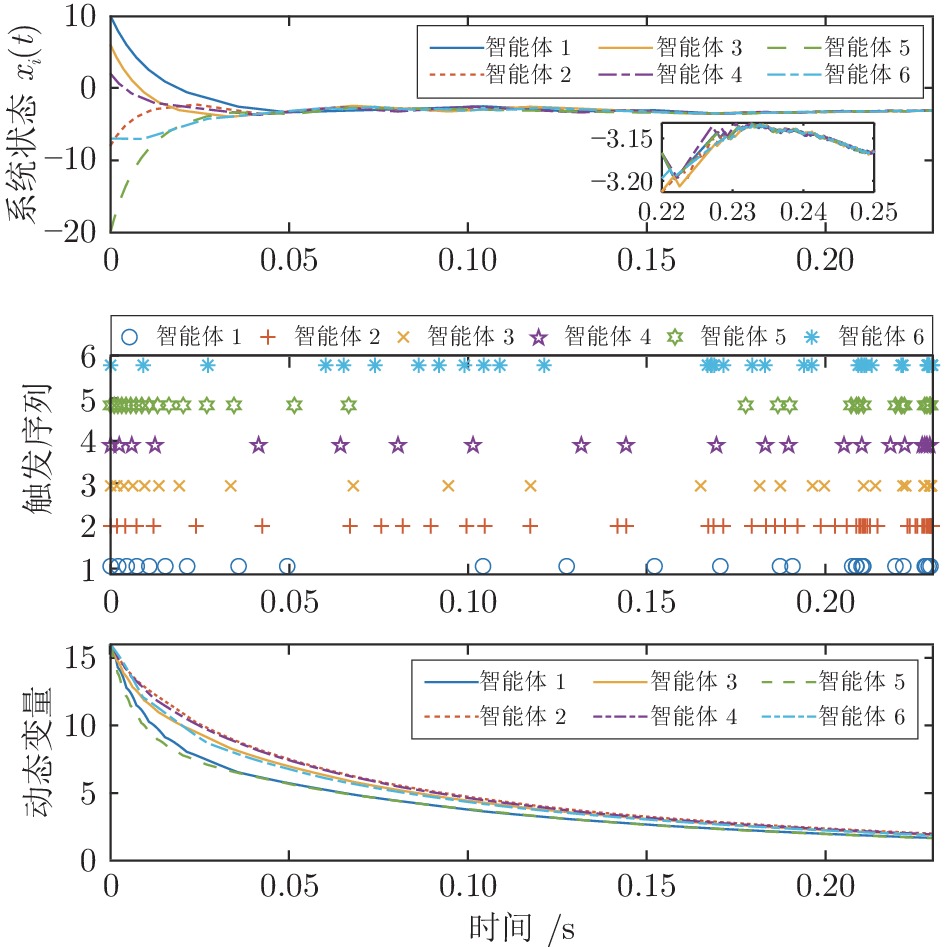
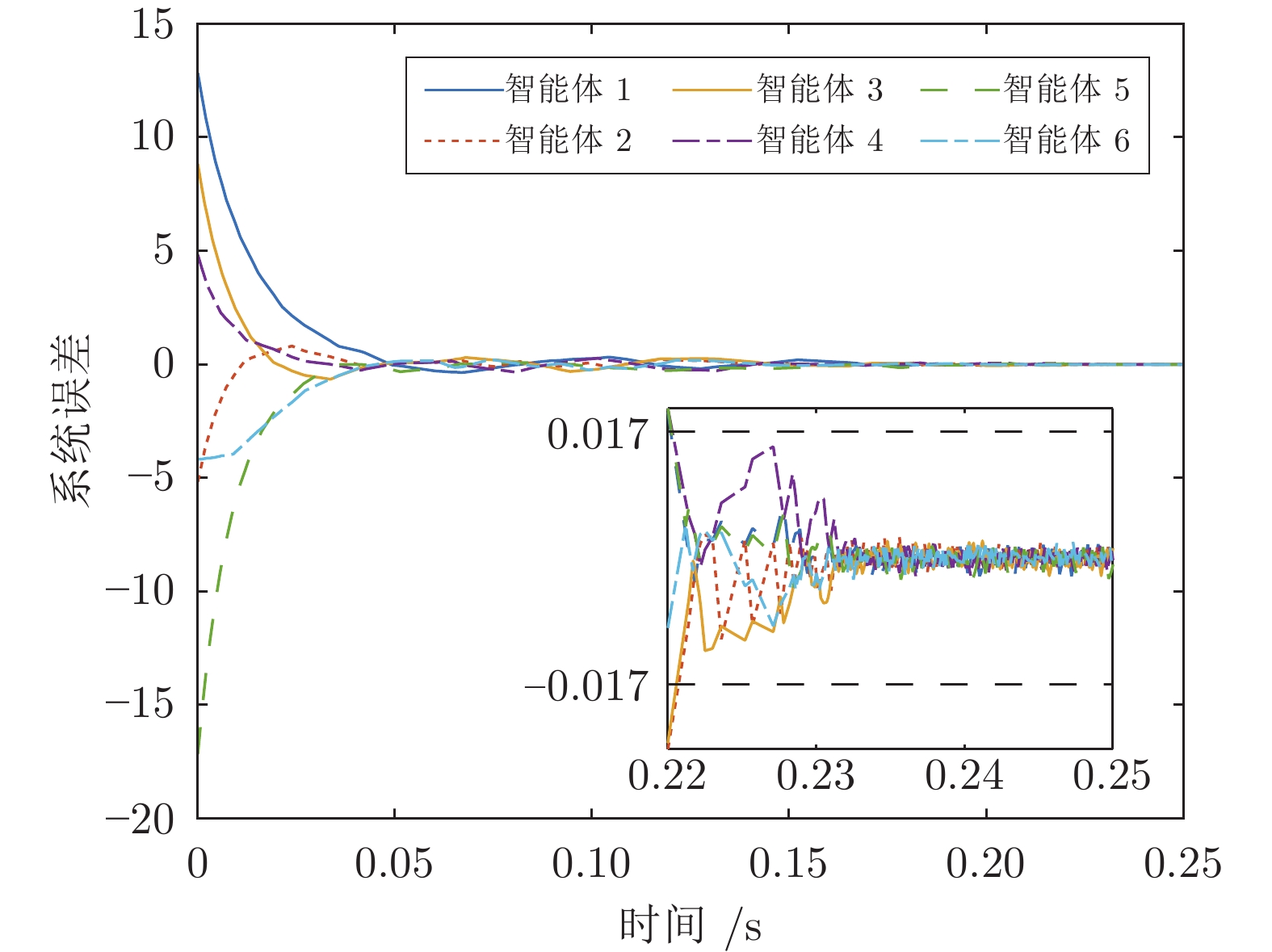
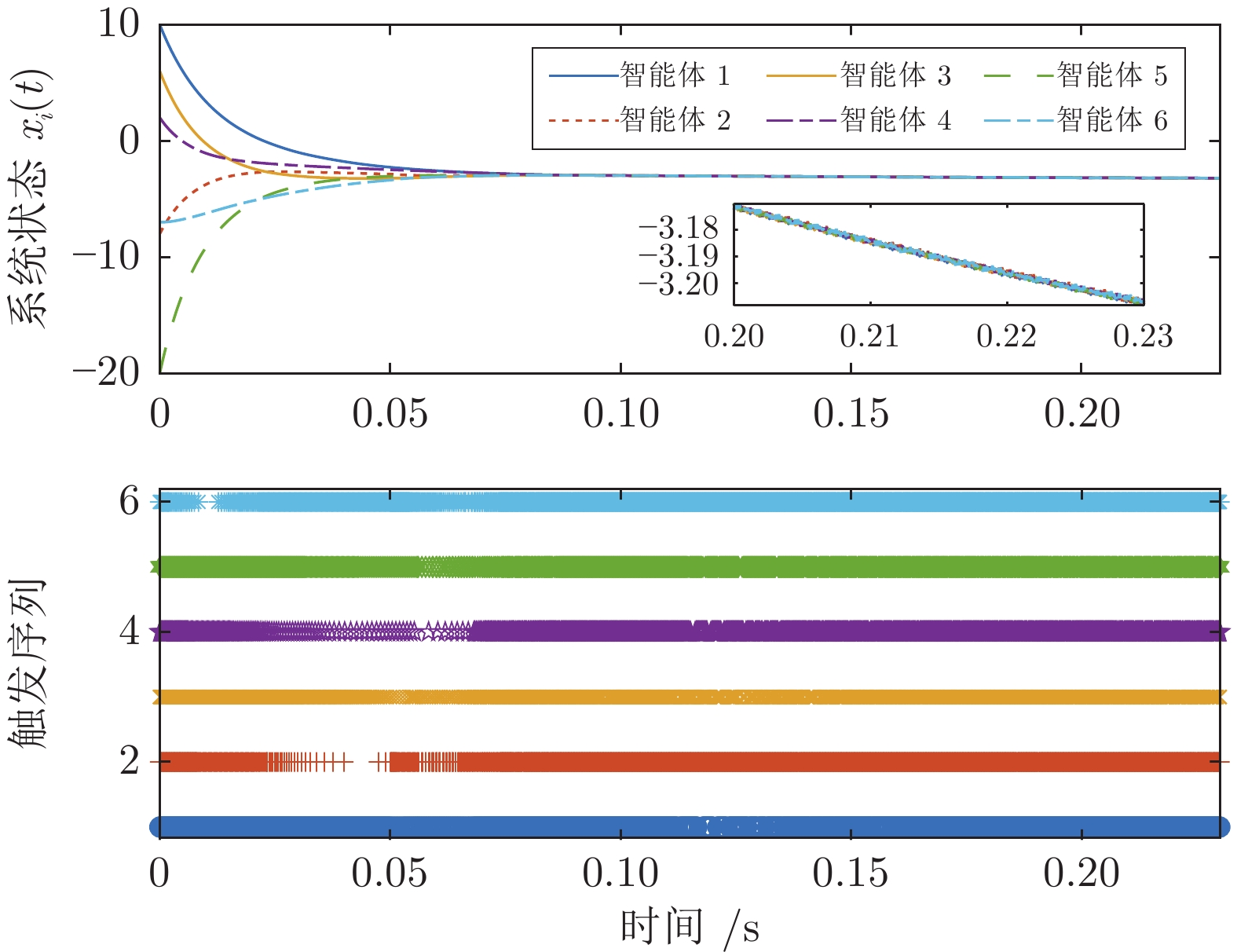
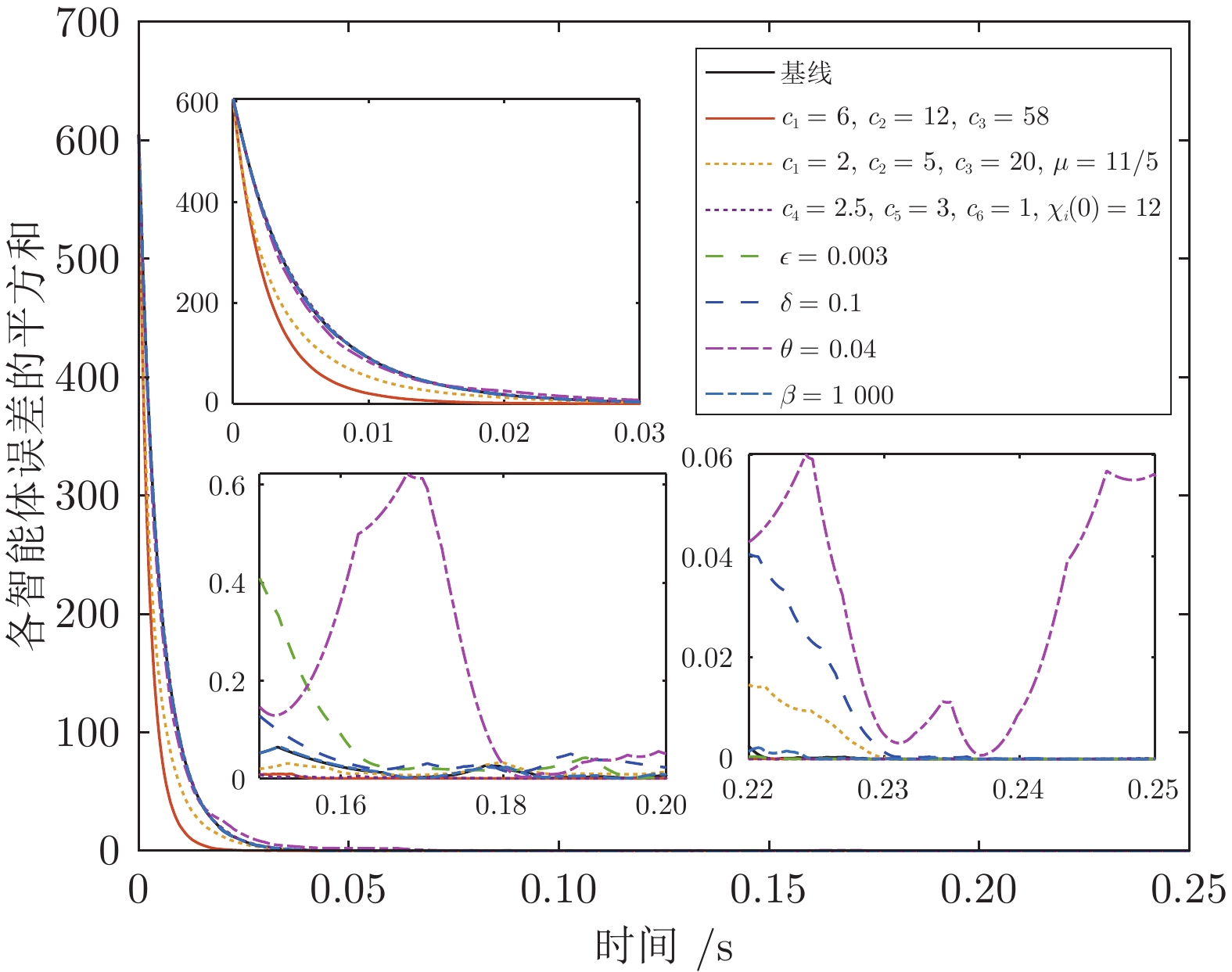
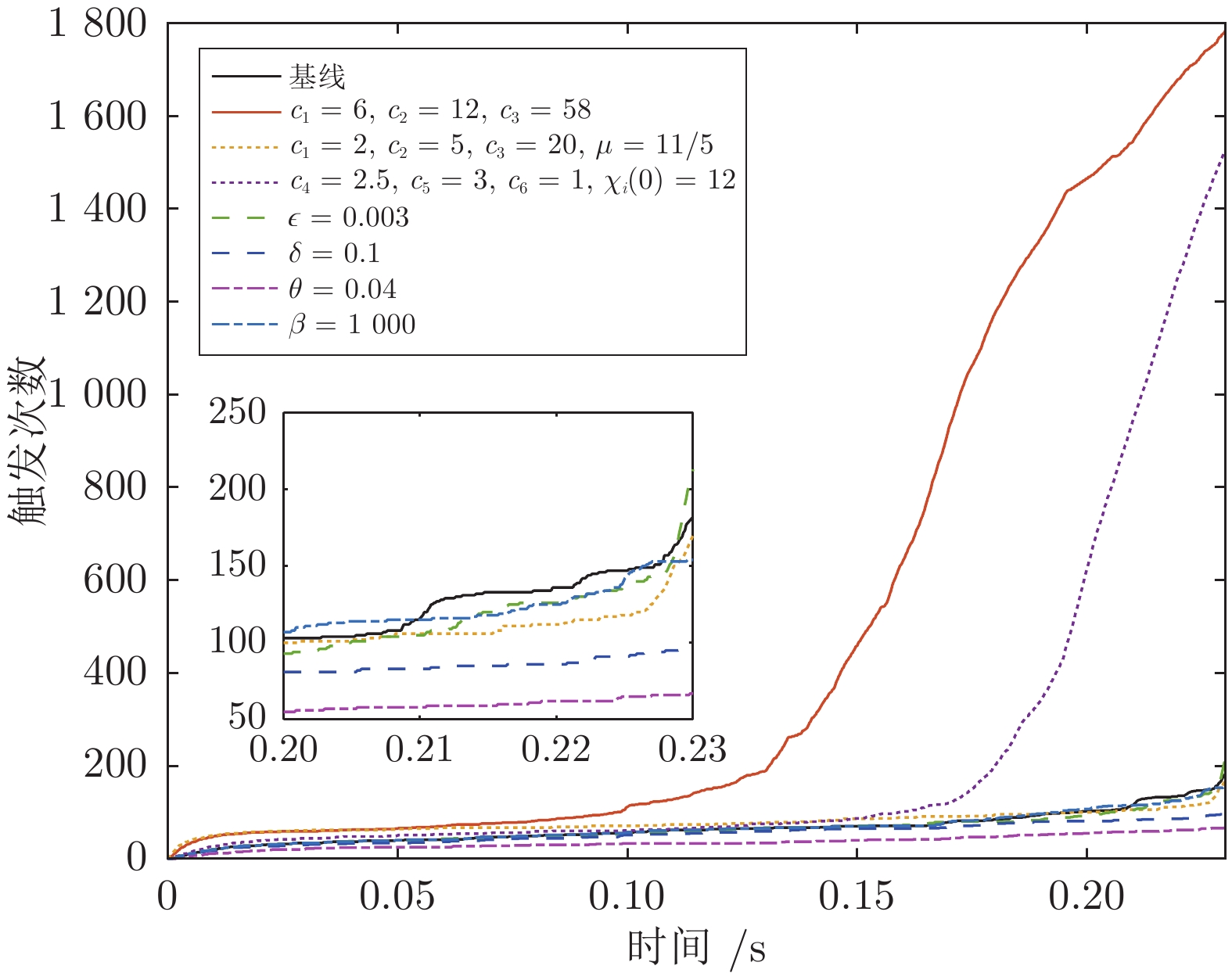
|
[1]
|
杨甜甜, 刘志远, 陈虹, 裴润. 多移动机器人避障编队控制. 自动化学报, 2008, 34(5): 588-592 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2008.00588Yang Tian-Tian, Liu Zhi-Yuan, Chen Hong, Pei Run. Formation control and obstacle avoidance for multiple mobile robots. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(5): 588-592 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2008.00588
|
|
[2]
|
尹瞾, 贺威, 邹尧, 穆新星, 孙长银. 基于“雁阵效应”的扑翼飞行机器人高效集群编队研究. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(6): 1355-1367Yin Zhao, He Wei, Zou Yao, Mu Xin-Xing, Sun Chang-Yin. Efficient formation of flapping-wing aerial vehicles based on wild geese queue effect. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(6): 1355-1367
|
|
[3]
|
王帅磊, 周绍磊, 代飞扬, 刘伟, 闫实. 多航天器分布式事件触发分组姿态协同控制. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(2): 323-332Wang Shuai-Lei, Zhou Shao-Lei, Dai Fei-Yang, Liu Wei, Yan Shi. Distributed event-triggered group attitude coordinated control of multi-spacecraft. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(2): 323-332
|
|
[4]
|
蔡光斌, 闫杰, 赵玉山, 胡昌华. 具有随机多跳时变时延的多航天器协同编队姿态一致性. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(10): 1415-1421Cai Guang-Bin, Yan Jie, Zhao Yu-Shan, Hu Chang-Hua. Attitude consensus of multi-spacecraft cooperative formation with stochastic multi-hop time-varying delay. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(10): 1415-1421
|
|
[5]
|
Shobole A A, Wadi M. Multiagent systems application for the smart grid protection. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 149: Article No. 111352 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111352
|
|
[6]
|
Olfati-Saber R, Murray R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1520-1533 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113
|
|
[7]
|
王兴平, 宋艳荣, 程兆林. 切换网络下时变线性多智能体系统的指数同步. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(8): 1528-1532Wang Xing-Ping, Song Yan-Rong, Cheng Zhao-Lin. Exponential synchronization of time-varying linear multi-agent systems with switching topology. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(8): 1528-1532
|
|
[8]
|
Huang N, Duan Z S, Zhao Y. Consensus of multi-agent systems via delayed and intermittent communications. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 9(1): 62-73
|
|
[9]
|
Wen G X, Chen C L P, Liu Y J, Liu Z. Neural network-based adaptive leader-following consensus control for a class of nonlinear multiagent state-delay systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(8): 2151-2160 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2608499
|
|
[10]
|
Bechlioulis C P, Rovithakis G A. Decentralized robust synchronization of unknown high order nonlinear multi-agent systems with prescribed transient and steady state performance. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(1): 123-134 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2535102
|
|
[11]
|
Zhang J X, Yang G H. Distributed fuzzy adaptive output-feedback control of unknown nonlinear multiagent systems in strict-feedback form. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(6): 5607-5617 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3086094
|
|
[12]
|
Cortés J. Finite-time convergent gradient flows with applications to network consensus. Automatica, 2006, 42(11): 1993-2000 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.06.015
|
|
[13]
|
Wang L, Xiao F. Finite-time consensus problems for networks of dynamic agents. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010, 55(4): 950-955 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2041610
|
|
[14]
|
Zhao L W, Hua C C. Finite-time consensus tracking of second-order multi-agent systems via nonsingular TSM. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2014, 75(1-2): 311-318 doi: 10.1007/s11071-013-1067-5
|
|
[15]
|
Tong P, Chen S H, Wang L. Finite-time consensus of multi-agent systems with continuous time-varying interaction topology. Neurocomputing, 2018, 284: 187-193 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.01.004
|
|
[16]
|
Zuo Z Y, Tie L. A new class of finite-time nonlinear consensus protocols for multi-agent systems. International Journal of Control, 2014, 87(2): 363-370 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2013.834484
|
|
[17]
|
Zhang B, Jia Y M. Fixed-time consensus protocols for multi-agent systems with linear and nonlinear state measurements. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2015, 82(4): 1683-1690 doi: 10.1007/s11071-015-2269-9
|
|
[18]
|
Defoort M, Polyakov A, Demesure G, Djemai M, Veluvolu K. Leader-follower fixed-time consensus for multi-agent systems with unknown non-linear inherent dynamics. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 9(14): 2165-2170
|
|
[19]
|
Ning B D, Jin J, Zheng J C. Fixed-time consensus for multi-agent systems with discontinuous inherent dynamics over switching topology. International Journal of Systems Science, 2017, 48(10): 2023-2032 doi: 10.1080/00207721.2017.1308579
|
|
[20]
|
孙小童, 郭戈, 张鹏飞. 非匹配扰动下的多智能体系统固定时间一致跟踪. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(6): 1368-1376Sun Xiao-Tong, Guo Ge, Zhang Peng-Fei. Fixed-time consensus tracking of multi-agent systems under unmatched disturbances. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(6): 1368-1376
|
|
[21]
|
Zuo Z Y, Tian B L, Defoort M, Ding Z T. Fixed-time consensus tracking for multiagent systems with high-order integrator dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(2): 563-570 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2729502
|
|
[22]
|
Ding L, Han Q L, Ge X H, Zhang X M. An overview of recent advances in event-triggered consensus of multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(4): 1110-1123 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2771560
|
|
[23]
|
Yu W W, Zheng W X, Chen G R, Ren W, Cao J D. Second-order consensus in multi-agent dynamical systems with sampled position data. Automatica, 2011, 47(7): 1496-1503 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.02.027
|
|
[24]
|
Wen G H, Duan Z S, Yu W W, Chen G R. Consensus of multi-agent systems with nonlinear dynamics and sampled-data information: A delayed-input approach. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2013, 23(6): 602-619 doi: 10.1002/rnc.2779
|
|
[25]
|
Dimarogonas D V, Frazzoli E, Johansson K H. Distributed event-triggered control for multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(5): 1291-1297 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2174666
|
|
[26]
|
Garcia E, Cao Y C, Casbeer D W. Decentralized event-triggered consensus with general linear dynamics. Automatica, 2014, 50(10): 2633-2640 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.08.024
|
|
[27]
|
Zhang H P, Yue D, Yin X X, Hu S L, Dou C X. Finite-time distributed event-triggered consensus control for multi-agent systems. Information Sciences, 2016, 339: 132-142 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.12.031
|
|
[28]
|
Liu J, Zhang Y L, Yu Y, Sun C Y. Fixed-time event-triggered consensus for nonlinear multiagent systems without continuous communications. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(11): 2221-2229 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2876334
|
|
[29]
|
Sharifi A, Pourgholi M. Fixed-time bipartite consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems using event-triggered control design. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2021, 358(17): 9178-9198 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.09.023
|
|
[30]
|
Zhou D, Zhang A, Yang P. Fixed-time event-triggered consensus of second-order multi-agent systems with fully continuous communication free. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 14(16): 2385-2394
|
|
[31]
|
陈世明, 邵赛, 姜根兰. 基于事件触发二阶多智能体系统的固定时间比例一致性. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 261-270 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190128Chen Shi-Ming, Shao Sai, Jiang Gen-Lan. Distributed event-triggered fixed-time scaled consensus control for second-order multi-agent systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 261-270 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190128
|
|
[32]
|
Liu J, Zhang Y L, Sun C Y, Yu Y. Fixed-time consensus of multi-agent systems with input delay and uncertain disturbances via event-triggered control. Information Sciences, 2019, 480: 261-272 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.12.037
|
|
[33]
|
Ran G T, Liu J, Li C J, Chen L M, Li D Y. Event-based finite-time consensus control of second-order delayed multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2021, 68(1): 276-280 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.2999480
|
|
[34]
|
Liu J, Zhang Y L, Yu Y, Sun C Y. Fixed-time leader-follower consensus of networked nonlinear systems via event/self-triggered control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(11): 5029-5037 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2957069
|
|
[35]
|
Ni J K, Shi P, Zhao Y, Pan Q, Wang S Y. Fixed-time event-triggered output consensus tracking of high-order multiagent systems under directed interaction graphs. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(7): 6391-6405 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3034013
|
|
[36]
|
Ai X L, Wang L. Distributed fixed-time event-triggered consensus of linear multi-agent systems with input delay. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 31(7): 2526-2545 doi: 10.1002/rnc.5404
|
|
[37]
|
Liu J, Yu Y, Xu Y, Zhang Y L, Sun C Y. Fixed-time average consensus of nonlinear delayed MASs under switching topologies: An event-based triggering approach. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(5): 2721-2733 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3051156
|
|
[38]
|
Girard A. Dynamic triggering mechanisms for event-triggered control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(7): 1992-1997 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2366855
|
|
[39]
|
Yi X L, Liu K, Dimarogonas D V, Johansson K H. Dynamic event-triggered and self-triggered control for multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(8): 3300-3307 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2874703
|
|
[40]
|
Liu J, Ran G T, Wu Y B, Xue L, Sun C Y. Dynamic event-triggered practical fixed-time consensus for nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(4): 2156-2160 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3128624
|




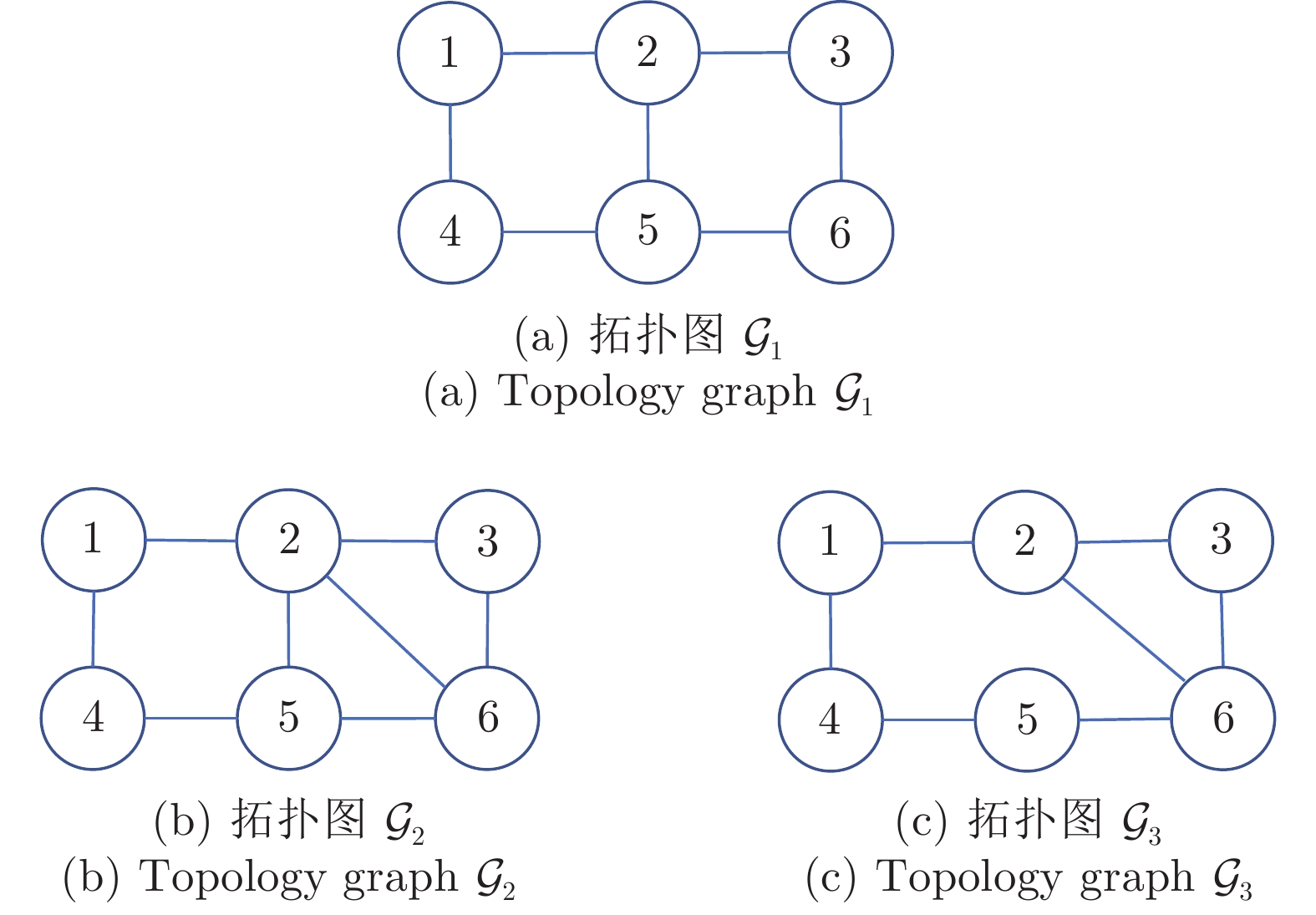
 下载:
下载: