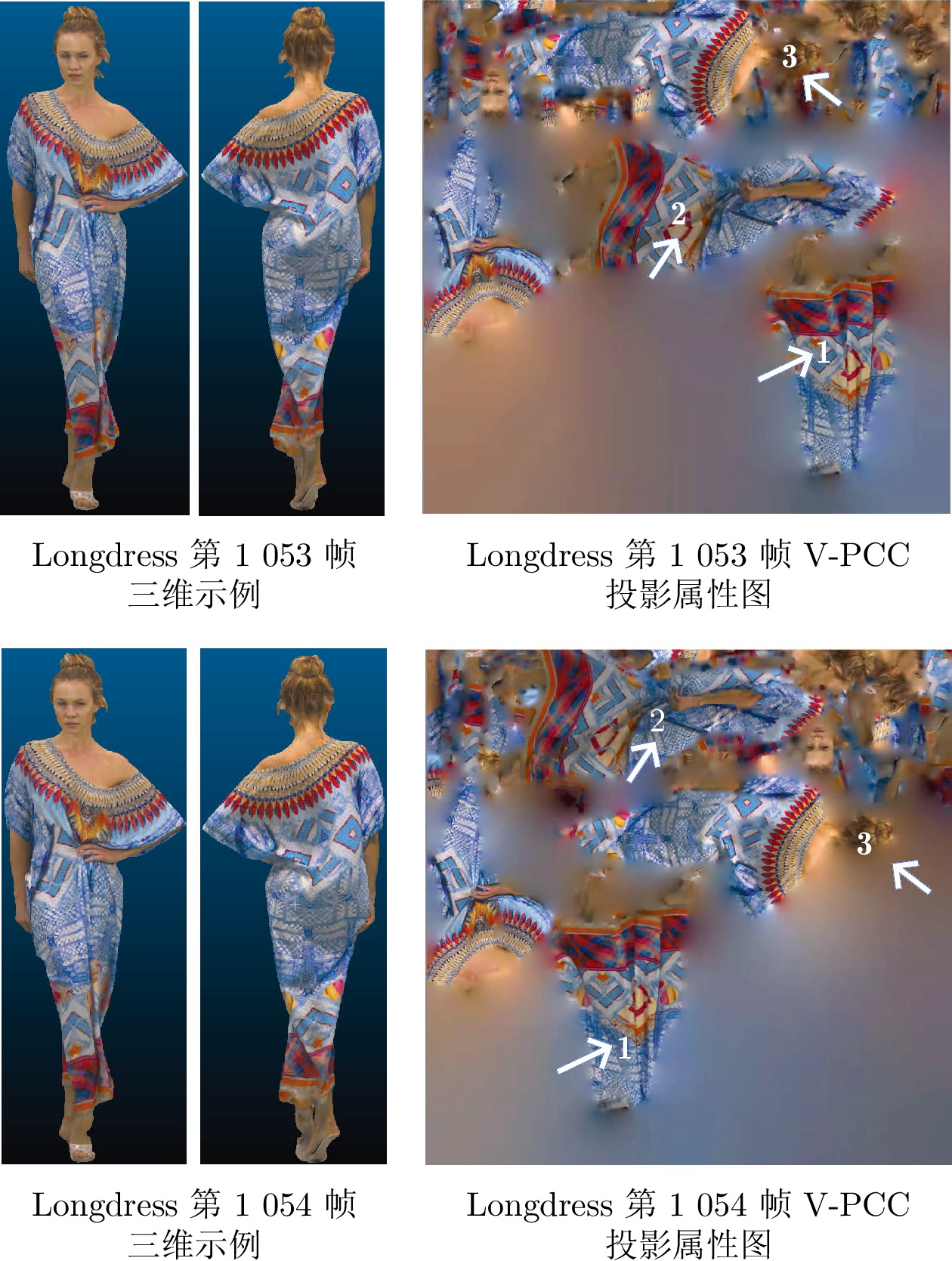
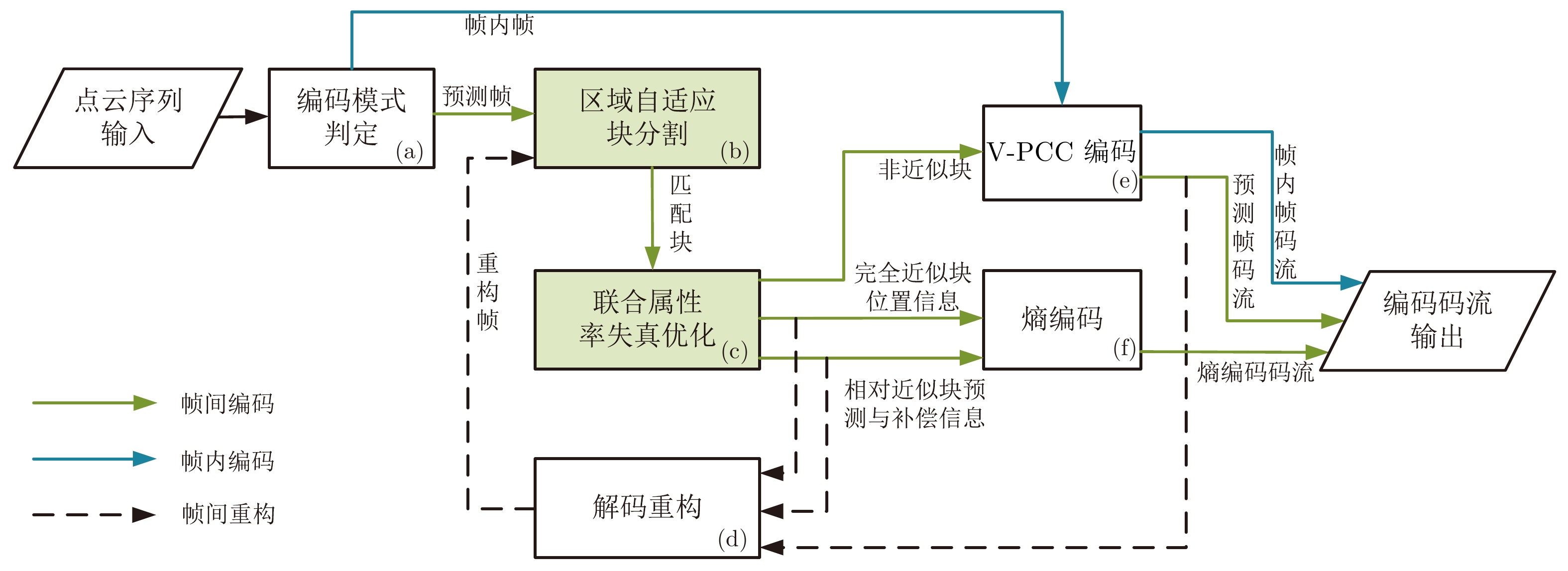
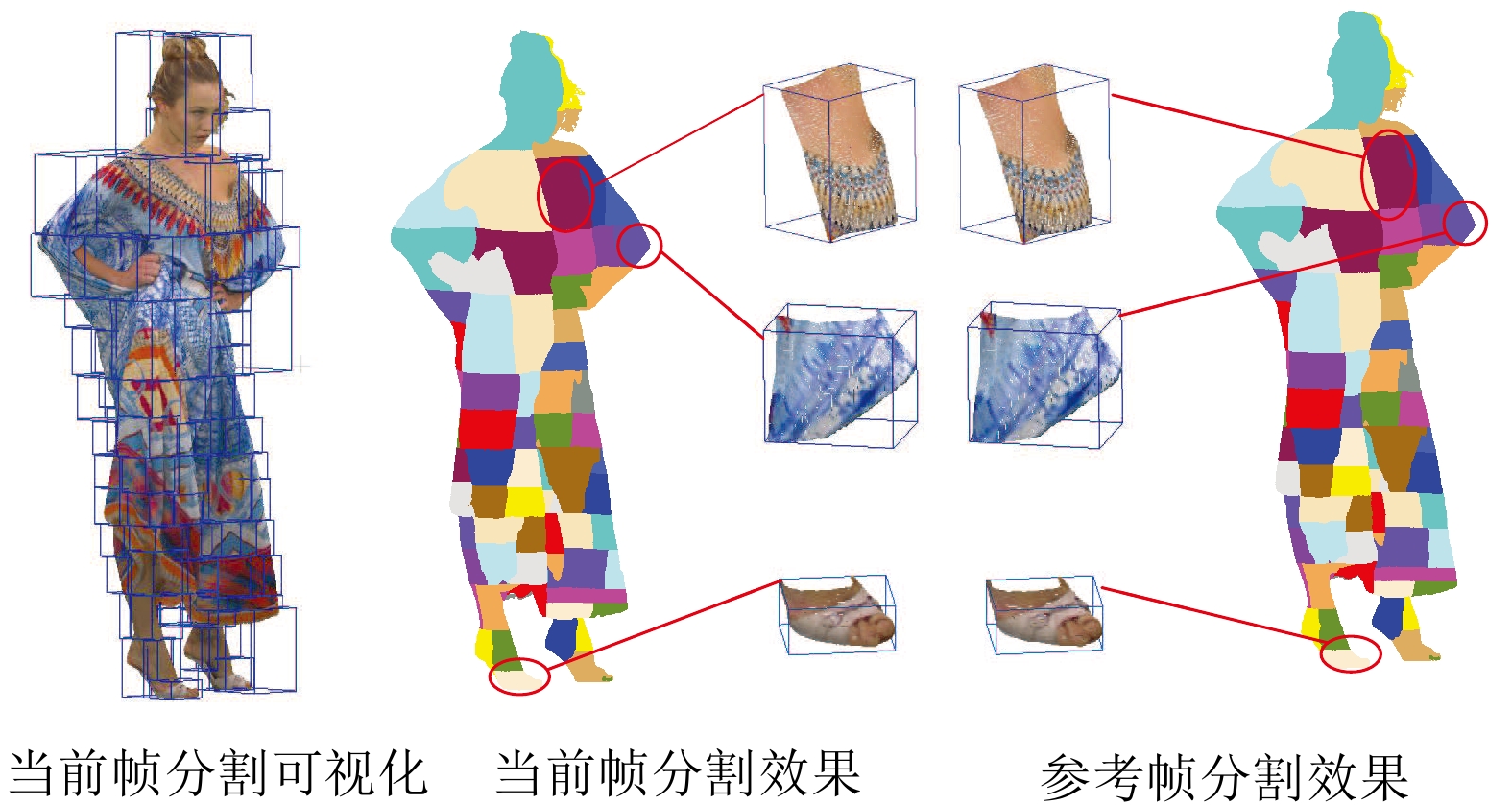
An Adaptive Segmentation Based Multi-mode Inter-frame Coding Method for Video Point Cloud
-
摘要: 基于视频的点云压缩(Video based point cloud compression, V-PCC)为压缩动态点云提供了高效的解决方案, 但V-PCC从三维到二维的投影使得三维帧间运动的相关性被破坏, 降低了帧间编码性能. 针对这一问题, 提出一种基于V-PCC改进的自适应分割的视频点云多模式帧间编码方法, 并依此设计了一种新型动态点云帧间编码框架. 首先, 为实现更精准的块预测, 提出区域自适应分割的块匹配方法以寻找最佳匹配块; 其次, 为进一步提高帧间编码性能, 提出基于联合属性率失真优化(Rate distortion optimization, RDO)的多模式帧间编码方法, 以更好地提高预测精度和降低码率消耗. 实验结果表明, 提出的改进算法相较于V-PCC实现了−22.57%的BD-BR (Bjontegaard delta bit rate)增益. 该算法特别适用于视频监控和视频会议等帧间变化不大的动态点云场景.Abstract: Video based point cloud compression (V-PCC) provides an efficient solution for compressing dynamic point clouds, but the projection of V-PCC from 3D to 2D destroys the correlation of 3D inter-frame motion and reduces the performance of inter-frame coding. To solve this problem, we proposes an adaptive segmentation based multi-mode inter-frame coding method for video point cloud to improve V-PCC, and designs a new dynamic point cloud inter-frame encoding framework. Firstly, in order to achieve more accurate block prediction, a block matching method based on adaptive regional segmentation is proposed to find the best matching block; Secondly, in order to further improve the performance of inter coding, a multi-mode inter-frame coding method based on joint attribute rate distortion optimization (RDO) is proposed to increase the prediction accuracy and reduce the bit rate consumption. Experimental results show that the improved algorithm proposed in this paper achieves −22.57% Bjontegaard delta bit rate (BD-BR) gain compared with V-PCC. The algorithm is especially suitable for dynamic point cloud scenes with little change between frames, such as video surveillance and video conference.
-
表 1 相对近似块帧间编码比特占用
Table 1 RSB inter coding bits occupancy
编码类型 编码信息 数据类型 比特占用(bits) 位置信息 $(X,Y,Z)_{{\rm{min}},{\rm{max}}}$ Int 96 旋转矩阵 $3\times3$矩阵 Float 288 平移向量 $3\times 1$向量 Float 96 属性偏移 $(R,G,B)$ Int 48 总编码消耗 $R_{\rm{RSB}}$ Int、Float 528 表 2 提出的改进算法量化参数
Table 2 Quantization parameters of proposed improved algorithm
量化参数 编码模式判定$\Omega$ 最小块阈值$N_D$ 分割截止阈值$T$ R1 3.5 14000 2.0 R2 3.0 12000 2.2 R3 2.5 10000 2.5 R4 2.0 8000 2.8 R5 1.5 6000 3.0 表 3 区域自适应分割的块匹配方法性能测试
Table 3 Performance test of block matching method based on adaptive regional segmentation
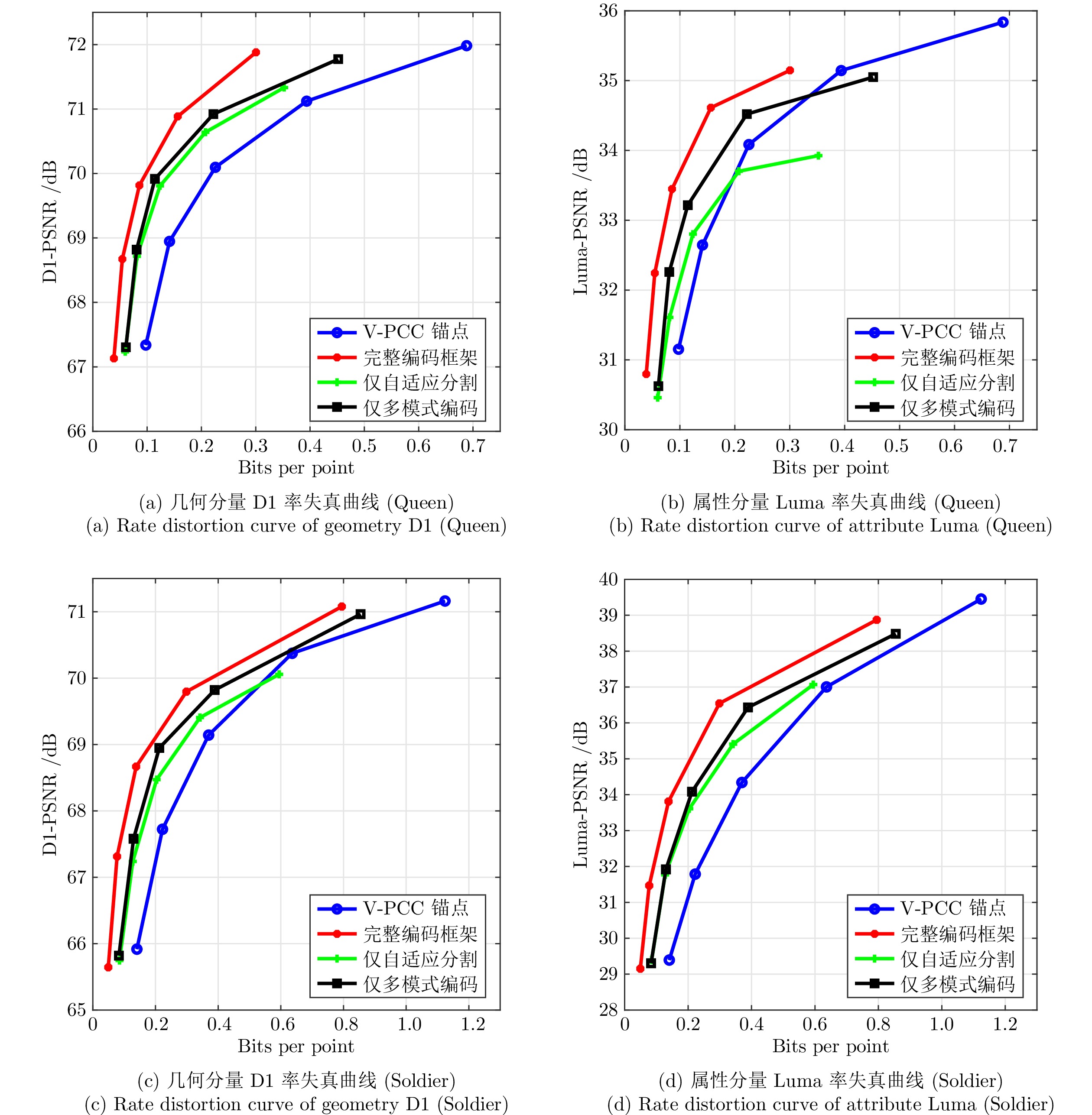
Name D1 (%) D2 (%) Luma (%) Cb (%) Cr (%) 均匀块分割 Loot 33.93 49.67 4.48 −18.07 −15.08 Redandblack 13.51 19.42 13.41 −3.01 10.79 Soldier −34.75 −34.66 −40.82 −42.91 −44.52 Queen −33.64 −33.33 −18.33 −28.58 −12.74 Longdress 11.97 13.15 27.48 −4.88 11.13 Average −1.80 −2.85 −2.76 −18.51 −10.08 改进的自适应块分割 Loot 27.10 39.28 2.22 −24.14 −21.19 Redandblack 6.03 8.14 16.06 4.14 13.72 Soldier −37.69 −37.57 −42.87 −45.10 −46.42 Queen −35.72 −33.94 −9.36 −12.93 −14.92 Longdress 6.74 6.46 4.83 5.02 12.49 Average −6.71 −3.53 −5.82 −14.60 −11.26 相对BD-BR增益 −4.91 −6.38 −3.06 3.91 −1.18 表 4 联合属性率失真优化的多模式帧间编码性能测试
Table 4 Performance test of multi-mode inter-frame coding based on joint attribute rate distortion optimization
Name D1 (%) D2 (%) Luma (%) Cb (%) Cr (%) 完全帧间运动预测 Loot 32.31 42.75 11.16 −19.63 −16.09 Redandblack 14.16 15.52 7.88 −11.11 6.35 Soldier −31.21 −31.21 −37.47 −41.07 −42.48 Queen −29.34 −30.23 −12.47 −17.84 −6.77 Longdress 12.28 14.79 17.74 −13.26 0.79 Average −0.36 2.32 −2.63 −20.58 −13.70 改进的多模式帧间运动预测 Loot −0.06 0.70 10.07 5.44 5.80 Redandblack −3.31 −2.09 11.73 1.66 9.45 Soldier −35.88 −34.59 −36.31 −36.28 −38.70 Queen −39.55 −39.37 −39.16 −44.46 −44.97 Longdress −0.64 1.28 6.50 3.10 10.23 Average −18.13 −17.09 −9.43 −16.06 −11.64 相对BD-BR增益 −17.77 −19.41 −6.80 4.52 2.06 表 5 相较于V-PCC相互消融性能(平均BD-BR)
Table 5 Mutual ablation performance compared to V-PCC (Average BD-BR)
应用算法 D1 (%) D2 (%) Luma (%) Cb (%) Cr (%) 多模式帧间编码 −18.13 −17.09 −9.43 −16.06 −11.64 自适应块分割 −6.71 −3.53 −5.82 −14.60 −11.26 完整算法框架 −22.57 −20.94 −22.01 −23.67 −21.90 表 6 提出的改进算法相较于V-PCC的性能比较
Table 6 Performance of proposed improved algorithm compared with V-PCC
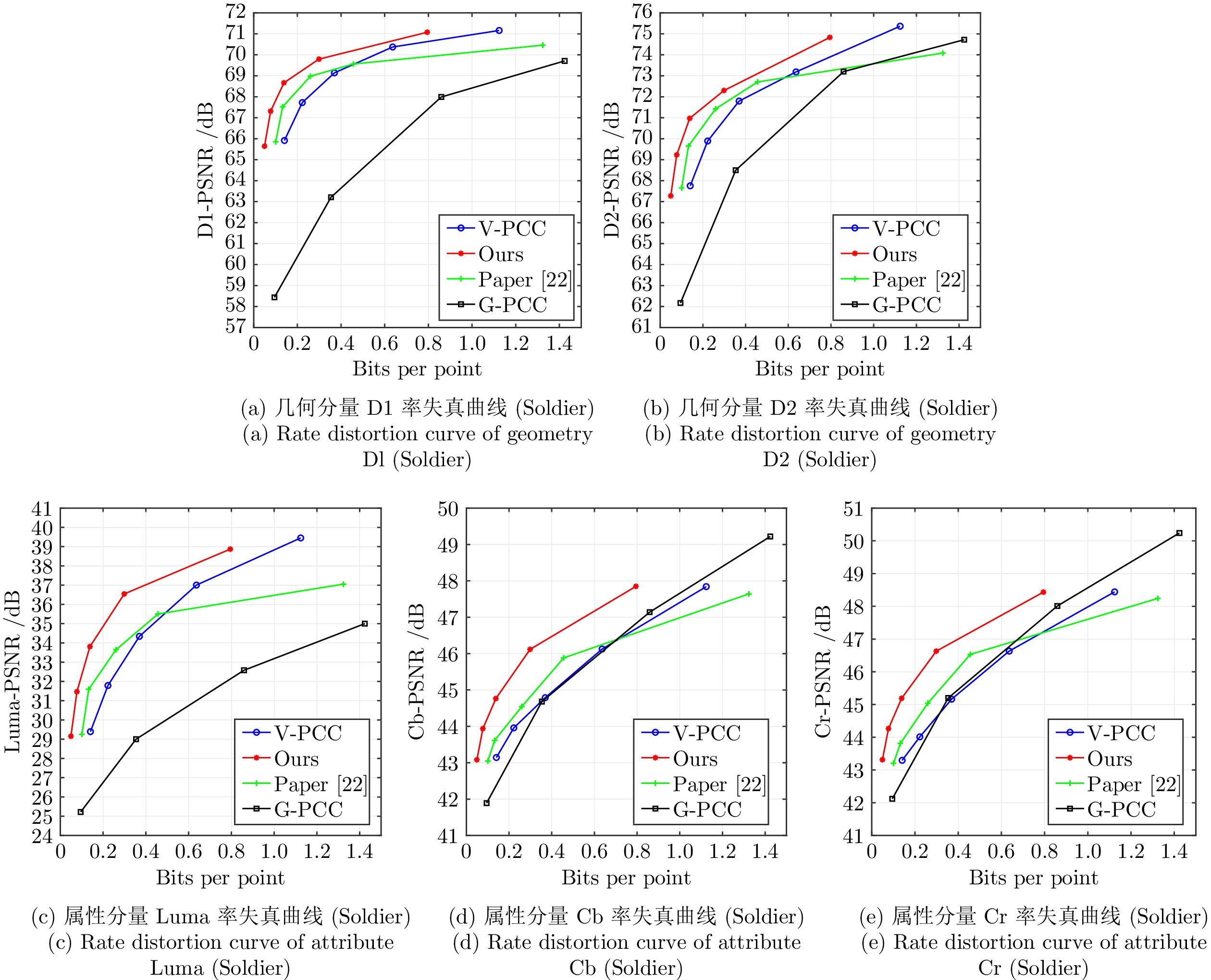
Name D1 (%) D2 (%) Luma (%) Cb (%) Cr (%) Loot −2.64 −0.69 −3.57 −4.74 −4.85 Redandblack −1.65 −0.95 −1.75 −2.01 −2.12 Soldier −51.53 −46.99 −54.12 −55.65 −55.95 Queen −56.58 −56.45 −51.62 −55.12 −46.27 Longdress −0.44 0.40 0.99 −0.80 −0.30 Overall −22.57 −20.94 −22.01 −23.67 −21.90 表 8 相较于V-PCC的编码开销与时间复杂度
Table 8 Encoding overhead and time complexity compared to V-PCC
量化
等级预测
编码
(bits)NSB
编码
(bits)V-PCC
帧内
编码(bits)相对编码
开销(%)相对编码
时间(%)Queen R1 5722 33065 97363 39.83 85.01 R2 6099 48154 140968 38.49 84.74 R3 6841 78773 225197 38.02 84.99 R4 6797 149308 392872 39.71 85.77 R5 7494 292382 686758 43.67 92.08 Soldier R1 4986 47469 149301 35.13 82.17 R2 5692 76517 236022 34.83 81.79 R3 7986 138810 392283 37.42 81.27 R4 11836 305130 675218 46.94 83.38 R5 16182 826968 1192585 70.69 94.29 Average 7955 199658 418857 49.56 85.55 -
[1] 李厚强, 李礼, 李竹. 点云编码综述. 中兴通讯技术, 2021, 27(01):5−9Li Hou-Qiang, Li Li, Li Zhu. A review of point cloud compression. ZTE Technology Journal, 2021, 27(01):5−9 [2] Ishikawa Y, Hachiuma R, Ienaga N, Kuno W, Sugiura Y, Saito H. Semantic segmentation of 3D point cloud to virtually manipulate real living space. In: Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Workshop on Mixed and Augmented Reality. Ikoma, Japan: IEEE, 2019. 1−7 [3] Deng X M, Zhu Y Y, Zhang Y D, Cui Z P, Tan P, Qu W, et al. Weakly supervised learning for single depth-based hand shape recovery. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 532−545 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3037479 [4] 田永林, 沈宇, 李强, 王飞跃. 平行点云:虚实互动的点云生成与三维模型进化方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(12): 2572−2582 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200800Tian Yong-Lin, Shen Yu, Li Qiang, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel point clouds: point clouds generation and 3D model evolution via virtual-real interaction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(12): 2572−2582 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200800 [5] Sun P P, Zhao X M, Xu Z G, Wang R M, Min H G. A 3D LiDAR data-based dedicated road boundary detection algorithm for autonomous vehicles. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 29623−29638 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2902170 [6] Huang X Y, Wang P, Cheng X J, Zhou D F, Geng Q C, Yang R G. The apolloscape open dataset for autonomous driving and its application. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2702−2719 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2926463 [7] Gan Z P, Xu H R, He Y R, Cao W, Chen G H. Autonomous landing point retrieval algorithm for UAVs based on 3D environment perception. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Conference on Virtual Reality. Foshan, China: IEEE, 2021. 104−108 [8] 曹成坤, 张琮毅, 汪国平. 精度可控的字典全局相似性点云压缩. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(6):869−877Cao Cheng-Kun, Zhang Cong-Yi, Wang Guo-Ping. Precision controllable point clouds compression using global similarity in dictionary. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(6): 869−877 [9] Maja K, Chou P A, Savill P. 8i voxelized surface light field (8iVSLF) dataset. ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 MPEG, input document m42914, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2018 [10] Kammerl J, Blodow N, Rusu R B, Gedikli S, Beetz M, Steinbach E. Real-time compression of point cloud streams. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Saint Paul, USA: IEEE, 2012. 778−785 [11] Thanou D, Chou P A, Frossard P. Graph-based compressionof dynamic 3D point cloud sequences. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(4): 1765−1778 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2529506 [12] Queiroz R L, Chou P A. Motion-compensated compression of dynamic voxelized point clouds. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(8): 3886−3895 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2707807 [13] Mekuria R, Blom K, Cesar P. Design, implementation, and evaluation of a point cloud codec for tele-immersive video. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(4): 828−842 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2543039 [14] Besl P J, McKay N D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(2):239−256 doi: 10.1109/34.121791 [15] Santos C, Goncalves M, Correa G, Porto M. Block-based inter-frame prediction for dynamic point cloud compression. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Anchorage, USA: IEEE, 2021. 3388−3392 [16] Lasserre S, Llach J, Guede C, Ricard J. Technicolor's response to the CfP for point cloud compression. ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 MPEG, input document m41822, Macau, China, 2017 [17] Budagavi M, Faramarzi E, Ho T, Najaf-Zadeh H, Sinharoy I. Samsung's response to CfP for point cloud compression (Category2). ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 MPEG, input document m41808, Macau, China, 2017 [18] Schwarz S, Sheikhipour N, Sevom V F, Hannuksela M M. Video coding of dynamic 3D point cloud data. APSIPA Transactions on Signal and Information Processing, DOI: 10.1017/ATSIP.2019.24 [19] Mammou K, Tourapis A M, SINGER D. Video-based and hierarchical approaches point cloud compression. ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 MPEG, input document m41779, Macua, China, 2017 [20] Graziosi D, Nakagami O, Kuma S, Zaghetto A, Suzuki T, Tabatabai A. An overview of ongoing point cloud compression standardization activities: Video-based (V-PCC) and geometry-based (G-PCC). APSIPA Transactions on Signal and Information Processing, DOI: 10.1017/ATSIP.2020.12 [21] Li L, Zhu L, Zakharchenko V, Chen J L, Li H Q. Advanced 3D motion prediction for Video-based dynamic point cloud compression. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29:289−302 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2931621 [22] Kim J, Im J, Rhyu S, Kim K. 3D motion estimation and compensation method for Video-based point cloud compression. IEEE Access, 2020, 8:83538−83547 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2991478 [23] Costa A, Dricot A, Brites C, Ascenso J, Pereira F. Improved patch packing for the MPEG V-PCC standard. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 21st International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: IEEE, 2019. 1−6 [24] Li L, Li Z, Liu S, Li H Q. Occupancy-map-based rate distortion optimization and partition for video-based point cloud compression. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 31(1): 326−338 [25] Li L, Li Z, Liu S, Li H Q. Efficient projected frame padding for video-based point cloud compression. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 23: 2806−2819 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2020.3016894 [26] Xu Y Q, Hu W, Wang S S, Zhang X F, et al. Predictive generalized graph fourier transform for attribute compression of dynamic point clouds. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(5): 1968−1982 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.3015901 [27] Schwarz S, Martin-Cocher G, Flynn D, Budagavi M. Common test conditions for point cloud compression. ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 MPEG, input docment w17766, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2020 [28] Jang E S, Preda M, Mammou K, Tourapis A M, et al. Video-based point-cloud-compression standard in MPEG: from evidence collection to committee draft. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2019, 36(3): 118−123 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2019.2900721 -




 下载:
下载: