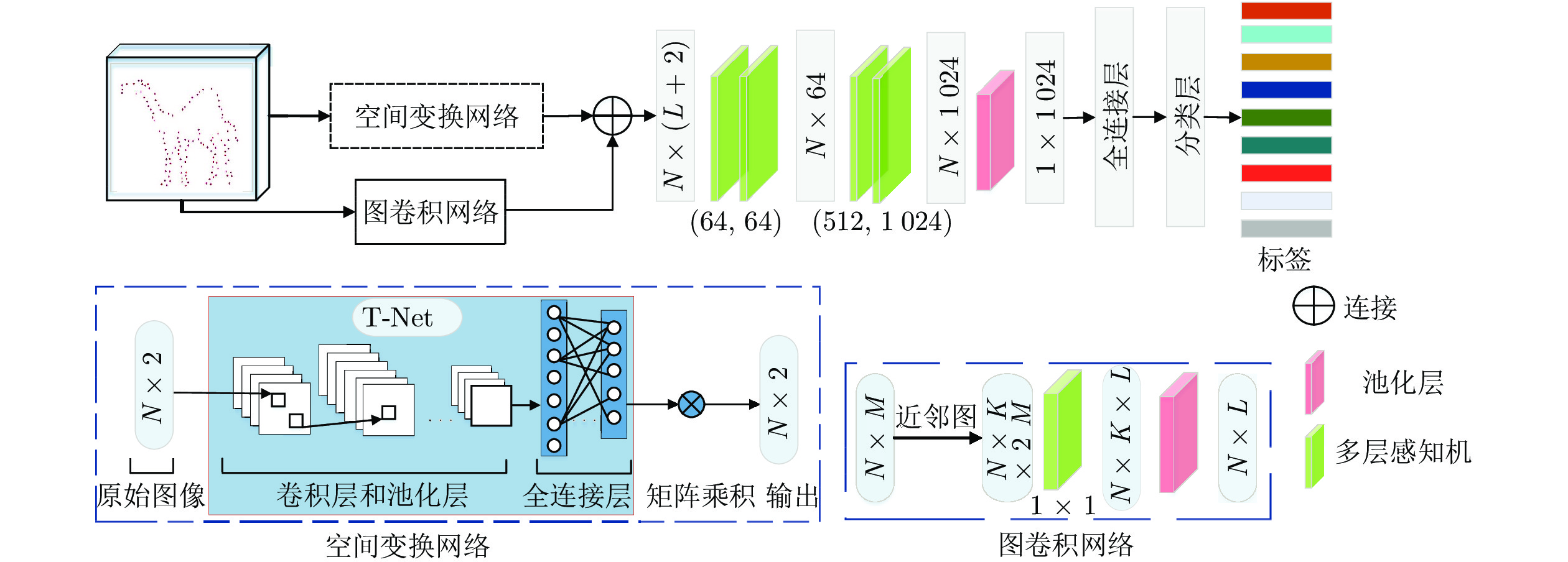
-
摘要: 人类具有很强的草图识别能力. 然而, 由于草图具有稀疏性和缺少细节的特点, 目前的深度学习模型在草图分类任务上仍然面临挑战. 目前的工作只是将草图看作灰度图像而忽略了不同草图类别间的形状表示差异. 提出一种端到端的手绘草图识别模型, 简称双模型融合网络, 它可以通过相互学习策略获取草图的纹理和形状信息. 具体地, 该模型由2个分支组成: 一个分支能够从图像表示(即原始草图)中自动提取纹理特征, 另一个分支能够从图形表示(即基于点的草图)中自动提取形状特征. 此外, 提出视觉注意一致性损失来度量2个分支之间视觉显著图的一致性, 这样可以保证2个分支关注相同的判别性区域. 最终将分类损失、类别一致性损失和视觉注意一致性损失结合完成双模型融合网络的优化. 在两个具有挑战性的数据集TU-Berlin数据集和Sketchy数据集上进行草图分类实验, 评估结果说明了双模型融合网络显著优于基准方法并达到最佳性能.Abstract: Human has a strong ability to recognize hand-drawn sketches. However, state-of-the-art models on sketch classification tasks remain challenging due to the sparse lines and limited details of sketches. Previous deep neural networks treat sketches as general images and ignore the shape representations for different categories. In this paper, we aim to address the problem by an end-to-end hand-drawn sketch recognition model, named dual-model fusion network, which can capture both texture and shape information of sketches via a mutual learning strategy. Specifically, our model is composed of two branches: one branch can automatically extract texture features from an image-based representation, i.e., the raw sketches, and the other branch can obtain shape information from a graph-based representation, i.e., point-based sketches. Moreover, we propose an attention consistency loss to measure the attention heat-map consistency between the two branches, which can simultaneously enable the same concentration of discriminative regions in the two representations. Finally, the proposed dual-model fusion network is optimized by combining classification loss, category consistency loss and attention consistency loss. We conduct extensive experiments on two challenging data sets, TU-Berlin and Sketchy, for sketch classification tasks. Our dual-model fusion network significantly outperforms baselines, and achieves the new state-of-the-art performance.
-
表 1 不同算法下在TU-Berlin数据集上分类准确率的比较 (%)
Table 1 Comparison of sketch classification accuracy with different algorithms on the TU-Berlin dataset (%)
方法 图像数量 8 40 64 72 Eitz (KNN hard) 22 33 36 38 Eitz (KNN soft) 26 39 43 44 Eitz (SVM hard) 32 48 53 53 Eitz (SVM soft) 33 50 55 55 FV size 16 39 56 61 62 FV size 16 (SP) 44 60 65 66 FV size 24 41 60 64 65 FV size 24 (SP) 43 62 67 68 SketchPoint 50 68 71 74 AlexNet 55 70 74 75 NIN 51 70 75 75 VGGNet 54 67 75 76 GoogLeNet 52 69 76 77 Sketch-a-Net 58 73 77 78 SketchNet 58 74 77 80 Cousin Network 59 75 78 80 Hybrid CNN 57 75 80 81 LN 58 76 82 82 SSDA 59 76 82 84 DMF-Net 60 77 85 86 表 2 在TU-Berlin数据集和Sketchy数据集上实现草图分类的网络结构分析 (%)
Table 2 Architecture design analysis for sketch classification on TU-Berlin and Sketchy (%)
方法 TU-Berlin Sketchy BN 82.71 85.75 BN + GC 83.93 86.49 BN + AC 84.12 87.07 BN + CC 84.75 87.36 BN + GC + CC 85.47 87.64 BN + AC + CC 85.51 87.71 BN + GC + AC + CC 86.12 88.01 表 3 利用双分支神经网络的草图分类准确率 (%)
Table 3 Classification accuracy results using two-branch neural networks (%)
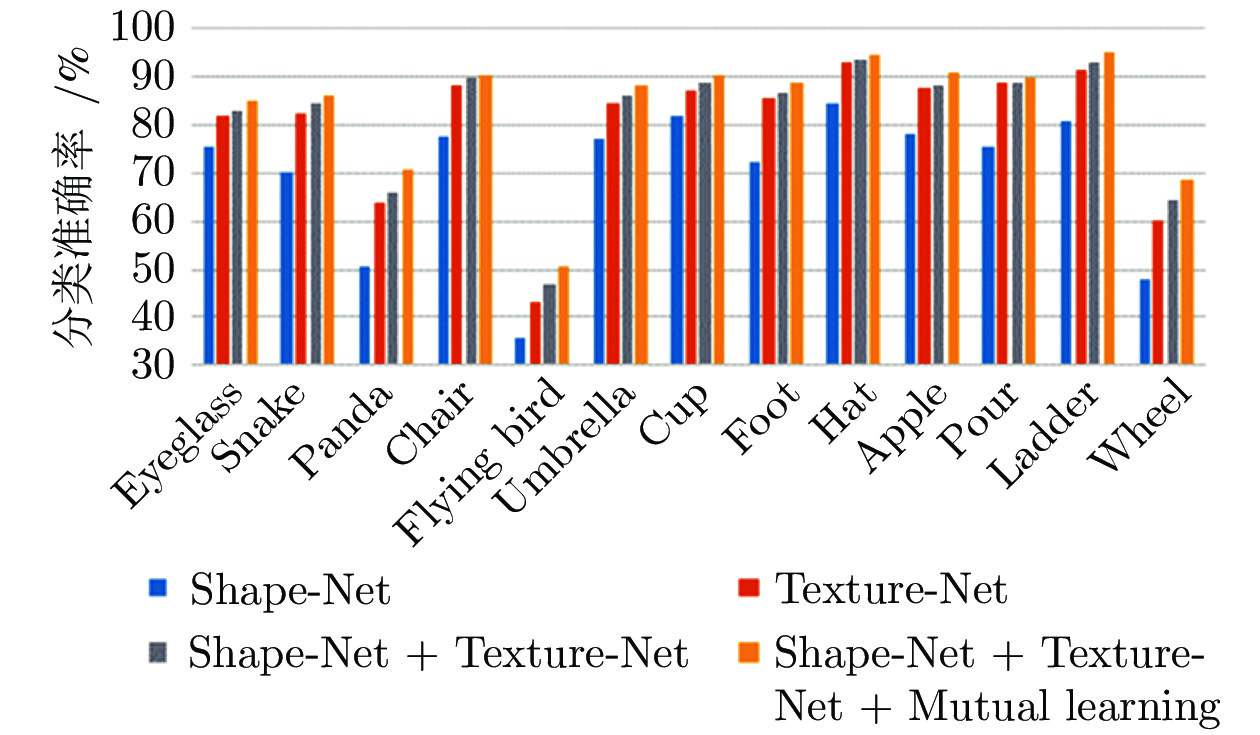
方法 TU-Berlin Sketchy 纹理网络 81.05 83.18 形状网络 70.87 70.43 基础网络 82.71 85.75 表 4 不同层的分类准确率结果 (%)
Table 4 Classification accuracy results using given feature levels (%)
方法 TU-Berlin Sketchy {4} 85.83 87.23 {3, 4} 86.01 87.87 {2, 3, 4} 86.06 87.93 {1, 2, 3, 4} 86.12 88.01 表 5 2种采样策略在TU-Berlin数据集的分类准确率 (%)
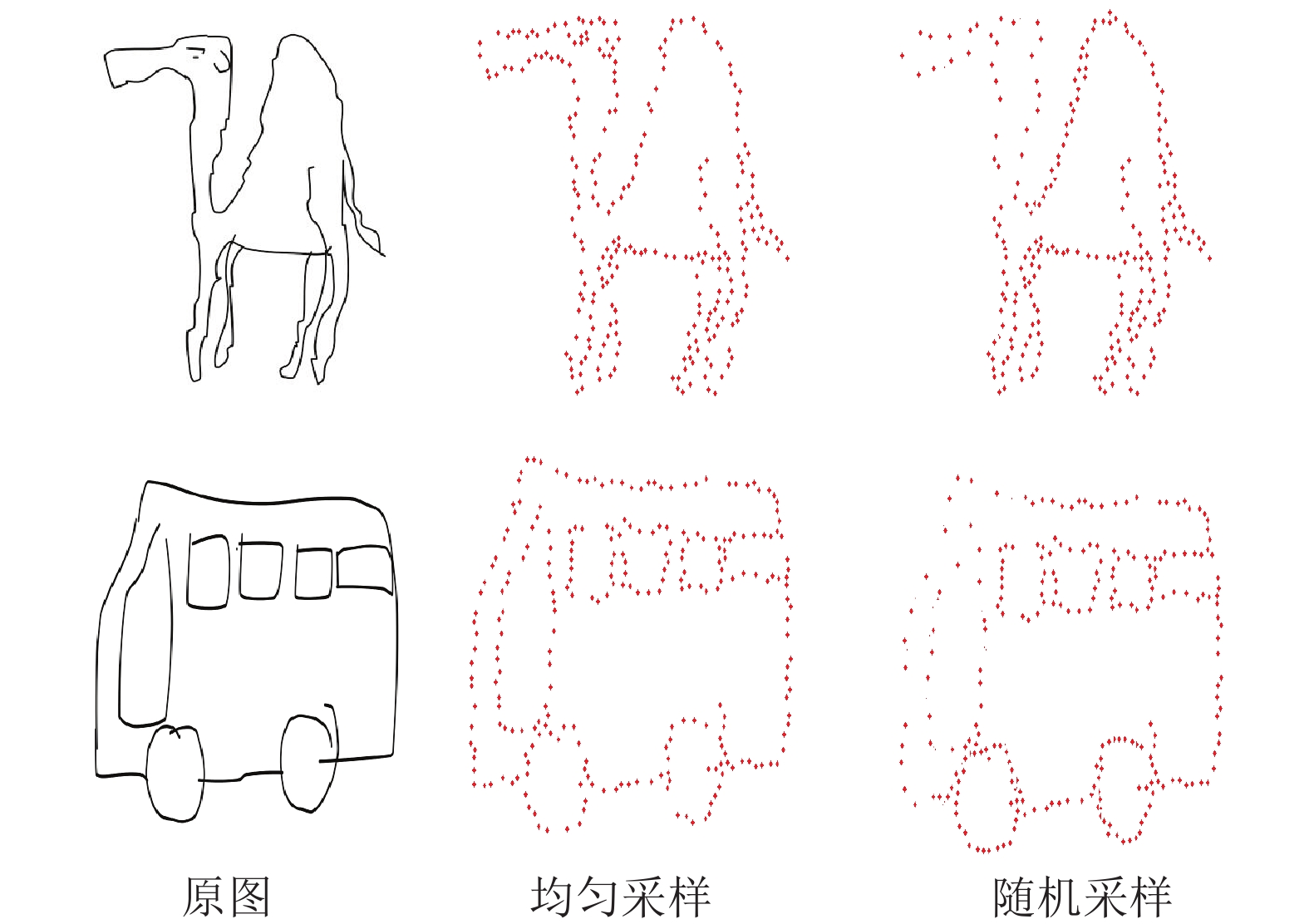
Table 5 Classification accuracy on TU-Berlin dataset using two sampling strategies (%)
方法 分类准确率 均匀采样 86.12 随机采样 86.09 表 6 不同采样点数对分类准确率的影响 (%)
Table 6 Effects of the point number for the classification accuracy (%)
数据集点数 TU-Berlin Sketchy 32 81.87 83.37 64 82.75 84.35 128 83.23 84.83 256 84.34 85.90 512 85.42 87.36 600 85.75 87.5 750 86.00 88.00 1024 86.12 88.01 1200 86.13 88.04 1300 86.08 88.01 -
[1] Huang F, Canny J F, Nichols J. Swire: Sketch-based user interface retrieval. In: Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Glasgow, UK: 2019. 1−10 [2] Dutta A, Akata Z. Semantically tied paired cycle consistency for zero-shot sketch-based image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: 2019. 5084−5093 [3] Muhammad U R, Yang Y X, Song Y Z, Xiang T, Hospedales T M. Learning deep sketch abstraction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake, USA: 2018. 8014−8023 [4] Li K, Pang K Y, Song J F, Song Y Z, Xiang T, Hospedales T M, et al. Universal sketch perceptual grouping. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: 2018. 593−609 [5] Chen W L, Hays J. SketchyGAN: Towards diverse and realistic sketch to image synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/ CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake, USA: 2018. 9416−9425 [6] Zhang M J, Zhang J, Chi Y, Li Y S, Wang N N, Gao X B. Cross-domain face sketch synthesis. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 98866-98874 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931012 [7] Pang K Y, Li K, Yang Y X, Zhang H G, Hospedales T M, Xiang T, et al. Generalising fine-grained sketch-based image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: 2019. 677−686 [8] 付晓, 沈远彤, 李宏伟, 程晓梅. 基于半监督编码生成对抗网络的图像分类模型. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(3): 531-539Fu Xiao, Shen Yuan-Tong, Li Hong-Wei, Cheng Xiao-Mei. A semi-supervised encoder generative adversarial networks model for image classification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 531-539 [9] Zheng Y, Yao H X, Sun X S, Zhang S P, Zhao S C, Porikli F. Sketch-specific data augmentation for freehand sketch recognition. Neurocomputing, 2021, 456: 528-539 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.124 [10] Hayat S, She K, Mateen M, Yu Y. Deep CNN-based features for hand-drawn sketch recognition via transfer learning approach. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2019, 10(9):438-448 [11] Zhu M, Chen C, Wang N, Tang J, Bao W X. Gradually focused fine-grained sketch-based image retrieval. PLoS One, 2019, 14(5): Article No. e0217168 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217168 [12] Jabal M F A, Rahim M S M, Othman N Z S, Jupri Z. A comparative study on extraction and recognition method of CAD data from CAD drawings. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Management and Engineering. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: 2009. 709−713 [13] Eitz M, Hays J, Alexa M. How do humans sketch objects? ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(4): Article No. 44 [14] Schneider R G, Tuytelaars T. Sketch classification and classification-driven analysis using fisher vectors. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, 33(6): Article No. 174 [15] Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, USA: 2005. 886−893 [16] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110 doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [17] Chang C C, Lin C J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2011, 2(3): Article No. 27 [18] Yu Q, Yang Y X, Liu F, Song Y Z, Xiang T, Hospedales T M. Sketch-a-Net: A deep neural network that beats humans. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017, 122(3): 411-425 doi: 10.1007/s11263-016-0932-3 [19] Bui T, Ribeiro L, Ponti M, Collomosse J. Sketching out the details: Sketch-based image retrieval using convolutional neural networks with multi-stage regression. Computers & Graphics, 2018, 71: 77-87 [20] 刘丽, 赵凌君, 郭承玉, 王亮, 汤俊. 图像纹理分类方法研究进展和展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(4): 584-607Liu Li, Zhao Ling-Jun, Guo Cheng-Yu, Wang Liang, Tang Jun. Texture classification: State-of-the-art methods and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(4): 584-607 [21] Xu P, Song Z Y, Yin Q Y, Song Y Z, Wang L. Deep self-supervised representation learning for free-hand sketch. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(4): 1503-1513 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.3003048 [22] Xu P, Huang Y Y, Yuan T T, Pang K Y, Song Y Z, Xiang T, et al. SketchMate: Deep hashing for million-scale human sketch retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake, USA: 2018. 8090−8098 [23] 林景栋, 吴欣怡, 柴毅, 尹宏鹏. 卷积神经网络结构优化综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 24-37Lin Jing-Dong, Wu Xin-Yi, Chai Yi, Yin Hong-Peng. Structure optimization of convolutional neural networks: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 24-37 [24] Liu Y J, Tang K, Joneja A. Sketch-based free-form shape modelling with a fast and stable numerical engine. Computers & Graphics, 2005, 29(5): 771-786 [25] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: 2016. 770−778 [26] Hua B S, Tran M K, Yeung S K. Pointwise convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake, USA: 2018. 984−993 [27] Wang Y F, Wu S H, Huang H, Cohen-Or D, Sorkine-Hornung O. Patch-based progressive 3D point set upsampling. In: Proce-edings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: 2019. 5951−5960 [28] Mikolajczyk K, Schmid C. An affine invariant interest point detector. In: Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Computer Vision. Copenhagen, Denmark: 2002. 128−142 [29] Wang C, Samari B, Siddiqi K. Local spectral graph convolution for point set feature learning. In: Proceedings of the 15th Euro-pean Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: 2018. 56−71 [30] Simonovsky M, Komodakis N. Dynamic edge-conditioned filters in convolutional neural networks on graphs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: 2017. 29−38 [31] Eldar Y, Lindenbaum M, Porat M, Zeevi Y Y. The farthest point strategy for progressive image sampling. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(9): 1305-1315 doi: 10.1109/83.623193 [32] Selvaraju R R, Cogswell M, Das A, Vedantam R, Parikh D, Batra D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: 2017. 618−626 [33] Gold S, Rangarajan A, Lu C P, Pappu S, Mjolsness E. New algorithms for 2D and 3D point matching: Pose estimation and correspondence. Pattern Recognition, 1998, 31(8): 1019-1031 doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(98)80010-1 [34] Wang Y, Sun Y B, Liu Z W, Sarma S E, Bronstein M M, Solomon J M. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(5): Article No. 146 [35] Ho J, Yang M H, Rangarajan A, Vemuri B. A new affine registration algorithm for matching 2D point sets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision. Austin, USA: 2007. 25 [36] De R, Dutt R, Sukhatme U. Mapping of shape invariant potentials under point canonical transformations. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 1992, 25(13): L843-L850 doi: 10.1088/0305-4470/25/13/013 [37] Shen Y R, Feng C, Yang Y Q, Tian D. Mining point cloud local structures by kernel correlation and graph pooling. In: Proce-edings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake, USA: 2018. 4548−4557 [38] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: 2012. 1097−1105 [39] Sangkloy P, Burnell N, Ham C, James H. The sketchy database: Learning to retrieve badly drawn bunnies. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2016, 35(4): Article No. 119 [40] Dey S, Riba P, Dutta A, Lladós J L, Song Y Z. Doodle to search: Practical zero-shot sketch-based image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: 2019. 2174−2183 [41] Zhang H, Liu S, Zhang C Q, Ren W Q, Wang R, Cao X C. SketchNet: Sketch classification with web images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: 2016. 1105−1113 [42] Wang X X, Chen X J, Zha Z J. Sketchpointnet: A compact network for robust sketch recognition. In: Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Athens, Greece: 2018. 2994−2998 [43] Hanley J A, McNeil B J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology, 1982, 143(1): 29-36 doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063747 [44] Kipf T N, Max W. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France: 2017. [45] Lin M, Chen Q, Yan S C. Network in network. arXiv preprint, 2013, arXiv: 1312.4400 [46] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint, 2014, arXiv: 1409.1556 [47] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: 2015. 1−9 [48] Zhang X Y, Huang Y P, Zou Q, Pei Y T, Zhang R S, Wang S. A hybrid convolutional neural network for sketch recognition. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 130: 73-82 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.01.006 [49] Zhang K H, Luo W H, Ma L, Li H D. Cousin network guided sketch recognition via latent attribute warehouse. In: Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Honolulu, USA: 2019. 9203−9210 [50] Lee W H, Gader P D, Wilson J N. Optimizing the area under a receiver operating characteristic curve with application to landmine detection. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(2): 389-397 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.887018 [51] Zhang H, She P, Liu Y, Gan J H, Cao X C, Foroosh H. Learning structural representations via dynamic object landmarks discovery for sketch recognition and retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(9): 4486-4499 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2910398 -




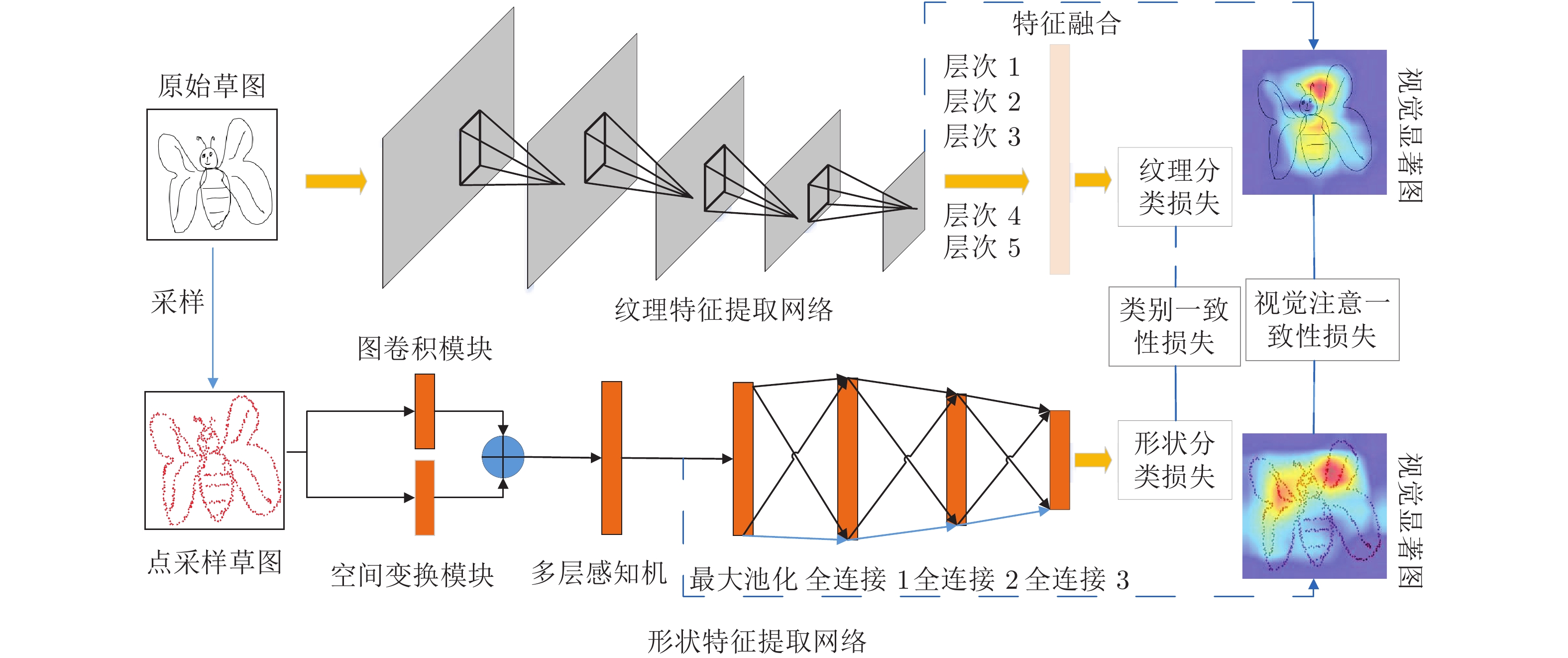
 下载:
下载: