-
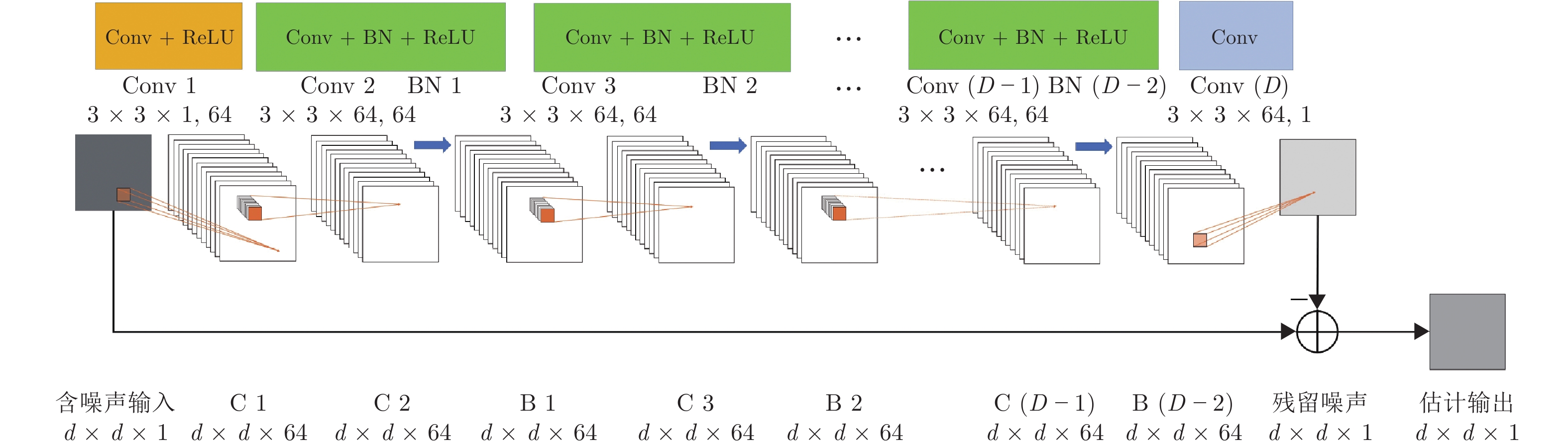
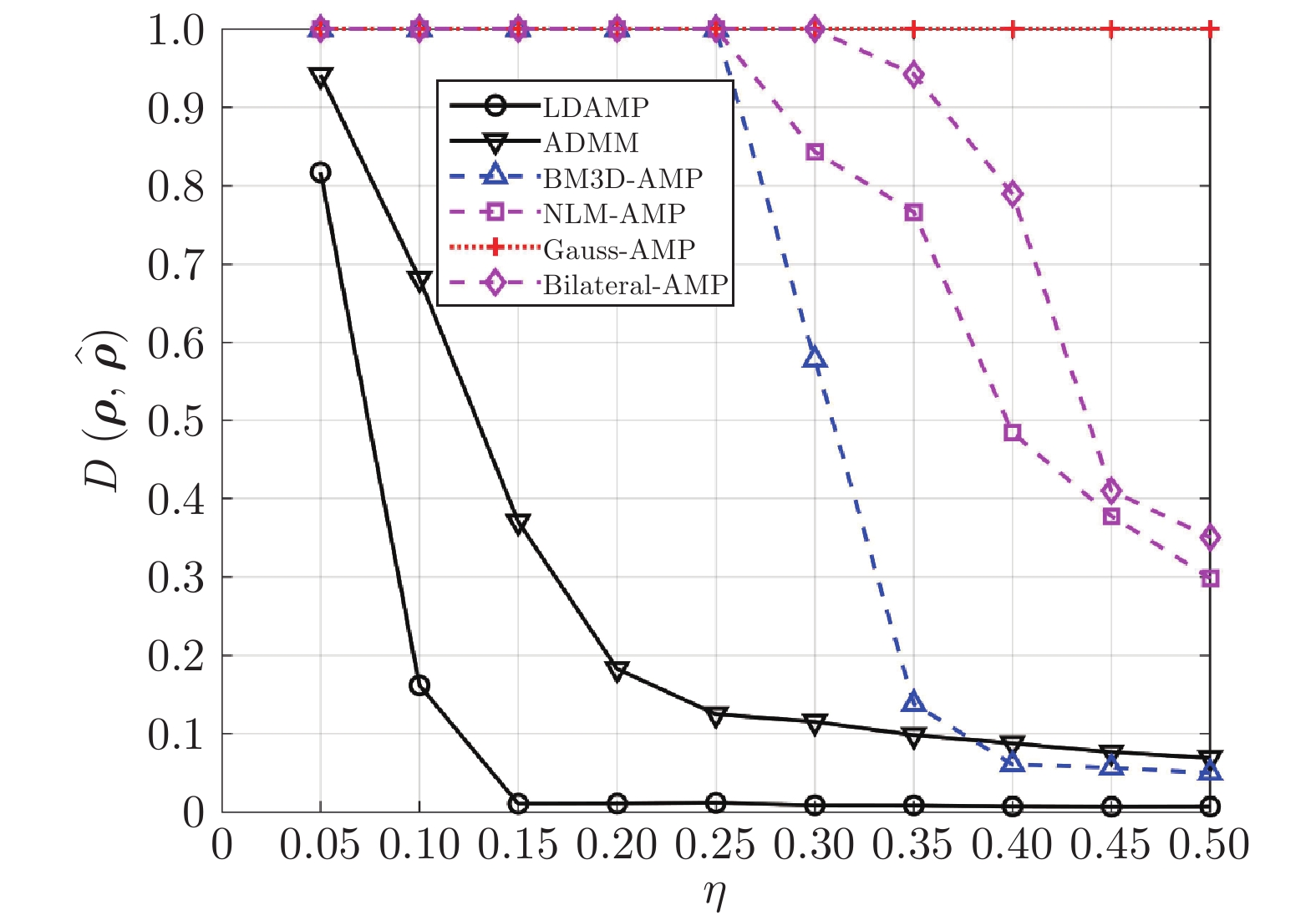
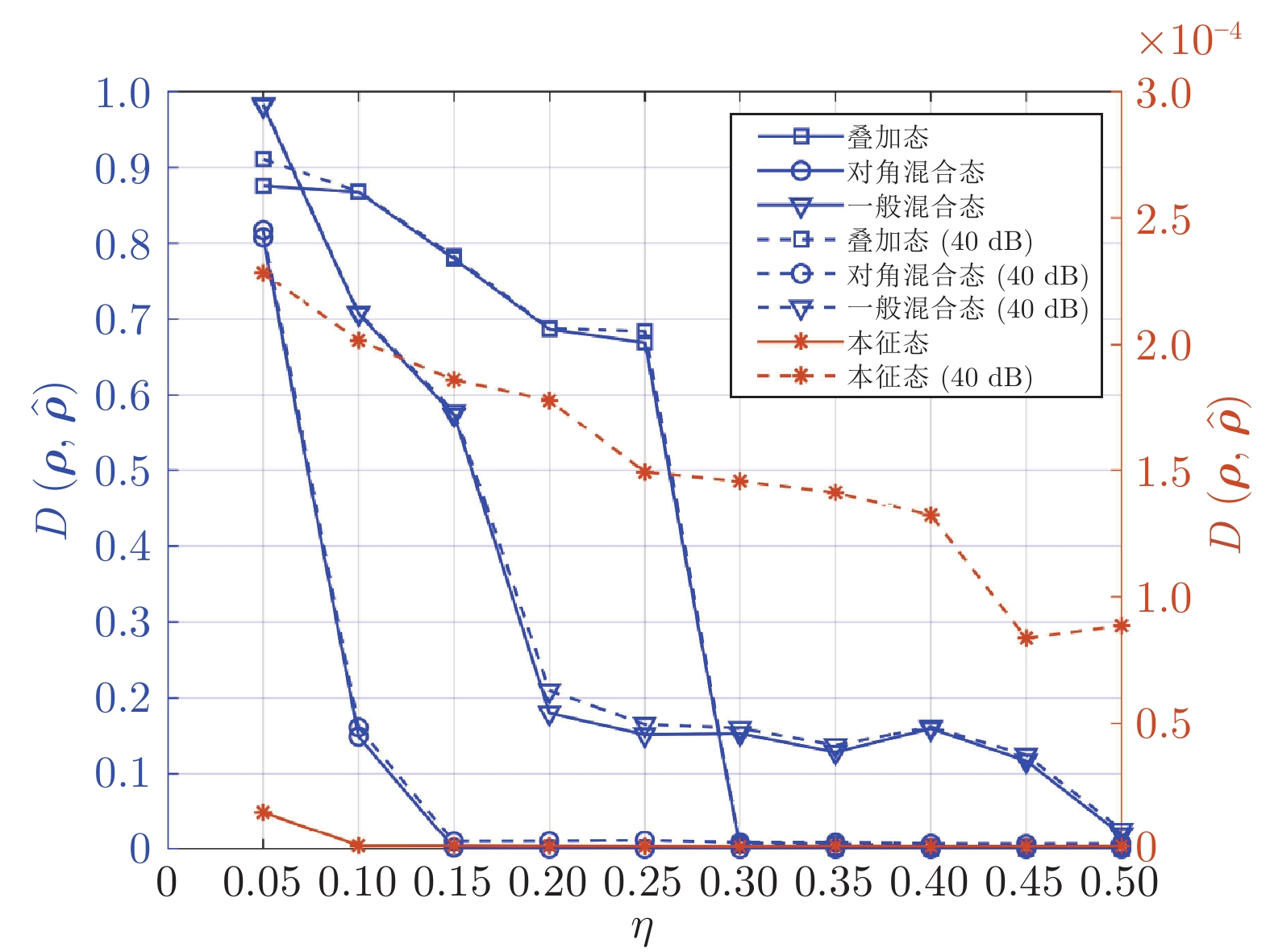
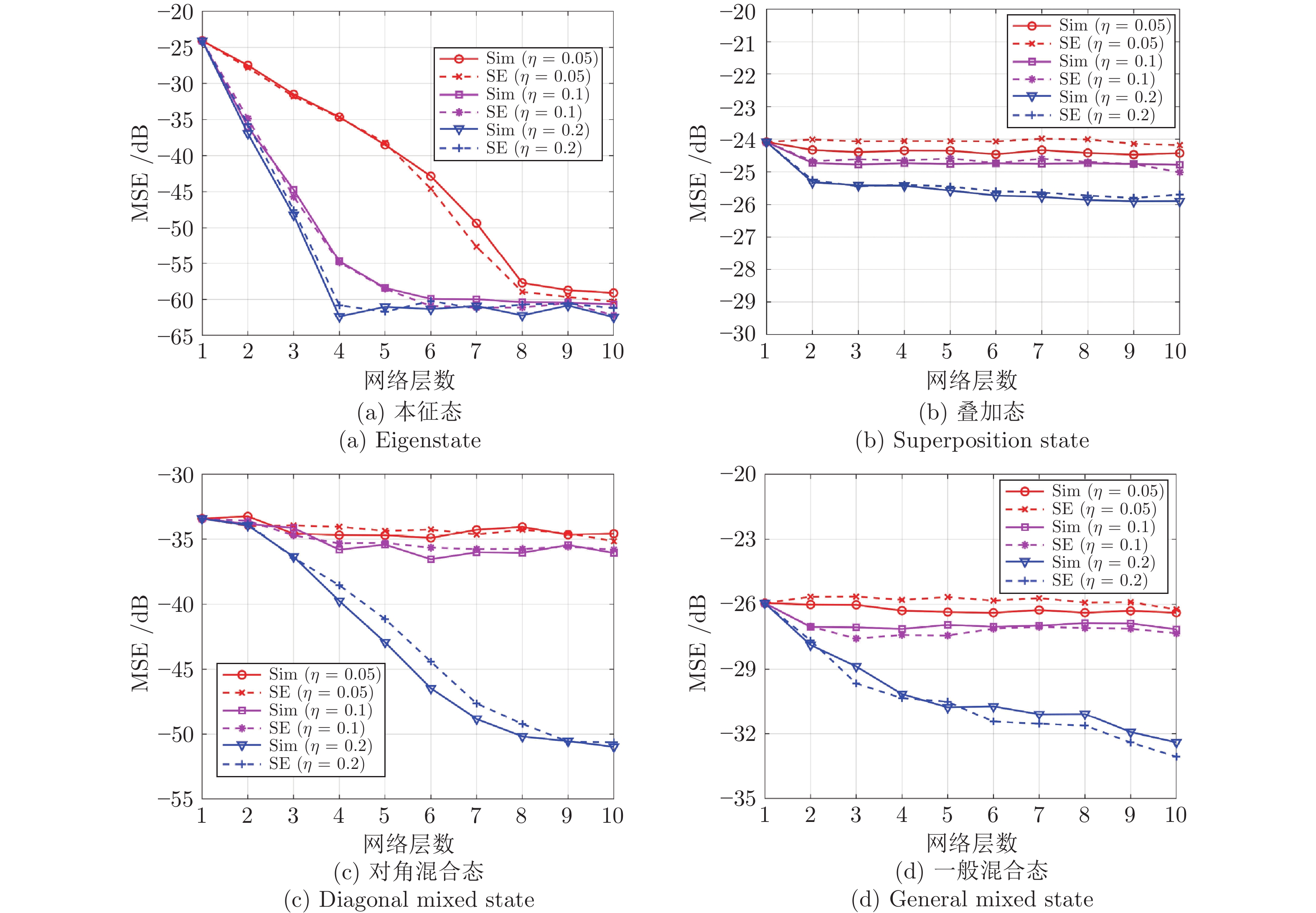
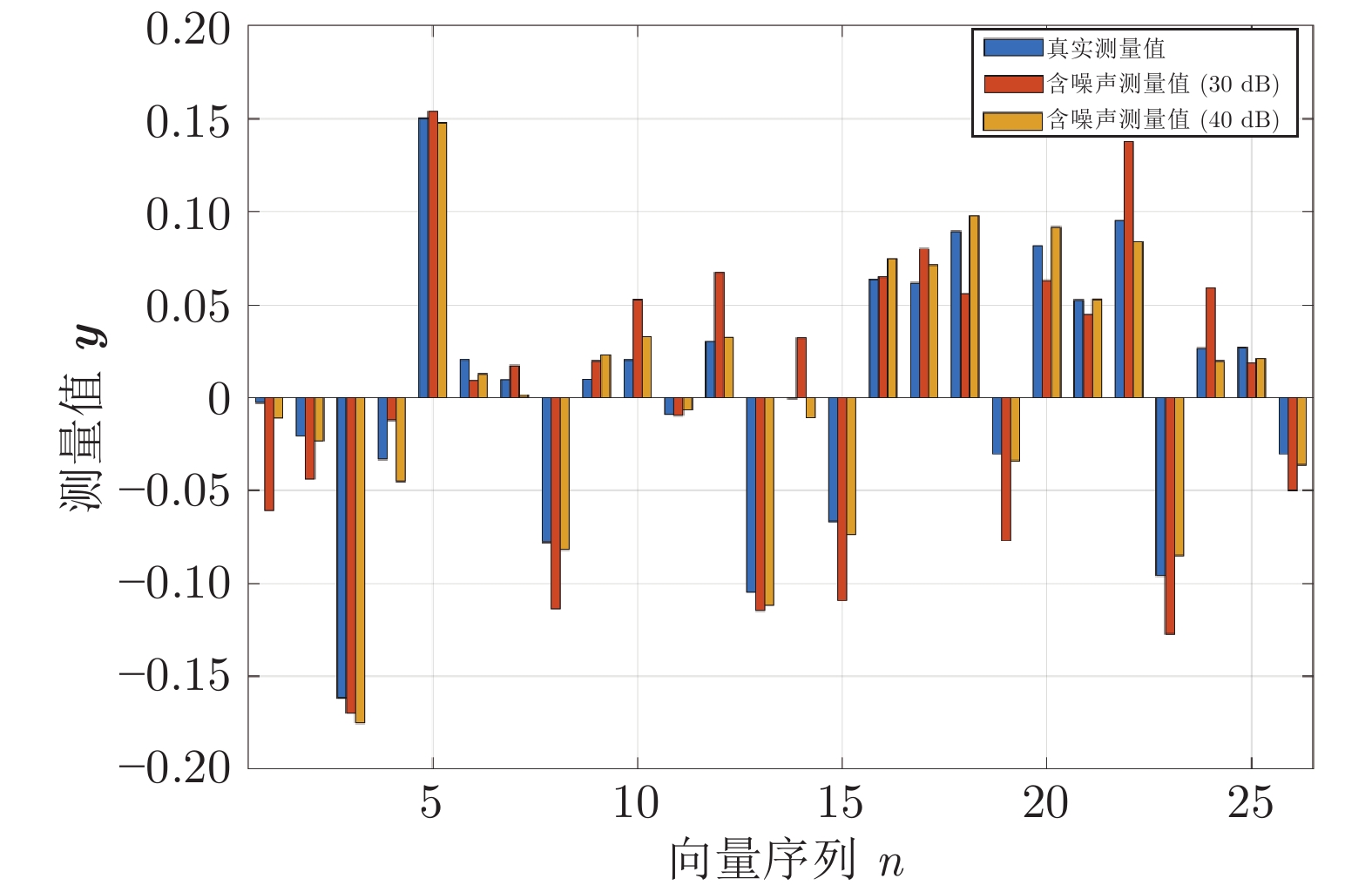
摘要: 设计出一种基于学习去噪的近似消息传递(Learned denoising-based approximate message passing, LDAMP)的深度学习网络, 将其应用于量子状态的估计. 该网络将去噪卷积神经网络与基于去噪的近似消息传递算法相结合, 利用量子系统输出的测量值作为网络输入, 通过设计出的带有去噪卷积神经网络的LDAMP网络重构出原始密度矩阵, 从大量的训练样本中提取各种不同类型密度矩阵的结构特征, 来实现对量子本征态、叠加态以及混合态的估计. 在对4个量子位的量子态估计的具体实例中, 分别在无和有测量噪声干扰情况下, 对基于LDAMP网络的量子态估计进行了仿真实验性能研究, 并与基于压缩感知的交替方向乘子法和三维块匹配近似消息传递等算法进行估计性能对比研究. 数值仿真实验结果表明, 所设计的LDAMP网络可以在较少的测量的采样率下, 同时完成对4种量子态的更高精度估计.Abstract: A learned denoising-based approximate message passing (LDAMP) deep learning network is proposed and trained in this paper, which is applied to the estimation of quantum states. This network combines denoising convolutional neural network with denoising-based approximate message passing algorithm. Using the measured output of the quantum system as the network input, the original density matrix was reconstructed by the designed LDAMP network with denoising convolutional neural network, and the structural features of various density matrices were extracted from a large number of training samples to realize the estimation of superposition and mixed states of quantum eigenstates. In the specific examples of quantum state estimation of four qubits, we study the performance of the quantum state estimation based on the LDAMP networks in the absence and presence of measurement interference, respectively, and compare the estimation performance with other algorithms which is based on compressed sensing such as alternating direction multiplier method and block matching 3D AMP. The numerical simulation results show that the LDAMP network can simultaneously estimate the four quantum states with higher accuracy in a small number of measurements.
-
表 1 当
$\eta = 0.1$ 时, LDAMP网络和其他方法的MSE (dB)性能比较Table 1 Comparison of MSE (dB) performance between LDAMP network and other methods with
$\eta = 0.1$ SNR 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 无干扰 LDAMP −25.7984 −29.0129 −32.8600 −33.6109 −36.0653 −36.5386 −38.0527 −38.9837 −40.0702 −41.0905 ADMM −14.6620 −23.0837 −30.2725 −33.0952 −34.5782 −35.3161 −35.4256 −35.5693 −35.9288 −36.1332 BM3D-AMP −24.8475 −25.1181 −25.3271 −25.7576 −26.2451 −26.4625 −26.7987 −26.7337 −26.9364 −27.3626 NLM-AMP −25.6457 −25.2723 −25.1595 −25.3828 −25.4296 −25.5618 −25.7596 −25.9587 −26.0826 −26.2108 Gauss-AMP −25.6424 −25.6433 −25.6620 −25.6991 −25.6728 −25.6729 −25.6786 −25.6985 −25.6940 −25.7053 Bilateral-AMP −25.1949 −25.1813 −25.1152 −25.1163 −25.1209 −25.1663 −25.2087 −25.2193 −25.2296 −25.2332 -
[1] Mackey G W. Mathematical Foundations Of Quantum Mechanics. Physics Today, 1958, 17(4): 68-68. [2] Cahill K E, Glauber R J. Density Operators and Quasiprob-ability Distributions. Physical Review, 1969, 177(5): 1882-1902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.177.1882 [3] Fano U. Description of States in Quantum Mechanics by Density Matrix and Operator Techniques. Rev. mod. phys, 1957, 29(1): 74-93. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.29.74 [4] D'Alessandro D. On Quantum State Observability and Measurement. Journal of Physics A General Physics, 2003, 36(37): 9721-9735. [5] Baraniuk R G. Compressive Sensing [Lecture Notes]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(4): 118-121. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.4286571 [6] Candès E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing. Comptes Rendus Mathematique, 2008, 346(9–10): 589-592. doi: 10.1016/j.crma.2008.03.014 [7] Flammia S T, Gross D, Liu Y K, Eisert J. Quantum tomography via compressed sensing: error bounds, sample complexity and efficient estimators. New Journal of Physics, 2012, 14(9): 95022-95049. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/14/9/095022 [8] Miosso C J, Von Borries R, Argaez M, Velazquez L, Quintero C, Potes C M. Compressive Sensing Reconstruction With Prior Information by Iteratively Reweighted Least-Squares. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(6): 2424-2431. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2016889 [9] 练秋生, 富利鹏, 陈书贞, 石保顺. 基于多尺度残差网络的压缩感知重构算法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2082-2091.Lian Qiu-Sheng, Fu Li-Peng, Chen Shu-Zhen, Shi Bao-Shun. A compressed sensing algorithm based on multi-scale residual reconstruction network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45 (11): 2082-2091. [10] Smith A, Riofrío C A, Anderson B E, Sosa-Martinez H, Deutsch I H, Jessen P S. Quantum state tomography by continuous measurement and compressed sensing. Physical Review A, 2012, 87(3): 184-191. [11] Li K Z, Cong S. A Robust Compressive Quantum State Tomography Algorithm Using ADMM. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2014, 47(3): 6878-6883. doi: 10.3182/20140824-6-ZA-1003.01815 [12] Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, Peleato B, Eckstein J. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Boston: Now publishers Incorporat-ed, 2011. [13] Smolin J A, Gambetta J M, Smith G. Efficient Method for Computing the Maximum-Likelihood Quantum State from Measurements with Additive Gaussian Noise. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(7): 070502. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.070502 [14] Mézard M, Montanari A. Information, Physics, Computation: Probabilistic approaches. Cambridge: Cambridge University Pre-ss, 2008. [15] Donoho D L, Maleki A, Montanari A. Message-passing algorithms for compressed sensing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(45): 18914-18919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909892106 [16] Liu X M, Lu S C, Wu R B. Machine learning for data Reduction in quantum state tomography. In: Proceedings of the 37th Chinese Control Conference. Wuhan, China: 2018. 227−231 [17] Metzler C A, Mousavi A, Baraniuk R. Learned DAMP: A principled CNN-based compressive image recovery algorithm. arXiv preprint, 2017, arXiv: 1704.06625 [18] Zhang K, Zuo W M, Chen Y J, Meng D Y, Zhang L. Beyond a Gaussian Denoiser: Residual Learning of Deep CNN for Image Denoising. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 26(7): 3142-3155. [19] Metzler C A, Maleki A, Baraniuk R G. From Denoising to Compressed Sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2016, 62(9): 5117-5144. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2556683 [20] Borgerding M, Schniter P, Rangan S. AMP-Inspired Deep Networks for Sparse Linear Inverse Problems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65: 4293-4308. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2708040 [21] 郑凯, 杨靖北, 丛爽. 基于泡利测量的量子本征态估计最优测量配置集的构造方法. 第18届中国系统仿真技术及其应用学术年会. 兰州, 中国: 2017. 216−219Zheng Kai, Yang Jing-Bei, Cong Shuang. A construction method of optimal measurement configuration set for quantum eigenstate estimation based on pauli measurement. In: Proceedings of the 18th China Conference on System Simulation Technology and Its Applications. Lanzhou, China: 2017. 216−219 [22] Zheng K, Li K Z, Cong S. A reconstruction algorithm for compressive quantum tomography using various measurement sets. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 38497. doi: 10.1038/srep38497 [23] Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage selection via the LASSO. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Statistical Methodology), 2011, 73(3): 273-282. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2011.00771.x [24] Chen S S, Saunders D. Atomic Decomposition by Basis Pursuit. Siam Review, 2001, 43(1): 129-159. doi: 10.1137/S003614450037906X [25] Borgerding M, Schniter P. Onsager-corrected deep learning for sparse linear inverse problems. In: Proceedings of IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing. Washington DC, USA: IEEE, 2016. 227−231 [26] Ramani S, Blu T, Unser M. Monte-Carlo Sure: A Black-Box Optimization of Regularization Parameters for General Denoising Algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(9): 1540-1554. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.2001404 [27] He H T, Wen C K, Jin S, Li G Y. Deep Learning-Based Channel Estimation for Beamspace mmWave Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(5): 852-855. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2832128 [28] Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K. Image Denoising by Sparse 3-D Transform-Domain Collaborative Filtering. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080-2095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238 [29] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: 2012. 1097−1105 [30] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv prepr-int, 2015, arXiv: 1502.03167 [31] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778. [32] 盖杉, 鲍中运. 基于深度学习的高噪声图像去噪算法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(12): 2672-2680.Gai Shan, Bao Zhong-Yun. High noise image denoising algorithm based on deep learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(12): 2672-2680. [33] 周登文, 赵丽娟, 段然, 柴晓亮. 基于递归残差网络的图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1157-1165.Zhou Deng-Wen, Zhao Li-Juan, Duan Ran, Cai Xiao-Liang. Image Super-resolution Based on Recursive Residual Networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1157-1165. [34] Schmidt U, Roth S. Shrinkage fields for effective image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: 2014. 2774−2781 [35] Zyczkowski K, Penson K A, Nechita I, Collins B. Generating random density matrices. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 2010, 52(6): 062201. [36] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: 2015. 1026−1034 [37] Vedaldi A, Lenc K. MatConvNet: Convolutional neural netwo-rks for Matlab. arXiv preprint, 2014, arXiv: 1412.4564 [38] Michael A N, Isaac L C, Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002. [39] Flammia S T, Liu Y K. Direct Fidelity Estimation from Few Pauli Measurements. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106(23): 230501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.230501 [40] 唐雅茹, 丛爽, 杨靖北. 单量子比特系统状态的在线估计, 自动化学报, 2020, 46(8): 1592-1599.Tang Ya-Ru, Cong Shuang, Yang Jing-Bei. On-line state estimation of one-qubit system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1592−1599. -





 下载:
下载: