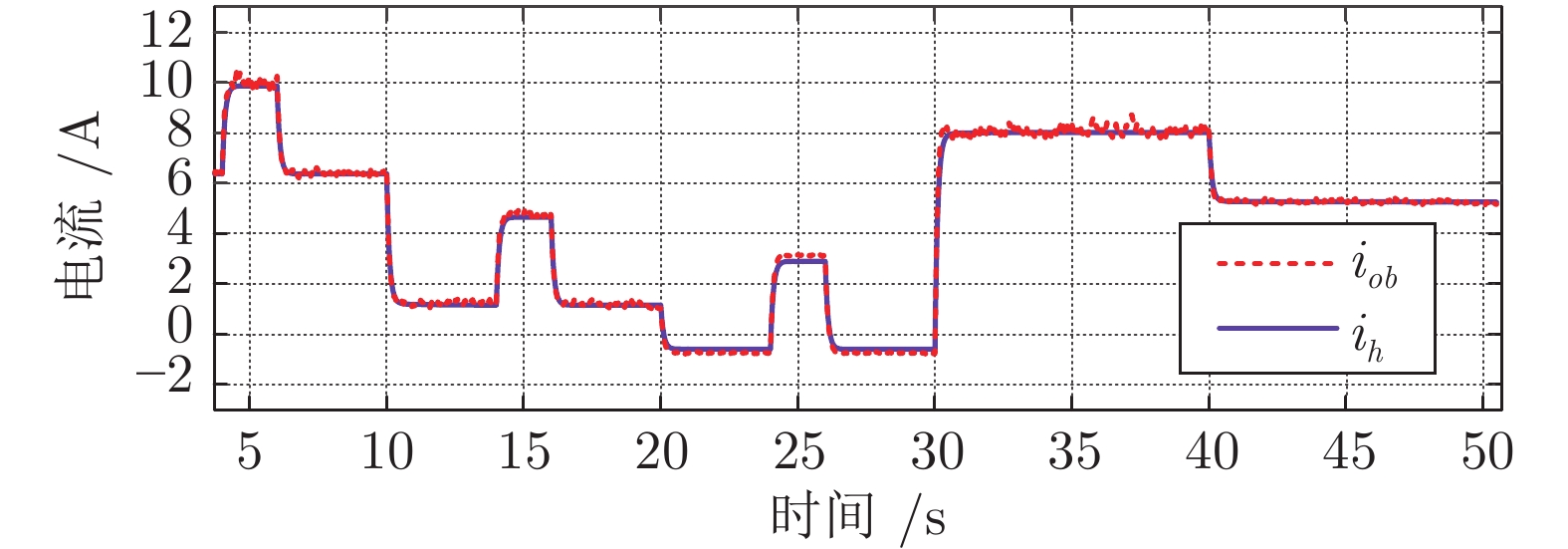
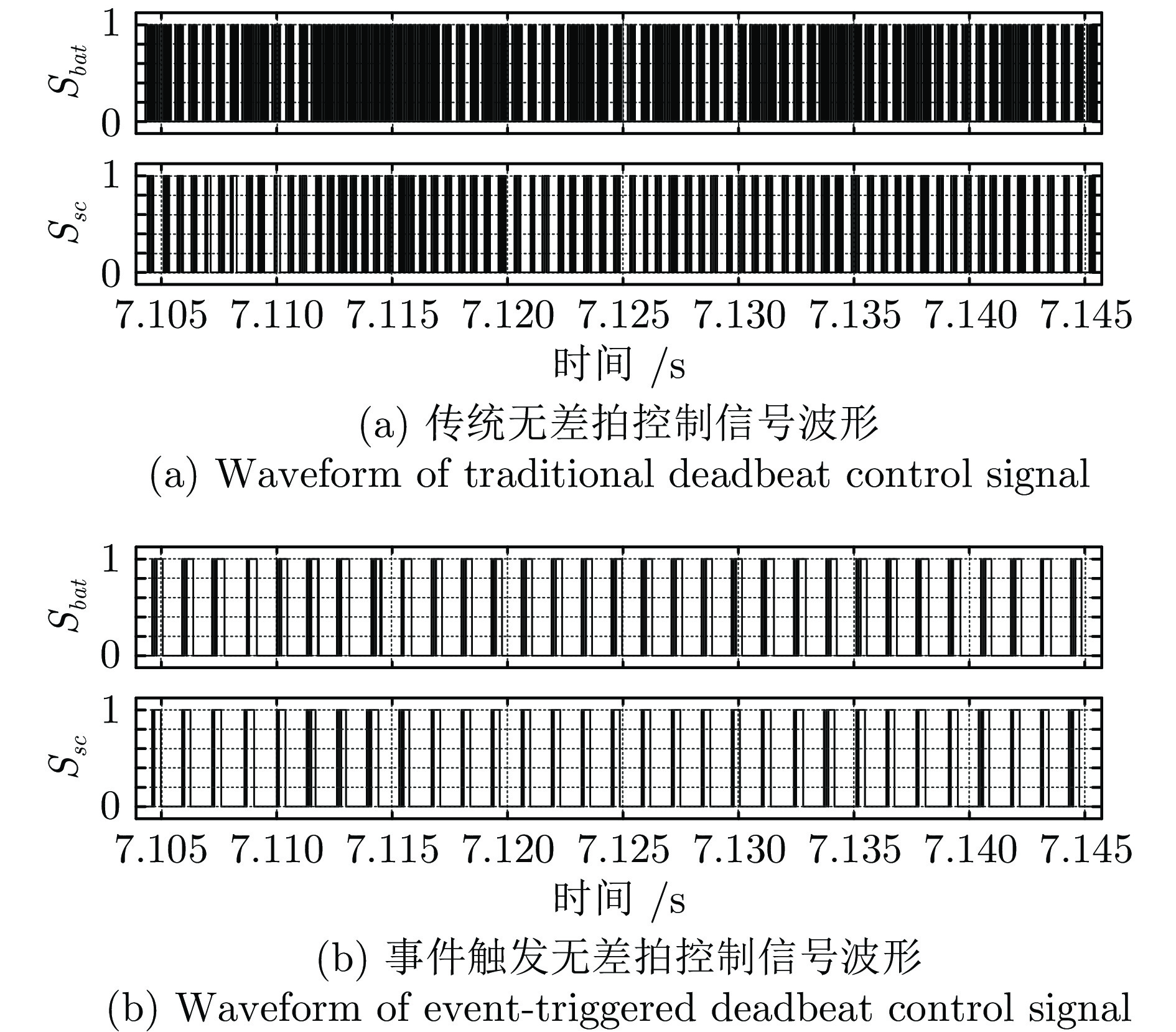
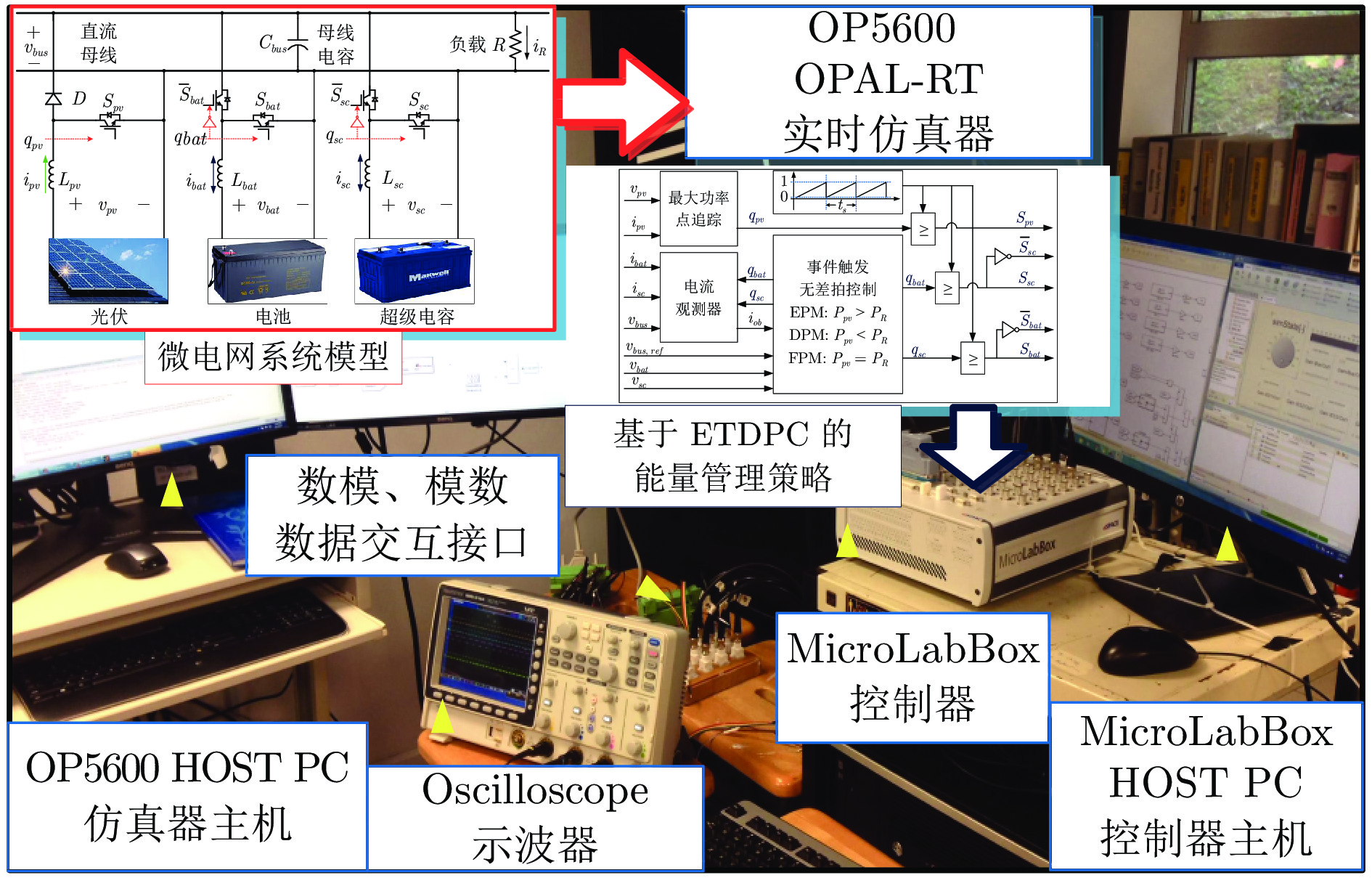
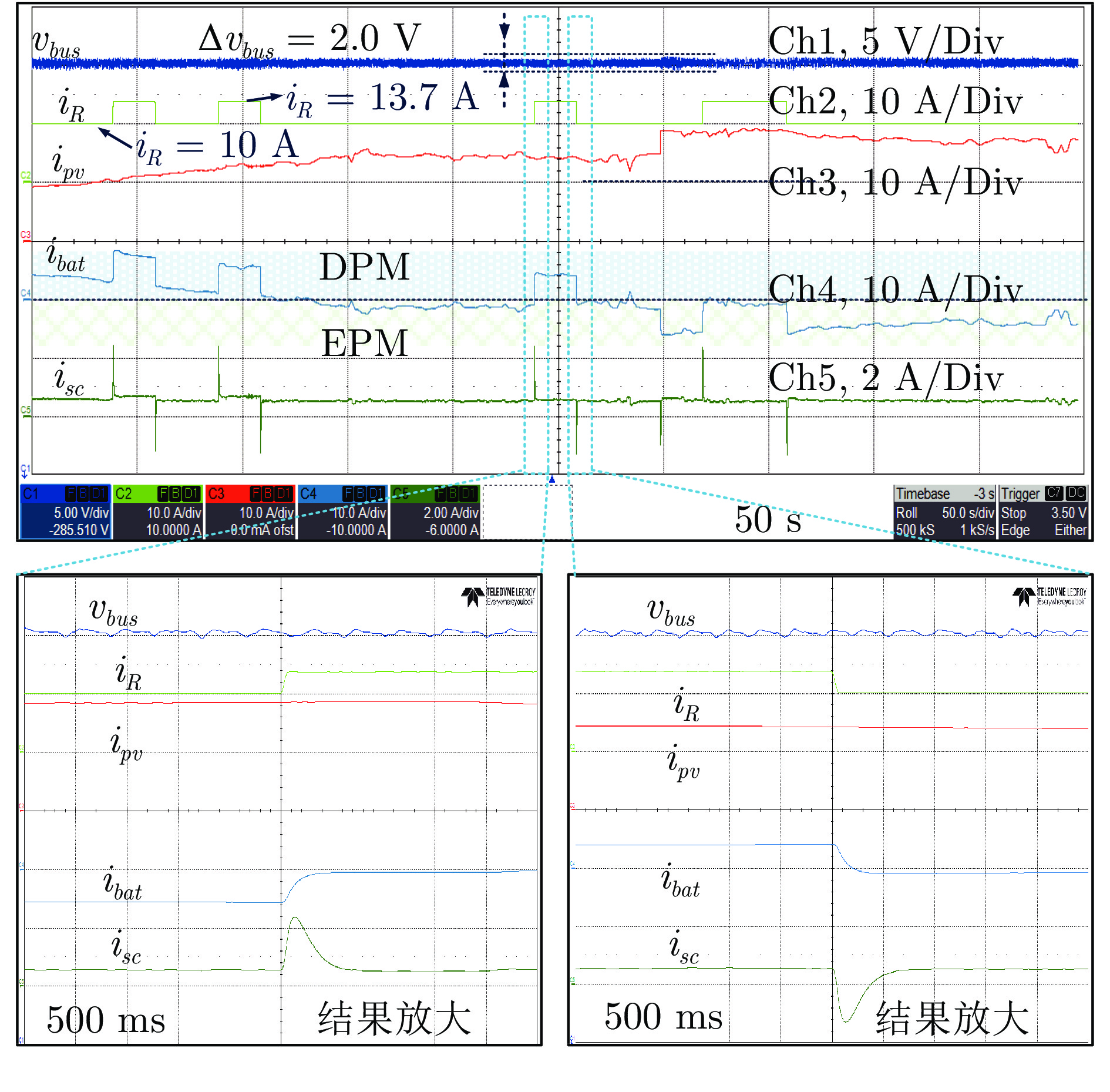
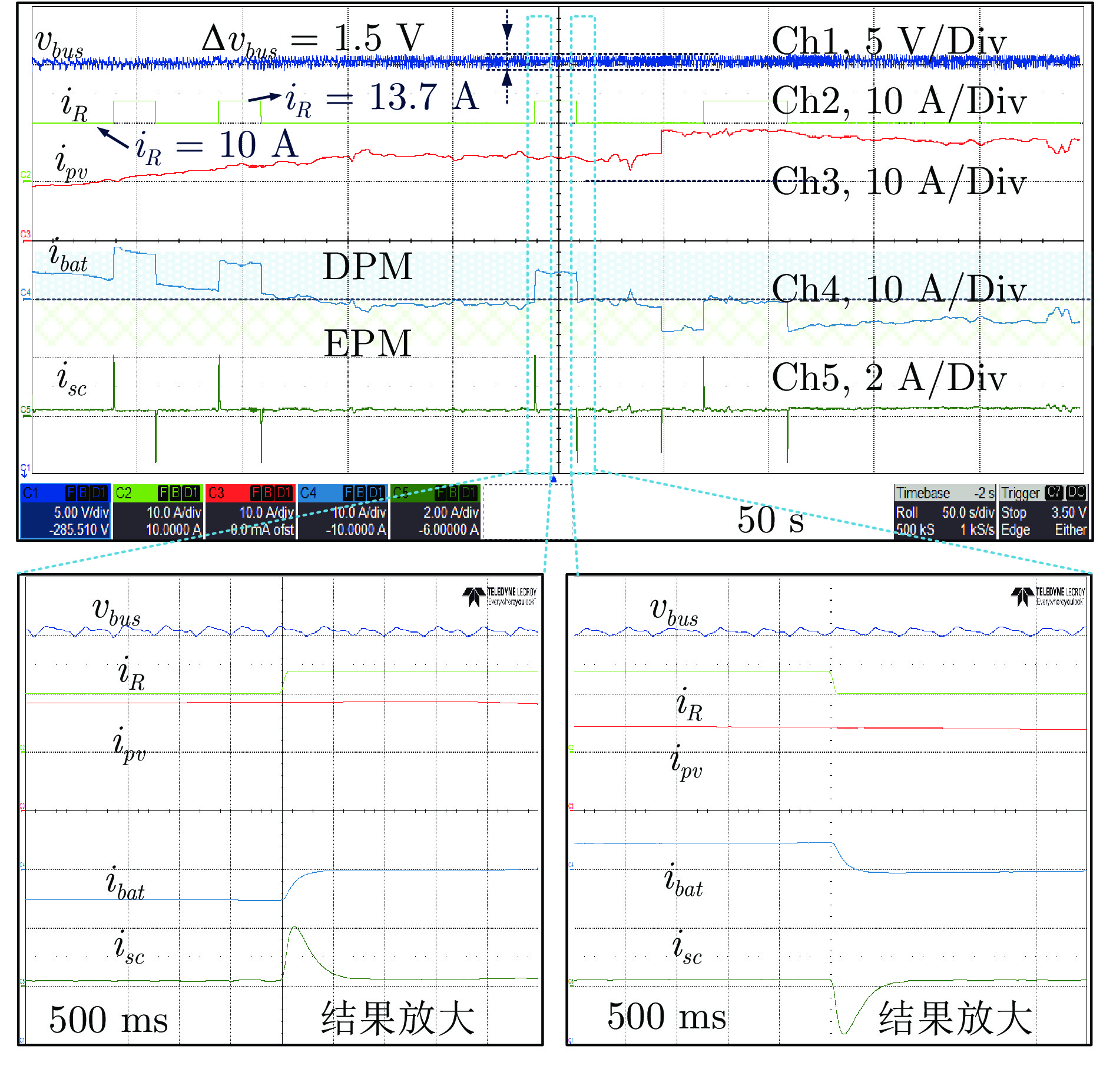
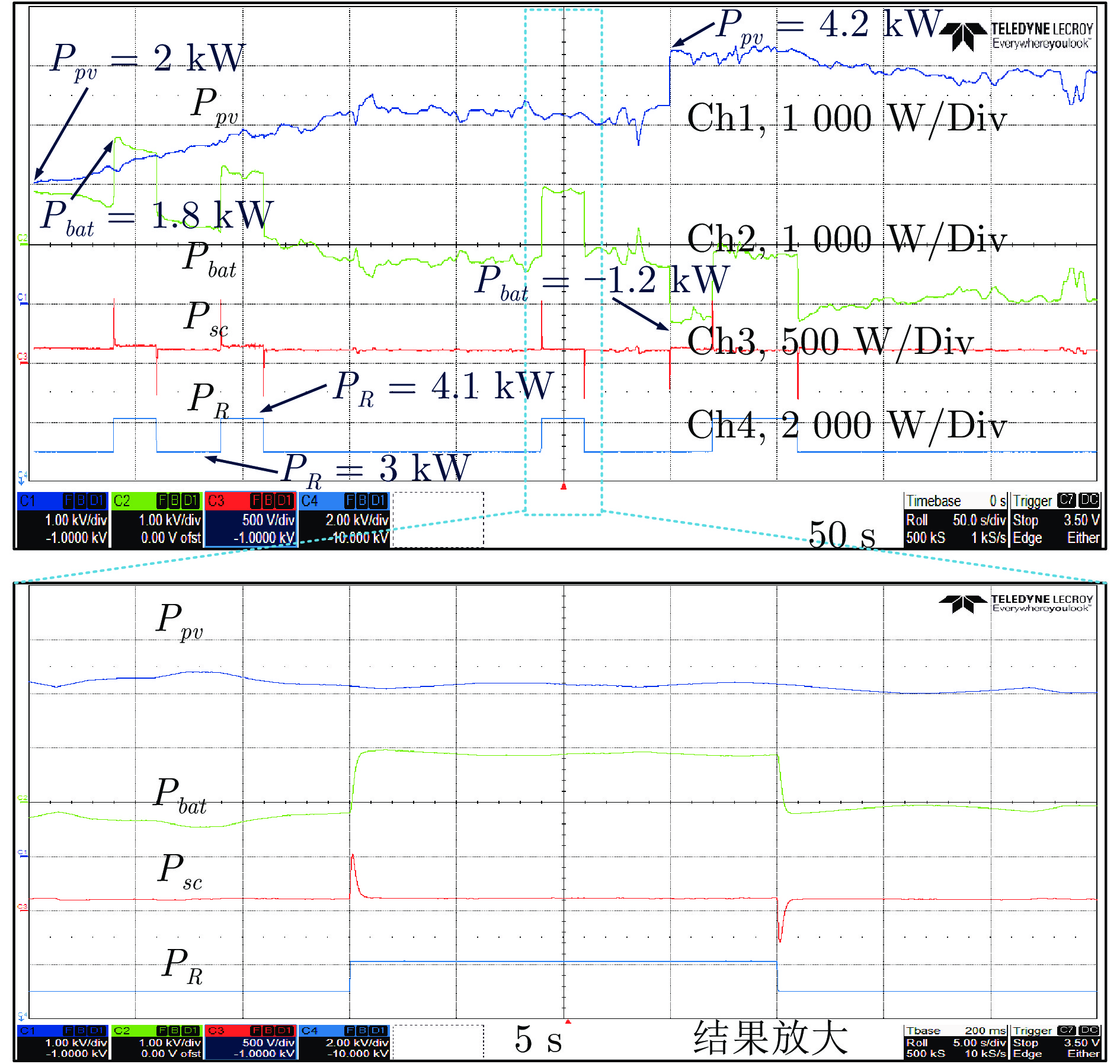
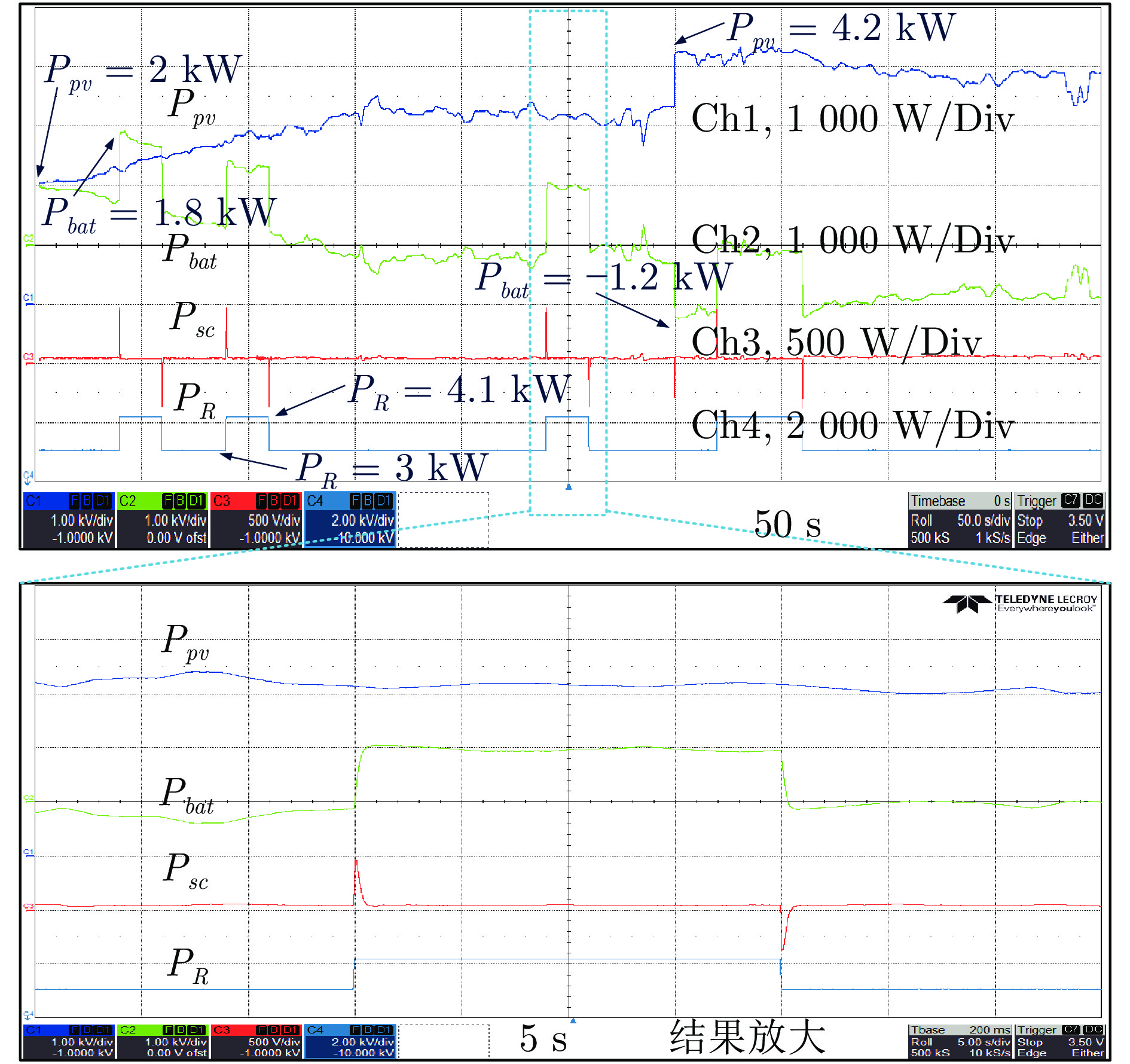
-
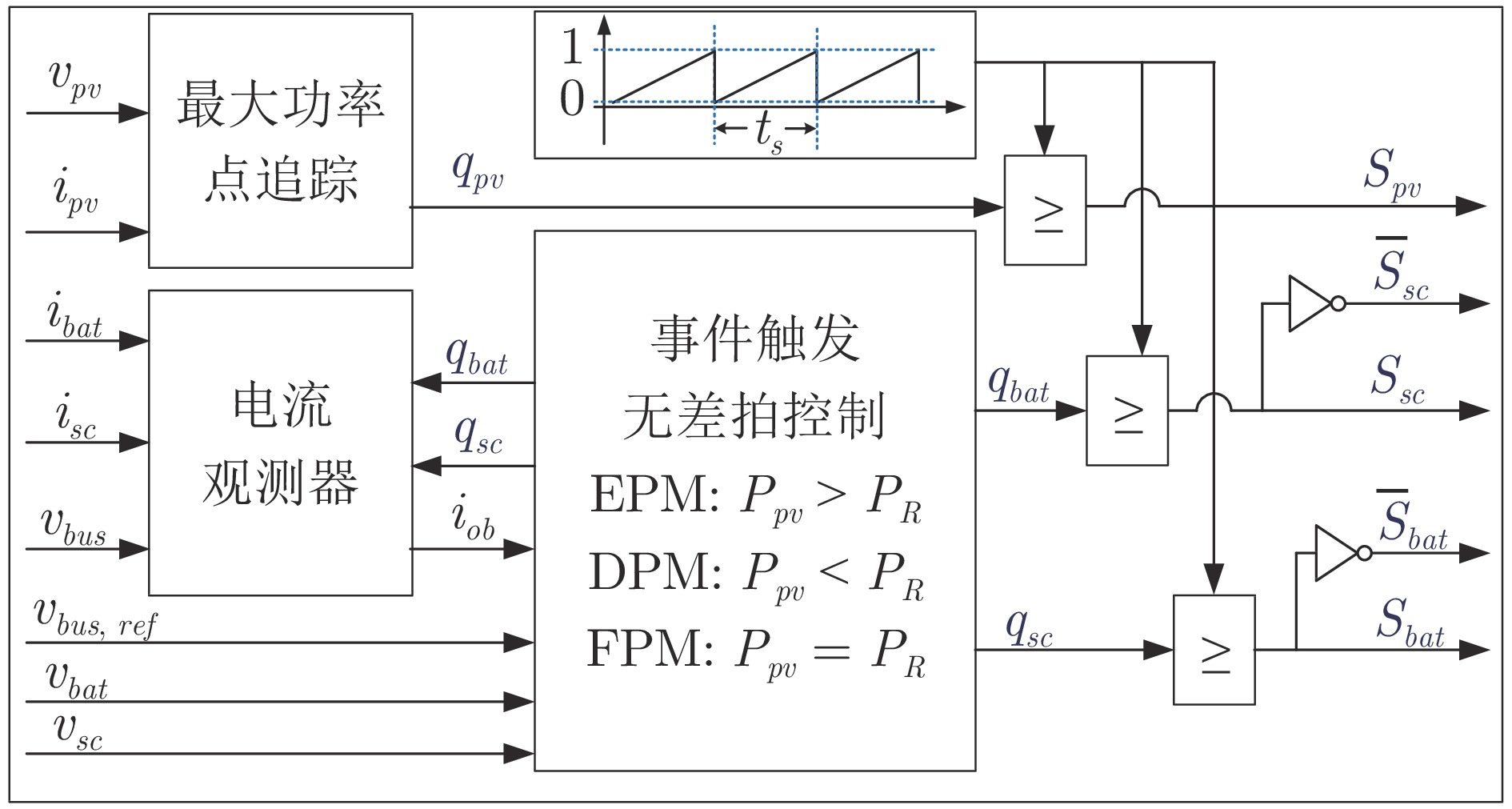
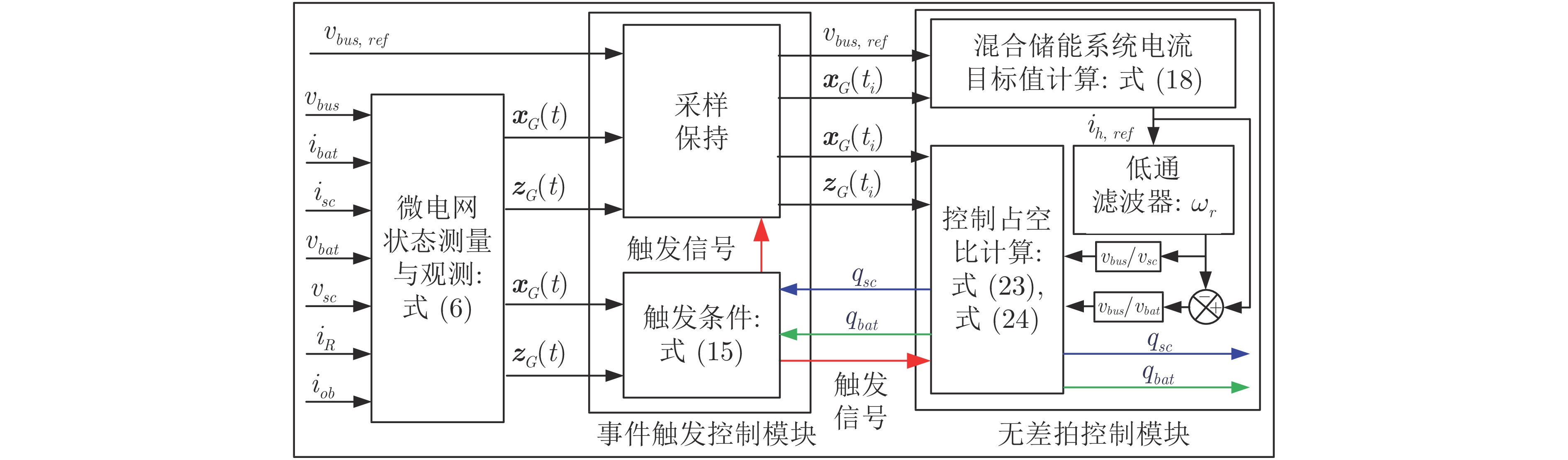
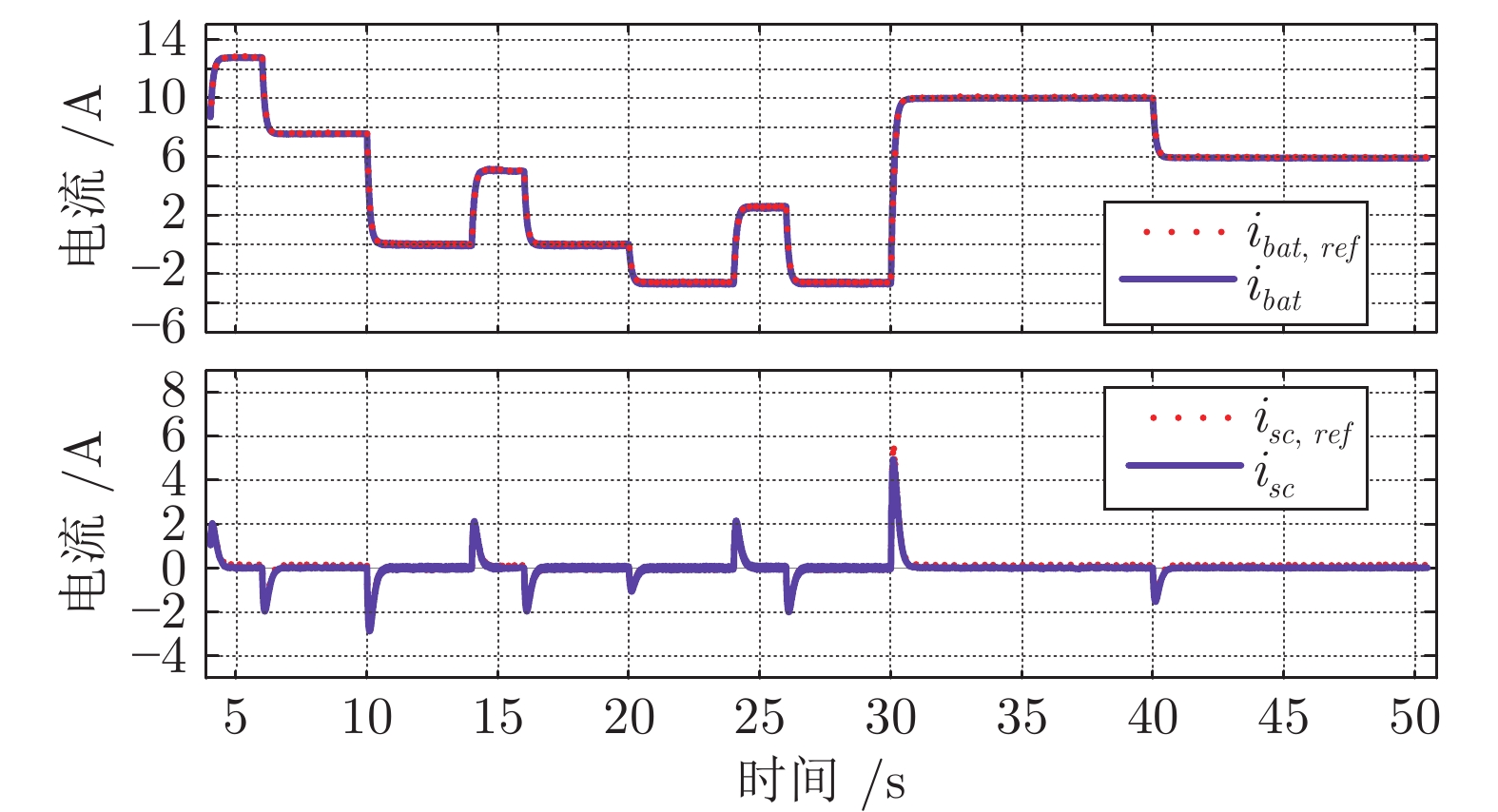
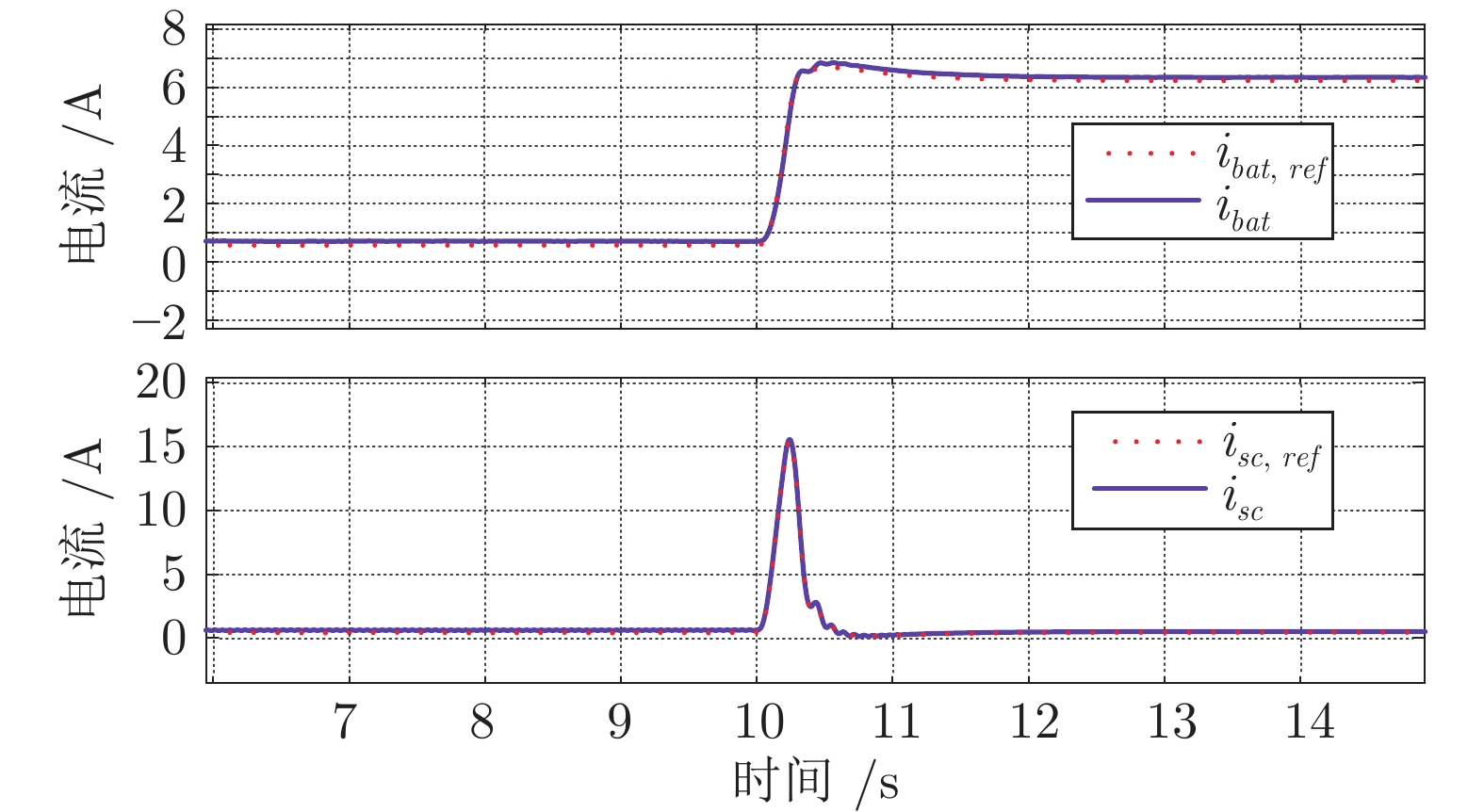
摘要: 针对光伏(Photovoltaic, PV)−电池−超级电容直流微电网系统中光伏发电间歇性造成的功率失配问题, 提出一种基于事件触发的无差拍预测控制(Event-triggered deadbeat predictive control, ETDPC)方法, 以实现有效的能量管理. ETDPC方法结合事件触发控制策略和无差拍预测控制策略(Deadbeat predictive control, DPC)的优点, 根据微电网的拓扑结构构建状态空间模型, 用于设计适用于微电网能量管理的触发条件: 当ETDPC的触发条件满足时, ETDPC中无差拍预测控制模块被激活, 可以在一个控制周期内产生最优控制信号, 实现对于扰动的快速响应, 减小母线电压纹波; 当系统状态不满足ETDPC中的触发条件时, 无差拍预测控制模块被挂起, 从而消除非必要运算, 以减轻实现能量管理的运算负担. 因此, 对于电池−超级电容器混合储能系统(Hybrid energy storage system, HESS), ETDPC能够缓解间歇性光伏发电与负荷需求之间的功率失衡, 以稳定母线电压. 最后, 数字仿真和硬件在环(Hardware-in-loop, HIL)实验结果表明, 相较于传统无差拍控制方法, 运算负担减小了50.63%, 母线电压纹波小于0.73%, 验证了ETDPC方法的有效性与性能优势, 为直流微电网的能量管理提供了一种参考.Abstract: This paper presents an event-triggered deadbeat predictive control (ETDPC) method for the mitigation of power mismatch in a photovoltaic (PV)-battery-supercapacitor microgrid. The proposed ETDPC method combines the event-triggered control strategy and the deadbeat predictive control (DPC) strategy and inherits their advantages accordingly. Based on the topology of the DC microgrid, the state-space model can be built for the design of the triggering condition for the energy management: When the triggering condition of ETDPC is activated, the deadbeat control block of ETDPC will be conducted and the optimal control signal can be generated within one control cycle, so that the DC bus voltage ripple can be reduced based on the fast response to the disturbance; When the state of the DC microgrid cannot satisfy the triggering condition, the deadbeat control block of ETDPC will be suspended to eliminate the redundant computations, so that the computational burden of the DC microgrid energy management can be reduced. Therefore, ETDPC can be fully utilized for battery-supercapacitor hybrid energy storage system (HESS) to mitigate the power unbalance between the load demand and the intermittent photovoltaic power generation and stabilize the bus voltage. To validate the effectiveness of the method, various simulations and hardware-in-loop (HIL) experiments are conducted based on a digital simulation system and the HIL platform, which show that the computational burden is reduced by 50.63% compared to the conventional deadbeat predictive control and the voltage ripple is regulated less than 0.73% of the reference. This work provides a reference of the control strategy for microgrid energy management.
-
表 1 仿真参数表
Table 1 Parameters for the simulation studies
类别 参数名称 数值 双向
半桥
变换器$v_{bus }$ 300 V $C $ 4 700 μF $L\,(L_{bat},\;L_{sc})$ 47 mH 混合储能系统 电池 $v_{bat }$ 200 V Capacity (容量) 65 Ah 超级
电容$v_{sc} $ 200 V Capacitance (容值) 50 F 光伏电池单元 $v_{pv }$ (开路电压) 30.2 V $i_{pv} $ (短路电流) 5.0 A 控制方法时间步长 $t_s $ 100 μs $t_{et} $ 100 μs 表 2 运算执行次数统计表
Table 2 Statistics table of the number of operation times
时间 (s) 执行次数 (万次) DPC ETDPC 100 100 48.2 200 200 98.1 300 300 148.2 400 400 197.8 500 500 247.2 600 600 297.4 平均执行次数 (万次/百秒) 100 49.37 纹波(V) 1.8 2.2 表 3 硬件在环运算执行次数统计表
Table 3 Operation times of the HIL experiments
时间 (s) 执行次数 (万次) DPC ETDPC 100 100 57.9 200 200 108.1 300 300 158.2 400 400 207.6 500 500 257.2 平均执行次数 (万次/百秒) 100 52.6 纹波(V) 1.5 2.0 -
[1] 梅生伟, 朱建全. 智能电网中的若干数学与控制科学问题及其展望. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(02): 119-131 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60014-2Mei S, Zhu J. Mathematical and control scientiflc issues of smart grid and its prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(02): 119-131. doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60014-2 [2] Dragičević T, Lu X, Vasquez J C, Guerrero JM. DC microgrids—Part II: A review of power architectures, applications, and standardization issues. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2016, 31(5): 3528-3549. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2015.2464277 [3] 王澄, 刘德荣, 魏庆来, 赵冬斌, 夏振超. 有储能设备的智能电网电能迭代自适应动态规划最优控制. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(9): 1984-1990Wang C, Liu D, Wei Q, Zhao D, Xia Z. Iterative adaptive dynamic programming approach to power optimal control for smart grid with energy storage devices. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9): 1984-1990. [4] Xu Q et al.. A decentralized dynamic power sharing strategy for hybrid energy storage system in autonomous DC Microgrid. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(7): 5930-5941. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2608880 [5] 卢自宝, 钟尚鹏, 郭戈. 基于分布式策略的直流微电网下垂控制器设计. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(10): 2472−2483Lu Zi-Bao, Zhong Shang-Peng, Guo Ge. Design of droop controller for DC microgrid based on distributed strategy. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(10): 2472−2483 [6] 刘建刚, 杨胜杰. 具有容性负载的直流微电网系统分布式协同控制. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(06): 1283-1290Liu J, Yang S. Distributed cooperative control of DC micro-grid systems with capacitive load. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(06): 1283-1290. [7] Baros S, Ilić M D. A consensus approach to real-time distributed control of energy storage systems in wind farms. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 10(1): 613-625. [8] Wang B. et al.. Consensus-based control of hybrid energy storage system with a cascaded multiport converter in DC microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2020, 11(4): 2356-2366. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2019.2956054 [9] Teleke S, Baran M E, Bhattacharya S, Huang A Q. Rule-based control of battery energy storage for dispatching intermittent renewable sources. IEEE Transactions on Sustain Energy, 2010, 1(3): 117-124. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2010.2061880 [10] Tummuru N R, Mishra M K, Srinivas S. Dynamic energy management of renewable grid integrated hybrid energy storage system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(12): 7728–7737. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2455063 [11] Manandhar U. et al. Energy management and control for grid connected hybrid energy storage system under different operating modes, IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(2): 1626-1636. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2017.2773643 [12] Xiao J, Wang Pe, Setyawan L. Hierarchical control of hybrid energy storage system in DC microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(8): 4915-4924. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2400419 [13] Xiao J, Wang Pe, Setyawan L. Multilevel energy management system for hybridization of energy storages in DC microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(2): 847-856. [14] Abeywardana D B W, Hredzak B, Agelidis V G. A fixed frequency sliding mode controller for a boost-inverter-based battery supercapacitor hybrid energy storage system. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2017, 32(1): 668–680. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2016.2527051 [15] Wang B, Xu J, Wai R J, Cao B. Adaptive sliding-mode with hysteresis control strategy for simple multimode hybrid energy storage system in electric vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(2): 1404–1414. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2618778 [16] Kouro S, Perez M A, Rodriguez J, Llor A M, Young H A. Model predictive control: MPC's role in the evolution of power electronics. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine, 2015, 9(4): 8-21. doi: 10.1109/MIE.2015.2478920 [17] Zhang X, Wang B, Manandhar U, Gooi H B, Foo G. A model predictive current controlled bidirectional three-level DC/DC converter for hybrid energy storage system in DC microgrids, IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(5): 4025-4030. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2018.2873765 [18] 张彦, 张涛, 王锐, 刘亚杰, 郭波. 基于模型预测控制的含多微电网的能源互联网分布式协同优化(英文). 自动化学报, 2017, 43(08): 1443-1456Zhang Y, Zhang T, Wang R, Liu Y, Guo B. A model predictive control based distributed coordination of multi-microgrids in energy internet. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1443-1456. [19] Shan Y, Hu J, Chan K W, Fu Q, Guerrero J M. Model predictive control of bidirectional DC-DC converters and AC/DC interlinking converters—a new control method for PV-wind-battery microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, 10 (4): 1823-1833. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2018.2873390 [20] B. Wang, V. R. K. Kanamarlapudi, L. Xian, X. Peng, K. T. Tan and P. L. So. Model predictive voltage control for single-inductor multiple-output DC–DC converter with reduced cross regulation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Jul. 2016, 63(7): 4187-4197. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2532846 [21] Wang B, Manandhar U, Zhang X, Gooi H B, Ukil A. Deadbeat control for hybrid energy storage systems in DC microgrids, IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2018, 10(4): 1867-1877. [22] Wang B et al.. Event-Triggered Model Predictive Control for Power Converters, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 68(1): 715-720. -




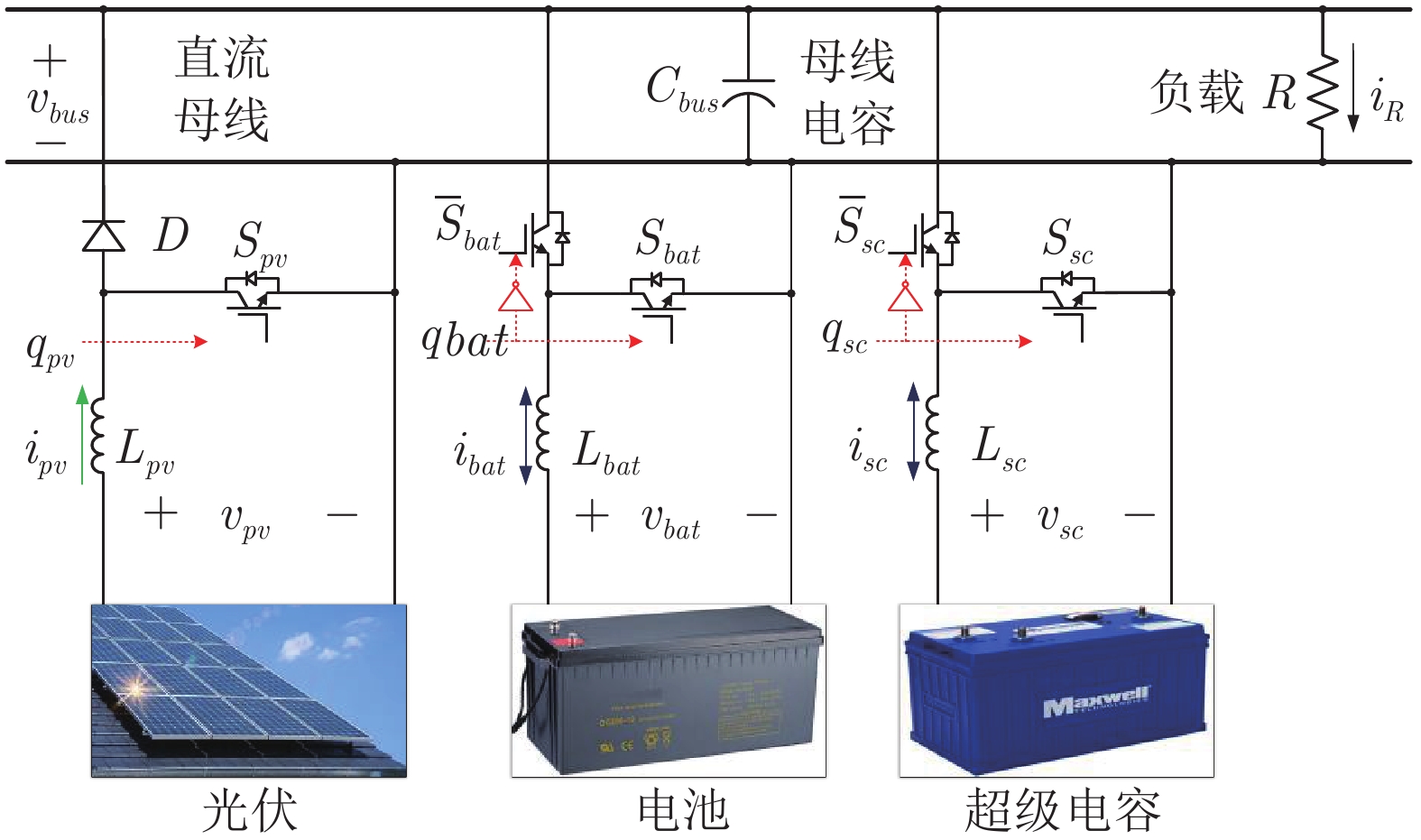
 下载:
下载: