Riemannian Metric Based Performance Monitoring and Diagnosis for a Class of Feedback Control Systems
-
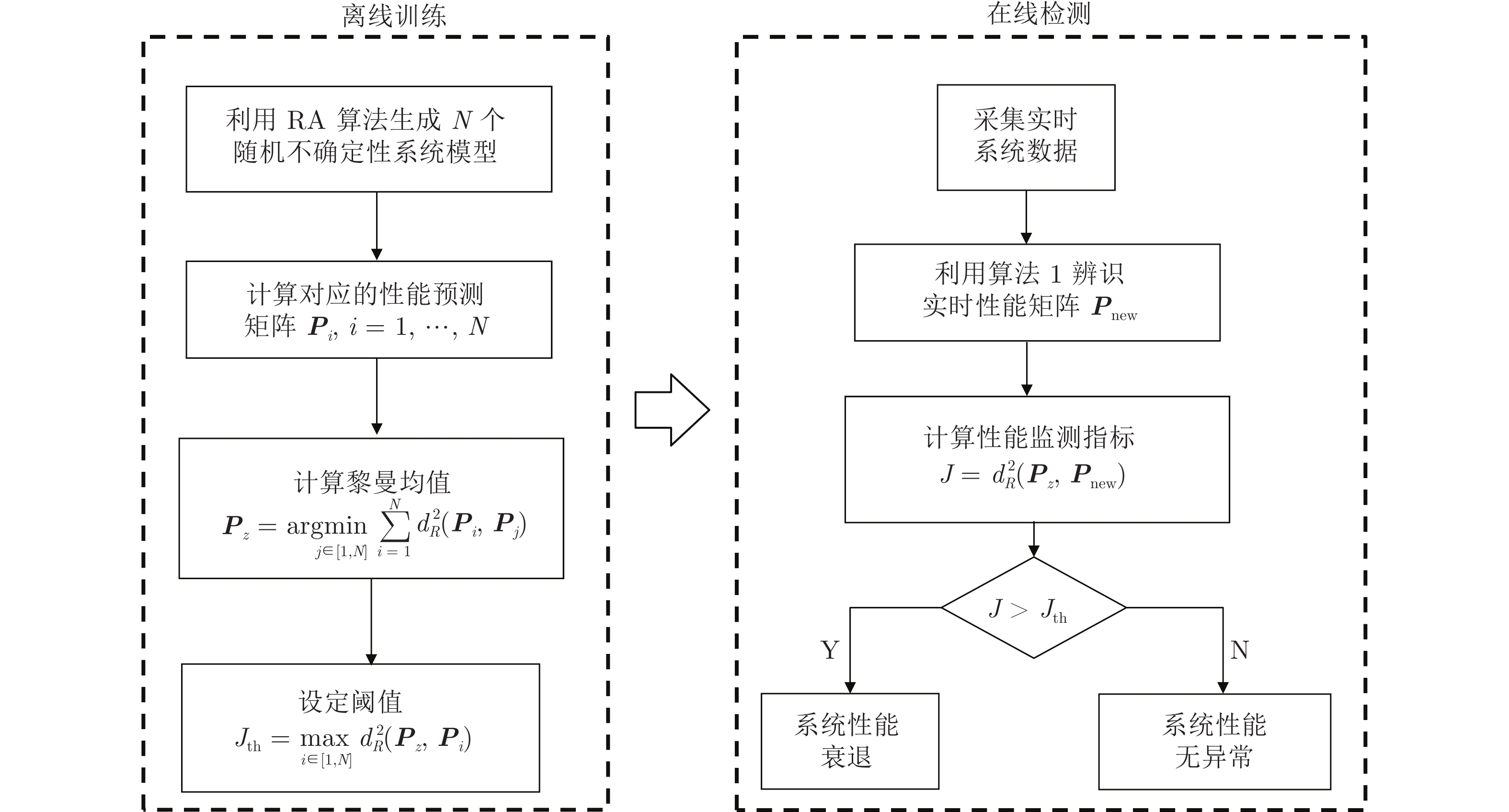
摘要: 针对复杂工业系统对性能衰退的容忍度低等问题, 提出基于系统性能预测的一类反馈控制系统过程监测方法, 通过黎曼度量对控制性能衰退程度进行预测与监测, 并给出发生故障的类型, 以提升过程监测系统的实时性与准确性. 首先, 利用系统的实时数据, 计算系统性能衰退的预测指标; 其次, 利用黎曼度量对系统性能衰退程度进行预测与监测, 并利用随机算法给出对应的阈值来诊断系统性能衰退; 最后, 通过计算各类引发系统性能衰退的故障的性能预测指标集合的中心和阈值, 实现故障的实时定位. 所提出的方法通过三容水箱仿真实验平台进行验证.Abstract: Associated with the issue that the industrial processes have low tolerance in performance degradation, a performance monitoring and diagnosis scheme for a class of feedback control systems is developed based on system performance prediction. The Riemannian metric is then adopted to predict and monitor the degree of the control performance degradation, and classify the fault type, so as to improve the real-time ability and accuracy of the performance monitoring systems. Firstly, a prediction indicator is introduced to predict the system performance degradation using online process data. Then, the Riemannian metric is implemented to predict and monitor the degree of the control performance degradation, and the randomized algorithm is adopted to set the threshold for diagnosing the performance degradation. Finally, by computing the center and threshold for the performance predictor set caused by all the possible faults, the fault localization can be achieved. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by a case study on a three-tank system.
-
Key words:
- Performance monitoring /
- Riemannian metric /
- performance diagnosis /
- fault location
-
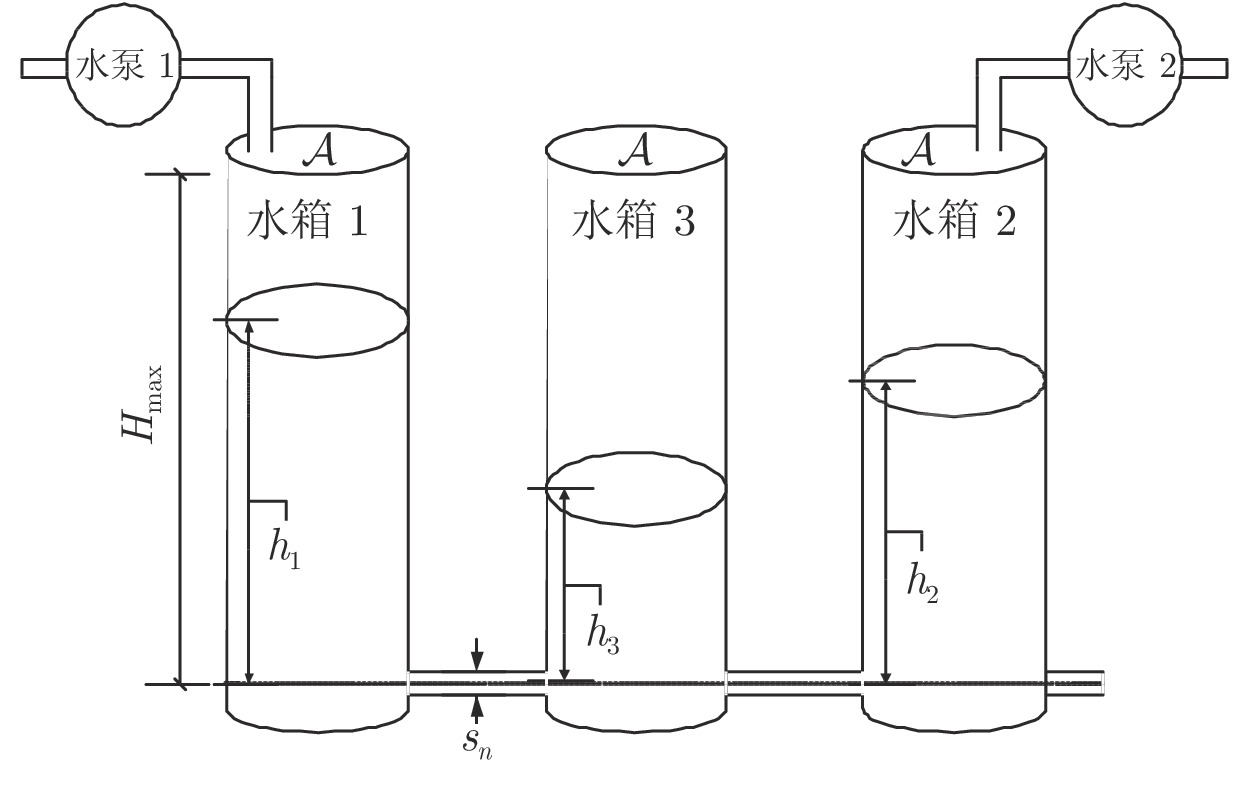
表 1 水箱DTS200的参数
Table 1 Parameters of tank DTS200
参数 符号 值 单位 水箱面积 $ {\cal{A}} $ 154 $ \mathrm{cm}^{2} $ 水箱间管道面积 $s_{{n} }$ 0.5 $ \mathrm{cm}^{2} $ 水箱最高水位 $ H_{\mathrm{max}} $ 62 $ \mathrm{cm} $ 泵 1 的最大进水量 $ Q_{1_{\mathrm{max}}} $ 120 $ \mathrm{cm}^{3}/\mathrm{s} $ 泵 2 的最大进水量 $ Q_{2_{\mathrm{max}}} $ 120 $ \mathrm{cm}^{3}/\mathrm{s} $ 管道 1 水流系数 $ a_{1} $ 0.45 管道 2 水流系数 $ a_{2} $ 0.60 管道 3 水流系数 $ a_{3} $ 0.45 表 2 水箱堵塞故障隔离
Table 2 Isolation of pipe plugging
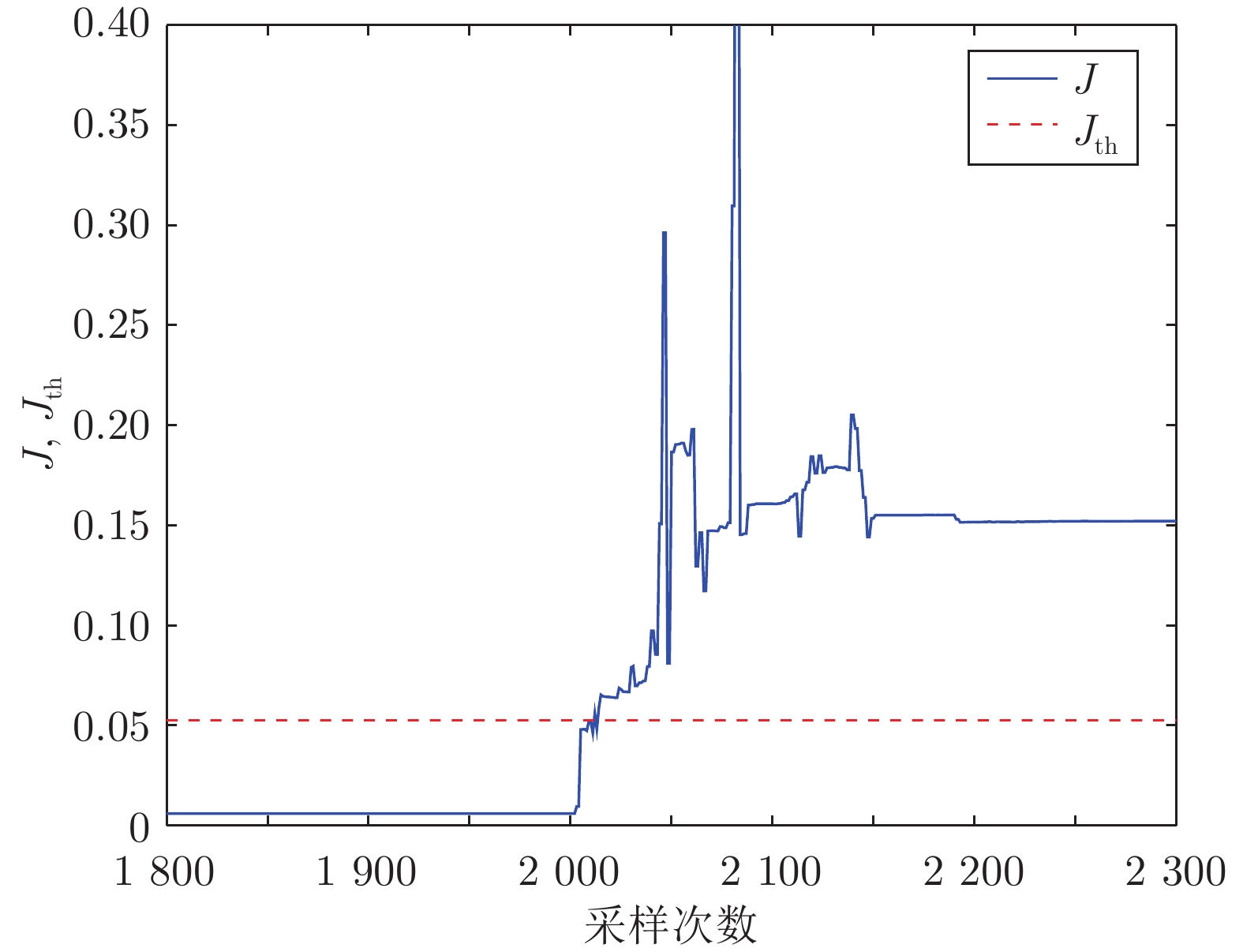
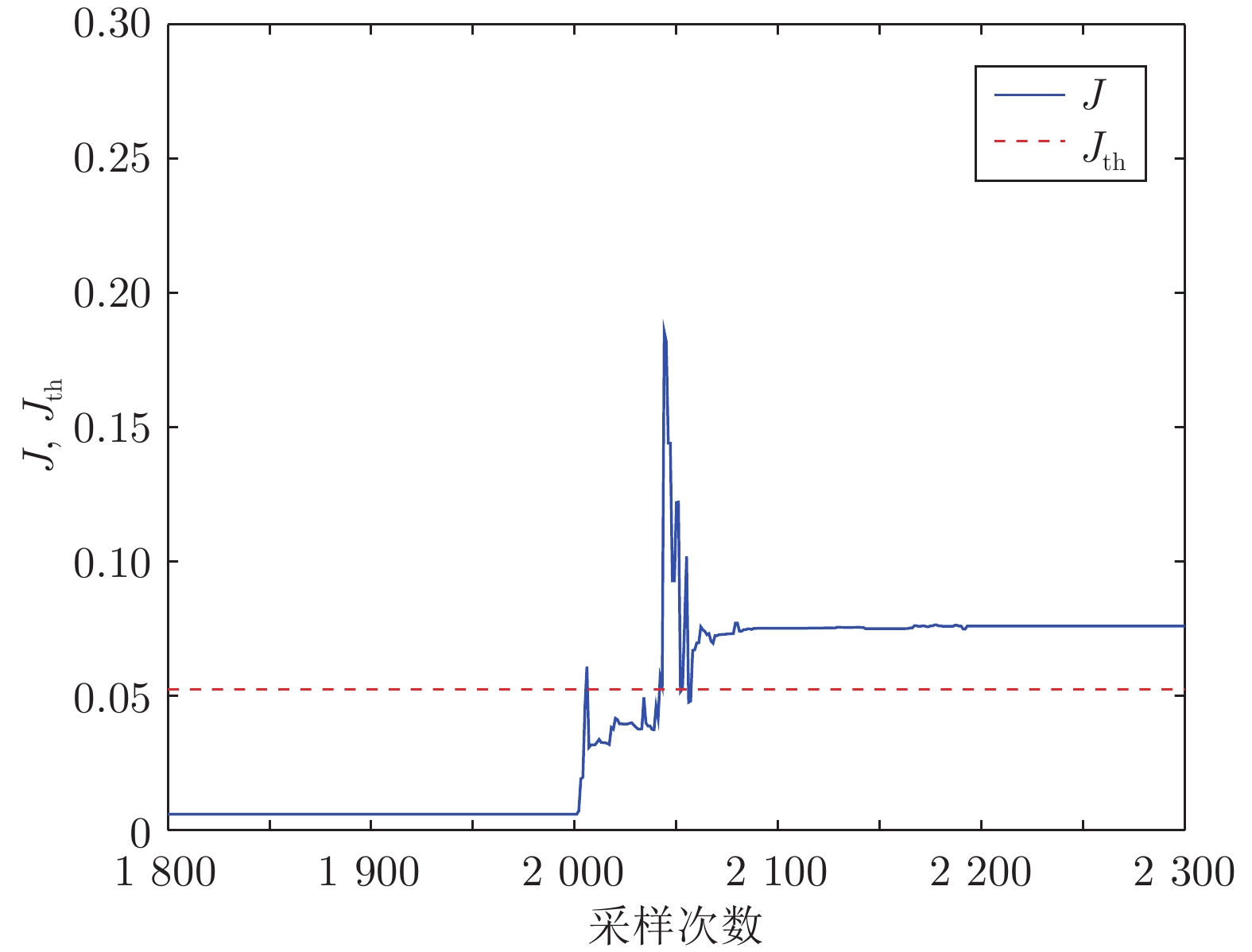
故障 $ d_R^2({\boldsymbol P},{\boldsymbol P}_{z,1}) $ $ d_R^2({\boldsymbol P},{\boldsymbol P}_{z,2}) $ $ d_R^2({\boldsymbol P},{\boldsymbol P}_{z,3}) $ 故障隔离 $a_1 = 0.30$ $ 0.0388 $ $ 0.1088 $ $ 0.1193 $ 故障簇 1 $ a_2 = 0.35 $ $ 0.0894 $ $ 0.0270 $ $ 0.0810 $ 故障簇 2 $ a_3 = 0.28 $ $ 0.1258 $ $ 0.1099 $ $ 0.0478 $ 故障簇 3 $ a_1 = 0.27 $ $ 0.0636 $ $ 0.1325 $ $ 0.1409 $ 故障簇 1 $a_2 = 0.40$ $ 0.0809 $ $ 0.0139 $ $ 0.0732 $ 故障簇 2 -
[1] 何潇, 郭亚琦, 张召, 贾繁林, 周东华. 动态系统的主动故障诊断技术. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(8): 1557-1570He Xiao, Guo Ya-Qi, Zhang Zhao, Jia Fan-Lin, Zhou Dong-Hua. Active fault diagnosis for dynamic systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1557-1570 [2] Ding S X. Data-driven Design of Fault Diagnosis and Fault-tolerant Control Systems. Berlin: Springer, 2014. [3] 彭开香, 马亮, 张凯. 复杂工业过程质量相关的故障检测与诊断技术综述. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 349-365Peng Kai-Xiang, Ma Liang, Zhang Kai. Review of quality-related fault detection and diagnosis techniques for complex industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 349-365 [4] 钱峰, 杜文莉, 钟伟民, 唐漾. 石油和化工行业智能优化制造若干问题及挑战. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(6): 893-901Qian Feng, Du Wen-Li, Zhong Wei-Min, Tang Yang. Problems and challenges of smart optimization manufacturing in petrochemical industries. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(6): 893-901 [5] Li L L, Ding S X. Gap metric techniques and their application to fault detection performance analysis and fault isolation schemes. Automatica, 2020, 118: Article No. 109029 [6] 陈晓露, 王瑞璇, 王晶, 周靖林. 基于混合型判别分析的工业过程监控及故障诊断. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(8): 1600-1614Chen Xiao-Lu, Wang Rui-Xuan, Wang Jing, Zhou Jing-Lin. Industrial process monitoring and fault diagnosis based on hybrid discriminant analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1600-1614 [7] Huang B, Kadali R. Dynamic modeling, predictive control and performance monitoring: A data-driven subspace approach. Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences. London: Springer, 2008. [8] Jelali M. An overview of control perormance assessment technology and industrial applications. Control Engineering Practice, 2006, 14: 441-466 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2005.11.005 [9] Schafer J, Cinar A. Multivariable MPC system performance assessment, monitoring, and diagnosis. Journal of Process Control, 2004, 14(2): 113-129 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2003.07.003 [10] Verenich I, Dumas M, Rosa M L, Nguyen H. Predicting process performance: A white-box approach based on process models. Journal of Software: Evolution and Process, 2019, 31(6): Article No. e2170 [11] Ding S X, Yin S, Peng K, Hao H. A novel scheme for key performance indicator prediction and diagnosis with application to an industrial hot strip mill. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(4): 2239-2247 doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2214394 [12] Xie X, Sun W, Cheung K. An advanced PLS approach for key performance indicator related prediction and diagnosis in case of outliers. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(4): 2587-2594 [13] Duan Y, Liu M, Dong M. A metric-learning-based nonlinear modeling algorithm and its application in key-performance-indicator prediction. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(8): 7073-7082 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2935979 [14] Li L, Luo H, Ding S X, Yang Y, Peng K. Performance-based fault detection and fault-tolerant control for automatic control systems. Automatica, 2019, 99: 309-316 [15] Tao X, Lu C, Lu C, Wang Z. An approach to performance assessment and fault diagnosis for rotating machinery equipment. Eurasip Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013, 2013(1): 1-16 doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2013-1 [16] Li L, Ding S X. Performance supervised fault detection schemes for industrial feedback control systems and their data-driven implementation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(4): 2849-2858 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2940099 [17] Seem J E. Method and System for Assessing Performance of Control Systems, U.S. US7729882 B2, 2009. [18] Yin S, Zhu X, Kaynak O. Improved PLS focused on key-performance-indicator-related fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(3): 1651-1658 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2345331 [19] He S, Wang Y, Liu C. Modified partial least square for diagnosing key-performance-indicator-related faults. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 96(2): 444-454 doi: 10.1002/cjce.23002 [20] Song B, Zhou X, Shi H, Tao Y. Performance-indicator-oriented concurrent subspace process monitoring method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(7): 5535-5545 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2868316 [21] Li H, Zhao J, Zhang X, Teng H. Gear fault diagnosis and damage level identification based on Hilbert transform and Euclidean distance technique. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2014, 16(8): 4137-4151 [22] Tian Y, Lu C, Wang Z. Self-adaptive bearing fault diagnosis based on permutation entropy and manifold-based dynamic time warping. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2019, 114: 658-673 [23] Patel S, Upadhyay S H. Euclidean distance based feature ranking and subset selection for bearing fault diagnosis. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113400 [24] Liang H. Fault analysis of hierarchical cluster and fault diagnosis of Mahalanobis distance in analog circuit. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument, 2010, 24(7): 610-615 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1187.2010.00610 [25] 艾延廷, 冯研研, 周海仑.小波变换和EEMD-马氏距离的轴承故障诊断.噪声与振动控制, 2015, 1: 235-239 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2015.01.050Ai Yan-Ting, Feng Yan-Yan, Zhou Hai-Lun. Fault diagnosis of roller bearings using wavelet transform and EEMD-Mahalanobis distance. Noise and Vibration Control, 2015, 1: 235-239\\ doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2015.01.050 [26] Ji H. Statistics Mahalanobis distance for incipient sensor fault detection and diagnosis. Chemical Engineering Sience, 2021, DOI: 10.1016/j.ces.2020.116233 [27] 吕鹏飞, 闫云聚, 荔越. 基于马氏距离的改进核Fisher化工故障诊断研究. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(11): 2379-2392Lv Peng-Fei, Yan Yun-Ju, Li Yue. Research on fault diagnosis of improved kernel Fisher based on Mahalanobis distance in the field of chemical industry. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(11): 2379-2391 [28] Amari S. Information Geometry and Its Applications. Berlin: Springer, 2016. [29] Boothby W M. An Introduction to Differentiable Manifolds and Riemannian Geometry. Pittsburgh: Academic Press, 1975. [30] An J, Ai P. Deep domain adaptation model for bearing fault diagnosis with Riemann metric correlation alignment. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 1: 1-12 [31] 周美含, 姜宏, 孙帅. 基于黎曼流形的MIMO雷达目标检测方法. 吉林大学学报: 信息科学版, 2020, 3: 237-242Zhou Mei-Han, Jiang Shuai, Suan Shuai. Target detection method for MIMO radar based on Riemannian manifold. Journal of Jilin University(Information Science Edition), 2020, 3: 237-242 [32] Wang S, Sun X, Li C. Wind turbine gearbox fault diagnosis method based on Riemannian manifold. Mathematical Problems in Engineering: Theory, Methods and Applications, 2014, 8: 1-10 [33] Wang Z, Jia L, Qin Y. Adaptive diagnosis for rotating machineries using information geometrical Kernel-ELM based on VMD-SVD. Entropy, 2018, 20(1): 73-91 doi: 10.3390/e20010073 [34] 孙小婷. 主测地线分析技术在汽轮机系统中的应用. 自动化应用, 2020, 1: 22-25Sun Xiao-Ting. Application of main geodesic analysis technology in steam turbine system. Automation Application, 2020, 1: 22-25 [35] Hiriart-Urruty J B, Malick J. A fresh variational-analysis look at the positive semidefinite matrices world. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2012, 153(3): 551-577 doi: 10.1007/s10957-011-9980-6 [36] Moakher M. A differential geometric approach to the geometric mean of symmetric positive-definite matrices. Siam Journal on Matrix Analysis & Applications, 2005, 26: 735-747 [37] Moakher M, Bathelor P G. Symmetric Positive-definite Matrices: From Geometry to Applications and Visualization. Berlin: Springer, 2006. [38] Ding S X. Advanced Methods for Fault Diagnosis and Fault-tolerant Control. Berlin: Springer, 2021. [39] Magnus J R. Linear Structures. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998. [40] Tempo R, Calcfiro G, Dabbene F. Randomized Algorithms for Analysis and Control of Uncertain Systems. Berlin: Springer, 2005. [41] Cryan M. Probability and computing: Randomized algorithms and probabilistic analysis. Bulletin of Symbolic Logic, 2006, 12(2): 304-308 doi: 10.1017/S107989860000278X [42] Ding S X, Li L, Krüger M. Application of randomized algorithms to assessment and design of observer-based fault detection systems. Automatica, 2019, 107: 175-182 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.05.037 [43] Lewis F L, Vrabie D, Vamvoudakis K G. Reinforcement learning and feedback control using natural decision methods to design optimal adaptive controllers. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2012, 32(6): 76-105 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2012.2214134 [44] 杨浩, 姜斌, 周东华. 互联系统容错控制的研究回顾与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(1): 9-19Yang Hao, Jiang Bin, Zhou Dong-Hua. Review and perspectives on fault tolerant control for interconnected systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1): 9-19 -




 下载:
下载: