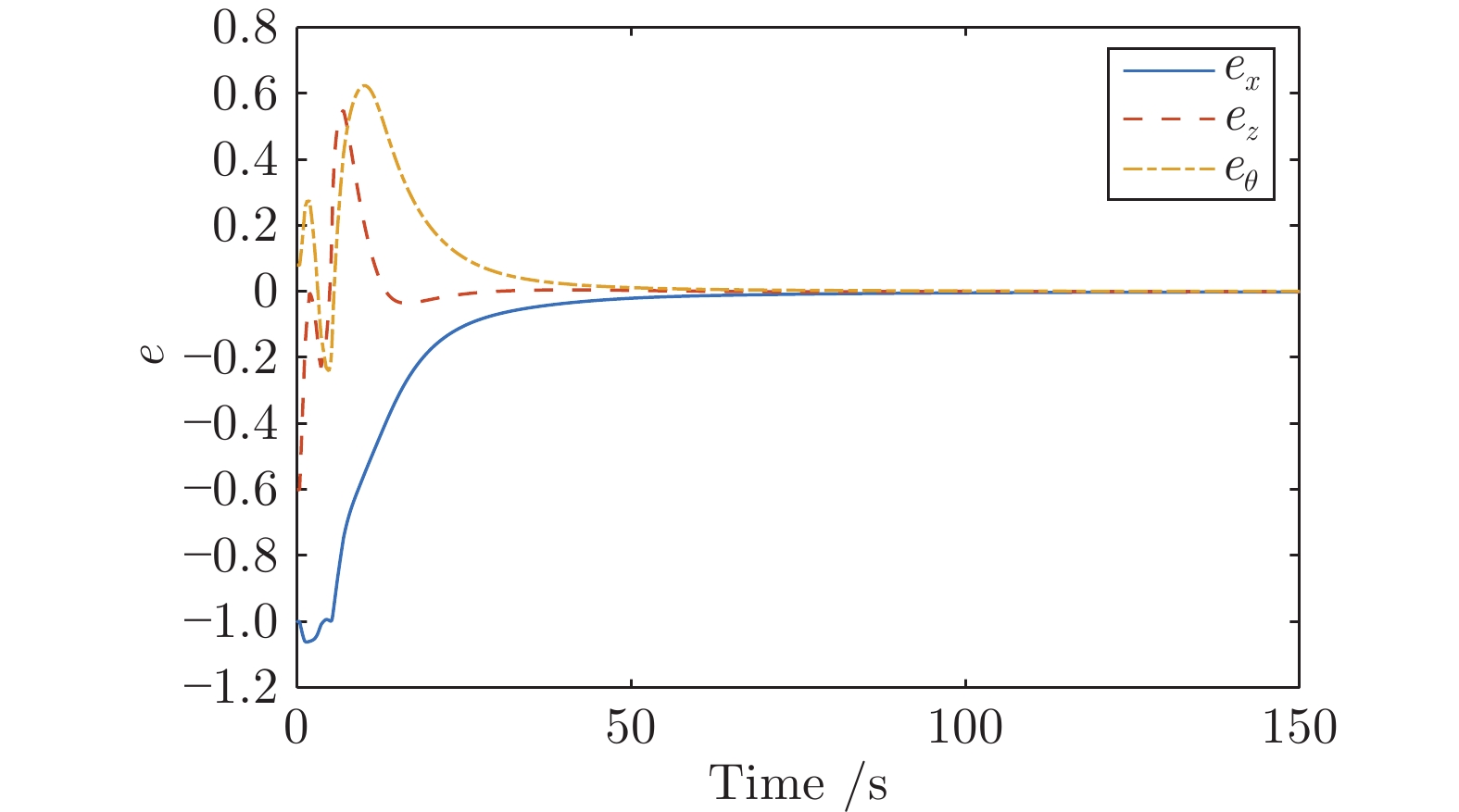
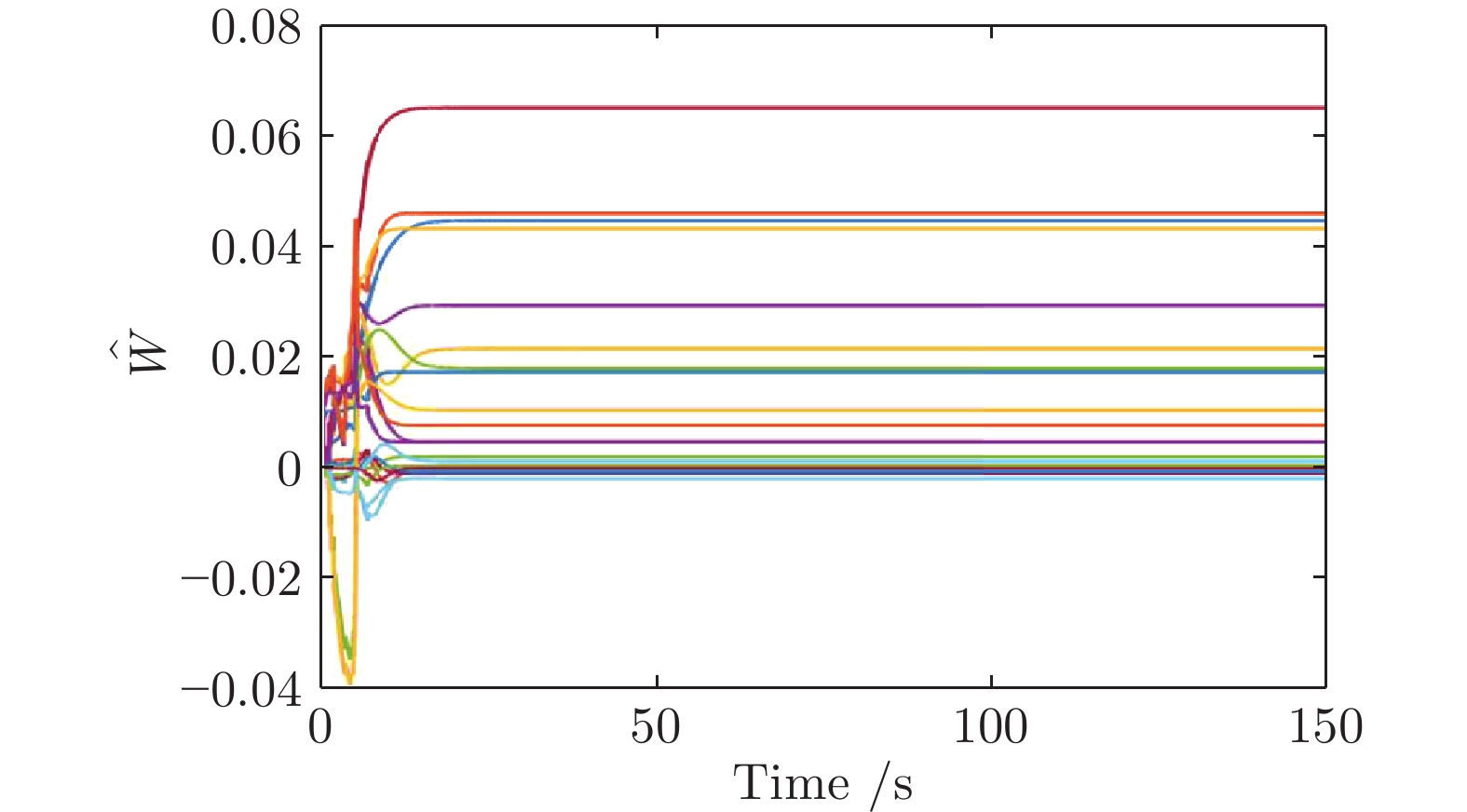
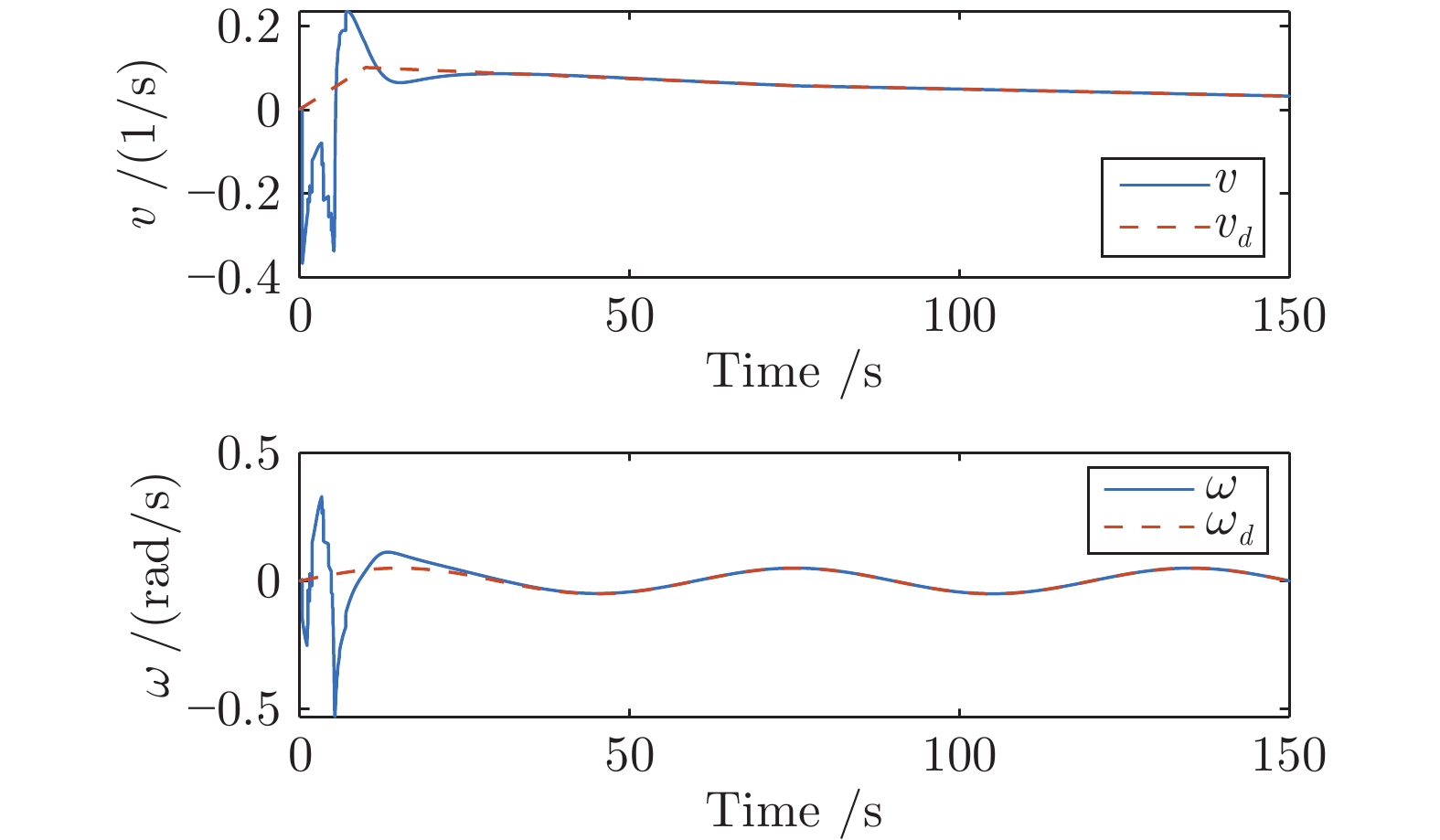
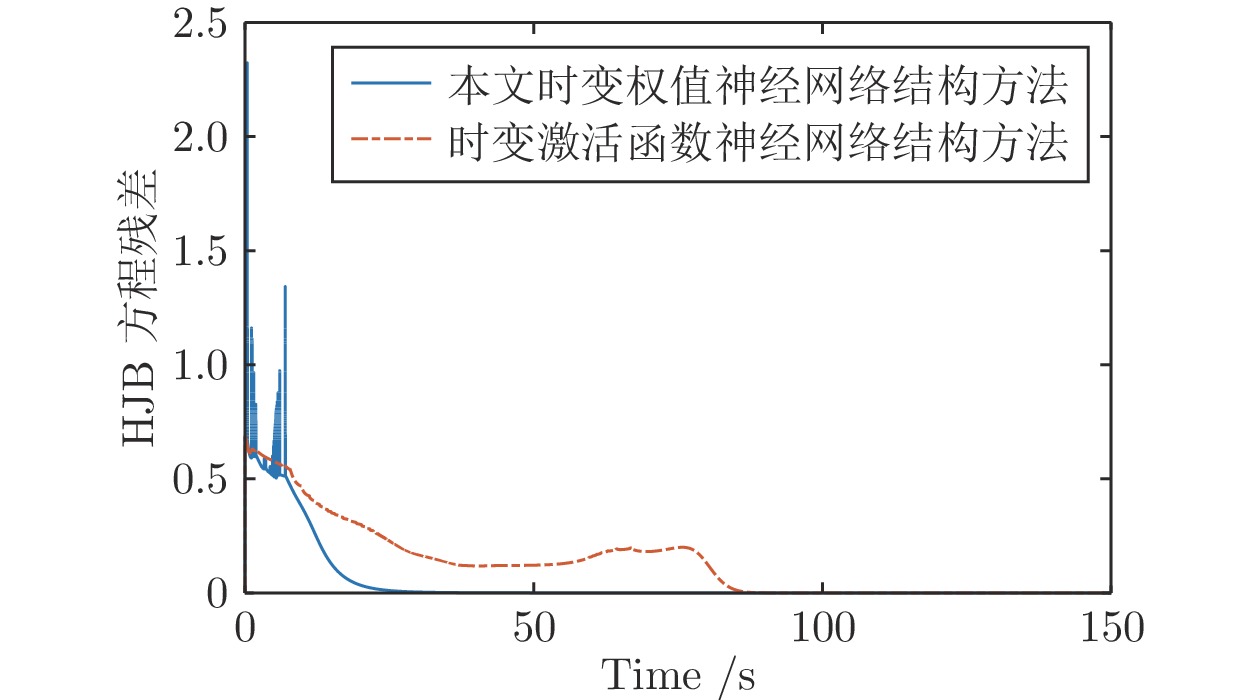
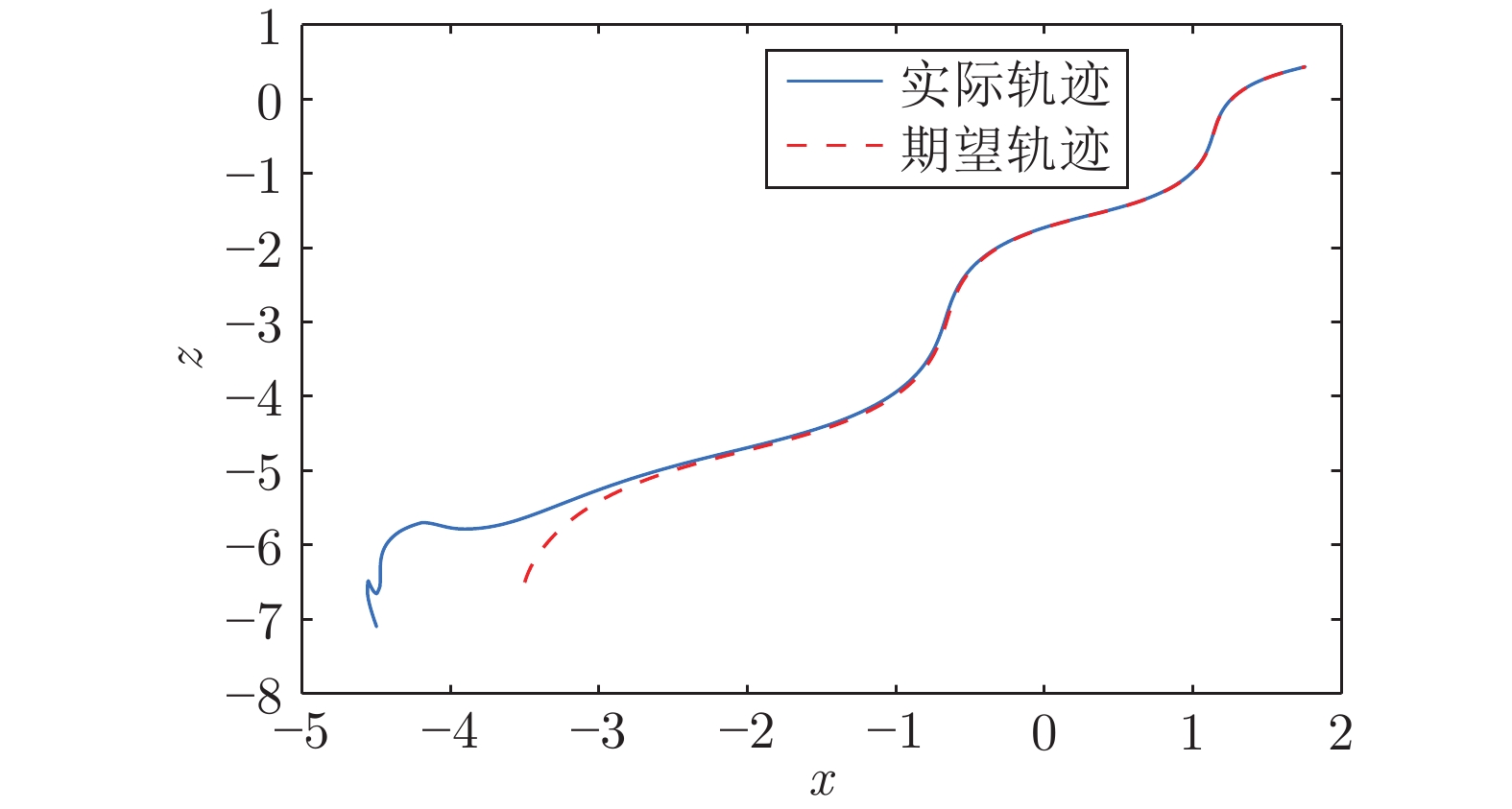
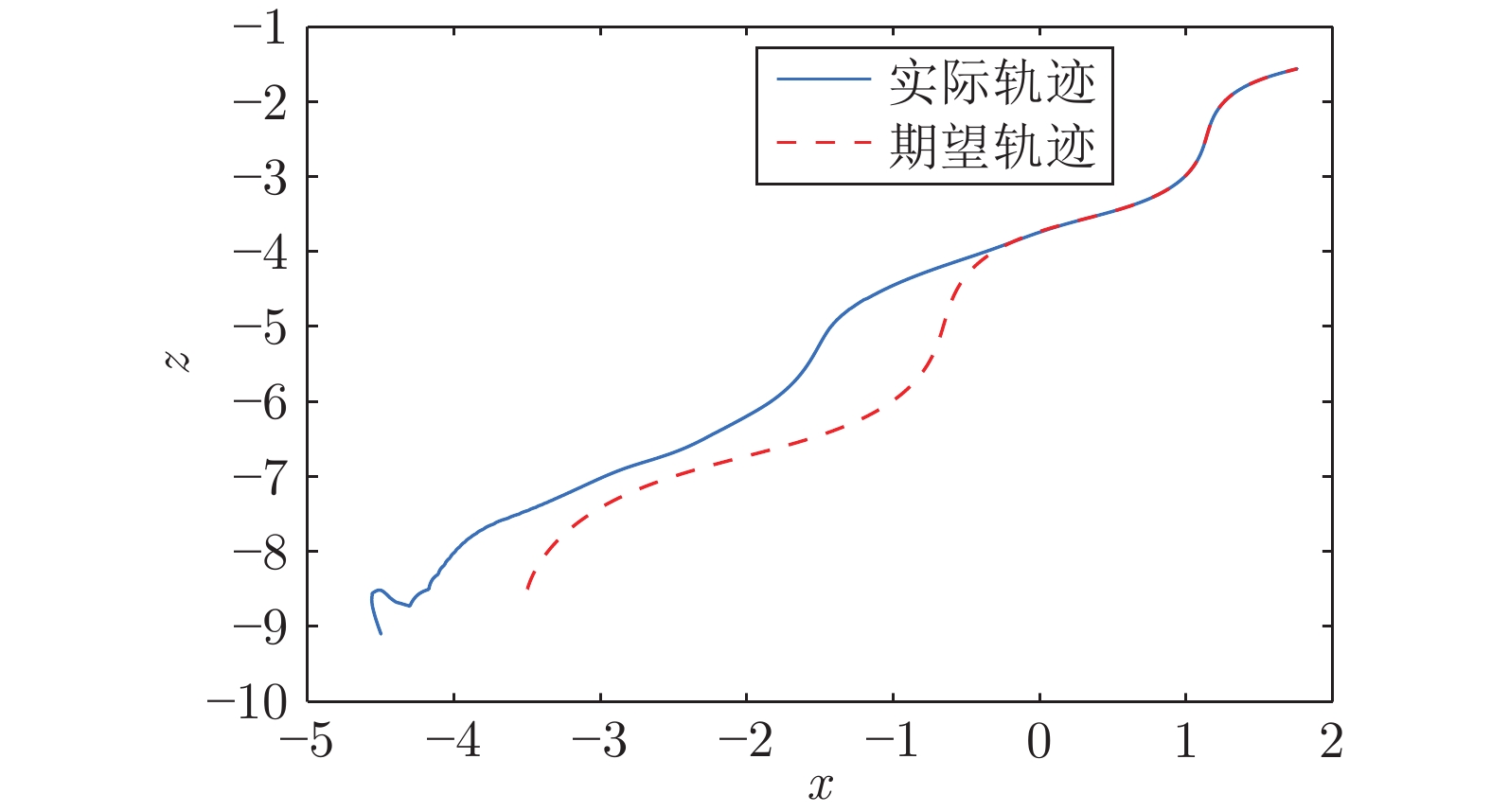
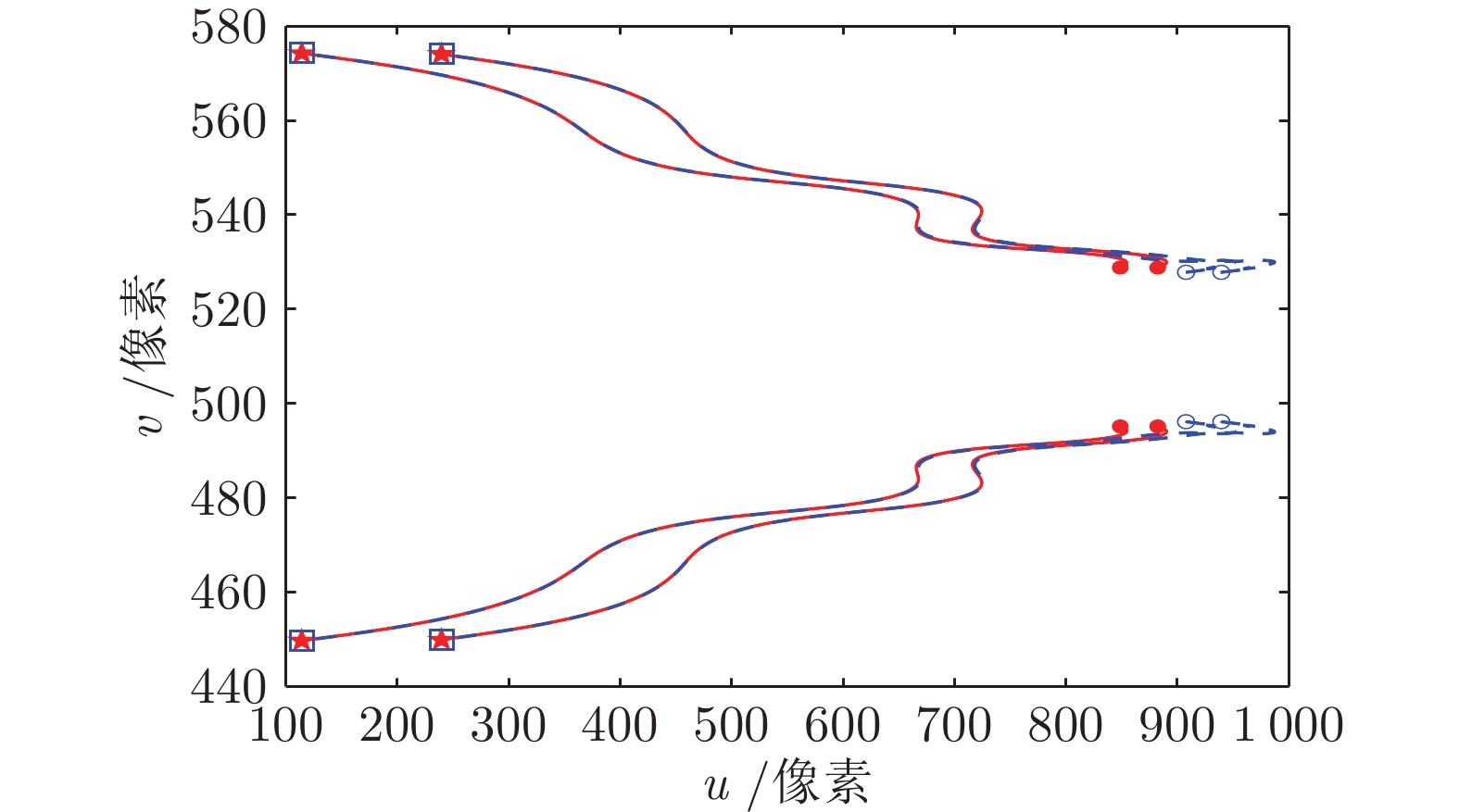
|
[1]
|
贾丙西, 刘山, 张凯祥, 陈剑. 机器人视觉伺服研究进展: 视觉系统与控制策略. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(5): 861-873Jia Bing-Xi, Liu Shan, Zhang Kai-Xiang, Chen Jian. Survey on robot visual servo control: Vision system and control strategies. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5): 861-873
|
|
[2]
|
Fomena R T, Tahri O, Chaumette F. Distance-based and orientation-based visual servoing from three points. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2011, 27(2): 256-267 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2011.2104431
|
|
[3]
|
杨芳, 王朝立. 基于视觉伺服反馈的不确定非完整动态移动机器人的自适应镇定. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(7): 857-864 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(11)60211-5Yang Fang, Wang Chao-Li. Adaptive stabilization for uncertain nonholonomic dynamic mobile robots based on visual servoing feedback. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(7): 857-864 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(11)60211-5
|
|
[4]
|
Jiang Z P. Robust exponential regulation of nonholonomic systems with uncertainties. Automatica, 2000, 36(2): 189-209 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00115-6
|
|
[5]
|
Chen, J, Dixon, W E, Dawson, D M, McIntire, M. Homography-based visual servo tracking control of a wheeled mobile robot. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2006, 22(2): 406-415 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2006.862476
|
|
[6]
|
Liang X, Wang H, Chen W, Guo D, Liu T. Adaptive image-based trajectory tracking control of wheeled mobile robots with an uncalibrated fixed camera. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 23(6): 2266-2282 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2015.2411627
|
|
[7]
|
徐德. 单目视觉伺服研究综述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1729-1746Xu De. A tutorial for monocular visual servoing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1729-1746
|
|
[8]
|
Brockett R W, Millman R S, Sussmann H J. Differential Geometric Control Theory. Michigan: Birkhauser Boston, 1983.
|
|
[9]
|
Jiang Z P, Nijmeijer H. Tracking control of mobile robots: A case study in backstepping. Automatica, 1997, 33(7): 1393-1399 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(97)00055-1
|
|
[10]
|
Li B, Fang Y, Hu G, Zhang X. Model-free unified tracking and regulation visual servoing of wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 24(4): 1328-1339
|
|
[11]
|
Li L, Liu Y H, Jiang T, Wang K, Fang M. Adaptive trajectory tracking of nonholonomic mobile robots using vision-based position and velocity estimation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 48(2): 571-582
|
|
[12]
|
Miao Z, Zhong H, Lin J, Wang Y, Chen Y, Fierro R. Vision-based bormation control of mobile robots with FOV constraints and unknown feature depth. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2021, 29(5): 2231-2238 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2020.3023415
|
|
[13]
|
Zhang K, Chen J, Li Y, Zhang X. Visual tracking and depth estimation of mobile robots without desired velocity information. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(1): 361-373 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2869623
|
|
[14]
|
Lee S, Chwa D. Dynamic image-based visual servoing of monocular camera mounted omnidirectional mobile robots considering actuators and target motion via fuzzy integral sliding mode control. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 29(7): 2068-2076 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2985931
|
|
[15]
|
Wang R, Zhang X, Fang Y, Li B. Virtual-goal-guided RRT for visual servoing of mobile robots with FOV constraint. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(4): 2073-2083 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3044347
|
|
[16]
|
Kiumarsi B, Lewis F L. Actor-critic-based optimal tracking for partially unknown nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 26(1): 140-151
|
|
[17]
|
Luo B, Wu H N, Li H X. Adaptive optimal control of highly dissipative nonlinear spatially distributed processes with neuro-dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(4): 684-696 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2320744
|
|
[18]
|
Liu D, Xue S, Zhao B, Luo B, Wei Q. Adaptive dynamic programming for control: A survey and recent advances. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(1): 142-160 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3042876
|
|
[19]
|
Ming Z, Zhang H, Yan Y, Zhang J. Tracking control of discrete-time system with dynamic event-based adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(8): 3570-3574 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2022.3168428
|
|
[20]
|
Li S, Ding L, Gao H, Liu Y J, Huang L, Deng Z. ADP-based online tracking control of partially uncertain time-delayed nonlinear system and application to wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(7): 3182-3194 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2900326
|
|
[21]
|
Kong L, He W, Yang C, Sun C. Robust neurooptimal control for a robot via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(6): 2584-2594 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3006850
|
|
[22]
|
张化光, 张欣, 罗艳红, 杨珺. 自适应动态规划综述. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 303-311 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60031-2Zhang Hua-Guang, Zhang Xin, Luo Yan-Hong, Yang Jun. An overview of research on adaptive dynamic programming. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 303-311 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60031-2
|
|
[23]
|
Liu D, Wang D, Wang F Y, Li H, Yang, X. Neural-network-based online HJB solution for optimal robust guaranteed cost control of continuous-time uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(12): 2834-2847 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2357896
|
|
[24]
|
王鼎, 穆朝絮, 刘德荣. 基于迭代神经动态规划的数据驱动非线性近似最优调节. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 366-375 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160272Wang Ding, Mu Chao-Xu, Liu De-Rong. Data-driven nonlinear near-optimal regulation based on iterative neural dynamic programming. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 366-375 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160272
|
|
[25]
|
Bhasin S, Kamalapurkar R, Johnson M, Vamvoudakis K G, Lewis F L, Dixon W E. A novel actor-critic-identifier architecture for approximate optimal control of uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica, 2013, 49(1): 82-92 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.09.019
|
|
[26]
|
Lin W S, Yang P C. Adaptive critic motion control design of autonomous wheeled mobile robot by dual heuristic programming. Automatica, 2008, 44(11): 2716-2723 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2008.03.029
|
|
[27]
|
Cheng T, Lewis F L, Abu-Khalaf M. A neural network solution for fixed-final time optimal control of nonlinear systems. Automatica, 2007, 43(3): 482-490 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.09.021
|
|
[28]
|
Heydari A, Balakrishnan S N. Fixed-final-time optimal tracking control of input-affine nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing, 2014, 129(10): 528-539
|
|
[29]
|
Wang F Y, Jin N, Liu D, Wei Q. Adaptive dynamic programming for finite-horizon optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems with ε-error bound. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 22(1): 24-36
|
|
[30]
|
Zhao Q, Xu H, Jagannathan S. Neural network-based finite-horizon optimal control of uncertain affine nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 26(3): 486-499
|
|
[31]
|
Hartley R, Zisserman A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003.
|
|
[32]
|
Siciliano B, Sciavicco L, Villani L, Oriolo G. Robotics: Modelling, Planning and Control. London: Springer-Verlag, 2009.
|
|
[33]
|
Zhang K, Chen J, Li Y, Zhang X. Visual tracking and depth estimation of mobile robots without desired velocity information. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 50(1): 361-373
|
|
[34]
|
Lewis F L, Vrabie D L, Syrmos V L. Optimal Control, Third Edition. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
|
|
[35]
|
Finlayson B A. The Method of Weighted Residuals and Variational Principles. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2013.
|
|
[36]
|
Abu-Khalaf M, Lewis F L. Nearly optimal control laws for nonlinear systems with saturating actuators using a neural network HJB approach. Automatica, 2005, 41(5): 779-791 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.11.034
|
|
[37]
|
Pakkhesal S, Shamaghdari S. Sum-of-squares-based policy iteration for suboptimal control of polynomial time-varying systems. Asian Journal of Control, 2022, 24(6): 3022-3031 doi: 10.1002/asjc.2689
|
|
[38]
|
Wei Q, Liao Z, Yang Z, Li B, Liu D. Continuous-time time-varying policy iteration. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(12): 4958-4971 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2926631
|
|
[39]
|
Zhang H, Cui L, Zhang X, Luo Y. Data-driven robust approximate optimal tracking control for unknown general nonlinear systems using adaptive dynamic programming method. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(12): 2226-2236 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2168538
|




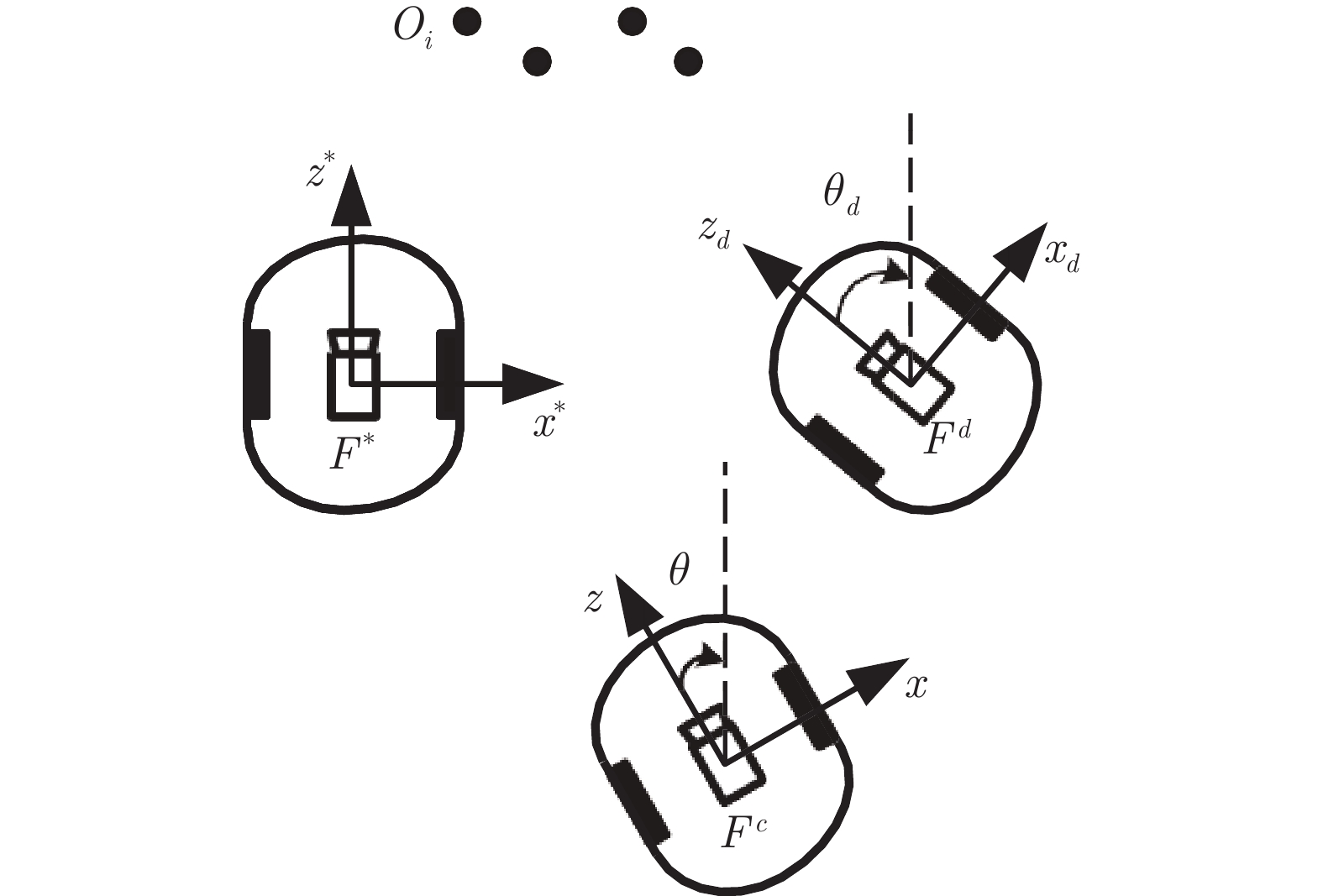
 下载:
下载: