-
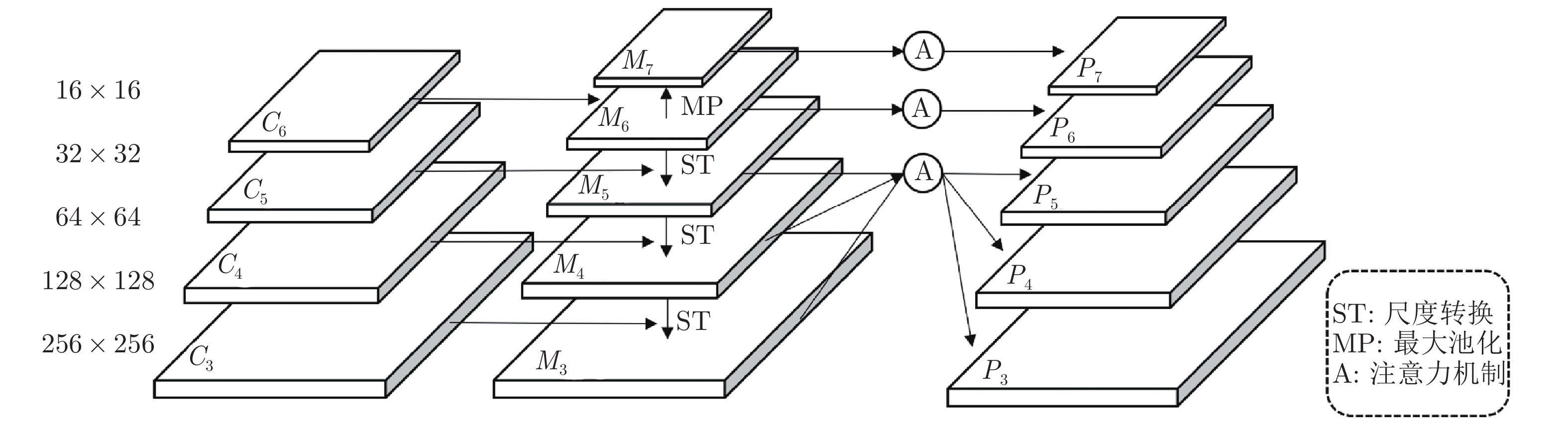
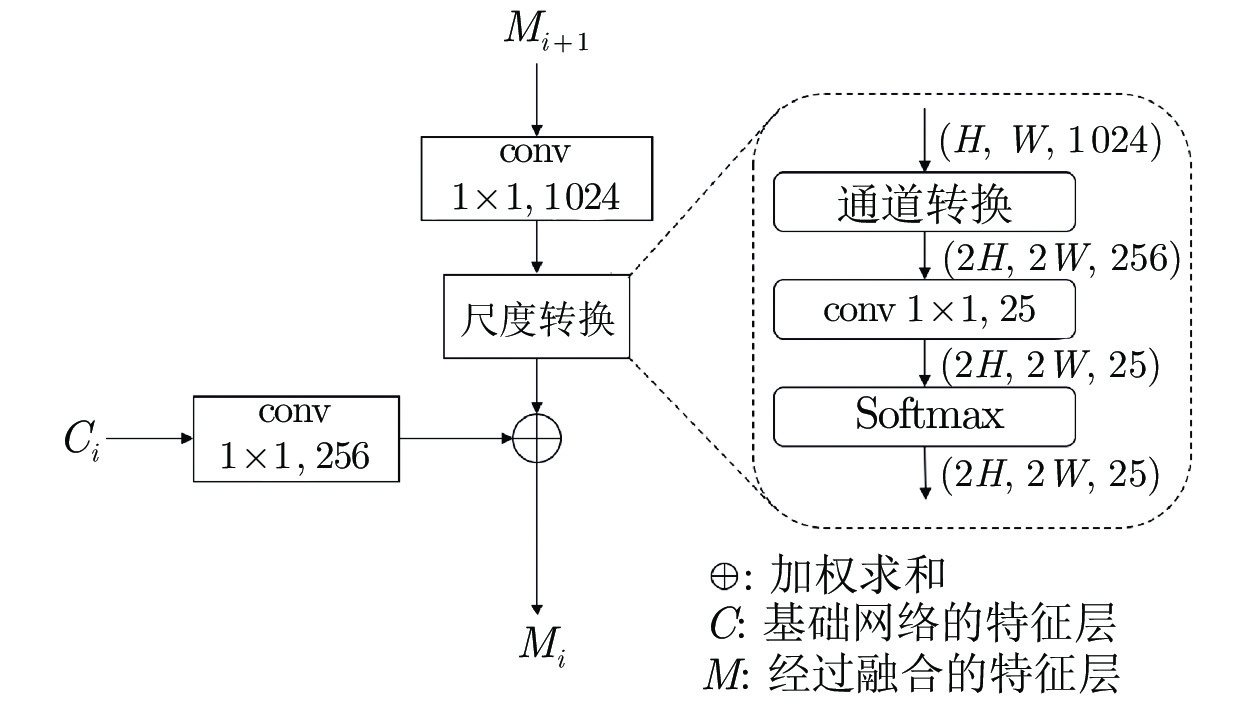
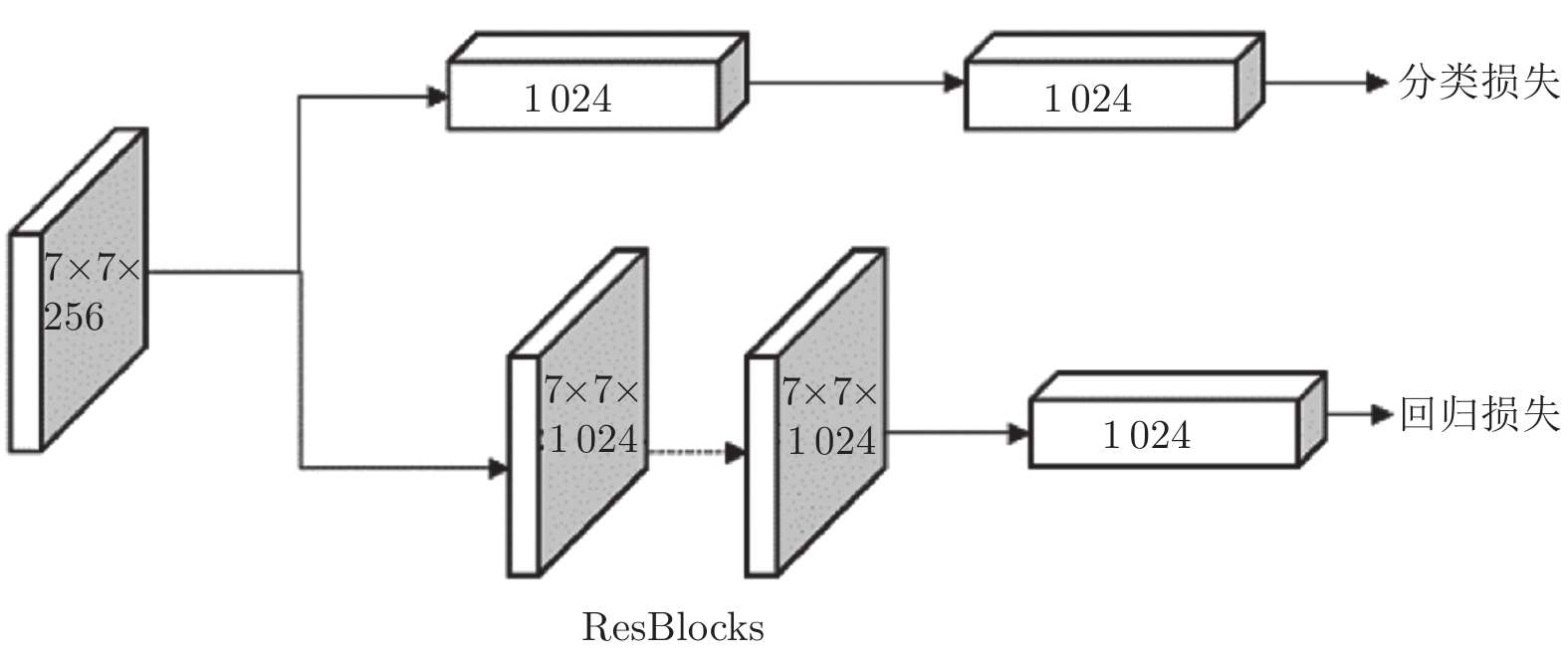
摘要: 遥感图像中的目标往往呈现出任意方向排列, 而常见的目标检测算法均采用水平框检测, 并不能满足这类场景的应用需求. 因此提出一种旋转框检测网络R2-FRCNN. 该网络利用粗调与细调两阶段实现旋转框检测, 粗调阶段将水平框转换为旋转框, 细调阶段进一步优化旋转框的定位. 针对遥感图像存在较多小目标的特点, 提出像素重组金字塔结构, 融合深浅层特征, 提升复杂背景下小目标的检测精度. 此外, 为了在金字塔各层中提取更加有效的特征信息, 在粗调阶段设计一种积分与面积插值法相结合的感兴趣区域特征提取方法, 同时在细调阶段设计旋转框区域特征提取方法. 最后在粗调和细调阶段均采用全连接层与卷积层相结合的预测分支, 并且利用SmoothLn作为网络的回归损失函数, 进一步提升算法性能. 提出的网络在大型遥感数据集DOTA上进行评估, 评估指标平均准确率达到0.7602. 对比实验表明了R2-FRCNN网络的有效性.Abstract: The objects in remote sensing images are often shown in any direction. The common algorithms of object detection adopt horizontal detection, which cannot fulfill the application requirements in remote sensing. Therefore, this paper proposes an object detector of rotated boxes named R2-FRCNN. The network adopts two stages of rough and refined adjustments to realize the detection of rotated boxes. The rough adjustment stage is used to transform the horizontal boxes into rotated boxes, and the refined adjustment stage is used to further optimize the position of the rotated boxes. In view of the fact that there are many small objects in remote sensing images, this paper proposes a pixel-recombination pyramid structure to improve the detection accuracy of small objects in a complex background by integrating deep and shallow features. In addition, in order to extract more effective feature information from each layer of the pyramid, this paper designs a region pooling method combining integration and area interpolation in the rough adjustment stage, and a region pooling method of rotated boxes in the refined adjustment stage. Finally, this paper adopts the prediction branch combining the fully connected layers and the convolutional layers, and takes the SmoothLn as the regression loss function of the network to further improve the performance of the algorithm. The network proposed in this paper is evaluated on a large remote sensing dataset DOTA, and the evaluation mean average precision reaches 0.7602. Comparative experiments show the effectiveness of R2-FRCNN modules.
-
表 1 不同方法在DOTA数据集的检测精度对比(%)
Table 1 Comparison of detection accuracy of different methods in DOTA (%)
类别 R2CNN[10] RT[12] CADNet[13] SCRDet[15] R3Det[16] GV[17] 本文方法 飞机 80.94 88.64 87.80 89.98 89.24 89.64 89.10 棒球场 65.67 78.52 82.40 80.65 80.81 85.00 81.22 桥梁 35.34 43.44 49.40 52.09 51.11 52.26 54.47 田径场 67.44 75.92 73.50 68.36 65.62 77.34 72.97 小型车辆 59.92 68.81 71.10 68.36 70.67 73.01 79.99 大型车辆 50.91 73.68 64.50 60.32 76.03 73.14 82.28 船舶 55.81 83.59 76.60 72.41 78.32 86.82 87.64 网球场 90.67 90.74 90.90 90.85 90.83 90.74 90.54 篮球场 66.92 77.27 79.20 87.94 84.89 79.02 87.31 储油罐 72.39 81.46 73.30 86.86 84.42 86.81 86.33 足球场 55.06 58.39 48.40 65.02 65.10 59.55 54.20 环形车道 52.23 53.54 60.90 66.68 57.18 70.91 68.18 港口 55.14 62.83 62.00 66.25 68.10 72.94 76.12 游泳池 53.35 58.93 67.00 68.24 68.98 70.86 70.83 直升机 48.22 47.67 62.20 65.21 60.88 57.32 59.19 平均准确率 60.67 69.56 69.90 72.61 72.81 75.02 76.02 表 2 R2-FRCNN模块分离检测结果
Table 2 R2-FRCNN module separates detection results
模块 R2-FRCNN 基准设置 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ 精细调整 √ √ √ √ √ √ IRoIPool √ √ √ √ √ RRoIPool √ √ √ √ PFPN √ √ √ SmoothLn √ √ ConvFc √ 平均准确率 (%) 69.52 73.62 73.99 74.31 74.97 75.13 75.96 表 3 不同水平框特征提取方法的实验结果
Table 3 Experimental results of feature extraction methods of different horizontal boxes
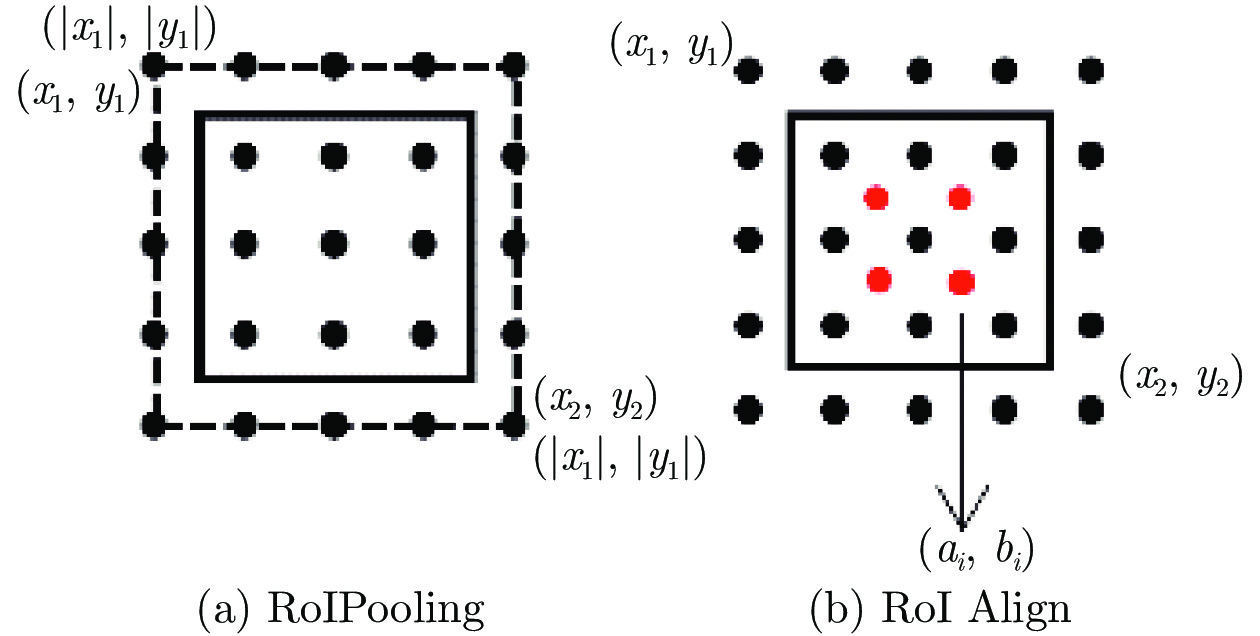
模块 平均准确率 + 精细调整 方法 RoIPooling RoI Align IRoIPool 平均准确率 (%) 71.21 73.62 73.99 表 4 不同旋转框特征提取方法的实验结果
Table 4 Experimental results of different featureextraction methods of rotated boxes
模块 平均准确率 + 精细调整 + IRoIPool 方法 RRoI A-Pooling RRoI Align RRoIPool 平均准确率 (%) 73.38 73.99 74.31 -
[1] Ya Y, Pan H, Jing Z L, Ren X G, Qiao L F. Fusion object detection of satellite imagery with arbitrary-oriented region convolutional neural network. Aerospace Systems, 2019, 2(2): 163-174 doi: 10.1007/s42401-019-00033-x [2] 王彦情, 马雷, 田原. 光学遥感图像舰船目标检测与识别综述. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(9): 1029-1039Wang Yan-Qing, Ma Lei, Tian Yuan. State-of-the-art of ship detection and recognition in optical remotely sensed imagery. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(9): 1029-1039 [3] 张慧, 王坤峰, 王飞跃. 深度学习在目标视觉检测中的应用进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305Zhang Hui, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Advances and perspec-tives on applications of deep learning in visual object detection. Acta Auto-matica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305 [4] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [5] Dai J F, Li Y, He K M, Sun J. R-FCN: Object detection via re-gion-based fully convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: 2016. 379−387 [6] Cai Z W, Vasconcelos N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6154−6162 [7] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 [8] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C Y, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: 2016. 21−37 [9] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K M, Dollár P. Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318-327 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 [10] Jiang Y Y, Zhu X Y, Wang X B, Yang S L, Li W, Wang H, et al. R2CNN: Rotational region CNN for orientation robust scene text detection [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706. 09579, June 29, 2017 [11] Ma J Q, Shao W Y, Ye H, Wang L, Wang H, Zheng Y B, et al. Ar-bitrary-oriented scene text detection via rotation proposals. IEEE Transac-tions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(11): 3111-3122 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2818020 [12] Ding J, Xue N, Long Y, Xia G S, Lu Q K. Learning RoI transformer for oriented object detection in aerial images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 2844−2853 [13] Zhang G J, Lu S J, Zhang W. CAD-Net: A context-aware detection network for objects in remote sensing imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 10015-10024 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2930982 [14] Azimi S M, Vig E, Bahmanyar R, Körner M, Reinartz P. To-wards multi-class object detection in unconstrained remote sensing imagery. In: Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Perth, Australia: 2019. 150−165 [15] Yang X, Yang J R, Yan J C, Zhang Y, Zhang T F, Guo Z, et al. SCRDet: Towards more robust detection for small, cluttered and rotated objects. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 8231−8240 [16] Yang X, Yan J C, Feng Z N, He T. R3DET: Refined single-stage detector with feature refinement for rotating object. In: Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Virtual Event: 2021. 3163−3171 [17] Xu Y C, Fu M T, Wang Q M, Wang Y K, Chen K, Xia G S, et al. Gliding vertex on the horizontal bounding box for multi-oriented object detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelli-gence, 2019, 43(4): 1452-1459 [18] Wei H R, Zhang Y, Cheng Z H, Li H, Wang H Q, Sun X. Oriented objects as pairs of middle lines [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.10694, December 23, 2019 [19] Li Y Y, Huang Q, Pei X, Jiao L C, Shang R H. RADet: Refine feature pyramid network and multi-layer atten-tion network for arbitrary-oriented ob-ject detection of remote sensing images. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(3): Article No. 389 doi: 10.3390/rs12030389 [20] Wang J W, Ding J, Guo H W, Cheng W S, Pan T, Yang W. Mask OBB: A semantic attention-based mask ori-ented bounding box representation for multi-category object detection in aerial images. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(24): Article No. 2930 doi: 10.3390/rs11242930 [21] Xia G S, Bai X, Ding J, Zhu Z, Belongie S, Luo J B, et al. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Com-puter Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3974−3983 [22] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [23] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, He K M, Hariharan B, Be-longie S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 936−944 [24] Yi J R, Wu P X, Metaxas D N. ASSD: Attentive single shot multibox detector. Computer Vision and Im-age Understanding, 2019, 189: Article No. 102827 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2019.102827 [25] Zeiler M D, Krishnan D, Taylor G W, Fergus R. Deconvolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 2528−2535 [26] Wang J Q, Chen K, Xu R, Liu Z W, Loy C C, Lin D. CARAFE: Content-aware reassembly of features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3007−3016 [27] Zhou P, Ni B B, Geng C, Hu J G, Xu Y. Scale-transferrable object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 528−537 [28] Bridle J S. Probabilistic interpretation of feedforward classification network outputs, with relationships to statistical pattern recognition. Neurocomputing: Algorithms, Architectures and Applications, 1990: 227−236 [29] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R. Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2980−2988 [30] Jiang B R, Luo R X, Mao J Y, Xiao T T, Jiang Y N. Acquisition of localization confidence for accurate object detection. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: 2018. 816−832 [31] Wu Y, Chen Y P, Yuan L, Liu Z C, Wang L J, Li H Z, et al. Rethinking classification and localization for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 10183− 10192 [32] Liu Y L, Jin L W. Deep matching prior network: Toward tighter multi-oriented text detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3454−3461 [33] Dai J F, Qi H Z, Xiong Y W, Li Y, Zhang G D, Hu H, et al. Deformable convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 764−773 -





 下载:
下载: