Task Allocation and Reallocation for Heterogeneous Multiagent Systems Based on Potential Game
-
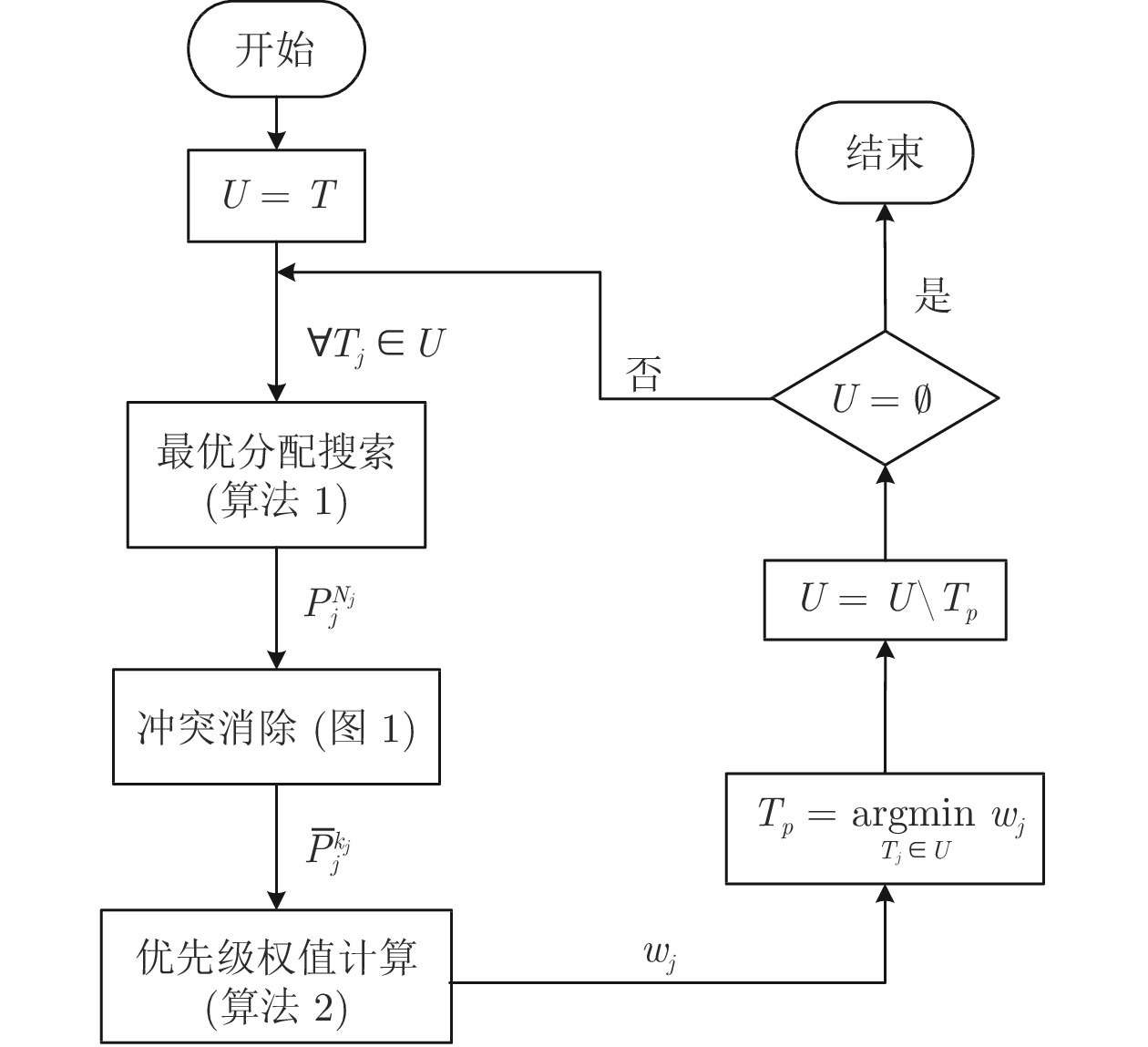
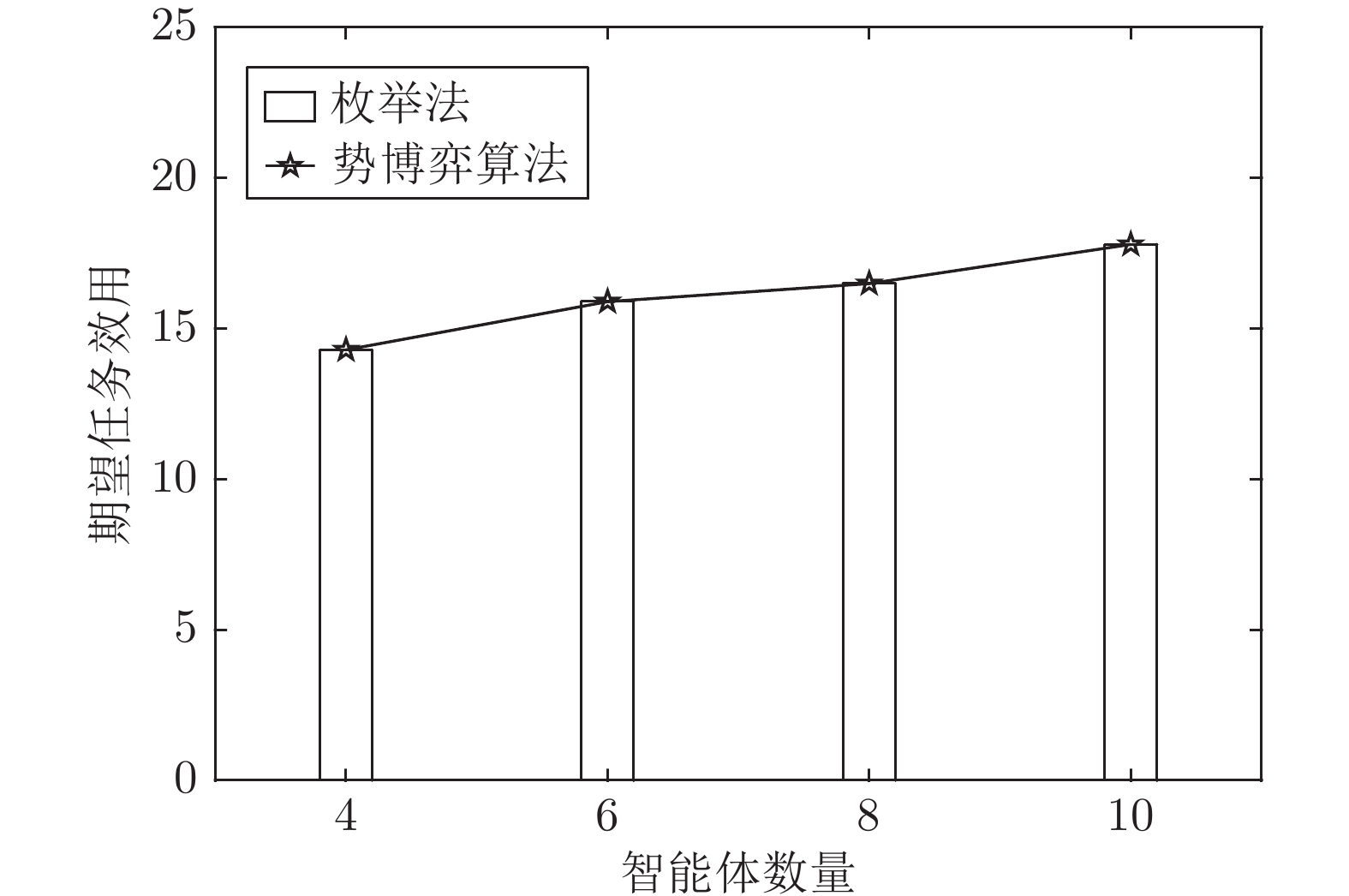
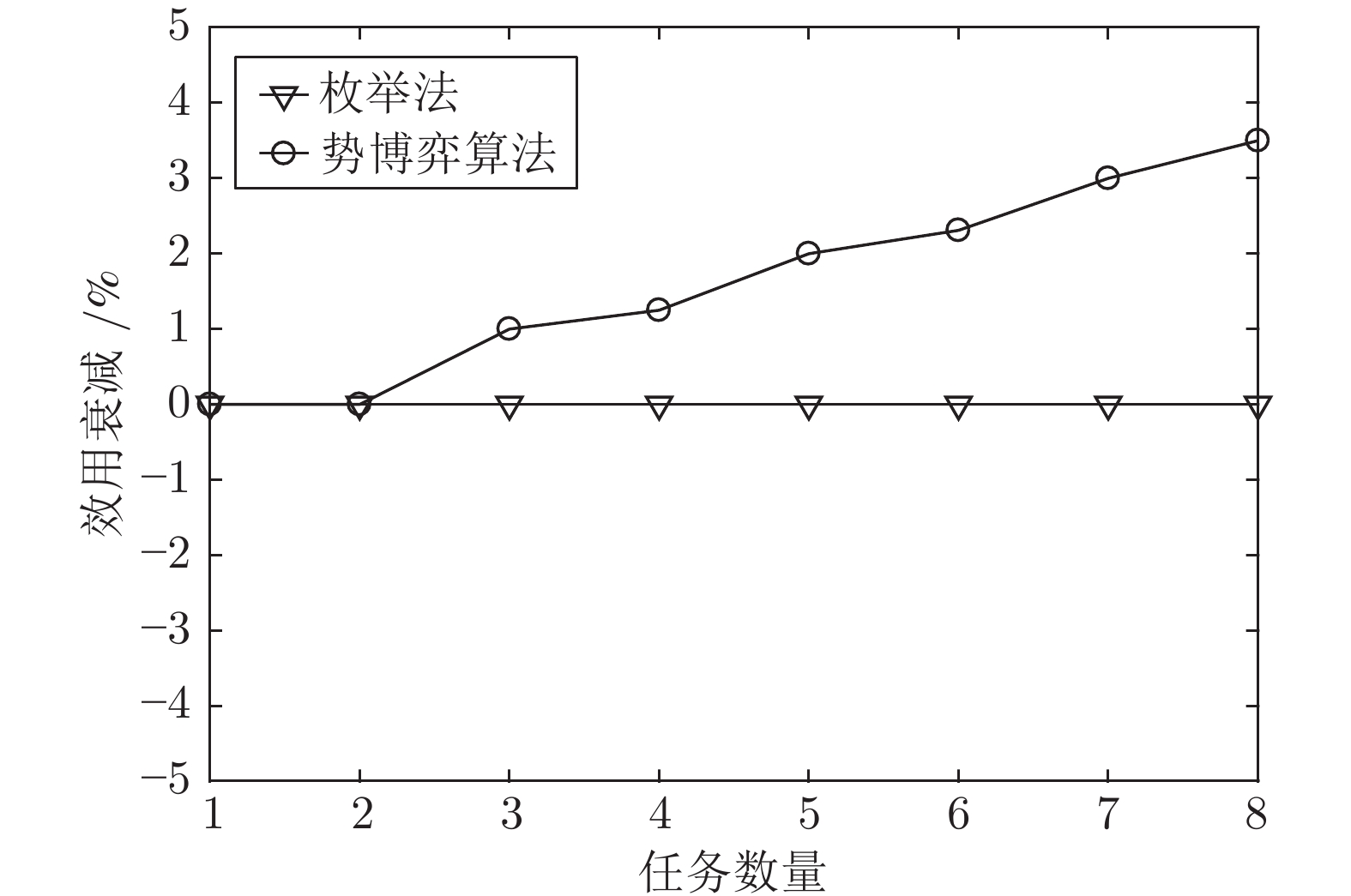
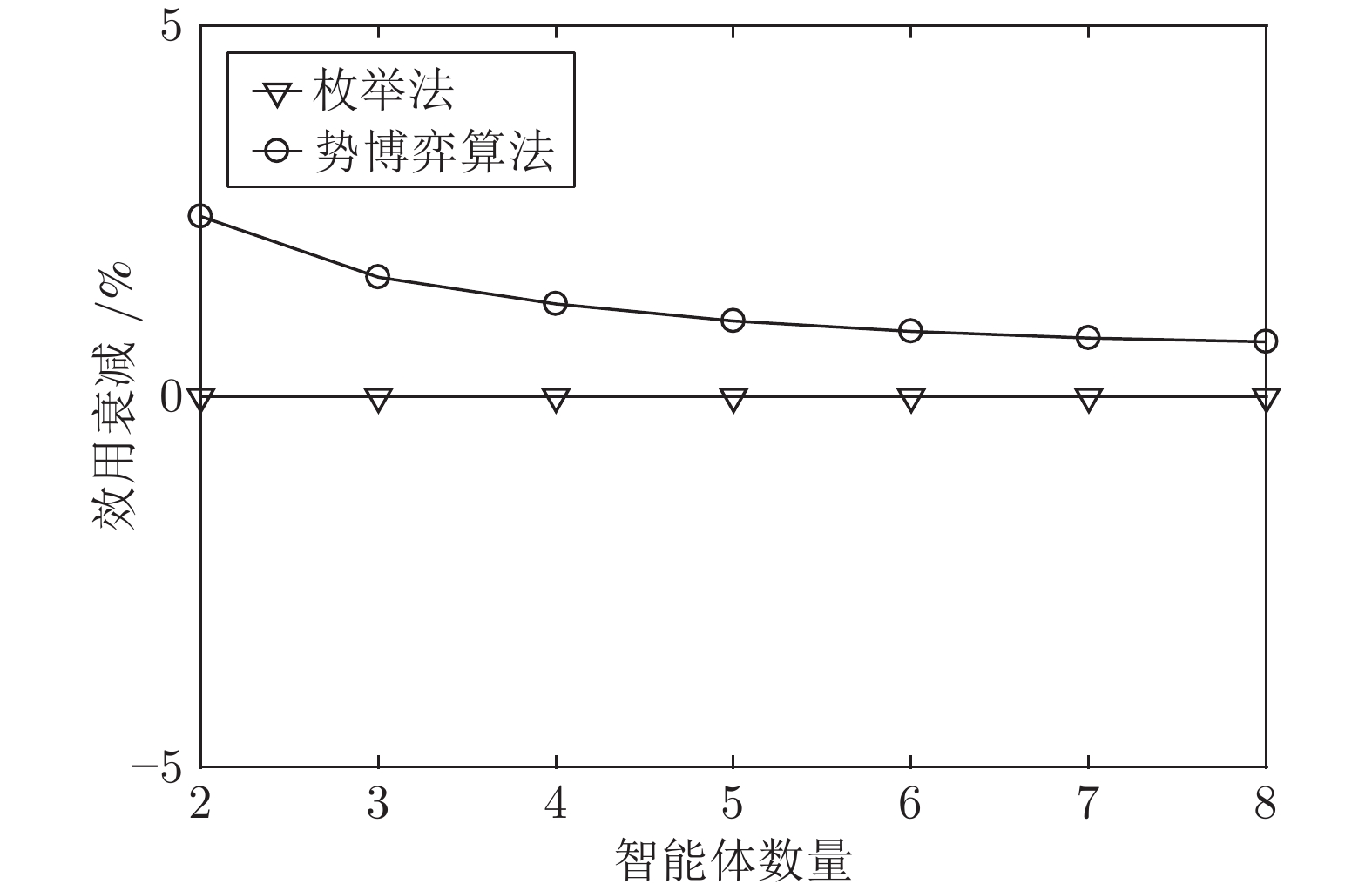
摘要: 针对异构多智能体系统, 基于势博弈理论提出一种新的任务分配和重分配算法. 考虑任务执行同步性和任务时效性的多重约束, 导致异构多智能体系统中各个体任务执行时间受到多种限制, 建立一个基于势博弈的算法结构, 使系统以分布式方式工作. 在此基础上, 基于势博弈理论设计任务分配算法, 保证在较低复杂度的同时, 可以得到近似最大化期望全局效用的良好分配方案, 并且随后将所提出的方法推广到任务重分配方案实现故障下的容错. 最后, 针对攻击任务场景对所提算法进行仿真验证, 结果表明, 在期望全局效用、容错能力和算法复杂度方面具有全面的性能.Abstract: This paper presents a novel task allocation and reallocation algorithm for heterogeneous multiagent systems based on potential game theory. Considering the multiple constraints of task execution synchronization and task timeliness, which lead to various restrictions on the execution time of each individual task in the heterogeneous multiagent systems, a potential game-based algorithm structure is established to make agents work in a distributed manner. On this basis, the task allocation algorithm is designed based on potential game theory, which produces a promising solution that nearly maximizes the expected global utility and guarantees lower complexity, and afterwards the fault tolerance is achieved by generalizing the proposed algorithm to task reallocation schemes. Finally, the proposed algorithm is verified by simulation of the attack task scenario, and results reveal the comprehensive performance in terms of the expected global utility, the fault tolerance and the algorithm complexity.
-
Key words:
- Task allocation /
- multiagent systems /
- potential game /
- constrained optimization /
- fault tolerance
-
表 1 智能体初始信息
Table 1 Initial information of agents
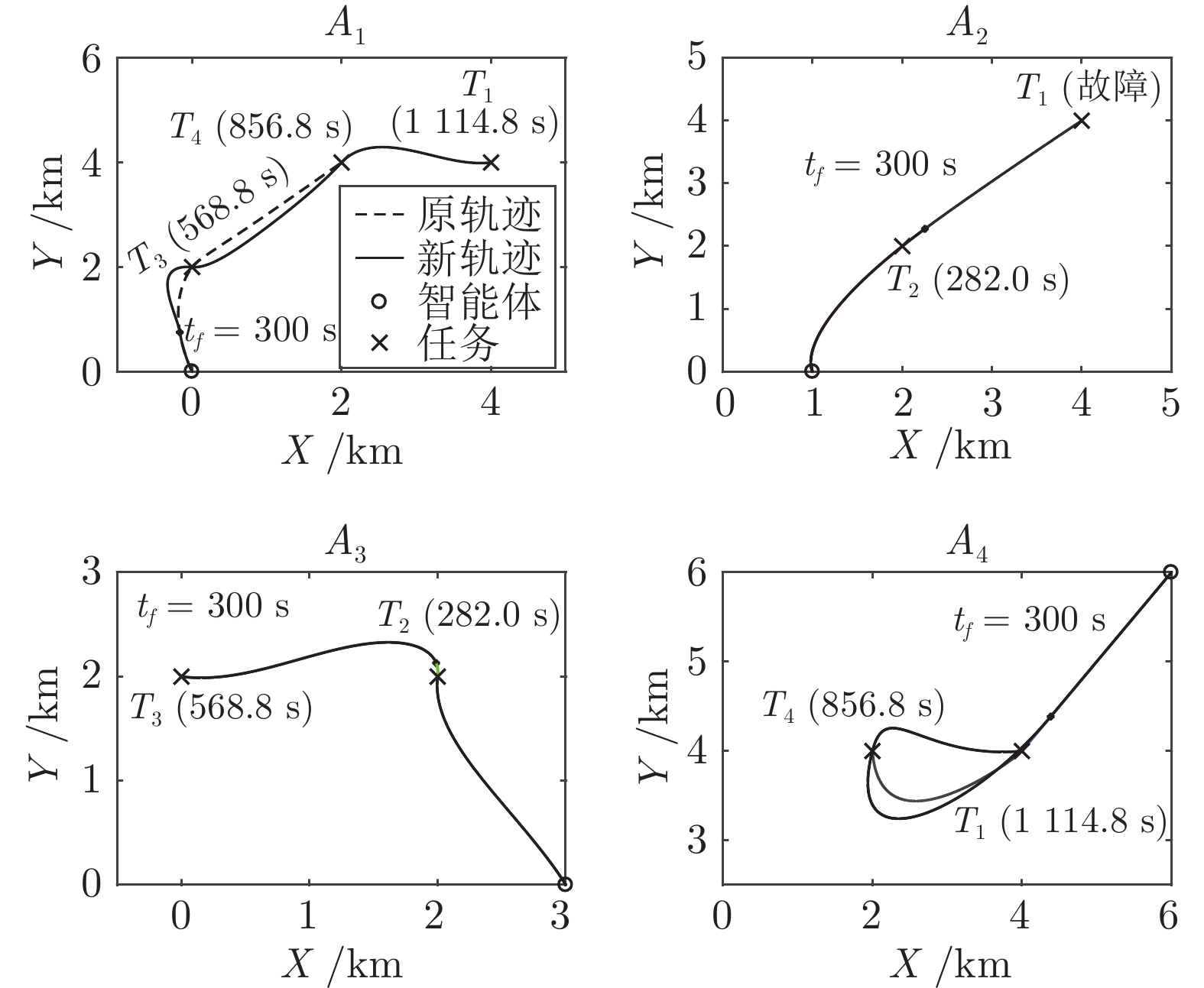
智能体$A_i$ 位置 (m, m) 能力$(\lambda_{i1},\lambda_{i2},\lambda_{i3},\lambda_{i4})$ 最大速度 (m/s) 最大加速度 (m/s2) $A_1$ (0, 0) (0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0) 10 0.25 $A_2$ (1000, 0) (1.0, 1.0, 0.5, 0.5) 20 0.25 $A_3$ (3000, 0) (0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 0.5) 10 0.25 $A_4$ (6000, 6000) (1.0, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0) 20 0.25 表 2 任务初始信息
Table 2 Initial information of tasks
任务$T_j$ 位置 (m, m) 基础效用$r_j$ 所需智能体数量$N_j$ 折扣系数$\mu_j$ $T_1$ (4000, 4000) 10 2 5$\times 10^{-4}$ $T_2$ (2000, 2000) 20 2 5$\times 10^{-4}$ $T_3$ (0, 2000) 10 2 5$\times 10^{-4}$ $T_4$ (2000, 4000) 10 2 5$\times 10^{-4}$ -
[1] Yang Y, Li Y F, Yue D, Tian Y C, Ding X H. Distributed secure consensus control with event-triggering for multiagent systems under DoS attacks. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(6): 2916-2928 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2979342 [2] Zhang K, Jiang B, Shi P. Adjustable parameter-based distributed fault estimation observer design for multiagent systems with directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(2): 306-314 [3] 田磊, 董希旺, 赵启伦, 李清东, 吕金虎, 任章. 异构集群系统分布式自适应输出时变编队跟踪控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(10): 2386-2401Tian Lei, Dong Xi-Wang, Zhao Qi-Lun, Li Qing-Dong, Lv Jin-Hu, Ren Zhang. Distributed adaptive time-varying output formation tracking for heterogeneous swarm systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(10): 2386-2401 [4] 黄刚, 李军华. 基于 AC-DSDE 进化算法多 UAVs 协同目标分配. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(1): 173-184Huang Gang, Li Jun-Hua. Multi-UAV cooperative target allocation based on AC-DSDE evolutionary algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 47(1): 173-184 [5] Li M C, Wang Z D, Li K L, Liao X K, Hone K, Liu X H. Task allocation on layered multiagent systems: When evolutionary many-objective optimization meets deep Q-learning. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 25(5): 842-855 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2021.3049131 [6] 李勇, 李坤成, 孙柏青, 张秋豪, 王义娜, 杨俊友. 智能体 Petri 网融合的多机器人-多任务协调框架. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(8): 2029-2049Li Yong, Li Kun-Cheng, Sun Bai-Qing, Zhang Qiu-Hao, Wang Yi-Na, Yang Jun-You. Multi-robot-multi-task coordination framework based on the integration of intelligent agent and petri net. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 47(8): 2029-2049 [7] Gerkey B P, Mataric M J. A formal analysis and taxonomy of task allocation in multi-robot systems. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2004, 23(9): 939-954 doi: 10.1177/0278364904045564 [8] Alencar R C, Santana C J, Bastos-Filho C J A. Optimizing routes for medicine distribution using team ant colony system. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 2020, 923: 40-49 [9] Zhang F. Intelligent task allocation method based on improved QPSO in multi-agent system. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2020, 11: 655-662 doi: 10.1007/s12652-019-01242-0 [10] Rahman S M M, Wang Y. Mutual trust-based subtask allocation for human-robot collaboration in flexible lightweight assembly in manufacturing. Mechatronics, 2018, 54: 94-109 doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2018.07.007 [11] Chen J X, Wu Q H, Xu Y H, Qi N, Guan X, Zhang Y L, et al. Joint task assignment and spectrum allocation in heterogeneous UAV communication networks: A coalition formation game-theoretic approach. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 440-452 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3025316 [12] Wang D, Li K M, Zhang Q, Lu X F, Luo Y. A cooperative task allocation game for multi-target imaging in radar networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(6): 7541-7550 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3049899 [13] Sullivan N, Grainger S, Cazzolato B. Sequential single-item auction improvements for heterogeneous multi-robot routing. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 115: 130-142 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2019.02.016 [14] Lee D H. Resource-based task allocation for multi-robot systems. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2018, 103: 151-161 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2018.02.016 [15] Huang X W, Gong S M, Yang J M, Zhang W J, Yang L W, Yeo C K. Hybrid market-based resources allocation in mobile edge computing systems under stochastic information. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2022, 127: 80-91 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2021.08.029 [16] Xu Y H, Jiang B, Yang H. Two-level game-based distributed optimal fault-tolerant control for nonlinear interconnected systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(11): 4892-4906 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2958948 [17] 刘坤, 郑晓帅, 林业茗, 韩乐, 夏元清. 基于微分博弈的追逃问题最优策略设计. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(8): 1840-1854Liu Kun, Zheng Xiao-Shuai, Lin Ye-Ming, Han Le, Xia Yuan-Qing. Design of optimal strategies for the pursuit-evasion problem based on differential game. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1840-1854 [18] Duan H B, Li P, Yu Y X. A predator-prey particle swarm optimization approach to multiple UCAV air combat modeled by dynamic game theory. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2015, 2(1): 11-18 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2015.7032901 [19] Chapman A C, Micillo R A, Kota R, Jennings N R. Decentralised dynamic task allocation: A practical game theoretic approach. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2009. 915−922 [20] Wu H, Shang H L. Potential game for dynamic task allocation in multi-agent system. ISA Transactions, 2020, 102: 208-220 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.03.004 [21] Monderer D, Shapley L S. Potential games. Games and Economic Behavior, 1996, 14(1): 124-143 doi: 10.1006/game.1996.0044 [22] Xu X L, Mo R C, Dai F, Lin W M, Wan S H, Dou W C. Dynamic resource provisioning with fault tolerance for data-intensive meteorological workflows in cloud. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(9): 6172-6181 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2959258 [23] Paul S, Chatterjee N, Ghosal P. A permanent fault tolerant dynamic task allocation approach for network-on-chip based multicore systems. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2019, 97: 287-303 doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2018.10.003 [24] Das G P, McGinnity T M, Coleman S A, Behera L. A fast distributed auction and consensus process using parallel task allocation and execution. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2011. 4716−4721 [25] Farinelli A, Iocchi L, Nardi D. Distributed on-line dynamic task assignment for multi-robot patrolling. Autonomous Robots, 2017, 41(6): 1321-1345 doi: 10.1007/s10514-016-9579-8 [26] Guo S C, Huang H Z, Wang Z L, Xie M. Grid service reliability modeling and optimal task scheduling considering fault recovery. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2011, 60(1): 263-274 doi: 10.1109/TR.2010.2104190 [27] Shatz S M, Wang J P. Models and algorithms for reliability-oriented task-allocation in redundant distributed-computer systems. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 1989, 38(1): 16-27 doi: 10.1109/24.24570 [28] Shoham Y, Brown K L. Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic, Game-theoretic, and Logical Foundations. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008. 174−177 [29] 唐嘉钰, 李相民, 代进进, 薄宁. 复杂约束条件下异构多智能体联盟任务分配. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(11): 2413-2422 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90868Tang Jia-Yu, Li Xiang-Min, Dai Jin-Jin, Bo Ning. Coalition task allocation of heterogeneous multiple agents with complex constraints. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(11): 2413-2422 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90868 [30] Elhoseny M, Tharwat A, Hassanien A E. Bezier curve based path planning in a dynamic field using modified genetic algorithm. Journal of Computational Science, 2018, 25: 339-350 doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2017.08.004 [31] Mellinger D, Kumar V. Minimum snap trajectory generation and control for quadrotors. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2011. 2520−2525 -




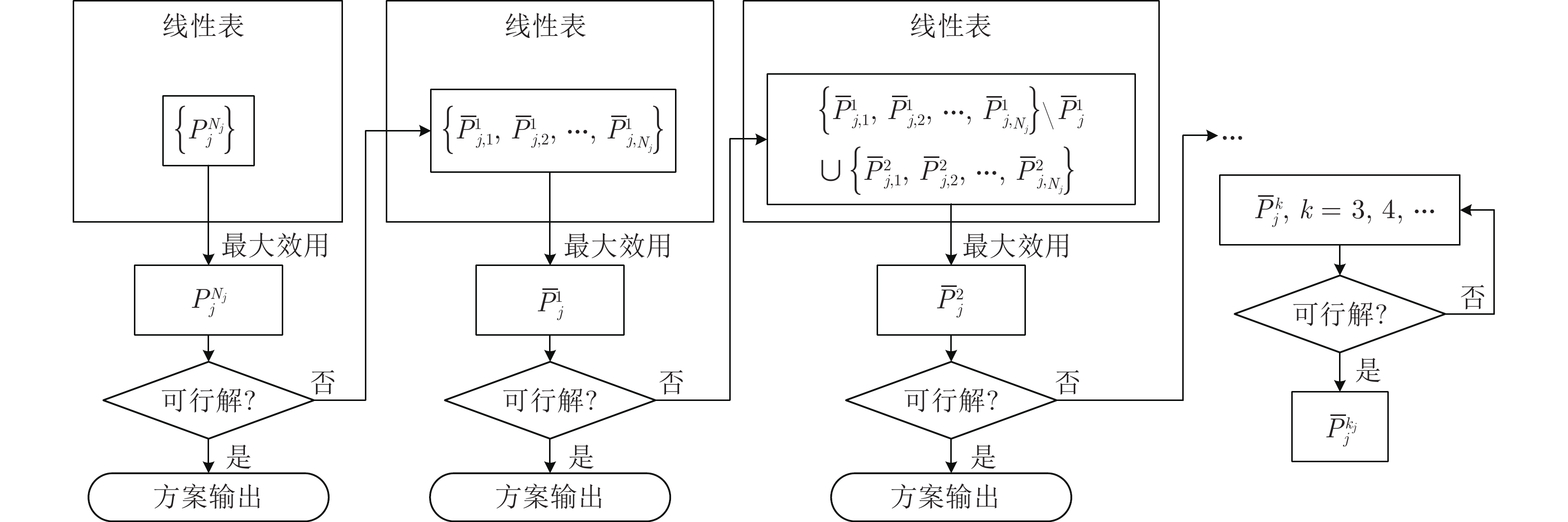
 下载:
下载: