The Integrated Method of Scheduling and Control for Manufacturing Systems Based on Parallel Petri Nets
-
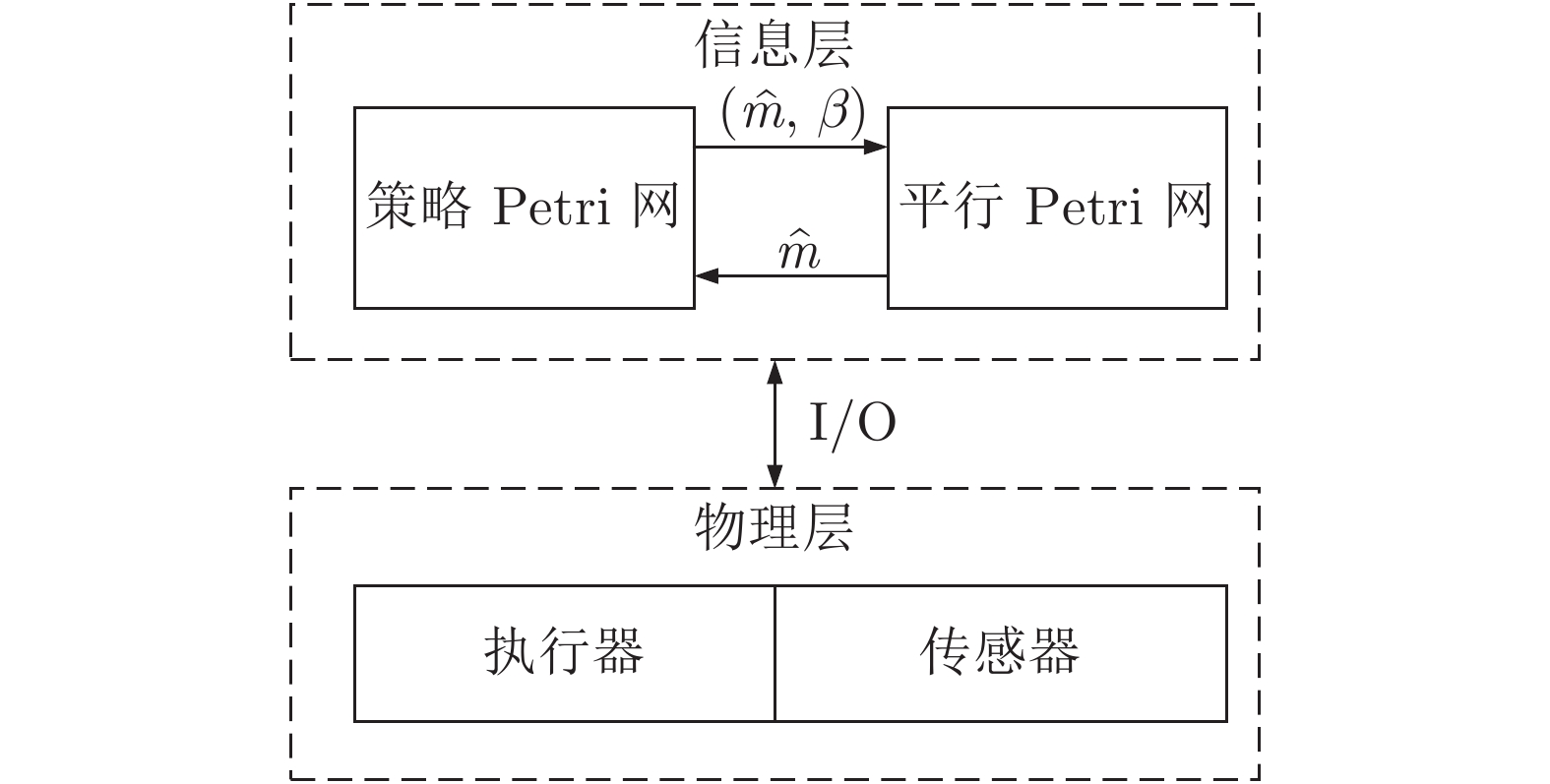
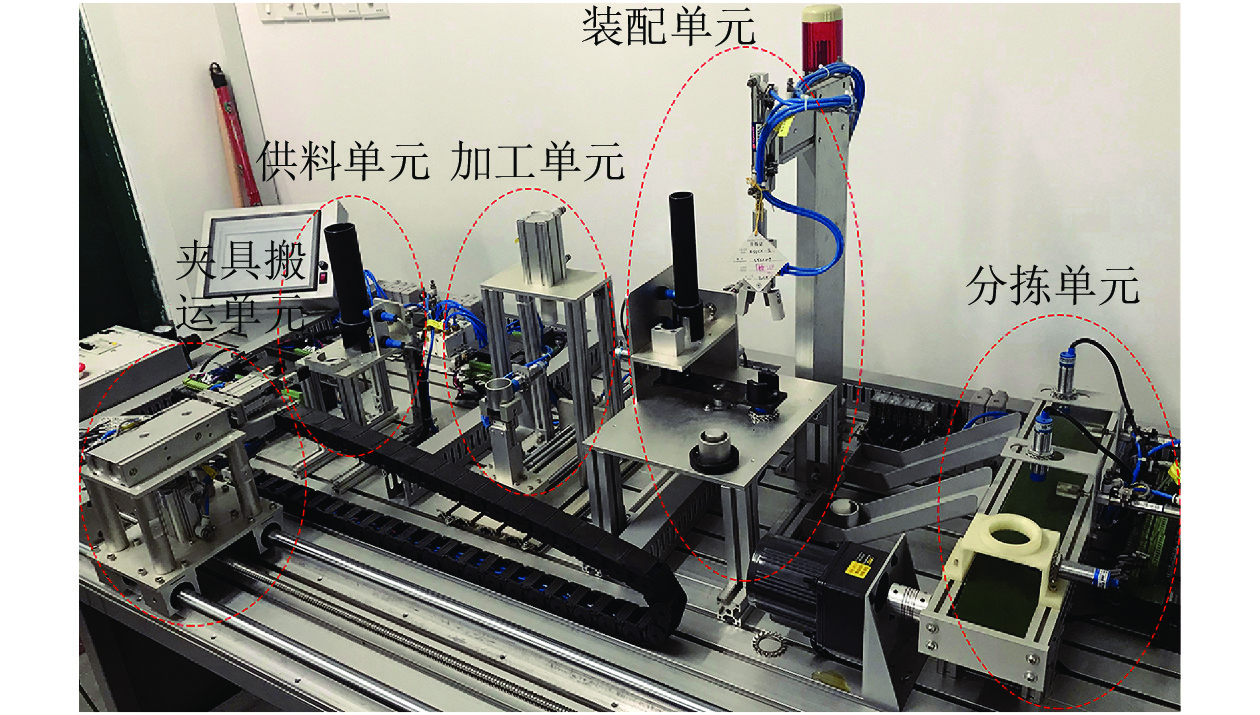
摘要: 为了消除制造系统调度层与控制层之间的隔阂, 实现对生产事件快速灵活响应, 本文提出了一种调度与控制一体化的方法. 首先, 定义了一种新型Petri网模型, 即平行Petri网, 从而集成地描述了传感器、执行器、任务和资源信息, 构建制造系统的信息物理系统模型; 其次, 提出了一种从平行Petri网到赋时Petri网的抽象简化方法, 大规模压缩优化调度所需搜索的状态空间; 再次, 定义了策略Petri网以描述最优调度策略. 最后, 给出了平行Petri网与策略Petri网同步执行算法, 使得平行Petri网与物理系统同步执行.Abstract: In order to eliminate the gap between the scheduling layer and the control layer and achieve fast and flexible response to production events of manufacturing systems, an integrated method of scheduling and control is proposed in this paper. First, a novel Petri-net model that is called a parallel Petri net is defined, which integrates sensors, actuators, tasks and resources to establish the cyber-physical system model of a manufacturing system. Secondly, a method of transforming parallel Petri nets to timed Petri nets is proposed to much compress the state space required to be searched for optimal scheduling. Thirdly, a strategy Petri net is defined to describe an optimal scheduling strategy. Finally, the algorithm for synchronizing executions of a parallel Petri net and a strategy Petri net is given, which realizes the synchronous execution of parallel Petri nets and physical systems.
-
Key words:
- Scheduling /
- control /
- parallel Petri nets /
- timed Petri nets
-
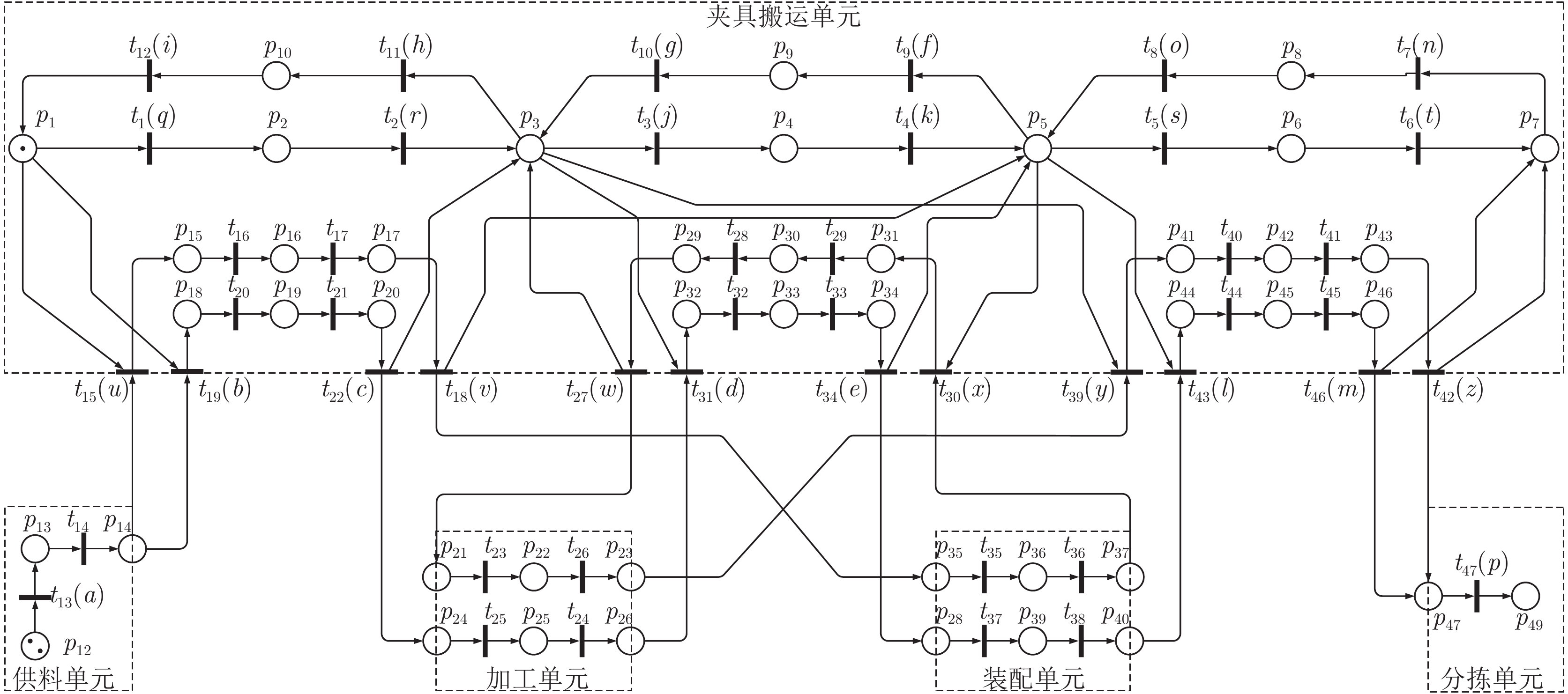
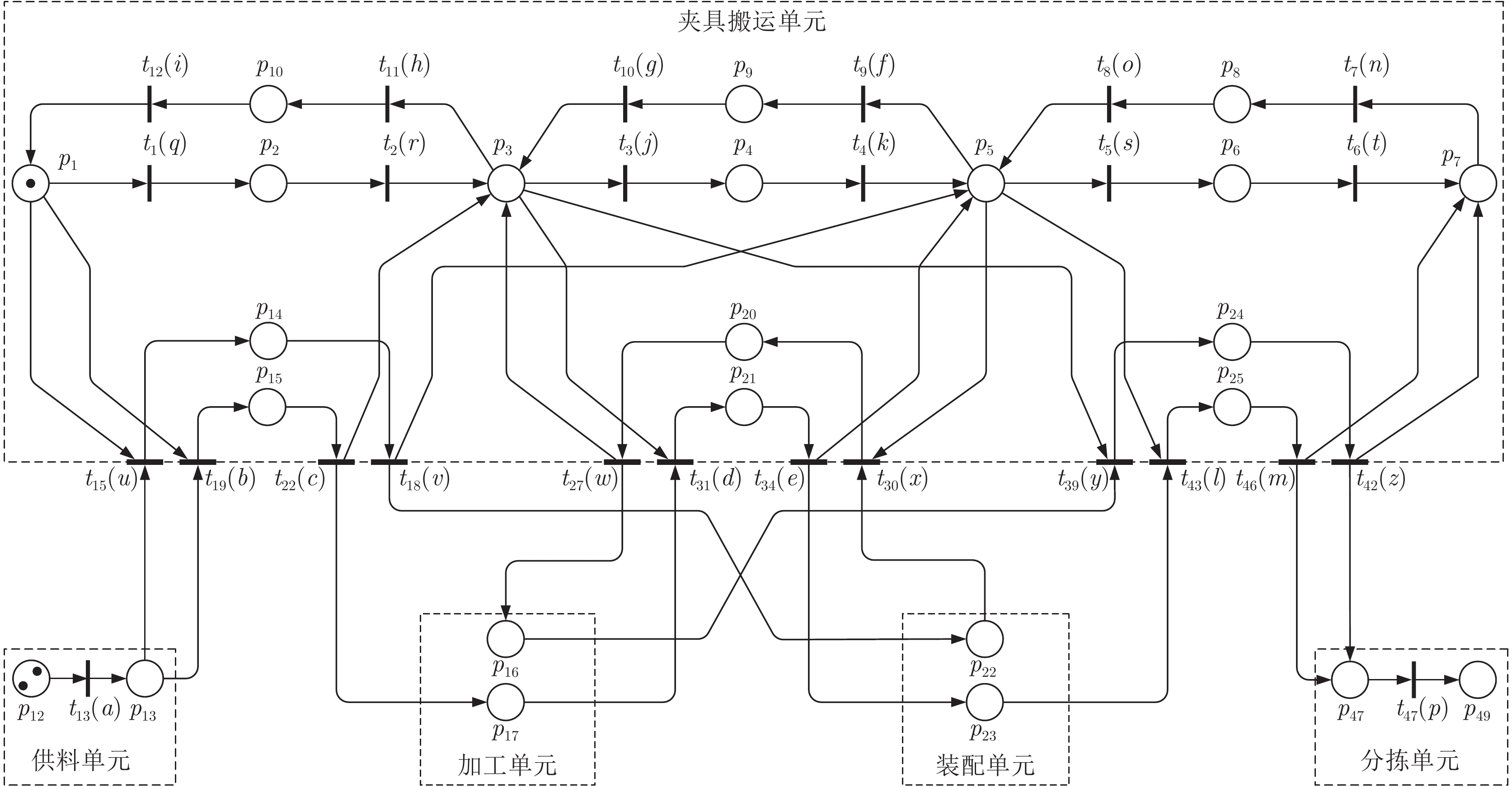
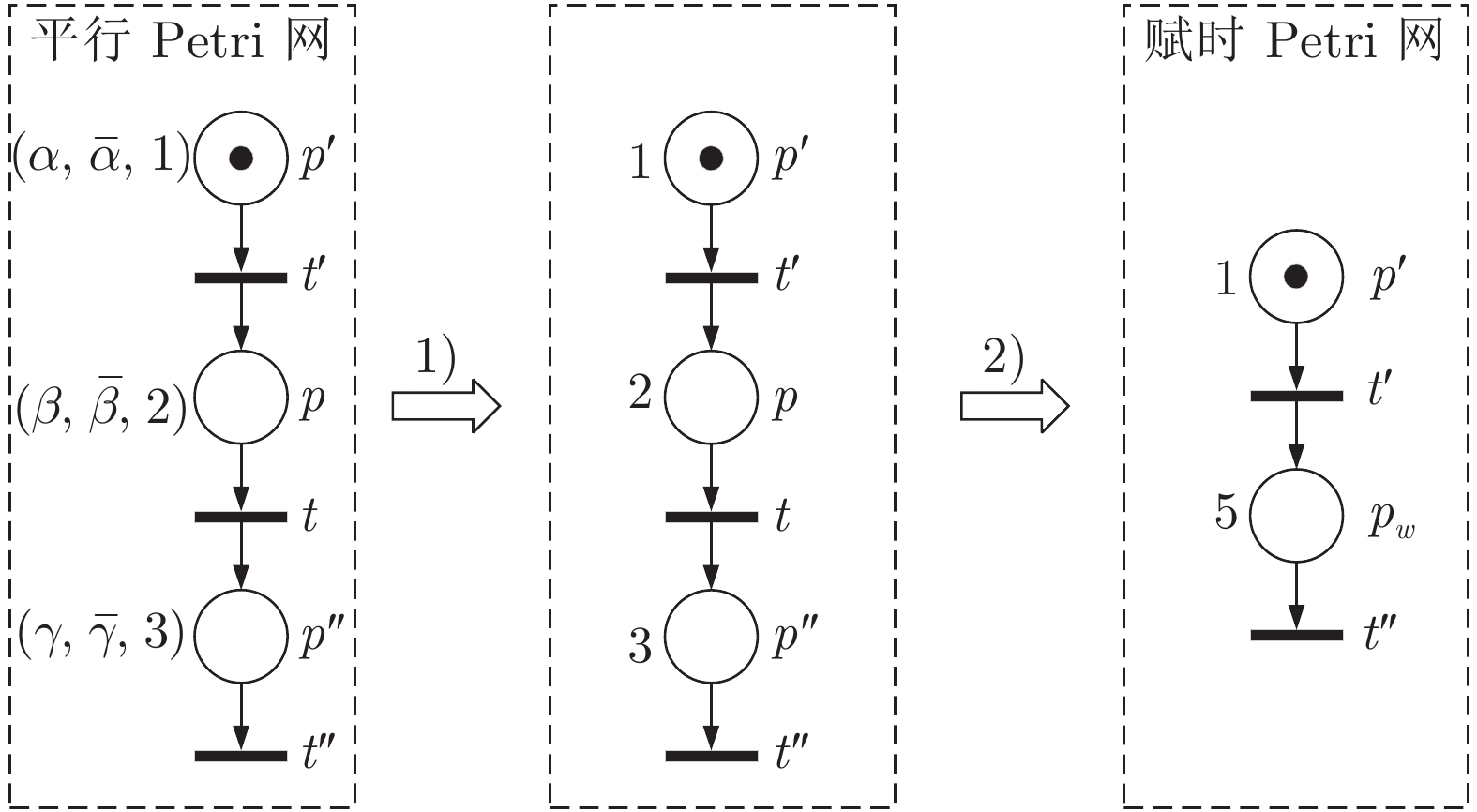
表 1 平行Petri网到赋时Petri网转换表
Table 1 Conversion table from parallel Petri nets to timed Petri nets
$t\in\omega$ $p\not\in\omega$ $p\in\omega$ $p_w$ $\lambda_{\rm{z}}(p)$ $\bar{\lambda}_{\rm d}(p)$ $\bar{\lambda}_{\rm d}(p_w)$ $t_{16}$, $t_{17}$ $p_{15}$, $p_{16}$, $p_{17}$ $p_{14}$ 3, 70, 3 76 $t_{20}$, $t_{21}$ $p_{18}$, $p_{19}$, $p_{20}$ $p_{15}$ 2, 35, 3 40 $t_{28}$, $t_{29}$ $p_{29}$, $p_{30}$, $p_{31}$ $p_{20}$ 2, 35, 3 40 $t_{32}$, $t_{33}$ $p_{32}$, $p_{33}$, $p_{34}$ $p_{21}$ 2, 35, 3 40 $t_{40}$, $t_{41}$ $p_{41}$, $p_{42}$, $p_{43}$ $p_{24}$ 3, 70, 3 76 $t_{44}$, $t_{45}$ $p_{44}$, $p_{45}$, $p_{46}$ $p_{25}$ 2, 35, 3 40 $t_{14}$ $p_{13}$, $p_{14}$ $p_{13}$ 0, 30 30 $t_{23}$, $t_{24}$ $p_{21}$, $p_{22}$, $p_{23}$ $p_{16}$ 0, 35, 0 35 $t_{25}$, $t_{26}$ $p_{24}$, $p_{25}$, $p_{26}$ $p_{17}$ 0, 40, 0 40 $t_{35}$, $t_{36}$ $p_{35}$, $p_{36}$, $p_{37}$ $p_{22}$ 0, 40, 0 40 $t_{37}$, $t_{38}$ $p_{38}$, $p_{39}$, $p_{40}$ $p_{23}$ 0, 45, 0 45 $p_{1}$, $p_{3}$, $p_{5}$ 0 0 $p_{7}$, $p_{12}$, $p_{49}$ 0 0 $p_{2}$, $p_{4}$, $p_{6}$ 35 35 $p_{8}$, $p_{9}$, $p_{10}$, $p_{47}$ 35 35 -
[1] 王飞跃. 平行系统方法与复杂系统的管理和控制. 控制与决策, 2004, 19(5): 485−490 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2004.05.002Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel system methods for management and control of complex systems. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(5): 485−490 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2004.05.002 [2] 杨林瑶, 陈思远, 王晓, 张俊, 王成红. 数字孪生与平行系统: 发展现状、对比及展望. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2001−2031Yang Lin-Yao, Chen Si-Yuan, Wang Xiao, Zhang Jun, Wang Cheng-Hong. Digital twins and parallel systems: state of the art, comparisons and prospect. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2001−2031 [3] 傅健丰, 董利达, 徐珊珊, 朱丹, 朱承丞. 一种改进型的S4PR网活性条件. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(9): 1439−1446Fu Jian-Feng, Dong Li-Da, Xu Shan-Shan, Zhu Dan, Zhu Cheng-Cheng. An improved liveness condition for S4PR nets. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(9): 1439−1446 [4] Luo J L, Zhou M C. Petri-net controller synthesis for partially controllable and observable discrete event systems. IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(3): 1301−1313 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2586604 [5] Basile F, Faraut G, Ferrara L, Lesage J. An optimization-based approach to discover the unobservable behaviour of a discrete-event system through interpreted Petri nets. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(2): 784−798 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2019.2944299 [6] Yu H Y, Wu X Y, Wu X Y. An extended object-oriented Petri net model for mission reliability evaluation of phased-mission system with time redundancy Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2020, 197: Article No. 106786 [7] Uzam M, Ko B, Gelen G, Aksebzeci B H. Asynchronous implementation of discrete event controllers based on safe automation Petri nets. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 41(5): 595−612 [8] Yadav A, Jayswal S C. Modeling of flexible manufacturing system: a review. International Journal of Production Research, 2018, 56(7): 2467−2487 [9] Moreira M V, Basilio J C. Bridging the gap between design and implementation of discrete-event controllers. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineer, 2014, 11(1): 48−65 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2013.2281733 [10] Jakovljevic Z, Lesi V, Mitrovic S, Pajic M. Distributing sequential control for manufacturing systems. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2020, 28(4): 1586−1594 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2912776 [11] Kaid H, Al-Ahmari A, Li Z W, Davidrajuh R. Intelligent colored token Petri nets for modeling, control, and validation of dynamic changes in reconfigurable manufacturing systems. Processes, 2020, 8(3): Article No. 358 [12] Luo J L, Zhang Q, Chen X K, Zhou M C. Modeling and race detection of ladder diagrams via ordinary Petri nets. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 48(7): 1166−1176 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2647219 [13] Lu J, Ou C Y, Liao C, Zhang Z K, Chen K, Liao X P. Formal modelling of a sheet metal smart manufacturing system by using Petri nets and first-order predicate logic. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020 [14] Hajduk Z, Wojtowicz J. FPGA Implementation of Fuzzy Interpreted Petri Net. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 61442−61452 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2983276 [15] Lee G B, Zandong H, Lee J S. Automatic generation of ladder diagram with control Petri net. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2004, 15(2): 245−252 doi: 10.1023/B:JIMS.0000018036.84607.37 [16] 李大成, 罗继亮, 孙莎莎, 聂维余, 方慧娟. 可编程逻辑控制器的平行Petri网设计与实现方法. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(12): 2611−2617Li Da-Cheng, Luo Ji-Liang, Sun Sha-Sha, Nie Wei-Yu, Fang Hui-Juan. Methods on synthesis and implementation of programmable logical controllers via parallel Petri nets. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(12): 2611−2617 [17] Al-Ahmari A. Optimal robotic cell scheduling with controllers using mathematically based timed Petri nets. Information Sciences, 2016, 329: 638−648 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.09.053 [18] Kammoun M A, Ezzeddine W, Rezg N, Achour Z. FMS scheduling under availability constraint with supervisor based on timed Petri nets. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(4): 399−418 doi: 10.3390/app7040399 [19] Li C, Wu W M. Scheduling FMS problems with heuristic search function and transition-timed Petri nets. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2015, 26: 933−944 doi: 10.1007/s10845-014-0943-2 [20] Lee T, Kim H, Roh D, Sreenivas R S. Characterizing token delays of timed event graphs for k-cyclic schedules. IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(2): 961−966 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2570122 [21] Declerck P. Extremum cycle times in time interval models. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(6): 1821−1827 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2757085 [22] Lee Y D, DiCesare F. Scheduling flexible manufacturing ststems using Petri nets and heuristic search. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1994, 10(2): 123−132 doi: 10.1109/70.282537 [23] Huang B, Zhou M C, Abusorrah A, Sedraoui K. Scheduling robotic cellular manufacturing systems with timed Petri nets, A* search, and admissible heuristic function. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2020: 1−8 [24] Mejia G, Nino K, Montoya C, Sanchez M A, Palacios J, Amodeo L. A Petri net based framework for realistic project management and scheduling: an application in animation and videogames. Computer & Operations, 2016, 66: 190−198 [25] 任磊, 王峰, 邢科义. 基于Petri网的柔性制造系统无死锁遗传调度算法. 控制理论与应用, 2010, 27(1): 13−18Ren Lei, Wang Feng, Xing Ke-Yi. A Petri-net-based deadlock-free genetic scheduling for flexible manufacturing systems. Control Theory & Applications, 2010, 27(1): 13−18 [26] 李勇, 李坤成, 孙柏青, 张秋豪, 王义娜, 杨俊友. 智能体 Petri 网融合的多机器人-多任务协调框架. 自动化学报, 2019, 45: 1−21Li Yong, Li Kun-Cheng, Sun Bai-Qing, Zhang Qiu-Hao, Wang Yi-Na, Yang Jun-You. Multi-robot-multi-task coordination framework based on the integration of intelligent agent and Petri net. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45: 1−21 [27] Davidrajuh R. Modeling humanoid robot as a discrete event system: A modular approach based on Petri nets. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation. Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia: IEEE, 2015. 277−282 [28] Zeller A, Jazdi N, Weyrich M. Functional verification of distributed automation systems. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 105: 3991−4004 doi: 10.1007/s00170-019-03791-2 [29] Hoffman A J, Basson A H. IEC 61131-3-based holonic control of a reconfigurable manufacturing subsystem. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2016, 29(5): 520−534 doi: 10.1080/0951192X.2015.1067915 -




 下载:
下载: