-
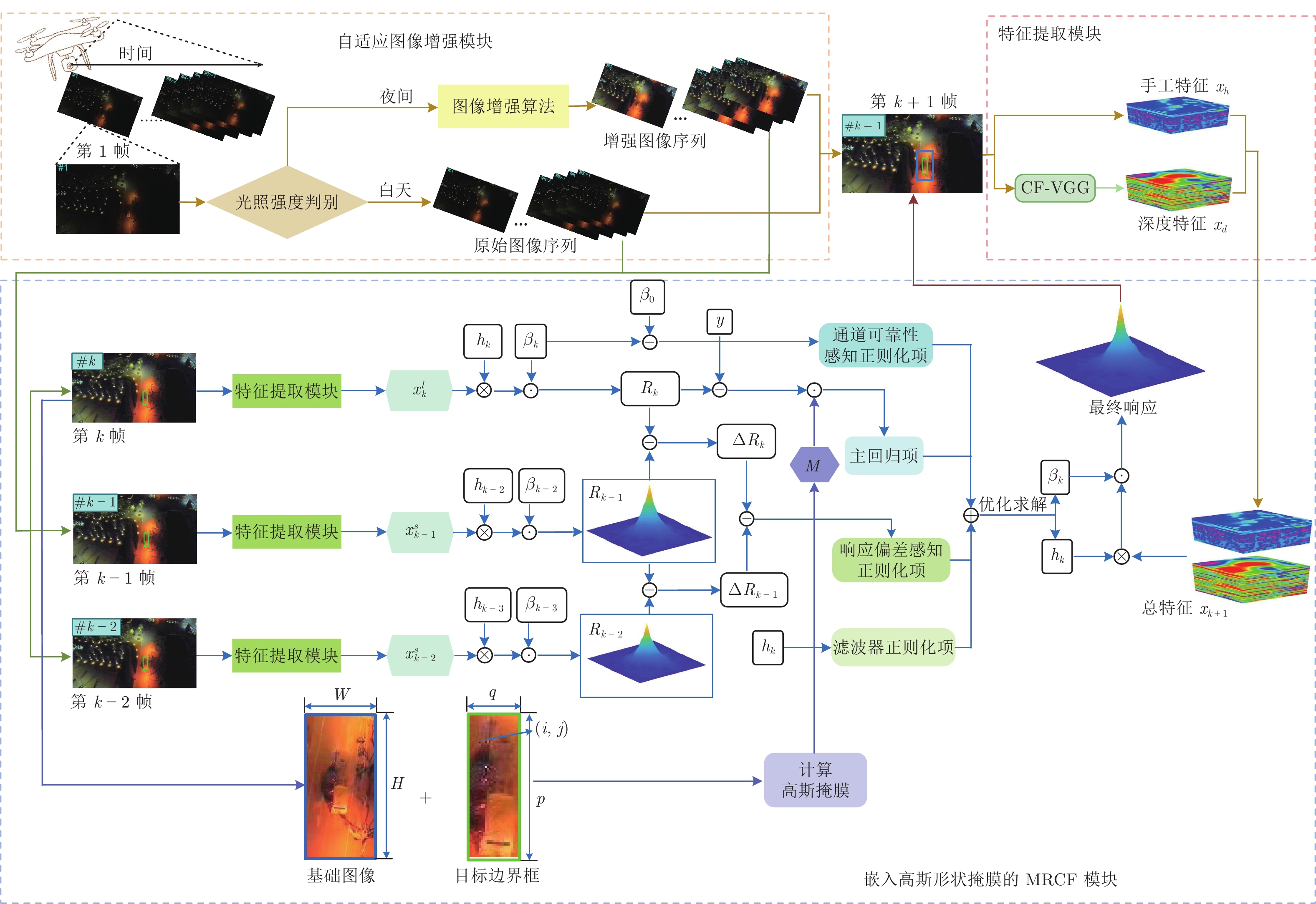
摘要: 相关滤波算法(Correlation filter, CF)已广泛应用于无人机目标跟踪. 然而, 受无人机 (Unmanned aerial vehicle, UAV) 平台本身计算性能的制约, 现有的无人机相关滤波跟踪算法大都仅采用手工特征来描述目标的外观, 难以获得目标的全面语义信息. 并且这些跟踪算法仅能较好地进行光照条件良好场景下的跟踪, 而在跟踪夜间场景下的目标时性能严重下降. 此外, 相关滤波跟踪器采用余弦窗口来抑制循环移位产生的边界效应, 缩小了样本提取区域, 产生了训练样本污染的问题, 这不可避免地降低了跟踪器的性能. 针对以上问题, 提出全天实时多正则化相关滤波算法(All-day and real-time multi-regularized correlation filter, AMRCF)跟踪无人机目标. 首先, 引入一个自适应图像增强模块, 在不影响图像各通道颜色比例的前提下, 对获得的图像进行增强, 以提高夜间目标跟踪性能. 其次, 引入一个轻量型的深度网络来提取目标的深度特征, 并与手工特征一起来表示目标的语义信息. 此外, 在算法框架中嵌入高斯形状掩膜, 在抑制边界效应的同时, 有效避免训练样本污染. 最后, 在5个公开的无人机基准数据集上进行充分的实验. 实验结果表明, 所提出的算法与多个先进的相关滤波跟踪器相比, 取得了有竞争力的结果, 且算法的实时速度约为25 fps, 能够胜任无人机的目标跟踪任务.Abstract: Correlation filter (CF) has been widely used in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) object tracking. Due to the computational limitation of the UAV platform, the existing UAV tracking algorithms rely heavily on the hand-crafted features, which cannot obtain all the semantic information of the target. Meanwhile, the existing tracking algorithms focus on the tracking of daytime targets, and ignore the tracking problem of nighttime targets. In addition, when the correlation filter-based tracker uses the cosine window to suppress the boundary effect caused by the cyclic shift, the sampling area is shrunk, which causes the contamination of training samples and inevitably deteriorates the performance of the tracker. Aiming at the above problems, we propose an all-day and real-time multi-regularized correlation filter (AMRCF) for UAV object tracking. Firstly, an adaptive image enhancement module is introduced to enhance the image without affecting its color ratio of each channel and improve the nighttime tracking performance. Secondly, a lightweight deep network is introduced to extract the deep features of the target and represent the semantic information together with the hand-crafted features. Thirdly, a Gaussian-shaped mask is embedded in the correlation filter framework, which can effectively avoid the contamination of training samples while suppressing the boundary effect. Finally, extensive experiments are conducted on five publicly available UAV benchmark datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves competitive result compared with several state-of-the-art correlation filter-based trackers, and the real-time speed is about 25 fps, which makes it competent for UAV object tracking task.
-
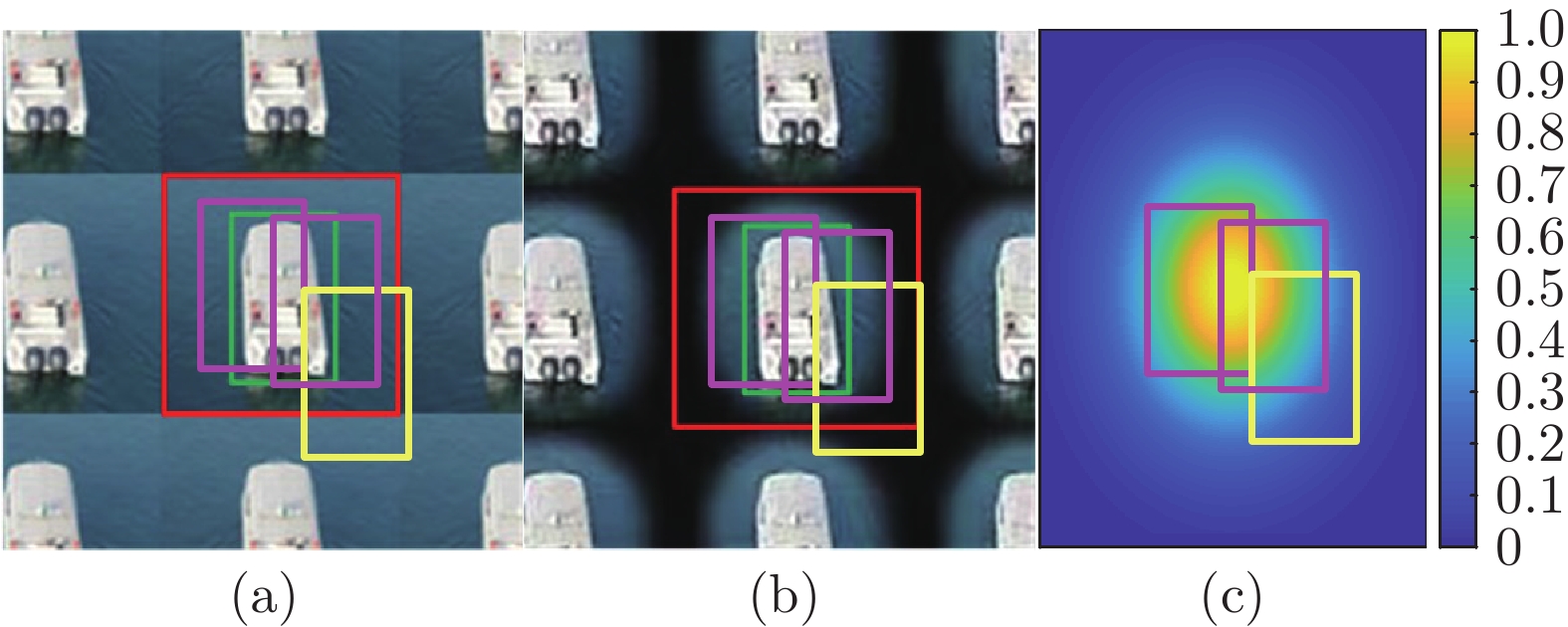
图 5 边界效应抑制可视化图((a)空间域循环移位产生的带有边界效应的训练样本; (b)加入余弦窗口后, 带有污染的训练样本; (c)高斯形状掩膜可视化图, 样本的中心距离图像中心越近, 其权重越大, 重要性越高, 反之则越低)
Fig. 5 Visualization of boundary effect suppression ((a) Training samples with boundary effect generated by cyclic shifts in the spatial domain; (b) Training samples with contamination after adding cosine window; (c) Gaussian-shaped mask visualization, the closer the center of the sample is to the center of the image, the higher the weight and importance, and vice versa)
表 1 消融实验结果对比
Table 1 Comparison of ablation experiment results
基准数据集 评价指标 Baseline Baseline+Ada Baseline+CF-VGG Baseline+M Baseline+Ada+CF-VGG Baseline+Ada+CF-VGG+M DTB70 精确度 0.666 0.666 0.689 0.656 0.689 $\underline{\underline {\boldsymbol{0.726}}} $ 成功率 0.466 0.466 0.479 0.457 0.479 $\underline{\underline {\boldsymbol{0.488}}} $ UAVDark135 精确度 0.593 0.602 0.598 0.590 0.608 $\underline{\underline {\boldsymbol{0.610}}} $ 成功率 0.455 0.463 0.462 0.458 0.461 $\underline{\underline {\boldsymbol{0.464}}} $ UAVTrack112 精确度 0.681 0.672 0.692 0.678 0.713 $\underline{\underline {{0.712} } }$ 成功率 0.467 0.463 0.469 0.466 0.481 $\underline{\underline {\boldsymbol{0.484}}} $ UAV123 精确度 0.693 0.693 0.689 0.674 0.708 $\underline{\underline {{0.694}}} $ 成功率 0.485 0.485 0.471 0.475 0.487 0.478 VisDrone-SOT2018 精确度 0.812 0.811 0.802 0.795 0.811 $ \underline{\underline{{\boldsymbol{0.816}}}} $ 成功率 0.600 0.600 0.591 0.584 0.596 0.598 表 2 消融实验帧率对比
Table 2 Frame rate comparison of ablation experiment
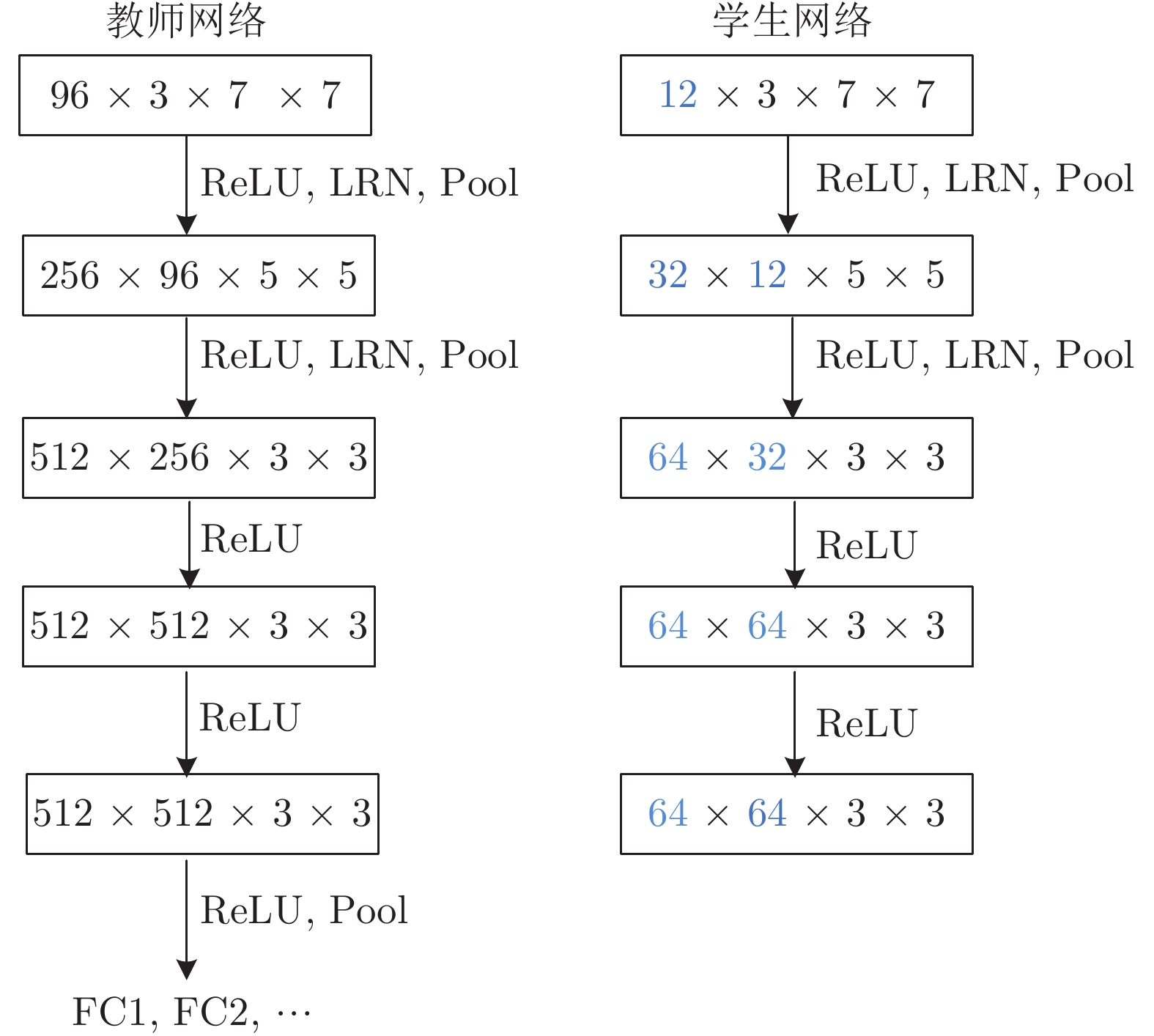
基准数据集 Baseline Baseline+Ada Baseline+CF-VGG Baseline+M Baseline+Ada+CF-VGG+M DTB70 34.2662 34.5329 27.2841 32.7516 26.56060 UAVDark135 25.9653 21.3622 22.5572 23.4383 14.59290 UAVTrack112 36.5963 31.9615 30.6200 34.6642 28.57300 UAV123 35.0628 34.3915 28.0824 34.6348 27.30980 VisDrone-SOT2018 33.3641 32.9790 27.1486 31.8434 25.77150 平均 33.0509 31.0454 27.1385 31.4665 24.56156 表 3 CF-VGG与教师网络VGG性能对比
Table 3 Comparison of performance between CF-VGG and teacher network VGG
基准数据集 评价指标 Baseline Baseline+Ada+
M+VGGBaseline+Ada+
M+CF-VGG精确度 0.6660 0.7080 0.7260 DTB70 成功率 0.4660 0.4670 0.4880 帧率 34.2662 13.5239 26.5606 精确度 0.5930 0.6040 0.6100 UAVDark135 成功率 0.4550 0.4630 0.4640 帧率 25.9653 9.2928 14.5929 精确度 0.6810 0.7110 0.7120 UAVTrack112 成功率 0.4670 0.4820 0.4840 帧率 36.5963 14.7906 28.5730 表 4 各跟踪算法在无人机目标跟踪基准上的帧率比较
Table 4 Comparison of frame rates of various tracking algorithms on UAV target tracking benchmarks
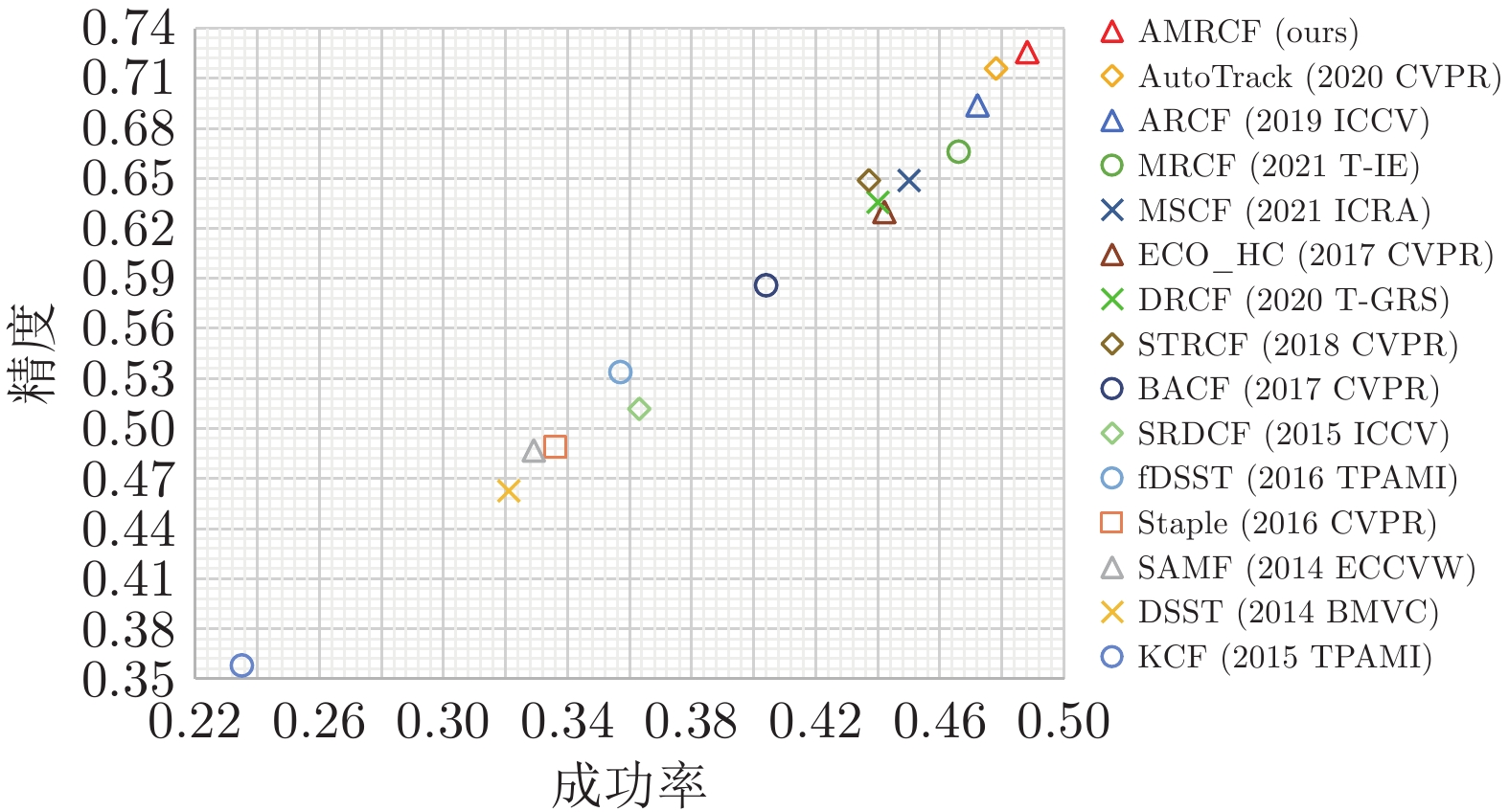
DTB70 UAVDark135 UAVTrack112 VisDrone-SOT2018 UAV123 平均 MRCF 34.2662 25.9653 36.5963 33.3641 35.0628 33.0509 MSCF 24.4487 20.0218 23.1446 24.8189 23.3937 23.1655 BACF 34.6232 23.7905 42.4856 37.0889 39.5027 35.4982 DSST 59.5299 25.2672 95.0388 61.7457 84.6391 65.2441 ECO_HC 50.2676 46.2619 60.8356 58.2079 59.6936 55.0533 fDSST $\underline{\underline {137.9438}} $ $\underline{\underline {165.0210}} $ $\underline{\underline {178.2769}} $ $\underline{\underline {146.0930}} $ $\underline{\underline {164.2684}} $ $\underline{\underline {158.3206}} $ KCF 546.8368 291.7405 970.2931 619.1967 894.7070 664.5548 SAMF 8.0580 5.5381 7.6382 7.5533 9.9559 7.7487 SRDCF 8.0273 5.5125 10.4828 8.0745 10.2923 8.4779 STRCF 20.4708 15.3309 21.9033 20.9129 21.2095 19.9655 AutoTrack 38.9684 33.1091 41.0309 41.8124 40.8652 39.1572 ARCF 21.8288 17.4036 22.7775 21.1463 22.4400 21.1192 DRCF 29.9372 22.0180 31.8315 30.2080 31.9774 29.1944 Staple 76.8257 59.0852 77.7228 90.2850 79.1470 76.6131 AMRCF 26.5606 14.5929 28.5730 25.7715 27.3098 24.5616 表 5 AMRCF与无人机目标跟踪算法的性能比较
Table 5 Performance comparison of AMRCF and UAV target tracking algorithms
基准数据集 评价指标 MRCF MSCF AutoTrack DRCF ARCF AMRCF DTB70 精确度 0.666 0.649 $\underline{\underline {0.716}} $ 0.636 0.694 0.726 成功率 0.466 0.450 $\underline{\underline {0.478}} $ 0.440 0.472 0.488 UAVDark135 精确度 0.593 $\underline{\underline {0.600}} $ 0.599 0.481 0.584 0.610 成功率 0.455 $\underline{\underline {0.459}} $ 0.454 0.388 0.448 0.464 UAVTrack112 精确度 0.681 0.688 $\underline{\underline {0.695}} $ 0.675 0.672 0.712 成功率 0.467 $\underline{\underline {0.468}} $ 0.464 0.458 0.457 0.484 UAV123 精确度 0.693 0.690 0.689 0.700 0.671 $\underline{\underline {0.694}} $ 成功率 0.485 $\underline{\underline {0.483}} $ 0.472 0.482 0.468 0.478 VisDrone-SOT2018 精确度 $\underline{\underline {0.812}} $ 0.776 0.788 0.782 0.797 0.816 成功率 0.600 0.570 0.573 0.573 0.584 $\underline{\underline {0.598}} $ 表 6 各算法在DTB70基准不同属性上的性能比较
Table 6 Performance comparison of each algorithm on different attributes of the DTB70 benchmark
属性 评价指标 SRDCF STRCF Staple SAMF ECO_HC DSST fDSST SV 精确度 0.462 0.568 0.489 0.456 0.538 0.473 0.543 成功率 0.359 0.417 0.349 0.339 0.431 0.361 0.378 ARV 精确度 0.343 0.492 0.430 0.375 0.487 0.366 0.405 成功率 0.268 0.347 0.314 0.289 0.361 0.290 0.275 OCC 精确度 0.478 0.617 0.528 0.500 0.639 0.423 0.467 成功率 0.310 0.400 0.349 0.321 $\underline{\underline {0.430}} $ 0.275 0.310 DEF 精确度 0.289 0.554 0.419 0.387 0.561 0.339 0.390 成功率 0.208 0.390 0.283 0.293 0.391 0.261 0.243 FCM 精确度 0.554 0.713 0.494 0.499 0.678 0.485 0.587 成功率 0.398 0.467 0.331 0.333 0.461 0.322 0.388 IR 精确度 0.419 0.586 0.457 0.409 0.548 0.400 0.489 成功率 0.312 0.393 0.318 0.301 0.393 0.282 0.326 OR 精确度 0.220 0.385 0.371 0.225 0.390 0.237 0.226 成功率 0.204 0.257 0.283 0.218 0.271 0.255 0.153 OV 精确度 0.552 0.652 0.420 0.537 0.515 0.474 0.564 成功率 0.378 0.424 0.278 0.324 0.380 0.309 0.381 BC 精确度 0.393 0.611 0.393 0.352 0.553 0.312 0.356 成功率 0.256 0.369 0.231 0.221 0.335 0.198 0.225 SOA 精确度 0.569 0.677 0.529 0.499 0.654 0.528 0.562 成功率 0.379 0.447 0.346 0.319 0.445 0.334 0.351 属性 评价指标 BACF ARCF AutoTrack DRCF MSCF MRCF AMRCF SV 精确度 0.545 $\underline{\underline {0.707}} $ 0.688 0.574 0.610 0.613 0.735 成功率 0.398 0.487 $\underline{\underline {0.493}} $ 0.446 0.450 0.451 0.522 ARV 精确度 0.370 $\underline{\underline {0.608}} $ 0.605 0.526 0.542 0.556 0.661 成功率 0.274 0.393 $\underline{\underline {0.405}} $ 0.377 0.377 0.384 0.442 OCC 精确度 0.556 $\underline{\underline {0.638}} $ 0.631 0.585 0.585 0.587 0.624 成功率 0.368 0.446 0.415 0.414 0.412 0.418 0.406 DEF 精确度 0.410 0.654 $\underline{\underline {0.670}} $ 0.559 0.610 0.628 0.748 成功率 0.282 0.426 $\underline{\underline {0.452}} $ 0.392 0.419 0.416 0.492 FCM 精确度 0.640 $\underline{\underline {0.742}} $ 0.744 0.699 0.694 0.719 0.738 成功率 0.434 0.496 0.496 0.472 0.471 0.496 0.494 IR 精确度 0.537 0.636 $\underline{\underline {0.684}} $ 0.594 0.603 0.615 0.696 成功率 0.374 0.429 $\underline{\underline {0.454}} $ 0.413 0.416 0.429 0.466 OR 精确度 0.270 $\underline{\underline {0.451}} $ 0.439 0.346 0.385 0.412 0.524 成功率 0.223 0.321 $\underline{\underline {0.343}} $ 0.263 0.297 0.323 0.369 OV 精确度 0.575 0.642 0.690 0.611 0.629 0.675 $\underline{\underline {0.680}} $ 成功率 0.383 0.427 0.407 0.430 0.414 0.448 $\underline{\underline {0.435}} $ BC 精确度 0.491 0.585 $\underline{\underline {0.635}} $ 0.594 0.610 0.616 0.640 成功率 0.311 0.377 0.394 0.365 0.376 $\underline{\underline {0.399}} $ 0.400 SOA 精确度 0.641 $\underline{\underline {0.730}} $ 0.731 0.700 0.678 0.695 0.694 成功率 0.421 0.484 $\underline{\underline {0.473}} $ 0.453 0.452 0.471 0.447 -
[1] Zhang F, Ma S P, Yu L X, Zhang Y L, Qiu Z L, Li Z Y. Learning future-aware correlation filters for efficient UAV tracking. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(20): Article No. 4111 doi: 10.3390/rs13204111 [2] 孟琭, 杨旭. 目标跟踪算法综述. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1244-1260Meng Lu, Yang Xu. A survey of object tracking algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1244-1260 [3] Xu L B, Li Q L, Jiang J, Zou G F, Liu Z, Gao M L. Adaptive spatio-temporal regularized correlation filters for UAV-based tracking. In: Proceedings of the 15th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV). Kyoto, Japan: Springer, 2020. 391−404 [4] Henriques J F, Caseiro R, Martins P, Batista J. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583-596 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390 [5] Danelljan M, Hager G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 4310−4318 [6] 熊丹, 卢惠民, 肖军浩, 郑志强. 具有尺度和旋转适应性的长时间目标跟踪. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(2): 289-304Xiong Dan, Lu Hui-Min, Xiao Jun-Hao, Zheng Zhi-Qiang. Robust long-term object tracking with adaptive scale and rotation estimation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 289-304 [7] 张伟俊, 钟胜, 徐文辉, Wu Ying. 融合显著性与运动信息的相关滤波跟踪算法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(7): 1572-1588Zhang Wei-Jun, Zhong Sheng, Xu Wen-Hui, Wu Ying. Correlation filter based visual tracking integrating saliency and motion cues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1572-1588 [8] Galoogahi H K, Fagg A, Lucey S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1144−1152 [9] Wu X D, Xu J, Zhu Z Y, Wang Y N, Zhang Q, Tang S M, et al. Correlation filter tracking algorithm based on spatial-temporal regularization and context awareness. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52: 17772-17783 doi: 10.1007/s10489-022-03458-8 [10] 蒲磊, 冯新喜, 侯志强, 查宇飞, 余旺盛. 基于深度空间正则化的相关滤波跟踪算法. 电子学报, 2020, 48(10): 2025-2032Pu Lei, Feng Xin-Xi, Hou Zhi-Qiang, Cha Yu-Fei, Yu Wang-Sheng. Correlation filter tracking based on deep spatial regularization. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(10): 2025-2032 [11] Wang F S, Yin S S, Mbelwa J T, Sun F M. Context and saliency aware correlation filter for visual target tracking. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81: 27879-27893 doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12760-z [12] Yuan D, Chang X J, Li Z H, He Z Y. Learning adaptive spatial-temporal context-aware correlation filters for UAV tracking. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2022, 18(3): Article NO. 70 [13] Wang L, Li J, Huang B, Chen J, Li X, Wang J, et al. Auto-perceiving correlation filter for uav tracking. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(9): 5748-5761 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3155731 [14] 丁新尧, 张鑫. 基于显著性特征的选择性目标跟踪算法. 电子学报, 2020, 48(1): 118-123Ding Xin-Yao, Zhang Xin. Visual tracking with salient features and selective mechanism. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(1): 118-123 [15] Bolme D S, Beveridge J R, Draper B A, Lui Y M. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 2544−2550 [16] Wang Y B, Wang F S, Wang C, He J J, Sun F M. Learning saliency-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. The Computer Journal, 2022, 65(7): 1846-1859 doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxab026 [17] 蒲磊, 冯新喜, 侯志强, 余旺盛. 基于二阶池化网络的鲁棒视觉跟踪算法. 电子学报, 2020, 48(8): 1472-1478Pu Lei, Feng Xin-Xi, Hou Zhi-Qiang, Yu Wang-Sheng. Robust visual tracking based on second order pooling network. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(8): 1472-1478 [18] Ma C, Huang J B, Yang X K, Yang M H. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 3074−3082 [19] Javed S, Danelljan M, Khan F S, Khan M H, Felsberg M, Matas J. Visual object tracking with discriminative filters and Siamese networks: A survey and outlook. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(5): 6552-6574 [20] Zheng G Z, Fu C H, Ye J J, Lin F L, Ding F Q. Mutation sensitive correlation filter for real-time UAV tracking with adaptive hybrid label. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2021. 503−509 [21] Ye J J, Fu C H, Lin F L, Ding F Q, An S, Lu G. Multi-regularized correlation filter for UAV tracking and self-localization. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(6): 6004-6014 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3088366 [22] Li Y M, Fu C H, Ding F Q, Huang Z Y, Lu G. AutoTrack: Towards high-performance visual tracking for UAV with automatic spatio-temporal regularization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 11920−11929 [23] Li S Y, Yeung D Y. Visual object tracking for unmanned aerial vehicles: A benchmark and new motion models. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-first AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, California, USA: AAAI, 2017. 4140−4146 [24] Wang N, Zhou W G, Song Y B, Ma C, Li H Q. Real-time correlation tracking via joint model compression and transfer. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 6123-6135 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2989544 [25] Fu C H, Cao Z A, Li Y M, Ye J J, Feng C. Onboard real-time aerial tracking with efficient Siamese anchor proposal network. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: Article No. 5606913 [26] Li B W, Fu C H, Ding F Q, Ye J J, Lin F L. All-day object tracking for unmanned aerial vehicle. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(8): 4515-4529 doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3162892 [27] Wen L Y, Zhu P F, Du D W, Bian X, Ling H B, Hu Q H, et al. VisDrone-SOT2018: The vision meets drone single-object tracking challenge results. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 469−495 [28] Mueller M, Smith N, Ghanem B. A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 445−461 [29] Henriques J F, Caseiro R, Martins P, Batista J. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Florence, Italy: Springer, 2012. 702−715 [30] Danelljan M, Hager G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. Discriminative scale space tracking. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(8): 1561-1575 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2609928 [31] Wang C, Zhang L, Xie L H, Yuan J S. Kernel cross-correlator. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New Orleans, USA: AAAI, 2018. 4179−4186 [32] Zhang Y, Liu G X, Zhang H Y, Huang H L. Robust visual tracker combining temporal consistent constraint and adaptive spatial regularization. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(14): 8355-8374 doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05589-w [33] Deng C W, He S C, Han Y Q, Zhao B Y. Learning dynamic spatial-temporal regularization for UAV object tracking. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1230-1234 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3086675 [34] Li F, Tian C, Zuo W M, Zhang L, Yang M H. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4904−4913 [35] Xu T Y, Feng Z H, Wu X J, Kittler J. Joint group feature selection and discriminative filter learning for robust visual object tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 7950−7960 [36] Feng S, Hu K L, Fan E, Zhao L P, Wu C D. Kalman filter for spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 3263-3278 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3060164 [37] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. ECO: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6931−6939 [38] Zhao J W, Wei F Y, Chen N N, Zhou Z H. Spatial and long-short temporal attention correlation filters for visual tracking. IET Image Processing, 2022, 16(11): 3011-3024 doi: 10.1049/ipr2.12535 [39] Hua X, Wang X Q, Rui T, Shao F M, Wang D. Light-weight UAV object tracking network based on strategy gradient and attention mechanism. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 224: Article No. 107071 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107071 [40] Zhang Z P, Liu Y F, Li B, Hu W M, Peng H W. Toward accurate pixelwise object tracking via attention retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 8553-8566 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3117077 [41] Xu T Y, Feng Z H, Wu X J, Kittler J. Adaptive channel selection for robust visual object tracking with discriminative correlation filters. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129: 1359-1375 doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01435-1 [42] Zhu X F, Wu X J, Xu T Y, Feng Z H, Kittler J. Robust visual object tracking via adaptive attribute-aware discriminative correlation filters. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2022, 24: 301-312 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2021.3050073 [43] 王科平, 朱朋飞, 杨艺, 费树岷. 多时空感知相关滤波融合的目标跟踪算法. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2020, 32(11): 1840-1852Wang Ke-Ping, Zhu Peng-Fei, Yang Yi, Fei Shu-Min. Target tracking algorithm based on multi-time-space perception correlation filters fusion. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2020, 32(11): 1840-1852 [44] Li F, Wu X H, Zuo W M, Zhang D, Zhang L. Remove cosine window from correlation filter-based visual trackers: When and how. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7045-7060 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2997521 [45] Tang M, Zheng L Y, Yu B, Wang J Q. Fast kernelized correlation filter without boundary effect. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE, 2021. 2998−3007 [46] Fu C H, Xu J T, Lin F L, Guo F Y, Liu T C, Zhang Z J. Object saliency-aware dual regularized correlation filter for real-time aerial tracking. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(12): 8940-8951 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2992301 [47] Hinton G, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1503.02531, 2015. [48] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115: 211-252 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [49] Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, Peleato B, Eckstein J. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1-122 [50] Huang Z Y, Fu C H, Li Y M, Lin F L, Lu P. Learning aberrance repressed correlation filters for real-time UAV tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 2891−2900 [51] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Golodetz S, Miksik O, Torr P H S. Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1401−1409 [52] Li Y, Zhu J K. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerlan: Springer, 2014. 254−265 [53] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 2411−2418 -




 下载:
下载: