-
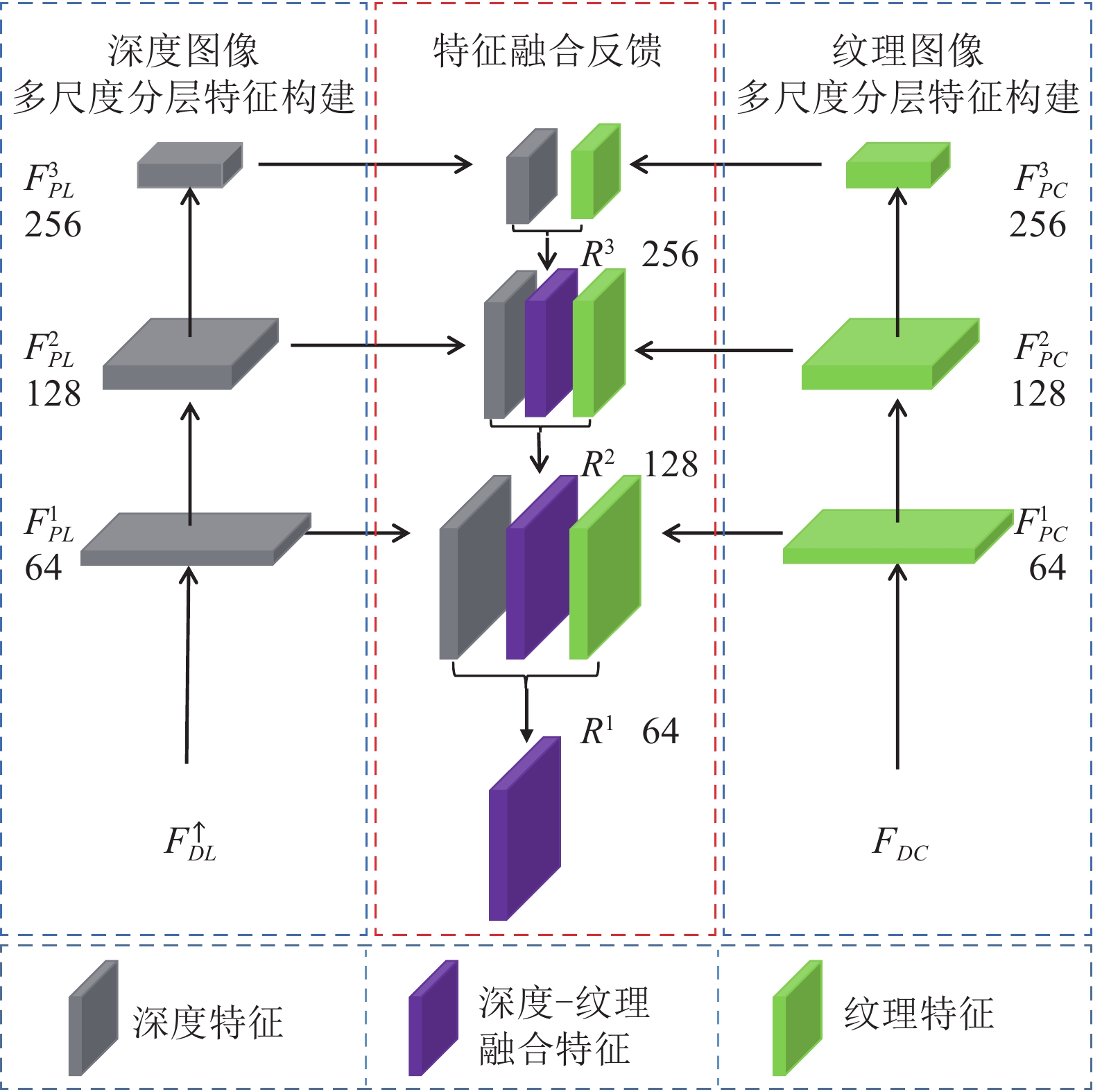
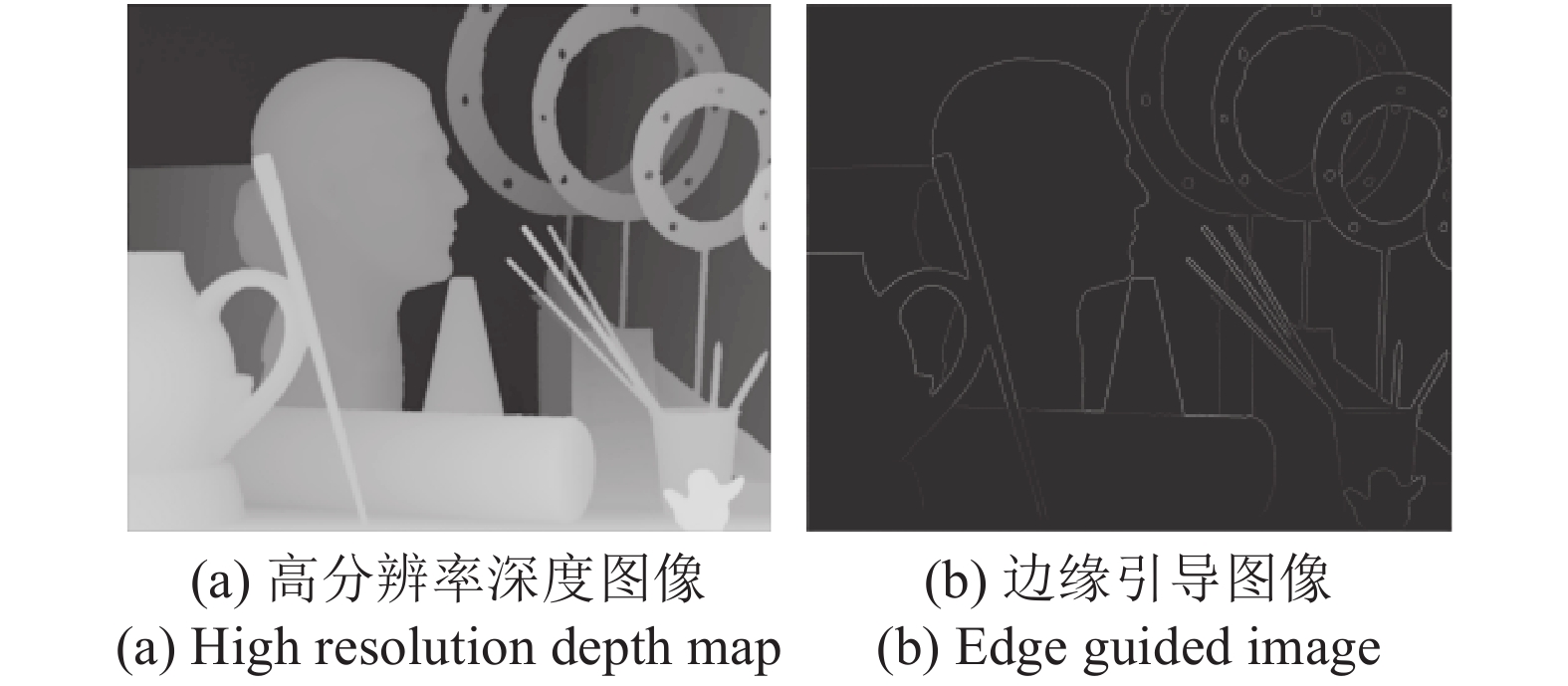
摘要: 受采集装置的限制, 采集的深度图像存在分辨率较低、易受噪声干扰等问题. 本文构建了分级特征反馈融合网络 (Hierarchical feature feedback network, HFFN), 以实现深度图像的超分辨率重建. 该网络利用金字塔结构挖掘深度−纹理特征在不同尺度下的分层特征, 构建深度−纹理的分层特征表示. 为了有效利用不同尺度下的结构信息, 本文设计了一种分级特征的反馈式融合策略, 综合深度−纹理的边缘特征, 生成重建深度图像的边缘引导信息, 完成深度图像的重建过程. 与对比方法相比, 实验结果表明HFNN网络提升了深度图像的主、客观重建质量.Abstract: Due to the limitations of the depth acquisition devices, the depth maps are easily distorted by noise and with low resolution. In this paper, we propose a hierarchical feature feedback network (HFFN) to reconstruct depth map with high-resolution. The HFFN uses a pyramid structure to mine the features of depth-texture at different scales, and constructs the hierarchical feature representations of depth-texture. In order to effectively utilize the structural information at different scales, a feedback fusion strategy based on hierarchical features is designed, which integrates the edge features of depth-texture to generate edge guidance information to assist the reconstruction process of depth map. Compared with the comparison methods, the experimental results show that the HFFN can achieve better subjective and objective quality.
-
Key words:
- Depth map /
- super-resolution reconstruction /
- feature fusion /
- residual learning
-
表 1 残差块数目对HFFN网络性能的影响
Table 1 Influence of the number of residual blocks on the performance of HFFN
网络模型 H_R3 H_R5 H_R7 H_R10 训练时间(h) 3 3.8 4.4 5.4 模型参数(M) 2.67 2.96 3.26 3.70 重建结果(dB) 48.14 48.23 48.45 48.54 表 2 金字塔层数对HFFN网络性能的影响
Table 2 Influence of pyramid layers on the performance of HFFN
网络模型 H_P2 H_ P3 H_ P4 训练时间(h) 3.6 3.8 8.6 模型参数(M) 1.62 2.96 8.34 重建结果(dB) 48.04 48.24 48.32 表 3 消融分析结果
Table 3 Results of ablation study
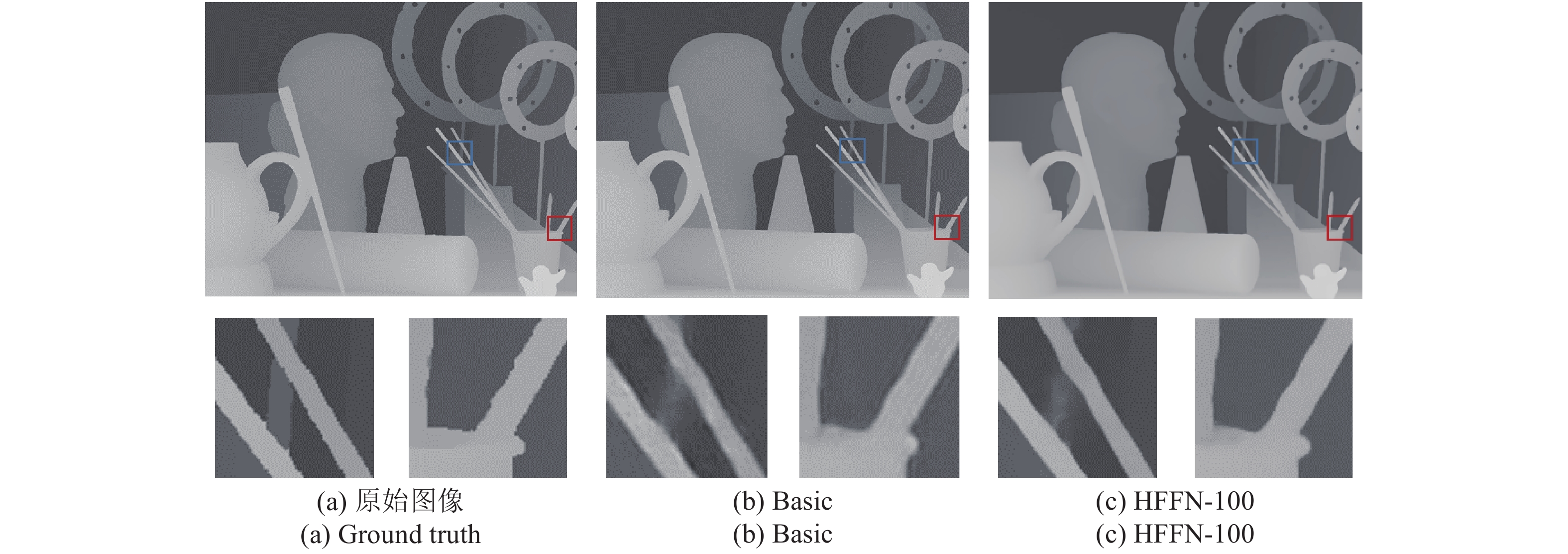
网络 纹理 分层 深层 融合 结果(RMSE/PSNR) Basic $ \checkmark$ 3.2238/40.071 H_Color $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ 2.8239/41.438 H_CP $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ 2.8544/41.578 H_Res $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ 2.9352/41.285 HFFN-100 $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ 2.7483/41.671 表 4 测试数据集A的客观对比结果 (RMSE)
Table 4 Objective comparison results (RMSE) on test dataset A
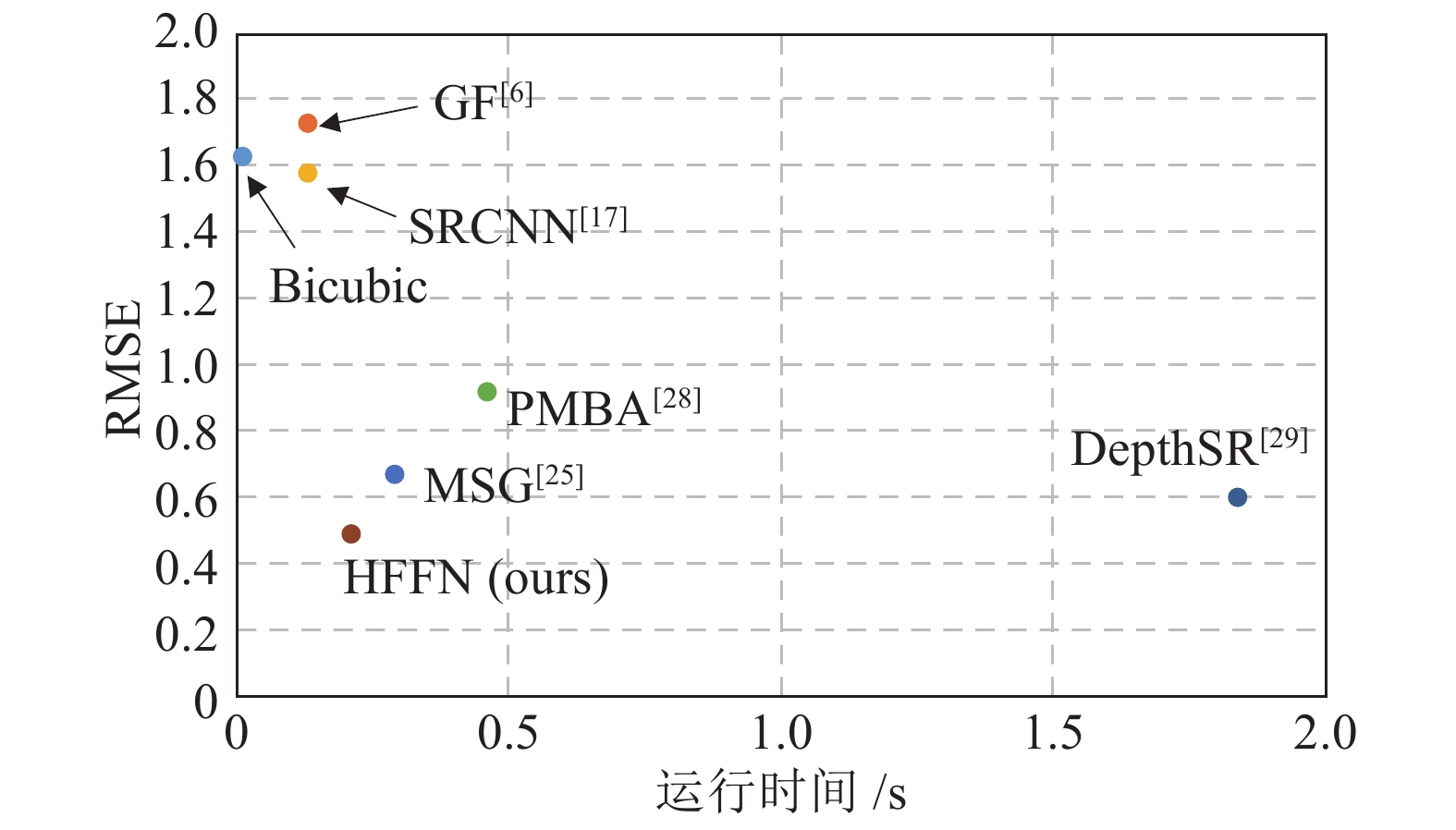
对比算法 Art Books Moebius $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ Bicubic 2.66 3.34 3.90 5.50 1.08 1.39 1.63 2.36 0.85 1.08 1.29 1.89 GF[6] 3.63 3.84 4.14 5.49 1.49 1.59 1.73 2.35 1.25 1.32 1.42 1.91 TGV[14] 3.03 3.31 3.78 4.79 1.29 1.41 1.60 1.99 1.13 1.25 1.46 1.91 JID[16] 1.24 1.63 2.01 3.23 0.65 0.76 0.92 1.27 0.64 0.71 0.89 1.27 SRCNN[17] 2.48 3.05 3.71 5.28 1.03 1.26 1.58 2.30 0.81 1.03 1.23 1.84 Huang[21] 0.66 / 1.59 2.71 0.54 / 0.83 1.19 0.52 / 0.86 1.21 MSG[25] 0.66 / 1.47 2.46 0.37 / 0.67 1.03 0.36 / 0.66 1.02 RDN-GDE[26] 0.56 / 1.47 2.60 0.36 / 0.62 1.00 0.38 / 0.69 1.05 MFR-SR[27] 0.71 / 1.54 2.71 0.42 / 0.63 1.05 0.42 / 0.72 1.10 PMBA[28] 0.61 / 2.04 3.63 0.41 / 0.92 1.68 0.39 / 0.84 1.41 DepthSR[29] 0.53 0.89 1.20 2.22 0.42 0.56 0.60 0.89 / / / / HFFN 0.41 0.84 1.28 2.29 0.28 0.37 0.49 0.87 0.31 0.45 0.57 0.89 HFFN+ 0.38 0.81 1.24 2.19 0.27 0.36 0.47 0.84 0.30 0.44 0.55 0.85 表 6 测试数据集C的客观对比结果 (RMSE)
Table 6 Objective comparison results (RMSE) on test dataset C
对比算法 Tsukuba Venus Teddy Cones $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ Bicubic 5.81 7.17 8.56 12.3 1.32 1.64 1.91 2.76 1.99 2.48 2.90 4.07 2.45 3.06 3.60 5.30 GF[6] 8.12 8.63 9.40 12.5 1.63 1.75 1.93 2.69 2.49 2.67 2.93 3.98 3.33 3.55 3.87 5.29 TGV[14] 7.20 7.78 10.3 17.5 2.15 2.34 2.52 4.04 2.71 2.99 3.3 5.39 3.51 3.97 4.45 7.14 JID[16] 3.48 4.91 5.95 10.9 0.8 0.91 1.17 1.76 1.28 1.53 2.94 2.76 1.69 2.42 4.17 5.11 SRCNN[17] 5.47 6.32 8.11 11.8 1.27 1.43 1.85 2.67 1.88 2.25 2.77 3.95 2.34 2.52 3.43 5.15 Huang[21] 1.41 / 3.73 7.79 0.56 / 0.72 1.09 0.85 / 1.58 2.88 0.88 / 2.38 4.66 MSG[25] 1.85 / 4.29 8.42 0.14 / 0.35 1.04 0.71 / 1.49 2.76 0.90 / 2.60 4.23 DepthSR[29] 1.33 2.25 3.26 6.89 / / / / 0.83 1.15 1.37 1.85 / / / / HFFN 1.37 2.49 3.53 7.67 0.21 0.28 0.42 0.84 0.61 0.93 1.21 2.27 0.65 1.24 1.71 3.91 HFFN+ 1.14 2.22 3.21 7.60 0.20 0.28 0.40 0.78 0.56 0.86 1.13 2.12 0.61 1.14 1.59 3.66 表 5 测试数据集B的客观对比结果 (RMSE)
Table 5 Objective comparison results (RMSE) on test dataset B
对比算法 Dolls Laundry Reindeer $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ $ 2\times $ $ 3\times $ $ 4\times $ $ 8\times $ Bicubic 0.94 1.15 1.33 1.87 1.61 2.05 2.39 3.43 1.97 2.46 2.86 4.05 GF[6] 1.25 1.31 1.41 1.86 2.21 2.36 2.54 3.42 2.68 2.84 3.05 4.06 TGV[14] 1.12 1.21 1.36 1.86 1.99 2.22 2.51 3.76 2.40 2.56 2.71 3.79 JID[16] 0.70 0.79 0.92 1.26 0.75 0.94 1.21 2.08 0.92 1.21 1.56 2.58 SRCNN[17] 0.90 1.01 1.28 1.82 1.52 1.74 2.31 3.32 1.84 2.17 2.73 3.92 Huang[21] 0.58 / 0.91 1.31 0.52 / 0.92 1.52 0.59 / 1.11 1.80 MSG[25] 0.35 / 0.69 1.05 0.37 / 0.79 1.51 0.42 / 0.98 1.76 RDN-GDE[26] 0.56 / 0.88 1.21 0.48 / 0.96 1.63 0.51 / 1.17 2.05 MFR-SR[27] 0.60 / 0.89 1.22 0.61 / 1.11 1.75 0.65 / 1.23 2.06 PMBA[28] 0.36 / 0.95 1.47 0.38 / 1.14 2.19 0.40 / 1.39 2.74 DepthSR[29] / / / / 0.44 0.62 0.78 1.31 0.51 0.77 0.96 1.57 HFFN 0.36 0.59 0.75 1.11 0.32 0.52 0.73 1.33 0.35 0.66 0.96 1.64 HFFN+ 0.34 0.57 0.74 1.09 0.30 0.51 0.70 1.26 0.34 0.63 0.92 1.58 -
[1] Kopf J, Cohen M F, Lischinski D, Uyttendaele M. Joint bilateral upsampling. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2007, 26(3): 96-es. doi: 10.1145/1276377.1276497 [2] Liu M Y, Tuzel O, Taguchi Y. Joint geodesic upsampling of depth images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013: 169−176 [3] Lei J, Li L, Yue H, Wu F, Ling N, Hou C. Depth map super-resolution considering view synthesis quality. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4): 1732-1745. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2656463 [4] 杨宇翔, 曾毓, 何志伟, 高明煜. 基于自适应权值滤波的深度图像超分辨率重建. 中国图象图形学报, 2014, 19(8): 1210-1218.Yang Yu-Xiang, Zeng Yu, He Zhi-Wei, Gao Ming-Yu. Depth map super-resolution via adaptive weighting filter. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2014, 19(8): 1210-1218. [5] Lu J, Forsyth D. Sparse depth super resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015: 2245−2253 [6] He K, Sun J, Tang X. Guided image filtering. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Heraklion, Greece: Springer, 2010: 1−14 [7] Barron J T, Poole B. The fast bilateral solver. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016: 617−632 [8] Yang Y, Lee H S, Oh B T. Depth map upsampling with a confidence-based joint guided filter. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2019, 77: 40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2019.05.014 [9] Diebel J, Thrun S. An application of Markov random fields to range sensing. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NIPS, 2006: 291−298 [10] 安耀祖, 陆耀, 赵红. 一种自适应正则化的图像超分辨率算法. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(4): 601-608. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00601An Yao-Zu, Lu Yao, Zhao Hong. An Adaptive-regularized Image Super-resolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(4): 601-608. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00601 [11] Park J, Kim H, Tai Y W, Brown M S, Kweon I. High quality depth map upsampling for 3D-TOF cameras. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011: 1623−1630 [12] 严徐乐, 安平, 郑帅, 左一帆, 沈礼权. 基于边缘增强的深度图超分辨率重建[J]. 光电子·激光, 2016, 27(4): 437-447.Yan Xu-Le, An Ping, Zheng Shuai, Zuo Yi-Fan, Shen Li-Quan. Super-resolution reconstruction for depth map based on edge enhancement. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2016, 27(4): 437-447. [13] Yang J, Ye X, Li K, Hou C, Wang Y. Color-guided depth recovery from RGB-D data using an adaptive autoregressive model. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3443-3458. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2329776 [14] Ferstl D, Reinbacher C, Ranftl R, Ruether M, Bichof H. Image guided depth upsampling using anisotropic total generalized variation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013: 993−1000 [15] Li Y, Min D, Do M N, Lu J. Fast guided global interpolation for depth and motion. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016: 717−733 [16] Kiechle M, Hawe S, Kleinsteuber M. A joint intensity and depth co-sparse analysis model for depth map super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013: 1545−1552 [17] Dong C, Loy C C, He K, Tang X. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014: 184−199 [18] Shi W, Caballero J, Huszár F, Totz J, Aitken A P, Bishop R et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016: 1874−1883 [19] Lim B, Son S, Kim H, Nah S, Mu Lee K. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017: 136−144 [20] 周登文, 赵丽娟, 段然, 柴晓亮. 基于递归残差网络的图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1157-1165.Zhou Deng-Wen, Zhao Li-Juan, Duan Ran, Chai Xiao-Liang. Image super-resolution based on recursive residual networks. Acta Automatica sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1157-1165. [21] 张毅锋, 刘袁, 蒋程, 程旭. 用于超分辨率重建的深度网络递进学习方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(2): 274-282.Zhang Yi-Feng, Liu Yuan, Jiang Cheng, Cheng Xu. A curriculum learning approach for single image super resolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(2): 274-282. [22] Huang L, Zhang J, Zuo Y, Wu Q. Pyramid-structured depth map super-resolution based on deep dense-residual network. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(12): 1723-1727. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2944646 [23] Song X, Dai Y, Zhou D, Liu L, Li W, Li H et al. Channel attention based iterative residual learning for depth map super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020: 5631−5640 [24] Zhao L, Bai H, Liang J, Zeng B, Wang A, Zhao Y. Simultaneous color-depth super-resolution with conditional generative adversarial networks. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 88: 356-369. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.11.028 [25] Hui T W, Loy C C, Tang X. Depth map super-resolution by deep multi-scale guidance. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016: 353−369 [26] Zuo Y, Fang Y, Yang Y, Shang X, Wang B. Residual dense network for intensity-guided depth map enhancement. Information Sciences, 2019, 495: 52-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.05.003 [27] Zuo Y, Wu Q, Fang Y, An P, Huang L Chen Z. Multi-scale frequency reconstruction for guided depth map super-resolution via deep residual network. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2019, 30(2): 297-306. [28] Ye X, Sun B, Wang Z, Yang J, Xu R, Li H, Li B. PMBANet: Progressive multi-branch aggregation network for scene depth super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7427-7442. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3002664 [29] Guo C, Li C, Guo J, Cong R, Fu H, Han P. Hierarchical features driven residual learning for depth map super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(5): 2545-2557. [30] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, CA, USA, 2015: 1−15 [31] Scharstein D, Szeliski R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2002, 47(1-3): 7-42. [32] Scharstein D, Pal C. Learning conditional random fields for stereo. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, USA: IEEE, 2007: 1−8 [33] Scharstein D, Hirschmüller H, Kitajima Y, Krathwohl G, Nešić N, Wang X, et al. High-resolution stereo datasets with subpixel-accurate ground truth. In: Proceedings of the German Conference on Pattern Recognition. Münster, Germany: Springer, 2014: 31−42 [34] Butler D J, Wulff J, Stanley G B, Black M J. A naturalistic open source movie for optical flow evaluation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Florence, Italy: Springer, 2012: 611−625 [35] Scharstein D, Szeliski R. High-accuracy stereo depth maps using structured light. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Madison, USA: IEEE, 2003, 1: I−I [36] Hirschmuller H, Scharstein D. Evaluation of cost functions for stereo matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Minneapolis, USA: IEEE, 2007: 1−8 [37] Timofte R, Rothe R, Van Gool L. Seven ways to improve example-based single image super resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016: 1865−1873 -





 下载:
下载: