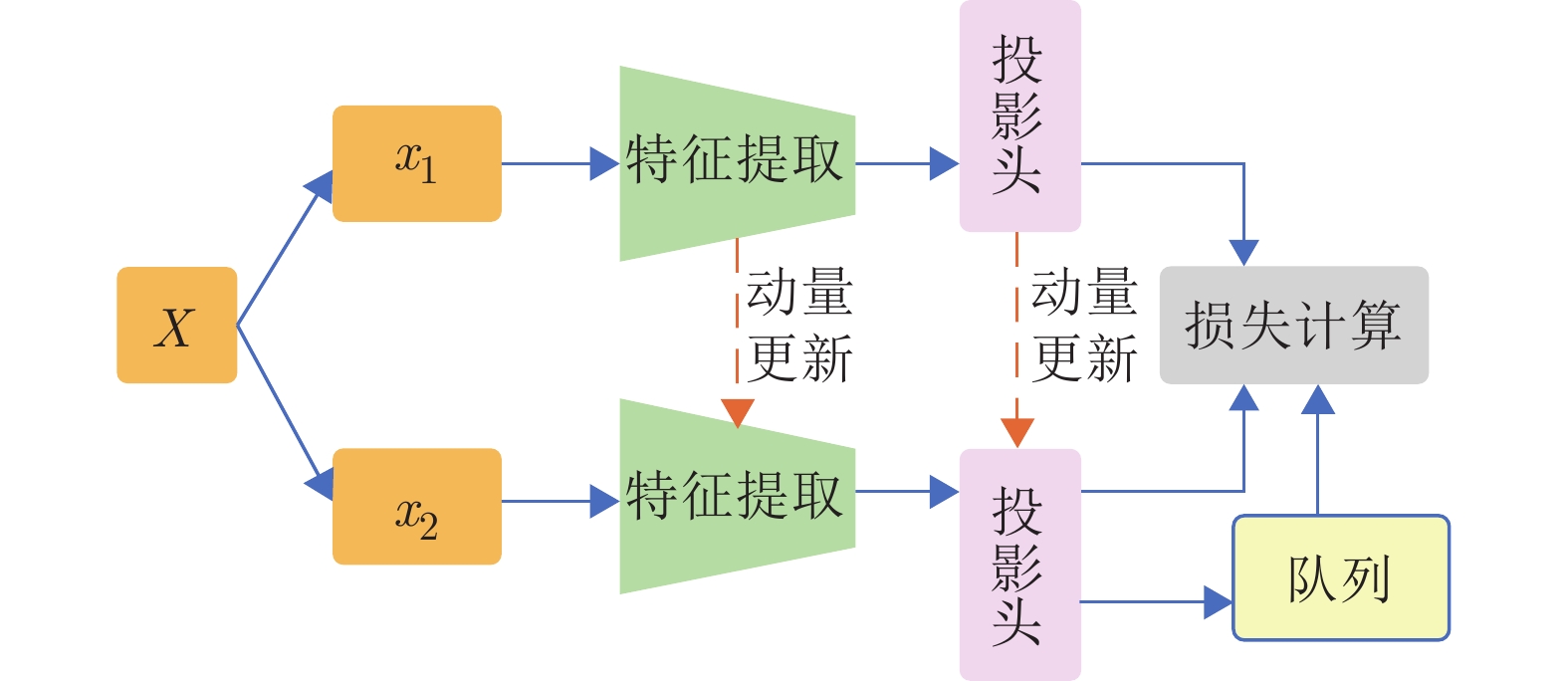
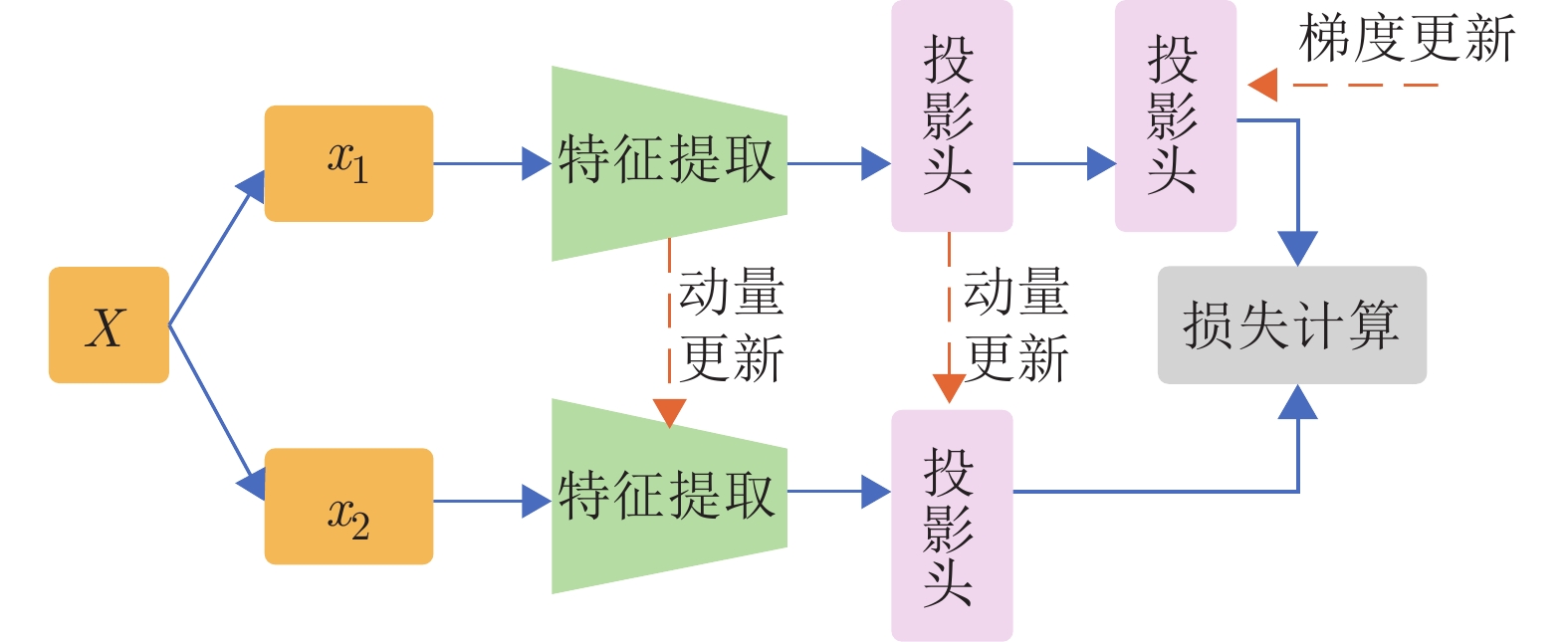
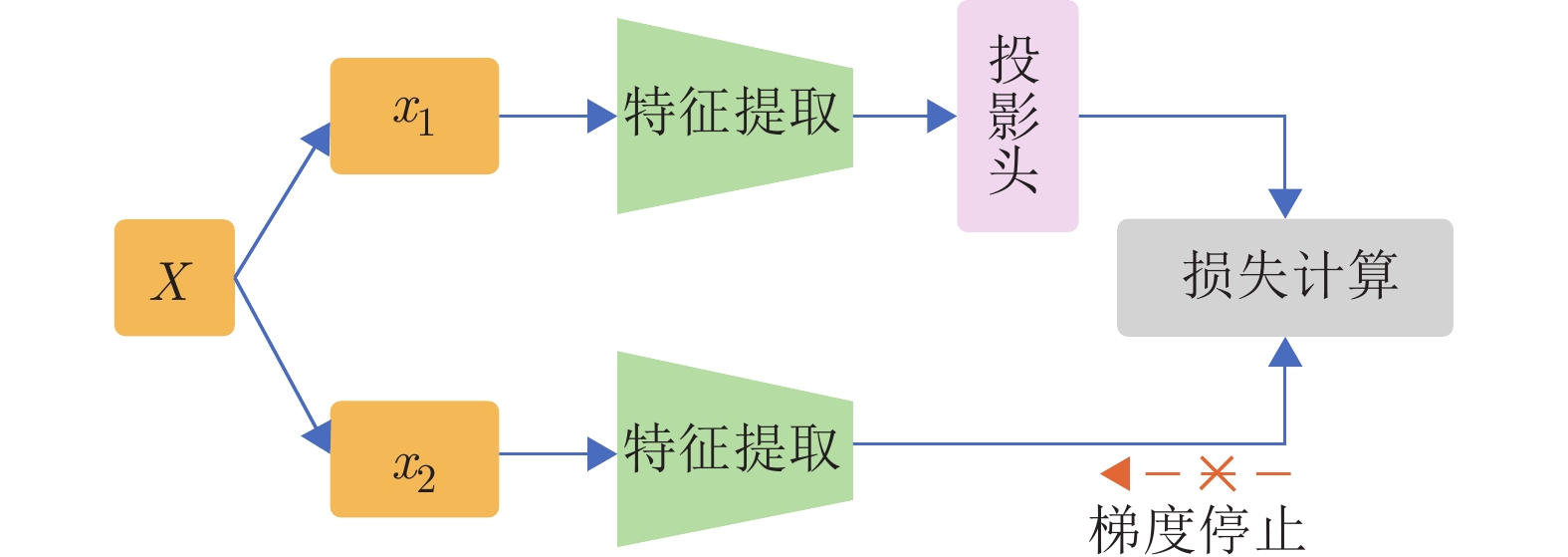
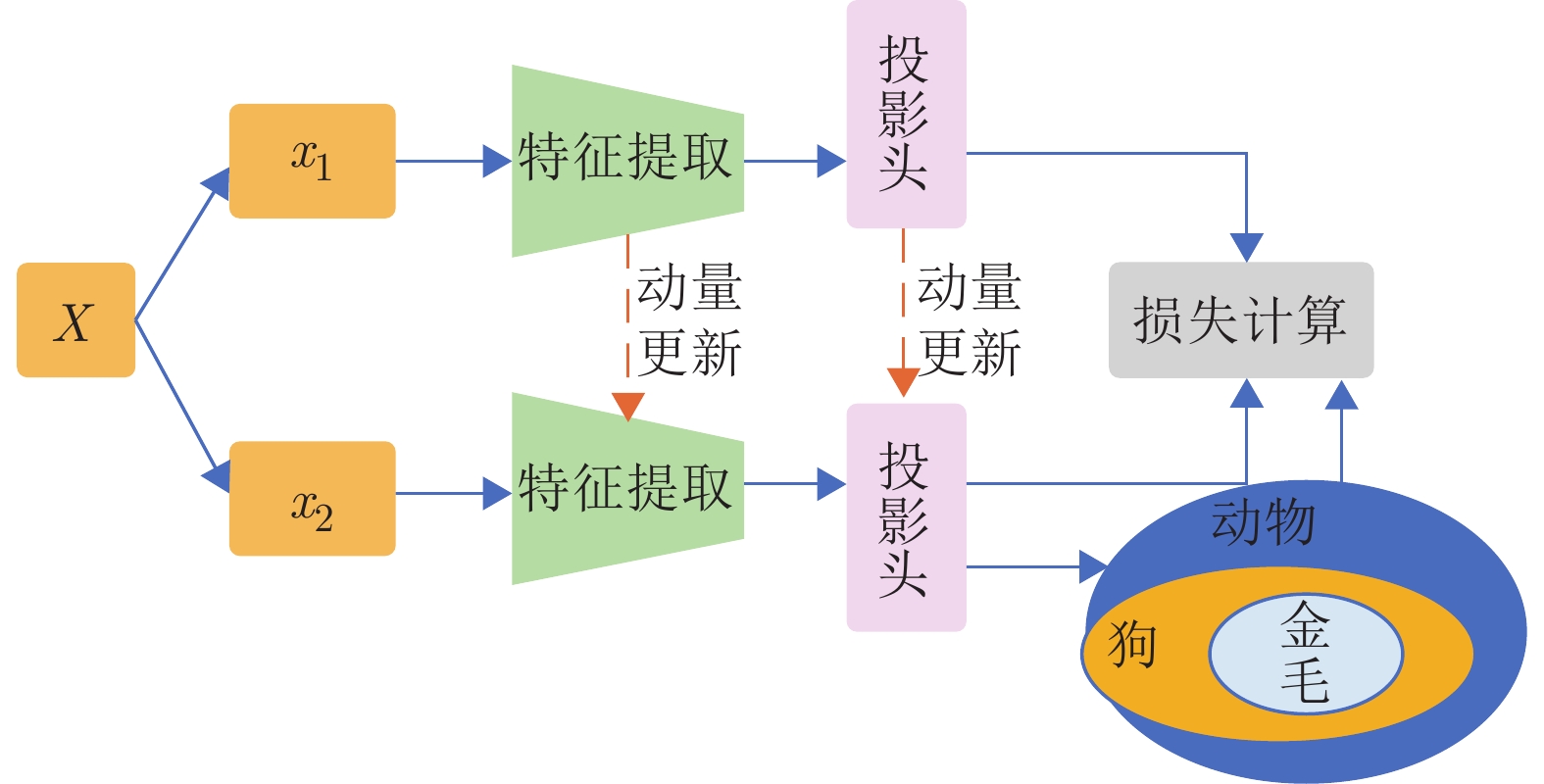
-
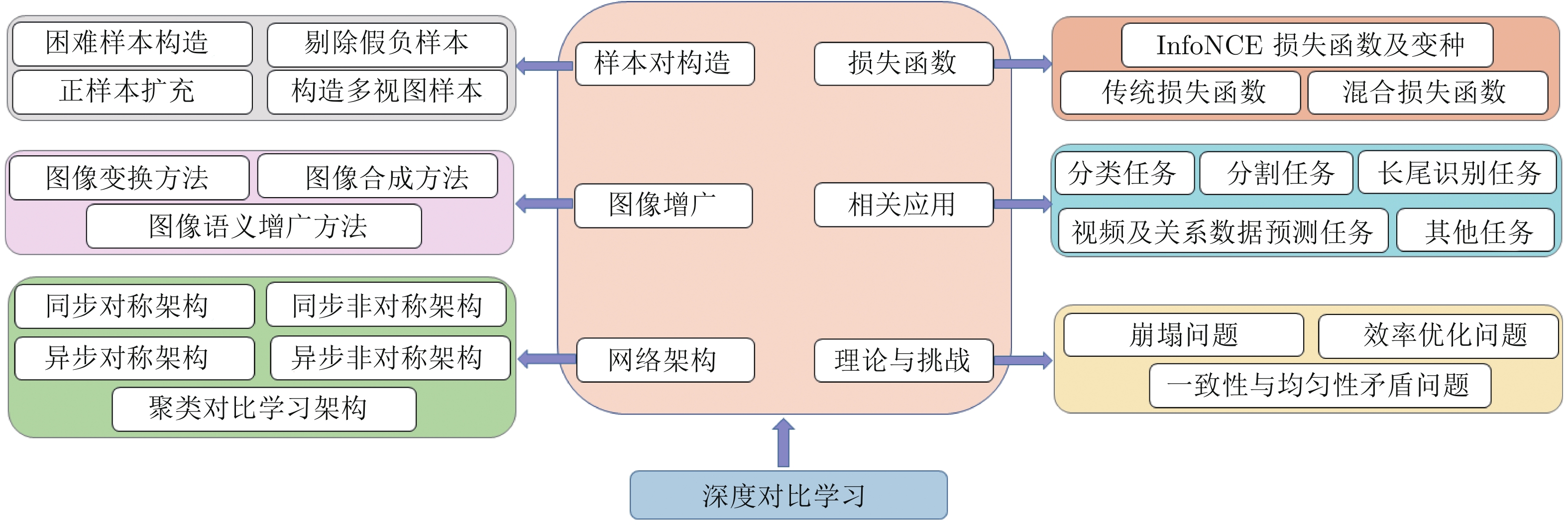
摘要: 在深度学习中, 如何利用大量、易获取的无标注数据增强神经网络模型的特征表达能力, 是一个具有重要意义的研究问题, 而对比学习是解决该问题的有效方法之一, 近年来得到了学术界的广泛关注, 涌现出一大批新的研究方法和成果. 本文综合考察对比学习近年的发展和进步, 提出一种新的面向对比学习的归类方法, 该方法将现有对比学习方法归纳为5类, 包括: 1) 样本对构造; 2) 图像增广; 3) 网络架构; 4) 损失函数; 5) 应用. 基于提出的归类方法, 对现有对比研究成果进行系统综述, 并评述代表性方法的技术特点和区别, 系统对比分析现有对比学习方法在不同基准数据集上的性能表现. 本文还将梳理对比学习的学术发展史, 并探讨对比学习与自监督学习、度量学习的区别和联系. 最后, 本文将讨论对比学习的现存挑战, 并展望未来发展方向和趋势.Abstract: In deep learning, it has been a crucial research concern on how to make use of the vast amount of unlabeled data to enhance the feature extraction capability of deep neural networks, for which contrastive learning is an effective approach. It has attracted significant research effort in the past few years, and a large number of contrastive learning methods have been proposed. In this paper, we survey recent advances and progress in contrastive learning in a comprehensive way. We first propose a new taxonomy for contrastive learning, in which we divide existing methods into 5 categories, including 1) sample pair construction methods, 2) image augmentation methods, 3) network architecture level methods, 4) loss function level methods, and 5) applications. Based on our proposed taxonomy, we systematically review the methods in each category, and analyze the characteristics and differences of representative methods. Moreover, we report and compare the performance of different contrastive learning methods on the benchmark datasets. We also retrospect the history of contrastive learning and discuss the differences and connections among contrastive learning, self-supervised learning, and metric learning. Finally, we discuss remaining issues and challenges in contrastive learning and outlook its future directions.
-
Key words:
- Contrastive learning /
- deep learning /
- feature extraction /
- self-supervised learning /
- metric learning
-
表 1 对比学习常用数据集总结
Table 1 Summary of common datasets
表 2 本文所用符号总结
Table 2 Summary of the symbols used in this paper
符号 说明 $X$ 数据集合, 小写为其中的数据 $Y$ 标签集合, 小写为其中的数据 $T$ 图像增广方法 $f$ 特征提取网络 $g$ 投影头 $s$ 相似度度量函数 $h$ 特征向量, $h = f(x)$ $z$ 投影向量, $z = g(h)$ $c$ 聚类中心向量 $\tau$ 温度系数 表 3 InfoNCE损失函数及其变种
Table 3 InfoNCE loss and some varieties based on InfoNCE
损失名 文献 年份 会议/刊物 公式 主要改进 InfoNCE [7] 2019 arXiv $-\ln \dfrac{{\exp (s(q,{h^ + }))}}{{\sum\nolimits_{{x_i} \in X} {\exp (s(q,{h_i}))} }}$ 初始的InfoNCE损失. 文献[3, 9, 30−31, 38]等均采用InfoNCE损失函数. ProtoNCE [63] 2021 ICLR $ - \ln \dfrac{{\exp (s({z_i},{c_i})/\tau )}}{{\sum\limits_{j = 0}^r {\exp (s({z_i},{c_j})/\tau )} }}$ 从两个样本增广间的对比变为样本增广与聚类中心的对比. 注: ${c_i}$, ${c_j}$为聚类中心.
总损失包括实例间的对比和实例−原型对比损失, 此处只列出实例-原型对比损失.DCL [71] 2021 ECCV $- \dfrac{ {s({z_i},z_i^ + )} }{\tau } + \ln \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^{2N} { {1_{[j \ne i]} } } \exp (s({z_i},{z_j})/\tau)$ 去除负正耦合系数后通过化简得到该损失. DirectNCE [72] 2022 ICLR $-\ln \dfrac{\exp s((\widehat{h}'_i, \widehat{h}'^+_{i})/\tau)}{\sum\nolimits_j \exp s((\widehat{h}'_i, \widehat{h}'^+_{i})/\tau)}$ $\widehat{h}_i' = \widehat{h}_i'[0:d]$, 即取特征向量的前$d$个维度. FNCL [35] 2022 WACV $- \ln \dfrac{{\exp (s({z_i},z_i^ + )/\tau )}}{{\sum\limits_{j = 1}^{2N} {{1_{[j \ne i,j \ne {F_i}]}}\exp (s({z_i},{z_j})/\tau)}}}$ ${F_i}$为第$i$个样本的假负样本集. SCL [8] 2020 NIPS $- \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i \in I} {\dfrac{1}{ {p(i)} } } \sum\limits_{p \in p(i)} {\ln \dfrac{ {\exp (s({z_i},{z_p})/\tau )} }{ {\sum\nolimits_{a \in A(i)} {\exp (s({z_i},{z_a})/\tau )} } } }$ 将标签引入对比学习, $P(i)$是与第$i$个样本相同类的数据集合. 表 4 对比学习方法整体归类分析
Table 4 Analysis of different contrastive learning methods based on our proposed taxonomy
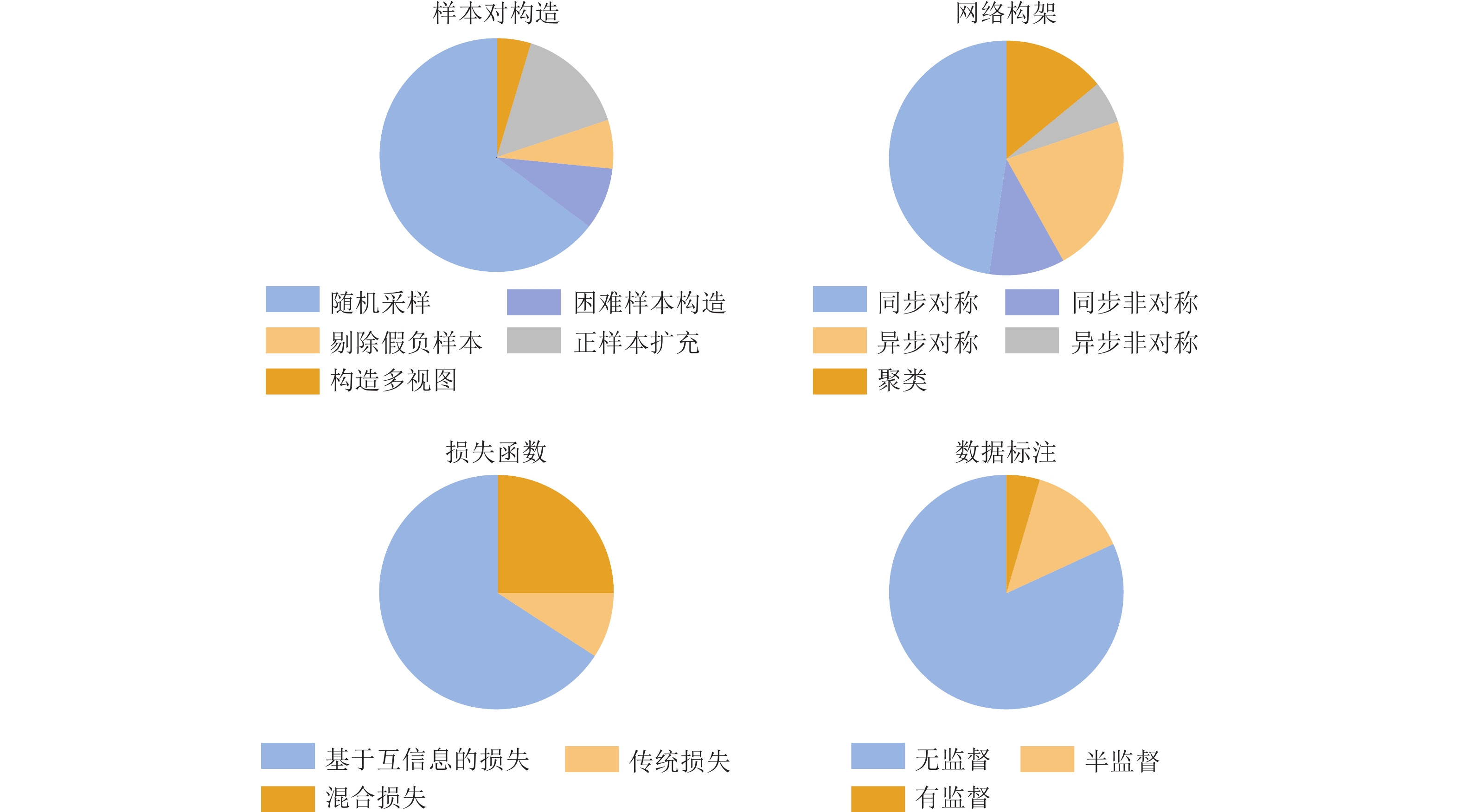
文献 年份 会议/刊物 样本对构造 图像增广 网络架构 损失函数 数据标注 [7] 2019 arXiv 随机采样 图像变换 同步非对称 InfoNCE类 无 [2] 2020 ICML 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [3] 2020 CVPR 随机采样 图像变换 异步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [4] 2020 NIPS 随机采样 图像变换 异步非对称 传统损失 无 [5] 2020 NIPS 随机采样 图像变换 聚类/同步对称 传统损失 无 [8] 2020 NIPS 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 有 [9] 2020 NIPS 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 混合损失 部分 [33] 2020 NIPS 困难样本构造 图像变换 异步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [36] 2020 NIPS 剔除假负样本 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [37] 2020 arXiv 正样本扩充 图像变换 异步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [42] 2020 NIPS 正样本扩充 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [45] 2020 ECCV 构造多视图 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [52] 2020 NIPS 随机采样 语义增广 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [55] 2020 CVPR 随机采样 图像变换 同步非对称 InfoNCE类 无 [57] 2020 NIPS 随机采样 图像变换 同步非对称 InfoNCE类 无 [70] 2020 arXiv 随机采样 图像变换 异步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [109] 2020 ECCV 随机采样 图像变换 同步非对称 InfoNCE类 无 [6] 2021 CVPR 随机采样 图像变换 异步非对称 传统损失 无 [32] 2021 ICCV 困难样本构造 图像变换 异步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [34] 2021 CVPR 困难样本构造 图像变换 同步对称 混合损失 部分 [39] 2021 ICCV 正样本扩充 图像变换 异步对称 混合损失 无 [40] 2021 CVPR 正样本扩充 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [46] 2021 CVPRW 构造多视图 图像变换 同步对称 混合损失 无 [61] 2021 ICCV 随机采样 图像变换 异步非对称 InfoNCE类 无 [63] 2021 ICLR 随机采样 图像变换 聚类/异步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [64] 2021 CVPR 随机采样 图像变换 聚类架构 InfoNCE类 无 [66] 2021 AAAI 随机采样 图像变换 聚类/同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [77] 2021 CVPR 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 混合损失 有 [79] 2021 ICCV 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 混合损失 部分 [83] 2021 TGRS 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 混合损失 部分 [78] 2021 TGRS 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [85] 2021 CVPR 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [35] 2022 WACV 剔除假负样本 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [41] 2022 CVPR 正样本扩充 图像变换 同步非对称 混合损失 无 [43] 2022 ICLR 正样本扩充 图像变换 异步对称 混合损失 部分 [44] 2022 CVPR 正样本扩充 图像变换 同步对称 混合损失 部分 [47] 2022 CVPR 随机采样 图像变换 任意架构 InfoNCE类 无 [48] 2022 CVPR 随机采样 图像合成 异步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [54] 2022 TAI 随机采样 图像变换 同步非对称 InfoNCE类 无 [65] 2022 CVPR 剔除假负样本 图像变换 聚类/异步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [72] 2022 ICLR 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [76] 2022 AAAI 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 传统损失 无 [94] 2022 ICLR 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [98] 2022 CVPR 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 InfoNCE类 无 [103] 2022 ICLR 随机采样 图像变换 同步对称 混合损失 无 表 5 不同对比学习算法在ImageNet数据集上的分类效果
Table 5 The classification results of different contrastive learning methods on ImageNet
文献 主干网络 Top 1 (%) Top 5 (%) 数据标注 MoCov1[3] ResNet50 60.6 — 无 CPCv2[100] ResNet50 63.8 85.3 ResNet161 71.5 90.1 PCL[63] ResNet50 67.6 — SimCLR[2] ResNet50 69.3 89 MoCov2[70] ResNet50 71.1 — SimSiam[6] ResNet50 71.3 — BT[101] ResNet50 73.2 91 VICReg[103] ResNet50 73.2 91.1 HCSC[65] ResNet50 73.3 — MoCov3[61] ResNet50 73.8 — Transformer 76.5 — BYOL[4] ResNet50 74.3 91.6 SwAV[5] ResNet50 75.3 — DINO[59] ResNet50 75.3 Transormer 77 — TSC[96] ResNet50 77.1 — 有 SCL[8] ResNet50 78.7 94.3 PaCo[67] ResNet50 79.3 — 表 6 不同对比学习算法在各数据集上的迁移学习效果
Table 6 The transfer learning results of different contrastive learning methods on each dataset
文献 Food (%) Cifar10/Cifar100 (%) Birds (%) SUN (%) Cars (%) Aircraft (%) VOC (%) DTD (%) Pets (%) Caltech (%) Flowers (%) 线性评估 SimCLR[2] 68.4 90.6/71.6 37.4 58.8 50.3 50.3 80.5 74.5 83.6 90.3 91.2 SimCLRv2[9] 73.9 92.4/76 44.7 61 54.9 51.1 81.2 76.5 85 91.2 93.5 BYOL[4] 75.3 91.3/78.4 57.2 62.2 67.8 60.6 82.5 75.5 90.4 94.2 96.1 微调评估 MMCL[76] 82.4 96.24/82.1 — — 89.2 85.4 — 73.5 — 87.8 95.2 SimCLR[2] 88.2 97.7/85.9 75.9 63.5 91.3 88.1 84.1 73.2 89.2 92.1 97 SimCLRv2[9] 88.2 97.5/86 74.9 64.6 91.8 87.6 84.1 74.7 89.9 92.3 97.2 BYOL[4] 88.5 97.8/86.1 76.3 63.7 91.6 88.1 85.4 76.2 91.7 93.8 97 FNC[35] 88.3 97.7/86.8 76.3 64.2 92 88.5 84.7 76 90.9 93.6 97.5 SCL[8] 87.2 97.42/84.3 75.2 58 91.7 84.1 85.2 74.6 93.5 91 96 表 7 不同半监督对比学习算法在ImageNet上的分类效果
Table 7 The classification results of different semi-supervised contrastive learning methods on ImageNet
-
[1] Jing L L, Tian Y L. Self-supervised visual feature learning with deep neural networks: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(11): 4037-4058 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2992393 [2] Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Vitual: ACM, 2020, 1597−1607 [3] He K M, Fan H Q, Wu Y X, Xie S N, Girshick R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 9726−9735 [4] Grill J B, Strub F, Altché F, Tallec C, Richemond P H, Buchatskaya E, et al. Bootstrap your own latent a new approach to self-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. 21271−21284 [5] Caron M, Misra I, Mairal J, Goyal P, Bojanowski P, Joulin A. Unsupervised learning of visual features by contrasting cluster assignments. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. 9912−9924 [6] Chen X L, He K M. Exploring simple Siamese representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 15745−15753 [7] Van Den Oord A, Li Y Z, Vinyals O. Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.03748, January 22, 2019 [8] Khosla P, Teterwak P, Wang C, et al. Supervised contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 18661−18673 [9] Chen T, Kornblith S, Swersky K, Norouzi M, Hinton G. Big self-supervised models are strong semi-supervised learners. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 1865 [10] Jaiswal A, Babu A R, Zadeh M Z, Banerjee D, Makedon F. A survey on contrastive self-supervised learning. Technologies, 2020, 9(1): 2 doi: 10.3390/technologies9010002 [11] Le-Khac P H, Healy G, Smeaton A F. Contrastive representation learning: A framework and review. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 193907-193934 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3031549 [12] Liu X, Zhang F J, Hou Z Y, Mian L, Wang Z Y, Zhang J, et al. Self-supervised learning: Generative or contrastive. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2021, 35(1): 857-576 [13] Hadsell R, Chopra S, LeCun Y. Dimensionality reduction by learning an invariant mapping. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York, USA: IEEE, 2006. 1735−1742 [14] Wu Z R, Xiong Y J, Yu S X, Lin D H. Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance discrimination. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Salt Lake City, USA: 2018. 3733−3742 [15] Bromley J, Guyon I, LeCun Y, Säckinger E, Shah R. Signature verification using a “Siamese” time delay neural network. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 1993. 737−744 [16] Li D W, Tian Y J. Survey and experimental study on metric learning methods. Neural Networks, 2018, 105: 447-462 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2018.06.003 [17] Jia D, Wei D, Richard S, Li J L, Kai L, Li F F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, USA: IEEE, 2009. 248−255 [18] Krizhevsky A. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images [Master thesis], University of Toronto, Canada, 2009 [19] Bossard L, Guillaumin M, Van Gool L. Food-101-mining discriminative components with random forests. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 446−461 [20] Berg T, Liu J X, Lee S W, Alexander M L, Jacobs D W, Belhumeur P N. Birdsnap: Large-scale fine-grained visual categorization of birds. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 2019−2026 [21] Xiao J X, Hays J, Ehinger K A, Oliva A, Torralba A. SUN database: Large-scale scene recognition from abbey to zoo. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 3485−3492 [22] Jonathan K, Michael S, Jia D, and Li F F. 3D object representations for fine-grained categorization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV). Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013: 554−561 [23] Maji S, Rahtu E, Kannala J, Blaschko M, Vedaldi A. Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1306.5151, June 6, 2013 [24] Cimpoi M, Maji S, Kokkinos I, Mohamed S, Vedaldi A. Describing textures in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 3606−3613 [25] Parkhi O M, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A, Jawahar C V. Cats and dogs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 3498−3505 [26] Li F F, Rob F, Pietro P. Learning generative visual models from few training examples: An incremental bayesian approach tested on 101 object categories. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (CVPR-W). Washington, USA: IEEE, 2004: 178−178 [27] Nilsback M E, Zisserman A. Automated flower classification over a large number of classes. In: Proceedings of the Sixth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics & Image Processing (ICVGIP). Bhubaneswar, India: IEEE, 2008. 722−729 [28] Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams C K I, Winn J, Zisserman A. The PASCAL visual object classes (VOC) challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303-338 doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [29] Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, et al. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 740−755 [30] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [31] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A N, et al. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 6000−6010 [32] Zhu R, Zhao B C, Liu J E, Sun Z L, Chen C W. Improving contrastive learning by visualizing feature transformation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 10286−10295 [33] Kalantidis Y, Sariyildiz M B, Pion N, Weinzaepfel P, Larlus D. Hard negative mixing for contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 1829 [34] Zhong Z, Fini E, Roy S, Luo Z M, Ricci E, Sebe N. Neighborhood contrastive learning for novel class discovery. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 10862−10870 [35] Huynh T, Kornblith S, Walter M R, Maire M, Khademi M. Boosting contrastive self-supervised learning with false negative cancellation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2022. 986−996 [36] Chuang C Y, Robinson J, Yen-Chen L, Torralba A, Jegelka S. Debiased contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. 8765−8775 [37] Kim S, Lee G, Bae S, Yun S Y. MixCo: Mix-up contrastive learning for visual representation [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.06300, November 15, 2020 [38] 王梦琳. 基于对比学习的行人重识别[博士学位论文], 浙江大学, 中国, 2021Wang Meng-Lin. Contrastive Learning Based Person Re-identification. [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, China, 2021 [39] Ayush K, Uzkent B, Meng C L, Tanmay K, Burke M, Lobell D, et al. Geography-aware self-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 10161−10170 [40] Qian R, Meng T J, Gong B Q, Yang M H, Wang H S, Belongie S, et al. Spatiotemporal contrastive video representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 6960−6970 [41] Kumar S, Haresh S, Ahmed A, Konin A, Zia M Z, Tran Q H. Unsupervised action segmentation by joint representation learning and online clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 20142−20153 [42] Han T D, Xie W D, Zisserman A. Self-supervised co-training for video representation learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 477 [43] Wang H B, Xiao R, Li S, et al. Contrastive Label Disambiguation for Partial Label Learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual: ICLR, 2022. [44] Yang F, Wu K, Zhang S Y, Jiang G N, Liu Y, Zheng F, et al. Class-aware contrastive semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 14401−14410 [45] Tian Y L, Krishnan D, Isola P. Contrastive multiview coding. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 776−794 [46] Rai N, Adeli E, Lee K H, Gaidon A, Niebles J C. CoCon: Cooperative-contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 3379−3388 [47] Peng X Y, Wang K, Zhu Z, Wang M, You Y. Crafting better contrastive views for siamese representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 16010−16019 [48] Ding S R, Li M M, Yang T Y, Qian R, Xu H H, Chen Q Y, et al. Motion-aware contrastive video representation learning via foreground-background merging. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 9706−9716 [49] Li S, Gong K X, Liu C H, Wang Y L, Qiao F, Cheng X J. MetaSAug: Meta semantic augmentation for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 5208−5217 [50] Wang Y L, Pan X R, Song S J, Zhang H, Wu C, Huang G. Implicit semantic data augmentation for deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2019. Article No. 1132 [51] Li S, Xie M X, Gong K X, Liu C H, Wang Y L, Li F. Transferable semantic augmentation for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 11511−11520 [52] Tian Y L, Sun C, Poole B, Krishnan D, Schmid C, Isola P. What makes for good views for contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 573 [53] Han T D, Xie W D, Zisserman A. Video representation learning by dense predictive coding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCV). Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 1483−1492 [54] Nguyen N, Chang J M. CSNAS: Contrastive self-supervised learning neural architecture search via sequential model-based optimization. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 3(4): 609-624 doi: 10.1109/TAI.2021.3121663 [55] Misra I, Van Der Maaten L. Self-supervised learning of pretext-invariant representations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6706−6716 [56] Bae S, Kim S, Ko J, Lee G, Noh S, Yun S Y. Self-contrastive learning [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.15499, February 9, 2021 [57] Chaitanya K, Erdil E, Karani N, Konukoglu E. Contrastive learning of global and local features for medical image segmentation with limited annotations. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 1052 [58] Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X H, Unterthiner T, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In: Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Austria: ICLR, 2021. [59] Caron M, Touvron H, Misra I, Jegou H, Mairal J, Bojanowski P, et al. Emerging properties in self-supervised vision transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9630−9640 [60] Richemond P H, Grill J B, Altché F, Tallec C, Strub F, Brock A, et al. BYOL works even without batch statistics [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10241, October 20, 2020 [61] Chen X L, Xie S N, He K M. An empirical study of training self-supervised vision transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9620−9629 [62] Caron M, Bojanowski P, Joulin A, Douze M. Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 139−156 [63] Li J N, Zhou P, Xiong C, et al. Prototypical contrastive learning of unsupervised representations. In: Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Austria: ICLR, 2021. [64] Wang X D, Liu Z W, Yu S X. Unsupervised feature learning by cross-level instance-group discrimination. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 12581−12590 [65] Guo Y F, Xu M H, Li J W, Ni B B, Zhu X Y, Sun Z B, et al. HCSC: Hierarchical contrastive selective coding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 9696−9705 [66] Li Y F, Hu P, Liu Z T, Peng D Z, Zhou J T, Peng X. Contrastive clustering. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(10): 8547-8555 doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i10.17037 [67] Cui J Q, Zhong Z S, Liu S, Yu B, Jia J Y. Parametric contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 695−704 [68] Gutmann M U, Hyvärinen A. Noise-contrastive estimation of unnormalized statistical models, with applications to natural image statistics. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2012, 13: 307-361 [69] Poole B, Ozair S, Van Den Oord A, Alemi A A, Tucker G. On variational bounds of mutual information. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach, USA: PMLR, 2019. 5171−5180 [70] Chen X L, Fan H Q, Girshick R, He K M. Improved baselines with momentum contrastive learning [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.04297, March 9, 2020 [71] Yeh C H, Hong C Y, Hsu Y C, Liu T L, Chen Y B, LeCun Y. Decoupled contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference. Tel Aviv, Israel: ECCV, 2021. [72] Jing L, Vincent P, LeCun Y, et al. Understanding dimensional collapse in contrastive self-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual: ICLR, 2022. [73] Zhang Z L, Sabuncu M R. Generalized cross entropy loss for training deep neural networks with noisy labels. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2018. 8792−8802 [74] Weinberger K Q, Saul L K. Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2009, 10: 207-244 [75] Sohn K. Improved deep metric learning with multi-class n-pair loss objective. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona: Spain, Curran Associates Inc., 2016. 1857−1865 [76] Shah A, Sra S, Chellappa R, Cherian A. Max-margin contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 36(8): 8220−8230 [77] Wang P, Han K, Wei X S, Zhang L, Wang L. Contrastive learning based hybrid networks for long-tailed image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 943−952 [78] Li X M, Shi D Q, Diao X L, Xu H. SCL-MLNet: Boosting few-shot remote sensing scene classification via self-supervised contrastive learning. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: Article No. 5801112 [79] Li J N, Xiong C M, Hoi S C H. CoMatch: Semi-supervised learning with contrastive graph regularization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9455−9464 [80] Park T, Efros A A, Zhang R, Zhu J Y. Contrastive learning for unpaired image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 319−345 [81] Yang J Y, Duan J L, Tran S, Xu Y, Chanda S, Chen L Q, et al. Vision-language pre-training with triple contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 15650−15659 [82] Dong X, Zhan X L, Wu Y X, Wei Y C, Kampffmeyer M C, Wei X Y, et al. M5Product: Self-harmonized contrastive learning for e-commercial multi-modal pretraining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 21220−21230 [83] Hou S K, Shi H Y, Cao X H, Zhang X H, Jiao L C. Hyperspectral imagery classification based on contrastive learning. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: Article No. 5521213 [84] 郭东恩, 夏英, 罗小波, 丰江帆. 基于有监督对比学习的遥感图像场景分类. 光子学报, 2021, 50(7): 0710002Guo Dong-En, Xia Ying, Luo Xiao-Bo, Feng Jiang-Fan. Remote sensing image scene classification based on supervised contrastive learning. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2021, 50(7): 0710002 [85] Aberdam A, Litman R, Tsiper S, Anschel O, Slossberg R, Mazor S, et al. Sequence-to-sequence contrastive learning for text recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 15297−15307 [86] Zhang S, Xu R, Xiong C M, Ramaiah C. Use all the labels: A hierarchical multi-label contrastive learning framework. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 16639−16648 [87] 卢绍帅, 陈龙, 卢光跃, 管子玉, 谢飞. 面向小样本情感分类任务的弱监督对比学习框架. 计算机研究与发展, 2022, 59(9): 2003−2014Lu Shao-Shuai, Chen Long, Lu Guang-Yue, Guan Zi-Yu, Xie Fei. Weakly-supervised contrastive learning framework for few-shot sentiment classification tasks. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2022, 59(9): 2003−2014 [88] 李巍华, 何琛, 陈祝云, 黄如意, 晋刚. 基于对称式对比学习的齿轮箱无监督故障诊断方法. 仪器仪表学报, 2022, 43(3): 131-131 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2108555Li Wei-Hua, He Chen, Chen Zhu-Yun, Huang Ru-Yi, Jin Gang. Unsupervised fault diagnosis of gearbox based on symmetrical contrast learning. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2022, 43(3): 131-131 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2108555 [89] Wang X L, Zhang R F, Shen C H, Kong T, Li L. Dense contrastive learning for self-supervised visual pre-training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 3023−3032 [90] 康健, 王智睿, 祝若鑫, 孙显. 基于监督对比学习正则化的高分辨率SAR图像建筑物提取方法. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 157-167 doi: 10.12000/JR21124Kang Jian, Wang Zhi-Rui, Zhu Ruo-Xin, Sun Xian. Supervised contrastive learning regularized high-resolution synthetic aperture radar building footprint generation. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 157-167 doi: 10.12000/JR21124 [91] Wang X H, Zhao K, Zhang R X, Ding S H, Wang Y, Shen W. ContrastMask: Contrastive Learning to Segment Every Thing. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 11594−11603 [92] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R. Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2980−2988 [93] Zhang L, She Q, Shen Z Y, Wang C H. Inter-intra variant dual representations for self-supervised video recognition. In: Proceedings of 32nd British Machine Vision Conference. UK: BMVA Press, 2021. [94] Bahri D, Jiang H, Tay Y, et al. SCARF: Self-supervised contrastive learning using random feature corruption. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual: ICLR, 2022. [95] Kang B, Li Y, Xie S, Yuan Z, Feng J. Exploring Balanced Feature Spaces for Representation Learning. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Australia: ICLR, 2021. [96] Li T H, Cao P, Yuan Y, Fan L J, Yang Y Z, Feris R, et al. Targeted supervised contrastive learning for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6908−6918 [97] Zhu J G, Wang Z, Chen J J, Chen Y P P, Jiang Y G. Balanced contrastive learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6898−6907 [98] Afham M, Dissanayake I, Dissanayake D, Dharmasiri A, Thilakarathna K, Rodrigo R. CrossPoint: Self-supervised cross-modal contrastive learning for 3D point cloud understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 9892−9902 [99] Laskin M, Srinivas A, Abbeel P. CURL: Contrastive unsupervised representations for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Vitual: ACM, 2020. 5639−5650 [100] Hénaff O, Srinivas A, De FauwJ, Razavi A, Doersch C, Ali Eslami S M, et al. Data-efficient image recognition with contrastive predictive coding. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Vitual: ACM, 2020. 4182−4192 [101] Zbontar J, Jing L, Misra I, et al. Barlow twins: Self-supervised learning via redundancy reduction. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Vitual: ACM, 2021: 12310−12320 [102] Hua T Y, Wang W X, Xue Z H, Ren S C, Wang Y, Zhao H. On feature decorrelation in self-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9578−9588 [103] Bardes A, Ponce J, Lecun Y. VICReg: Variance-Invariance-Covariance Regularization for Self-Supervised Learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual: ICLR, 2022. [104] Bao H, Nagano Y, Nozawa K. Sharp learning bounds for contrastive unsupervised representation learning [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02501v1, October 6, 2021 [105] Wang F, Liu H P. Understanding the behaviour of contrastive loss. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 2495−2504 [106] Ren P Z, Xiao Y, Chang X J, Huang P Y, Li Z H, Gupta B B, et al. A survey of deep active learning. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 54(9): Article No. 180 [107] 孙琦钰, 赵超强, 唐漾, 钱锋. 基于无监督域自适应的计算机视觉任务研究进展. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2022, 52(1): 26-54 doi: 10.1360/SST-2021-0150Sun Qi-Yu, Zhao Chao-Qiang, Tang Yang, Qian Feng. A survey on unsupervised domain adaptation in computer vision tasks. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2022, 52(1): 26-54 doi: 10.1360/SST-2021-0150 [108] 范苍宁, 刘鹏, 肖婷, 赵巍, 唐降龙. 深度域适应综述: 一般情况与复杂情况. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(3): 515-548Fan Cang-Ning, Liu Peng, Xiao Ting, Zhao Wei, Tang Xiang-Long. A review of deep domain adaptation: General situation and complex situation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(3): 515-548 [109] Han T D, Xie W D, Zisserman A. Memory-augmented dense predictive coding for video representation learning. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 312−329 -




 下载:
下载: