Soft Sensing Method of Dioxin Emission in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Process Based on Broad Hybrid Forest Regression
-
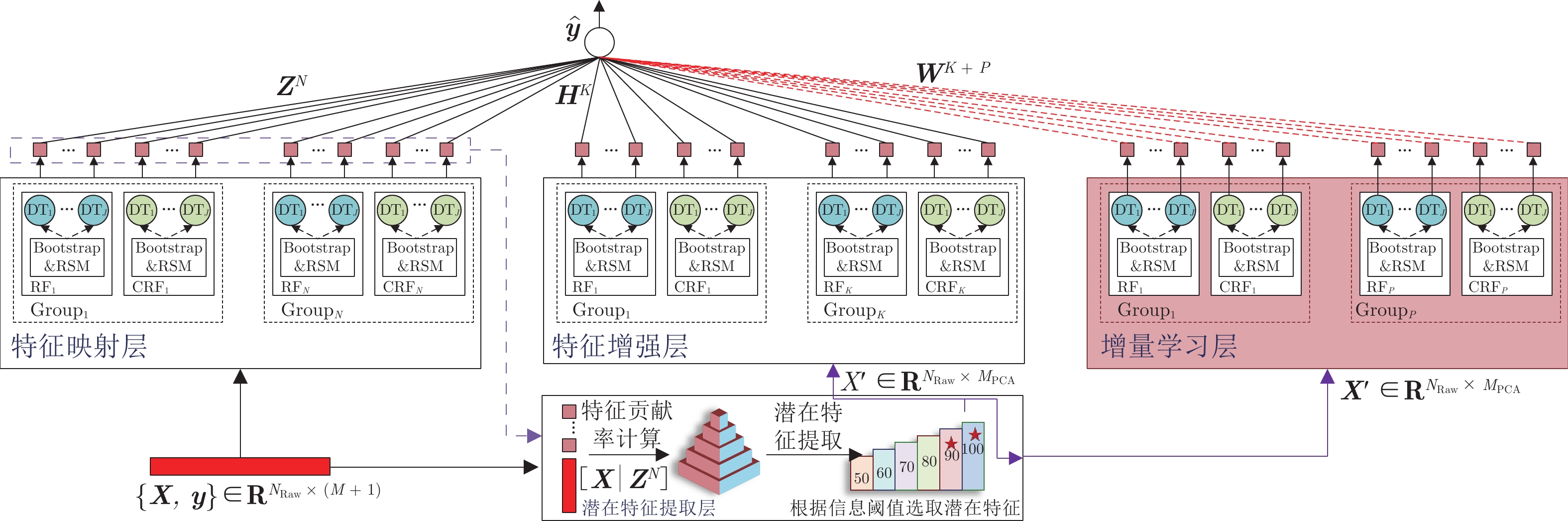
摘要: 二噁英是城市固废焚烧过程排放的痕量有机污染物. 受限于相关技术的复杂度和高成本, 二噁英排放浓度检测的大时滞已成为制约城市固废焚烧过程优化控制的关键因素之一. 虽然具有低成本、快响应、高精度等特点的数据驱动软测量模型能够有效解决上述问题, 但二噁英建模方法必须要契合数据的小样本、高维度特性. 对此, 提出了由特征映射层、潜在特征提取层、特征增强层和增量学习层组成的宽度混合森林回归软测量方法. 首先, 构建由随机森林和完全随机森林构成的混合森林组进行高维特征映射; 其次, 依据贡献率对全联接混合矩阵进行潜在特征提取, 采用信息度量准则保证潜在有价值信息的最大化传递和最小化冗余, 降低模型的复杂度和计算消耗; 然后, 基于所提取潜在信息训练特征增强层以增强特征表征能力; 最后, 通过增量式学习策略构建增量学习层后采用Moore-Penrose伪逆获得权重矩阵. 在基准数据集和城市固废焚烧过程二噁英数据集上的实验结果表明了方法的有效性和优越性.Abstract: Dioxin is a trace organic pollutant emitted from municipal solid waste incineration process. Limited by the complexity and high cost of relative technology, the big time delay of dioxin emission concentration detection has become one of the key factors restricting the optimize control of municipal solid waste incineration process. Although the data-driven soft sensing model with the characteristics of low cost, fast response and high precision can effectively solve the above problems, the dioxin modeling method must fit the small sample and high-dimensional characteristics of the modeling data. In this paper, a broad hybrid forest regression soft sensing method is proposed, which consists of feature mapping layer, latent feature extraction layer, feature enhancement layer and incremental learning layer. Firstly, a hybrid forest group composed of random forest and completely random forest is constructed for high-dimensional feature mapping. Secondly, the latent features extraction of the fully connected mixed matrix is carried out according to the contribution rate, and the information measurement criterion is used to ensure the maximum transmission and minimize redundancy of potential valuable information. Thus, the model complexity and computational consumption are reduced. Then, the feature enhancement layer is trained based on the extracted potential information to enhance the feature representation ability. Finally, the incremental learning layer is constructed by using incremental learning strategy, and the weight matrix is obtained by using the Moore-Penrose pseudo inverse. The experimental results on high-dimensional benchmark and dioxin datasets of municipal solid waste incineration process show the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method.
-
表 1 符号说明
Table 1 Symbol description
缩写词 中文全称 英文全称 MSWI 城市固废焚烧 Municipal solid waste incineration DXN 二噁英 Dioxin HRGC/HRMS 高分辨色谱质谱联用 High-resolution chromatography combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry NN 神经网络 Neural network PCDDs/PCDFs 多氯二苯并二噁英/多氯二苯并呋喃 Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/Polychlorinated dibenzofurans BPNN 反向传播神经网络 Back-propagation neural network SVR 支持向量回归 Support vector regression SEN 选择性集成 Selective ensemble RF 随机森林 Random forest DFR 深度森林回归 Deep forest regression BLS 宽度学习系统 Broad learning system BLS-NN 神经网络宽度学习系统 Broad learning system neural network BHFR 宽度混合森林回归 Broad hybrid forest regression CRF 完全随机森林 Completely random forest MSW 城市固废 Municipal solid waste TEQ 毒性当量 Toxic equivalent quangtity G 1 烟气 1 Gas 1 NOx 氮氧化物 Nitrogen oxides HCL 氯化氢 Hydrogen chloride HF 氟化氢 Hydrogen fluoride SO2 二氧化硫 Sulfur dioxide Pb 铅 Plumbum Hg 汞 Mercury Cd 镉 Cadmium G 2 烟气 2 Gas 2 G 3 烟气 3 Gas 3 RSM 随机子空间法 Random subspace method PCA 主成分分析 Principal components analysis MI 互信息 Mutual information CT CT 切片在轴轴数据上的相对位置 The relative location of CT slices on the axial axis data RB 住宅建筑数据 Residential building data NIR 橙汁近红外光谱数据 The orange juice near infrared spectra data RMSE 均方根误差 Root mean square error MAE 平均绝对误差 Mean absolute error R2 决定系数 Coefficient of determination DFR-clfc 基于跨层全连接的深度森林回归 Deep forest regression based on cross-layer full connection 表 2 实验数据统计结果
Table 2 Statistical results of experimental datasets
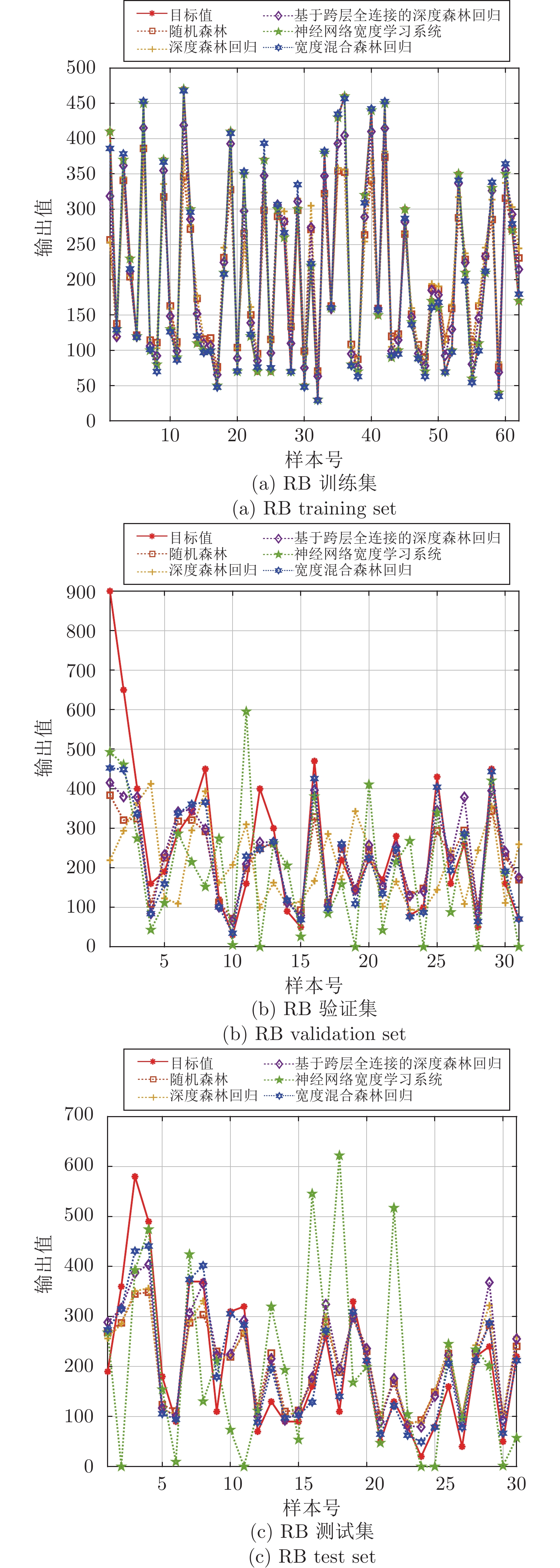
数据集 实际样本量 实际样本量 特征维数 总数 训练集 验证集 测试集 NIR 218 109 55 27 27 700 CT 583 117 59 29 29 291 RB 372 124 62 31 31 106 DXN 141 141 71 35 35 116 表 3 NIR数据集实验结果
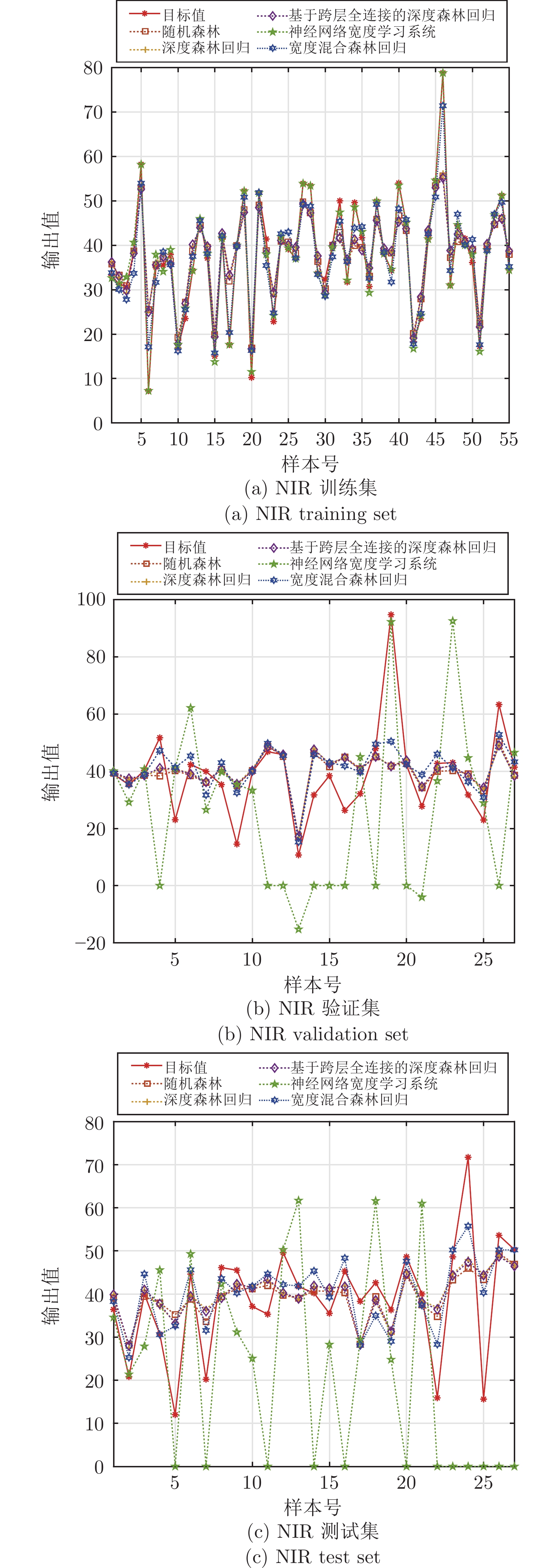
Table 3 Experimental results of NIR dataset
方法 数据集 RMSE MAE ${ {{R} } }^{2}$ 平均值 方差 平均值 方差 平均值 方差 RF 训练集 5.7142$\times {10} ^{0}$ 2.1347$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 3.8799$\times {10} ^{0}$ 9.4469$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 8.1131$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 9.2887$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 验证集 1.3522$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.3660$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.3125$\times {10} ^{0}$ 7.2473$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 2.6715$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.6048$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 测试集 1.0925$\times {10} ^{1}$ 3.2313$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.1093$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.7493$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 3.0986$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 5.1625$\times {10} ^{-4}$ DFR 训练集 5.8836$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.4331$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 4.1004$\times \text{10}^{0}$ 6.1766$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 8.0007$\times \text{10}^{-1}$ 6.5971$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 验证集 1.3585$\times {10} ^{1}$ 3.7257$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 8.3057$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.5854$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 2.6036$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.4251$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 测试集 1.0842$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.4742$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 8.0306$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.8258$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 3.2046$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 2.3176$\times {10} ^{-5}$ DFR-clfc 训练集 5.7742$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.7160$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 4.0139$\times {10} ^{0}$ 9.6271$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 8.0735$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 7.6485$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 验证集 1.3569$\times {10} ^{1}$ 3.1520$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 8.3265$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.3592$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 2.6219$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.7318$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 测试集 1.0793$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.5668$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 7.9746$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.3925$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 3.2664$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.9879$\times {10} ^{-5}$ BLS-NN 训练集 7.4226$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.7588$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.6530$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.5602$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 9.9476$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.2486$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 验证集 7.8288$\times {10} ^{3}$ 4.9487$\times {10} ^{7}$ 2.5450$\times {10} ^{3}$ 4.6180$\times {10} ^{6}$ −4.3402$\times {10} ^{5}$ 7.2220$\times {10} ^{11}$ 测试集 6.4945$\times {10} ^{3}$ 1.4866$\times {10} ^{7}$ 2.1689$\times {10} ^{3}$ 1.5496$\times {10} ^{6}$ −3.2544$\times {10} ^{5}$ 8.9669$\times {10} ^{10}$ BHFR 训练集 2.8931$\times {10} ^{0}$ 5.5126$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 2.1335$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.3004$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 9.4864$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 6.0585$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 验证集 1.3782$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.7263$\times {10} ^{0}$ 9.2584$\times {10} ^{0}$ 6.5031$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 2.3224$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 2.1525$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 测试集 9.9505$\times {10} ^{0}$ 5.6804$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 7.3675$\times {10} ^{0}$ 2.4515$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.2455$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 7.3749$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 表 4 CT数据集实验结果
Table 4 Experimental results of CT dataset
方法 数据集 RMSE MAE ${ {{R} } }^{2}$ 平均值 方差 平均值 方差 平均值 方差 RF 训练集 1.5839$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.2389$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.2676$\times {10} ^{0}$ 6.1900$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 9.7215$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.4862$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 验证集 1.8907$\times {10} ^{0}$ 2.2323$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.4978$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.4923$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 9.5761$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.2488$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 测试集 2.2138$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.6173$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.8254$\times {10} ^{0}$ 2.1898$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 9.5706$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 5.3991$\times {10} ^{-5}$ DFR 训练集 4.1046$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.3520$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 3.4579$\times {10} ^{0}$ 9.5891$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 8.1383$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.1086$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 验证集 4.1864$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.2940$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 3.5658$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.4003$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 7.9338$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.2646$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 测试集 4.8124$\times {10} ^{0}$ 2.1197$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 4.2219$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.4647$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 7.9851$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.4815$\times {10} ^{-5}$ DFR-clfc 训练集 3.7411$\times {10} ^{0}$ 4.1351$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 3.1392$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.2494$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.4491$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 2.8032$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 验证集 3.8251$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.9698$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 3.2193$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.5889$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.2708$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.1969$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 测试集 4.3811$\times {10} ^{0}$ 4.9342$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 3.8122$\times {10} ^{0}$ 4.5453$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.3262$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 2.8693$\times {10} ^{-4}$ BLS-NN 训练集 1.0447$\times {10} ^{-7}$ 4.7677$\times {10} ^{-15}$ 4.1145$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 5.7001$\times {10} ^{-16}$ $1.0000\times {10} ^{0}$ 7.4604$\times {10} ^{-32}$ 验证集 2.5527$\times {10} ^{0}$ 6.9348$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.7606$\times {10} ^{0}$ 2.0416$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 9.1542$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.2479$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 测试集 2.9466$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.3019$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.8882$\times {10} ^{0}$ 4.4686$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 9.1371$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.5944$\times {10} ^{-3}$ BHFR 训练集 4.4458$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 8.4237$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 3.7023$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.5597$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 9.9773$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.6195$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 验证集 9.5728$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.3354$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 7.4450$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 6.1644$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 9.8905$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.0451$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 测试集 9.3108$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.2802$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 6.7034$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.2237$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 9.9235$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 5.1917$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 表 5 RB数据集实验结果
Table 5 Experimental results of RB dataset
方法 数据集 RMSE MAE ${ {{R} } }^{2}$ 平均值 方差 平均值 方差 平均值 方差 RF 训练集 5.3243$\times {10} ^{1}$ 3.7463$\times {10} ^{0}$ 4.2919$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.4224$\times {10} ^{0}$ 8.4698$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.2156$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 验证集 1.3211$\times {10} ^{2}$ 6.6035$\times {10} ^{0}$ 8.1855$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.9950$\times {10} ^{0}$ 5.3824$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.2140$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 测试集 7.5697$\times {10} ^{1}$ 4.3622$\times {10} ^{0}$ 6.0986$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.7466$\times {10} ^{0}$ 7.0126$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 2.7457$\times {10} ^{-4}$ DFR 训练集 4.8752$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.4944$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.9200$\times {10} ^{1}$ 8.4396$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.7185$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.1370$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 验证集 1.2600$\times {10} ^{2}$ 1.6487$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 7.8890$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.1939$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 5.8012$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 7.3315$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 测试集 7.4221$\times {10} ^{1}$ 3.1170$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 6.0387$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.4493$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 7.1299$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.8723$\times {10} ^{-5}$ DFR-clfc 训练集 3.0978$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.6657$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.4856$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.7056$\times {10} ^{1}$ 9.4690$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.4386$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 验证集 1.1830$\times {10} ^{2}$ 4.9405$\times {10} ^{0}$ 7.2901$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.7676$\times {10} ^{0}$ 6.2977$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.9820$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 测试集 6.9427$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.7460$\times {10} ^{0}$ 5.5570$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.1741$\times {10} ^{0}$ 7.4879$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 9.2839$\times {10} ^{-5}$ BLS-NN 训练集 9.4877$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 4.8003$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 4.3563$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 7.7161$\times {10} ^{-7}$ 1.0000$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.1561$\times {10} ^{-18}$ 验证集 5.0098$\times {10} ^{2}$ 1.3099$\times {10} ^{5}$ 2.6163$\times {10} ^{2}$ 2.6950$\times {10} ^{4}$ −8.9285$\times {10} ^{0}$ 1.6631$\times {10} ^{2}$ 测试集 5.2093$\times {10} ^{2}$ 1.5354$\times {10} ^{5}$ 2.8934$\times {10} ^{2}$ 3.2539$\times {10} ^{4}$ −2.0737$\times {10} ^{1}$ 9.3226$\times {10} ^{2}$ BHFR 训练集 8.4893$\times {10} ^{0}$ 6.4125$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 6.4970$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.1874$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 9.9608$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 5.6404$\times {10} ^{-7}$ 验证集 9.9275$\times {10} ^{1}$ 2.2922$\times {10} ^{0}$ 5.4880$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.0407$\times {10} ^{0}$ 7.3930$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 6.3926$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 测试集 4.5645$\times {10} ^{1}$ 1.7188$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.2284$\times {10} ^{1}$ 9.0105$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 8.9137$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.8975$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 表 6 DXN数据集实验结果
Table 6 Experimental results of DXN dataset
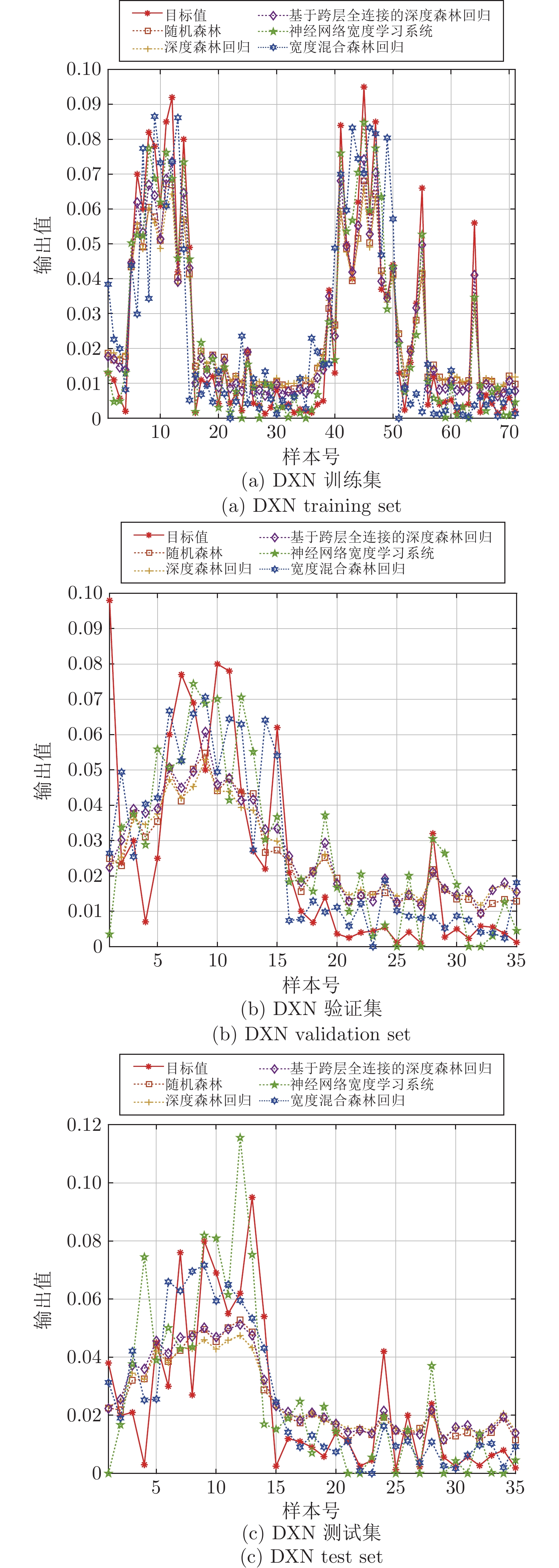
方法 数据集 RMSE MAE ${ {{R} } }^{2}$ 平均值 方差 平均值 方差 平均值 方差 RF 训练集 1.1159$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 5.7497$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 9.0221$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 4.0684$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 8.5346$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.9360$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 验证集 2.0051$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.8026$\times {10} ^{-7}$ 1.4677$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.2255$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 5.0196$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.3515$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 测试集 1.6922$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.6150$\times {10} ^{-7}$ 1.3548$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.9520$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 5.9001$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.7817$\times {10} ^{-4}$ DFR 训练集 1.1493$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 8.7413$\times {10} ^{-9}$ 9.4568$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 4.6626$\times {10} ^{-9}$ 8.4463$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 6.3663$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 验证集 2.0735$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 9.7835$\times {10} ^{-9}$ 1.5780$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.1121$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 4.6759$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 2.5813$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 测试集 1.7791$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.7308$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 1.4608$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.5235$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 5.4701$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.5066$\times {10} ^{-5}$ DFR-clfc 训练集 8.0852$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 2.9078$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 6.6040$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 2.0819$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 9.1986$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 1.1887$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 验证集 2.0187$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.4562$\times {10} ^{-7}$ 1.5626$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 2.3355$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 4.9520$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.6404$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 测试集 1.7025$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.5755$\times {10} ^{-7}$ 1.4068$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 6.0233$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 5.8501$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.7843$\times {10} ^{-4}$ BLS-NN 训练集 1.2924$\times {10} ^{-9}$ 1.5756$\times {10} ^{-18}$ 9.5358$\times {10} ^{-10}$ 7.2150$\times {10} ^{-19}$ 1.0000$\times {10} ^{0}$ 8.2358$\times {10} ^{-29}$ 验证集 6.8845$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 7.0040$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 5.3153$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 3.3474$\times {10} ^{-4}$ −5.6928$\times {10} ^{0}$ 3.7799$\times {10} ^{1}$ 测试集 7.8396$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 6.7692$\times {10} ^{-4}$ 6.0922$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 4.1785$\times {10} ^{-4}$ −8.7153$\times {10} ^{0}$ 4.7630$\times {10} ^{1}$ BHFR 训练集 6.0665$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 1.6330$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 3.9665$\times {10} ^{-3}$ 8.4708$\times {10} ^{-9}$ 9.5669$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 3.3481$\times {10} ^{-6}$ 验证集 2.1551$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 3.5181$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 1.2384$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 3.5083$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 4.2484$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 9.8731$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 测试集 1.6189$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 2.2474$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 1.1226$\times {10} ^{-2}$ 1.0102$\times {10} ^{-8}$ 6.2491$\times {10} ^{-1}$ 4.8607$\times {10} ^{-5}$ 表 7 BHFR超参数及其区间设置
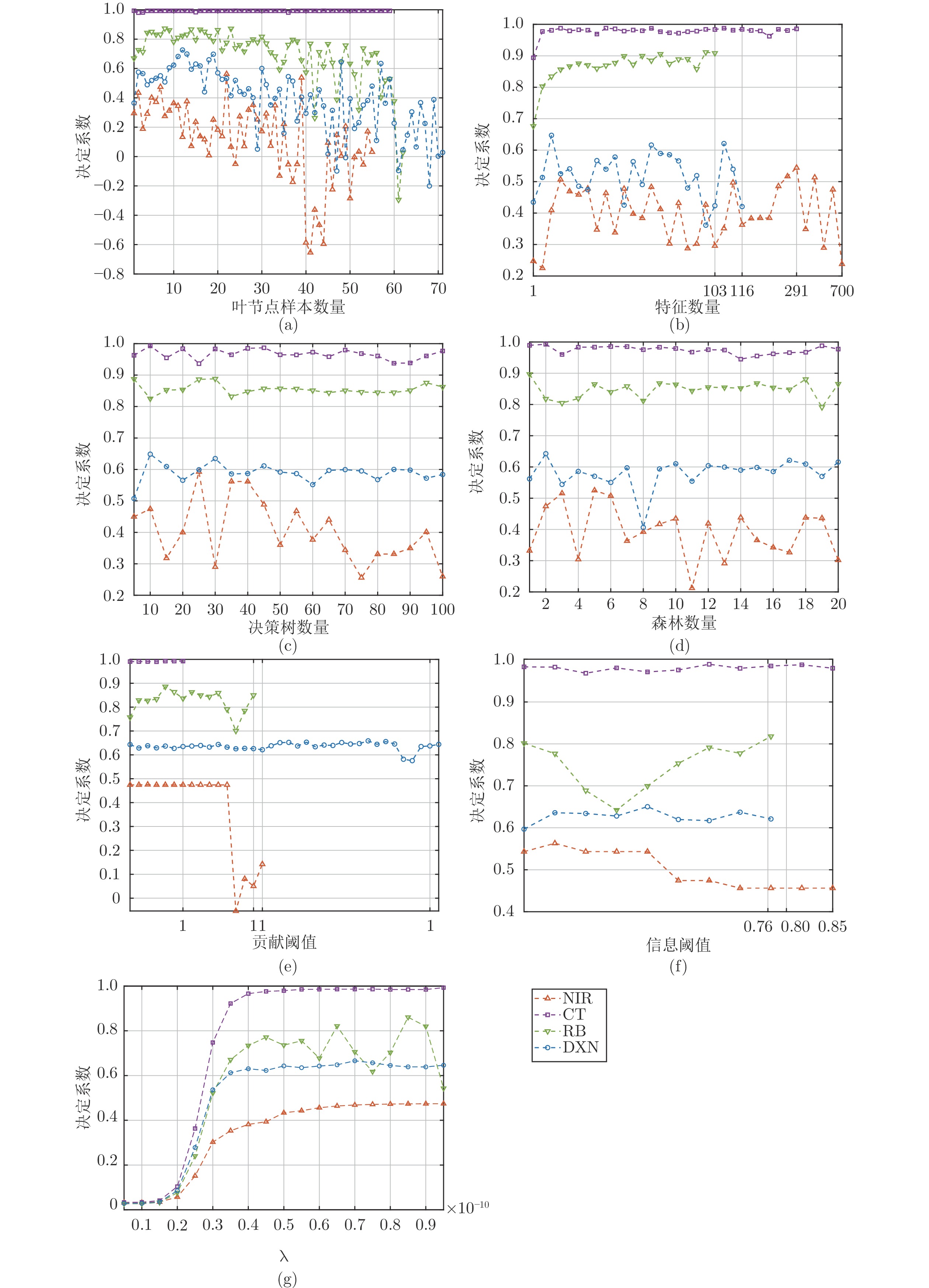
Table 7 Super parameters and interval setting of BHFR
模型超参数 符号 NIR CT RB DXN 决策树叶
节点最小
样本数Nsamples [1, 55] [1, 59] [1, 62] [1, 71] RSM特征
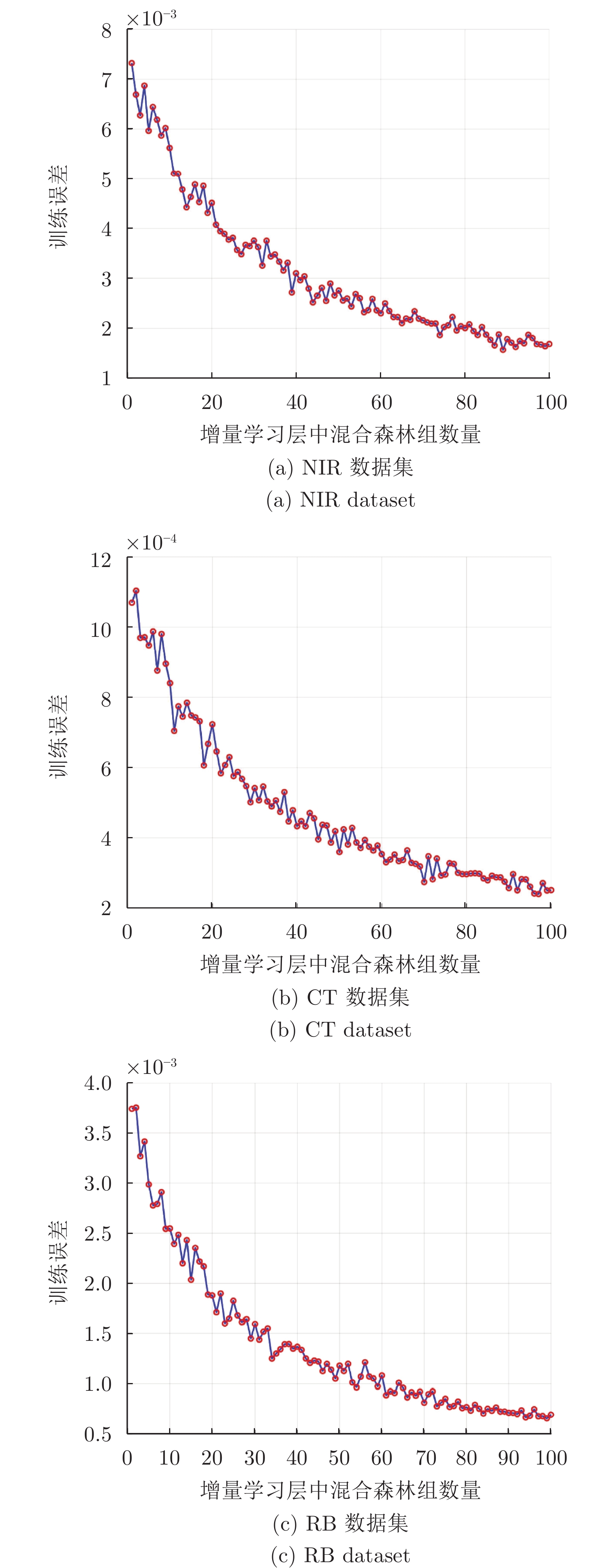
选择数量MRSM [1, 700] [1, 291] [1, 103] [1, 116] 决策树数量 Mtree [5, 100] [5, 100] [5, 100] [5, 100] 混合森林组
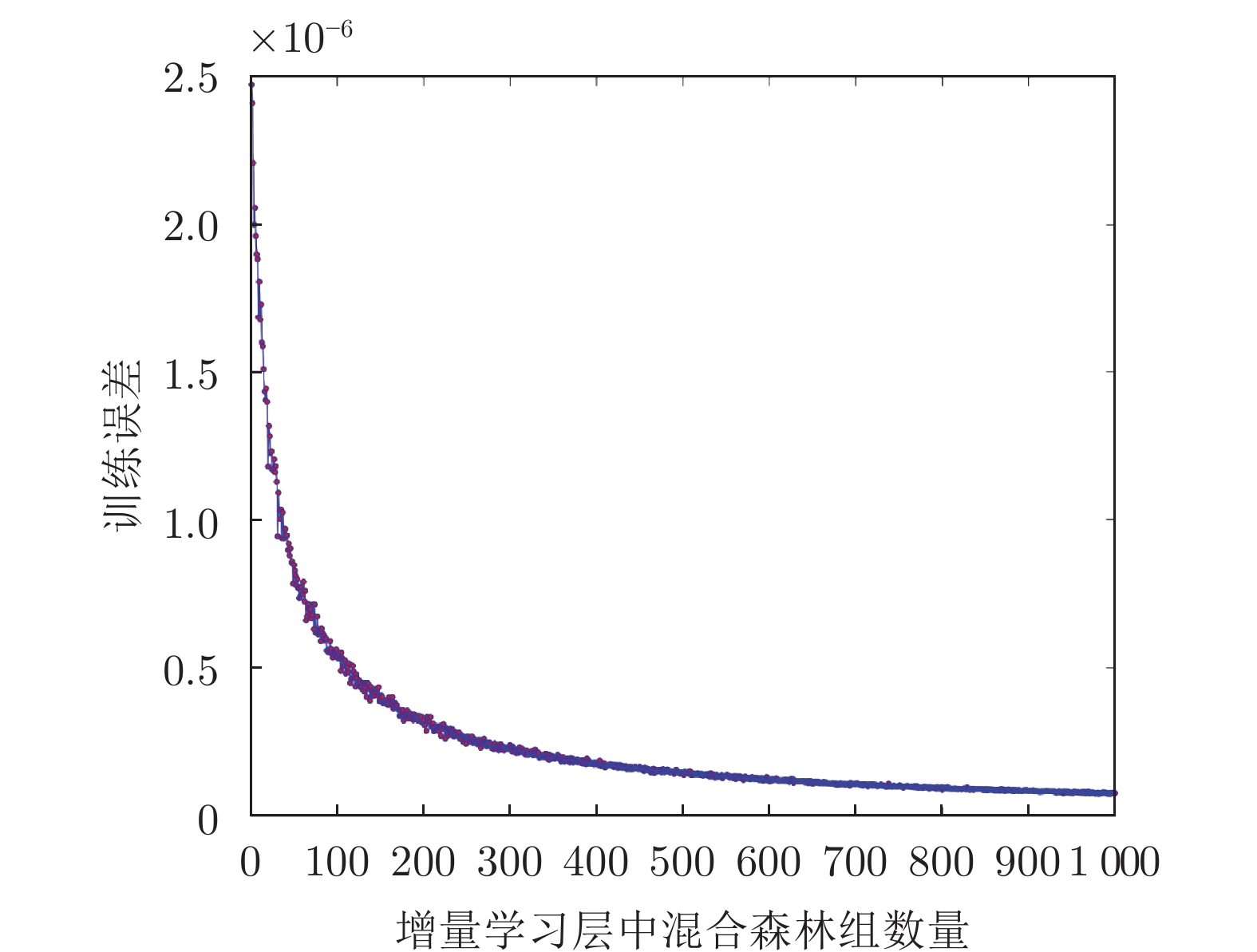
数量NForest [5, 100] [5, 100] [5, 100] [5, 100] 潜在特征
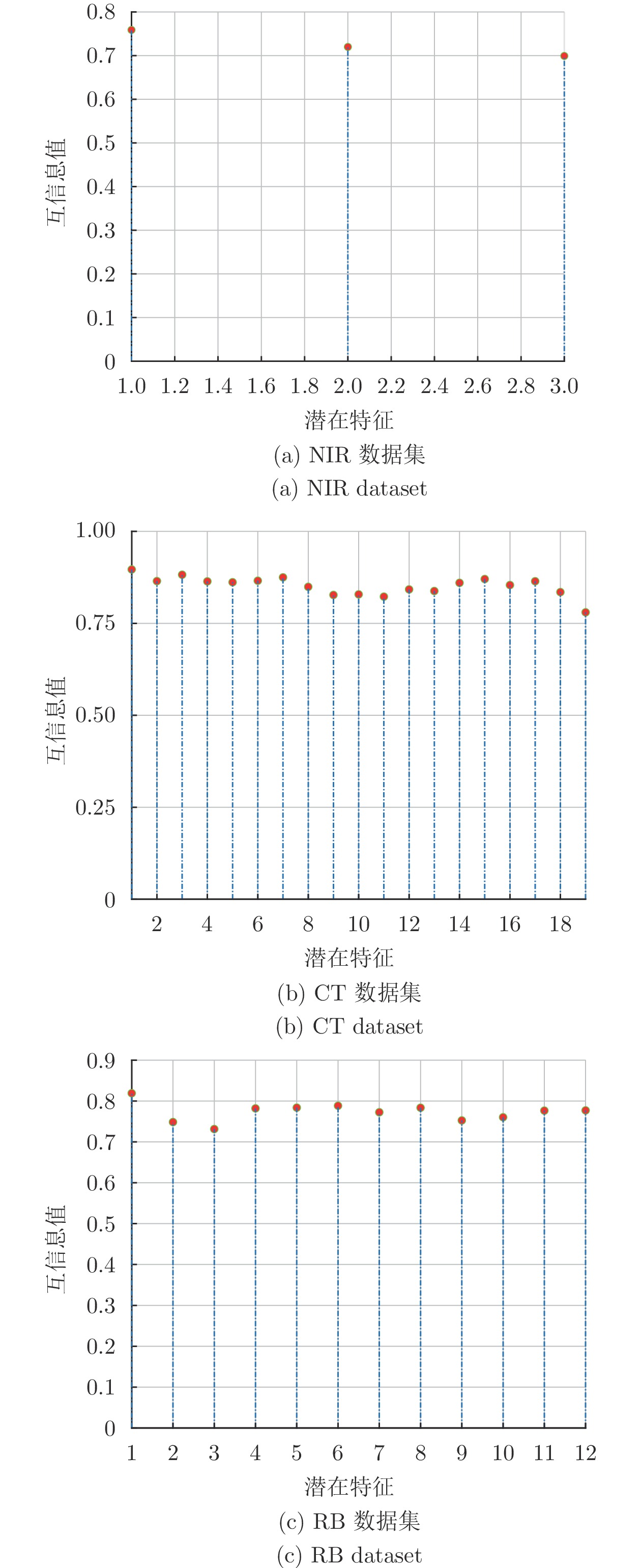
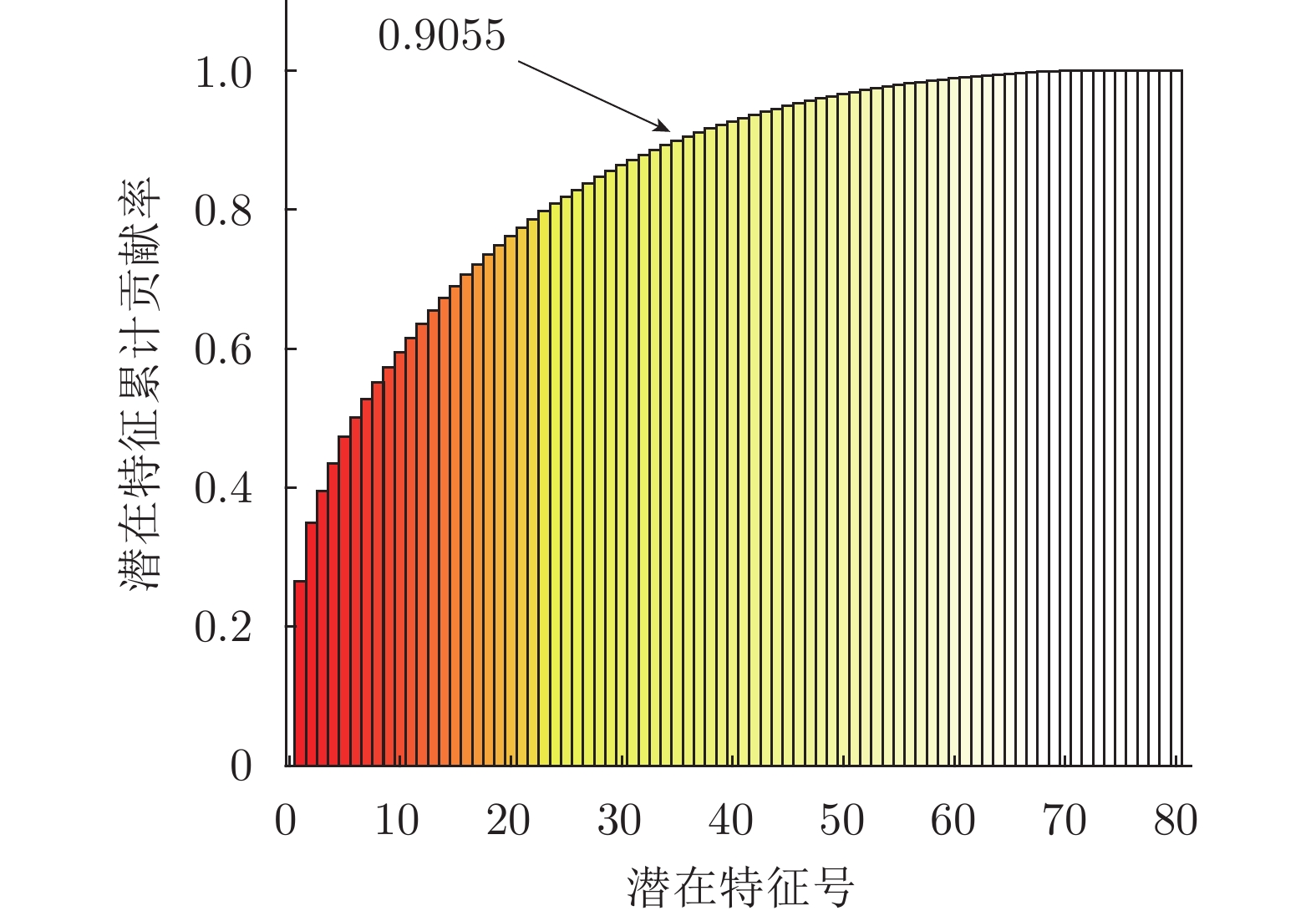
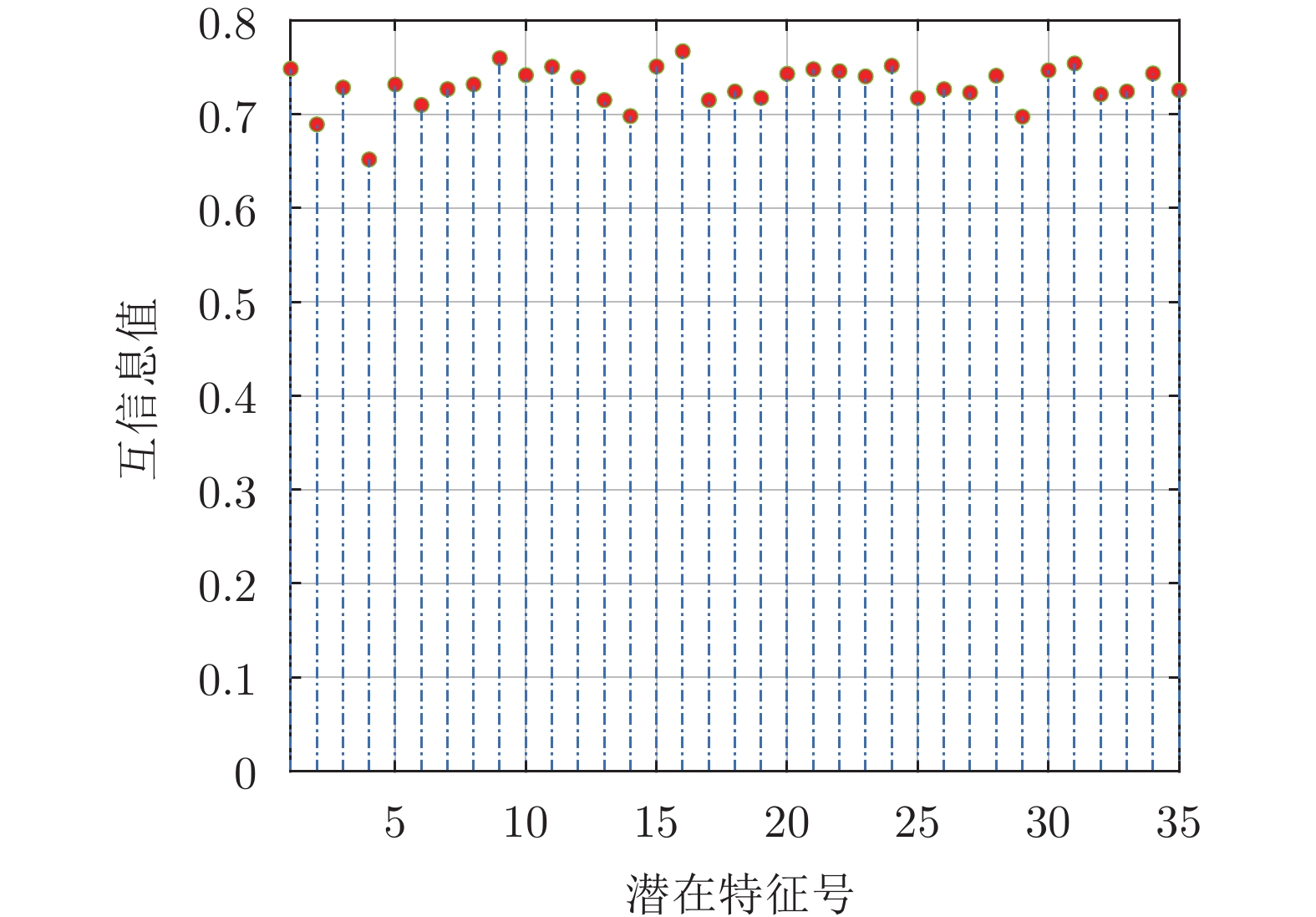
贡献率阈值$\eta $ [0.7, 1] [0.4, 1] [0.71, 1] [0.3, 1] 互信息阈值 $\zeta $ [0.65, 0.75] [0.75, 0.85] [0.72, 0.8] [0.68, 0.76] 正则化参数 $\lambda$ [0.1−10, 1] [0.1−10, 1] [0.1−10, 1] [0.1−10, 1] A1 DXN数据集的过程变量信息
A1 The process variable information for DXN datasets
序号 过程变量 单位 1 燃烧室左侧温度 1 ℃ 2 燃烧室左侧温度 2 ℃ 3 燃烧室右侧温度 3 ℃ 4 燃烧室左侧温度4 ℃ 5 燃烧室右侧温度 5 ℃ 6 燃烧室右侧温度 6 ℃ 7 燃烬段炉排顶端气温左 ℃ 8 燃烬段炉排顶端气温右 ℃ 9 干燥炉排温度左入口 ℃ 10 干燥炉排温度左出口 ℃ 11 干燥炉排温度右入口 ℃ 12 干燥炉排温度右出口 ℃ 13 干燥段与燃烧段炉排的炉墙左侧内温度 ℃ 14 干燥段与燃烧段炉排的炉墙左侧外温度 ℃ 15 干燥段与燃烧段炉排的炉墙右侧内温度 ℃ 16 干燥段与燃烧段炉排的炉墙右侧外温度 ℃ 17 燃烧炉排 1-1 左内侧温度 ℃ 18 燃烧炉排 1-1左外侧温度 ℃ 19 燃烧炉排 1-1 右内侧温度 ℃ 20 燃烧炉排 1-1 右外侧温度 ℃ 21 燃烧炉排 1-2 左内侧温度 ℃ 22 燃烧炉排 1-2 左外侧温度 ℃ 23 燃烧炉排1-2右内侧温度 ℃ 24 燃烧炉排1-2右外侧温度 ℃ 25 燃烧炉排 2-1 左内侧温度 ℃ 26 燃烧炉排 2-1 左外侧温度 ℃ 27 燃烧炉排 2-1 右内侧温度 ℃ 28 燃烧炉排 2-1 右外侧温度 ℃ 29 燃烧炉排 2-2 左内侧温度 ℃ 30 燃烧炉排 2-2 左外侧温度 ℃ 31 燃烧炉排 2-2 右内侧温度 ℃ 32 燃烧炉排 2-2 右外侧温度 ℃ 33 二次燃烧室出口温度左 ℃ 34 二次燃烧室出口温度右 ℃ 35 一次空预器出口空气温度 ℃ 36 燃烧炉排入口空气温度 ℃ 37 干燥炉排入口空气温度 ℃ 38 二次空预器出口空气温度 ℃ 39 炉墙左侧冷却风出口温度 ℃ 40 炉墙右侧冷却风出口温度 ℃ 41 炉排左侧冷却风出口温度 ℃ 42 炉排右侧冷却风出口温度 ℃ 43 一级过热器出口蒸汽温度 ℃ 44 二级过热器出口蒸汽温度 ℃ 45 三级过热器出口蒸汽温度 ℃ 46 省煤器出口给水温度 ℃ 47 反应器入口温度 ℃ 48 布袋 A 入口温度 ℃ 49 布袋 B 入口温度 ℃ 50 流化风机出口温度 ℃ 51 FGD 出口烟气温度 A ℃ 52 FGD 出口烟气温度 B ℃ 53 烟道入口烟气温度 ℃ 54 干燥炉排左 1 空气流量 km3N/h 55 干燥炉排右 1 空气流量 km3N/h 56 干燥炉排左 2 空气流量 km3N/h 57 干燥炉排右 2 空气流量 km3N/h 58 燃烧炉排左 1-1 空气流量 km3N/h 59 燃烧炉排右 1-1空气流量 km3N/h 60 燃烧炉排左 1-2 空气流量 km3N/h 61 燃烧炉排右 1-2 空气流量 km3N/h 62 燃烧炉排左 2-1 空气流量 km3N/h 63 燃烧炉排右 2-1 空气流量 km3N/h 64 燃烧炉排左 2-2 空气流量 km3N/h 65 燃烧炉排右 2-2 空气流量 km3N/h 66 燃烬炉排左空气流量 km3N/h 67 燃烬炉排右空气流量 km3N/h 68 二次风流量 km3N/h 69 省煤器 No.2 给水流量 t/h 70 省煤器 No.1 给水流量 t/h 71 一级过热器冷却水流量 t/h 72 二级过热器冷却水流量 t/h 73 锅炉出口主蒸汽流量 t/h 74 烟道入口烟气流量 km3N/h 75 混合器水流量 A kg/h 76 混合器水流量 B kg/h 77 尿素溶剂供应流量 L/h 78 石灰储仓给料量 kg/h 79 活性炭储仓给料量 kg/h 80 一次风机出口空气压力 kPa 81 二次风机出口空气压力 kPa 82 省煤器出口压力 kPa 83 烟道入口烟气压力 Pa 84 汽包压力 MPa 85 三级过热器出口蒸汽压力 MPa 86 FGD 出口烟气压力 Pa 87 布袋压差 A kPa 88 布袋压差 B kPa 89 进料器左内侧速度 % 90 进料器左外侧速度 % 91 进料器右内侧速度 % 92 进料器右外侧速度 % 93 干燥炉排左内侧速度 % 94 干燥炉排左外侧速度 % 95 干燥炉排右内侧速度 % 96 干燥炉排右外侧速度 % 97 燃烧炉排 1 左内侧速度 % 98 燃烧炉排 1 左外侧速度 % 99 燃烧炉排 1 右内侧速度 % 100 燃烧炉排 1 右外侧速度 % 101 燃烧炉排 2 左内侧速度 % 102 燃烧炉排 2 左外侧速度 % 103 燃烧炉排 2 右内侧速度 % 104 燃烧炉排 2 右外侧速度 % 105 燃烬炉排左侧速度 % 106 燃烬炉排右侧速度 % 107 汽包水位 mm 108 FGD 出口烟气压力-O2 % 109 出口烟气分析-O2 % 110 出口烟气分析−灰尘 mg/m3N 111 出口烟气分析-NO mg/m3N 112 出口烟气分析-SO2 mg/m3N 113 出口烟气分析-HCL mg/m3N 114 出口烟气分析-CO mg/m3N 115 出口烟气分析-CO2 % 116 出口烟气分析-HF mg/m3N -
[1] Kammen D M, Sunter D A. City-integrated renewable energy for urban sustainability. Science, 2016, 352(6288): 922-928 doi: 10.1126/science.aad9302 [2] Tobias W, Ludwig K L, Robert B, Esther E, Luca F, Bodo H, et al. Persistence of engineered nanoparticles in a municipal solid-waste incineration plant. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7(8): 520-524 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.64 [3] 乔俊飞, 郭子豪, 汤健. 面向城市固废焚烧过程的二噁英排放浓度检测方法综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(6): 1063-1089 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190005Qiao Jun-Fei, Guo Zi-Hao, Tang Jian. Dioxin emission concentration measurement approaches for municipal solid wastes incineration process: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 1063-1089 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190005 [4] Bin Wang, Peilong Wang, Xie Lin-Hua, Lin Rui-Biao, Lv Jie, Li Jian-Rong, et al. A stable zirconium based metal-organic framework for specific recognition of representative polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin molecules. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1-8 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 [5] Wei J X, Li H, Liu J G. Fate of dioxins in a municipal solid waste incinerator with state-of-the-art air pollution control devices in China. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 289: 1-10 doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117798 [6] 代伟, 陆文捷, 付俊, 马小平. 工业过程多速率分层运行优化控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1946-1959Dai Wei, Lu Wen-Jie, Fu Jun, Ma Xiao-Ping. Multi-rate layered optimal operational control of industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1946-1959 [7] Xue W Q, Fan J L, Victor G L, Li J N, Jiang Y, Chai T Y, et al. New methods for optimal operational control of industrial processes using reinforcement learning on two time scales. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(5): 3085-3099 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2912018 [8] 国家标准. HJ 77.2-2008. 环境空气和废气. 二噁英类的测定. 同位素稀释高分辨气相色谱−高分辨质谱法. 2008National standard. HJ 77.2-2008. Ambient air and flue gas. Determination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxions (PCDDs) and ploychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) Isotope dilution HRCC-HRMS. 2008 [9] 李阿丹, 洪伟, 王晶. 激光解吸 /激光电离-质谱法二恶英及其关联物的在线检测. 燕山大学学报, 2015, 39(6): 511-515 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2015.06.007Li A-Dan, Hong Wei, Wang Jing. Online detection of dioxins and their related substances by laser desorption/laser ionization mass spectrometry. Journal of Yanshan University, 2015, 39(6): 511-515 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2015.06.007 [10] Nakui H, Koyama H, Takakura A, Watanabe N. Online measurements of low-volatile organic chlorine for dioxin monitoring at municipal waste incinerators. Chemosphere, 2011, 85(2): 151-155 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.042 [11] Zhang H J, Ni Y W, Chen J P, Zhang Q. Influence of variation in the operating conditions on pcdd/f distribution in a full-scale msw incinerator. Chemosphere, 2008, 70(4): 721-730 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.054 [12] 王通, 段泽文. 基于模糊评估自适应更新的油井动液面软测量建模. 化工学报, 2019, 70(12): 4760-4769Wang Tong, Duan Ze-Wen. Soft sensor modeling for dynamic liquid level of oil well based on fuzzy inference adaptive updating. Ciesc Journal, 2019, 70(12): 4760-4769 [13] 秦美华, 朱红求, 李勇刚, 陈俊名, 张凤雪, 李文婷, 等. 基于STA-K均值聚类的电化学废水处理过程离子浓度软测量. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3458-3464Qin Mei-Hua, Zhu Hong-Qiu, Li Yong-Gang, Chen Jun-Ming, Zhang Feng-Xue, Li Wen-ting, et al. Soft-sensor method for ion concentration of electrochemical wastewater treatment based on sta-k-means clustering. Ciesc Journal, 2019, 70(9): 3458-3464 [14] 刘卓, 汤健, 柴天佑, 余文. 基于多模态特征子集选择性集成建模的磨机负荷参数预测方法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(8): 1921-1931Liu Zhuo, Tang Jian, Chai Tian-You, Yu Wen. Selective ensemble modeling approach for mill load parameter forecasting based on multi-modal feature sub-sets. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1921-1931 [15] 乔景慧, 柴天佑. 数据与模型驱动的水泥生料分解率软测量模型. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1564-1578 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180734Qiao Jing-Hui, Chai Tian-You. Data and model-based soft measurement model of cement raw meal decomposition ratio. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1564-1578 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180734 [16] Chang N B, Chen W C. Prediction of pcdds/pcdfs emissions from municipal incinerators by genetic programming and neural network modeling. Waste Management & Research, 2000, 18(4): 341-351 [17] Bunsan S, Chen W Y, Chen H W, Chuang Y H, Grisdanurak N. Modeling the dioxin emission of a municipal solid waste incinerator using neural networks. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(3): 258-264 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.083 [18] 肖晓东, 卢加伟, 海景, 廖利. 垃圾焚烧烟气中二噁英类浓度的支持向量回归预测. 可再生能源, 2017, 35(8): 1107-1114Xiao Xiao-Dong, Lu Jia-Wei, Hai Jing, Liao Li. Prediction of dioxin emissions in flue gas from waste incineration based on support vector regression. Renewable Energy Resources, 2017, 35(8): 1107-1114 [19] Wu J, Yang H. Linear regression-based efficient svm learning for large-scale classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(10): 2357-2369 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2382123 [20] 乔俊飞, 郭子豪, 汤健. 基于多层特征选择的固废焚烧过程二噁英排放浓度软测量. 信息与控制, 2021, 50(1): 75-87 doi: 10.13976/j.cnki.xk.2021.9663Qiao Jun-Fei, Guo Zi-Hao, Tang Jian. Soft sensing of dioxin emission concentration in solid waste incineration process based on multi-layer feature selection. Information and Control, 2021, 50(1): 75-87 doi: 10.13976/j.cnki.xk.2021.9663 [21] 汤健, 乔俊飞. 基于选择性集成核学习算法的固废焚烧过程二噁英排放浓度软测量. 化工学报, 2019, 70(2): 696-706 doi: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20181354Tang Jian, Qiao Jun-Fei. Dioxin emission concentration soft measuring approach of municipal solid waste incineration based on selective ensemble kernel learning algorithm. Ciesc Journal, 2019, 70(2): 696-706 doi: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20181354 [22] Chang N B, Huang S H. Statistical modelling for the prediction and control of pcdds and pcdfs emissions from municipal solid waste incinerators. Waste Management & Research, 1995, 13(4): 379-400. [23] 汤健, 乔俊飞, 徐喆, 郭子豪. 基于特征约简与选择性集成算法的城市固废焚烧过程二噁英排放浓度软测量. 控制理论与应用, 2021, 38(1): 110-120 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90874Tang Jian, Qiao Jun-Fei, Xu Zhe, Guo Zi-Hao. Soft measuring approach of dioxin emission concentration in municipal solid waste incineration process based on feature reduction and selective ensemble algorithm. Control Theory & Applications, 2021, 38(1): 110-120 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90874 [24] Xia H, Tang J, Qiao J F, Yan A J, Guo Z H. Soft measuring method of dioxin emission concentration for mswi process based on rf and gbdt. In: Proceedings of the Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Hefei, China: IEEE, 2020. 2173−2178 [25] 段艳杰, 吕宜生, 张杰, 赵学亮, 王飞跃. 深度学习在控制领域的研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 643-654Duan Yan-Jie, Lv Yi-Sheng, Zhang Jie, Zhao Xue-Liang, Wang Fei-Yue. Deep learning for control: The state of the art and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 643-654 [26] Zhou Z H, Ji F. Deep forest. National Science Review, 2019, 6: 74-86. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwy108 [27] 汤健, 夏恒, 乔俊飞, 郭子豪. 深度集成森林回归建模方法及应用. 北京工业大学学报, 2021, 47(11): 1219-1229Tang Jian, Xia Heng, Qiao Jun-Fei, Guo Zi-Hao. Modeling method of deep ensemble forest regression with its application. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2021, 47(11): 1219-1229 [28] Tang J, Xia H, Zhang J, Qiao J F, Yu W. Deep forest regression based on cross-layer full connection. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(15): 9307-9328 doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-05691-7 [29] Xu W, Tang J, Xia H, Sun Z J. Prediction method of dioxin emission concentration based on PCA and deep forest regression. In: Proceedings of the 40th Chinese Control Conference. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2021. 1212−1217 [30] Graybill F A, Meyer C D, Painter R J. Note on the computation of the generalized inverse of a matrix. Siam Review, 1966, 8(4): 522-524 doi: 10.1137/1008108 [31] Chen C L P, Liu Z. Broad learning system: An effective and efficient incremental learning system without the need for deep architecture. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(1): 10−24 [32] Chen C L P, Liu Z, Feng S. Universal approximation capability of broad learning system and its structural variations. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(4): 1191-1204 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2866622 [33] Fan J C, Wang X, Wang X X, Zhao J H, Liu X. Incremental wishart broad learning system for fast polsar image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(12): 1854-1858 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2913999 [34] Ye H L, Li H, Chen C L P. Adaptive deep cascade broad learning system and its application in image denoising. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(9): 4450-4463 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2978500 [35] Chu Y H, Lin H F, Liang Y, Zhang D Y, Diao Y F, Fan X C, et al. Hyperspectral image classification based on discriminative locality preserving broad learning system. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 206: 1-17 [36] Cheng C, Wang W J, Chen H T, Zhang B C, Shao J J, Teng W X. Enhanced fault diagnosis using broad learning for traction systems in high-speed trains. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 36(7): 7461-7469 [37] Pu X K, Li C G. Online semisupervised broad learning system for industrial fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(10): 6644-6654 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3048990 [38] Yu W K, Zhao C H. Broad convolutional neural network based industrial process fault diagnosis with incremental learning capability. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(6): 5081-5091 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2931255 [39] Sui S, Chen P L C, Tong S C, Feng S. Finite-time adaptive quantized control of stochastic nonlinear systems with input quantization: A broad learning system based identification method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(10): 8555-8565 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2947844 [40] Feng J, Yao Y, S, Lu S X, Liu Y. Domain knowledge-based deep-broad learning framework for fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(4): 3454-3464 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2982085 [41] Han H G, Yang F F, Yang Y H, Wu X L. Type-2 fuzzy broad learning controller for wastewater treatment process. Neurocomputing, 2021, 459(4): 188-200 [42] Tang H, Dong P, Shi Y. A construction of robust representations for small data sets using broad learning system. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(10): 6074-6084 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2957818 [43] Qi G J, Luo J. Small data challenges in big data era: A survey of recent progress on unsupervised and semi-supervised methods. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(4): 2168-2187 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3031898 [44] 应雨轩, 林晓青, 吴昂键, 李晓东. 生活垃圾智慧焚烧的研究现状及展望. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 886-900Ying Yu-Xuan, Lin Xiao-Qing, Wu Ang-Jian, Li Xiao-Dong. Review and outlook on municipal solid waste smart incineration. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 886-900 [45] Xia H, Tang J, Aljerf L, Wang T Z, Qiao J F, Xu Q D, Wang Q, Ukaogo P. Investigation on Dioxins Emission Characteristic during Complete Maintenance Operating Period of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration, Environmental Pollution, 2023, 318: 120949 [46] Deng D Y, Qiao J Q, Liu M Q, Dorota K, Zhang M W, Dionysios D D F, et al. Detoxification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash by single-mode microwave irradiation: Addition of urea on the degradation of dioxin and mechanism. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 369: 279-289 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.001 [47] Stanmore B R. The formation of dioxins in combustion systems. Combustion and Flame, 2004, 136(3): 398-427 doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2003.11.004 [48] Zhang S, Chen Z L, Lin X Q, Wang F, Yan J H. Kinetics and fusion characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash during thermal treatment. Fuel, 2020, 279: 1-13 [49] Zhang M M, Alfons G B. De novo synthesis of dioxins: A review. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 2016, 60: 63-110 doi: 10.1504/IJEP.2016.082115 [50] Zhou H, Meng A H, Long Y Q, Li Q H, Zhang Y G. A review of dioxin-related substances during municipal solid waste incineration. Waste Management, 2015, 36: 106-118 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.11.011 [51] Peng Y Q, Lu S Y, Li X D, Yan J H, Cen K F. Formation, measurement, and control of dioxins from the incineration of municipal solid wastes: Recent advances and perspectives. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34: 13247-13267 [52] , Influence factors and mass balance of memory effect on PCDD/F emissions from the full-scale municipal solid waste incineration in China. Chemosphere, 2020, 239: 1-8Chemosphere, 2001, 45(8): 1151-1157 [53] Breiman L. Bagging predictors. Mach Learn, 1996, 24: 123-140 [54] Ho T K. The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(8): 832-844 [55] Blake C L, Merz C J. UCI repository of machine learning databases [Online], available: http://www.archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/k datasets.html, January 1, 2022 -





 下载:
下载: