Research on Optimal Selection for Cold/Warm/Hot-standby Patterns of Dual-standby Systems
-
摘要: 对运行设备安装双贮备设备是实现系统高可靠性的有效方法. 在双贮备系统冷/温/热三种贮备模型中, 选择哪种贮备模型对系统性能指标和经济指标均有重要影响, 因此对如何选择双贮备系统的贮备模型从而使系统性能最优或经济效益最大的问题进行研究具有现实意义. 而现有研究成果很少涉及双贮备系统贮备模型的优化选择问题. 为此, 本文创新性地提出一种确定双贮备系统最优贮备模型的选择方法. 分别建立系统冷/温/热贮备模型, 分析每个模型的系统状态及系统半Markov核函数, 利用Markov更新方程、Laplace变换以及Laplace-Stieltjes变换技术推导系统稳态可用度、稳态平均维修次数、维修人员稳态忙期概率以及冷贮备模型的平均激活时间, 并从经济角度给出系统单位时间内的净收益函数. 最后分别以性能指标和经济指标作为研究目标, 通过模型对比分析给出不同条件下的系统贮备模型的优化选择算法, 并对每个研究目标下的优化选择算法进行实例计算. 计算结果表明以不同性能指标和不同费用作为参考得出的最优贮备模型不尽相同, 从而验证了所提方法能够有效地确定不同衡量标准下的系统最优贮备模型.
-
关键词:
- 双贮备系统 /
- Markov更新方程 /
- Laplace-Stieltjes变换 /
- 模型对比分析
Abstract: It is an effective way to realize the system high reliability by installing dual-standby device. Among the three standby models of cold, warm and hot, which standby model to select has a significant impact on the system performance and economic indicators. However, existing research works rarely involved the optimal selection of standby models. Thus, this study innovatively presents an approach to determine the optimal standby mode for dual-standby systems. The models of cold, warm and hot standby are constructed respectively, and system states and corresponding state transition probabilities of each model are analyzed. Subsequently, the availability, average number of maintenance, probability of the repairman busying and average activation time of the cold standby system in steady state are deduced using the Markov renewal equation, Laplace transform and Laplace-Stieltjes transform technologies. Furthermore, the function with respect to net revenue per unit time of the system is given from the viewpoint of economic principles. Finally, the optimal selection algorithm of the system standby model under different conditions is given in terms of performance and economic indicators through comparative analysis among models, and numerical examples of optimal selection algorithm in each objective are given based on a practical application. The numerical results demonstrate that the obtained optimal standby pattern is not always the same when taking different performance indicators and different costs as references, which validates that the presented approach can effectively determine the optimal system standby model under different indicators. -
表 1 模型中主要变量说明
Table 1 Main variables involved in models
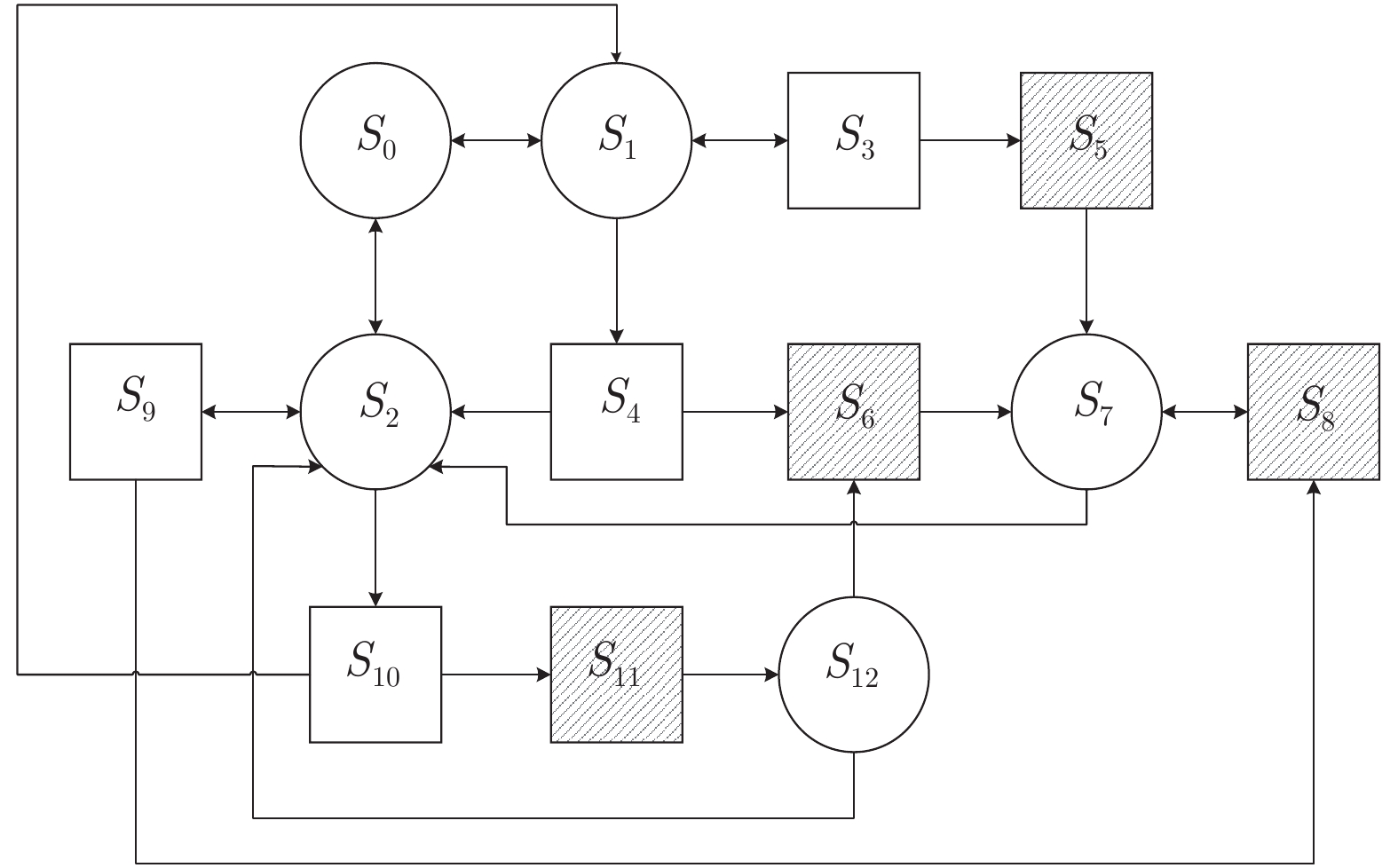
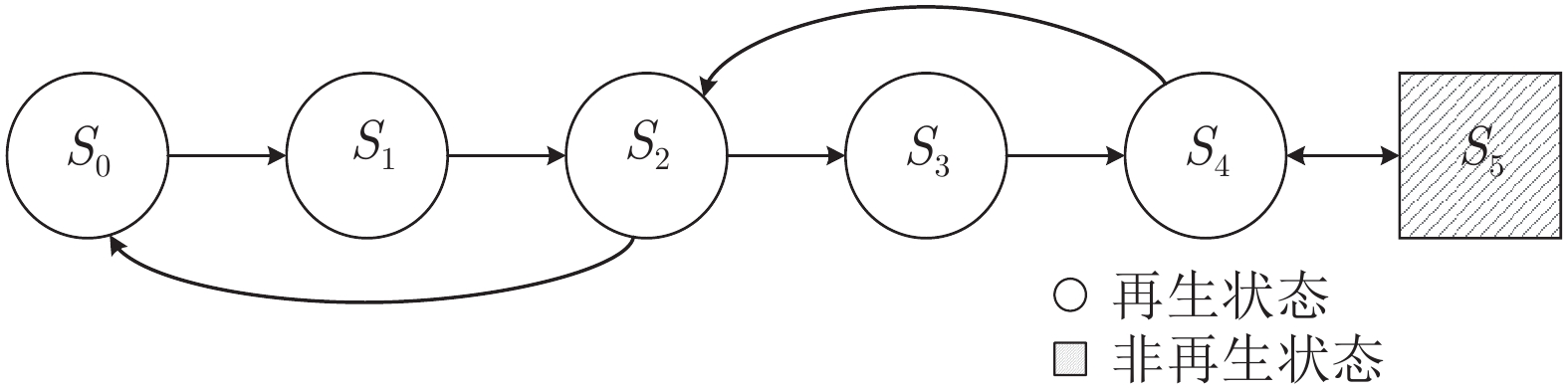
变量符号 变量含义 $\lambda$ 运行设备失效率 $\lambda _1$ 温贮备设备失效率 X 冷贮备模型中设备运行时的寿命 Z 冷贮备模型中设备失效后的维修时间 Xi 温贮备模型中第 i 个设备运行时的寿命 Yi 温贮备模型中第 i 个设备贮备时的寿命 Zi 温贮备模型中第 i 个设备失效后的维修时间 μi 系统在状态$S_i $的平均停留时间 Qij(t) 系统从进入状态$S_i $开始经过时间$ t $后, 直接进入状态$S_j $的概率分布函数 Qij(k)(t) 系统从进入状态$S_i $开始经过时间t后, 中间经过状态$S_k$后, 再进入状态$S_j $的概率分布函数 qij(t) Qij(t) 的导数, 系统由状态$S_i $到状态$S_j $的转移率 $F( t;\lambda)$ 参数为$ \lambda $的指数分布函数 $G(t)$,${G_1}(t)$ 分别为运行设备失效后和温贮备设备失效后的维修时间分布函数 W(t) 激活时间分布函数 $P_i(t) $ 系统在状态$S_i $的存活函数, 即$P_i(t)=P\{X > t \}$ $F^*(s)$ 函数$F(t) $经 Laplace 变换后的象函数 $\hat F(s)$ 函数$F(t) $经 Laplace-Stieltjes 变换后的象函数 Ai(t) 系统从进入状态$S_i $开始 (t = 0), 在 t 时刻的可用度 ${\bar A_1}$,${\bar A_2}$,${\bar A_3}$ 分别为冷、温、热贮备系统稳态可用度 Bi(t) 系统从进入状态$S_i $开始(t = 0), 维修人员在t时刻正在维修(即忙期)的概率 ${\bar B_1}$,${\bar B_2}$,${\bar B_3}$ 分别为冷、温、热贮备系统稳态维修概率, 即维修人员忙期稳态概率 $V_i(t) $ 系统从进入状态$S_i $开始 (t = 0), 维修人员在(0, $t $) 期间的维修次数 ${\bar V_1}$,${\bar V_2}$,${\bar V_3}$ 分别为冷、温、热贮备系统稳态平均维修次数 ${\omega _i}(t)$ 系统从进入状态$S_i $开始$(t $= 0), 在 t时刻处于激活状态的概率 ${\bar \omega _1}$ 冷贮备系统稳态激活概率 表 2 模型中主要符号说明
Table 2 Main symbols involved in models
符号 符号含义 $S_i $ 系统状态 $( i=0, 1, \cdots )$ $Op $ 设备处于运行状态 $Cs $ 设备处于冷贮备状态 $Ws $ 设备处于温贮备状态 $Fr $ 运行设备失效后处于维修状态 $Fr1 $ 温贮备设备失效后处于维修状态 $FR $ 失效后的运行设备继续维修的状态 $FR1 $ 失效后的温贮备设备继续维修的状态 $Fwr $ 运行设备失效后处于等待维修状态 $Fwr1 $ 温贮备设备失效后处于等待维修状态 $Fra $ 正在维修的设备暂停维修的状态 $Csa $ 冷贮备设备处于被激活状态 表 3 系统稳态可用度
Table 3 System steady-state availability
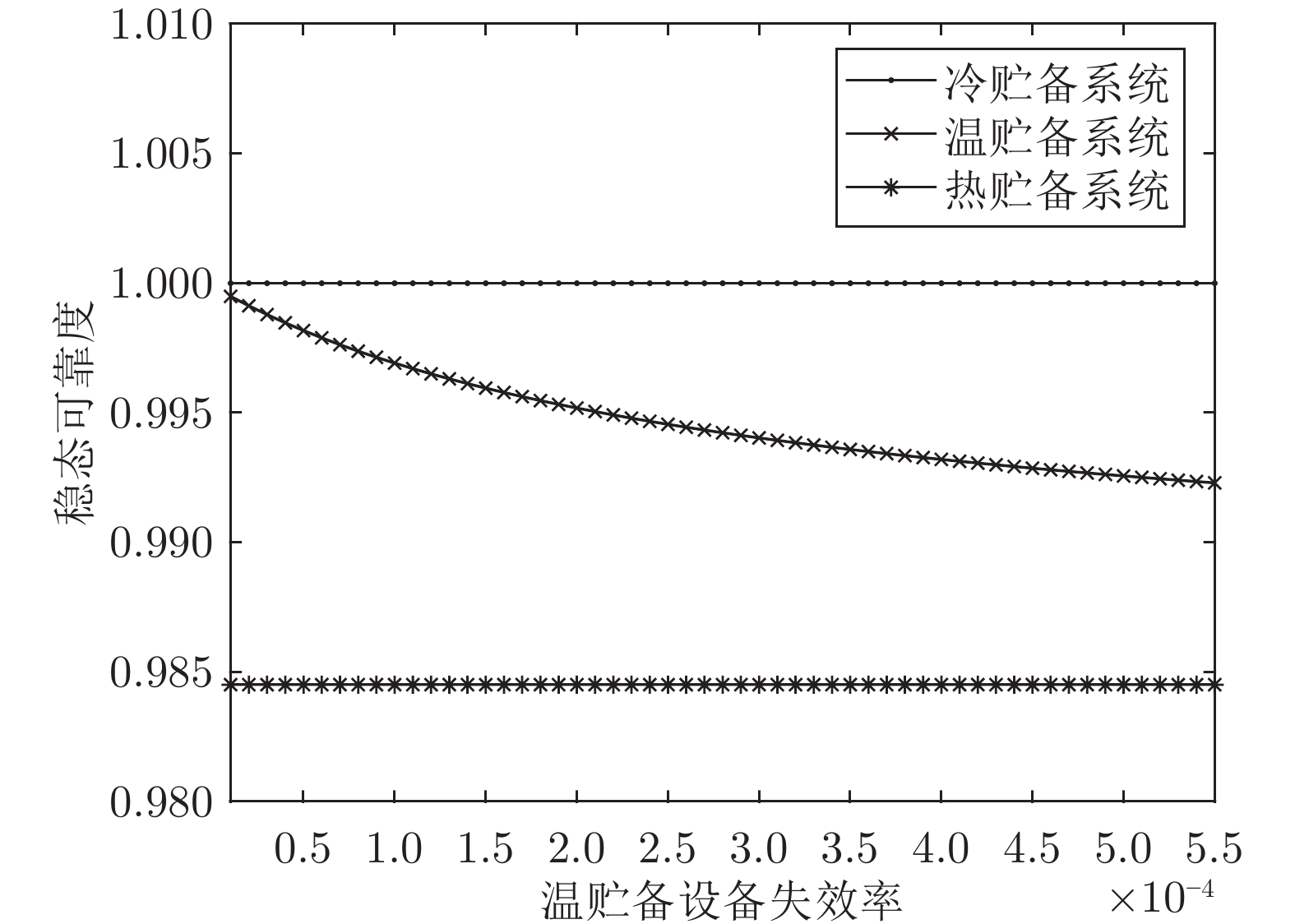
系统模型 模型 Ⅰ 模型 Ⅱ 模型 Ⅲ ${\bar A_i}$ 1.0000 0.9967 0.9845 表 4 维修人员忙期稳态概率
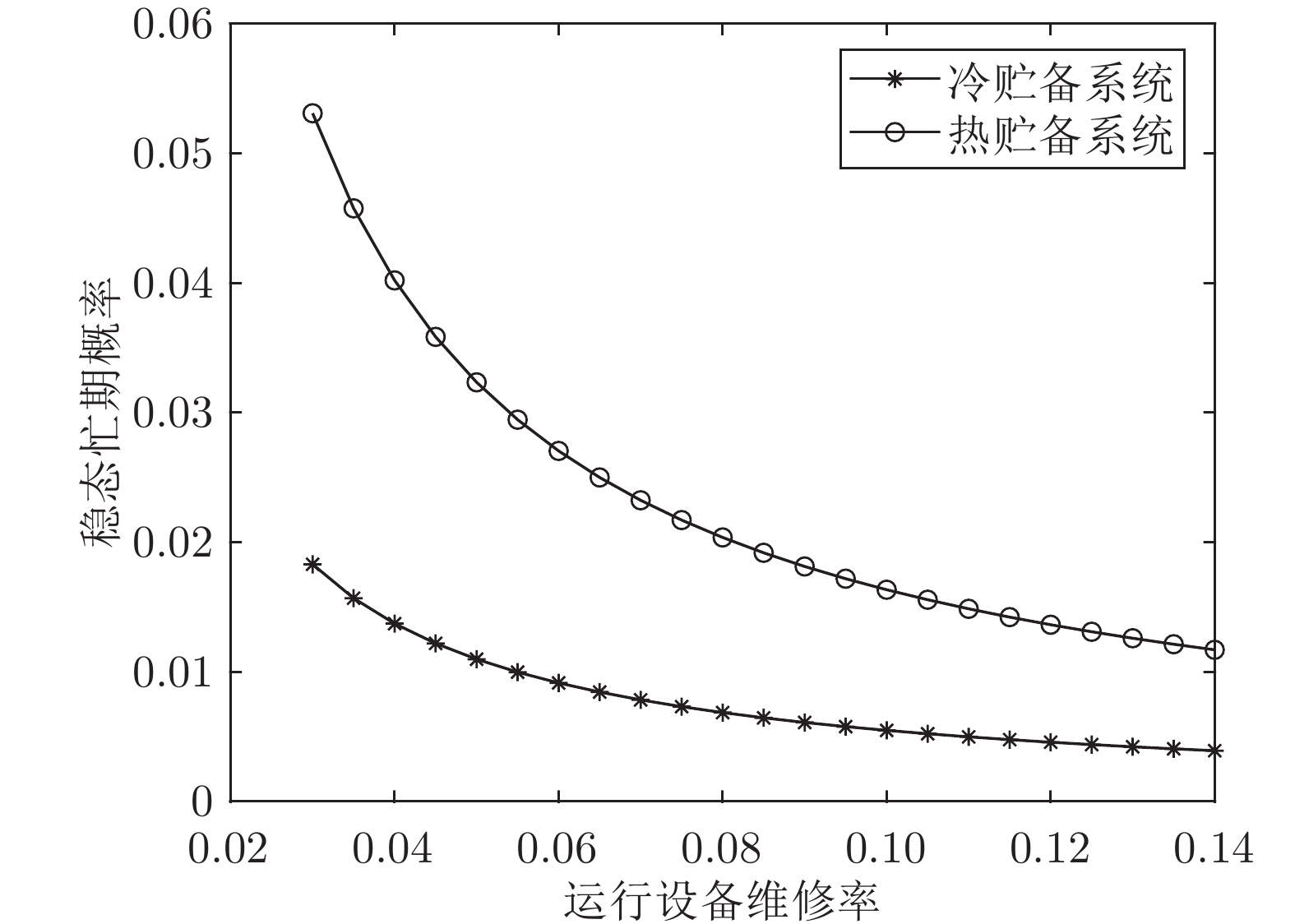
Table 4 Steady-state probability of repairmen busy
系统模型 模型 Ⅰ 模型 Ⅱ 模型 Ⅲ ${\bar B_i}$ 0.0110 0.0131 0.0323 表 5 系统稳态平均维修次数
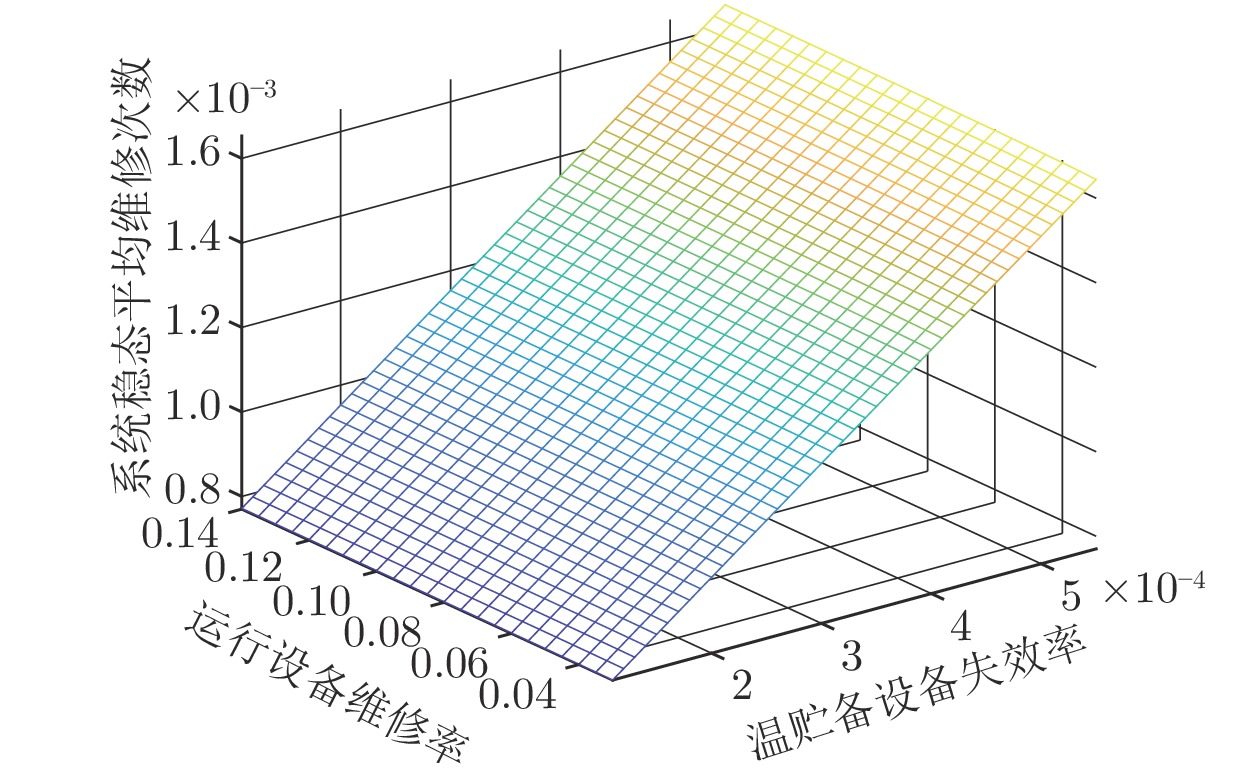
Table 5 Mean repair number of the system in steady-state
系统模型 模型 Ⅰ 模型 Ⅱ 模型 Ⅲ ${\bar V_i}$ 0.00056 0.00077 0.00170 -
[1] Kim H, Kim P. Reliability models for a nonrepairable system with heterogeneous components having a phase-type time-to-failure distribution. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2017, 159: 37-46 [2] 尹东亮, 胡涛, 陈童, 谢经伟. 考虑多维修台异步多重休假的温贮备冗余系统可靠性模型. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(4): 973−984 doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0946Yin Dong-Liang, Hu Tao, Chen Tong, Xie Jing-Wei. Reliability analysis for warm standby redundancy system considering multiple asynchronous vacations of multiple maintenance stations. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(4): 973−984 doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0946 [3] Castellan S, Menis R, Tessarolo A, Luise F, Mazzuca T. A review of power electronics equipment for all-electric ship MVDC power systems. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2018, 96: 306−323 [4] Roy A, Gupta N. Reliability of a coherent system equipped with two cold standby components. Metrika, 2020, 83(6): 677−697 doi: 10.1007/s00184-019-00752-3 [5] Zhai Q Q, Xing L D, Peng R, Yang J. Multi-valued decision diagram-based reliability analysis of k-out-of-n cold standby systems subject to scheduled backups. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2015, 64(4): 1310−1324 doi: 10.1109/TR.2015.2404891 [6] Coppit D, Sullivan K J, Dugan J B. Formal semantics of models for computational engineering: A case study on dynamic fault trees. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering. ISSRE 2000. San Jose, USA: IEEE, 2000. 270−282 [7] Levitin G, Xing L D, Dai Y S. Heterogeneous non-repairable warm standby systems with periodic inspections. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 65(1): 394−409 doi: 10.1109/TR.2015.2455976 [8] Peng R, Tannous O, Xing L D, Xie M. Reliability of smart grid systems with warm standby spares and imperfect coverage. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Smart Grids and Green IT Systems. Porto, Portugal: SciTePress, 2012. 61−66 [9] Cruyt A L M, Ghobbar A A, Curran R. A value-based assessment method of the supportability for a new aircraft entering into service. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2014, 63(4): 817−829 doi: 10.1109/TR.2014.2335972 [10] Zhao J B, Li Y K, Yang G F, Jiang K, Lin H R, Ade H, et al. Efficient organic solar cells processed from hydrocarbon solvents. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(2): Article No. 15027 [11] Elerath J, Pecht M. A highly accurate method for assessing reliability of redundant arrays of inexpensive disks (RAID). IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2009, 58(3): 289−299 doi: 10.1109/TC.2008.163 [12] Hsieh C C, Hsieh Y C. Reliability and cost optimization in distributed computing systems. Computers & Operations Research, 2003, 30(8): 1103−1119 [13] Johnson B W, Julich P M. Fault tolerant computer system for the A129 helicopter. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1985, AES-21(2): 220−229 doi: 10.1109/TAES.1985.310619 [14] 陆宁云, 陈闯, 姜斌, 邢尹. 复杂系统维护策略最新研究进展: 从视情维护到预测性维护. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(1): 1−17Lu Ning-Yun, Chen Chuang, Jiang Bin, Xing Yin. Latest progress on maintenance strategy of complex system: From condition-based maintenance to predictive maintenance. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(1): 1−17 [15] 袁烨, 张永, 丁汉. 工业人工智能的关键技术及其在预测性维护中的应用现状. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2013−2030 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200333Yuan Ye, Zhang Yong, Ding Han. Research on key technology of industrial artificial intelligence and its application in predictive maintenance. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2013−2030 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200333 [16] Chen Y, Wang Z, Li Y Y, Kang R, Mosleh A. Reliability analysis of a cold-standby system considering the development stages and accumulations of failure mechanisms. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2018, 180: 1−12 [17] Zhong C Q, Jin H B. A novel optimal preventive maintenance policy for a cold standby system based on semi-Markov theory. European Journal of Operational Research, 2014, 232(2): 405−411 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2013.07.020 [18] Wang J Y, Ye J M. A new repair model and its optimization for cold standby system. Operational Research, 2022, 22(1): 105−122 doi: 10.1007/s12351-020-00545-x [19] 陈童, 谢经伟, 狄鹏, 尹东亮. 考虑两种失效竞争的多状态冷贮备系统可靠性模型. 航空学报, 2019, 40(3): 110−125Chen Tong, Xie Jing-Wei, Di Peng, Yin Dong-Liang. Reliability analysis of multi-state cold standby system with two competing failures. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(3): 110−125 [20] 曹晋华, 程侃. 两部件热贮备系统的可靠性分析. 应用数学学报, 1980, 3(2): 147−160Chao Jin-Hua, Cheng Kan. Reliability analysis of two - component thermal storage system. Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica, 1980, 3(2): 147−160 [21] Patowary M, Panda G, Deka B C. Reliability modeling of microgrid system using hybrid methods in hot standby mode. IEEE Systems Journal, 2019, 13(3): 3111−3119 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2925453 [22] Huang W, Loman J, Song T. A reliability model of a warm standby configuration with two identical sets of units. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2015, 133: 237−245 [23] Ma X Y, Liu B, Yang L, Peng R, Zhang X D. Reliability analysis and condition-based maintenance optimization for a warm standby cooling system. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2020, 193: Article No. 106588 [24] 尹东亮, 胡涛, 陈童. 考虑维修优先权的多状态温贮备系统可靠性模型. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(11): 2029−2036 doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2017.0718Yin Dong-Liang, Hu Tao, Chen Tong. Reliability analysis for multi-state warm standby system with repair priority. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(11): 2029−2036 doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2017.0718 [25] 刘宝亮, 温艳清, 丰月姣. 修理设备和开关不完全可靠的温贮备可修系统的可靠性. 运筹与管理, 2018, 27(10): 113−117Liu Bao-Liang, Wen Yan-Qing, Feng Yue-Jiao. Reliability for warm standby repairable system with unreliable server and switching failure. Operations Research and Management Science, 2018, 27(10): 113−117 [26] Kuo C C, Ke J C. Comparative analysis of standby systems with unreliable server and switching failure. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2016, 145: 74−82 [27] Guo L, Gui W H. Statistical inference of the reliability for generalized exponential distribution under progressive type-II censoring schemes. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2018, 67(2): 470−480 doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2800039 [28] Wang K H, Liu Y C, Pearn W L. Cost benefit analysis of series systems with warm standby components and general repair time. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 2005, 61(2): 329−343 doi: 10.1007/s001860400385 -




 下载:
下载: