Multimodal Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm Considering Global and Local Pareto Fronts
-
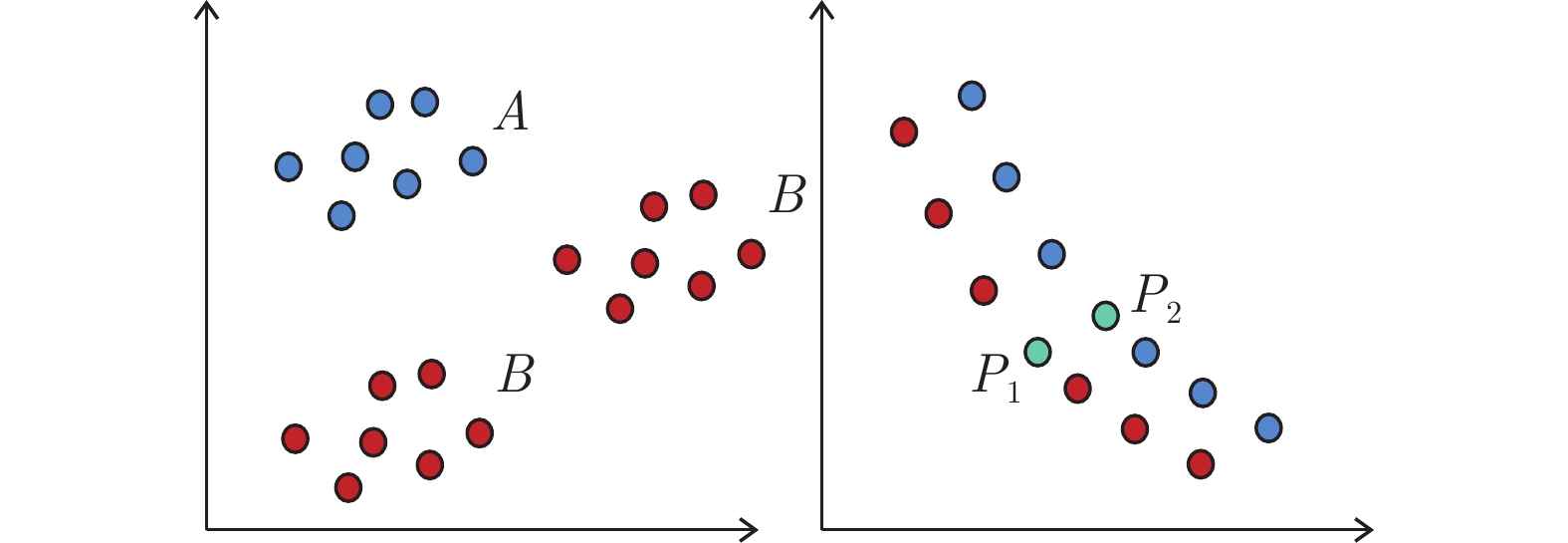
摘要: 多模态多目标优化问题 (Multimodal multi-objective optimization problems, MMOPs)是指具有多个全局或局部Pareto解集(Pareto solution sets, PSs)的多目标优化问题 (Multi-objective optimization problems, MOPs). 在这类问题中, Pareto前沿(Pareto front, PF)上相距很近的目标向量, 可能对应于决策空间中相距较远的不同解. 在实际应用中全局或局部最优解的缺失可能导致决策者缺乏对问题的整体认识, 造成不必要的困难或经济损失. 大部分多模态多目标进化算法 (Multimodal multi-objective evolutionary algorithms, MMEAs) 仅关注获取尽可能多的全局最优解集, 而忽略了对局部最优解集的搜索. 为了找到局部最优解集并提高多模态优化算法的性能, 首先提出了一种局部收敛性指标 (
$ I_{LC}$ ), 并设计了一种基于该指标和改进种群拥挤度的环境选择策略. 基于此提出了一种用于获取全局和局部最优解集的多模态多目标优化算法. 经实验验证, 该算法在对比的代表性算法中性能较好.Abstract: Multimodal multi-objective optimization problems (MMOPs) refer to problems with multiple global or local Pareto solution sets (PSs). Different solutions far apart in the decision space may correspond to objective vectors in the Pareto front (PF) that are closed. The lack of global or local optimal solutions in practical applications may lead to the lack of overall understanding of the problem for decision-makers, resulting in unnecessary difficulties or economic losses. Most of the multimodal multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MMEAs) mainly focus on obtaining the global optimal solution sets and pay little attention to the local optimal solutions. In order to find the local optimal solution sets and improve the performance of MMEAs, this paper proposes a local convergence indicator ($ I_{LC}$ ) and designs an environment selection strategy. Then, a multimodal multi-objective optimization algorithm for obtaining global and local optimal solution sets is proposed. Experiments show that the performance of the proposed algorithm is better than that of the compared representative algorithms. -
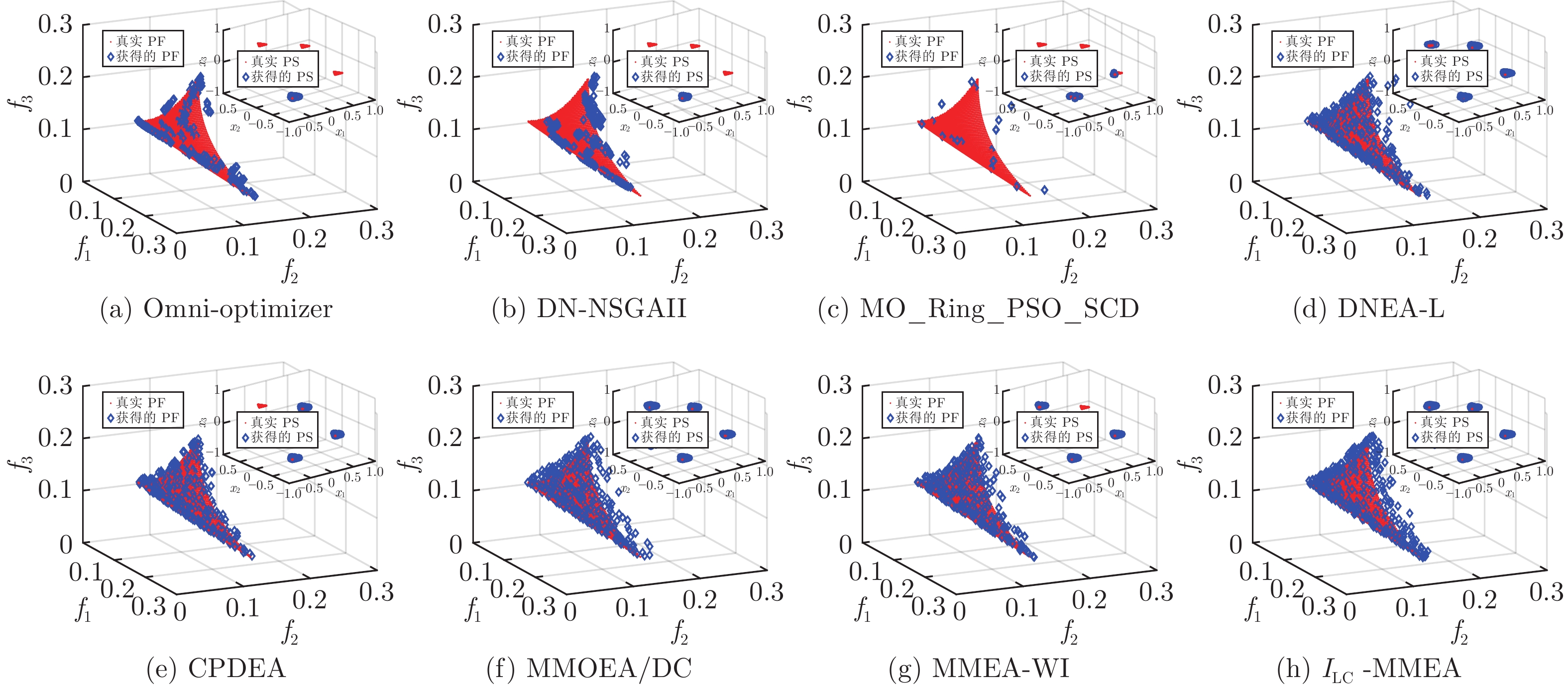
表 1 不同算法在IDMP测试问题上31次独立运行的IGDX平均值和方差
Table 1 Mean and variance of 31 independent runs of IGDX for different algorithms on IDMP test problems
测试问题 Omni-optimizer DN-NSGAII MO_Ring_
PSO_SCDDNEA-L CPDEA MMOEA/DC MMEA-WI $I_{LC}$-MMEA IDMPM2T1 3.88×10−1 2.84×10−1 5.90×10−2 1.27×10−3 1.03×10−3 8.76×10−4 9.32×10−4 6.55×10−4 3.31×10−1 3.24×10−1 1.67×10−1 2.39×10−3 5.41×10−4 1.15×10−4 7.13×10−5 2.30×10−9 IDMPM2T2 2.99×10−1 2.99×10−1 5.58×10−3 1.75×10−3 9.55×10−4 1.03×10−3 1.12×10−3 8.65×10−4 3.33×10−1 3.34×10−1 2.91×10−3 1.39×10−3 1.33×10−4 1.14×10−4 8.61×10−5 4.71×10−9 IDMPM2T3 1.19×10−1 1.19×10−1 3.35×10−3 2.65×10−3 3.70×10−3 1.85×10−3 1.99×10−3 1.42×10−3 2.57×10−1 2.55×10−1 4.22×10−4 1.62×10−3 1.47×10−3 1.92×10−4 2.49×10−4 8.51×10−9 IDMPM2T4 5.44×10−1 6.10×10−1 8.67×10−2 1.30×10−2 2.32×10−2 9.06×10−2 4.58×10−2 6.12×10−4 2.63×10−1 1.94×10−1 2.00×10−1 2.16×10−2 1.23×10−1 2.32×10−1 1.71×10−1 7.82×10−10 IDMPM3T1 3.50×10−1 3.49×10−1 1.19×10−1 3.26×10−2 1.53×10−2 8.41×10−3 7.48×10−3 8.67×10−3 2.30×10−1 2.42×10−1 1.47×10−1 7.42×10−2 4.42×10−2 3.97×10−4 1.78×10−4 1.68×10−8 IDMPM3T2 6.00×10−1 6.14×10−1 1.45×10−1 2.78×10−2 7.23×10−3 8.17×10−3 7.69×10−3 8.73×10−3 2.29×10−1 2.90×10−1 1.25×10−1 6.21×10−2 2.56×10−4 2.71×10−4 2.01×10−4 1.51×10−8 IDMPM3T3 3.71×10−1 4.75×10−1 2.65×10−2 3.65×10−2 2.65×10−2 1.01×10−2 2.55×10−2 9.66×10−3 2.03×10−1 2.32×10−1 4.34×10−2 7.41×10−2 6.09×10−2 6.01×10−4 6.29×10−2 5.89×10−8 IDMPM3T4 8.24×10−1 8.13×10−1 2.64×10−1 8.16×10−2 5.71×10−2 1.84×10−2 1.54×10−1 8.43×10−3 2.16×10−1 2.27×10−1 1.82×10−1 1.08×10−1 9.87×10−2 3.13×10−2 1.52×10−1 1.91×10−8 IDMPM4T1 7.94×10−1 6.36×10−1 9.36×10−1 1.07×10−1 7.03×10−1 4.44×10−2 2.68×10−2 9.15×10−3 3.07×10−1 3.33×10−1 2.75×10−1 1.50×10−1 2.89×10−1 7.50×10−2 6.77×10−2 2.40×10−6 IDMPM4T2 9.72×10−1 9.24×10−1 5.59×10−1 2.89×10−1 5.47×10−1 2.62×10−2 3.62×10−1 4.45×10−2 2.28×10−1 2.37×10−1 2.64×10−1 2.51×10−1 2.36×10−1 5.25×10−2 2.81×10−1 2.79×10−3 IDMPM4T3 7.44×10−1 7.25×10−1 8.04×10−2 1.32×10−1 4.07×10−1 1.66×10−2 4.16×10−1 1.82×10−2 3.18×10−1 3.05×10−1 8.42×10−2 1.59×10−1 2.56×10−1 1.33×10−3 2.92×10−1 9.53×10−4 IDMPM4T4 1.08 1.11 6.86×10−1 1.70×10−1 7.94×10−1 3.87×10−2 7.28×10−1 2.86×10−2 1.68×10−1 1.53×10−1 3.44×10−1 2.38×10−1 3.19×10−1 6.08×10−2 3.28×10−1 3.95×10−3 +/−/= 0/10/2 0/12/0 0/12/0 0/11/1 1/10/1 1/7/4 1/8/3 表 2 不同算法在具有局部PS测试问题上31次独立运行的IGDX平均值和方差
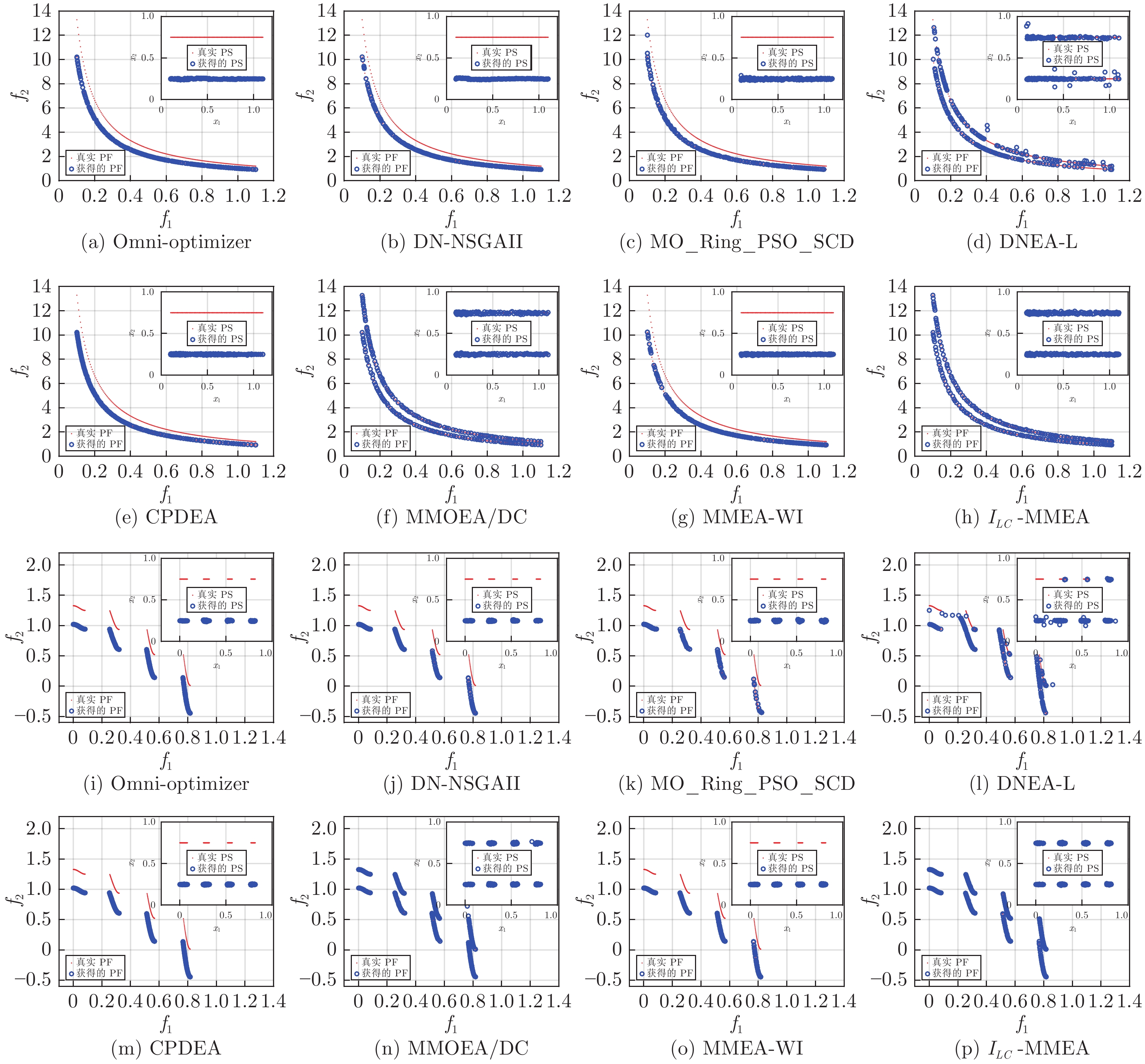
Table 2 Mean and variance of 31 independent runs of IGDX for different algorithms on MMOPs with local PS
测试问题 Omni-optimizer DN-NSGAII MO_Ring_
PSO_SCDDNEA-L CPDEA MMOEA/DC MMEA-WI $ I_{LC}$-MMEA MMF10 1.76×10−1 1.48×10−1 1.69×10−1 1.76×10−2 2.01×10−1 1.55×10−2 1.99×10−1 1.40×10−2 3.11×10−2 2.97×10−2 8.40×10−3 2.03×10−2 4.68×10−5 3.18×10−2 8.00×10−3 2.64×10−3 MMF11 2.50×10−1 2.50×10−1 2.10×10−1 9.08×10−3 2.49×10−1 7.51×10−3 2.48×10−1 7.26×10−3 3.63×10−4 4.16×10−4 2.49×10−2 9.42×10−4 3.24×10−4 3.33×10−4 2.17×10−3 1.05×10−7 MMF12 2.45×10−1 2.47×10−1 1.90×10−1 3.01×10−2 2.45×10−1 3.21×10−3 2.44×10−1 2.88×10−3 9.24×10−3 5.35×10−4 4.29×10−2 3.22×10−2 2.11×10−4 2.01×10−4 3.62×10−4 2.83×10−8 MMF13 2.86×10−1 2.86×10−1 2.35×10−1 2.59×10−1 2.53×10−1 8.85×10−2 2.52×10−1 8.08×10−2 9.28×10−3 9.59×10−3 1.57×10−2 2.31×10−3 7.32×10−4 1.59×10−2 7.26×10−4 1.94×10−5 MMF15 2.44×10−1 2.26×10−1 1.51×10−1 6.69×10−2 2.31×10−1 5.36×10−2 2.58×10−1 5.54×10−2 2.05×10−2 2.38×10−2 1.04×10−2 4.36×10−3 1.78×10−2 1.56×10−3 9.91×10−4 1.00×10−6 +/–/ = 0/5/0 0/5/0 0/5/0 0/4/1 0/5/0 0/3/2 0/5/0 -
[1] 公茂果, 焦李成, 杨咚咚, 马文萍. 进化多目标优化算法研究. 软件学报, 2009, 20(2): 271-289 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2009.00271Gong Mao-Guo, Jiao Li-Cheng, Yang Dong-Dong, Ma Wen-Ping. Research on evolutionary multi-objective optimization Algorithms. Journal of Software, 2009, 20(2): 271-289 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2009.00271 [2] 冀俊忠, 邹爱笑, 刘金铎. 基于功能磁共振成像的人脑效应连接网络识别方法综述. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(2): 278-296 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190491Ji Jun-Zhong, Zou Ai-Xiao, Liu Jin-Duo. An overview of identification methods on human brain effective connectivity networks based on functional magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(2): 278-296 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190491 [3] Ouyang T C, Su Z X, Gao B X, Pan M Z, Chen N, Huang H Z. Design and modeling of marine diesel engine multistage waste heat recovery system integrated with flue-gas desulfurization. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 196: 1353-68 doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.06.065 [4] Ma L B, Cheng S, Shi M L, Guo Y N. Angle-based multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on pruning-power indicator for game map generation. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2021, 6(2): 341-354 [5] 岳彩通, 梁静, 瞿博阳, 于坤杰, 王艳丽, 胡毅. 多模态多目标优化综述. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(11): 2577-2588 doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1509Yue Cai-Tong, Liang Jing, Qu Bo-Yang, Yu Kun-Jie, Wang Yan-Li, Hu Yi. A survey on multimodal multiobjective optimization. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(11): 2577-2588 doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1509 [6] Schutze O, Vasile M, Coello C A C. Computing the set of Epsilon-efficient solutions in multiobjective space mission design. Journal of Aerospace Computing, Information, and Communication, 2011, 8(3): 53-70 doi: 10.2514/1.46478 [7] 王丽芳, 曾建潮. 基于微粒群算法与模拟退火算法的协同进化方法. 自动化学报, 2006, 32(4): 630-635 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2006.04.019Wang Li-Fang, Zeng Jian-Chao. A cooperative evolutionary algorithm based on particle swarm optimization and simulated annealing algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2006, 32(4): 630-635 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2006.04.019 [8] 马永杰, 陈敏, 龚影, 程时升, 王甄延. 动态多目标优化进化算法研究进展. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(11): 2302-2318 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190489Ma Yong-Jie, Chen Min, Gong Ying, Cheng Shi-Sheng, Wang Zhen-Yan. Research progress of dynamic multi-objective optimization evolutionary algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(11): 2302-2318 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190489 [9] Tanabe R, Ishibuchi H. A review of evolutionary multimodal multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 24(1): 193-200 [10] Liu Y P, Ishibuchi H, Nojima Y, Masuyama N, Han Y Y. Searching for local Pareto optimal solutions: A case study on polygon-based problems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). Wellington, New Zealand: IEEE, 2019. 896−903 [11] Gong W Y, Liao Z W, Mi X Y, Wang L, Guo Y Y. Nonlinear equations solving with intelligent optimization algorithms: A survey. Complex System Modeling and Simulation, 2021, 1(1): 15-32 doi: 10.23919/CSMS.2021.0002 [12] Lin C M, Tian D X, Duan X T, Zhou J S. 3D environmental perception modeling in the simulated autonomous-driving systems. Complex System Modeling and Simulation, 2021, 1(1): 45-54 doi: 10.23919/CSMS.2021.0004 [13] Deb K, Tiwari S. Omni-optimizer: A generic evolutionary algorithm for single and multi-objective optimization. European Journal of Operational Research, 2008, 185(3): 1062-87 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.042 [14] Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan TA. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182-97 doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [15] Shir O M, Preuss M, Naujoks B, Emmerich M. Enhancing decision space diversity in evolutionary multiobjective algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. Nantes, France: Springer, 2009. 95−109 [16] Liu Y P, Ishibuchi H, Nojima Y, Masuyama N, Shang K. A double-niched evolutionary algorithm and its behavior on polygon-based problems. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature. Coimbra, Portugal: Springer, 2018. 262−273 [17] Liang J J, Yue C T, Qu B Y. Multimodal multi-objective optimization: A preliminary study. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2016. 2454−2461 [18] Liang J, Guo Q Q, Yue C T, Qu B Y, Yu K J. A self-organizing multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm for multimodal multi-objective problems. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Swarm Intelligence. Shanghai, China: Springer, 2018. 550−560 [19] Yue C T, Qu B Y, Liang J. A multiobjective particle swarm optimizer using ring topology for solving multimodal multiobjective problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2017, 22(5): 805-17 [20] Wang D S, Tan D P, Liu L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(2): 387-408 doi: 10.1007/s00500-016-2474-6 [21] Bilal, Pant M, Zaheer H, Garcia-Hernandez L, Abraham A. Differential evolution: A review of more than two decades of research. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 90: Article No. 103479 [22] Liang J, Xu W W, Yue C T, Yu K J, Song H, Crisalle O D, et al. Multimodal multiobjective optimization with differential evolution. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 44: 1028-59 doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2018.10.016 [23] Li Z H, Shi L, Yue C T, Shang Z G, Qu B Y. Differential evolution based on reinforcement learning with fitness ranking for solving multimodal multiobjective problems. warm and Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 49: 234-44 doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2019.06.010 [24] Liu Y P, Ishibuchi H, Yen G G, Nojima Y, Masuyama N. Handling imbalance between convergence and diversity in the decision space in evolutionary multimodal multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 24(3): 551-65 [25] Li W H, Zhang T, Wang R, Ishibuchi H. Weighted indicator-based evolutionary algorithm for multimodal multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 25(6): 1064-78 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2021.3078441 [26] Fan Q Q, Ersoy O K. Zoning search with adaptive resource allocating method for balanced and imbalanced multimodal multi-objective optimization. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2021, 8(6): 1163-1176 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2021.1004027 [27] Li H, Deng J D, Zhang Q F, Sun J Y. Adaptive epsilon dominance in decomposition-based multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 45: 52-67 doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2018.12.007 [28] Hu Y, Wang J, Liang J, Yu K J, Song H, Guo Q Q, et al. A self-organizing multimodal multi-objective pigeon-inspired optimization algorithm. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(7): 1-7 [29] Tanabe R, Ishibuchi H. A framework to handle multimodal multiobjective optimization in decomposition-based evolutionary algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 24(4): 720-34 [30] Ulrich T, Bader J, Thiele L. Defining and optimizing indicator-based diversity measures in multiobjective search. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature. Krakov, Poland: Springer, 2010. 707−717 [31] Liang J, Qu B Y, Gong D W, Yue C T. Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for the CEC 2019 Special Session on Multimodal Multiobjective Optimization, Technical Report, School of Electrical Engineering, Zhengzhou University, China, 2019 [32] Lin Q Z, Lin W, Zhu Z X, Gong M G, Li J Q, Coello C A C. Multimodal multiobjective evolutionary optimization with dual clustering in decision and objective spaces. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 25(1): 130-44 [33] Li W H, Yao X Y, Zhang T, Wang R, Wang L. Hierarchy ranking method for multimodal multi-objective optimization with local Pareto fronts. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, DOI: 10.1109/TEVC.2022.3155757 [34] Zitzler E, Laumanns M, Thiele L. SPEA2: Improving the Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm, Technical Report, Department of Electrical Engineering, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Switzerland, 2001 [35] Wang H D, Jiao L C, Yao X. Two_Arch2: An improved two-archive algorithm for many-objective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2015, 19(4): 524-541 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2014.2350987 [36] Tian Y, Cheng R, Zhang X Y, Jin Y C. PlatEMO: A MATLAB platform for evolutionary multi-objective optimization[educational forum]. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2017, 12(4): 73-87 doi: 10.1109/MCI.2017.2742868 [37] Bader J, Zitzler E. HypE: An algorithm for fast hypervolume-based many-objective optimization. Evolutionary computation, 2011, 19(1): 45-76 doi: 10.1162/EVCO_a_00009 [38] Riquelme N, Lücken C V, Baran B. Performance metrics in multi-objective optimization. In: Proceedings of the Latin American Computing Conference (CLEI). Arequipa, Peru: IEEE, 2015. 1−11 [39] Zhou A M, Zhang Q F, Jin Y C. Approximating the set of Pareto-optimal solutions in both the decision and objective spaces by an estimation of distribution algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(5): 1167-89 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2021467 [40] Liang J, Yue C T, Li G P, Qu B Y, Suganthan P N, Yu K J. Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for the CEC 2021 on Multimodal Multiobjective Path Planning Optimization, Technical Report, School of Electrical Engineering, Zhengzhou University, China, 2020 [41] Yao X Y, Li W H, Pan X G, Wang R. Multimodal multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for multiple path planning. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022, 169: Article No. 108145 -







 下载:
下载: