-
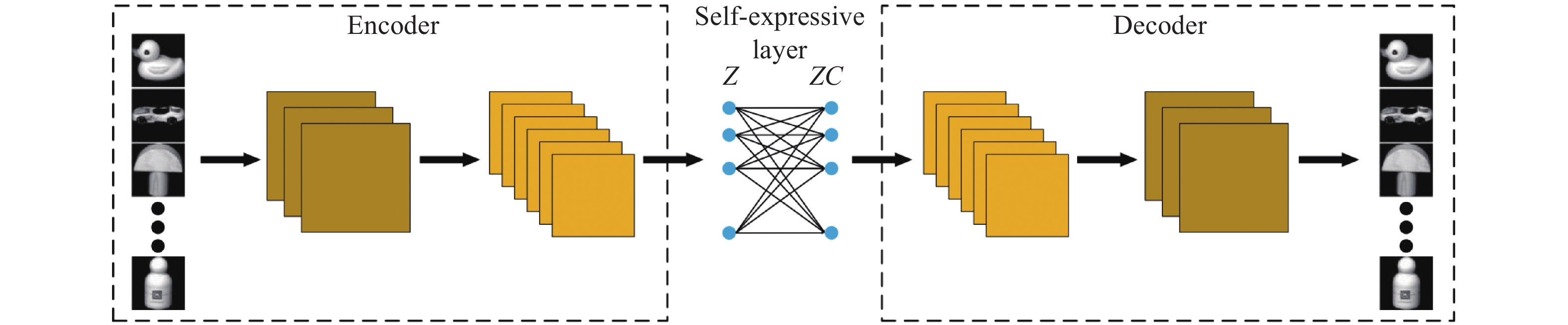
摘要: 子空间聚类(Subspace clustering)是一种当前较为流行的基于谱聚类的高维数据聚类框架. 近年来, 由于深度神经网络能够有效地挖掘出数据深层特征, 其研究倍受各国学者的关注. 深度子空间聚类旨在通过深度网络学习原始数据的低维特征表示, 计算出数据集的相似度矩阵, 然后利用谱聚类获得数据的最终聚类结果. 然而, 现实数据存在维度过高、数据结构复杂等问题, 如何获得更鲁棒的数据表示, 改善聚类性能, 仍是一个挑战. 因此, 本文提出基于自注意力对抗的深度子空间聚类算法(SAADSC). 利用自注意力对抗网络在自动编码器的特征学习中施加一个先验分布约束, 引导所学习的特征表示更具有鲁棒性, 从而提高聚类精度. 通过在多个数据集上的实验, 结果表明本文算法在精确率(ACC)、标准互信息(NMI)等指标上都优于目前最好的方法.Abstract: Subspace clustering is a popular spectral clustering framework for high-dimensional data. In recent years, deep neural networks are witnessed to effectively mine the features of data, which has attracted the attention from various fields. Deep subspace clustering aims to learn the low-dimensional feature representation of data via the deep network, and subsequently calculate the similarity matrix fed into spectral clustering framework for final clustering result. However, real data are often with too high dimensions and complex data structure. How to obtain a robust data representation and improve clustering performance remains a challenge. Therefore, this paper proposes a deep subspace clustering algorithm (SAADSC) based on the self-attention adversarial mechanism. Specifically, the self-attention adversarial network is developed to impose a priori distribution constraint in the feature learning of the autoencoder to guide the learned feature representation to be more robust, thereby improving clustering accuracy. Through the experiments on multiple datasets, the results show that the proposed algorithm in this paper is superior to the state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy rate (ACC) and standard mutual information (NMI).
-
表 1 数据集信息
Table 1 Information of the datasets
数据集 类别 数量 大小 MNIST 10 1000 28×28 FMNIST 10 1000 28×28 COIL-20 20 1440 32×32 YaleB 38 2432 48×32 USPS 10 9298 16×16 表 2 参数设置
Table 2 Parameter setting
数据集 $\lambda _1$ $\lambda _2$ $\lambda _3$ MNIST 1 0.5 10 FMNIST 1 0.0001 100 COIL-20 1 30 10 YaleB 1 0.06 24 USPS 1 0.1 10 表 3 网络结构参数
Table 3 Network structure parameter
数据集 卷积核大小 通道数 MNIST [5, 3, 3] [10, 20, 30] FMNIST [5, 3, 3, 3] [10, 20, 30, 40] COIL-20 [3] [15] YaleB [5, 3, 3] [64, 128, 256] USPS [5, 3, 3] [10, 20, 30] 表 4 5个数据集的实验结果
Table 4 Experimental results of five datasets
数据集 YaleB COIL-20 MNIST FMNIST USPS 度量方法 ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI DSC-L1 0.9667 0.9687 0.9314 0.9395 0.7280 0.7217 0.5769 0.6151 0.6984 0.6765 DSC-L2 0.9733 0.9703 0.9368 0.9408 0.7500 0.7319 0.5814 0.6133 0.7288 0.6963 DEC * * 0.6284 0.7789 0.8430 0.8000 0.5900 0.6010 0.7529 0.7408 DCN 0.4300 0.6300 0.1889 0.3039 0.7500 0.7487 0.5867 0.5940 0.7380 0.7691 StructAE 0.9720 0.9734 0.9327 0.9566 0.6570 0.6898 − − − − DASC 0.9856 0.9801 0.9639 0.9686 0.8040 0.7800 − − − − SAADSC 0.9897 0.9856 0.9750 0.9745 0.9540 0.9281 0.6318 0.6246 0.7850 0.8134 表 5 不同先验分布的实验结果
Table 5 Clustering results on different prior distributions
数据集 MNIST FMNIST USPS 度量方法 ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI 高斯分布 0.9540 0.9281 0.6318 0.6246 0.7850 0.8134 伯努利分布 0.9320 0.9043 0.6080 0.5990 0.7755 0.7917 确定性分布 0.8670 0.8362 0.5580 0.5790 0.7796 0.7914 表 6 SAADSC网络中不同模块的作用
Table 6 Ablation study on SAADSC
数据集 YaleB COIL-20 MNIST FMNIST USPS 度量方法 ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI Test1 0.9725 0.9672 0.9382 0.9493 0.8820 0.8604 0.6080 0.6110 0.7748 0.7838 Test2 0.0711 0.0961 0.4229 0.6263 0.6420 0.5940 0.5380 0.4917 0.6105 0.5510 Test3 0.0843 0.1222 0.6993 0.7855 0.6610 0.6763 0.6140 0.5922 0.3826 0.3851 Test4 0.9782 0.9702 0.9683 0.9741 0.9500 0.9275 0.6211 0.6143 0.7850 0.7986 DSC-L2 0.9733 0.9703 0.9368 0.9408 0.7500 0.7319 0.5814 0.6133 0.7288 0.6963 SAADSC 0.9897 0.9856 0.9750 0.9745 0.9540 0.9281 0.6318 0.6246 0.7850 0.8134 表 7 含有噪声的COIL-20聚类结果
Table 7 Clustering results on the noisy COIL-20
算法 SAADSC DSC-L1 DSC-L2 DASC 度量方法 ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI 无噪声 0.9750 0.9745 0.9314 0.9353 0.9368 0.9408 0.9639 0.9686 10%噪声 0.9590 0.9706 0.8751 0.8976 0.8714 0.9107 0.9021 0.9392 20%噪声 0.9111 0.9593 0.8179 0.8736 0.8286 0.8857 0.8607 0.9193 30%噪声 0.8708 0.9638 0.7989 0.8571 0.8072 0.8784 0.8357 0.9143 40%噪声 0.8569 0.9272 0.6786 0.7857 0.7250 0.8187 0.7805 0.8753 表 8 含有噪声的USPS聚类结果
Table 8 Clustering results on the noisy USPS
算法 SAADSC DSC-L1 DSC-L2 度量方法 ACC NMI ACC NMI ACC NMI 无噪声 0.7850 0.8134 0.6984 0.6765 0.7288 0.6963 10%噪声 0.7778 0.7971 0.6704 0.6428 0.6562 0.6628 20%噪声 0.7757 0.7901 0.6667 0.6158 0.6530 0.6429 30%噪声 0.7719 0.7844 0.6386 0.5987 0.6454 0.6394 40%噪声 0.7674 0.7750 0.6042 0.5752 0.6351 0.6164 -
[1] Aggarwal C C. An Introduction to Data Classification. Data Classification: Algorithms and Applications, 2014, 125(3): 142$-$147 [2] RMacQueen J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability. 1967, 1(14): 281−297 [3] Johnson S C. Hierarchical clustering schemes. Psychometrika, 1967, 32(3): 241-254. doi: 10.1007/BF02289588 [4] Ng A Y, Jordan M I, Weiss Y. "On spectral clustering: Analysis and an algorithm." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2002. [5] Basri R, Jacobs D W. Lambertian reflectance and linear subspaces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(2): 218-233. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1177153 [6] Agrawal R, Gehrke J, Gunopulos D, Raghavan P. Automatic subspace clustering of high dimensional data. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2005, 11(1): 5-33. doi: 10.1007/s10618-005-1396-1 [7] 王卫卫, 李小平, 冯象初, 王斯琪. 稀疏子空间聚类综述. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(8): 1373-1384.Wang Wei-Wei, Li Xiao-Ping, Feng Xiang-Chu, Wang Si-Qi. A survey on sparse subspace clustering. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(8): 1373-1384. [8] Bradley P S, Mangasarian O L. K-plane clustering. Journal of Global Optimization, 2000, 16(1): 23-32. doi: 10.1023/A:1008324625522 [9] Gear C W. Multibody grouping from motion images. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1998, 29(2): 133-150. doi: 10.1023/A:1008026310903 [10] Yang A Y, Rao S R, Ma Y. Robust statistical estimation and segmentation of multiple subspaces. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (CVPRW'06). IEEE, 2006. [11] Elhamifar E, Vidal R. Sparse subspace clustering. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2009: 2790−2797 [12] Liu G, Lin Z, Yu Y. Robust subspace segmentation by low-rank representation. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10). 2010: 663−670 [13] Luo D, Nie F, Ding C, Huang H. Multi-subspace representation and discovery. Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011: 405−420 [14] Zhuang L, Gao H, Lin Z, Ma Y, Zhang X, Yu N. Non-negative low rank and sparse graph for semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2012: 2328−2335 [15] Kang Z, Zhao X, Peng C, Zhu H, Zhou J T, Peng X, et al. Partition level multiview subspace clustering. Neural Networks, 2020, 122: 279-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.10.010 [16] Kang Z, Pan H, Hoi S C, Xu Z. Robust graph learning from noisy data. IEEE Transaction on Cybernetics. 2019: 1833-1843. [17] 周林, 平西建, 徐森, 张涛. 基于谱聚类的聚类集成算法. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(8): 1335-1342. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01335Zhou Lin, Ping Xi-Jian, Xu Sen Zhang Tao al. Cluster Ensemble Based on Spectral Clustering. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(8): 1335-1342. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01335 [18] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533-536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [19] Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527-1554. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [20] Vincent P, Larochelle H, Bengio Y, Manzagol P A. Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. 2008: 1096−1103 [21] Bengio Y, Lamblin P, Popovici D, Larochelle H. Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2007: 153-160. [22] Masci J, Meier U, Ciresan D, Schmidhuber J. Stacked convolutional auto-encoders for hierarchical feature extraction. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, pages 52−59. Springer, 2011 [23] Yang B, Fu X, Sidiropoulos N D, Hong, M. Towards k-means-friendly spaces: Simultaneous deep learning and clustering. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning-Volume 70. JMLR. org, 2017: 3861−3870 [24] Shah S A, Koltun V. Deep continuous clustering [Online]. available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.01449, March 5, 2018. [25] Xie J, Girshick R, Farhadi A. Unsupervised deep embedding for clustering analysis. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). 2016: 478−487 [26] Ren Y, Wang N, Li M. and Xu Z. Deep density-based image clustering. Knowledge-Based Systems. 2020: 105841. [27] Ren Y, Hu K, Dai X, Pan L, Hoi S C, Xu Z. Semi-supervised deep embedded clustering. Neurocomputing. 2019, 325: 121-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.10.016 [28] Yang J, Parikh D, Batra D. Joint unsupervised learning of deep representations and image clusters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2016: 5147−5156 [29] Cho k, Van M B, Bahdanau D, Bengio Y. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder–decoder approaches. In: Proceedings of SSST-8, Eighth Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation, pages 103−111, Doha, Qatar, October 2014. ACL. [30] Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In: Proceedings of SSST-8 Eighth Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation, 2014. [31] Xiao T, Xu Y, Yang K, Zhang J, Peng Y, Zhang Z. The application of two-level attention models in deep convolutional neural network for fine-grained image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition(CVPR). 2015: 842−850 [32] Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A, Salakhudinov R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). 2015: 2048−2057 [33] Cheng J, Dong L, Lapata M. Long short-term memory-networks for machine reading. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2016 [34] Luong M T, Pham H, Manning C D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2015. [35] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). 2014: 2672−2680 [36] Chen X, Duan Y, Houthooft R, Schulman J, Sutskever I, Abbeel P. Infogan: Interpretable representation learning by information maximizing generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). 2016: 2172−2180 [37] Mukherjee S, Asnani H, Lin E, Kannan S. Clustergan: Latent space clustering in generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2019, 33: 4610−4617 [38] Makhzani A, Shlens J, Jaitly N, Goodfellow I, Frey B. Adversarial autoencoders [Online]. available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05644, May 25, 2015. [39] Ji P, Salzmann M, Li H. Efficient dense subspace clustering. IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. IEEE, 2014: 461−468 [40] Ji P, Zhang T, Li H, Salzmann M, Reid I. Deep subspace clustering networks. In: Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). 2017: 24−33 [41] 王坤峰, 苟超, 段艳杰, 林懿伦, 郑心湖, 王飞跃. 生成式对抗网络GAN的研究进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 321$-$332Wang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Duan Yan-Jie, Lin Yi-Lun, Zheng Xin-Hu, Wang Fei-Yue. Generative Adversarial Networks: The State of the Art and Beyond. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 321$-$332 [42] Kingma D P, Welling M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2014 [43] Zhang H, Goodfellow I, Metaxas D, Odena A. Self-attention generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, California, USA: PMLR 97, 2019. 7354−7363 [44] Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein GAN. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2017. 214−223 [45] Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, Dumoulin V, Courville A C. Improved training of wasserstein GANs. In: Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). 2017: 5767−5777 [46] Wu J, Huang Z, Thoma J, Acharya D, Van G L. Wasserstein divergence for gans. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). 2018: 653−668 [47] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278−2324 [48] Nene S A, Nayar S K, Murase H. Columbia object image library (coil-20). 1996. [49] Lee K C, Ho J, Kriegman D J. Acquiring linear subspaces for face recognition under variable lighting. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2005, 27(5): 684-698. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.92 [50] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2015. [51] Xu W, Liu X, Gong Y. Document clustering based on non-negative matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Informaion Retrieval. 2003: 267−273 [52] Peng X, Feng J, Xiao S, Yau W Y, Zhou J T, Yang S. Structured autoencoders for subspace clustering. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(10): 5076-5086. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2848470 [53] Zhou P, Hou Y, Feng J. Deep adversarial subspace clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2018: 1596−1604. -




 下载:
下载: