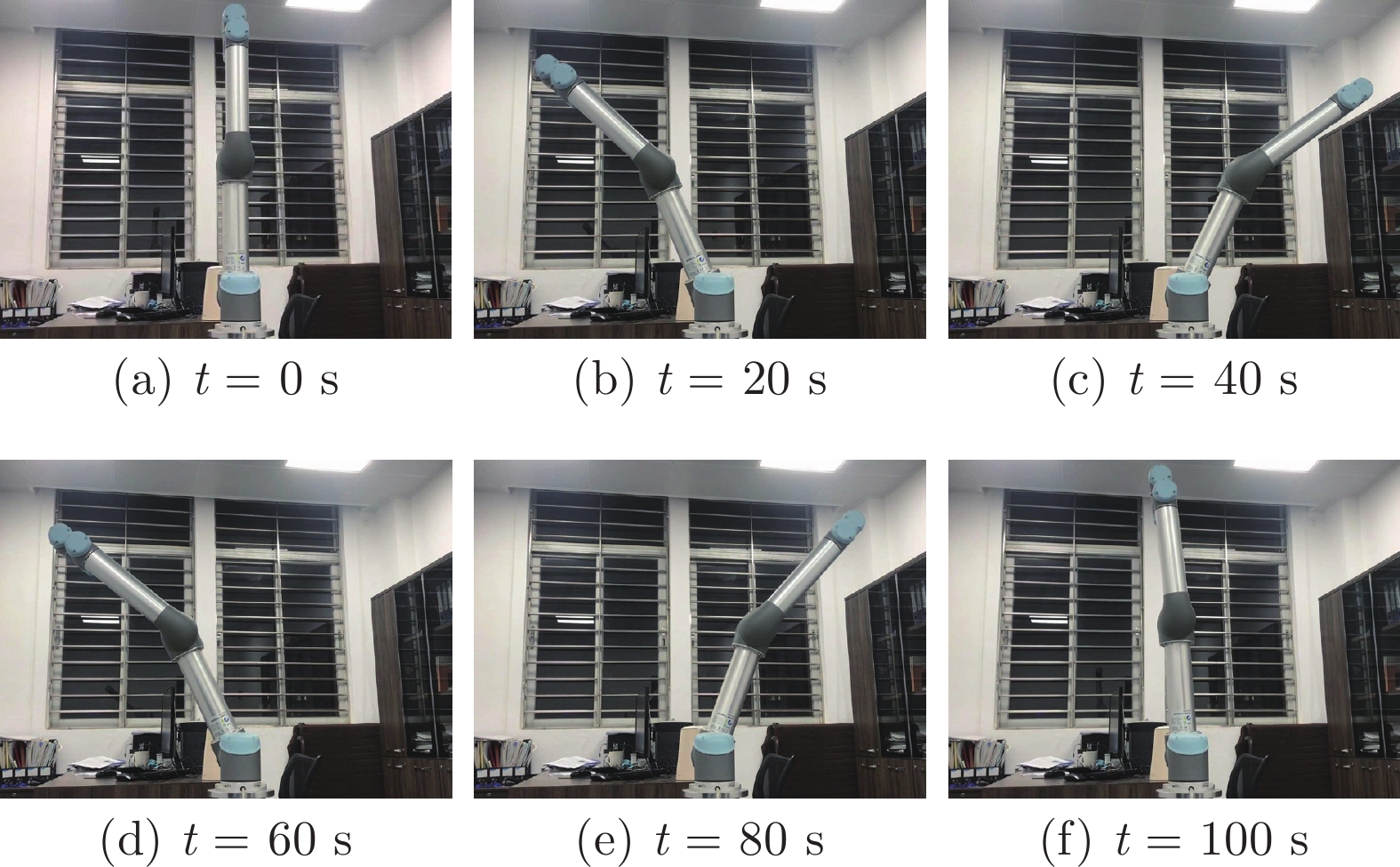
Deterministic Learning of Manipulators With Closed Architecture Based on Outer-loop Speed Compensation Control
-
摘要: 针对未开放力矩控制接口的一类封闭机器人系统, 提出一种基于外环速度补偿的确定学习控制方案. 该控制方案考虑机器人受到未知动力学影响, 且具有未知内环比例积分(Proportional-integral, PI)速度控制器. 首先, 利用宽度径向基函数(Radial basis function, RBF)神经网络对封闭机器人的内部未知动态进行逼近, 设计外环自适应神经网络速度控制指令. 在实现封闭机器人稳定控制的基础上, 结合确定学习理论证明了宽度RBF神经网络的学习能力, 提出基于确定学习的高精度速度控制指令. 该控制方案能够保证被控封闭机器人系统的所有信号最终一致有界且跟踪误差收敛于零的小邻域内. 在所提控制方案中, 通过引入外环补偿控制思想和宽度神经网络动态增量节点方式, 减小了设备计算负荷, 提高了速度控制下机器人的运动性能, 解决了市场上封闭机器人系统难以设计力矩控制的难题, 实现了不同工作任务下的高精度控制. 最后数值系统仿真结果和UR5机器人实验结果验证了该方案的有效性.Abstract: In this paper, a deterministic learning outer-loop speed compensation control scheme is proposed for a class of manipulator systems with closed architecture and without open torque control interface. The proposed scheme focuses on that the manipulator is affected by unknown modelling dynamics and has an unknown inner-loop proportional-integral (PI) speed controller. Firstly, the broad radial basis function (RBF) neural network is used to approximate the internal unknown dynamics of the manipulator with closed architecture, and the outer-loop adaptive neural network speed control command is designed by using the Lyapunov function. Based on the stable control of manipulator with closed architecture, the dynamic learning ability of RBF neural network is verified, and then the high-accuracy speed control command is designed based on the deterministic learning theory. The proposed control scheme guarantees that all signals of the manipulator system with closed architecture are ultimately uniformly bounded, and the tracking error converges to a small neighborhood of zero. By the combination of outer-loop compensation control and dynamic incremental node of broad neural networks, the proposed scheme reduces the computing load, improves the motion performance of the robot under speed control, solves the torque control design difficulty of the closed manipulator, and realizes high-precision control in different working tasks. Finally, simulation results of numerical system and experimental results of UR5 robot are used to show the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
-
表 1 仿真结果对比
Table 1 Comparison of simulation results
神经元数 MAE (前100 s) 仿真时长(s) ANC 500 s (均匀布点) 6561 $z_{1,1}$ 0.0166 403.61 $z_{1,2}$ 0.0131 ANC 500 s (宽度RBF网络) 425 $z_{1,1}$ 0.0192 147.16 $z_{1,2}$ 0.0196 LC 500 s (均匀布点) 6561 $z_{1,1}$ 0.0038 299.47 $z_{1,2}$ 0.0033 LC 500 s (宽度RBF网络) 425 $z_{1,1}$ 0.0056 82.11 $z_{1,2}$ 0.0061 -
[1] Li T S, Zhao R, Chen C L P, Fang L Y, Liu C. Finite-time formation control of under-actuated ships using nonlinear sliding mode control. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(11): 3243-3253 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2794968 [2] 曾超, 杨辰光, 李强, 戴诗陆. 人-机器人技能传递研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1813-1828Zeng Chao, Yang Chen-Guang, Li Qiang, Dai Shi-Lu. Research progress on human-robot skill transfer. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1813-1828 [3] 陈锦涛, 李鸿一, 任鸿儒, 鲁仁全. 基于RRT森林算法的高层消防无人机室内协同路径规划. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c210368Chen Jin-Tao, Li Hong-Yi, Ren Hong-Ru, Lu Ren-Quan. Cooperative indoor path planning of multi-UAVs for high-rise fire fighting based on RRT-forest algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c210368 [4] Peng Z H, Wang J, Wang D. Distributed containment maneuvering of multiple marine vessels via neurodynamics-based output feedback. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(5): 3831-3839 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2652346 [5] Wang H L. Adaptive control of robot manipulators with uncertain kinematics and dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(2): 948-954 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2575827 [6] Zhao Z J, He X Y, Ren Z G, Wen G L. Boundary adaptive robust control of a flexible riser system with input nonlinearities. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(10): 1971-1980 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2882734 [7] Garfalo G, Wu X W, Ott C. Adaptive passivity-based multi-task tracking control for robotic manipulators. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(4): 7129-7136 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3095930 [8] Zhao Z J, Liu Z J, He W, Hong K S, Li H X. Boundary adaptive fault-tolerant control for a flexible Timoshenko arm with backlash-like hysteresis. Automatica, 2021, 130: Article No. 109690 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109690 [9] Xu B, Wang X, Shou Y X, Shi P, Shi Z K. Finite-time robust intelligent control of strict-feedback nonlinear systems with flight dynamics application. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(11): 6173-6182 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3072552 [10] Peng Z H, Wang J, Wang D. Distributed maneuvering of autonomous surface vehicles based on neurodynamic optimization and fuzzy approximation. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 26(3): 1083-1090 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2017.2699167 [11] 乃永强, 杨清宇, 周文兴, 杨莹. 具有间歇性执行器故障的非线性系统自适应CFB控制. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(10): 2442-2461Nai Yong-Qiang, Yang Qing-Yu, Zhou Wen-Xing, Yang Ying. Adaptive CFB control for a class of nonlinear systems with intermittent actuator faults. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2442-2461 [12] 王敏, 黄龙旺, 杨辰光. 基于事件触发的离散MIMO系统自适应评判容错控制. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(5): 1234-1245Wang Min, Huang Long-Wang, Yang Chen-Guang. Event-triggered adaptive critic fault-tolerant control for a class of discrete-time MIMO systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(5): 1234-1245 [13] Swevers J, Verdonck W, Schutter J D. Dynamic model identification for industrial robots. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2007, 27(5): 58-71 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2007.904659 [14] Zhang Y Y, Li S, Zou J X, Khan A K. A passivity-based approach for kinematic control of manipulators with constraints. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 16(5): 3029-3038 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2908442 [15] Roy J, Whitcomb L L. Adaptive force control of position/velocity controlled robots: Theory and experiment. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 2002, 18(2): 121-137 doi: 10.1109/TRA.2002.999642 [16] Kelly R, Moreno J. Manipulator motion control in operational space using joint velocity inner loops. Automatica, 2005, 41(8): 1423-1432 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2005.03.008 [17] Whitney D E. Resolved motion rate control of manipulators and human prostheses. IEEE Transactions on Man-machine Systems, 1969, 10(2): 47-53 doi: 10.1109/TMMS.1969.299896 [18] Grotjahn M, Heimann B. Model-based feedforward control in industrial robotics. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2002, 21(1): 45-60 doi: 10.1177/027836402320556476 [19] Wang H L, Ren W, Cheah C C, Xie Y C, Lyu S K. Dynamic modularity approach to adaptive control of robotic systems with closed architecture. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(6): 2760-2767 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2922450 [20] 周琪, 林国怀, 马慧, 鲁仁全. 输入死区下的多输入多输出系统自适应神经网络容错控制. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2021, 51(4): 618-632 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0198Zhou Qi, Lin Guo-Huai, Ma Hui, Lu Ren-Quan. Adaptive neural network fault-tolerant control for MIMO systems with dead zone inputs. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2021, 51(4): 618-632 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0198 [21] Xu B, Shou Y X, Wang X, Shi P. Finite-time composite learning control of strict-feedback nonlinear system using historical stack. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, DOI: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3182981 [22] Wang C, Hill D J. Learning from neural control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2006, 17(1): 130-146 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2005.860843 [23] Wang M, Wang C. Learning from adaptive neural dynamic surface control of strict-feedback systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(6): Article No. 1247–1259 [24] Dai S L, Lu K, Fu J. Adaptive finite-time tracking control of nonholonomic multirobot formation systems with limited field-of-view sensors. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(10): 10695-10708 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3063481 [25] 孙庆华, 王磊, 王聪, 王乾, 吴伟明, 赵媛媛, 等. 基于确定学习及心电动力学图的心肌缺血早期检测研究. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(9): 1908-1926 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190899Sun Qing-Hua, Wang Lei, Wang Cong, Wang Qian, Wu Wei-Ming, Zhao Yuan-Yuan, et al. Early detection of myocardial ischemia based on deterministic learning and cardiodynamicsgram. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(9): 1908-1926 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190899 [26] Dai S L, He S D, Ma Y F, Yuan C Z. Cooperative learning-based formation control of autonomous marine surface vessels with prescribed performance. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 52(4): 2565-2577 [27] Shi H T, Wang M, Wang C. Pattern-based autonomous smooth switching control for constrained flexible joint manipulator. Neurocomputing, 2022, 492: 162-173 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.04.031 [28] Sanner R M, Slotine J J. Gaussian networks for direct adaptive control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1992, 3(6): 837-863 doi: 10.1109/72.165588 [29] Huang H H, Zhang T, Yang C G, Chen C L P. Motor learning and generalization using broad learning adaptive neural control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(10): 8608-8617 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2950853 [30] Khalil H K. Nonlinear Systems. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, 2002. -




 下载:
下载: