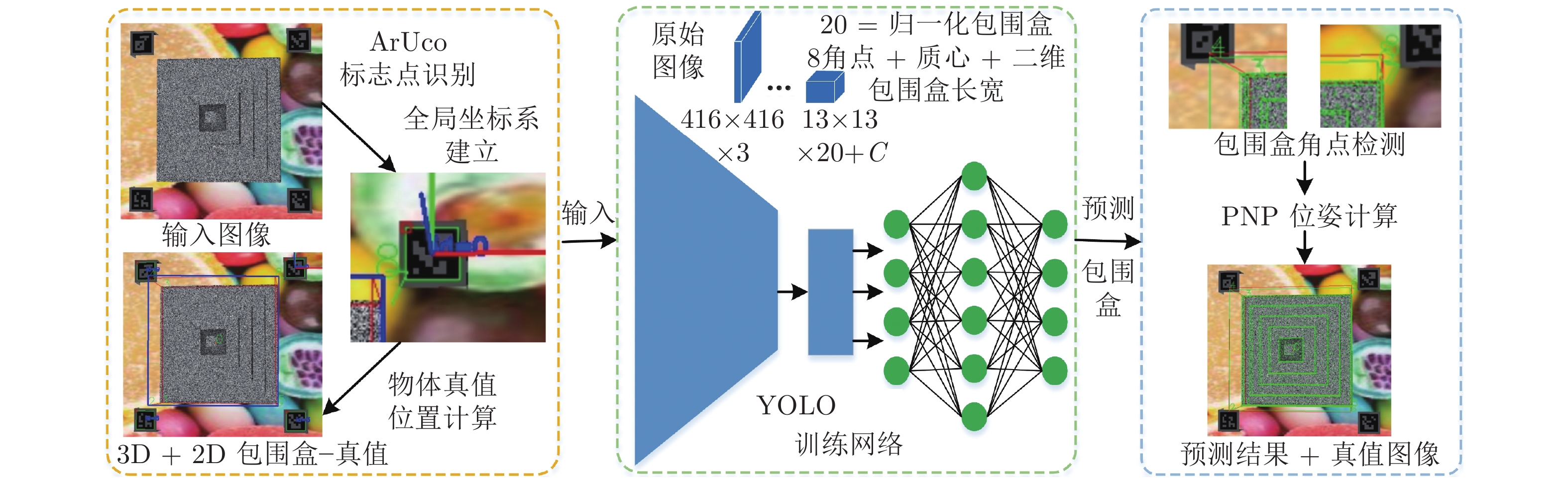
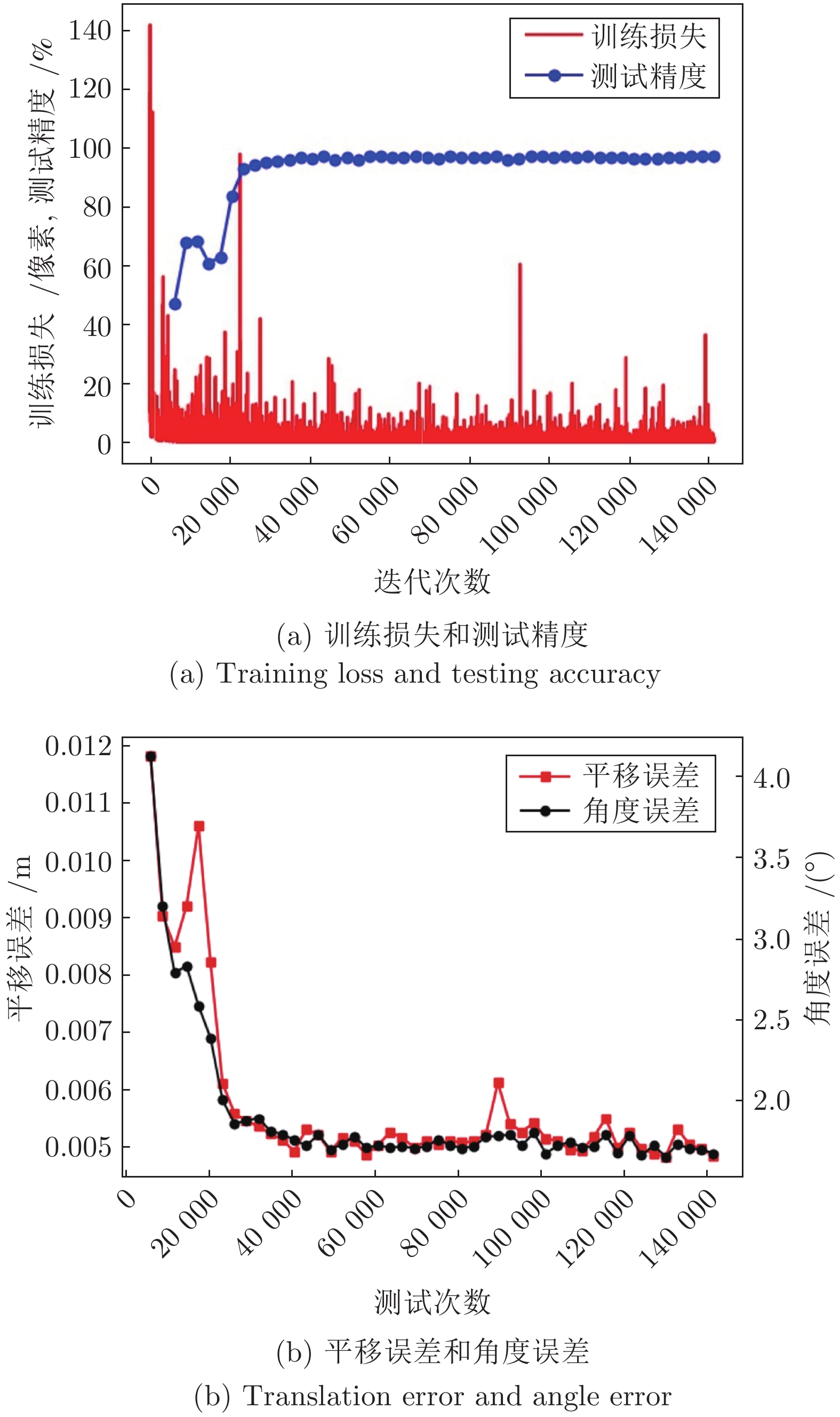
Viewpoint Planning for Robot Photogrammetry Based on Initial Pose Estimation via Deep Learning
-
摘要: 针对机器人摄影测量中离线规划受初始位姿标定影响的问题, 提出融合初始位姿估计的机器人摄影测量系统视点规划方法. 首先构建基于YOLO (You only look once) 的深度学习网络估计被测对象3D包围盒, 利用PNP (Perspective-N-point)算法快速求解对象姿态; 然后随机生成机器人无奇异无碰撞的视点, 基于相机成像的2D-3D正逆性映射, 根据深度原则计算每个视角下目标可见性矩阵; 最后, 引入熵权法, 以最小化重建信息熵为目标建立优化模型, 并基于旅行商问题(Travelling saleman problem, TSP)模型规划机器人路径. 结果表明, 利用深度学习估计的平移误差低于5 mm, 角度误差低于2°. 考虑熵权的视点规划方法提高了摄影测量质量, 融合深度学习初始姿态的摄影测量系统提高了重建效率. 利用本算法对典型零件进行摄影测量质量和效率的验证, 均获得优异的位姿估计和重建效果. 提出的算法适用于实际工程应用, 尤其是快速稀疏摄影重建, 促进了工业摄影测量速度与自动化程度提升.Abstract: Aiming at the problem that offline planning of robot photogrammetry is affected by the initial pose calibration, a viewpoint planning method of robot photogrammetry system incorporating initial pose estimation is proposed. First, we construct a YOLO (you only look once)-based deep learning network to estimate the 3D bounding box of the measured object, and utilize the PNP (perspective-N-point) algorithm to quickly solve the object pose; Second, we randomly generate non-singular and collision-free viewpoints. Based on the 2D-3D forward and inverse mapping of camera imaging, we calculate the target visibility matrix under each perspective according to the depth principle; Finally, the entropy-weighted method is introduced, the optimization model is established with the goal of minimizing the reconstruction information entropy afterward the robot path is planned based on the TSP (travelling salesman problem) model. The results show that the translation error estimated via deep learning is less than 5 mm, and the angular error is less than 2°. The viewpoint planning method considering entropy weight improves the quality of photogrammetry. Simultaneously, the reconstruction speed is increased. It obtains excellent pose estimation and reconstruction results when utilizing the algorithm to verify the photogrammetric quality and efficiency of more typical parts. The proposed algorithm is extendable to practical engineering applications, especially for rapid sparse photogrammetry, improving the speed and automation of industrial photogrammetry.
-
Key words:
- Photogrammetry /
- robot /
- deep learning /
- viewpoint planning /
- visibility matrix /
- entropy weight method
-
表 1 信息熵权有效性验证表
Table 1 Effectiveness test for entropy weight
对比实验 目标函数 优化的视
点数(个)点云数(个) A $x^*=\min \displaystyle \sum\limits_{i=1}^N { {w_i}{x_i} }$ 21 21509 B $x^*=\min \displaystyle \sum\limits_{i=1}^N { {x_i} }$ 20 18360 C $x^*=\min \displaystyle \sum\limits_{i=1}^N { {x_i} }$ 21 = 20 (B) +
1 (288)15344 表 2 综合权重和初始姿态下重建质量对比
Table 2 Comparison of reconstruction quality with weight and first-sight pose
有权重 无权重 有初始位姿约束 无初始位姿约束 有初始位姿约束 无初始位姿约束 视点索引 1, 13, 100, 113, 143,
149, 173, 189, 190,
196, 207, 269, 272, 28013, 100, 113, 143,
149, 173, 189, 190, 196,
207, 269, 272, 2801, 17, 28, 38, 45, 61,
66, 74, 89, 91, 92, 107,
113, 127, 185, 189,
207, 249, 269, 28014, 35, 43, 45, 56, 59,
73, 75, 89, 111, 127, 149,
162, 185, 189, 207, 249,
256, 274, 281三维点云 



点数量 10584 11451 7703 9571 注: 有初始位姿约束下,索引为1的视点需被约束保留. 表 3 利用深度学习位姿估计的摄影测量效率对比
Table 3 Comparison on effectiveness of photogrammetry with estimated pose using deep learning
点个数 重建时间 (s) 有初始位姿约束 无初始位姿约束 数量变化 (%) 无位姿估计 有位姿估计 效率提升 (%) 球体 15635 16489 5.18 157 133 15.29 柱体 10138 11503 11.87 182 155 14.84 凹台 11472 12640 9.24 102 83 18.63 -
[1] 郑太雄, 黄帅, 李永福, 冯明驰. 基于视觉的三维重建关键技术研究综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(4): 631-652 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170502Zheng Tai-Xiong, Huang Shuai, Li Yong-Fu, Feng Ming-Chi. Key techniques for vision based 3D reconstruction: A review. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(4): 631-652 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170502 [2] 李杰, 李响, 许元铭, 杨绍杰, 孙可意. 工业人工智能及应用研究现状及展望. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2031-2044 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.200501Lee J, Li Xiang, Xu Yuan-Ming, Yang Shao-Jie, Sun Ke-Yi. Recent advances and prospects in industrial AI and applications. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2031-2044 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.200501 [3] 柴天佑. 工业人工智能发展方向. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2005-2012 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200796Chai Tian-You. Development directions of industrial artificial intelligence. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2005-2012 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200796 [4] Sims-Waterhouse D, Bointon P, Piano S, Leach R K. Experimental comparison of photogrammetry for additive manufactured parts with and without laser speckle projection. In: Proceedings of SPIE 10329, Optical Measurement Systems for Industrial Inspection X. Munich, Germany: SPIE, 2017. Article No. 103290W [5] 许杰, 蒋山平, 杨林华, 肖大舟, 张景川. 卫星结构件常压热变形的数字摄影测量. 光学 精密工程, 2012, 20(12): 2667-2673 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20122012.2667Xu Jie, Jiang Shan-Ping, Yang Lin-Hua, Xiao Da-Zhou, Zhang Jing-Shang. Digital photogrammetry for thermal deformation of satellite structures in normal environment. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2012, 20(12): 2667-2673 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20122012.2667 [6] Filion A, Joubair A, Tahan A S, Bonev I A. Robot calibration using a portable photogrammetry system. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2018, 49: 77-87 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2017.05.004 [7] Kinnell P, Rymer T, Hodgson J, Justham L, Jackson M. Autonomous metrology for robot mounted 3D vision systems. CIRP Annals, 2017, 66(1): 483-486 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2017.04.069 [8] Kwon H, Na M, Song J B. Rescan strategy for time efficient view and path planning in automated inspection system. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2019, 20(10): 1747-1756 doi: 10.1007/s12541-019-00186-x [9] Raffaeli R, Mengoni M, Germani M, Mandorli F. Off-line view planning for the inspection of mechanical parts. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM), 2013, 7(1): 1-12 doi: 10.1007/s12008-012-0160-1 [10] Li L N, Xu D, Niu L K, Lan Y, Xiong X Y. A path planning method for a surface inspection system based on two-dimensional laser profile scanner. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2019, 16(4): Article No. 1729881419862463 [11] Alsadik B, Gerke M, Vosselman G. Visibility analysis of point cloud in close range photogrammetry. In: Proceedings of the ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences. Riva del Garda, Italy: ISPRS, 2014. 9−16 [12] Tarbox G H, Gottschlich S N. Planning for complete sensor coverage in inspection. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 1995, 61(1): 84-111 doi: 10.1006/cviu.1995.1007 [13] Jing W, Polden J, Lin W, Shimada K. Sampling-based view planning for 3D visual coverage task with unmanned aerial vehicle. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Daejeon, South Korea: IEEE, 2016. 1808−1815 [14] Jing W, Polden J, Tao P Y, Goh C F, Lin W, Shimada K. Model-based coverage motion planning for industrial 3D shape inspection applications. In: Proceedings of the 13th IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE). Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2017. 1293−1300 [15] 姜涛, 程筱胜, 崔海华, 田威. 面向机器人位姿测量的大视场变焦测量方法. 光学学报, 2018, 38(8): Article No. 0815012Jiang Tao, Cheng Xiao-Sheng, Cui Hai-Hua, Tian Wei. Large field of view vision method for robot pose measurement based on zoom lens. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(8): Article No. 0815012 [16] Jiang T, Cheng X, Cui H, Li X. Combined shape measurement based on locating and tracking of an optical scanner. Journal of Instrumentation, 2019, 14(1): Article No. P01006 [17] Tekin B, Sinha S N, Fua P. Real-time seamless single shot 6D object pose prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 292−301 [18] Su H, Qi C R, Li Y Y, Guibas L J. Render for CNN: Viewpoint estimation in images using CNNs trained with rendered 3D model views. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2686−2694 [19] Tulsiani S, Malik J. Viewpoints and keypoints. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1510−1519 [20] Kendall A, Grimes M, Cipolla R. PoseNet: A convolutional network for real-time 6-DOF camera relocalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2938−2946 [21] Xiang Y, Schmidt T, Narayanan V, Fox D. PoseCNN: A convolutional neural network for 6D object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.00199, 2017. [22] Kehl W, Manhardt F, Tombari F, Ilic S, Navab N. SSD-6D: Making RGB-based 3D detection and 6D pose estimation great again. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1530−1538 [23] Rad M, Lepetit V. BB8: A scalable, accurate, robust to partial occlusion method for predicting the 3D poses of challenging objects without using depth. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 3848−3856 [24] Carpin S, Pillonetto G. Motion planning using adaptive random walks. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2005, 21(1): 129-136 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2004.833790 [25] Cortsen J, Petersen H G. Advanced off-line simulation framework with deformation compensation for high speed machining with robot manipulators. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM). Kaohsiung, China: IEEE, 2012. 934−939 -





 下载:
下载: