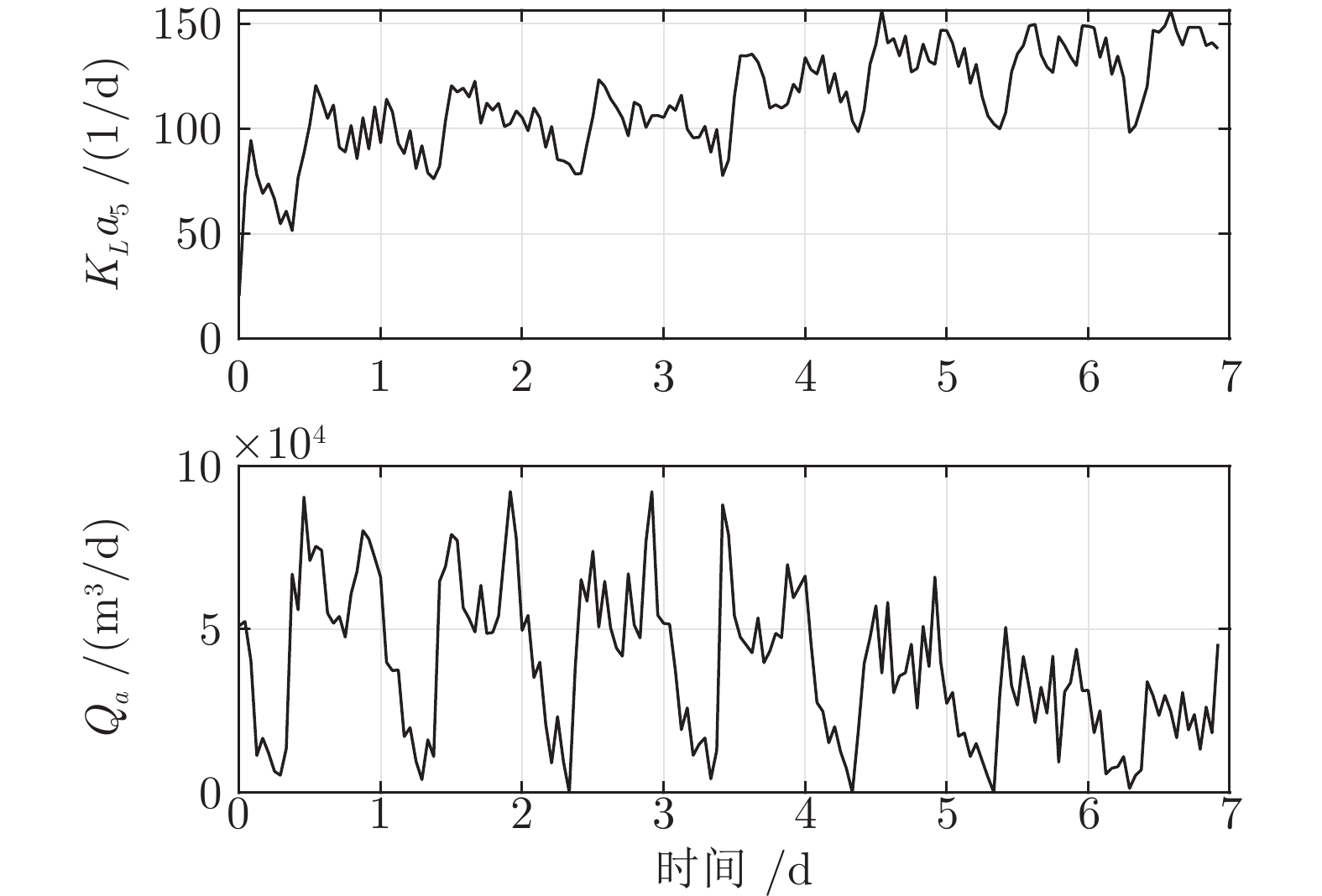
-
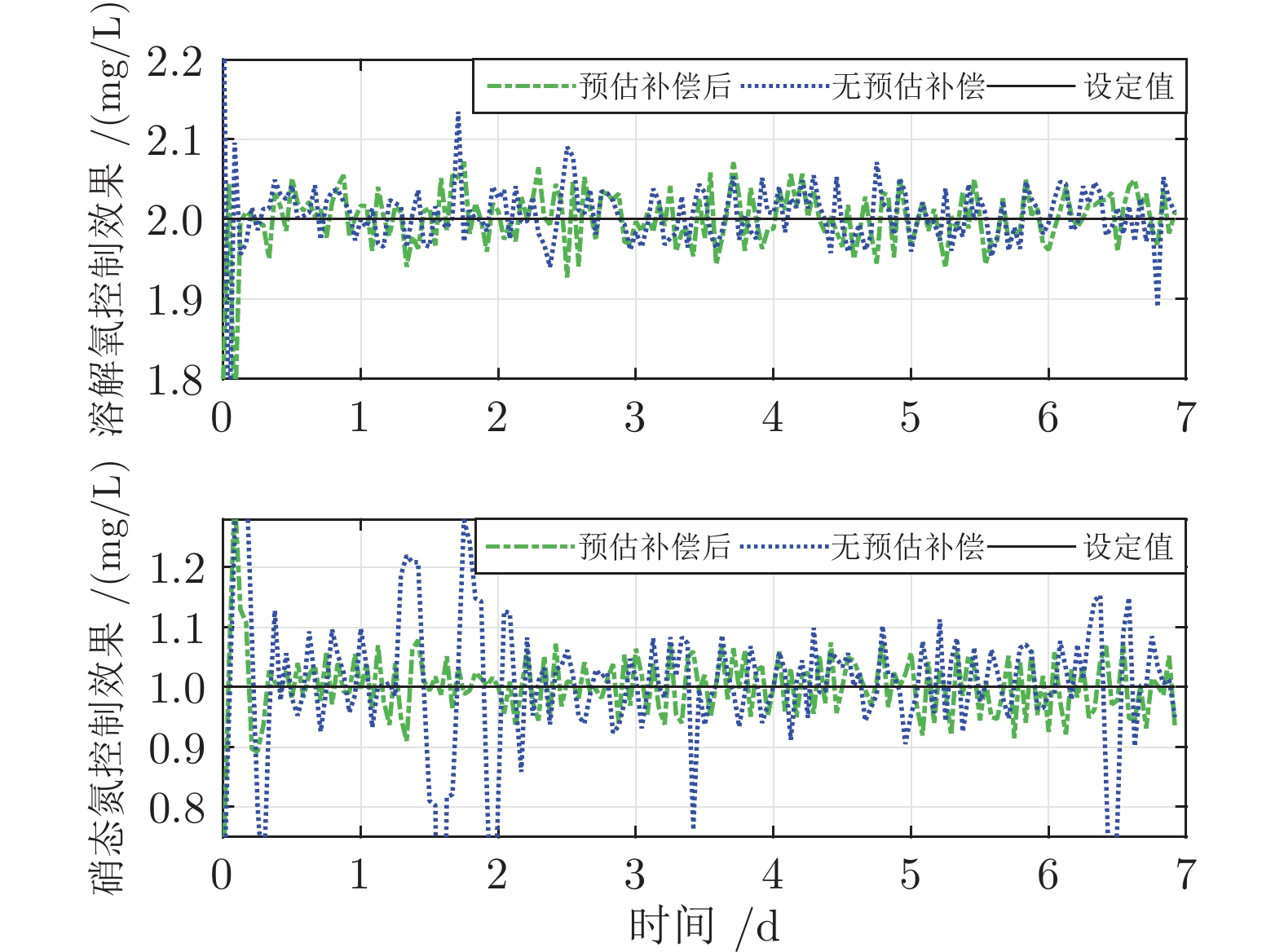
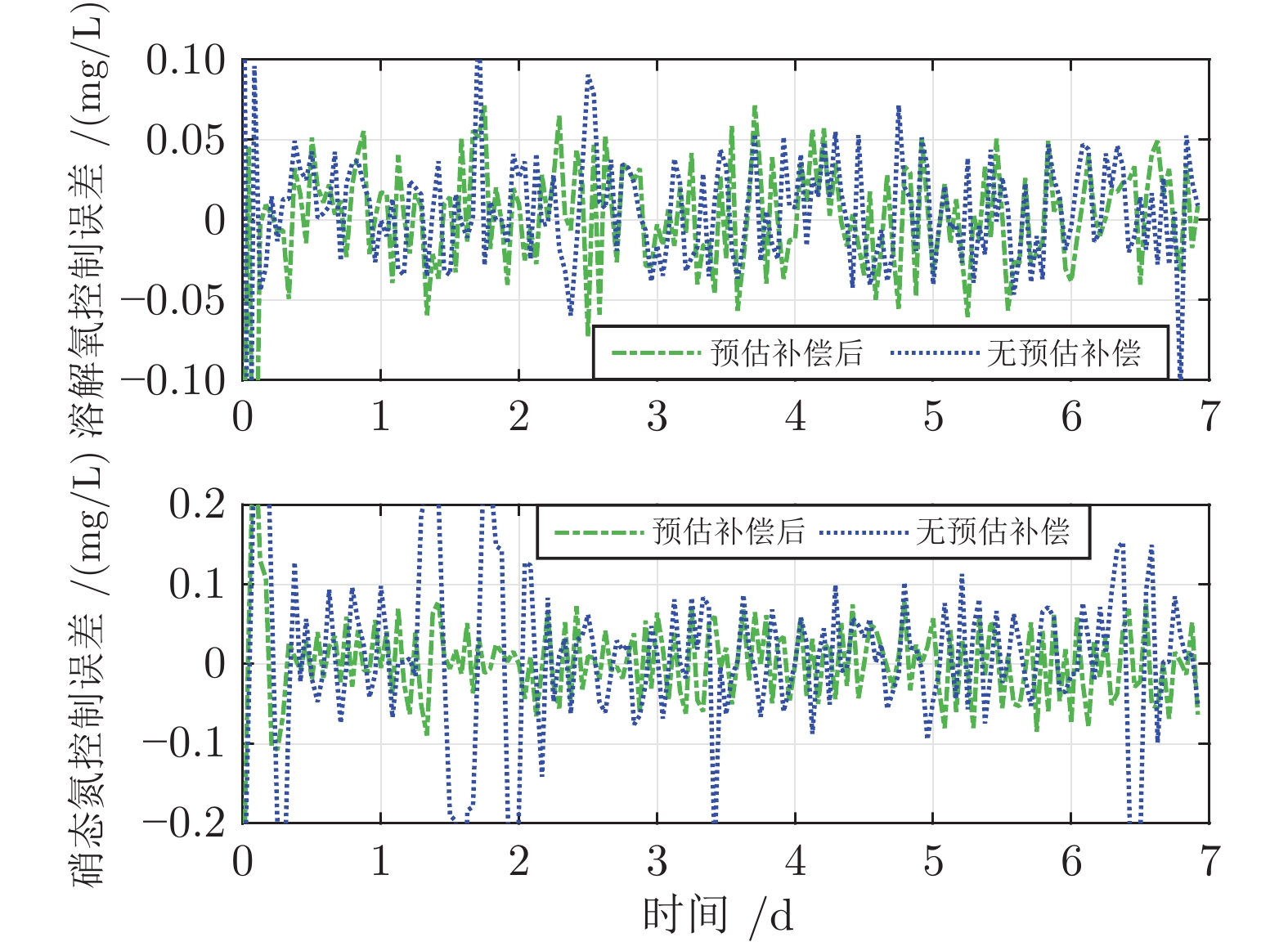
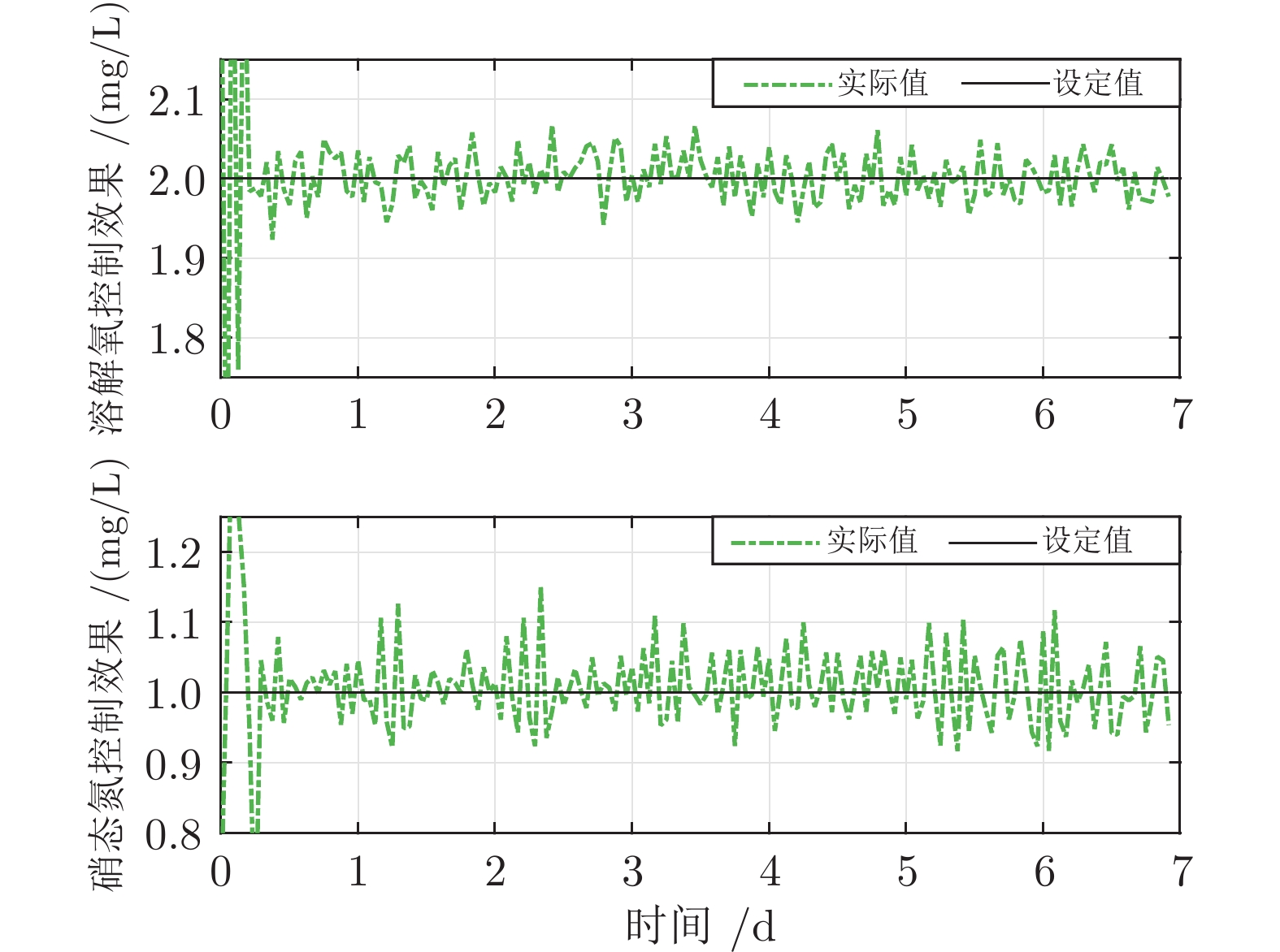
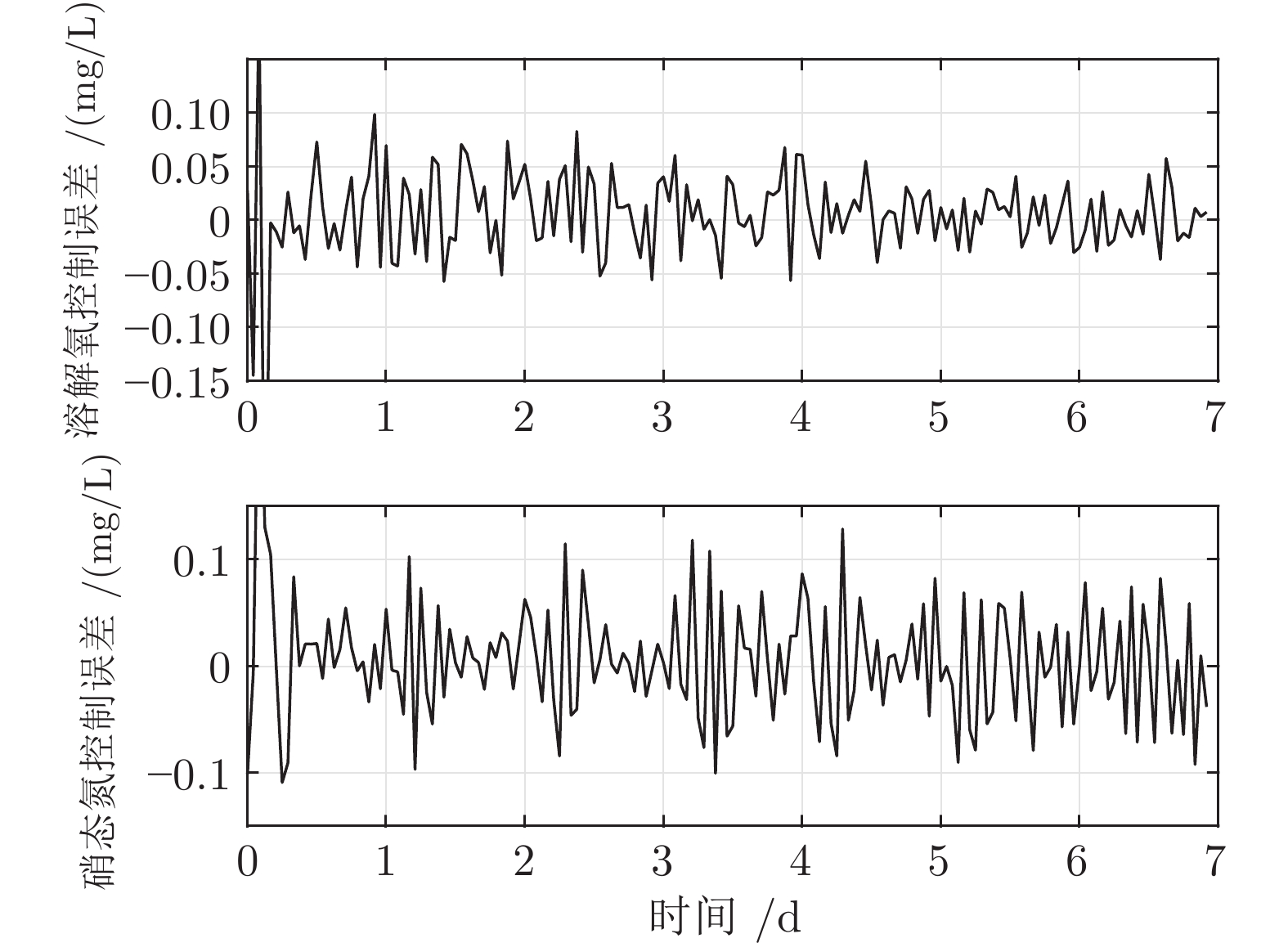
摘要: 针对城市污水处理过程时滞导致难以稳定控制的问题, 提出一种自适应滑模控制方法(Adaptive sliding mode control, ASMC). 首先, 分析推流时滞对城市污水处理生化反应过程的影响, 建立时滞影响下的城市污水处理运行控制模型; 其次, 设计一种基于模糊神经网络的预估补偿模型, 完成滞后变量的准确预测, 实现控制模型中变量时刻的统一; 最后, 设计一种具有自适应开关增益系数的滑模控制器(Sliding mode control, SMC), 实现溶解氧和硝态氮的稳定控制. 将提出的自适应滑模控制方法应用于城市污水处理过程基准仿真平台, 实验结果显示该方法能够实现城市污水处理运行过程稳定控制.Abstract: Aiming at the problem of time delay affecting stable control in municipal wastewater treatment processes, an adaptive sliding mode control (ASMC) method is proposed in this paper. First, the influence of push-flow time delay on biochemical reaction process of wastewater treatment processes is analyzed. Then, an operating control model of wastewater treatment processes is established. Second, an estimated compensation model, based on fuzzy neural network, is designed. Then, it can complete the accurate prediction of delay variables and realize the moment unification of variables in the control model. Finally, a sliding mode controller (SMC) with adaptive switching gain coefficient is designed. Then, it can realize stable control of dissolved oxygen and nitrate nitrogen. The proposed method is applied to the benchmark simulation model. Experimental results show it can realize stable control of wastewater treatment operating process.
-
表 1 不同控制器性能比较 (雨天天气且设定值恒定)
Table 1 The comparison results of different controllers (rain weather with constant settings)
控制策略 溶解氧 硝态氮 ISE IAE ${\rm{De}}{{\rm{v}}^{\max }}$ ISE IAE ${\rm{De}}{{\rm{v}}^{\max }}$ ASMC 4.930 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.035 0.490 5.270 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.046 0.420 SMC[20] 5.520 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.030 0.610 5.620 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.046 0.440 FNNC[34] 1.060 ×$10^{-2}$ 0.075 0.560 9.950 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.076 0.560 PID[12] 1.430 ×$10^{-2}$ 0.072 0.740 8.100 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.056 0.530 表 2 不同控制器性能比较 (晴天天气且设定值变化)
Table 2 The comparison results of different controllers (dry weather with changing settings)
控制策略 溶解氧 硝态氮 ISE IAE ${\rm{De}}{{\rm{v}}^{\max }}$ ISE IAE ${\rm{De}}{{\rm{v}}^{\max }}$ ASMC 2.120 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.030 0.340 3.310 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.043 0.330 SMC[20] 3.640 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.032 0.360 3.870 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.044 0.390 FNNC[34] 7.750 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.061 0.480 9.900 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.075 0.500 PID[12] 7.930 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.045 0.850 4.780 ×$10^{-3}$ 0.047 0.490 -
[1] 韩红桂, 张琳琳, 伍小龙, 乔俊飞. 数据和知识驱动的城市污水处理过程多目标优化控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(11): 2538-2546Han Hong-Gui, Zhang Lin-Lin, Wu Xiao-Long, Qiao Jun-Fei. Data-knowledge Driven Multiobjective Optimal Control for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2538−2546 [2] 黄俊熙, 岑玉铭, 关宇霆, 张伟龙. 污水处理过程中除磷加药智能控制系统及应用研究. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(1): 104-107Huang Jun-Xi, Cen Yu-Ming, Guan Yu-Ting, Zhang Wei-Long. Application of Intelligent Control System for Chemical Phosphorus Removal in Wastewater Treatment Process. China Water & Wastewater, 2022, 38(1): 104-107 [3] 杨翠丽, 武战红, 韩红桂, 乔俊飞. 城市污水处理过程优化设定方法研究进展. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2092-2108Yang Cui-Li, Wu Zhan-Hong, Han Hong-Gui, Qiao Jun-Fei. Perspectives on optimal setting methods for municipal wastewater treatment processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2092-2108 [4] 李永明, 史旭东, 熊伟丽. 基于工况识别的污水处理过程多目标优化控制. 化工学报, 2019, 70(11): 4325-4336Li Yong-Ming, Shi Xu-Dong, Xiong Wei-Li. Condition recognition based intelligent multi-objective optimal control for wastewater treatment. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(11): 4325-4336 [5] 乔俊飞, 卢超, 王磊, 韩红桂. 城市污水处理过程模型研究综述. 信息与控制, 2018, 47(2): 129-139Qiao Jun-Fei, Lu Chao, Wang Lei, Han Hong-Gui. Models of urban wastewater treatment process: An overview. Information and Control, 2018, 47(2): 129-139 [6] 张帅, 周平. 污水处理过程递推双线性子空间建模及无模型自适应控制. 自动化学报, to be publishedZhang Shuai, Zhou Ping. Recursive bilinear subspace modeling and model-free adaptive control of wastewater treatment. Acta Automatica Sinica, to be published [7] 权利敏, 杨翠丽, 乔俊飞. 数据驱动的溶解氧浓度在线自组织控制方法. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c210041Quan Li-Min, Yang Cui-Li, Qiao Jun-Fei. Data-driven online self-organizing control for dissolved oxygen concentration, Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c210041 [8] Han H G. Liu Z, Lu W, Hou Y, Qiao J F. Dynamic MOPSO-based optimal control for wastewater treatment process. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(5): 2518-2528 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2925534 [9] Chistiakova T, Wigren T, Carlsson B. Combined L2 -stable feedback and feedforward aeration control in a wastewater treatment plant. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2020, 28(3): 1017-1024 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2891410 [10] Iratni A, Chang N. Advances in control technologies for wastewater treatment processes: Status, challenges, and perspectives. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(2): 337-363 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911372 [11] 杜胜利, 张庆达, 曹博琦, 乔俊飞. 城市污水处理过程模型预测控制研究综述. 信息与控制, 2022, 51(1): 41-53Du Sheng-Li, Zhang Qing-Da, Cao Bo-Qi, Qiao Jun-Fei. A Review of Model Predictive Control for Urban Wastewater Treatment Process. Information and Control, 2022, 51(1): 41-53 [12] Flores V R, Sanchez E N, Béteau J F, Hernandez S C. Dissolved oxygen regulation by logarithmic/antilogarithmic control to improve a wastewater treatment process. Environmental Technology, 2013, 34(23): 3103-3116 doi: 10.1080/09593330.2013.803159 [13] Samsudin S I, Rahmat M F, Wahab N A, Razali M C, Gaya M S, Salim S N S. Improvement of activated sludge process using enhanced nonlinear PI controller. Arabian Journal for Science & Engineering, 2014, 39(8): 6575-6586 [14] Cristea S, Prada C D, Sarabia D, Gutierrez G. Aeration control of a wastewater treatment plant using hybrid NMPC. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2011, 35(4): 638-650 [15] Belchior C A C, Araújo R A M, Landeck J A C. Dissolved oxygen control of the activated sludge wastewater treatment process using stable adaptive fuzzy control. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2012, 37(1): 152-162 [16] Xu J, Niu Y G, Lam H K. Event-triggered sliding mode control of fuzzy systems via artificial time-delay estimation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 29(9): 2467-2478 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2999744 [17] Xie M Y, Yu S D, Lin H P, Ma J Y, Wu H T. Improved sliding mode control with time delay estimation for motion tracking of cell puncture mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2020, 67(9): 3199-3210 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.2981629 [18] Yan H C, Zhou X P, Zhang H, Yang F W, Wu Z G. A novel sliding mode estimation for microgrid control with communication time delays. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(2): 1509-1520 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2017.2771493 [19] Han Y Q, Kao Y G, Gao C C. Robust sliding mode control for uncertain discrete singular systems with time-varying delays and external disturbances. Automatica, 2017, 75(1): 210-216 [20] Munoz C, Young H, Antileo C, Bornhardt C. Sliding mode control of dissolved oxygen in an integrated nitrogen removal process in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR). Water Science & Technology, 2009, 60(10): 2545-2553 [21] Xu D, Zhou H M, Shao X Y, Wang T. Performance study of sliding mode controller with improved adaptive polynomial-based forward prediction. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 133(1): 1-18 [22] Alipouri Y, Alipour H, Huang B. Multiple step ahead prediction based high order discrete-time sliding mode control design with actuator and communication delays. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2020, 357(12): 7845-7863 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.05.050 [23] Shah D H, Patel D M. Design of sliding mode control for quadruple-tank MIMO process with time delay compensation. Journal of Process Control, 2019, 76(1): 46-61 [24] Ozturk M C, Serrat F M, Teymour F. Optimization of aeration profiles in the activated sludge process. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 139(1): 1-14 [25] 黄灿, 桂卫华, 阳春华, 蒋朝辉, 谢永芳. 多变量时滞过程解耦Smith控制. 控制理论与应用, 2010, 27(10): 1393-1398Huang Can, Gui Wei-Hua, Yang Chun-Hua, Jiang Zhao-Hui, Xie Yong-Fang. Decoupling Smith control for multivariable system with time-delays. Control Theory & Applications, 2010, 27(10): 1393-1398 [26] Xie S, Wang H Z, Peng J C, Liu X L, Yuan X F. A hierarchical data reconciliation based on multiple time-delay interval estimation for industrial processes. ISA Transactions, 2020, 105(1): 198-209 [27] 李旭光, 张颖伟, 冯琳. 时滞系统的完全稳定性研究综述. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(7): 1153-1170Li Xu-Guang, Zhang Ying-Wei, Feng Lin. Survey on complete stability study for time-delay systems. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(7): 1153-1170 [28] Canete J F, Saz-Orozco P, Gabriel J G, Baratti R, Ruano A, Rivas-Blanco I. Control and soft sensing strategies for a wastewater treatment plant using a neuro-genetic approach. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2021, 144(1): 1-14 [29] Asadi A, Verma A, Yang K. Wastewater treatment aeration process optimization: A data mining approach. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 203(2): 630-639 [30] Santin I, Pedret C, Vilanova R. Applying variable dissolved oxygen set point in a two level hierarchical control structure to a wastewater treatment process. Journal of Process Control, 2015, 28(1): 40-55 [31] Carpenter C M G, Helbling D E. Removal of micropollutants in biofilters: Hydrodynamic effects on biofilm assembly and functioning. Water Research, 2017, 120(1): 211-221 [32] Liu H B, Yoo C K. Cascade control of effluent nitrate and ammonium in an activated sludge process. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2015, 57(45): 21253-21263 [33] 吴菁, 刘乙奇, 刘坚, 黄道平, 邱禹, 于广平. 基于动态多核相关向量机的软测量建模研究. 化工学报, 2019, 70(4): 1472-1484Wu Jing, Liu Yi-Qi, Liu Jian, Huang Dao-Ping, Qiu Yu, Yu Guang-Ping. Study on the soft sensor of multi-kernel relevance vector machine based on time difference. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(4): 1472−1484 [34] Qiao J F, Hou Y, Zhang L, Han H G. Adaptive fuzzy neural network control of wastewater treatment process with multiobjective operation. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275(1): 383-393 -




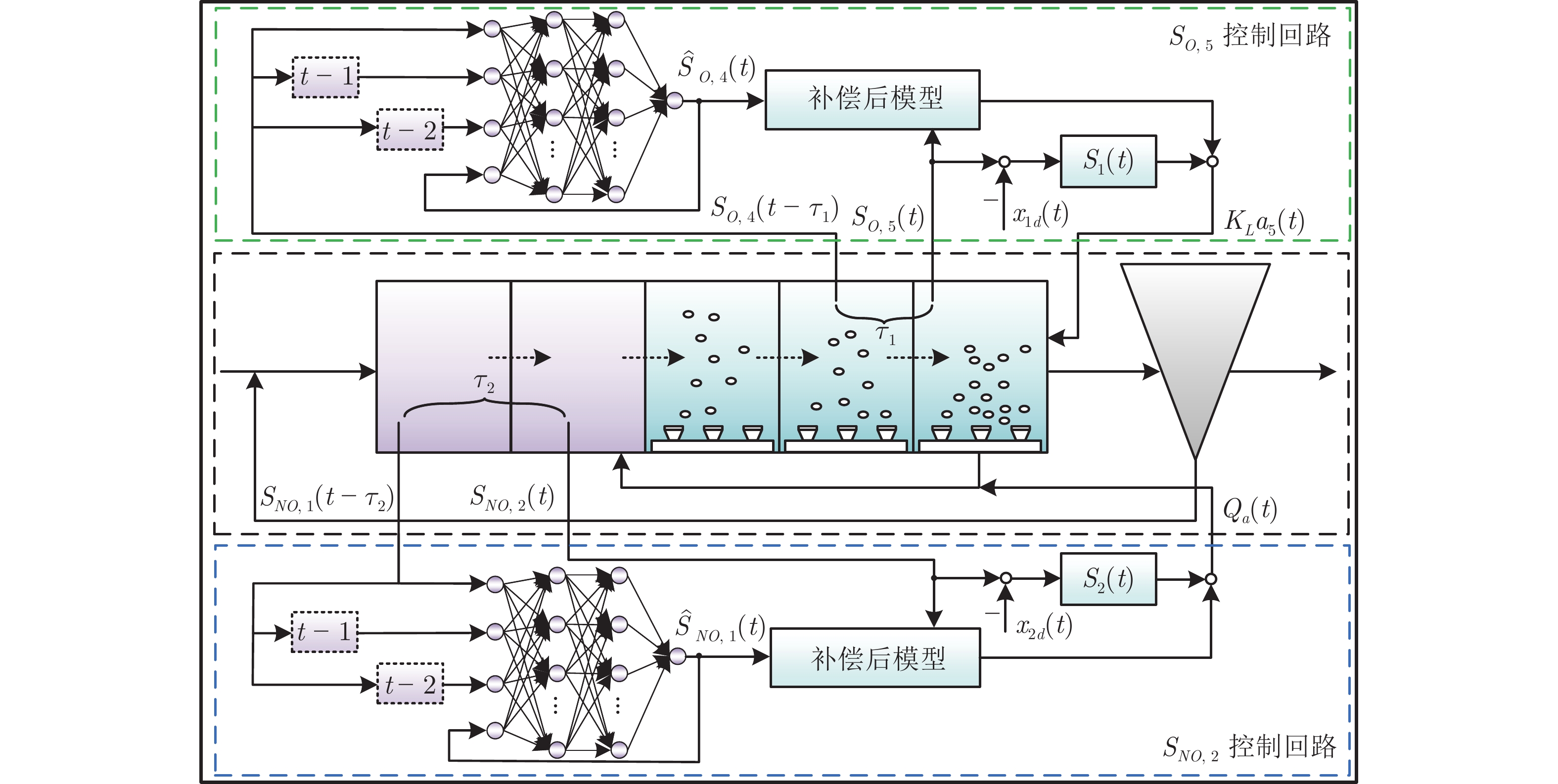
 下载:
下载: