Lifetime Prediction for Stochastic Deteriorating Systems Based on the Last Exit Time
-
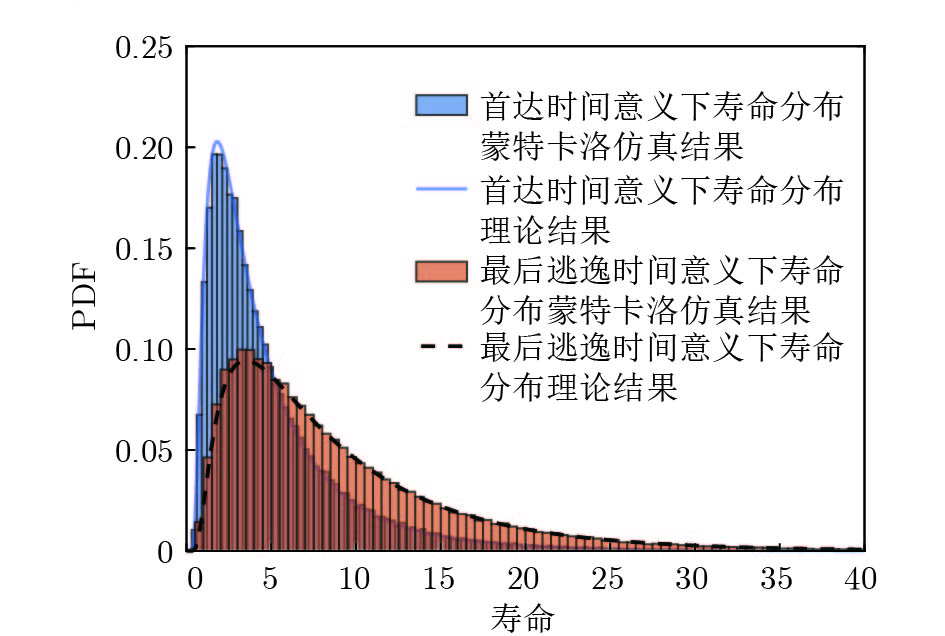
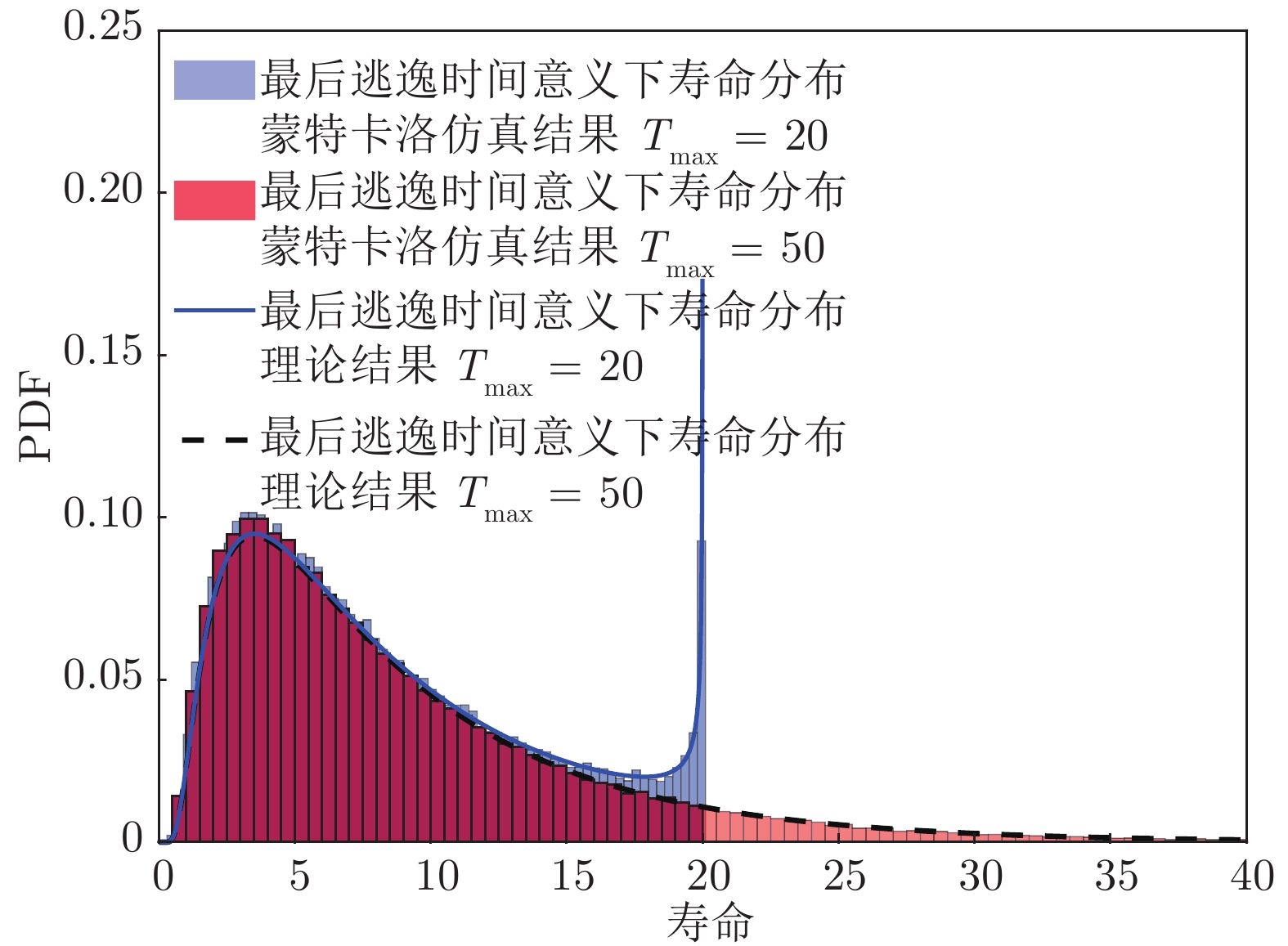
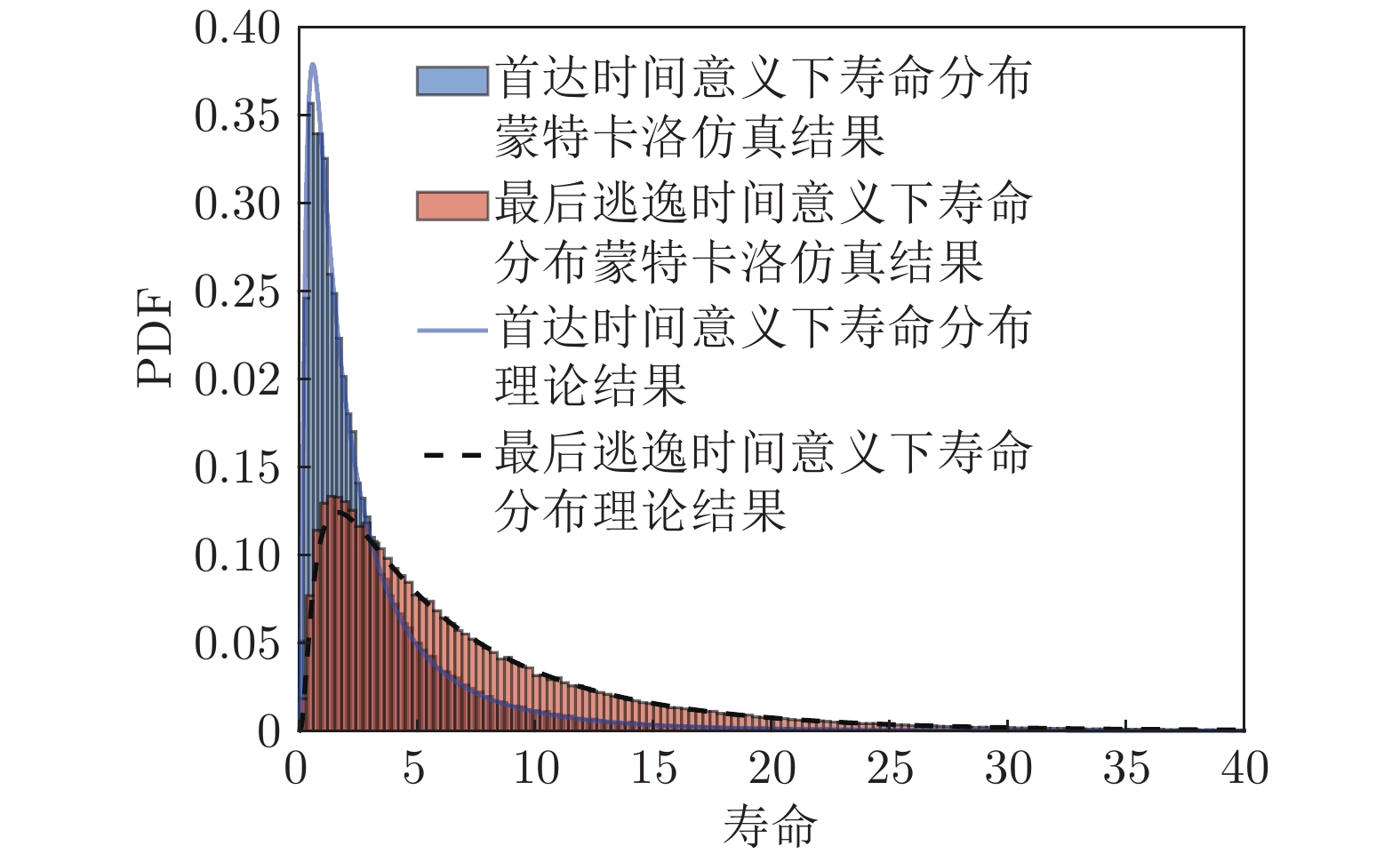
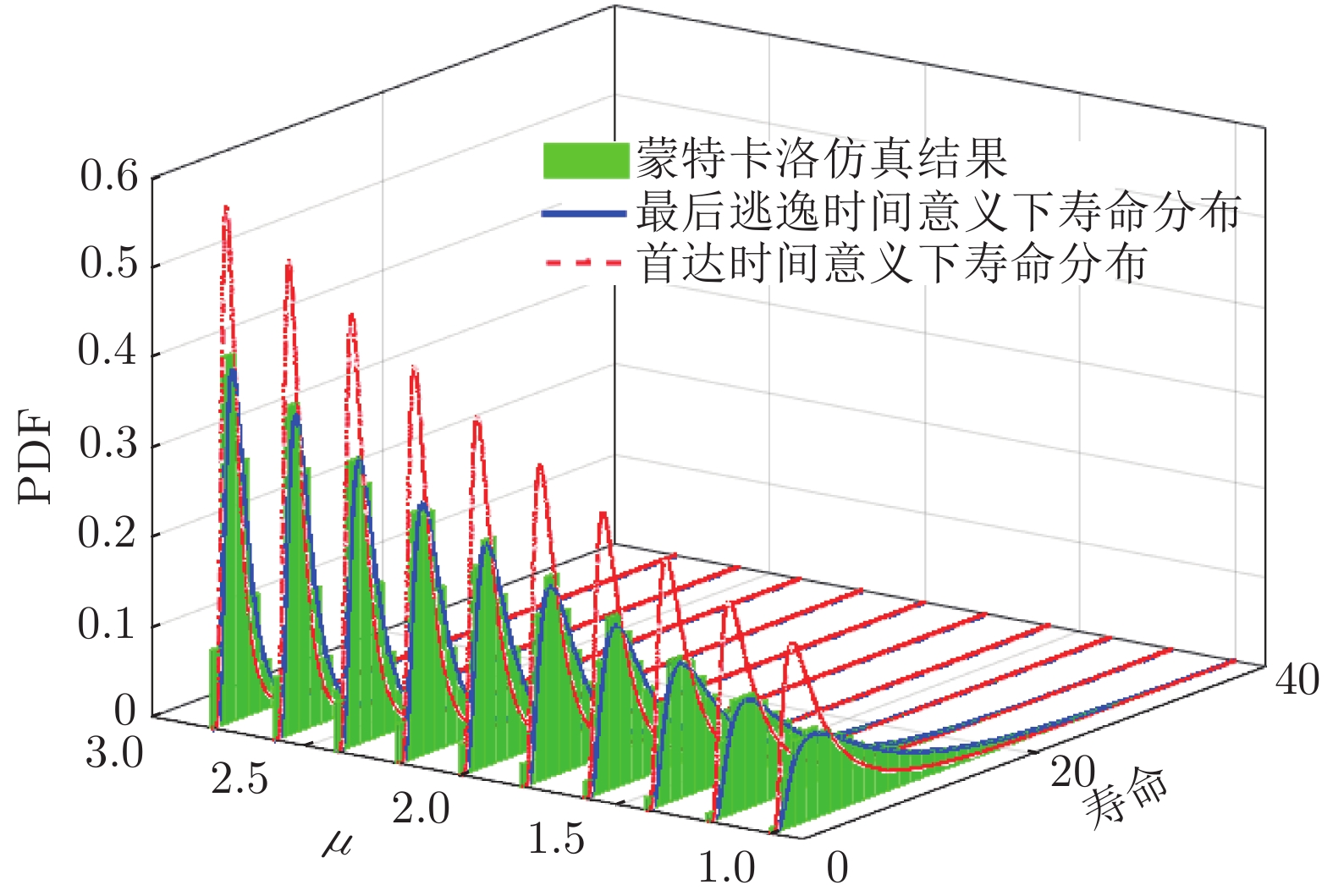
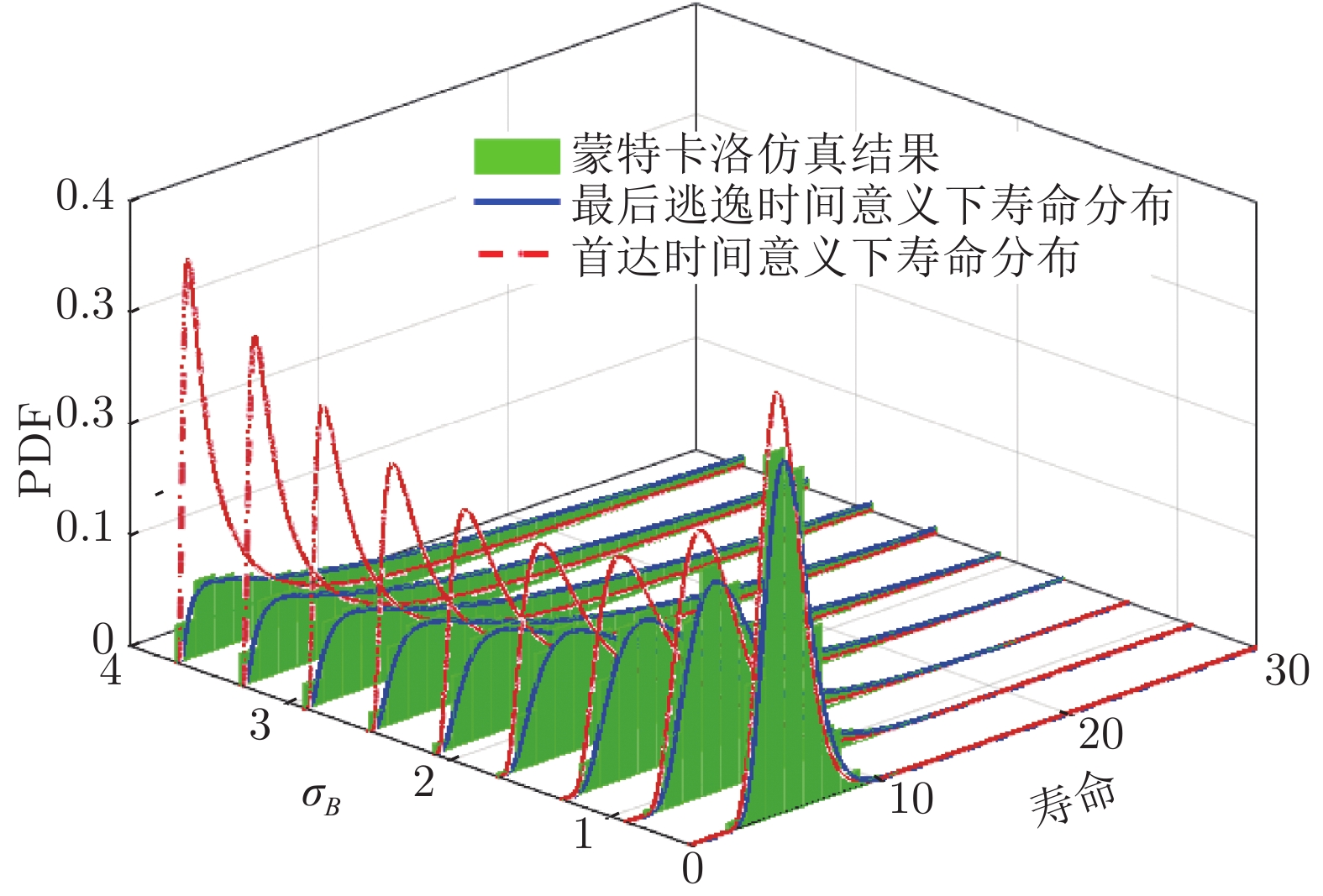
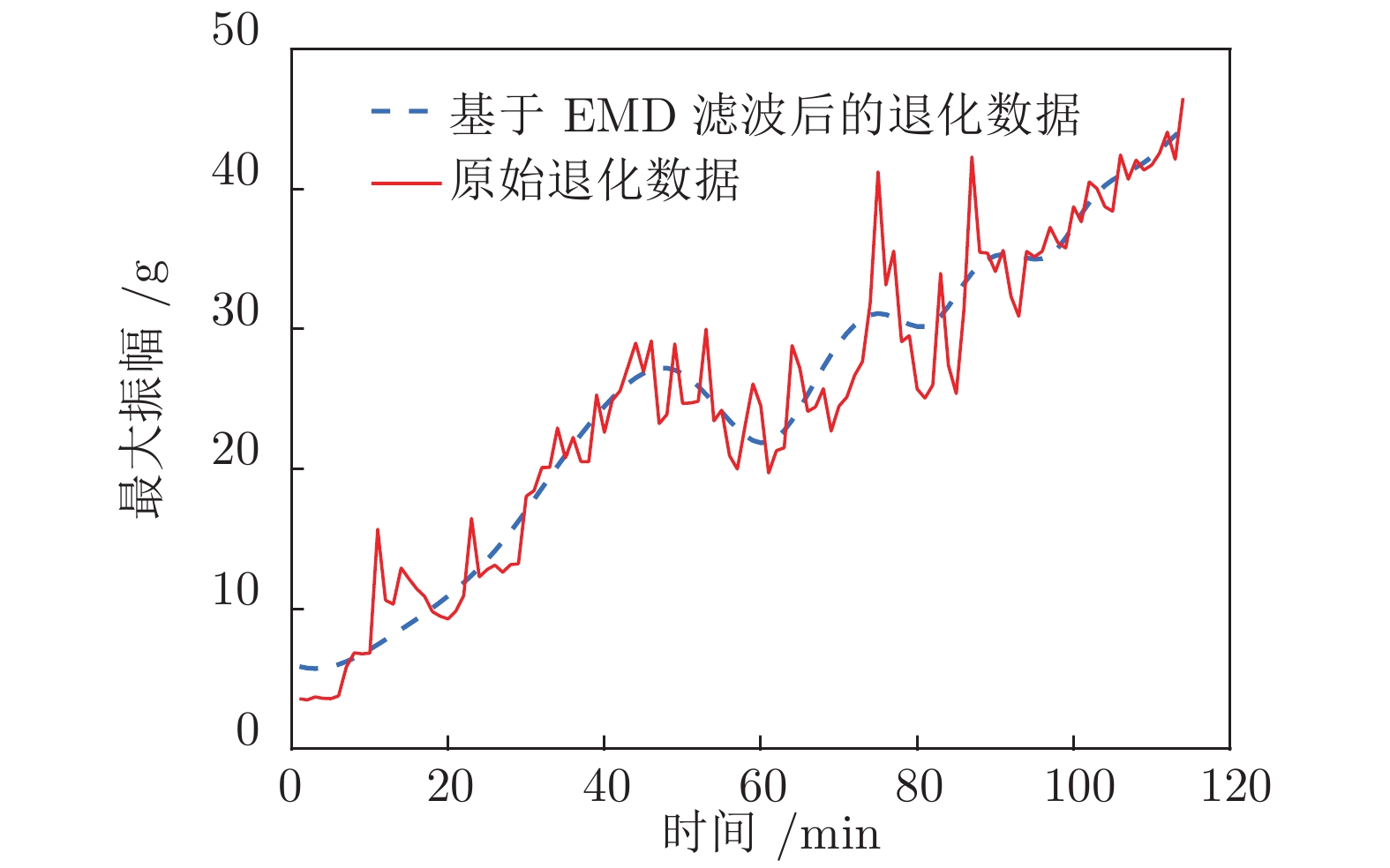
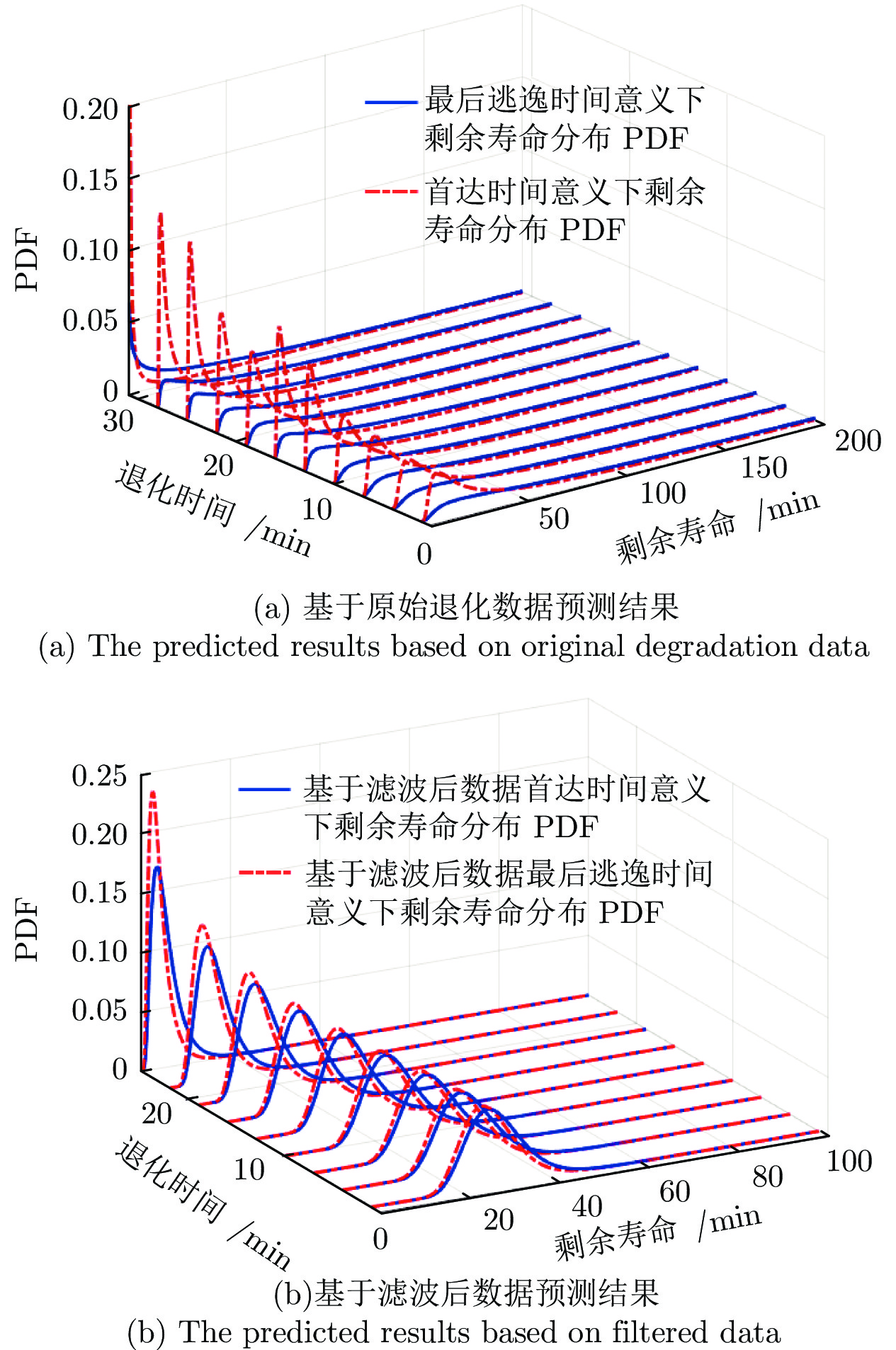
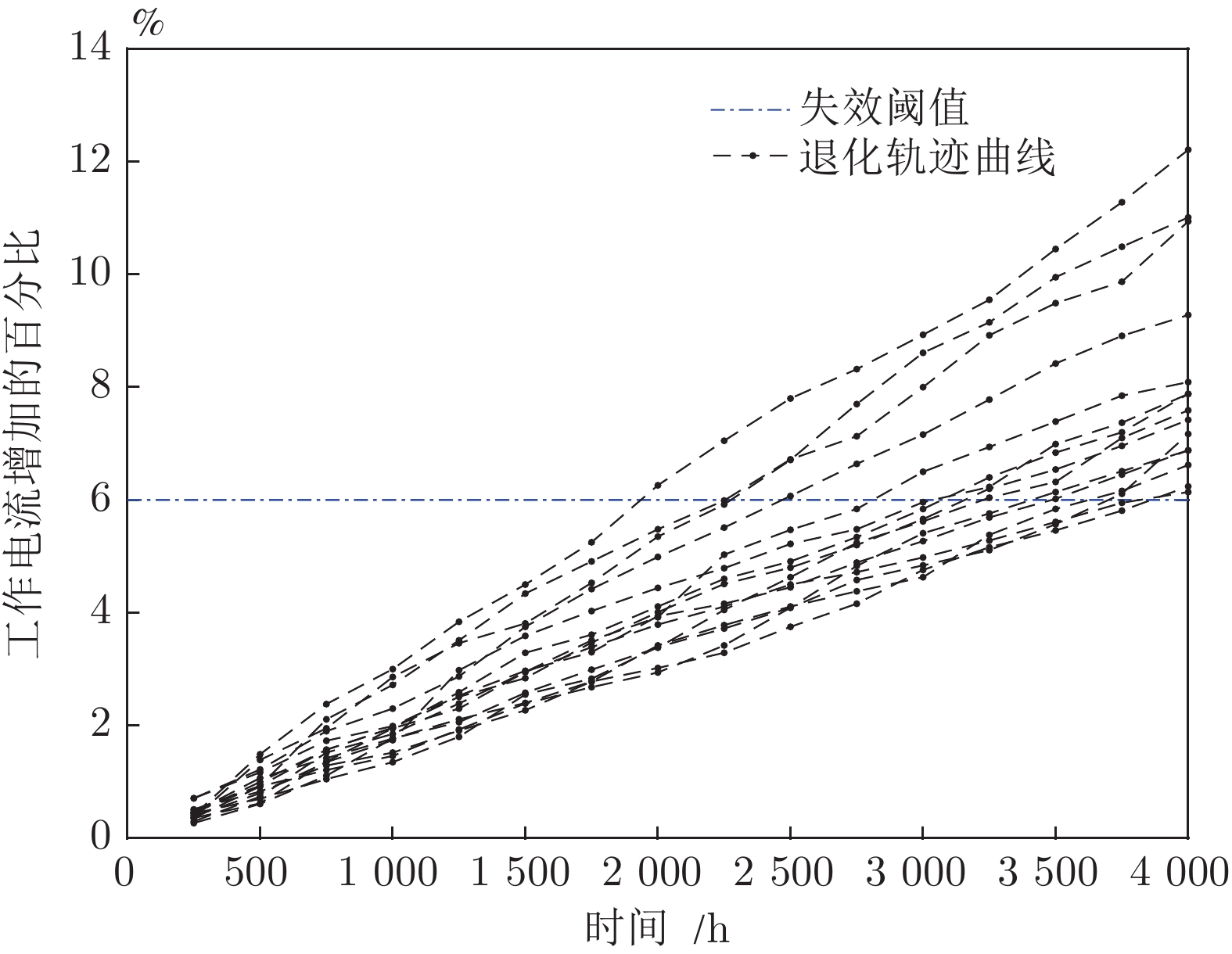
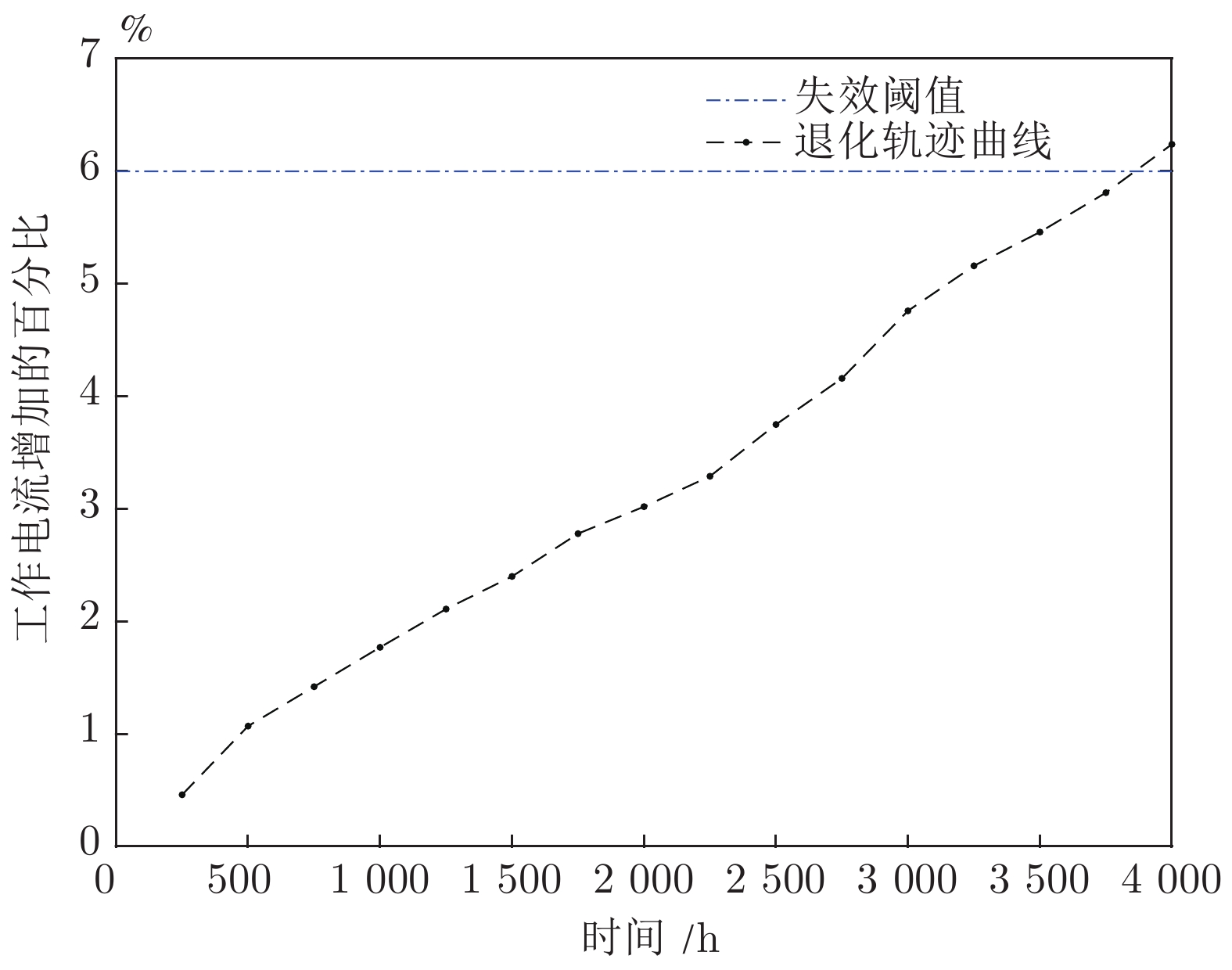
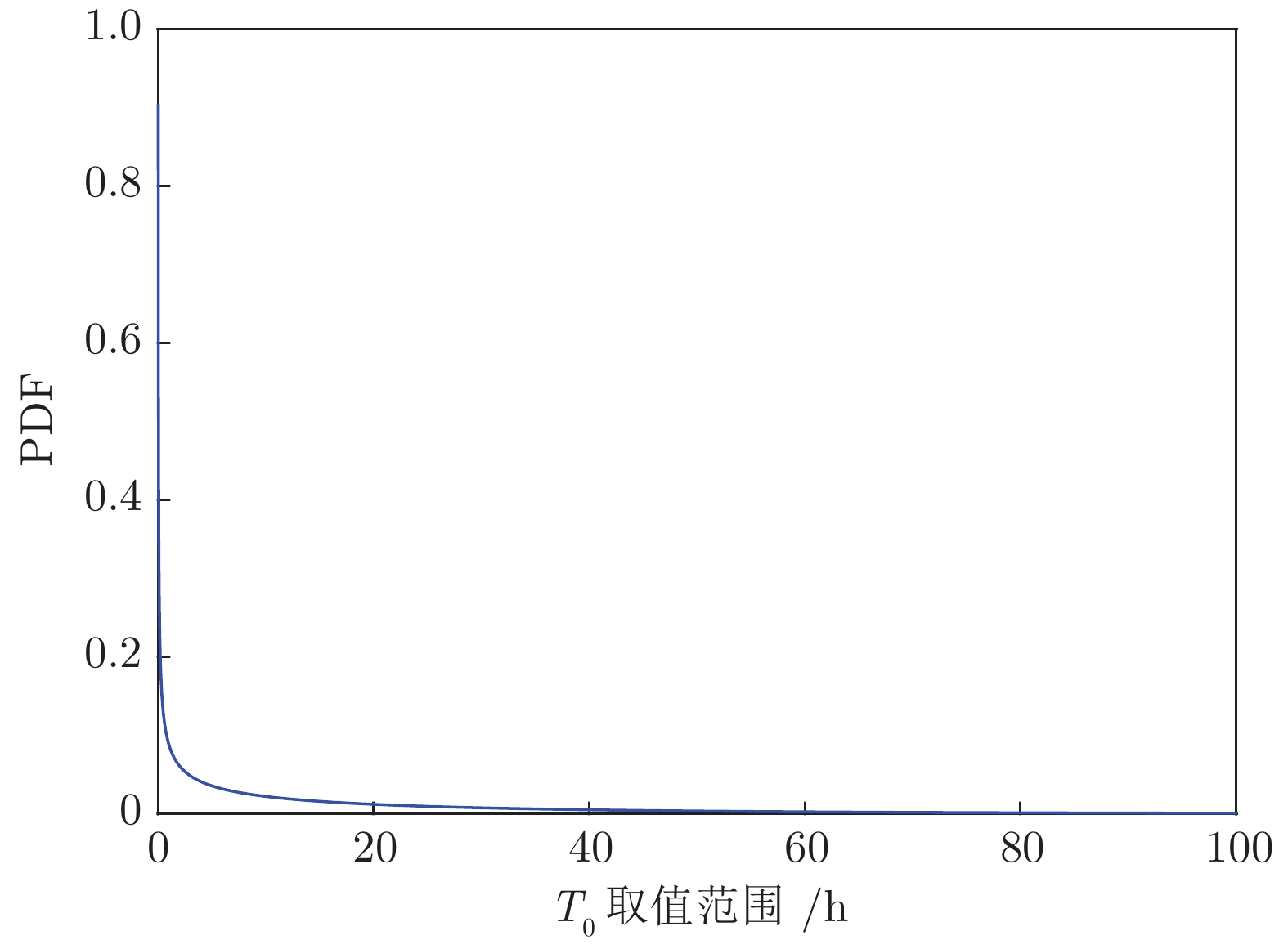
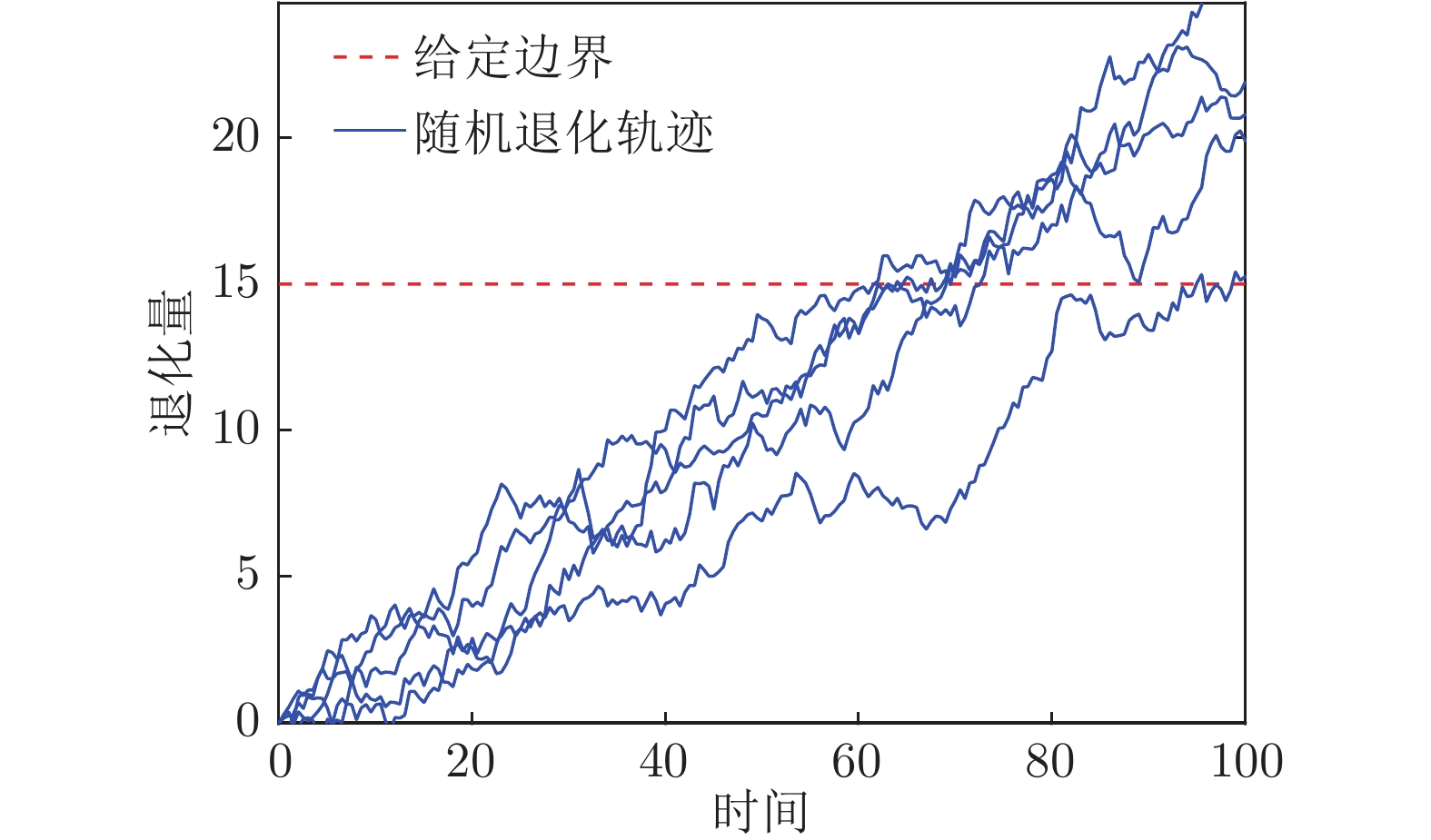
摘要: 现有基于随机退化过程建模的寿命预测研究中, 通常用退化过程的首达时间(First passage time, FPT)来定义寿命. 但是, 这种寿命定义较为保守, 可能会导致其明显小于设备实际寿命. 鉴于此, 基于最后逃逸时间(Last exit time, LET)的概念, 给出一种新的寿命与剩余寿命(Remaining useful life, RUL)定义方式. 在该新框架下, 提出一种基于最后逃逸时间的寿命预测方法, 推导得到最后逃逸时间下基于Wiener退化过程模型的寿命与剩余寿命表达形式, 讨论了该方法与传统首达时间下寿命预测方法之间的关系. 此外, 通过数值仿真验证了该方法的正确性, 并对模型参数进行了敏感性分析. 最后, 通过轴承以及激光器的实际退化数据说明了该方法的有效性、可行性以及潜在的工程应用价值.
-
关键词:
- 最后逃逸时间 /
- 可靠性 /
- 寿命预测 /
- Wiener 退化过程模型
Abstract: In existing studies of lifetime prediction based on stochastic process models, first passage time (FPT) is often used to determine the lifetime. However, this definition is generally conservative, and it may be obviously shorter than the actual lifetime. This paper provides a novel definition of lifetime and remaining useful life (RUL) based on the concept of the last exit time (LET). Under this framework, this paper proposes a lifetime prediction method based on the LET, the lifetime and RUL distributions under the concept of the LET have been derived based on the Wiener-process-based degradation model, and then the difference between the LET-based method and the FPT-based method is discussed carefully. Additionally, the proposed method is verified by numerical simulations, and the sensitive analysis is also completed. Finally, the practical degradation data of bearing and laser device are utilized to illustrate the validity, feasibility, and potential engineering value of the proposed method. -
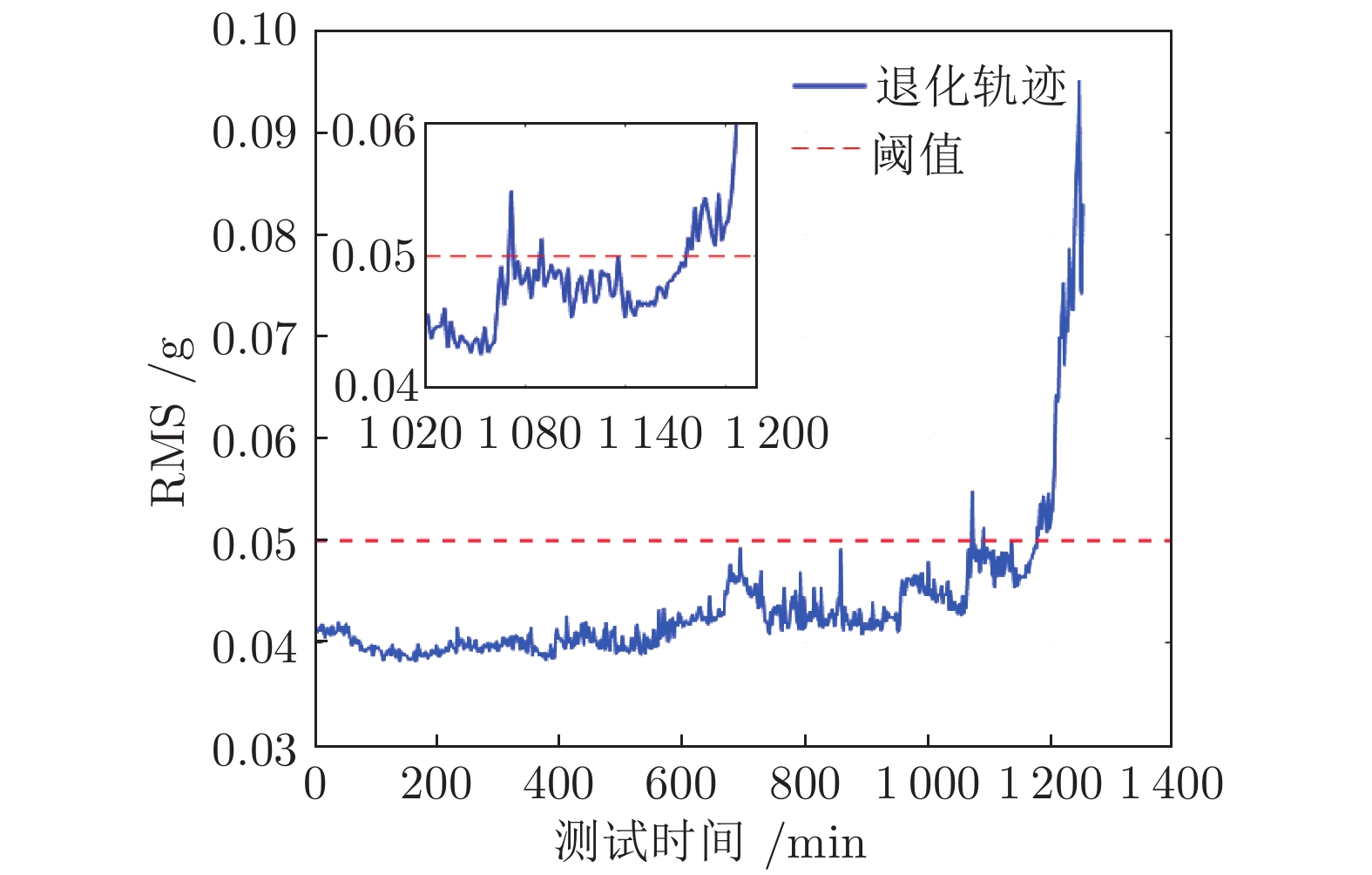
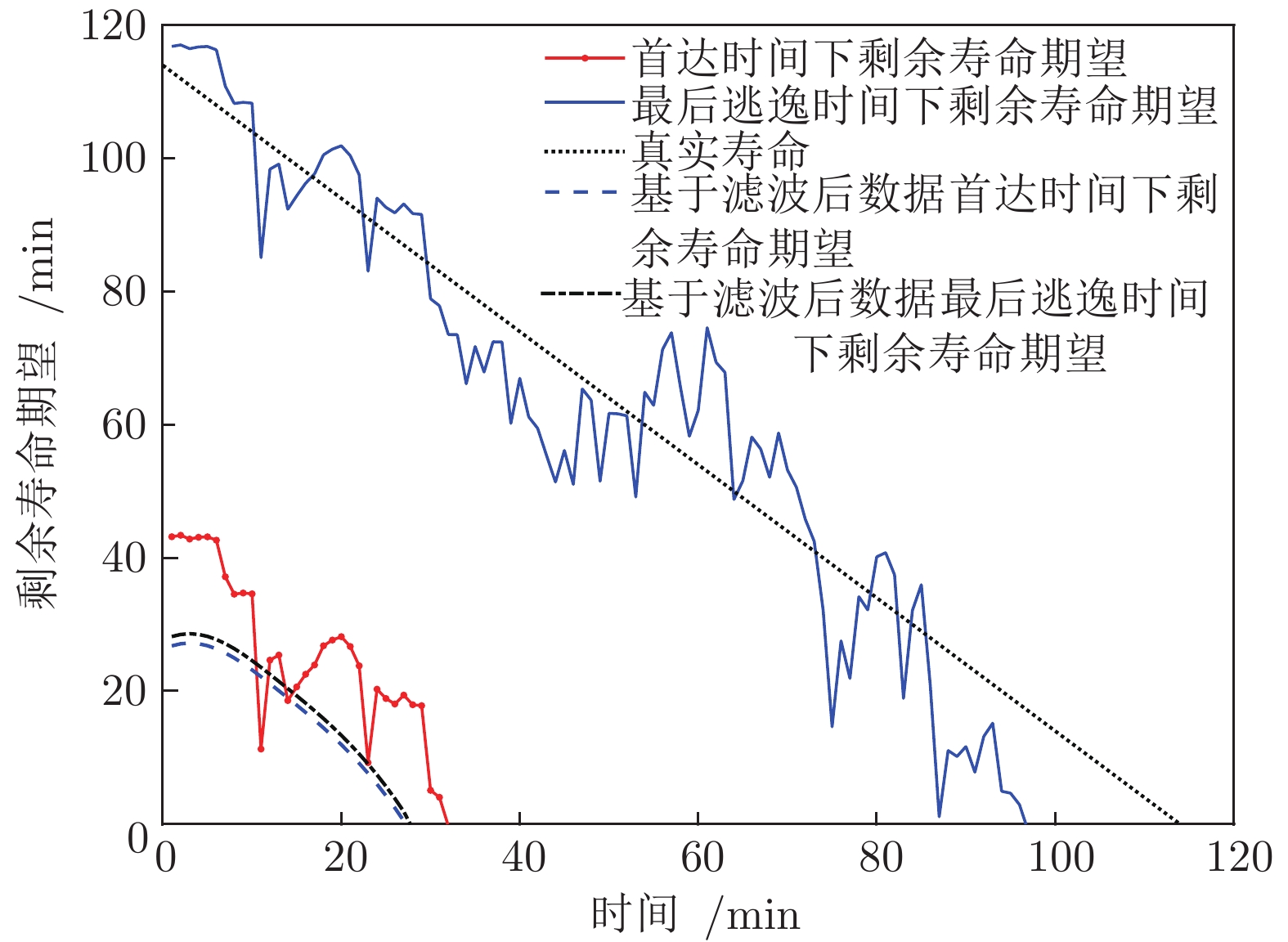
表 1 轴承真实寿命对比(min)
Table 1 Comparison of bearings' actual lifetime (min)
轴承数据 实际寿命 首达时间下寿命 最后逃逸时间下寿命 1_1 123 91 110 1_2 161 74 110 1_3 159 149 149 1_5 52 47 49 2_1 491 488 488 2_2 161 144 161 2_3 533 478 533 2_4 42 38 38 2_5 399 199 284 3_1 2538 2524 2529 3_3 371 352 362 3_4 1515 1456 1461 3_5 114 74 98 -
[1] Pecht M G. Prognostics and Health Management of Electronics. New Jersey, USA: John Wiley, 2008. [2] Zio E. Prognostics and health management of industrial equipment. Diagnostics and Prognostics of Engineering Systems: Methods and Techniques. Pennsylvania: IGI global, 2012. 333–356 [3] 周东华, 魏慕恒, 司小胜. 工业过程异常检测、寿命预测与维修决策的研究进展. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(6): 711−722Zhou Dong-Hua, Wei Mu-Heng, Si Xiao-Sheng. A survey on anomaly detection, life prediction and maintenance decision for industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(6): 711−722 [4] Omshi E M, Grall A, Shemehsavar S. A dynamic auto-adaptive predictive maintenance policy for degradation with unknown parameters. European Journal of Operational Research, 2020, 282(1): 81−92 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.08.050 [5] Lei Y G, Li N P, Guo L, Li N B, Yan T, Lin J. Machinery health prognostics: A systematic review from data acquisition to RUL prediction. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 799–836 [6] 郑建飞, 胡昌华, 司小胜, 张正新, 张鑫. 考虑不确定测量和个体差异的非线性随机退化系统剩余寿命估计. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(2): 259−270Zheng Jian-Fei, Hu Chang-Hua, Si Xiao-Sheng, Zhang Zheng-Xin, Zhang Xin. Remaining useful life estimation for nonlinear stochastic degrading systems with uncertain measurement and unit-to-unit variability. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(2): 259−270 [7] 司小胜, 胡昌华, 周东华. 带测量误差的非线性退化过程建模与剩余寿命估计. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(5): 530−541Si Xiao-Sheng, Hu Chang-Hua, Zhou Dong-Hua. Nonlinear degradation process modeling and remaining useful life estimation subject to measurement error. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(5): 530−541 [8] Si X S, Wang W B, Hu C H, Zhou D H. Remaining useful life estimation — A review on the statistical data driven approaches. European Journal of Operational Research, 2011, 213(1): 1−14 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2010.11.018 [9] Zhang Z X, Si X S, Hu C H, Lei Y G. Degradation data analysis and remaining useful life estimation: A review on wiener-process-based methods. European Journal of Operational Research, 2018, 271(3): 775−796 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2018.02.033 [10] Zhai Q Q, Ye Z S. RUL prediction of deteriorating products using an adaptive wiener process model. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(6): 2911−2921 doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2684821 [11] Wen Y, Wu J, Das D, Tseng T. Degradation modeling and RUL prediction using Wiener process subject to multiple change points and unit heterogeneity. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2018, 176: 113−124 [12] Wu S, Castro I T. Maintenance policy for a system with a weighted linear combination of degradation processes. European Journal of Operational Research, 2020, 280(1): 124−133 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.06.048 [13] Severson K A, Attia P M, Jin N, Perkins N, Jiang B B, Yang Z, et al. Data-driven prediction of battery cycle life before capacity degradation. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(5): 383−391 doi: 10.1038/s41560-019-0356-8 [14] 马静, 苑丹丹, 晁代宏, 陈淑英. 基于漂移布朗运动的光纤陀螺加速贮存寿命评估. 中国惯性技术学报, 2010, 18(06): 122−126Ma Jing, Yuan Dan-Dan, Chao Dai-Hong, Chen Shu-Ying. Accelerated storage life evaluation of FOG based on drift Brownian movement. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2010, 18(06): 122−126 [15] Wang B, Lei Y G, Li N P, Li N B. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful life of rolling element bearings. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(1): 401−412 doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2882682 [16] Doney R A. Last exit times for random walks. Stochastic Processes and Their Applications, 1989, 31(2): 321−331 doi: 10.1016/0304-4149(89)90096-3 [17] Li Y, Yin C, Zhou X. On the last exit times for spectrally negative Lévy processes. Journal of Applied Probability, 2017, 54(2): 474−489 doi: 10.1017/jpr.2017.12 [18] Sato K, Watanabe T. Last exit times for transient semistable processes. Annales De L Institut Henri Poincare-probabilites Et Statistiques, 2005, 41(5): 929−951 doi: 10.1016/j.anihpb.2004.09.003 [19] Salminen P. On the first hitting time and the last exit time for a Brownian motion to/from a moving boundary. Advances in Applied Probability, 1988, 20(2): 411−426 doi: 10.1017/S0001867800017043 [20] 雷亚国, 韩天宇, 王彪, 李乃鹏, 闫涛, 杨军. XJTU-SY滚动轴承加速寿命试验数据集解读. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(16): 1−6 doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.16.001Lei Ya-Guo, Han Tian-Yu, Wang Biao, Li Nai-Peng, Yan Tao, Yang Jun. XJTU-SY rolling element bearing accelerated life test datasets: A tutorial. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(16): 1−6 doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.16.001 [21] Wang H W, Xu T X, Mi Q L. Lifetime prediction based on Gamma processes from accelerated degradation data. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(1): 172−179 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2014.12.015 [22] Chen N, Ye Z S, Xiang Y S, Zhang L M. Condition-based maintenance using the inverse gaussian degradation model. European Journal of Operational Research, 2015, 243(1): 190−199 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2014.11.029 [23] Si X S, Wang W B, Hu C H, Zhou D H. Estimating remaining useful life with three-source variability in degradation modeling. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2014, 63(1): 167−190 doi: 10.1109/TR.2014.2299151 [24] Si X S, Zhang Z X, Hu C H. Data-driven Remaining Useful Life Prognosis Techniques: Stochastic Models, Methods and Applications. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2018. [25] Whitmore G A. Estimating degradation by a Wiener diffusion process subject to measurement error. Lifetime Data Analysis, 1995, 1(3): 307−319 doi: 10.1007/BF00985762 [26] Rai A, Upadhyay S H. A review on signal processing techniques utilized in the fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings. Tribology International, 2016, 96: 289−306 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2015.12.037 [27] Meeker W Q, Escobar L A. Statistical Methods for Reliability Data. New York, USA: John Wiley, 1988. -




 下载:
下载: