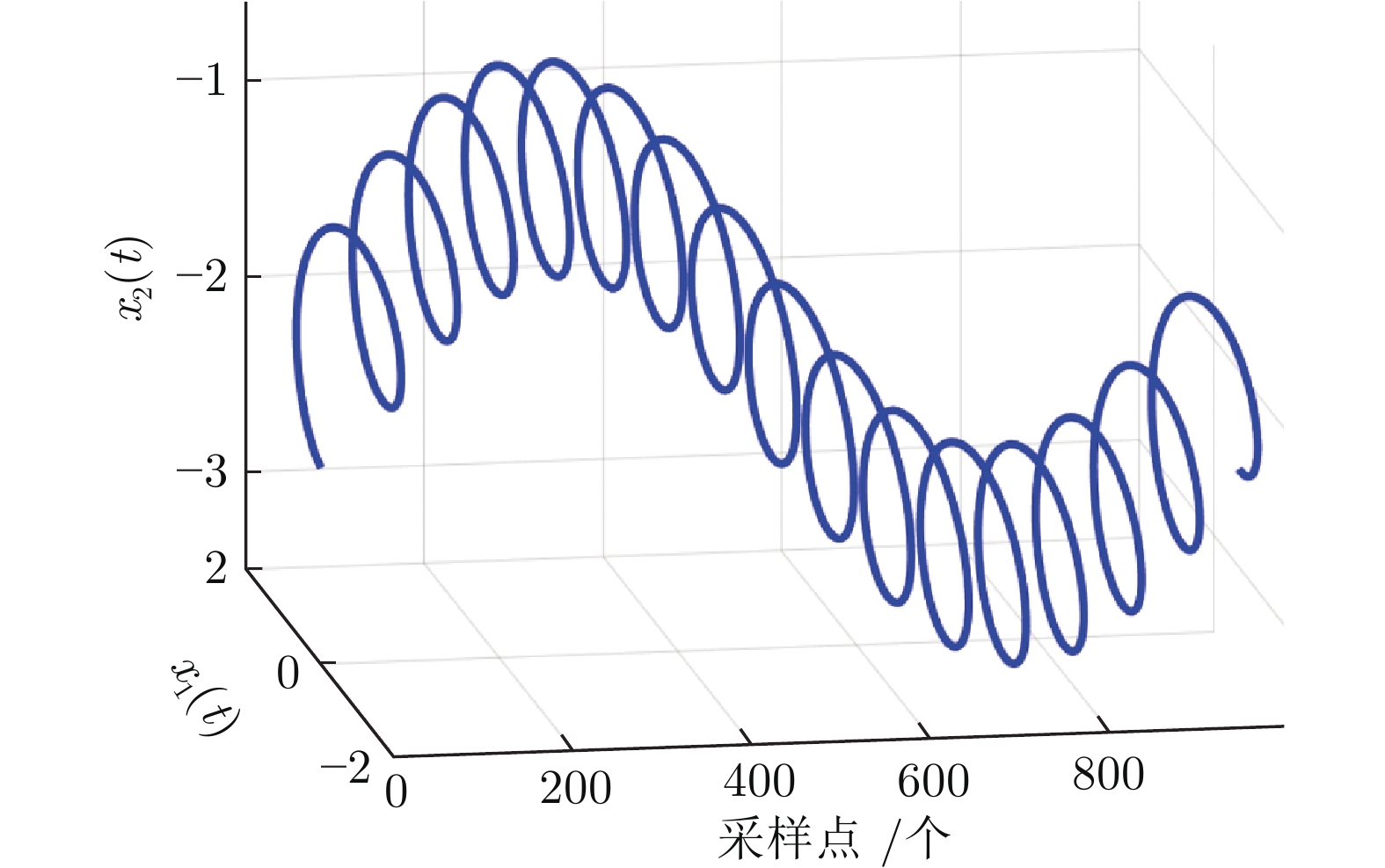
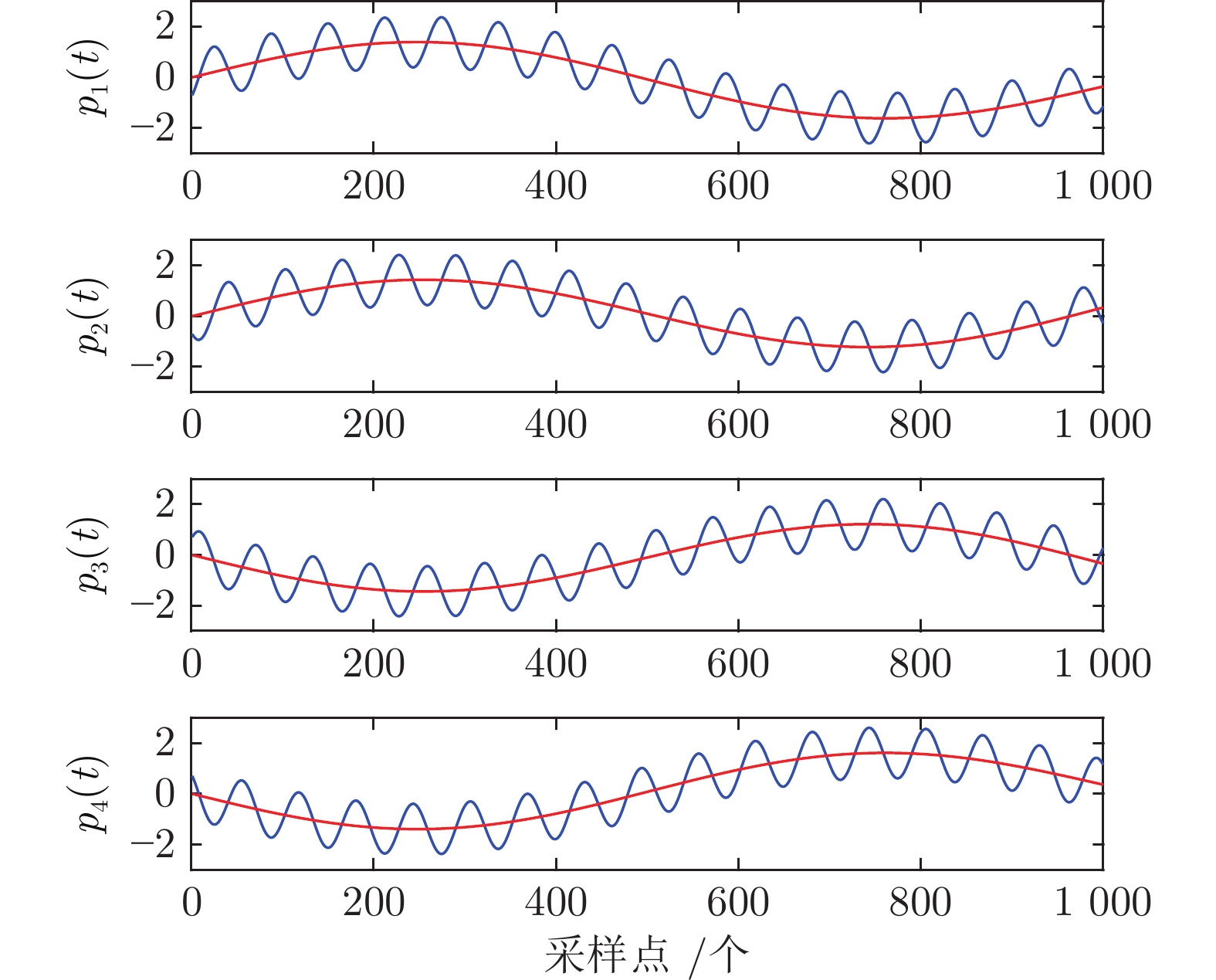
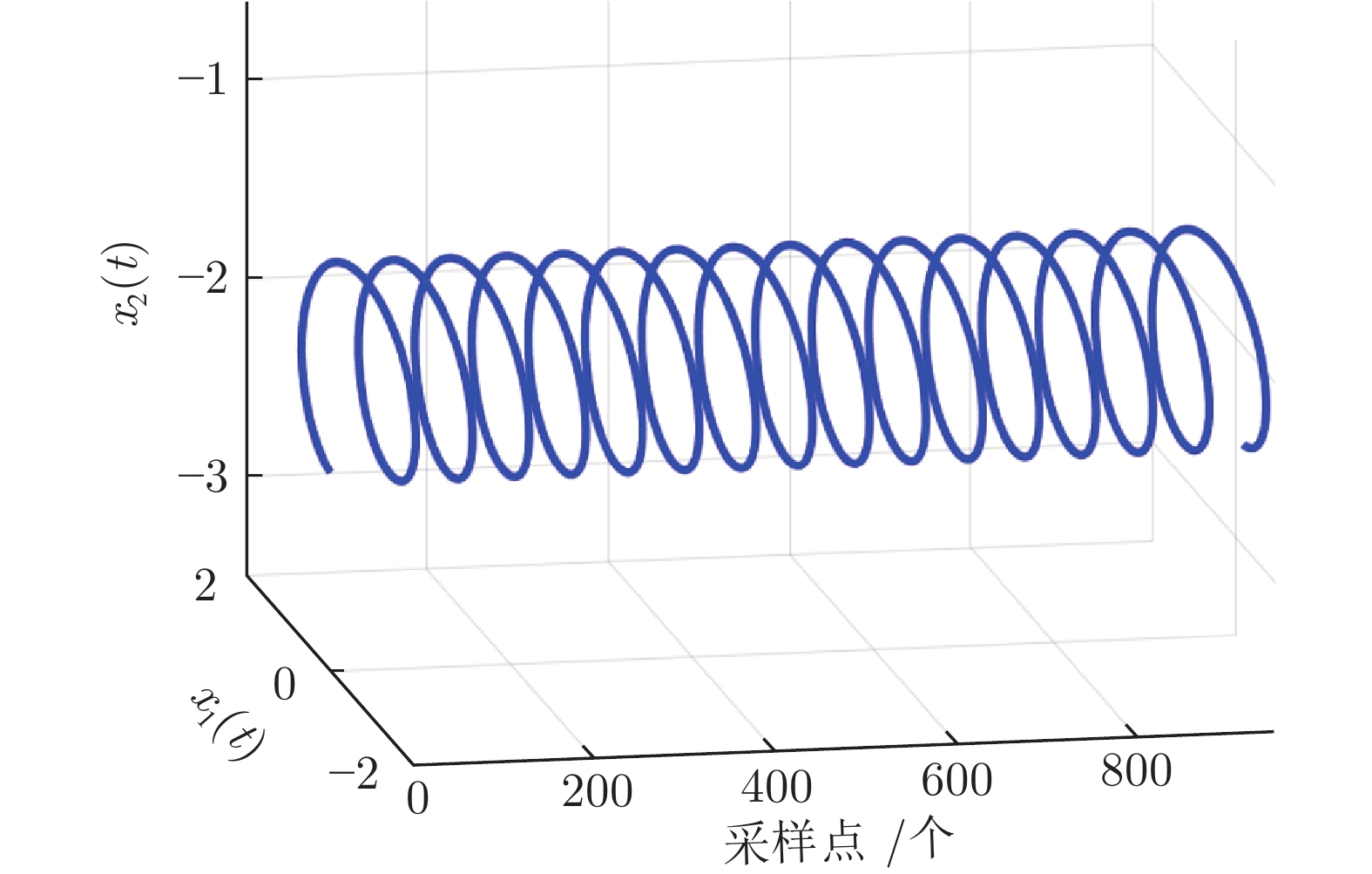
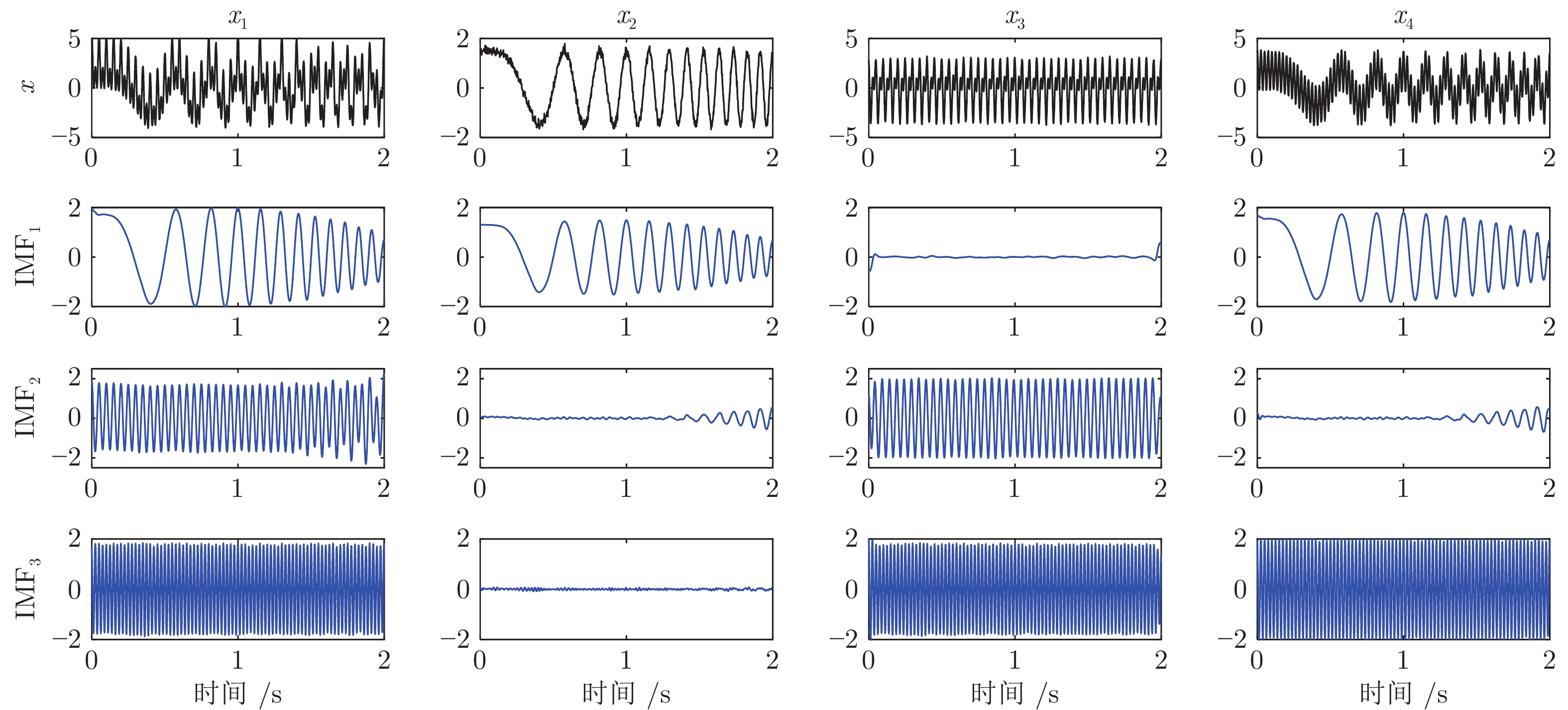
-
摘要: 现实世界中, 所获得的信号大部分都是非平稳和非线性的, 将此类复杂信号分解为多个简单的子信号是重要的信号处理方法. 1998年, 提出希尔伯特–黄变换(Hilbert-Huang transform, HHT)以来, 历经20余年的发展, 信号分解已经成为信号处理领域相对独立又具有创新性的重要内容. 特别是近10年, 多元/多变量/多通道信号分解理论方法方兴未艾, 在诸多领域得到了成功应用, 但目前尚未见到相关综述报道. 为填补这个空缺, 从单变量和多变量两个方面系统综述了国内/外学者对主要信号分解方法的研究现状, 对这些方法的时频表达性能进行分析和比较, 指出这些分解方法的优势和存在的问题. 最后, 对信号分解研究进行总结和展望.Abstract: Most signals obtained in the real world are non-stationary and nonlinear, decomposing such complex signals into several simple sub-signals is an important signal processing method. Since the Hilbert-Huang transform (HHT) was proposed in 1998, after more than 20 years of development, signal decomposition has become a relatively independent and innovative important content in the field of signal processing. Especially in the past decade, multivariate signal decomposition methods and theoretical research are in the ascendant, which have been successfully applied in many fields. However, there is no relevant overview report at present. Therefore, this paper systematically summarizes the development of signal decomposition theory and methods from both univariate and multivariate aspects. This work analyzes and compares the time-frequency expression performance of these methods, and points out the advantages and issues. Finally, the future research of signal decomposition is prospected and summarized.
-
表 1 常见单变量信号分解方法归类总结
Table 1 Classification and summary of common univariate signal decomposition methods
方法名称 作用域 优点 局限性 FT 频域 经典方法, 理论完备, 简单高效 仅适用于线性平稳信号 STFT 时频域 经典方法, 简单高效 窗函数选取问题, 分辨率固定 WVD 时频域 经典方法, 理论完备 不能处理交叉频率和多分量情况 WT 时频域 经典方法, 理论完备 母小波和尺度需人为指定 EMD 时域 自适应性强, 适用于非线性和非平稳信号, 应用场景广泛 噪声敏感, 模态混叠和端点效应问题严重, 缺乏理论基础 EEMD 时域 自适应性强, 对信号间歇性鲁棒 计算效率低, 重构误差大, 受辅助噪声参数影响大 CEEMD 时域 对信号间歇性鲁棒, 计算效率和重构误差优于EEMD 辅助噪声的参数会影响分解结果 MEEMD 时域 对信号间歇性鲁棒, 噪声鲁棒性好, 模态分裂概率低 计算效率低于EEMD MCEEMD 时域 噪声鲁棒性和分解完备性好、模态分裂概率低 计算效率低于CEEMD LMD 时域 能处理非平稳信号 噪声敏感、参数影响大 ITD 时域 计算效率优于EMD, 易于实施在线计算 噪声敏感、模态提取能力劣于EMD SST 时频域 能有效表征非平稳信号的时变调频特征 在处理强、变信号时, 会产生较大误差且无法处理时频面
交叉和重叠信号EWT 频域 数据驱动自适应划分频段 噪声鲁棒性弱, 分辨率有限 VMD 频域 噪声鲁棒性和采样频率鲁棒性好, 数学理论完善 局限于处理窄带信号, 参数影响大 NCMD 时频域 数学理论完善, 宽带信号处理能力强 需要提前指定参数 ICMD 时频域 宽带信号处理能力强, 计算效率高, 能处理交叉瞬时频率 需要提前指定参数 表 2 多元信号分解方法归类总结
Table 2 Classification and summary of multivariate signal decomposition methods
方法名称 拓展方式 优点 局限性 CEMD 复数性质 可处理复数信号 实部虚部模态数量可能不一致 RCEMD 复数空间
旋转概念复数空间中极值定义明确, 实部虚部模态一致 局限于处理复数信号 BEMD 单位圆投影向量 可分解双变量信号 局限于处理双变量信号 TEMD 球面投影 可分解三变量信号 局限于处理三变量信号 QEMD 超球面投影 可分解四变量信号 局限于处理四变量信号 MEMD 高维空间投影 适用于双变量及多变量信号分解 投影向量的数量和方向敏感, 抗噪声能力差, 计算效率低 FMEMD 高维空间投影 大幅提高了MEMD的计算效率 投影向量的数量和方向敏感, 噪声鲁棒性略低于MEMD IMITD 高维空间投影 局部特征处理效果好, 计算效率高于MEMD 投影向量的数量和方向会影响到基线提取 DMITD 高维空间投影 投影向量鲁棒性优于IMITD 运算效率低于IMITD MSST 多变量振荡 时频谱清晰, 适用于探索性数据分析 不能直接重构模态 MEWT 多变量振荡 可以重构模态 需要有效的频谱分割, 来显示构造自适应小波滤波器组 CVMD 复数性质 噪声和采样频率鲁棒性好 局限于处理复数窄带信号, 参数影响大 MVMD 多变量调制振荡 噪声和采样频率鲁棒性好, 模态之间信息泄露
少, 自适应多变量最优维纳滤波器局限于处理窄带多变量信号, 参数影响大 MNCMD 多变量调制振荡 可对时变多元信号进行分解 复杂度高, 需要预估信号中的噪声水平和调整参数 MICMD 多变量调制振荡 适用于宽带多元信号分解与时频分析, 计算复杂度低,
参数鲁棒性好, 模态正交性强, 信息泄露少在强噪声条件下, 分解性能下降, 零频分量波动较明显 表 3 常见多元信号分解方法的适用场景
Table 3 Applicable scenarios of common multivariate signal decomposition methods
方法 适用场景 CEMD 只适用于复数信号 BEMD 只适用于双变量信号 MEMD 适合分析信噪比高, 实时性要求低, 采样频率足够高, 模态频率间隔两倍以上的多元信号, 可以作为有效的探索性分析方法 FMEMD 适合分析信噪比高, 实时性要求高, 采样频率足够高, 模态频率间隔两倍以上的信号; 数据量大时, 建议采用FMEMD, 不采用MEMD IMITD 适合分析局部特征明显, 实时性要求高, 采样频率足够高的多元信号 DMITD 适合分析通道间差异大, 实时性要求低, 采样频率足够高的多元信号 CVMD 只适用于具有窄带性质的复数信号 MVMD 适用于分量频率范围不重叠的窄带多元信号, 处理宽带信号效果非常有限 MNCMD 适用于宽带多元信号, 但计算复杂度较高 MICMD 适用于宽带多元信号和时频曲线有交叉的多元信号, 计算复杂度较低 -
[1] 胡广书. 现代信号处理教程. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015.Hu Guang-Shu. Modern Signal Processing Tutorial. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015. [2] 郎恂. 基于时频分析的工业控制过程振荡检测及诊断研究 [博士学位论文], 浙江大学, 中国, 2019.Lang Xun. Research on Industrial Control Process Oscillation Detection and Diagnosis Based on Time-frequency Analysis [Ph.D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, China, 2019. [3] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, Wu M C, Shih H H, Zheng Q, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings Mathematical Physical & Engineering ences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995 [4] 邹红星, 周小波, 李衍达. 时频分析: 回溯与前瞻. 电子学报, 2000, 28(9): 78-84 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2000.09.022Zhou Hong-Xing, Zhou Xiao-Bo, Li Yan-Da. Time-frequency analysis: Backward and forward. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2000, 28(9): 78-84 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2000.09.022 [5] Cooley J W, Tukey J W. An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex fourier series. Mathematics of Computation, 1965, 19(90): 297-301 doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1965-0178586-1 [6] Qian S, Chen D. Joint Time-frequency Analysis: Methods and Applications. New York: Prentice-Hall, 1996. [7] Gabor D. Theory of communication. part 1: The analysis of information. Journal of the Institution of Electrical Engineers-Part III: Radio and Communication Engineering, 1946, 93(26): 429-441 [8] Cohen L. Generalized phase-space distribution functions. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 1966, 7(5): 781-786 doi: 10.1063/1.1931206 [9] Wigner E P. On the Quantum Correction for Thermodynamic Equilibrium. Berlin: Springer, 1997. 110−120 [10] Qian T, Zhang L M, Li Z X. Algorithm of adaptive Fourier decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(12): 5899-5906 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2168520 [11] Coifman R R, Steinerberger S, Wu H. Carrier frequencies, holomorphy, and unwinding. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 2017, 49(6): 4838-4864 doi: 10.1137/16M1081087 [12] Gilles J. Empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(16): 3999-4010 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2265222 [13] Khaldi K, Turki-Hadj Alouane M, Boudraa A O. Voiced speech enhancement based on adaptive filtering of selected intrinsic mode functions. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2010, 2(1): 65-80 doi: 10.1142/S1793536910000409 [14] Looney D, Mandic D P. Multiscale image fusion using complex extensions of EMD. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(4): 1626-1630 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2011836 [15] Lei Y, Lin J, He Z, Zuo M J. A review on empirical mode decomposition in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 35(1-2): 108-126 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.09.015 [16] Zhang J Y, Xu X Z, Chen Q M, Xie L, Su H Y. Extracting fetal heart rate from abdominal ECGs based on fast multivariate empirical mode decomposition. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision. New York, USA: IEEE, 2020. 648−653 [17] Basha G, Ouarda T B M J, Marpu P R. Long‐term projections of temperature, precipitation and soil moisture using non‐stationary oscillation processes over the UAE region. International Journal of Climatology, 2015, 35(15): 4606-4618. doi: 10.1002/joc.4310 [18] Huang N E, Wu Z. A review on Hilbert-Huang transform: Method and its applications to geophysical studies. Reviews of Geophysics, 2008, 46(2): Article No. 007RG000228 [19] Huang N E, Attoh-Okine N O. The Hilbert-Huang Transform in Engineering. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2005. [20] Huang N E. Hilbert-Huang Transform and Its Applications. Singapore: World Scientific, 2014. [21] Wu Z, Huang N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41 doi: 10.1142/S1793536909000047 [22] Yeh J R, Shieh J S, Huang N E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2010, 2(2): 135-156 doi: 10.1142/S1793536910000422 [23] Lang X, Ur Rehman N, Zhang Y F, Xie L, Su H Y. Median ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Signal Processing, 2020, 176: Article No. 107686 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107686 [24] 刘淞华, 何冰冰, 郎恂, 陈启明, 张榆锋, 苏宏业. 中值互补集合经验模态分解. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c201031Liu Song-Hua, He Bing-Bing, Lang Xun, Chen Qi-Ming, Zhang Yu-Feng, Su Hong-Ye. Median complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c201031 [25] Meignen S, Perrier V. A new formulation for empirical mode decomposition based on constrained optimization. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2007, 14(12): 932-935 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2007.904706 [26] Pustelnik N, Borgnat P, Flandrin P. Empirical mode decomposition revisited by multicomponent nonsmooth convex optimization. Signal Processing, 2014, 102: 313-331 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.03.014 [27] Colominas M A, Schlotthauer G, Torres M E. An unconstrained optimization approach to empirical mode decomposition. Digital Signal Processing, 2015, 40: 164-175 doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2015.02.013 [28] Lin L, Wang Y, Zhou H. Iterative filtering as an alternative algorithm for empirical mode decomposition. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(4): 543-560 doi: 10.1142/S179353690900028X [29] Wang Y, Wei G W, Yang S Y. Iterative filtering decomposition based on local spectral evolution kernel. Journal of scientific computing, 2012, 50(3): 629-664 doi: 10.1007/s10915-011-9496-0 [30] Cicone A, Liu J F, Zhou H M. Adaptive local iterative filtering for signal decomposition and instantaneous frequency analysis. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2016, 41(2): 384-411 doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2016.03.001 [31] Mallat S G, Zhang Z. Matching pursuits with timefrequency dictionaries. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1993, 41(12): 3397-3415 doi: 10.1109/78.258082 [32] 陈是扦, 彭志科, 周鹏. 信号分解及其在机械故障诊断中的应用研究综述. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(17): 91-107 doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.17.091Chen Shi-Xuan, Peng Zhi-Ke, Zhou Peng. A review of research on signal decomposition and its application in mechanical fault diagnosis. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(17): 91-107 doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.17.091 [33] Hou T Y, Shi Z. Adaptive data analysis via sparse time-frequency representation. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2011, 3(01n02): 1-28 doi: 10.1142/S1793536911000647 [34] Hou T Y, Shi Z. Data-driven time–frequency analysis. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2013, 35(2): 284-308 doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2012.10.001 [35] Hou T Y, Shi Z Q. Sparse time-frequency representation of nonlinear and nonstationary data. Science China Mathematics, 2013, 56(12): 2489-2506 doi: 10.1007/s11425-013-4733-7 [36] Hou T Y, Shi Z. Sparse time-frequency decomposition based on dictionary adaptation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2016, 374(2065): 1-16 [37] Peng S, Hwang W L. Adaptive signal decomposition based on local narrow band signals. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(7): 2669-2676 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.917360 [38] Guo B K, Peng S L, Hu X Y, Xu P C. Complex-valued differential operator-based method for multi-component signal separation. Signal Processing, 2017, 132: 66-76 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.09.015 [39] Smith J S. The local mean decomposition and its application to EEG perception data. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2005, 2(5): 443-454 doi: 10.1098/rsif.2005.0058 [40] Frei M G, Osorio I. Intrinsic time-scale decomposition: time–frequency–energy analysis and real-time filtering of nonstationary signals. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2007, 463(2078): 321-342 doi: 10.1098/rspa.2006.1761 [41] Daubechies I, Lu J, Wu H T. Synchrosqueezed wavelet transforms: An empirical mode decomposition-like tool. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2011, 30(2): 243-261 doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2010.08.002 [42] Daubechies I. Orthonormal bases of compactly supported wavelets. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 1988, 41(7): 909-996 doi: 10.1002/cpa.3160410705 [43] Auger F, Flandrin P. Improving the readability of time-frequency and time-scale representations by the reassignment method. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1995, 43(5): 1068-1089 doi: 10.1109/78.382394 [44] Zheng J D, Pan H Y, Yang S B, Cheng J S. Adaptive parameterless empirical wavelet transform based time-frequency analysis method and its application to rotor rubbing fault diagnosis. Signal Processing, 2017, 130: 305-314 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.07.023 [45] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 62(3): 531-544 [46] Chen S Q, Yang Y, Dong X J, Xing G P. Warped variational mode decomposition with application to vibration signals of varying-speed rotating machineries. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2018, 68(8): 2755-2767 [47] Zhang Y G, Pan G F, Chen B, Han J Y, Zhao Y, Zhang C H. Short-term wind speed prediction model based on GA-ANN improved by VMD. Renewable Energy, 2020, 156: 1373-1388 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.12.047 [48] Zhang T, Chen W Z, Li M Y. AR based quadratic feature extraction in the VMD domain for the automated seizure detection of EEG using random forest classifier. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2017, 31: 550-559 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2016.10.001 [49] Huang Y S, Gao Y L, Gan Y, Ye M. A new financial data forecasting model using genetic algorithm and long shortterm memory network. Neurocomputing, 2021, 425: 207-218 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.04.086 [50] Rabbouch H, Saadaoui H, Saâdaoui F. VMD-based multiscaled LSTM-ARIMA to forecast post-COVID-19 us air traffic. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Applications. New York, USA: IEEE, 2022. 1678−1683 [51] Huang N E, Wu Z, Long S R, Arnold K C, Chen X Y, Blank K. On instantaneous frequency. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(2): 177-229 doi: 10.1142/S1793536909000096 [52] Li Z P, Chen J L, Zi Y Y, Pan J. Independ-enceoriented VMD to identify fault feature for wheel set bearing fault diagnosis of high speed locomotive. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 85: 512-529 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.08.042 [53] Lian J J, Liu Z, Wang H J, Dong X F. Adaptive variational mode decomposition method for signal processing based on mode characteristic. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 107: 53-77 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.01.019 [54] Cai G W, Wang L X, Yang D Y, Sun Z L, Wang B. Harmonic detection for power grids using adaptive variational mode decomposition. Energies, 2019, 12(2): Article No. 232 doi: 10.3390/en12020232 [55] Chen Q M, Lang X, Xie L, Su H Y. Detecting non-linear oscillations in process control loop based on an improved VMD. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 91446-91462 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2925861 [56] Zhu J, Wang C, Hu Z Y, Kong F R, Liu X C. Adaptive variational mode decomposition based on artificial fish swarm algorithm for fault diagnosis of rolling bearings. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2017, 231(4): 635-654 doi: 10.1177/0954406215623311 [57] Zhang X, Miao Q, Zhang H, Wang L. A parameter-adaptive VMD method based on grasshopper optimization algorithm to analyze vibration signals from rotating machinery. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 108: 58-72 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.11.029 [58] Chen Q M, Chen J H, Lang X, Xie L, Rehman N U, Su H Y. Self-tuning variational mode decomposition. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2021, 358(15): 7825-7862 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.07.021 [59] Chen S Q, Dong X J, Peng Z K, Zhang W M, Meng G. Nonlinear chirp mode decomposition: A variational method. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(22): 6024-6037 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2731300 [60] Meignen S, Pham D H, McLaughlin S. On demodulation, ridge detection, and synchrosqueezing for multicomponent signals. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(8): 2093-2103 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2656838 [61] Park B K, Boric-Lubecke O, Lubecke V M. Arctangent demodulation with DC offset compensation in quadrature Doppler radar receiver systems. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2007, 55(5): 1073-1079 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2007.895653 [62] Chen S Q, Yang Y, Peng Z K, Wang S B, Zhang W M, Chen X F. Detection of rub-impact fault for rotor-stator systems: A novel method based on adaptive chirp mode decomposition. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 440: 83-99 doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2018.10.010 [63] Yin W F, Yang X Z, Li L, Zhang L, Kitsuwan, N, Oki E. Hear: Approach for heartbeat monitoring with body movement compensation by iruwb radar. Sensors, 2018, 18(9): Article No. 3077 doi: 10.3390/s18093077 [64] Chen S Q, Wang K Y, Chang C, Xie B, Zhai W M. A two-level adaptive chirp mode decomposition method for the railway wheel flat detection under variable-speed conditions. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2021, 498: Article No. 115963 doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2021.115963 [65] Chen S Q, Yang Y, Peng Z K, Dong X J, Zhang W M, Meng G. Adaptive chirp mode pursuit: Algorithm and applications. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 116: 566-584 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.06.052 [66] Chen Q M, Chen J H, Lang X, Xie L, Jiang C L, Su H Y. Diagnosis of nonlinearity-induced oscillations in process control loops based on adaptive chirp mode decomposition. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. New York, USA: IEEE, 2020. 2772−2777 [67] Chen Q M, Chen J H, Lang X, Xie L, Lu S, Su H Y. Detection and diagnosis of oscillations in process control by fast adaptive chirp mode decomposition. Control Engineering Practice, 2020, 97: Article No. 104307 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2020.104307 [68] Chen Q M, Lang X, Xie L, Su H Y. Detecting oscillations via adaptive chirp mode decomposition. In: Proceedings of the CAA Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety for Technical Processes. New York, USA: IEEE, 2019. 298−303 [69] Chen S Q, Peng Z K, Yang Y, Dong X J, Zhang W M. Intrinsic chirp component decomposition by using Fourier series representation. Signal Processing, 2017, 137: 319-327 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.01.027 [70] Chen S Q, Dong X J, Xing G P, Peng Z K, Zhang W M, Meng G. Separation of overlapped non-stationary signals by ridge path regrouping and intrinsic chirp component decomposition. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(18): 5994-6005 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2737467 [71] Yang Y, Peng Z K, Dong X J, Zhang W M, Meng G. General parameterized time-frequency transform. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(11): 2751-2764 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2314061 [72] Chen S Q, Dong X J, Xiong Y Y, Peng Z K, Zhang W M. Nonstationary signal denoising using an envelope-tracking filter. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 23(4): 2004-2015 [73] Dong X J, Chen S Q, Xing G P, Peng Z K, Zhang W M, Meng G. Doppler frequency estimation by parameterized time-frequency transform and phase compensation technique. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(9): 3734-3744 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2812848 [74] Tu X T, Bao W J, Hu Y, Abbas, S, Li F C. Parameterized synchrosqueezing transform with application to machine fault diagnosis. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(18): 8107-8115 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2919776 [75] Rehman N, Mandic D P. Multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2010, 466(2117): 1291-1302 doi: 10.1098/rspa.2009.0502 [76] Wang Z, Wong C M, Rosa A, Qian T, Wan Feng. Adaptive fourier decomposition for multi-channel signal analysis. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 903-918 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3143723 [77] Chen Q M, Xie L, Su H Y. Multivariate nonlinear chirp mode decomposition. Signal Processing, 2020, 176: Article No. 107667 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107667 [78] Zahra A, Kanwal N, Ur Rehman N, Ehsan S, McDonald-Maier K D. Seizure detection from EEG signals using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2017, 88: 132-141 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.07.010 [79] Han G, Lin B, Xu Z. Electrocardiogram signal denoising based on empirical mode decomposition technique: An overview. Journal of Instrumentation, 2017, 12(3): Article No. P03010 [80] Hao H, Wang H L, Rehman N U. A joint framework for multivariate signal denoising using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Signal Processing, 2017, 135: 263-273 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.01.022 [81] Ur Rehman N, Abbas S Z, Asif A, Javed A, Naveed K, Manilo D. Translation invariant multi-scale signal denoising based on goodness-of-fit tests. Signal Processing, 2017, 131: 220-234 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.08.019 [82] Mandic D P, Ur Rehman N, Wu Z H, Huang NE. Empirical mode decomposition-based time-frequency analysis of multivariate signals: The power of adaptive data analysis. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2013, 30(6): 74-86 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2013.2267931 [83] Ur Rehman N, Aftab H. Multivariate variational mode decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(23): 6039-6052 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2951223 [84] Rilling G, Flandrin P, Gonçalves P, Lilly, JM. Bivariate empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2007, 14(12): 936-939 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2007.904710 [85] Chen Q M, Lang X, Xie L, Su H Y. Multivariate intrinsic chirp mode decomposition. Signal Processing, 2021, 183: Article No. 108009 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108009 [86] Tanaka T, Mandic D P. Complex empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2007, 14(2): 101-104 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2006.882107 [87] Altaf M U B, Gautama T, Tanaka T, Mandic D P. Rotation invariant complex empirical mode decomposition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. New York, USA: IEEE, 2007. 1009−1012 [88] Ur Rehman N, Mandic D P. Empirical mode decomposition for trivariate signals. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 58(3): 1059-1068 [89] Ur Rehman N, Mandic D P. Quadrivariate empirical mode decomposition. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. New York, USA: IEEE, 2010. 1−7 [90] Park C, Looney D, Ur Rehman N, Ahrabian A, Mandic D P. Classification of motor imagery BCI using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2012, 21(1): 10-22 [91] Zhao X M, Patel T H, Zuo M J. Multivariate EMD and full spectrum based condition monitoring for rotating machinery. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2012, 27: 712-728 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2011.08.001 [92] Yu L A, Li J J, Tang L, Wang S. Linear and nonlinear granger causality investigation between carbon market and crude oil market: A multi-scale approach. Energy Economics, 2015, 51: 300-311 doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2015.07.005 [93] Quqa S, Landi L, Diotallevi P P. Seismic structural health monitoring using the modal assurance distribution. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2021, 50(9): 2379-2397 [94] Lang X, Zheng Q M, Zhang Z M, Lu S, Xie L, Horch A, et al. Fast multivariate empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 65521-65538 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2877150 [95] Lang X, Zhang Z M, Xie L, Horch A, Su H Y. Time-frequency analysis of plant-wide oscillations using multivariate intrinsic time-scale decomposition. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(3): 954-966 [96] Lang X, Zheng Q, Xie L, Horch A, Su, H Y. Direct multivariate intrinsic time-scale decomposition for oscillation monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 28(6): 2608-2615 [97] Ahrabian A, Looney D, Stanković L, Mandic D P. Synchrosqueezing-based time-frequency analysis of multivariate data. Signal Processing, 2015, 106: 331-341 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.08.010 [98] Yadav U, Abbas S N, Hatzinakos D. Evaluation of PPG biometrics for authentication in different states. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics. New York, USA: IEEE, 2018. 277−282 [99] Lilly J M. Modulated oscillations in three dimensions. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(12): 5930-5943 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2164914 [100] Lilly J M, Olhede S C. Analysis of modulated multivariate oscillations. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 60(2): 600-612 [101] Wang Y X, Liu F Y, Jiang Z S, He S L, Mo Q Y. Complex variational mode decomposition for signal processing applications. Mechanical systems and signal processing, 2017, 86: 75-85 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.09.032 [102] Yan X A, Liu Y, Xu Y D, Jia M P. Multichannel fault diagnosis of wind turbine driving system using multivariate singular spectrum decomposition and improved Kolmogorov complexity. Renewable Energy, 2021, 170: 724-748 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.02.011 [103] Das K, Pachori R B. Schizophrenia detection technique using multivariate iterative filtering and multichannel EEG signals. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 67: Article No. 102525 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102525 [104] Zheng Q, Chen T, Zhou W X, Xie L, Su H Y. Gene prediction by the noise-assisted MEMD and wavelet transform for identifying the protein coding regions. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 41(1): 196-210 doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2020.12.005 [105] Cao P P, Wang H L, Zhou K J. Multichannel signal denoising using multivariate variational mode decomposition with subspace projection. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 74039-74047 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988552 [106] Chen Q M, Xu X Z, Shi Y, Xie L, Su H Y. MNCMD-based causality analysis of plant-wide oscillations for industrial process control system. In: Proceedings of the Chinese Automation Congress. New York, USA: IEEE, 2020. 5617−5622 [107] Chen Q M, Fei X, Xie L, Wang Q B. Causality analysis in process control based on denoising and periodicity-removing CCM. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing and Special Equipment, 2020, 1(1): 25-41 doi: 10.1108/JIMSE-06-2020-0003 [108] Chen Q M, Lang X, Pan Y, Shi Y, Xie L, Su H Y. Detecting multiple plant-wide oscillations in process control systems based on multivariate intrinsic chirp component decomposition. In: Proceedings of the CAA Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision, and Safety for Technical Processes. New York, USA: IEEE, 2021. 1−6 [109] Gupta P, Sharma K K, Joshi S D. Baseline wander removal of electrocardiogram signals using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Healthcare Technology Letters, 2015, 2(6): 164-166 doi: 10.1049/htl.2015.0029 [110] Lang X, He B B, Zhang Y, Chen Q M, Xie L. Adaptive clutter filtering for ultrafast Doppler imaging of blood flow using fast multivariate empirical mode decomposition. In: Proceedings of the International Ultrasonics Symposium. New York, USA: IEEE, 2021. 1−4 [111] 刘源. 基于多元EMD的BCI信号处理研究 [硕士学位论文], 燕山大学, 中国, 2013.Liu Yuan. BCI Signal Processing Based on Multivariate EMD [Master thesis], Yanshan University, China, 2013. [112] Padhmashree V, Bhattacharyya A. Human emotion recognition based on time–frequency analysis of multivariate EEG signal. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 238: Article No. 107867 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107867 [113] Shi Y, Zhang Z M, Sun P, Xie L, Chen Q M, Su H Y, et al. Two-layer structure strategy for large-scale systems integrating online adaptive constraints adjustment method and cooperative distributed DMC algorithm. Control Engineering Practice, 2021, 116: Article No. 104932 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2021.104932 [114] Shi Y, Zhang Z M, Hu X R, Sun P, Xie L, Chen Q M, et al. SVD-based robust distributed MPC for tracking systems coupled in dynamics with global constraints. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022: 1-12 [115] Zhang Q, Lu S, Xie L, Chen Q M, Su H Y. Quality-relevant process monitoring with concurrent locality-preserving dynamic latent variable method. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(31): 27249-27262 doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02118 [116] Aftab M F, Hovd M, Sivalingam S. Plant-wide oscillation detection using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2018, 117: 320-330 [117] Chen Q M, Lang X, Lu S, Ur Rehman N, Xie L, Su H Y. Detection and root cause analysis of multiple plant-wide oscillations using multivariate nonlinear chirp mode decomposition and multivariate granger causality. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2021, 147: Article No. 107231 [118] Li S L, Ma J. Early fault feature extraction of nuclear main pump based on MEMD-1.5 dimensional Teager energy spectrum. In: Proceedings of the 9th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference. New York, USA: IEEE, 2020. 111−116 [119] Song Q Y, Jiang X X, Wang S, Guo J F, Huang W G, Zhu Z K. Self-adaptive multivariate variational mode decomposition and its application for bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1-13 [120] Huang J, Cui X L, Li C S, Xiao Z H, Chen Q M. Multivariate time-varying complex signal processing framework and its application in rotating machinery rotorbearing system. Measurement Science and Technology, 2022, 33(12): Article No. 125114 doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ac919b [121] Huang Y M, Hasan N, Deng C R, Bao Y K. Multivariate empirical mode decomposition based hybrid model for dayahead peak load forecasting. Energy, 2022, 239: Article No. 122245 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.122245 [122] Huang Y M, Deng C R, Zhang X Y, Bao Y K. Forecasting of stock price index using support vector regression with multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Journal of Systems and Information Technology, 2022, 24(2): 75-95 doi: 10.1108/JSIT-12-2019-0262 [123] Tang L, Zhang C Y, Li L, Wang S Y. A multiscale method for forecasting oil price with multifactor search engine data. Applied Energy, 2020, 257: Article No. 114033 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114033 [124] Prasad R, Ali M, Xiang Y, Khan H. A double decomposition-based modelling approach to forecast weekly solar radiation. Renewable Energy, 2020, 152: 9-22 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.01.005 [125] Prasad R, Ali M, Kwan P, Khan H. Designing a multistage multivariate empirical mode decomposition coupled with ant colony optimization and random forest model to forecast monthly solar radiation. Applied Energy, 2019, 236: 778-792 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.12.034 [126] Yuan W Y, Wang K Q, Bo X, Tang L, Wu J J. A novel multifactor & multiscale method for PM2.5 concentration forecasting. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: Article No. 113187 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113187 [127] Boashash B, Reilly A P. Algorithms for Time-frequency Signal Analysis. London: Longman Cheshire, 1992. [128] Nuttall A H, Bedrosian E. On the quadrature approximation to the Hilbert transform of modulated signals. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1966, 54(10): 1458-1459 doi: 10.1109/PROC.1966.5138 [129] Boashash B. Estimating and interpreting the instantaneous frequency of a signal. I. Fundamentals. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1992, 80(4): 520-538 doi: 10.1109/5.135376 [130] Xie L, Lang X, Horch A, Yang Y X. Online oscillation detection in the presence of signal intermittency. Control Engineering Practice, 2016, 55: 91-100 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2016.06.020 [131] Zhong T, Qu J F, Fang X Y, Li H, Wang Z P. The intermittent fault diagnosis of analog circuits based on EEMD-DBN. Neurocomputing, 2021, 436: 74-91 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.01.001 [132] Nazari M, Sakhaei S M. Successive variational mode decomposition. Signal Processing, 2020, 174: Article No. 107610 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107610 [133] He X Z, Zhou X Q, Yu W N, Hou Y X, Mechefske C K. Adaptive variational mode decomposition and its application to multi-fault detection using mechanical vibration signals. ISA transactions, 2021, 111: 360-375 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.10.060 [134] 刘建昌, 权贺, 于霞, 何侃, 李镇华. 基于参数优化VMD和样本熵的滚动轴承故障诊断. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 808-819Liu Jian-Chang, Quan He, Yu Xia, He Kan, Li Zhen-Hua. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on parameter optimization VMD and sample entropy. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 808-819 [135] Singh P, Singhal A, Joshi S D. Time-frequency analysis of gravitational waves. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications. New York, USA: IEEE, 2018. 197−201 [136] 毛文涛, 田思雨, 窦智, 张迪, 丁玲. 一种基于深度迁移学习的滚动轴承早期故障在线检测方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 302-314Mao Wen-Tao, Tian Si-Yu, Dou Zhi, Zhang Di, Ding Ling. A new deep transfer learning-based online detection method of rolling bearing early fault. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 302-314 [137] Liu S H, He B B, Chen Q M, Lang X, Zhang Y F. Median complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition and its application to time-frequency analysis of industrial oscillations. In: Proceedings of the Chinese Control Conference. New York, USA: IEEE, 2021. 2999−3004 [138] Hasan N. A methodological approach for predicting COVID-19 epidemic using EEMD-ANN hybrid model. Internet of Things, 2020, 11: Article No. 100228 doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2020.100228 [139] Wen Q S, Gao J K, Song X M, Sun L, Xu H, Zhu S H. RobustSTL: A robust seasonal-trend decomposition algorithm for long time series. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, USA: AAAI, 2019. 5409−5416 [140] Wen Q S, He K, Sun L, Zhang Y Y, Ke M, Xu H. RobustPeriod: Robust time-frequency mining for multiple periodicity detection. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Management of Data. New York, USA: ACM, 2021. 2328−2337 [141] Wen Q S, Yang L, Zhou T, Sun L. Robust time series analysis and applications: An industrial perspective. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York, USA: ACM, 2022. 4836−4837 [142] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A, et al. Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30 [143] Zhou T, Ma Z Q, Wen Q S, Wang X, Sun L, Jin R. FEDformer: Frequency enhanced decomposed transformer for long-term series forecasting. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: PMLR, 2022. 27268−27286 [144] Wen Q S, Zhou T, Zhang C L, Chen W Q, Ma Z Q, Yan J C, et al. Transformers in time series: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2202.07125, 2022. -




 下载:
下载: