-
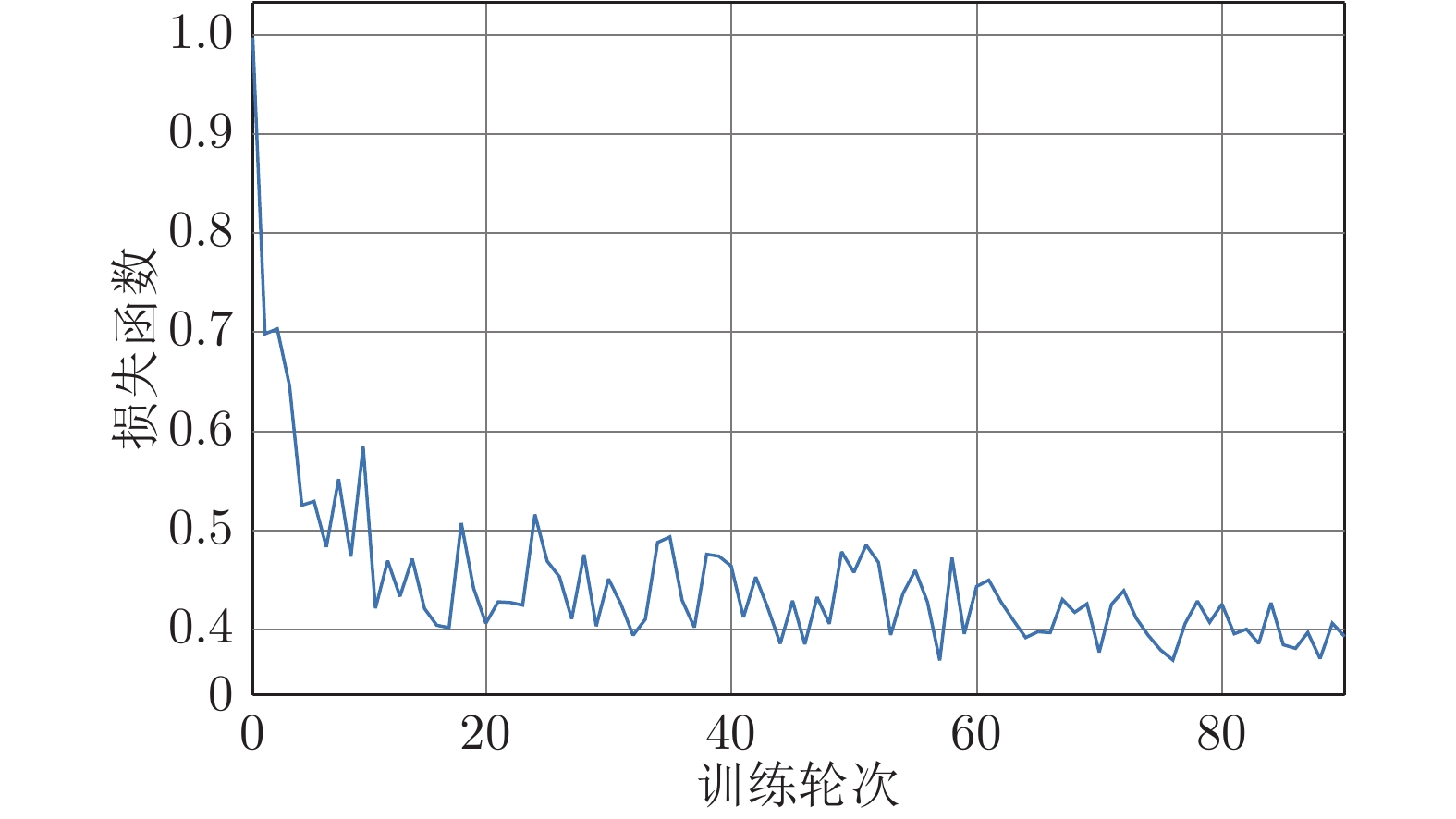
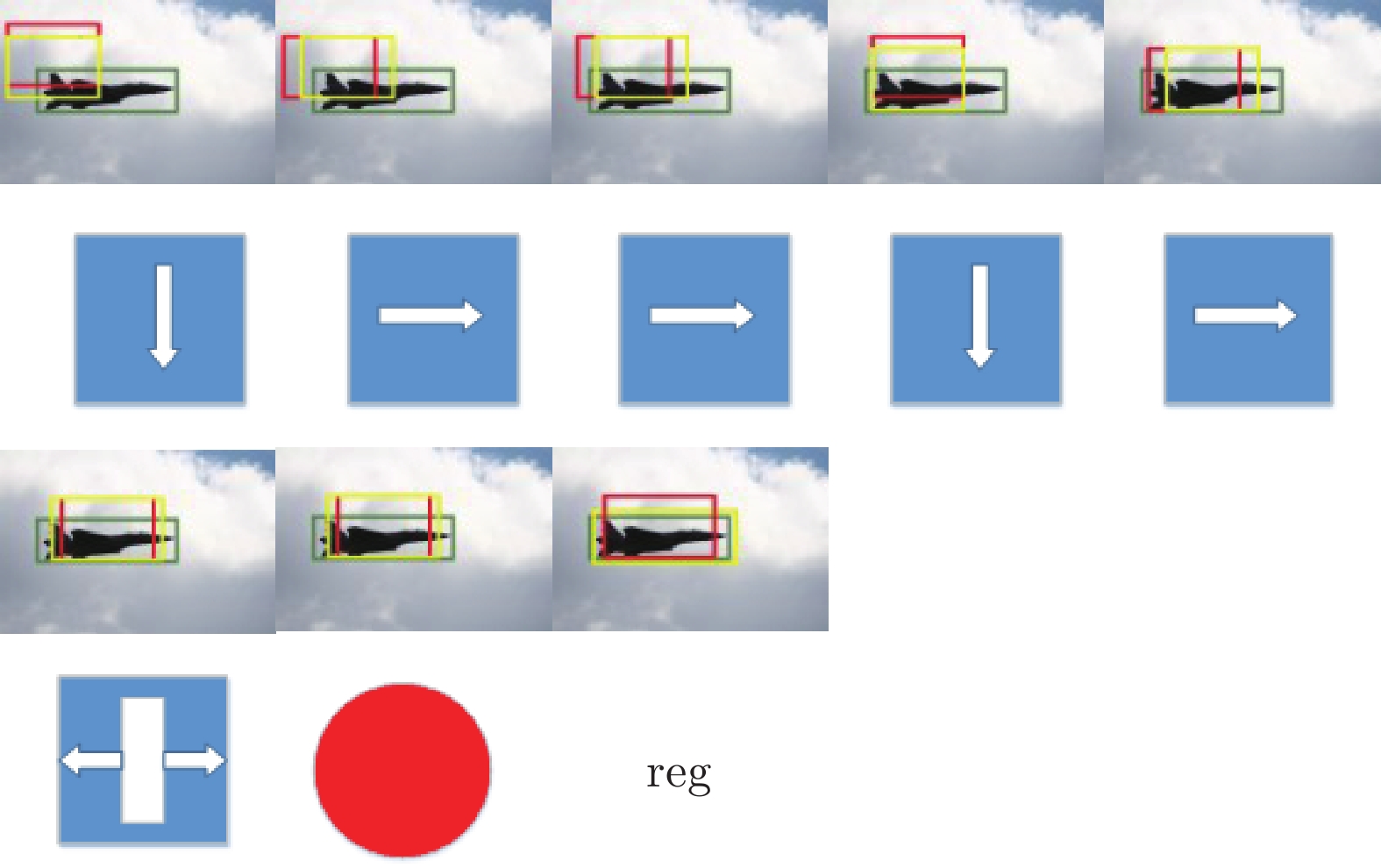
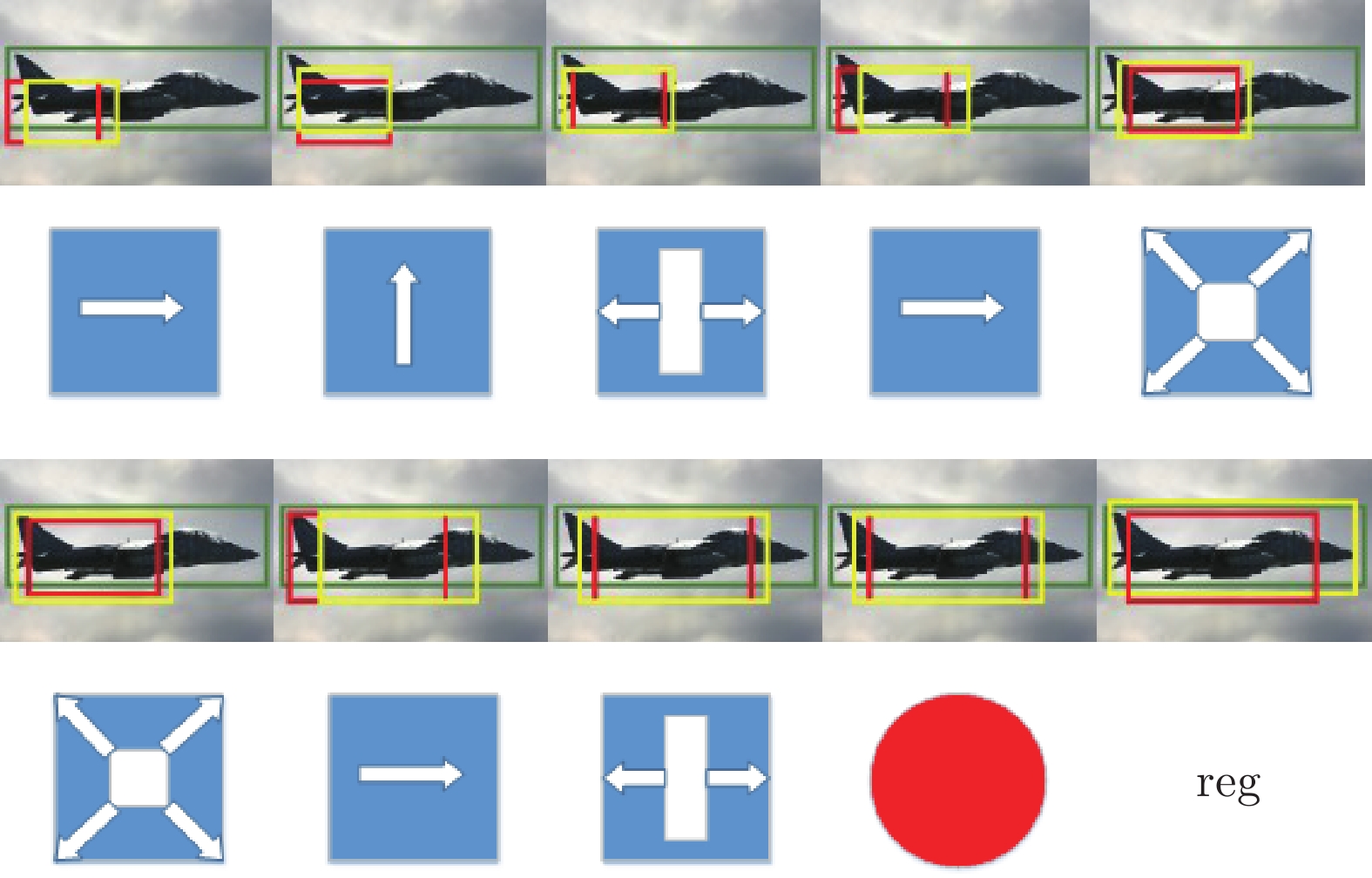
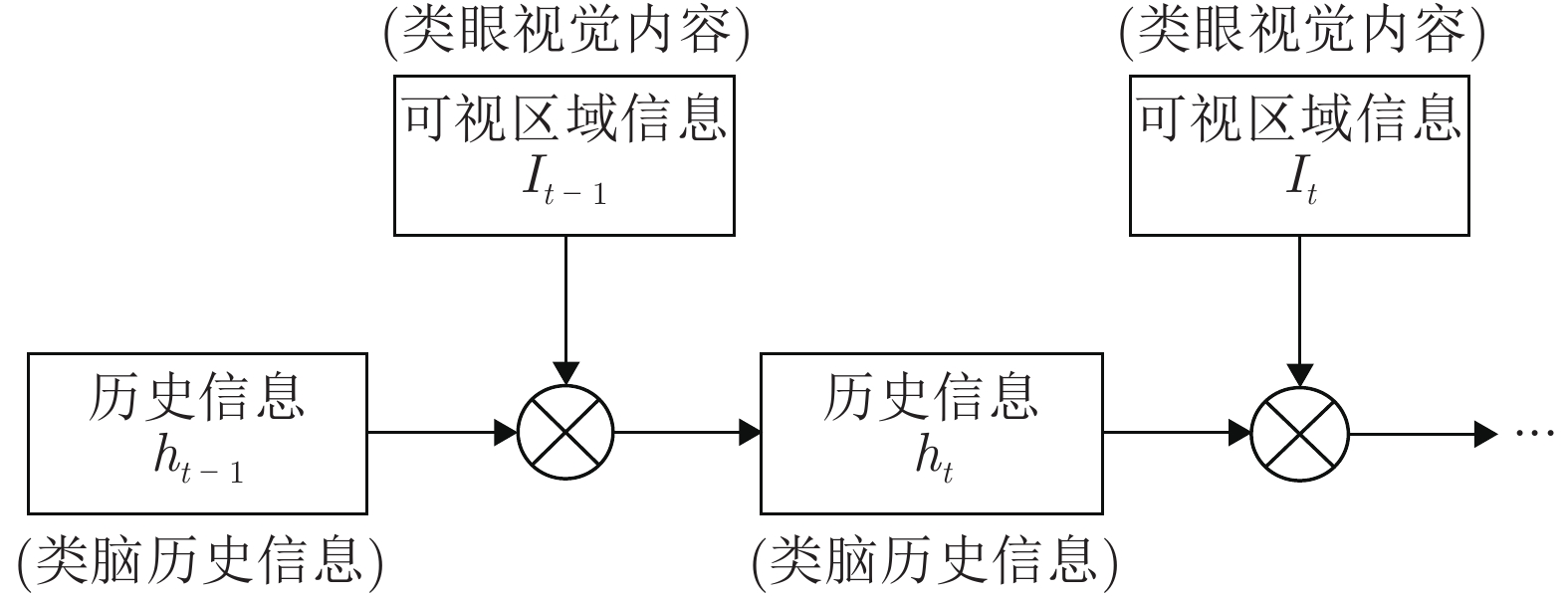
摘要: 为了模拟人眼的视觉注意机制, 快速、高效地搜索和定位图像目标, 提出了一种基于循环神经网络(Recurrent neural network, RNN)的联合回归深度强化学习目标定位模型. 该模型将历史观测信息与当前时刻的观测信息融合, 并做出综合分析, 以训练智能体快速定位目标, 并联合回归器对智能体所定位的目标包围框进行精细调整. 实验结果表明, 该模型能够在少数时间步内快速、准确地定位目标.Abstract: To simulate the visual attention mechanism of the human eye, search and locate image objection quickly and efficiently, this paper proposes a union regression deep reinforcement learning object localization model based on recurrent neural network (RNN), which fuses the historical observation information with the observation information at the current time, then makes a comprehensive analysis to train the agent to quickly locate the object, and combine with the regressor to fine-tune the object bounding box positioned by the agent. Experiments show that the proposed model can accurately and rapidly locate the object in a few time steps.
-
表 1 不同算法在VOC 2007测试集上的定位精度表现(节选部分种类)
Table 1 Positioning accuracy performance of different algorithms on VOC 2007 test set (category of excerpts)
算法 Aero Bike Bird Boat Bottle Bus Car Cat mAP Faster R-CNN 86.5 81.6 77.2 58.0 51.0 78.6 76.6 93.2 75.3 Caicedo 57.9 56.7 38.4 33.0 17.5 51.1 52.7 53.0 45.0 Bueno 56.1 52.0 42.2 38.4 22.1 46.7 42.2 52.6 44.0 UR-DRQN 59.4 58.7 44.6 36.1 28.3 55.3 48.4 52.4 47.9 表 2 不同算法平均每个轮次的定位耗时
Table 2 The average location time of each epoch in different algorithms
算法 Faster R-CNN Caicedo Bueno UR-DRQN 定位耗时 (s/轮次) 372 271 251 219 -
[1] 王亚珅, 黄河燕, 冯冲, 周强. 基于注意力机制的概念化句嵌入研究. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1390-1400WANG Ya-Shen, HUANG He-Yan, FENG Chong, ZHOU Qiang. Conceptual Sentence Embeddings Based on Attention Mechanism. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1390-1400. [2] Sherstinsky A. Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (rnn) and long short-term memory (lstm) network. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 2020, 404: 132306.. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2019.132306 [3] 孙长银, 穆朝絮. 多智能体深度强化学习的若干关键科学问题. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1301-1312Sun Chang-Yin, Mu Chao-Xu. Important scientific problems of multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1301-1312. [4] Hasselt H, Guez A, Silver D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning. In: Proceedings of the 13th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Arizona, USA: 2016. 2094−2100 [5] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Graves A, Antonoglou I, Wierstra D, et al. Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.5602, 2013. [6] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [7] Rahman M A, Wang Y. Optimizing intersection-over-union in deep neural networks for image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Visual Computing. Cham, Sw-itzerland: 2016. 234−244 [8] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 580−587 [9] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1440−1448 [10] Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press. 2015. 91−99 [11] Mnih V, Heess N, Graves A. Recurrent models of visual attention. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Pro-cessing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: 2014. 2204−2212 [12] Caicedo J C, Lazebnik S. Active object localization with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2488−2496 [13] Bueno M B, Giró-i-Nieto X, Marqués F, et al. Hierarchical object detection with deep reinforcement learning. Deep Learning for Image Processing Applications, 2017, 31(164): 3. [14] Hara K, Liu M Y, Tuzel O, Farahmand A M. Attentional network for visual object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1702.01478, 2017. [15] Shah S M, Borkar V S. Q-learning for Markov decision processes with a satisfiability criterion. Systems & Control Letters, 2018. 113: 45-51. [16] Garcia F, Thomas P S. A meta-MDP approach to exploration for lifelong reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press, 2019. 5691−5700 [17] Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018. [18] March J G. Exploration and exploitation in organizational learning. Organization Science, 1991, 2(1): 71-87. doi: 10.1287/orsc.2.1.71 [19] Bertsekas D P. Dynamic Programming and Optimal Control. Belmont: Athena Scientific, 1995. -




 下载:
下载: