-
摘要: 在显著性目标检测网络的设计中, U型结构使用广泛. 但是在U型结构显著性检测方法中, 普遍存在空间位置细节丢失和边缘难以细化的问题, 针对这些问题, 提出一种基于语义信息引导特征聚合的显著性目标检测网络, 通过高效的特征聚合来获得精细的显著性图. 该网络由混合注意力模块(Mixing attention module, MAM)、增大感受野模块(Enlarged receptive field module, ERFM)和多层次聚合模块(Multi-level aggregation module, MLAM)三个部分组成. 首先, 利用增大感受野模块处理特征提取网络提取出的低层特征, 使其在保留原有边缘细节的同时增大感受野, 以获得更加丰富的空间上/下文信息; 然后, 利用混合注意力模块处理特征提取网络的最后一层特征, 以增强其表征力, 并作为解码过程中的语义指导, 不断指导特征聚合; 最后, 多层次聚合模块对来自不同层次的特征进行有效聚合, 得到最终精细的显著性图. 在6个基准数据集上进行了实验, 结果验证了该方法能够有效地定位显著特征, 并且对边缘细节的细化也很有效.Abstract: In the field of the salient object detection, the U-shaped structure has attracted much attention. However, the spatial and boundary details are ignored in the U-shaped salient object detection task. To address the issues, this paper proposes a salient object detection network that uses semantic information to guide feature aggregation, mainly including three modules: Mixing attention module (MAM), enlarged receptive field module (ERFM) and multi-level aggregation module (MLAM). Specifically, utilizes ERFM to process the low-level features, so that it can increase the receptive field while retaining the original edge details to obtain richer spatial context information. Then, utilize the MAM to process the high-level features to enhance its semantic representation, which guides the feature aggregation in the decoding process. Finally, MLAM is employed to effectively combine the multi-level features for the predicted salient map. This paper conducts extensive experiments on 6 benchmarks, and the results have proved that the method can effectively locate salient object and refine edge details.
-
Key words:
- Salient object detection /
- mixing attention /
- multi-level aggregation /
- deep learning
-
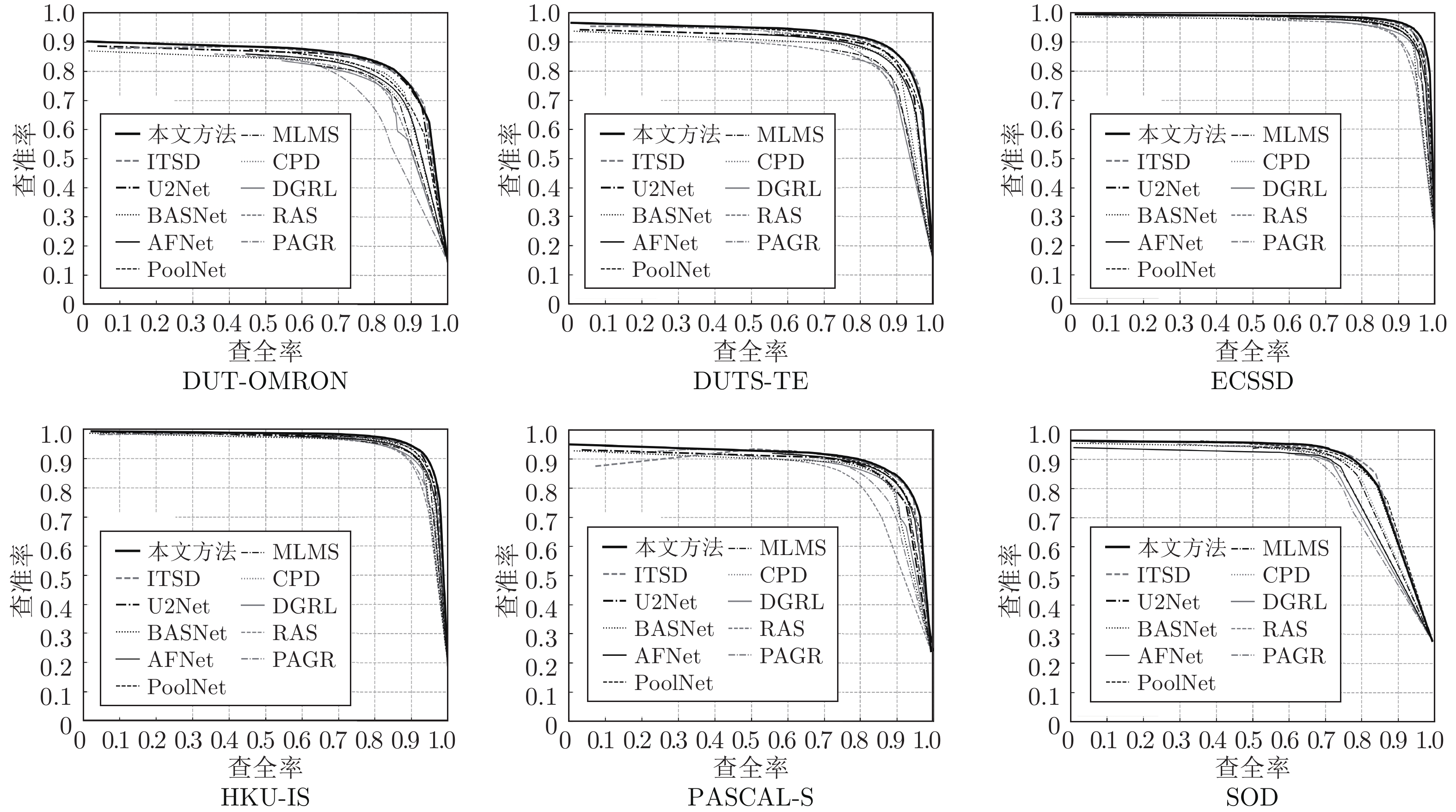
表 1 不同方法的${F_\beta }$指标结果比较
Table 1 Comparison of ${F_\beta }$ values of different models
数据集 本文方法 PAGR RAS DGRL CPD MLMS PoolNet AFNet BASNet U2Net ITSD ECSSD 0.951 0.924 0.921 0.921 0.936 0.930 0.944 0.935 0.942 0.951 0.947 DUT-OMRON 0.827 0.771 0.786 0.774 0.794 0.793 0.808 0.797 0.805 0.823 0.824 PASCAL-S 0.873 0.847 0.837 0.844 0.866 0.858 0.869 0.868 0.854 0.859 0.871 HKU-IS 0.937 0.919 0.913 0.910 0.924 0.922 0.933 0.923 0.928 0.935 0.934 DUTS-TE 0.888 0.855 0.831 0.828 0.864 0.854 0.880 0.862 0.860 0.873 0.883 SOD 0.873 0.838 0.810 0.843 0.850 0.862 0.867 — 0.851 0.861 0.880 注: ${F_\beta }$值越大越好, 加粗数字为最优结果, 加下划线数字为次优结果. 表 2 不同方法的MAE指标结果比较
Table 2 Comparison of MAE values of different models
数据集 本文方法 PAGR RAS DGRL CPD MLMS PoolNet AFNet BASNet U2Net ITSD ECSSD 0.034 0.064 0.056 0.043 0.040 0.038 0.039 0.042 0.037 0.034 0.035 DUT-OMRON 0.058 0.071 0.062 0.062 0.056 0.060 0.056 0.057 0.056 0.054 0.061 PASCAL-S 0.065 0.089 0.104 0.072 0.074 0.069 0.075 0.069 0.076 0.074 0.072 HKU-IS 0.032 0.047 0.045 0.036 0.033 0.034 0.033 0.036 0.032 0.031 0.031 DUTS-TE 0.042 0.053 0.060 0.049 0.043 0.045 0.040 0.046 0.047 0.044 0.041 SOD 0.093 0.145 0.124 0.103 0.112 0.106 0.100 — 0.114 0.108 0.095 注: MAE值越小越好. 表 3 不同方法的${S_m}$指标结果比较
Table 3 Comparison of ${S_m}$ values of different models
数据集 本文方法 PAGR RAS DGRL CPD MLMS PoolNet AFNet BASNet U2Net ITSD ECSSD 0.932 0.889 0.893 0.906 0.915 0.911 0.921 0.914 0.916 0.928 0.925 DUT-OMRON 0.847 0.775 0.814 0.810 0.818 0.817 0.836 0.826 0.836 0.847 0.840 PASCAL-S 0.865 0.749 0.795 0.869 0.844 0.849 0.845 0.850 0.838 0.844 0.859 HKU-IS 0.930 0.887 0.887 0.897 0.904 0.901 0.917 0.905 0.909 0.916 0.917 DUTS-TE 0.873 0.838 0.839 0.842 0.867 0.856 0.883 0.866 0.853 0.861 0.872 SOD 0.808 0.720 0.764 0.771 0.771 0.780 0.795 — 0.772 0.786 0.809 注: ${S_{{m} } }$值越大越好. 表 4 消融实验结果
Table 4 Results of ablation experiment
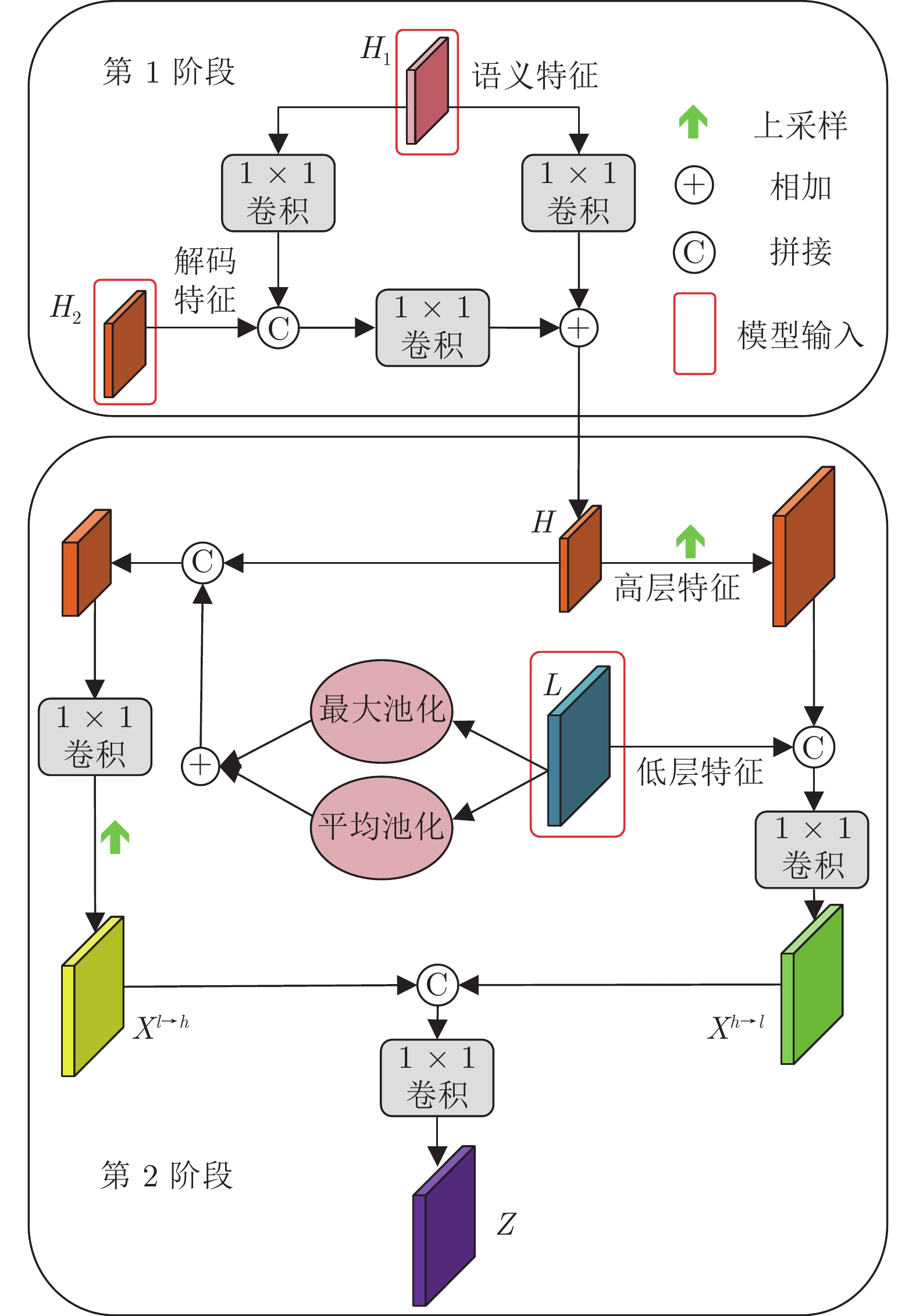
MAM ERFM MLAM MAE/${F_\beta }$ — — ✓ 0.049/0.935 ✓ ✓ — 0.045/0.937 — ✓ ✓ 0.042/0.942 ✓ — ✓ 0.039/0.944 ✓ ✓ ✓ 0.034/0.951 注: MAE值越小越好, 加粗字体为最优结果, “✓”为使用指定模块. 表 5 ERFM模块中, 不同扩张率设置的对比实验
Table 5 Comparative experiment of different dilation rate configurations in ERFM
扩张率的不同设置组合 MAE/${F_\beta }$ (1, 3, 5), (1, 3, 5), (1, 3, 5), (1, 3, 5) 0.039/0.946 (1, 3, 5), (1, 3, 5), (3, 5, 7), (1, 3, 5) 0.037/0.948 (1, 3, 5), (4, 6, 8), (3, 5, 7), (1, 3, 5) 0.036/0.950 (5, 8, 11), (4, 6, 8), (3, 5, 7), (1, 3, 5) 0.034/0.951 表 6 MLAM模块中, 两个分支的消融实验
Table 6 Ablation experiment of two branches in MLAM
自下而上分支 自上而下分支 MAE/${F_\beta }$ ✓ — 0.041/0.940 — ✓ 0.040/0.946 ✓ ✓ 0.034/0.951 表 7 MAM模块中, 注意力模块位置关系的消融实验
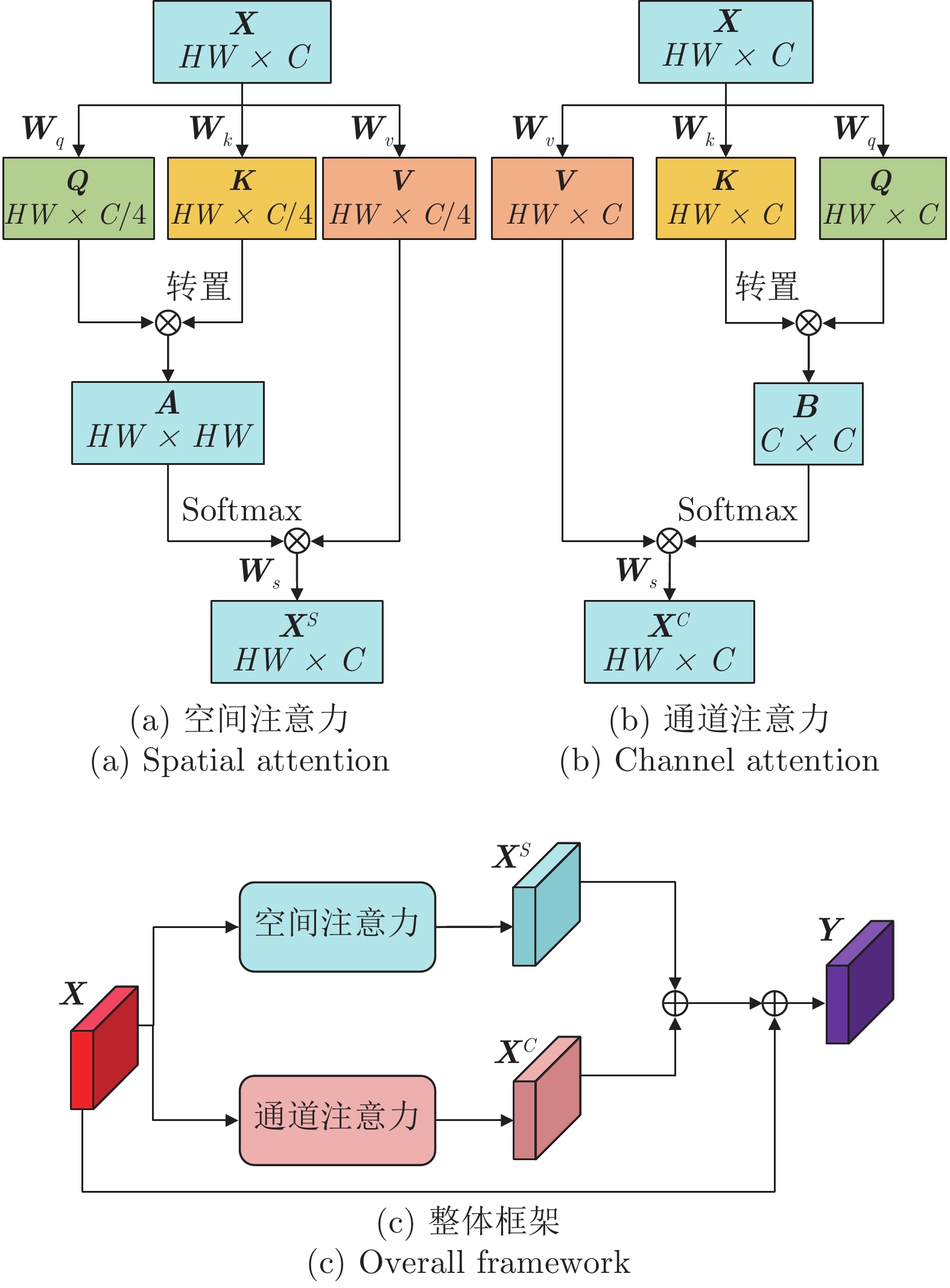
Table 7 Ablation experiment on the position relationship of attention module in MAM
注意力模块之间的位置关系 MAE/${F_\beta }$ 通道注意力在前 0.036/0.947 空间注意力在前 0.038/0.944 并行放置 (本文方法) 0.034/0.951 -
[1] Donoser M, Urschler M, Hirzer M, Bischof H. Saliency driven total variation segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2009. 817−824 [2] Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q. F3Net: Fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: Spring, 2020. 12321−12328 [3] 李东民, 李静, 梁大川, 王超. 基于多尺度先验深度特征的多目标显著性检测方法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2058-2070Li Dong-Min, Li Jing, Liang Da-Chuan, Wang Chao. Multiple Salient Objects Detection Using Multi-scale Prior and Deep Features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2058-2070 [4] 徐威, 唐振民. 利用层次先验估计的显著性目标检测. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(4): 799-812Xu Wei, Tang Zhen-Min. Exploiting Hierarchical Prior Estimation for Salient Object Detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(4): 799-812 [5] 杨赛, 赵春霞, 徐威. 一种基于词袋模型的新的显著性目标检测方法. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(8): 1259-1273Yang Sai, Zhao Chun-Xia, Xu Wei. A novel salient object detection method using bag-of-features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(8): 1259-1273 [6] Hong S, You T, Kwak S, Han B. Online tracking by learning discriminative saliency map with convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Miami, USA: IMLS, 2015. 597−606 [7] Ren Z, Gao S, Chia L, Tsang I W. Region-based saliency detection and its application in object recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2014, 24(5): 769−779 [8] Wang X, You S, Li X, Ma H. Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation by iteratively mining common object features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1354− 1362 [9] Goferman S, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A. Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(10): 1915−1926 [10] Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J, Jia J. Hierarchical saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. America, Portland: IEEE, 2013. 1155− 1162 [11] Hou Q, Cheng M M, Hu X, Borji A, Tu Z, Torr P. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5300−5309 [12] Luo Z, Mishra A, Achkar A, Eichel J, Jodoin P M. Non-local deep features for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6609−6617 [13] Zhang P, Wang D, Lu H, Wang H, Ruan X. Amulet: Aggregating multi-level convolutional features for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 202−211 [14] Li X, Zhao L M, Wei L, Yang M, Wu F, Zhuang Y T, et al. DeepSaliency: Multi-task deep neural network model for salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(8): 3919−3930 [15] Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, Dehghan M, Jagersand M. U2Net: Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 106: Article No. 107404 [16] Pang Y, Zhao X, Zhang L, Lu H. Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 9413−9422 [17] Wei J, Wang S, Wu Z, Su C, Huang Q, Tian Q. Label decoupling framework for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 13025−13034 [18] Borji A, Cheng M M, Jiang H, Li J. Salient object detection: A benchmark. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5706−5722 [19] Zhang X N, Wang T T, Qi J Q, Lu H C, Wang G. Progressive attention guided recurrent network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 714−722 [20] Zhao T, Wu X Q. Pyramid feature attention network for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Los Angeles, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3085−3094 [21] Chen S, Tan X, Wang B, Hu X. Reverse attention for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Europeon Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: IEEE, 2018. 234−250 [22] Wang W, Zhao S, Shen J, Hoi S C, Borji A. Salient object detection with pyramid attention and salient edges. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Los Angeles, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1448−1457 [23] Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Los Angeles, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3907−3916 [24] Deng Z J, Hu X W, Zhu L, Xu X M, Qin J, Han G Q, et al. R3Net: Recurrent residual refinement network for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm, Sweden: AAAI Press, 2018. 684−690 [25] Wang B, Chen Q, Zhou M, Zhang Z, Jin X, Gai K. Progressive feature polishing network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: Springer, 2020. [26] Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, Li Y, Bao Y, Fang Z, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Los Angeles, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3146−3154 [27] Zhao H S, Shi J P, Qi X J, Wang X G, Jia J Y. Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6230−6239 [28] Wang L J, Lu H C, Wang Y F, Feng M Y, Wang D, Yin B C, et al. Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3796− 3805 [29] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6980, 2014. [30] Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H C, Ruan X, Yang M. Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 3166−3173 [31] Li X H, Lu H C, Zhang L, Ruan X, Yang M. Saliency detection via dense and sparse reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Austra-lia: IEEE, 2013. 2976−2983 [32] Li G B, Yu Y Z. Visual saliency based on multi-scale deep features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 5455− 5463 [33] Li Y, Hou X, Koch C, Rehg J M, Yuille A L. The secrets of salient object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 280−287 [34] Movahedi V, Elder J H. Design and perceptual validation of performance measures for salient object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 49−56 [35] Fan D P, Cheng M M, Liu Y, Li T, Borji A. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4548−4557 [36] Wang T T, Zhang L, Wang S, Lu H C, Yang G, Ruan Y, et al. Detect globally, refine locally: A novel approach to saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3127−3135 [37] Wu R, Feng M, Guan W, Wang D, Lu H, Ding E. A mutual learning method for salient object detection with intertwined multi-supervision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Los Angeles, USA: IEEE, 2019. 8150−8159 [38] Liu J J, Hou Q, Cheng M M, Feng J, Jiang J. PoolNet: A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Los Angeles, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3917−3926 [39] Feng M Y, Lu H C, Ding E. Attentive feedback network for boundary-aware salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Los Angeles, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1623−1632 [40] Qin X B, Zhang Z C, Huang C Y, Gao C, Dehghan M, Jagersand M. BASNet: Boundary-aware salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Los Angeles, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7479−7489 [41] Zhou H, Xie X, Lai J H, Chen Z, Yang L. Interactive two-stream decoder for accurate and fast saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 9141−9150 -





 下载:
下载: