State Feedback Control for Dual-inertia Servo Mechanisms With Performance Enhancement
-
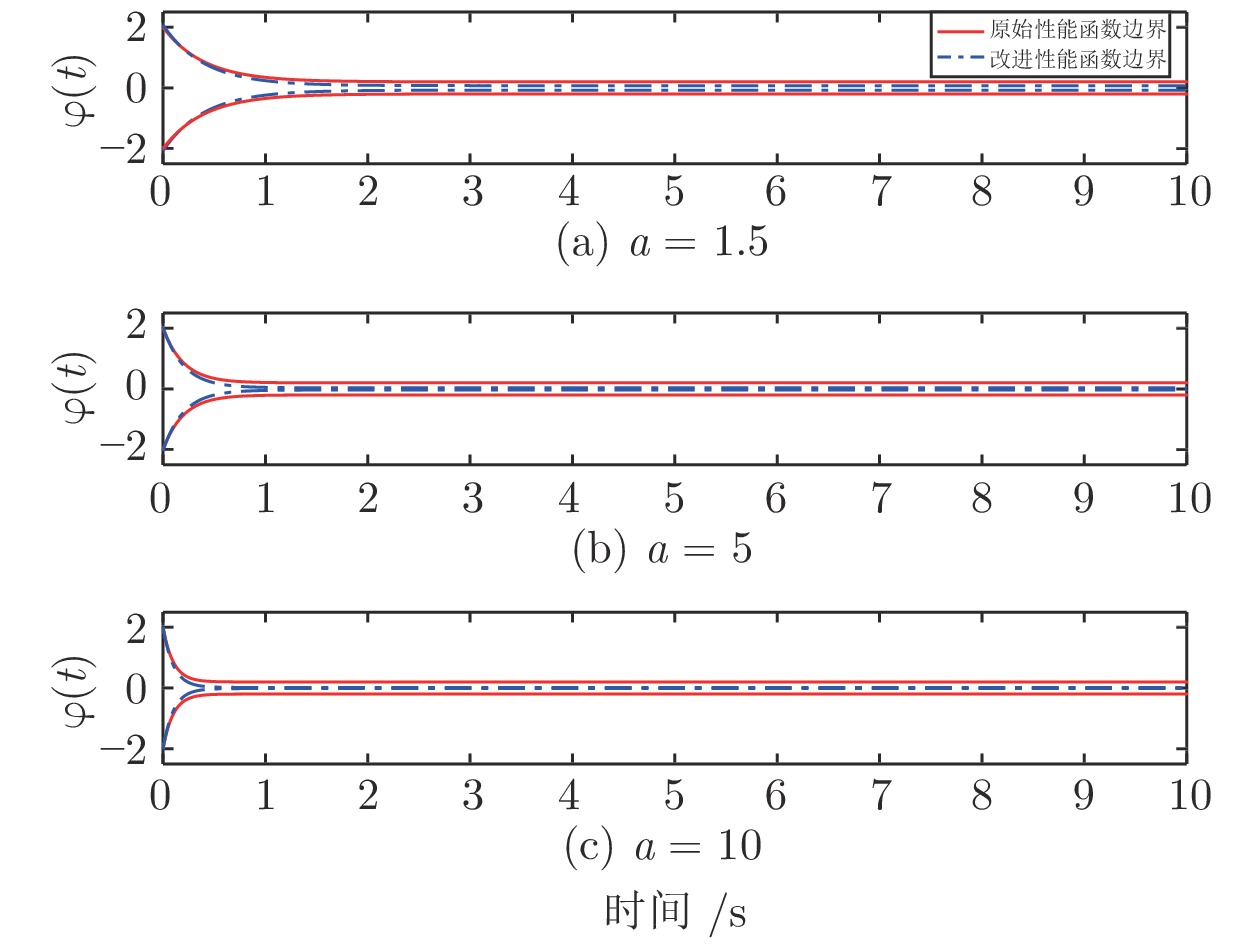
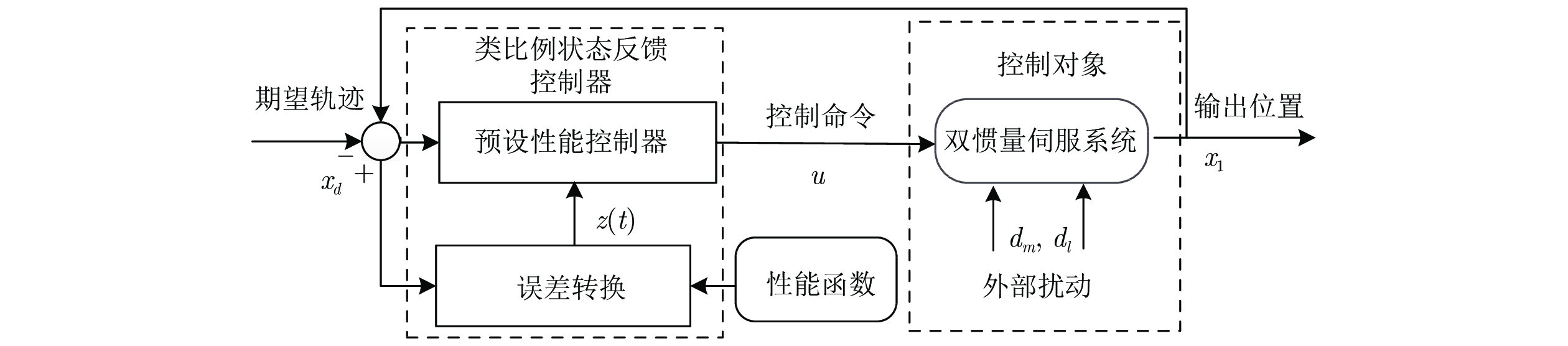
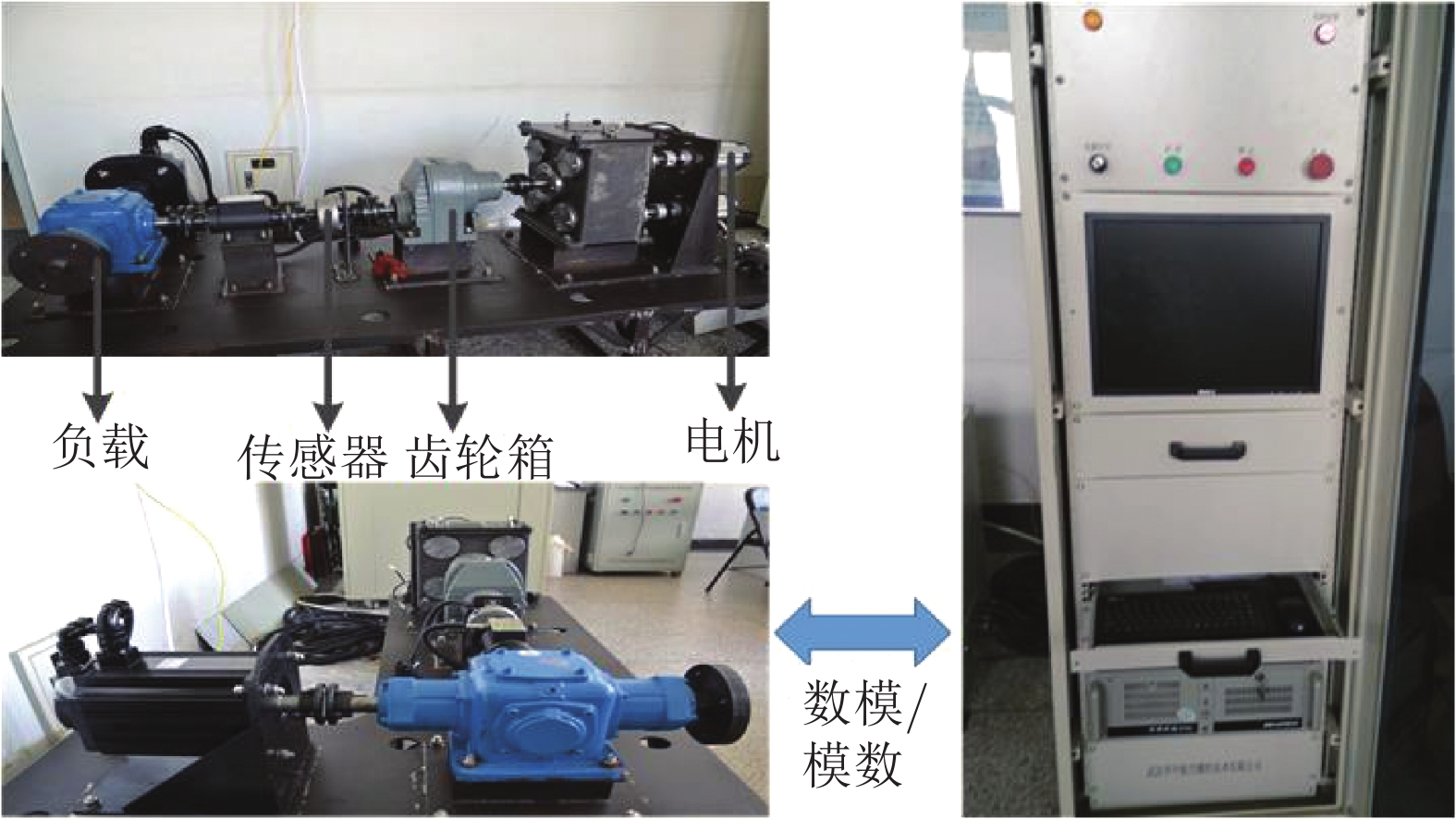
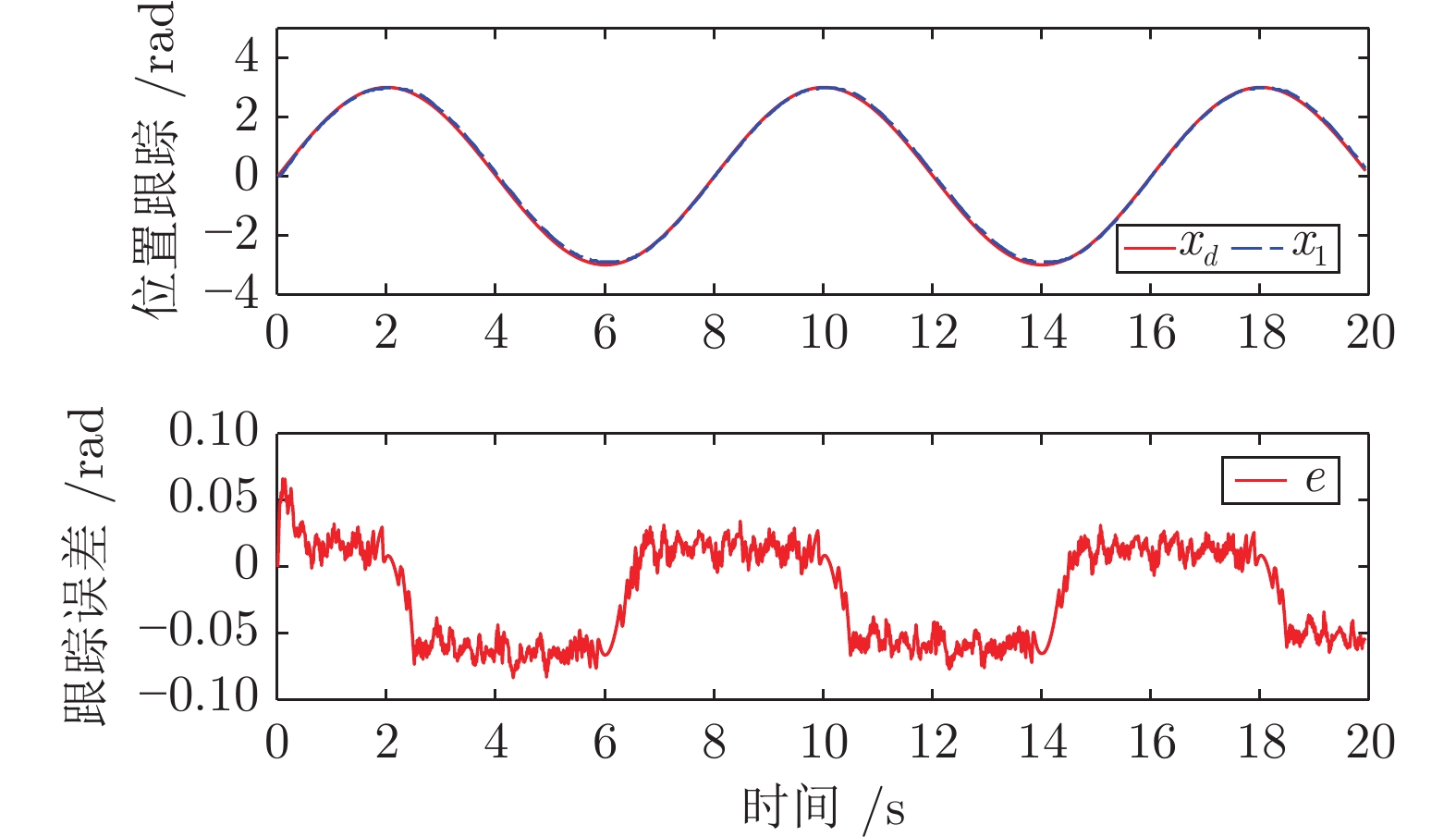
摘要: 为避免使用函数逼近器(神经网络或模糊系统), 并提高双惯量伺服系统的瞬态响应和稳态性能, 针对含外部扰动的双惯量伺服系统, 提出一种基于预设性能函数(Prescribed performance function, PPF)的类比例状态反馈控制策略. 首先, 提出一种改进的带有最大超调、收敛速率以及稳态误差的预设性能函数, 并将该函数融入控制器设计使二惯量伺服的跟踪误差保持在预定的边界之内. 其次, 基于预设性能函数设计了类比例状态反馈控制器实现跟踪控制. 与传统基于函数逼近控制方法相比较, 该方法可降低控制系统计算复杂度同时消除反演控制中存在的复杂度爆炸问题. 最后, 利用双惯量伺服系统实验平台开展了对比实验, 验证了所提出方法的有效性.Abstract: To avoid using the function approximation (neural networks or fuzzy logic systems) and enhance the transient and steady-state control performance, this paper proposes a proportional-integral feedback control strategy for dual-inertia servo systems with external disturbance based on prescribed performance functions (PPF). First, a modified prescribed performance function with guaranteed convergence rate, maximum overshoot and steady-state error boundary is employed, so that both the transient response and steady-state errors are retained within a predefined boundary. Second, a state-feedback control with this proposed PPF is suggested. Compared with the classical function approximation-based control approaches, the computational complexity of the developed control system is reduced and the explosion of complexity in the backstepping methods could be remedied. Finally, comparative experiments based on a dual-inertial test-rig are provided to show the effectiveness and superior performance of the proposed control scheme.
-
表 1 系统参数
Table 1 System parameters
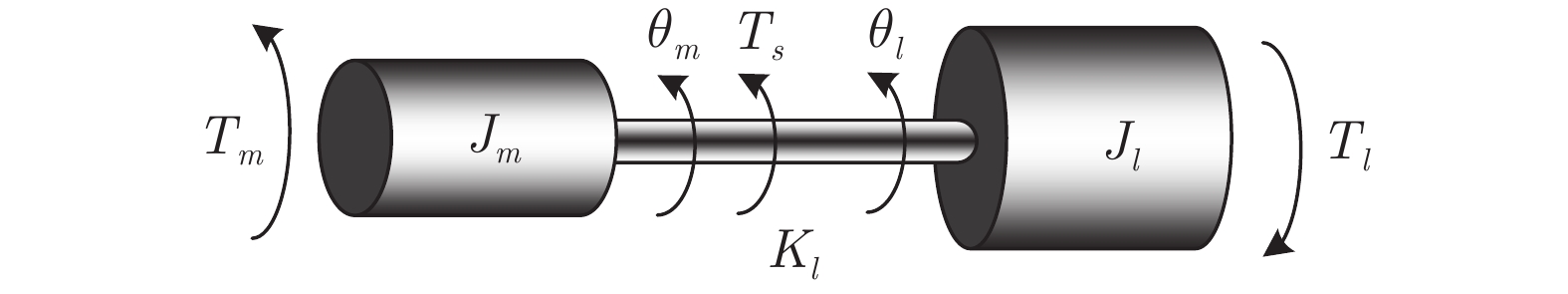
参数 数值 单位 电机惯量${J_m}$ 0.026 $ {\rm{kg \cdot {m^2}}}$ 负载惯量${J_l}$ 0.0113 ${\rm{kg \cdot {m^2}}}$ 弹性系数${K_l}$ 56 ${\rm{Nm/rad}}$ 表 2 性能指标
Table 2 Performance indexes
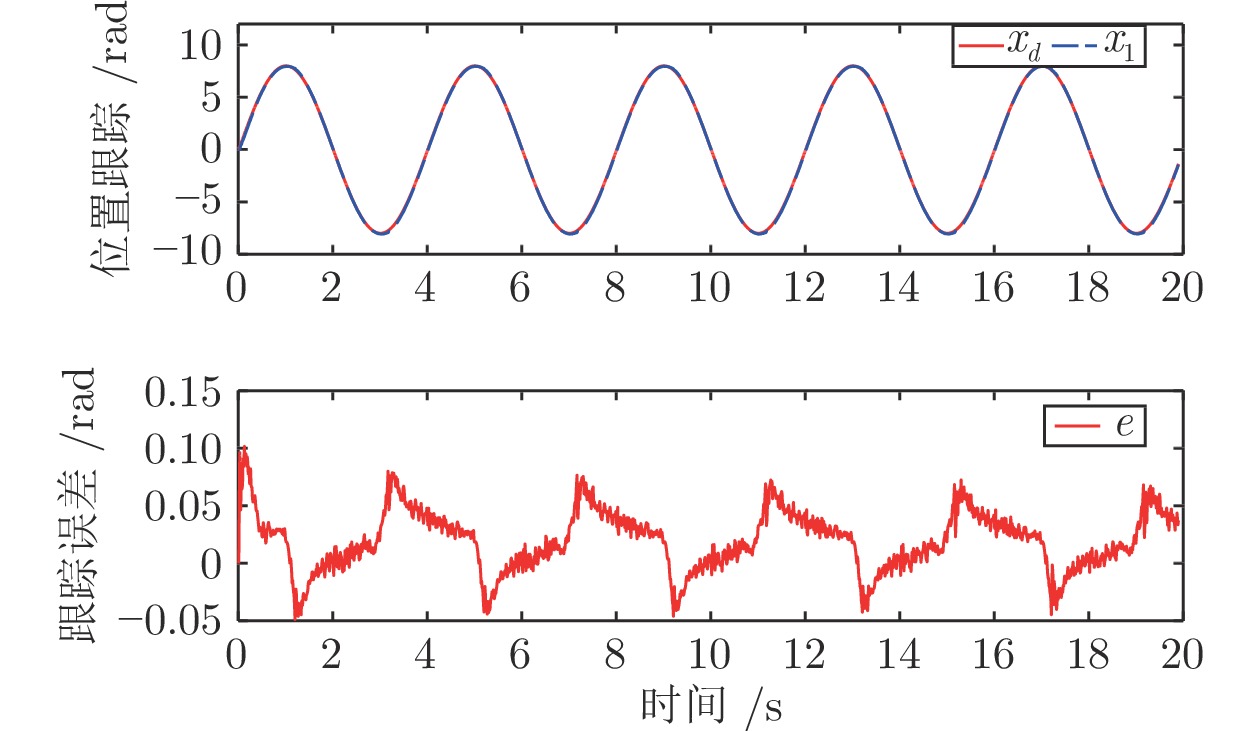
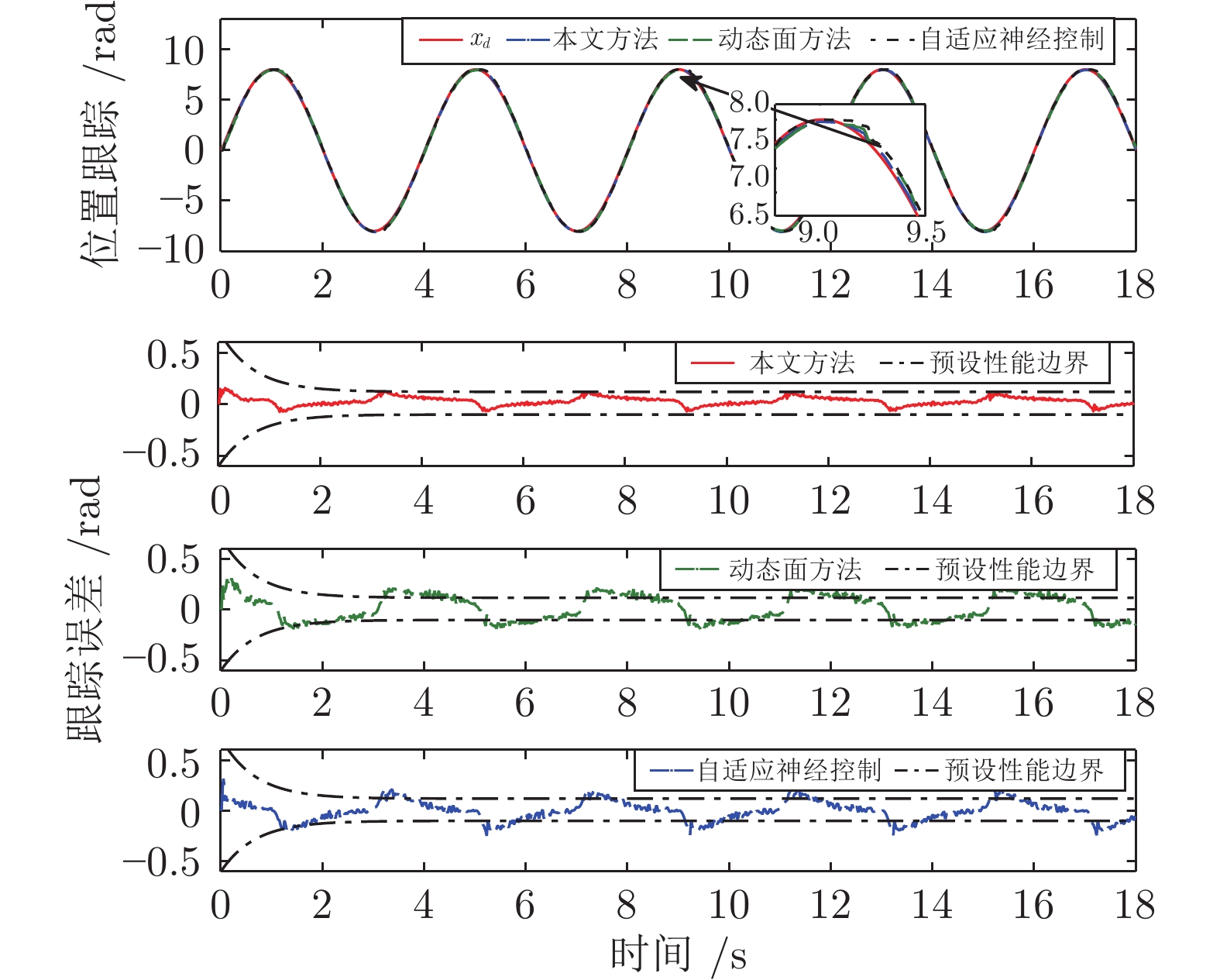
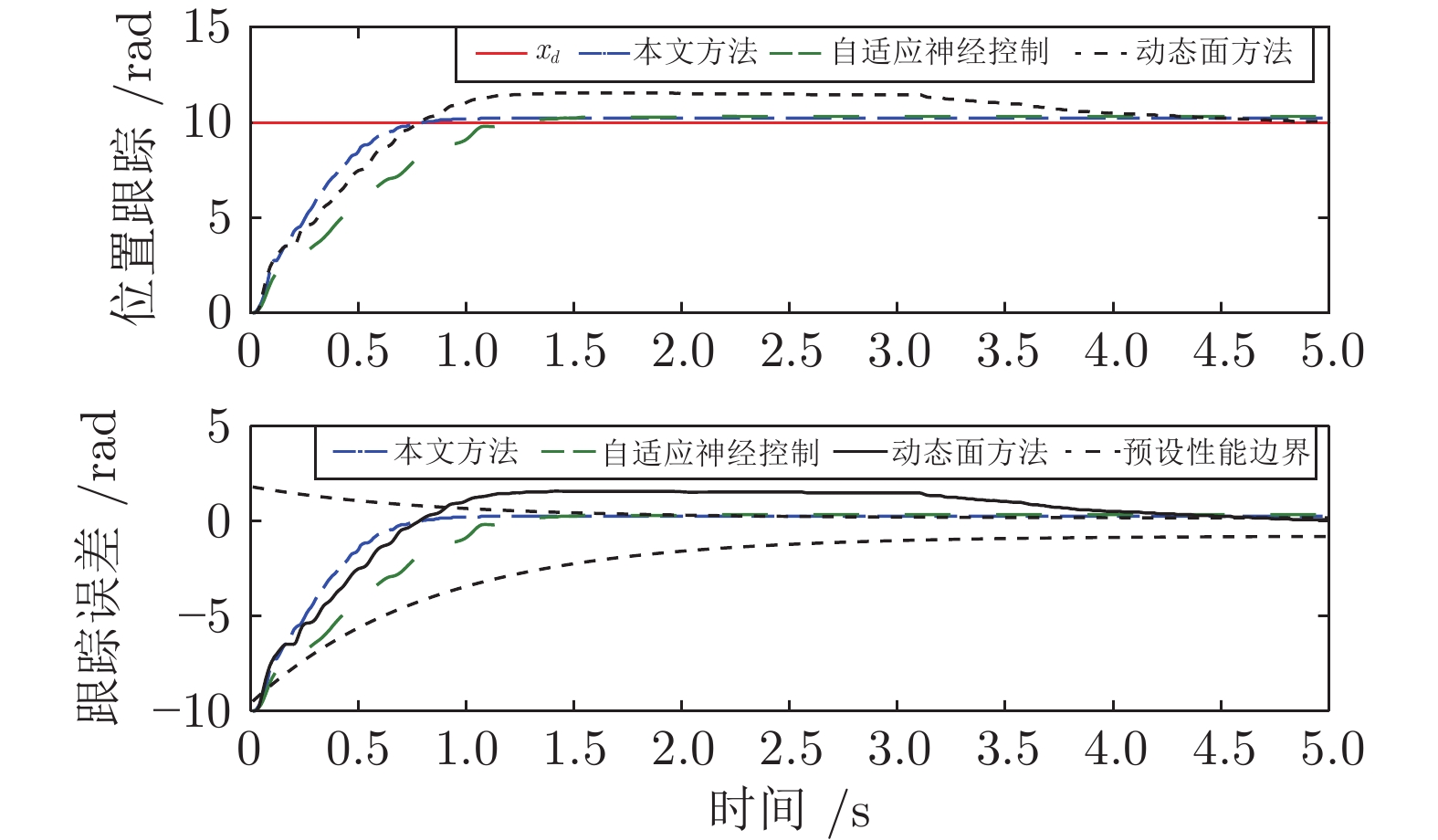
方法 $M_{e}$ $\mu_{e}$ $\sigma_{e}$ 本文方法 0.1587 0.0413 0.00004 动态面方法 0.3104 0.1171 0.00009 自适应神经控制 0.3081 0.0757 0.00007 -
[1] Wang S B, Na J, Xing Y S. Adaptive Optimal Parameter Estimation and Control of Servo Mechanisms: Theory and Experiments. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(1): 598-608 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2962445 [2] Wang C, Yang M, Zheng W L, Hu K, Xu D G. Analysis and suppression of limit cycle oscillation for transmission system with backlash nonlinearity. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(12): 9261–9270 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2711564 [3] Yan Y D, Yang J, Sun Z X, Zhang C L, Li S H, Yu X H. Robust speed regulation for pmsm servo system with multiple sources of disturbances via an augmented disturbance observer. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2018, 23(2): 769–780 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2018.2799326 [4] 张亚军, 魏萃, 柴天佑, 卢绍文, 崔东亮. 未建模动 态增量补偿驱动的非线性PID控制及应用. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(6): 1145-1153Zhang Ya-Jun, Wei Cui, Chai Tian-You, Lu Shao-Wen, Cui Dong-Liang. Un-modeled dynamics increment compensation driven nonlinear PID control and its application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 1145-1153 [5] Zhang G, Furusho J J. Speed control of twoinertia system by pi/pid control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2000, 47(3): 603–609 doi: 10.1109/41.847901 [6] Li S H, Liu Z G, Adaptive speed control for permanent-magnet synchronous motor system with variations of load inertia. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(8): 3050–3059 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2024655 [7] Yao J Y, Deng W X, Sun W C. Precision motion control for electro-hydraulic servo systems with noise alleviation: A desired compensation adaptive approach. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(4): 1859–1868 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2688353 [8] Zhang G Z, Chen J, Lee Z P. Adaptive robust control for servo mechanisms with partially unknown states via dynamic surface control approach. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2010, 18(3): 723–731 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2009.2025265 [9] 郭子杰, 白伟伟, 周琪, 鲁仁全. 基于性能指标约束的一类输入死区非线性系统最优控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2128-2136Guo Zi-Jie, Bai Wei-Wei, Zhou Qi, Lu RenQuan. Adaptive optimal control for a class of nonlinear systems with dead zone input and prescribed performance. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2128-2136 [10] El-Sousy F F M. Adaptive dynamic slidingmode control system using recurrent rbfn for high-performance induction motor servo drive. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(4): 1922–1936 doi: 10.1109/TII.2013.2238546 [11] Gao T T, Liu Y J, Liu L, Li D P. Adaptive neural network-based control for a class of nonlinear pure-feedback systems with time-varying full state constraints. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(5): 923–933 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2018.7511195 [12] Na J, Chen Q, Ren X M, Guo Y. Adaptive prescribed performance motion control of servo mechanisms with friction compensation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(1): 486–494 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2240635 [13] 李洋, 刘明雍, 张小件. 基于自适应RBF神经网络的超空泡航行体反演控制. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(4): 734-743LI Yang, LIU Ming-Yong, ZHANG Xiao-Jian. Adaptive RBF Neural Network Based Backsteppting Control for Supercavitating Vehicles. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2020, 46(4): 734-743 [14] Yang C G, Jiang Y M, Na J, Li Z J, Cheng L, Su C Y. Finite-time convergence adaptive fuzzy control for dual-arm robot with unknown kinematics and dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(3): 574-588 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2864940 [15] Cao L, Li H Y, Wang N, Zhou Q. Observerbased event-triggered adaptive decentralized fuzzy control for nonlinear large-scale systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(6): 1201–1214 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2873971 [16] Bechlioulis C P, Rovithakis G A. A lowcomplexity global approximation-free control scheme with prescribed performance for unknown pure feedback systems. Automatica, 2014, 50(4): 1217–1226 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.02.020 [17] Huang Y B, Na J, Wu X, Gao G B. Approximation-free control for vehicle active suspensions with hydraulic actuator. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(9): 7258–7267 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2798564 [18] Psomopoulou E, Theodorakopoulos A, Doulgeri Z, Rovithakis G A. Prescribed performance tracking of a variable stiffness actuated robot. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 23(5): 1914–1926 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2015.2394748 [19] Zheng Z W, Feroskhan M. Path following of a surface vessel with prescribed performance in the presence of input saturation and external disturbances. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(6): 2564–2575 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2756110 [20] Nguyen M L, Chen X K, Yang F, “Discretetime quasi-sliding-mode control with prescribed performance function and its application to piezo-actuated positioning systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(1): 942–950 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2708024 [21] Ren B B, Ge S S Z, Tee K P, Lee T H. Adaptive Neural Control for Output Feedback Nonlinear Systems Using a Barrier Lyapunov Function. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(8): 1339-1345 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2047115 [22] He X Y, He W, Shi J, Sun C Y. Boundary Vibration Control of Variable Length Crane Systems in Two-Dimensional Space With Output Constraints. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(5): 1952–1962 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2721553 [23] He W, Kong L H, Dong Y T, Yu Y, Yang C G, Sun C Y. Fuzzy Tracking Control for a Class of Uncertain MIMO Nonlinear Systems With State Constraints. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(3): 543-554 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2749124 [24] Liu L, Liu Y J, Chen A Q, Tong S C, Chen P C L. Integral barrier Lyapunov function-based adaptive control for switched nonlinear systems. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(3): 212−225 [25] Wang S B, Ren X M, Na J, Zeng T Y. Extended-State-Observer-Based Funnel Control for Nonlinear Servomechanisms With Prescribed Tracking Performance. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2017, 14(1): 98-108 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2016.2618010 [26] Wang S B, Ren X M, Na J. RISE-Based Asymptotic Prescribed Performance Tracking Control of Nonlinear Servo Mechanisms, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 48(12): 2359-2370 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2769683 [27] Sontag E D. Mathematical Control Theory. London: Springer, 1998. [28] Wang S B, Tao L, Chen Q, Na J, Ren X M. USDE-Based Sliding Mode Control for Servo Mechanisms With Unknown System Dynamics. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2020, 25(2): 1056-1066 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2020.2971541 [29] Wang S B, Ren X M, Na J, Gao X H. Robust tracking and vibration suppression for nonlinear two-inertia system via modified dynamic surface control with error constraint. Neurocomputing, 2016, 203: 73–85 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.03.040 [30] Zhao W, Ren X M, Wang S B. Parameter estimation-based time-varying sliding mode control for multimotor driving servo systems. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(5): 2330–2341 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2725344 -




 下载:
下载: