-
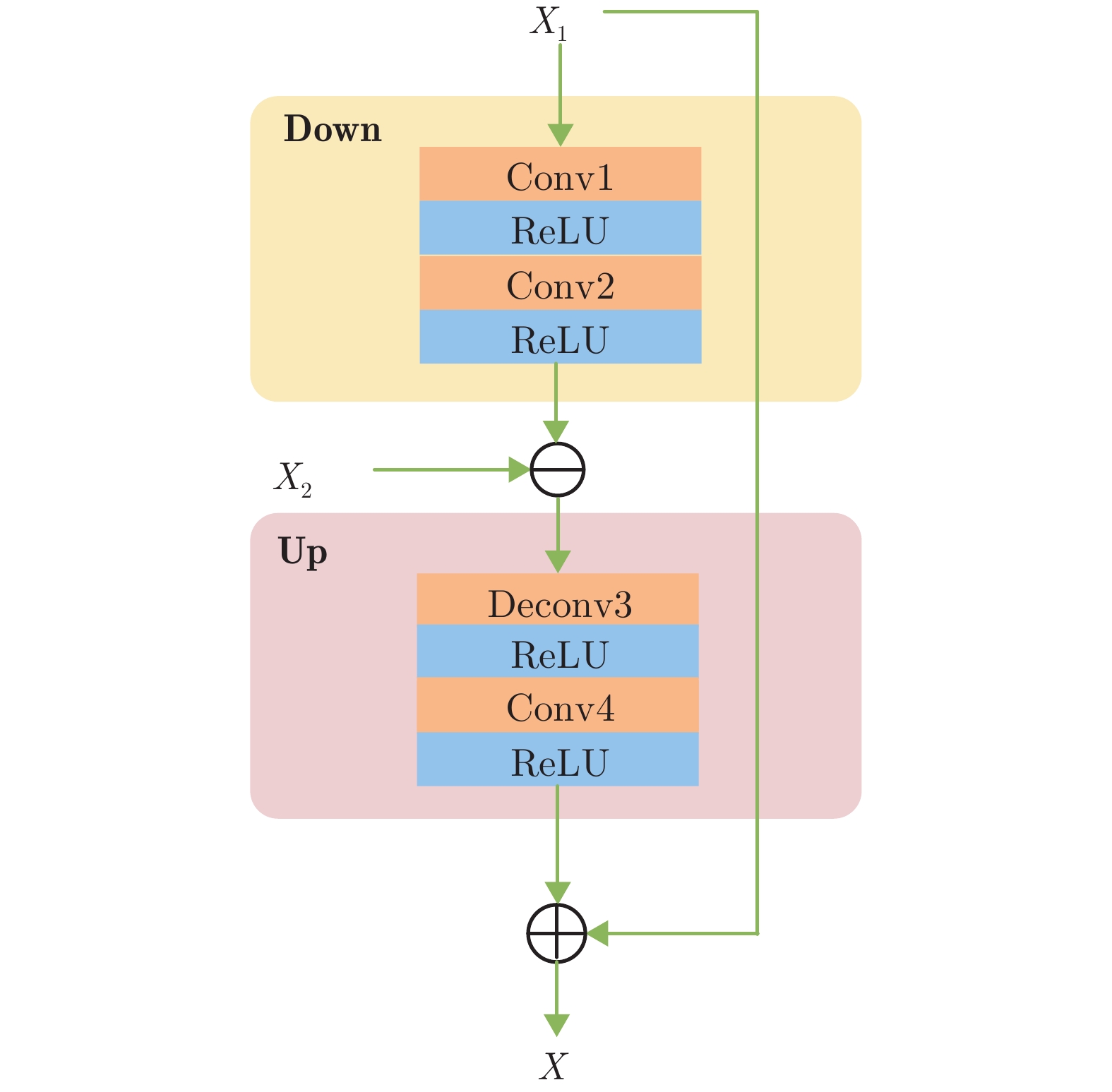
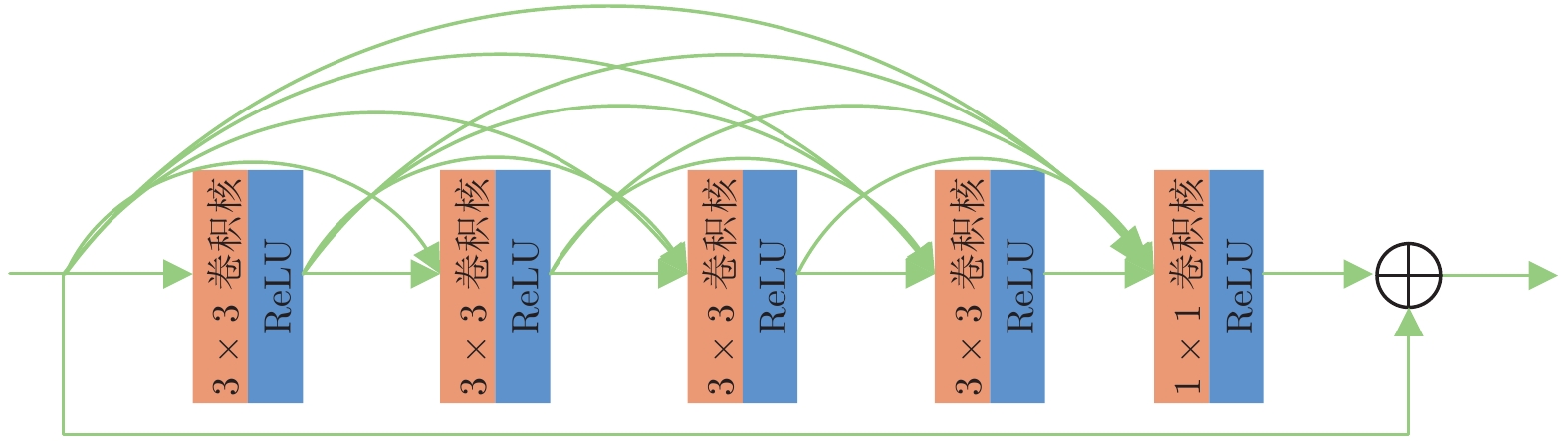
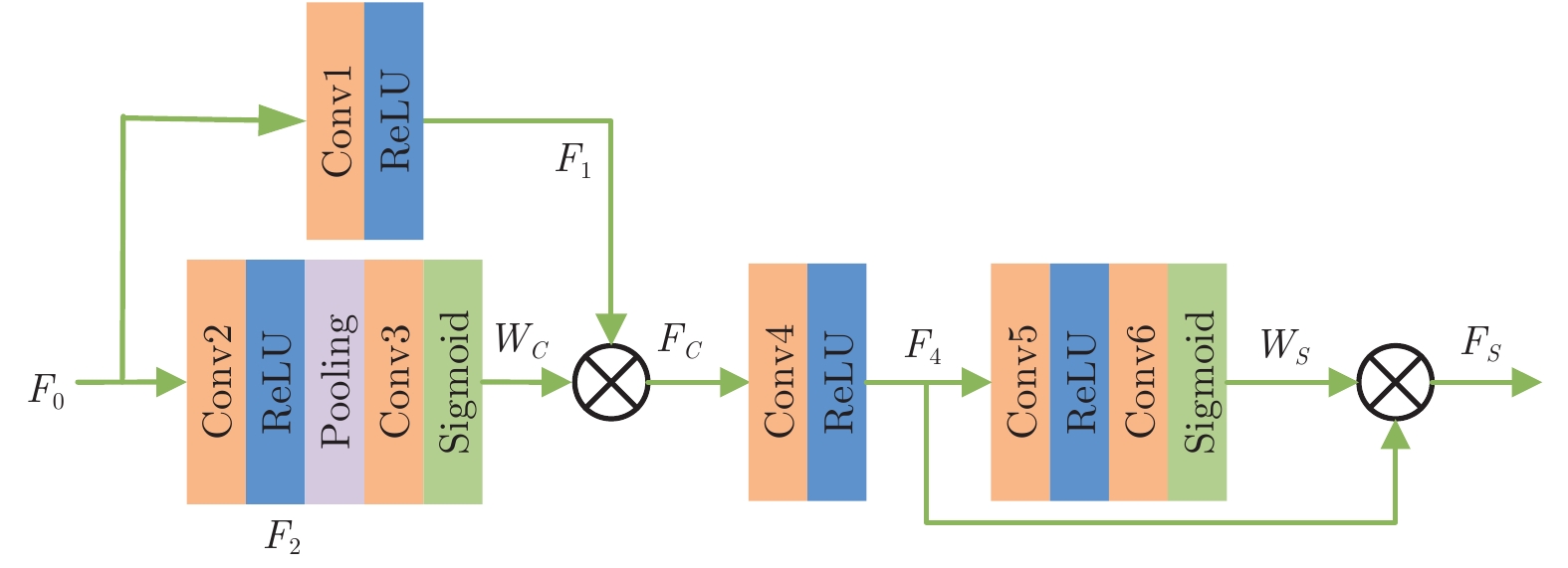
摘要: 针对现有图像去雾方法因空间上/下文信息丢失而无法准确估计大尺度目标特征, 导致图像结构被破坏或去雾不彻底等问题, 提出一种基于误差回传机制的多尺度去雾网络. 网络由误差回传多尺度去雾组(Error-backward multi-scale dehazing group, EMDG)、门控融合模块(Gated fusion module, GFM)和优化模块组成. 其中误差回传多尺度去雾组包括误差回传模块(Error-backward block, EB)和雾霾感知单元(Haze aware unit, HAU). 误差回传模块度量相邻尺度网络特征图之间的差异, 并将生成的差值图回传至上一尺度, 实现对结构信息和上/下文信息的有效复用; 雾霾感知单元是各尺度子网络的核心, 其由残差密集块(Residual dense block, RDB)和雾浓度自适应检测块(Haze density adaptive detection block, HDADB)组成, 可充分提取局部信息并能够根据雾浓度实现自适应去雾. 不同于已有融合方法直接堆叠各尺度特征, 提出的门控融合模块逐像素学习每个子网络特征图对应的最优权重, 有效避免了干扰信息对图像结构和细节信息的破坏. 再经优化模块, 可得到最终的无雾图像. 在合成数据集和真实数据集上的大量实验表明, 该方法优于目前的主流去雾方法, 尤其是对远景雾气去除效果更佳.Abstract: The existing dehazing methods can not estimate large-scale target features accurately due to the loss of spatial context information, leading to the destruction of image structure and remaining of haze. To solve this problem, we propose a novel multi-scale dehazing network based on error-backward mechanism, which is composed of error-backward multi-scale dehazing group (EMDG), gated fusion module (GFM) and optimization module. Error-backward multi-scale dehazing group consists of error-backward block (EB) and haze aware unit (HAU). With comparing the difference between feature maps of the coarse-scale sub-network and those of the fine-scale sub-network, error-backward block produces an error map and then transmits it to the last coarse-scale sub-network. So the structure and context information can be reused effectively. Haze aware unit is the core of all sub-networks, which consists of residual dense blocks (RDB) and haze density adaptive detection block (HDADB). It helps to extract local information and accomplish adaptive dehazing according to haze density. Differently from the existing fusion-based methods stacking features from different scales directly, the proposed gated fusion module learns the optimal weights of feature maps from different sub-networks, which prevents interferences to destroy image structure and details. The output of optimization module will be the final dehazed image. Extensive experiments on synthetic datasets and real datasets validate the superiority of our proposed network, especially for the haze removal at a distant view.
-
Key words:
- Image dehazing /
- deep learning /
- multi-scale network /
- error-backward
-
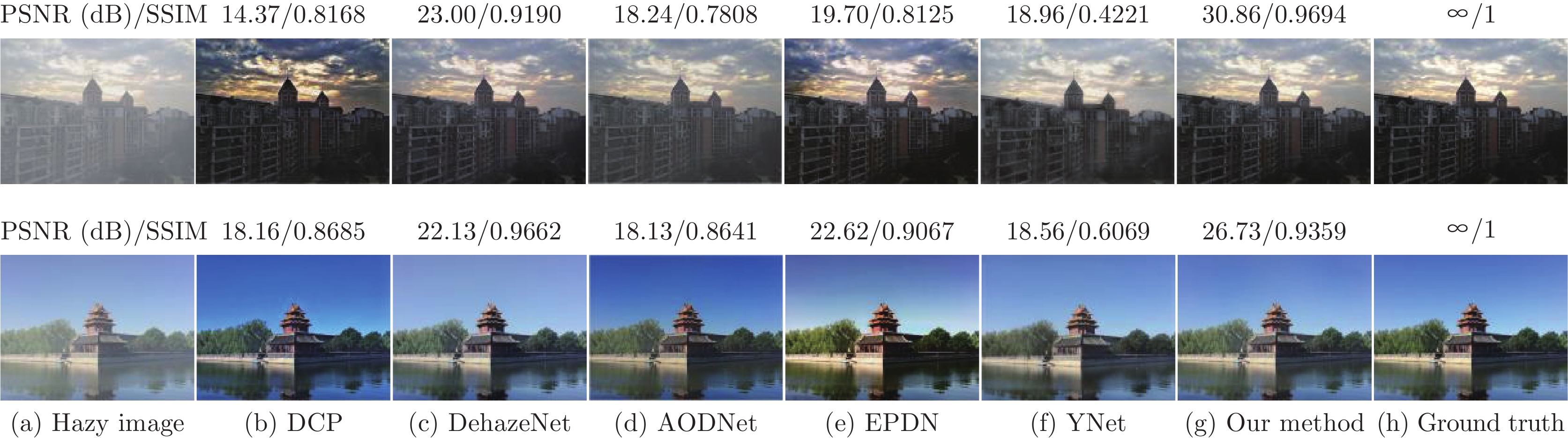
表 1 SOTS室内测试集去雾结果的定量比较
Table 1 Qualitative comparisons of dehazing results on SOTS indoor test-set
方法 DCP DehazeNet AODNet EPDN GCANet PSNR (dB) 16.62 21.14 19.06 25.06 30.23 SSIM 0.8179 0.8472 0.8504 0.9232 0.9800 方法 GridDehazeNet PFDN YNet MSBDN 本文方法 PSNR (dB) 32.16 32.68 19.04 33.79 33.83 SSIM 0.9836 0.9760 0.8465 0.9840 0.9834 表 2 SOTS室外测试集去雾结果的定量比较
Table 2 Qualitative comparisons of dehazing results on SOTS outdoor test-set
方法 DCP DehazeNet MSCNN AODNet PSNR (dB) 19.13 22.46 22.06 20.29 SSIM 0.8148 0.8514 0.9078 0.8765 方法 EPDN GridDehazeNet YNet 本文方法 PSNR (dB) 22.57 30.86 25.02 31.10 SSIM 0.8630 0.9819 0.9012 0.9765 表 3 O-Haze数据集去雾结果定量比较
Table 3 Qualitative comparisons of dehazing results on O-Haze data-set
方法 DCP MSCNN AODNet EPDN GCANet GridDehazeNet 本文方法 PSNR (dB) 16.78 17.26 15.03 16.00 16.28 18.92 19.28 SSIM 0.6530 0.6501 0.5394 0.6413 0.6450 0.6721 0.6756 表 4 HSTS测试集去雾结果的定量比较
Table 4 Qualitative comparisons of dehazing results on HSTS test-set
方法 DCP DehazeNet MSCNN AODNet EPDN YNet CCDID 本文方法 PSNR (dB) 14.84 24.48 18.64 20.55 23.38 18.37 17.22 30.07 SSIM 0.7609 0.9153 0.8168 0.8973 0.9059 0.4725 0.8218 0.9658 表 5 基于不同模块的网络性能比较
Table 5 Comparisons of network performance based on different modules
模块名称 A B C D E 5个RDB √ √ — — — 9个RDB — — √ √ √ GFM — √ √ √ √ EB — — — √ √ HDADB — — — — √ PSNR (dB) 28.79 29.52 31.53 32.45 33.83 表 6 各方法平均运行时间对比
Table 6 Average computing time comparison of various methods
方法 CPU/GPU 时间 (s) DCP CPU 25.08 DehazeNet CPU 2.56 MSCNN CPU 2.45 AODNet GPU 0.24 GridDehazeNet GPU 0.59 FFANet[28] GPU 1.23 本文方法 GPU 0.73 -
[1] Wonkyun K, Jong Y, Jechang J. Contrast enhancement using histogram equalization based on logarithmic mapping. Optical Engineering, 2012, 51(6), 067002: 1-11 [2] Li H, Xie W H, Wang X G. GPU implementation of multi-scale retinex image enhancement algorithm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/ACS International Conference of Computer Systems and Applications. Agadir, Morocco: IEEE, 2016. 1−5 [3] Stark J A. Adaptive image contrast enhancement using generalizations of histogram equalization. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2000, 9(5): 889-896 doi: 10.1109/83.841534 [4] He K, Sun J, Tang X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 33(12): 2341-2353 [5] Tarel J P, Hautière N. Fast visibility restoration from a single color or gray level image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2010. 2201−2208 [6] Zhu Q S, Mai J M, Shao L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015. 24(11): 3522–3533 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2446191 [7] Berman D, Treibitz T, Avidan S. Non-local image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1674−1682 [8] 张小刚, 唐美玲, 陈华, 汤红忠. 一种结合双区域滤波和图像融合的单幅图像去雾算法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(8): 1733-1739ZHANG Xiao-Gang, TANG Mei-Ling, CHEN Hua, TANG Hong-Zhong. A dehazing method in single image based on double-area filter and image fusion. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(8): 1733-1739 [9] 汪云飞, 冯国强, 刘华伟, 赵搏欣. 基于超像素的均值-均方差暗通道单幅图像去雾方法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 481-489WANG Yun-Fei, FENG Guo-Qiang, LIU Hua-Wei, ZHAO Bo-Xin. Superpixel-based mean and mean square deviation dark channel for single image fog removal. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 481-489 [10] Cai B L, Xu X M, Jia K, Qing C M, Tao D C. DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187-5198 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681 [11] Ren W Q, Liu S, Zhang H, Pan J S, Cao X C, Yang M H. Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: 2016. 154−169 [12] Zhang H, Patel V M. Densely connected pyramid dehazing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3194−3203 [13] Li B Y, Peng X L, Wang Z Y, Xu J Z, Feng D. AODNet: All-in-one dehazing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4780−4788 [14] Chen D D, He M M, Fan Q N, Liao J, Zhang L H, Hou D D, et al. Gated context aggregation network for image dehazing and deraining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1375−1383 [15] Liu X H, Ma Y R, Shi Z H, Chen J. GridDehazeNet: Attention-based multi-scale network for image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 7314−7323 [16] Dong J X, Pan J S. Physics-based feature dehazing networks. In: Proceedings of the Europeon Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: 2020. 188−204 [17] Yang H H, Yang C H H, Tsai Y C J. YNet: Multi-scale feature aggregation network with wavelet structure similarity loss function for single image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2020. 2628−2632 [18] Deng Q L, Huang Z L, Lin C W. HardGAN: A haze-aware representation distillation GAN for single image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the Europeon Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: 2020. 722−738 [19] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. Unet: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: 2015. 234– 241 [20] Johnson J, Alexandre A, Li F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the Europeon Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: 2016. 694−711 [21] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision. 2015. 211–252 [22] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA: ICLR, 2015. 1−14 [23] Li B Y, Ren W Q, Fu D P, Tao D C, Feng D, Zeng W J, et al. Benchmarking single image dehazing and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019. 28(1): 492-505 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2867951 [24] Ancuti C O, Ancuti C, Timofte R, Vleeschouwer C D. O-Haze: A dehazing benchmark with real hazy and haze-free outdoor images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 754−762 [25] Qu Y Y, Chen Y Z, Huang J Y, Xie Y. Enhanced Pix2pix dehazing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 8160−8168 [26] Dong H, Pan J S, Xiang L, Hu Z, Zhang X Y, Wang F, et al. Multi-scale boosted dehazing network with dense feature fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Virtual Event: IEEE, 2020. 2154−2164 [27] Dhara S K, Roy M, Sen D, Biswas P K. Color cast dependent image dehazing via adaptive airlight refinement and non-linear color balancing. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020: 1-5 [28] Qin X, Wang Z L, Bai Y C, Xie X D, Jia H Z. FFANet: Feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI Press, 2020. 11908−11915 -





 下载:
下载: